2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XPath
|
|
|
- Gervase Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data-centric XML XPath
2 XPath Overview Non-XML language for identifying particular parts of XML documents First person element of a document Seventh child element of third person element ID attribute of the first person element whose contents are Fred Jones All xml-stylesheet processing instructions Originally developed for XSLT Split off XSLT to support also Xpointer Also integrated into XML Schema, DOM, XPath 2.0 under development (candidate recommendation: 8 June 2005) 2
3 XML Tree Structure according to XPath Document made up of nodes containing other nodes Seven kinds of nodes: Root node Like DOM, different from document element Element nodes Text nodes Attribute nodes Excludes namespace attributes Comment nodes Processing instruction nodes Namespace nodes Not included: CDATA section, entity references, DTD things XPath 2: model uses infoset (possibly PSVI) 3
4 4 Location Path Typical top-level expression Identifies a set of nodes in the document Consists of location steps Each location step is evaluated in a context Root location path: / Identifies root node of the document independent of context
5 Child Location Steps A child location step selects all immediate child elements of the context Consists just of the element name: Relative location path, e.g. body Must have context to resolve the step Can be combined to form compound location paths With root location path: /html With compound location path, using / as the separator (immediate children): /html/body Using // as the separator (all descendents): /html//p Starting with // denotes all descendents of the context: //a 5
6 6 Attribute Location Steps Selects named attributes from a context Consists followed by the attribute name //a/@href selects the href attributes of all a elements //@id selects all id attributes in the document Location step selects the attribute nodes of the tree, not the attribute values Conversion to strings will cause attribute values to be retrieved
7 7 Other Location Steps comment() selects all comment nodes of the context text() selects all text nodes in the context CDATA sections and entity references are resolved Each text node is the maximum contiguous text block without intervening markup (like DOM normalize()) processing-instruction() selects all PIs in the context processing-instruction( name ) selects PIs with target name
8 Wildcards * selects all elements in the context regardless of element name //* selects all elements in the document Can be prefixed with a namespace: svg:* selects all elements with the same namespace that the svg prefix maps to node() selects all nodes in the selects all attributes in the context Can be prefixed again, 8
9 9 Alternatives forms the union of selections a link selects all elements named a selects all attributes of name id or xlink:type matches all element and attribute nodes
10 10 Traversing the Axis.. selects the parent node selects all element nodes which have an ID attribute. selects the context node Can be used to make // not start at the root:.//p selects all p nodes nested in the context node In XSLT, used to access the string value of the current node
11 11 Predicates Select subset of the selected node Evaluated in the context of each node Written in square brackets: //profession[. = physicist ] selects all profession nodes whose string value is physicist String value of an element is the text content of the element //p[@id = foo ] selects all p nodes for which the string value of the id attribute equals foo The string value of an attribute is the attribute value
12 Predicates (2) Predicate subexpressions can have multiple data types: Strings, numbers, booleans, node sets Various operators are available: Arithmetic and relational operations on numbers < 1970] Relational operations on strings Logical operations on booleans Implicit conversions between data types If the result is a number, the predicate holds if the position of the context node equals the number person[3] selects the third person in the context 12
13 Unabbreviated Location Paths Location step consists of three parts: axis, test, and predicates XPath defines 13 axes: ancestor: selects all ancestor nodes of the context ancestor-or-self: like ancestor, but includes the context attribute: selects all attributes child: selects immediate child nodes descendant: selects all descendents descendent-or-self: like descendant, but includes the context following, preceding: all nodes before or after the context (in document order) following-sibling, preceding-sibling: all sibling nodes parent: select the parent node namespace: selects all namespaces of the context self: selects the context 13
14 Unabbreviated Location Paths (2) child::para selects all immediate child elements of type para Abbreviated as para child::text() selects all text node children of the context Abbreviated as text() attribute::name selects all name attributes Abbreviated child::chapter/descendant::para selects all para descendants of all chapter children Abbreviated as chapter//para // is short for /descendant-or-self::node()/.//para is short for self::node()/descendant-or-self::node()/child::para //para[3] is the set of all para elements which are third para children 14
15 Unabbreviated Location Paths (3) following-sibling::chapter[1] selects the next chapter sibling No abbreviation possible self::para selects the current node if it is a para node, else selects nothing: child::*[self::chapter or self::appendix] selects all chapter and appendix children of the context child::*[self::chapter or self::appendix][position()=last()] selects the last such element Ordering of selected nodes depends on the axis An axis containing only elements before the context is a reverse axis The proximity position always follows the order on the axis, node numbers start with 1 15
16 16 Syntax: Location Paths [1] LocationPath ::= RelativeLocationPath AbsoluteLocationPath [2] AbsoluteLocationPath ::= '/' RelativeLocationPath? AbbreviatedAbsoluteLocationPath [3] RelativeLocationPath ::= Step RelativeLocationPath '/' Step AbbreviatedRelativeLocationPath
17 17 Syntax: Location Steps [4] Step ::= AxisSpecifier NodeTest Predicate* AbbreviatedStep [5] AxisSpecifier ::= AxisName '::' AbbreviatedAxisSpecifier
18 18 Syntax: Node Tests [7] NodeTest ::= NameTest NodeType '(' ')' 'processing-instruction' '(' Literal ')' [38] NodeType ::= 'comment' 'text' 'processing-instruction' 'node'
19 19 Syntax: Predicates [8] Predicate ::= '[' PredicateExpr ']' [9] PredicateExpr ::= Expr PredicateExpr is evaluated in the context of the selected steps Result is converted to boolean Numbers are converted to boolean by comparing them with position()
20 20 Syntax: Abbreviations [10] AbbreviatedAbsoluteLocationPath ::= '//' RelativeLocationPath [11] AbbreviatedRelativeLocationPath ::= RelativeLocationPath '//' Step [12] AbbreviatedStep ::= '.' '..' [13] AbbreviatedAxisSpecifier ::=
21 Syntax: Expressions [14] Expr ::= OrExpr [15] PrimaryExpr ::= VariableReference '(' Expr ')' Literal Number FunctionCall [36] VariableReference ::= '$' QName Variables are provided by the XPath application as part of the context 21
22 22 Syntax: Function Calls [16] FunctionCall ::= FunctionName '(' ( Argument ( ',' Argument )* )? ')' [17] Argument ::= Expr [35] FunctionName ::= QName - NodeType Functions are built-in or provided by the XPath application Arguments are converted to their argument types As if by calling string(), number(), boolean() built-ins
23 23 Syntax: Node Sets [18] UnionExpr ::= PathExpr UnionExpr ' ' PathExpr [19] PathExpr ::= LocationPath FilterExpr FilterExpr '/' RelativeLocationPath FilterExpr '//' RelativeLocationPath [20] FilterExpr ::= PrimaryExpr FilterExpr Predicate
24 Syntax: Boolean Expressions [21] OrExpr ::= AndExpr OrExpr 'or' AndExpr [22] AndExpr ::= EqualityExpr AndExpr 'and' EqualityExpr [23] EqualityExpr ::= RelationalExpr EqualityExpr '=' RelationalExpr EqualityExpr '!=' RelationalExpr [24] RelationalExpr ::= AdditiveExpr RelationalExpr '<' AdditiveExpr RelationalExpr '>' AdditiveExpr RelationalExpr '<=' AdditiveExpr RelationalExpr '>=' AdditiveExpr 24
25 Boolean Expressions Arguments of boolean operators (or, and) are converted to boolean first Comparing node sets in relational operations: If both arguments are node sets: True, if a node can be selected from each set so that their string values compare true If one argument is a number: True if a node can be converted to a string, then a number, so that it compares true If one argument is a string: True if a node can be converted to a string so that it compares true If one argument is boolean: True if the nodeset, when converted to boolean(), compares true 25
26 26 Boolean Expressions (2) Comparing other values for equality/inequality: If one value is a boolean, convert the other to boolean [Otherwise] If one value is a number, convert the other to a number [Otherwise] convert both arguments to strings Comparing values for <, <=, >, >=: Convert both arguments to numbers
27 Syntax: Numbers [25] AdditiveExpr ::= MultiplicativeExpr AdditiveExpr '+' MultiplicativeExpr AdditiveExpr '-' MultiplicativeExpr [26] MultiplicativeExpr ::= UnaryExpr MultiplicativeExpr MultiplyOperator UnaryExpr MultiplicativeExpr 'div' UnaryExpr MultiplicativeExpr 'mod' UnaryExpr [27] UnaryExpr ::= UnionExpr '-' UnaryExpr [34] MultiplyOperator ::= '*' Computations are floating-point normally; mod is the same as % in Java Whether * is a multiply operator or a wildcard depends on the lexical context 27
28 28 Core Functions Certain functions are provided built-in in XPath XSLT adds more built-in functions on top of that Applications may provide custom functions, in a proprietary fashion Should use QNames, to scope extensions by XML namespace Each function defined with name, parameter types, return type, semantics
29 Node Functions number last() number position() number count(node-set) node-set id(object) If argument is a node set, apply string() to each one, then id() Otherwise: convert argument to string, split at whitespace boundaries, then find node with id string local-name(node-set?) If nodeset is given, return local-name for first node, else for context node string namespace-uri(node-set?) string name(node-set?) 29
30 String Functions string string(object?) Node-set: convert first node in document order into string Empty string for empty node-set Numbers: decimal, with sign, possibly NaN, Infinity Booleans: true, false Nodes: Depending on type Root node/element node: concatenation of all string values of all text node descendants Attributes: attribute value Namespace node: namespace URI PI: PI contents Comment: Comment text Text: Text value (always non-empty) 30
31 String Functions (2) string concat(string, string, string*) boolean starts-with(string, string) boolean contains(string, string) string substring-before(string, string) string substring-after(string, string) string substring(string, number, number?) Character indices start at 1, indices are rounded number string-length(string?) string normalize-space(string?) string translate(string, string, string) 31
32 Boolean Functions boolean boolean(object) Number: true if!= +/-0,!=NaN Node-set: true if non-empty String: true if length is non-zero boolean not(boolean) boolean true() boolean false() boolean lang(string) Looks for xml:lang in the context node Case-insensitive, ignoring country separated by - 32
33 Number Functions number number(object?) Strings: convert to nearest IEEE-754 number, or NaN Boolean: true gives 1, false gives 0 Node-set: convert to string first number sum(node-set) number floor(number) number ceiling(number) number round(number) 33
Course: The XPath Language
 1 / 27 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble, 2012 2013 2 / 27 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any kind of
1 / 27 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble, 2012 2013 2 / 27 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any kind of
XPath. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 XPath Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Overview What is XPath? Queries The XPath Data Model Location Paths Expressions
XPath Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Overview What is XPath? Queries The XPath Data Model Location Paths Expressions
Course: The XPath Language
 1 / 30 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 30 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any
1 / 30 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 30 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any
XPath an XML query language
 XPath an XML query language Some XML query languages: XML-QL XPath XQuery Many others 1 XML-QL http://www.w3.org/tr/note-xml-ql (8/98) Features: regular path expressions patterns, templates Skolem Functions
XPath an XML query language Some XML query languages: XML-QL XPath XQuery Many others 1 XML-QL http://www.w3.org/tr/note-xml-ql (8/98) Features: regular path expressions patterns, templates Skolem Functions
XPath Expression Syntax
 XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XPath Basics. Mikael Fernandus Simalango
 XPath Basics Mikael Fernandus Simalango Agenda XML Overview XPath Basics XPath Sample Project XML Overview extensible Markup Language Constituted by elements identified by tags and attributes within Elements
XPath Basics Mikael Fernandus Simalango Agenda XML Overview XPath Basics XPath Sample Project XML Overview extensible Markup Language Constituted by elements identified by tags and attributes within Elements
XML Data Management. 6. XPath 1.0 Principles. Werner Nutt
 XML Data Management 6. XPath 1.0 Principles Werner Nutt 1 XPath Expressions and the XPath Document Model XPath expressions are evaluated over documents XPath operates on an abstract document structure
XML Data Management 6. XPath 1.0 Principles Werner Nutt 1 XPath Expressions and the XPath Document Model XPath expressions are evaluated over documents XPath operates on an abstract document structure
Semi-structured Data. 8 - XPath
 Semi-structured Data 8 - XPath Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline XPath Terminology XPath at First Glance Location Paths (Axis, Node Test, Predicate) Abbreviated Syntax What is
Semi-structured Data 8 - XPath Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline XPath Terminology XPath at First Glance Location Paths (Axis, Node Test, Predicate) Abbreviated Syntax What is
XML. <subtitle>xslt (cont)</subtitle> <author>prof. Dr. Christian Pape</author>
 XML xslt (cont) prof. Dr. Christian Pape Content Expressions and Functions Copying nodes Using variables and parameters Conditional Processing XSLT 5-2 Expressions
XML xslt (cont) prof. Dr. Christian Pape Content Expressions and Functions Copying nodes Using variables and parameters Conditional Processing XSLT 5-2 Expressions
Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef
 Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef Author(s) Thomas Eitzenberger Version 0.2 Status Ready for review Page 1 of 11 Content Selecting Nodes...3 Predicates...3 Selecting Unknown Nodes...4 Selecting Several Paths...5
Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef Author(s) Thomas Eitzenberger Version 0.2 Status Ready for review Page 1 of 11 Content Selecting Nodes...3 Predicates...3 Selecting Unknown Nodes...4 Selecting Several Paths...5
XML Technologies. Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. Web pages:
 XML Technologies Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Web pages: http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/nprg036/ Outline Introduction to XML format, overview of XML technologies DTD
XML Technologies Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Web pages: http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/nprg036/ Outline Introduction to XML format, overview of XML technologies DTD
XML databases. Jan Chomicki. University at Buffalo. Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9
 XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
APPROXIMATE XPATH LIN XU. A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN COMPUTER SCIENCE
 APPROXIMATE XPATH By LIN XU A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN COMPUTER SCIENCE WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY School of Electrical Engineering
APPROXIMATE XPATH By LIN XU A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE IN COMPUTER SCIENCE WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY School of Electrical Engineering
An XPath-based Preference Language for P3P
 An XPath-based Preference Language for P3P Rakesh Agrawal Jerry Kiernan Ramakrishnan Srikant Yirong Xu IBM Almaden Research Center 650 Harry Road, San Jose, CA 95120 ABSTRACT The Platform for Privacy Preferences
An XPath-based Preference Language for P3P Rakesh Agrawal Jerry Kiernan Ramakrishnan Srikant Yirong Xu IBM Almaden Research Center 650 Harry Road, San Jose, CA 95120 ABSTRACT The Platform for Privacy Preferences
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
Progress Report on XQuery
 Progress Report on XQuery Don Chamberlin Almaden Research Center May 24, 2002 History Dec. '98: W3C sponsors workshop on XML Query Oct. '99: W3C charters XML Query working group Chair: Paul Cotton About
Progress Report on XQuery Don Chamberlin Almaden Research Center May 24, 2002 History Dec. '98: W3C sponsors workshop on XML Query Oct. '99: W3C charters XML Query working group Chair: Paul Cotton About
Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 Learning Programming Using VISUAL BASIC.NET
 Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 APPENDIX D XSLT XSLT is a programming language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (http://www.w3.org/tr/xslt), that provides the mechanism to transform a
Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 APPENDIX D XSLT XSLT is a programming language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (http://www.w3.org/tr/xslt), that provides the mechanism to transform a
Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4
 Chapter 4 CHAPTER 4 Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4 Path expressions are used to navigate input documents to select elements and attributes of interest. This chapter explains how to use path expressions
Chapter 4 CHAPTER 4 Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4 Path expressions are used to navigate input documents to select elements and attributes of interest. This chapter explains how to use path expressions
The XQuery Data Model
 The XQuery Data Model 9. XQuery Data Model XQuery Type System Like for any other database query language, before we talk about the operators of the language, we have to specify exactly what it is that
The XQuery Data Model 9. XQuery Data Model XQuery Type System Like for any other database query language, before we talk about the operators of the language, we have to specify exactly what it is that
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 T O Y H Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 26 February 2013 Semester 2 Week 6 E H U N I V E R S I
T O Y H Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 26 February 2013 Semester 2 Week 6 E H U N I V E R S I
Written Exam XML Summer 06 Prof. Dr. Christian Pape. Written Exam XML
 Name: Matriculation number: Written Exam XML Max. Points: Reached: 9 20 30 41 Result Points (Max 100) Mark You have 60 minutes. Please ask immediately, if you do not understand something! Please write
Name: Matriculation number: Written Exam XML Max. Points: Reached: 9 20 30 41 Result Points (Max 100) Mark You have 60 minutes. Please ask immediately, if you do not understand something! Please write
Navigating an XML Document
 University of Dublin Trinity College Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie Athanasios.Staikopoulos@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Language for addressing parts of an XML document Used in XSLT,
University of Dublin Trinity College Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie Athanasios.Staikopoulos@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Language for addressing parts of an XML document Used in XSLT,
One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while
 1 One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while leaving the engine to choose the best way of fulfilling
1 One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while leaving the engine to choose the best way of fulfilling
XPath. Mario Alviano A.Y. 2017/2018. University of Calabria, Italy 1 / 21
 1 / 21 XPath Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 21 1 Introduction 2 XPath expressions Path expressions Value expressions Node set expressions 3 Examples 4 Exercises
1 / 21 XPath Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 21 1 Introduction 2 XPath expressions Path expressions Value expressions Node set expressions 3 Examples 4 Exercises
H2 Spring B. We can abstract out the interactions and policy points from DoDAF operational views
 1. (4 points) Of the following statements, identify all that hold about architecture. A. DoDAF specifies a number of views to capture different aspects of a system being modeled Solution: A is true: B.
1. (4 points) Of the following statements, identify all that hold about architecture. A. DoDAF specifies a number of views to capture different aspects of a system being modeled Solution: A is true: B.
Computer Science E-259
 Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 4: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0) 21 February 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time DOM Level 3 JAXP 1.3
Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 4: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0) 21 February 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time DOM Level 3 JAXP 1.3
Reading XML: Introducing XPath. Andrew Walker
 Reading XML: Introducing XPath Andrew Walker Why? Makes writing analysis scripts for your XML encoded results easy. Is used by many other XML technologies. XSLT, XPointer etc. A Fortran XPath API is in
Reading XML: Introducing XPath Andrew Walker Why? Makes writing analysis scripts for your XML encoded results easy. Is used by many other XML technologies. XSLT, XPointer etc. A Fortran XPath API is in
Example using multiple predicates
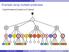 XPath Example using multiple predicates //performance[conductor][date] L C C C C p c s p p s o t d p p c p p Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 162 / 366 XPath Further examples with predicates //performance[composer='frederic
XPath Example using multiple predicates //performance[conductor][date] L C C C C p c s p p s o t d p p c p p Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 162 / 366 XPath Further examples with predicates //performance[composer='frederic
Experience with XML Signature and Recommendations for future Development
 1 2 3 4 Experience with XML Signature and Recommendations for future Development Version 01, 1 August 2007 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Document identifier: Experience-Recommendation-Oracle-01 Contributors: Pratik
1 2 3 4 Experience with XML Signature and Recommendations for future Development Version 01, 1 August 2007 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Document identifier: Experience-Recommendation-Oracle-01 Contributors: Pratik
XPath. Lecture 36. Robb T. Koether. Wed, Apr 16, Hampden-Sydney College. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, / 28
 XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
Part VII. Querying XML The XQuery Data Model. Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2005/06 153
 Part VII Querying XML The XQuery Data Model Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2005/06 153 Outline of this part 1 Querying XML Documents Overview 2 The XQuery Data Model The XQuery
Part VII Querying XML The XQuery Data Model Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2005/06 153 Outline of this part 1 Querying XML Documents Overview 2 The XQuery Data Model The XQuery
Introduction p. 1 An XML Primer p. 5 History of XML p. 6 Benefits of XML p. 11 Components of XML p. 12 BNF Grammar p. 14 Prolog p. 15 Elements p.
 Introduction p. 1 An XML Primer p. 5 History of XML p. 6 Benefits of XML p. 11 Components of XML p. 12 BNF Grammar p. 14 Prolog p. 15 Elements p. 16 Attributes p. 17 Comments p. 18 Document Type Definition
Introduction p. 1 An XML Primer p. 5 History of XML p. 6 Benefits of XML p. 11 Components of XML p. 12 BNF Grammar p. 14 Prolog p. 15 Elements p. 16 Attributes p. 17 Comments p. 18 Document Type Definition
XML & Databases. Tutorial. 3. XPath Queries. Universität Konstanz. Database & Information Systems Group Prof. Marc H. Scholl
 XML & Databases Tutorial Christian Grün, Database & Information Systems Group University of, Winter 2007/08 XPath Introduction navigational access to XML documents sub-language in XQuery, XSLT, or XPointer
XML & Databases Tutorial Christian Grün, Database & Information Systems Group University of, Winter 2007/08 XPath Introduction navigational access to XML documents sub-language in XQuery, XSLT, or XPointer
TDDD43. Theme 1.2: XML query languages. Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p:// TDDD43
 Theme 1.2: XML query languages Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p://www.ida.liu.se/~ Query languages for XML Xpath o Path expressions with conditions o Building block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer,
Theme 1.2: XML query languages Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p://www.ida.liu.se/~ Query languages for XML Xpath o Path expressions with conditions o Building block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer,
XPath and XQuery. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018
 XPath and XQuery Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 23) Homework #3 due in two weeks Project milestone #1 feedback : we are a bit behind, but will definitely release
XPath and XQuery Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 23) Homework #3 due in two weeks Project milestone #1 feedback : we are a bit behind, but will definitely release
A Structural Numbering Scheme for XML Data
 A Structural Numbering Scheme for XML Data Alfred M. Martin WS2002/2003 February/March 2003 Based on workout made during the EDBT 2002 Workshops Dao Dinh Khal, Masatoshi Yoshikawa, and Shunsuke Uemura
A Structural Numbering Scheme for XML Data Alfred M. Martin WS2002/2003 February/March 2003 Based on workout made during the EDBT 2002 Workshops Dao Dinh Khal, Masatoshi Yoshikawa, and Shunsuke Uemura
XPath Lecture 34. Robb T. Koether. Hampden-Sydney College. Wed, Apr 11, 2012
 XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
XPath Lecture 34 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 11, 2012 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPathLecture 34 Wed, Apr 11, 2012 1 / 20 1 XPath Functions 2 Predicates 3 Axes Robb T.
XPath and XSLT. Overview. Context. Context The Basics of XPath. XPath and XSLT. Nodes Axes Expressions. Stylesheet templates Transformations
 XPath and XSLT Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context The Basics of XPath Nodes
XPath and XSLT Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context The Basics of XPath Nodes
Foreword... v Introduction... vi. 1 Scope Normative references Terms and definitions Extensible Datatypes schema overview...
 Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 Extensible Datatypes schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types...
Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 Extensible Datatypes schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types...
XML Data Management. 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath
 XML Data Management 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath Werner Nutt based on slides by Sara Cohen, Jerusalem 1 Extracting Data from XML Data stored in an XML document must be extracted to use it with various
XML Data Management 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath Werner Nutt based on slides by Sara Cohen, Jerusalem 1 Extracting Data from XML Data stored in an XML document must be extracted to use it with various
Versa. Mike Olson ( Fourthought, Inc.), Uche Ogbuji ( Fourthought, Inc.) Revision (Initial release) [MO]
![Versa. Mike Olson ( Fourthought, Inc.), Uche Ogbuji ( Fourthought, Inc.) Revision (Initial release) [MO] Versa. Mike Olson ( Fourthought, Inc.), Uche Ogbuji ( Fourthought, Inc.) Revision (Initial release) [MO]](/thumbs/95/122745068.jpg) Versa Mike Olson ( Fourthought, Inc.), Uche Ogbuji ( Fourthought, Inc.) Revision (Initial release) [MO] Versa is a specialized language for addressing and querying an RDF model. It allows traversal of
Versa Mike Olson ( Fourthought, Inc.), Uche Ogbuji ( Fourthought, Inc.) Revision (Initial release) [MO] Versa is a specialized language for addressing and querying an RDF model. It allows traversal of
XML Information Set. Working Draft of May 17, 1999
 XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xml-infoset-19990517 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xml-infoset Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright
XML Information Set Working Draft of May 17, 1999 This version: http://www.w3.org/tr/1999/wd-xml-infoset-19990517 Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/xml-infoset Editors: John Cowan David Megginson Copyright
Foreword... v Introduction... vi. 1 Scope Normative references Terms and definitions DTLL schema overview...
 Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 DTLL schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types... 3 5.1.1 XPath
Contents Page Foreword... v Introduction... vi 1 Scope... 1 2 Normative references... 1 3 Terms and definitions... 1 4 DTLL schema overview... 2 5 Common constructs... 3 5.1 Common types... 3 5.1.1 XPath
Presentation. Separating Content and Presentation Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) XML and XSLT
 Presentation Separating Content and Presentation Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) XML and XSLT WordPress Projects Theme Generators WYSIWYG editor Look at tools to support generation of themes Design a new
Presentation Separating Content and Presentation Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) XML and XSLT WordPress Projects Theme Generators WYSIWYG editor Look at tools to support generation of themes Design a new
XML SCHEMA INFERENCE WITH XSLT
 XML SCHEMA INFERENCE WITH XSLT By SCOTT MCCOLLUM BUNTIN A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
XML SCHEMA INFERENCE WITH XSLT By SCOTT MCCOLLUM BUNTIN A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
September 3, 2001 XML Processing
 XPointer and XLink Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context XML adds new capabilities
XPointer and XLink Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context XML adds new capabilities
Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Introduction Chapter 2 - Designing XML Data and Applications Chapter 3 - Designing and Managing XML Storage Objects
 Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Introduction 1.1 Anatomy of an XML Document 1.2 Differences Between XML and Relational Data 1.3 Overview of DB2 purexml 1.4 Benefits of DB2 purexml over Alternative Storage
Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Introduction 1.1 Anatomy of an XML Document 1.2 Differences Between XML and Relational Data 1.3 Overview of DB2 purexml 1.4 Benefits of DB2 purexml over Alternative Storage
An introduction to searching in oxygen using XPath
 1/47 An introduction to searching in oxygen using XPath James Cummings @jamescummings 11 November 2014 2/47 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages (such as XSLT
1/47 An introduction to searching in oxygen using XPath James Cummings @jamescummings 11 November 2014 2/47 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages (such as XSLT
Parte IV: XPATH. Prof. Riccardo Torlone
 BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo Parte IV: XPATH Prof. Riccardo Torlone Università Roma Tre Outline Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions Riccardo Torlone: Basi di
BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo Parte IV: XPATH Prof. Riccardo Torlone Università Roma Tre Outline Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions Riccardo Torlone: Basi di
Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT. CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XPath Language for addressing parts of an XML document XSLT Xpointer XQuery Tree model based on DOM W3C Recommendation
Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XPath Language for addressing parts of an XML document XSLT Xpointer XQuery Tree model based on DOM W3C Recommendation
XPath. by Klaus Lüthje Lauri Pitkänen
 XPath by Klaus Lüthje Lauri Pitkänen Agenda Introduction History Syntax Additional example and demo Applications Xpath 2.0 Future Introduction Expression language for Addressing portions of an XML document
XPath by Klaus Lüthje Lauri Pitkänen Agenda Introduction History Syntax Additional example and demo Applications Xpath 2.0 Future Introduction Expression language for Addressing portions of an XML document
Introduction to XPath
 Introduction to XPath TEI@Oxford July 2009 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages. It is just a way of locating nodes in an XML document. Accessing your TEI document
Introduction to XPath TEI@Oxford July 2009 XPath XPath is the basis of most other XML querying and transformation languages. It is just a way of locating nodes in an XML document. Accessing your TEI document
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 9. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
XQuery 1.0: An XML Query Language
 XQuery 1.0: An XML Query Language W3C Recommendation 23 January 2007 This version: Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2007/rec-xquery-20070123/ http://www.w3.org/tr/xquery/ Previous version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2006/pr-xquery-20061121/
XQuery 1.0: An XML Query Language W3C Recommendation 23 January 2007 This version: Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2007/rec-xquery-20070123/ http://www.w3.org/tr/xquery/ Previous version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2006/pr-xquery-20061121/
XML, DTD, and XPath. Announcements. From HTML to XML (extensible Markup Language) CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems. Midterm has been graded
 XML, DTD, and XPath CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements 2 Midterm has been graded Graded exams available in my office Grades posted on Blackboard Sample solution and score distribution
XML, DTD, and XPath CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements 2 Midterm has been graded Graded exams available in my office Grades posted on Blackboard Sample solution and score distribution
Copyright 2007 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe. Slide 27-1
 Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Introduction to XQuery. Overview. Basic Principles. .. Fall 2007 CSC 560: Management of XML Data Alexander Dekhtyar..
 .. Fall 2007 CSC 560: Management of XML Data Alexander Dekhtyar.. Overview Introduction to XQuery XQuery is an XML query language. It became a World Wide Web Consortium Recommendation in January 2007,
.. Fall 2007 CSC 560: Management of XML Data Alexander Dekhtyar.. Overview Introduction to XQuery XQuery is an XML query language. It became a World Wide Web Consortium Recommendation in January 2007,
FOXpath - an expression language for selecting files and folders
 Link to the Balisage Proceedings Home Page at http://www.balisage.net/proceedings Link to this paper (entry page with links) at http://www.balisage.net/proceedings/vol17/html/rennau01/balisagevol17-rennau01.html
Link to the Balisage Proceedings Home Page at http://www.balisage.net/proceedings Link to this paper (entry page with links) at http://www.balisage.net/proceedings/vol17/html/rennau01/balisagevol17-rennau01.html
XML Path Language (XPath)
 2.0 W3C Recommendation 23 January 2007 This version: Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2007/rec-xpath20-20070123/ http://www.w3.org/tr/xpath20/ Previous version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2006/pr-xpath20-20061121/
2.0 W3C Recommendation 23 January 2007 This version: Latest version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2007/rec-xpath20-20070123/ http://www.w3.org/tr/xpath20/ Previous version: http://www.w3.org/tr/2006/pr-xpath20-20061121/
~ Ian Hunneybell: DIA Revision Notes ~
 XML is based on open standards, and is text-based, thereby making it accessible to all. It is extensible, thus allowing anyone to customise it for their own needs, to publish for others to use, and to
XML is based on open standards, and is text-based, thereby making it accessible to all. It is extensible, thus allowing anyone to customise it for their own needs, to publish for others to use, and to
6/3/2016 8:44 PM 1 of 35
 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 1 of 35 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 2 of 35 2) Background Well-formed XML HTML XSLT Processing Model 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 3 of 35 3) XPath XPath locates items within an XML file It relies on the XML
6/3/2016 8:44 PM 1 of 35 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 2 of 35 2) Background Well-formed XML HTML XSLT Processing Model 6/3/2016 8:44 PM 3 of 35 3) XPath XPath locates items within an XML file It relies on the XML
EXtensible Markup Language (XML) a W3C standard to complement HTML A markup language much like HTML
 XML and XPath EXtensible Markup Language (XML) a W3C standard to complement HTML A markup language much like HTML origins: structured text SGML motivation: HTML describes presentation XML describes content
XML and XPath EXtensible Markup Language (XML) a W3C standard to complement HTML A markup language much like HTML origins: structured text SGML motivation: HTML describes presentation XML describes content
B.V.Patel Institute of Business Management, Computer & Information Technology, UTU
 B.C.A (Semester 4) Teaching Schedule 030010408 exentisible Markup Language OBJECTIVE: To introduce the concept of creating, validating, parsing, formatting, transforming and linking the well formatted
B.C.A (Semester 4) Teaching Schedule 030010408 exentisible Markup Language OBJECTIVE: To introduce the concept of creating, validating, parsing, formatting, transforming and linking the well formatted
Hypermedia and the Web XSLT and XPath
 Hypermedia and the Web XSLT and XPath XSLT Extensible Stylesheet Language for Transformations Compare/contrast with CSS: CSS is used to change display characteristics of primarily HTML documents. But,
Hypermedia and the Web XSLT and XPath XSLT Extensible Stylesheet Language for Transformations Compare/contrast with CSS: CSS is used to change display characteristics of primarily HTML documents. But,
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. Part I: Introduction 1. Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3. Chapter 2: Well-Formed XML 23. Acknowledgments
 Acknowledgments Introduction ix xxvii Part I: Introduction 1 Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3 Of Data, Files, and Text 3 Binary Files 4 Text Files 5 A Brief History of Markup 6 So What Is XML? 7 What Does XML
Acknowledgments Introduction ix xxvii Part I: Introduction 1 Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3 Of Data, Files, and Text 3 Binary Files 4 Text Files 5 A Brief History of Markup 6 So What Is XML? 7 What Does XML
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
XPath. Web Data Management and Distribution. Serge Abiteboul Philippe Rigaux Marie-Christine Rousset Pierre Senellart
 XPath Web ata Management and istribution Serge Abiteboul Philippe Rigaux MarieChristine Rousset Pierre Senellart INRIA Saclay, Univ. Parisauphine, Univ. Grenoble, TELECOM ParisTech http://gemo.futurs.inria.fr/wdmd
XPath Web ata Management and istribution Serge Abiteboul Philippe Rigaux MarieChristine Rousset Pierre Senellart INRIA Saclay, Univ. Parisauphine, Univ. Grenoble, TELECOM ParisTech http://gemo.futurs.inria.fr/wdmd
Oracle 11g: XML Fundamentals
 Oracle 11g: XML Fundamentals Student Guide D52500GC10 Edition 1.0 December 2007 D53762 Authors Chaitanya Koratamaddi Salome Clement Technical Contributors and Reviewers Bijoy Choudhury Isabelle Cornu Ken
Oracle 11g: XML Fundamentals Student Guide D52500GC10 Edition 1.0 December 2007 D53762 Authors Chaitanya Koratamaddi Salome Clement Technical Contributors and Reviewers Bijoy Choudhury Isabelle Cornu Ken
XML, XPath, and XSLT. Jim Fawcett Software Modeling Copyright
 XML, XPath, and XSLT Jim Fawcett Software Modeling Copyright 1999-2017 Topics XML is an acronym for extensible Markup Language. Its purpose is to describe structured data. XPath is a language for navigating
XML, XPath, and XSLT Jim Fawcett Software Modeling Copyright 1999-2017 Topics XML is an acronym for extensible Markup Language. Its purpose is to describe structured data. XPath is a language for navigating
Chapter 5: XPath/XQuery Data Model
 5. XPath/XQuery Data Model 5-1 Chapter 5: XPath/XQuery Data Model References: Mary Fernández, Ashok Malhotra, Jonathan Marsh, Marton Nagy, Norman Walsh (Ed.): XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Data Model (XDM).
5. XPath/XQuery Data Model 5-1 Chapter 5: XPath/XQuery Data Model References: Mary Fernández, Ashok Malhotra, Jonathan Marsh, Marton Nagy, Norman Walsh (Ed.): XQuery 1.0 and XPath 2.0 Data Model (XDM).
BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo
 BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo COMPLMNTI DI BASI DI DATI Parte IV: XPATH Prof. Riccardo Torlone Università Roma Tre Outline Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions
BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo COMPLMNTI DI BASI DI DATI Parte IV: XPATH Prof. Riccardo Torlone Università Roma Tre Outline Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions
Developer's Guide Release 7.3.5
 [1]Oracle Communications Order and Service Management Developer's Guide Release 7.3.5 E79208-01 April 2017 Oracle Communications Order and Service Management Developer's Guide, Release 7.3.5 E79208-01
[1]Oracle Communications Order and Service Management Developer's Guide Release 7.3.5 E79208-01 April 2017 Oracle Communications Order and Service Management Developer's Guide, Release 7.3.5 E79208-01
Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach 2006 Addison-Wesley
 Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach 2006 Addison-Wesley Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions 2 Flexible notation for navigating around trees A basic technology
Anders Møller & Michael I. Schwartzbach 2006 Addison-Wesley Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions 2 Flexible notation for navigating around trees A basic technology
Presentation 19: XML technologies part 2: XSL, XSLT, XSL-FO, XPath & XML Programming
 Presentation 19: XML technologies part 2: XSL, XSLT, XSL-FO, XPath & XML Programming Outline XML recap Formatting CSS or XSL? XPath XSL/XSLT XSL-FO XML Programming Slide 2 XML markup recap XML based on
Presentation 19: XML technologies part 2: XSL, XSLT, XSL-FO, XPath & XML Programming Outline XML recap Formatting CSS or XSL? XPath XSL/XSLT XSL-FO XML Programming Slide 2 XML markup recap XML based on
Introduction to OXPath. Ruslan R. Fayzrakhmanov Christopher Michels Mandy Neumann
 Introduction to OXPath Ruslan R. Fayzrakhmanov Christopher Michels Mandy Neumann Contents Introduction............................................ 5 1 Working Environment.................................
Introduction to OXPath Ruslan R. Fayzrakhmanov Christopher Michels Mandy Neumann Contents Introduction............................................ 5 1 Working Environment.................................
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
META-MODEL SEARCH: USING XPATH FOR SEARCHING DOMAIN-SPECIFIC MODELS RAJESH SUDARSAN
 META-MODEL SEARCH: USING XPATH FOR SEARCHING DOMAIN-SPECIFIC MODELS by RAJESH SUDARSAN A THESIS Submitted to the graduate faculty of The University of Alabama at Birmingham, in partial fulfillment of the
META-MODEL SEARCH: USING XPATH FOR SEARCHING DOMAIN-SPECIFIC MODELS by RAJESH SUDARSAN A THESIS Submitted to the graduate faculty of The University of Alabama at Birmingham, in partial fulfillment of the
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language
 Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
516. XSLT. Prerequisites. Version 1.2
 516. XSLT Version 1.2 This comprehensive four-day course develops in-depth knowledge and skills in transforming XML documents using extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations, or XSLT. Students work
516. XSLT Version 1.2 This comprehensive four-day course develops in-depth knowledge and skills in transforming XML documents using extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations, or XSLT. Students work
Typescript on LLVM Language Reference Manual
 Typescript on LLVM Language Reference Manual Ratheet Pandya UNI: rp2707 COMS 4115 H01 (CVN) 1. Introduction 2. Lexical Conventions 2.1 Tokens 2.2 Comments 2.3 Identifiers 2.4 Reserved Keywords 2.5 String
Typescript on LLVM Language Reference Manual Ratheet Pandya UNI: rp2707 COMS 4115 H01 (CVN) 1. Introduction 2. Lexical Conventions 2.1 Tokens 2.2 Comments 2.3 Identifiers 2.4 Reserved Keywords 2.5 String
XML: Managing with the Java Platform
 In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML (Part 2): Data Model for XML documents and XPath Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4.
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML (Part 2): Data Model for XML documents and XPath Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4.
Big Data 12. Querying
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 12. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 12. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Introduction to XQuery and XML Databases
 Introduction to XQuery and XML Databases TEI@Oxford July 2009 XQuery While XSLT is good for transforming XML to other formats (XML, HTML, PDF, Text, etc.) sometimes you may wish to query a large database
Introduction to XQuery and XML Databases TEI@Oxford July 2009 XQuery While XSLT is good for transforming XML to other formats (XML, HTML, PDF, Text, etc.) sometimes you may wish to query a large database
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 23 February 2016 Semester 2 Week 6 http://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da16
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 23 February 2016 Semester 2 Week 6 http://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da16
IBM. XML and Related Technologies Dumps Braindumps Real Questions Practice Test dumps free
 000-141 Dumps 000-141 Braindumps 000-141 Real Questions 000-141 Practice Test 000-141 dumps free IBM 000-141 XML and Related Technologies http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/000-141 collections
000-141 Dumps 000-141 Braindumps 000-141 Real Questions 000-141 Practice Test 000-141 dumps free IBM 000-141 XML and Related Technologies http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/000-141 collections
XML. Jonathan Geisler. April 18, 2008
 April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
April 18, 2008 What is? IS... What is? IS... Text (portable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) What is? IS... Text (portable) Markup (human readable) Extensible (valuable for future)
XPath. Contents. Tobias Schlitt Jakob Westho November 17, 2008
 XPath Tobias Schlitt , Jakob Westho November 17, 2008 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 The XML tree model......................... 2 1.1.1 Clarication of terms.....................
XPath Tobias Schlitt , Jakob Westho November 17, 2008 Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 The XML tree model......................... 2 1.1.1 Clarication of terms.....................
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
Navigation. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Paths
 03Brundage_ch03.qxd 1/8/04 1:09 PM Page 63 C H A P T E R 3 Navigation 3.1 Introduction Once you ve constructed or loaded XML in a query, you need a way to navigate over that hierarchical data. In many
03Brundage_ch03.qxd 1/8/04 1:09 PM Page 63 C H A P T E R 3 Navigation 3.1 Introduction Once you ve constructed or loaded XML in a query, you need a way to navigate over that hierarchical data. In many
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
XPath Processing in a Nutshell
 XPath Processing in a Nutshell Georg Gottlob, Christoph Koch, and Reinhard Pichler Database and Artificial Intelligence Group Technische Universität Wien, A-1040 Vienna, Austria {gottlob, koch}@dbai.tuwien.ac.at,
XPath Processing in a Nutshell Georg Gottlob, Christoph Koch, and Reinhard Pichler Database and Artificial Intelligence Group Technische Universität Wien, A-1040 Vienna, Austria {gottlob, koch}@dbai.tuwien.ac.at,
DOM Interface subset 1/ 2
 DOM Interface subset 1/ 2 Document attributes documentelement methods createelement, createtextnode, Node attributes nodename, nodevalue, nodetype, parentnode, childnodes, firstchild, lastchild, previoussibling,
DOM Interface subset 1/ 2 Document attributes documentelement methods createelement, createtextnode, Node attributes nodename, nodevalue, nodetype, parentnode, childnodes, firstchild, lastchild, previoussibling,
XML Wrap-up. CS 431 March 1, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 XML Wrap-up CS 431 March 1, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XSLT Processing Model Input XSL doc parse Input XML doc parse Parsed tree serialize Input XML doc Parsed tree Xformed tree Output doc (xml,
XML Wrap-up CS 431 March 1, 2006 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XSLT Processing Model Input XSL doc parse Input XML doc parse Parsed tree serialize Input XML doc Parsed tree Xformed tree Output doc (xml,
Big Data 10. Querying
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 10. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 10. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML
 Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML XML - 1 The Web has generated a new class of data models, which are generally summarized under the notion semi-structured data models. The reasons for that
Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML XML - 1 The Web has generated a new class of data models, which are generally summarized under the notion semi-structured data models. The reasons for that
<Insert Picture Here> Experience with XML Signature and Recommendations for future Development
 Experience with XML Signature and Recommendations for future Development Prateek Mishra, Sep, 2007 Overview Two main recommendations: Working group should consider a simple profile
Experience with XML Signature and Recommendations for future Development Prateek Mishra, Sep, 2007 Overview Two main recommendations: Working group should consider a simple profile
Scheme Tutorial. Introduction. The Structure of Scheme Programs. Syntax
 Scheme Tutorial Introduction Scheme is an imperative language with a functional core. The functional core is based on the lambda calculus. In this chapter only the functional core and some simple I/O is
Scheme Tutorial Introduction Scheme is an imperative language with a functional core. The functional core is based on the lambda calculus. In this chapter only the functional core and some simple I/O is
