SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Safety for C
|
|
|
- Gerald Walton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Safety for C Santosh Nagarakatte, Jianzhou Zhao, Milo Martin, Steve Zdancewic University of Pennsylvania {santoshn, jianzhou, milom, stevez}@cis.upenn.edu
2 This work licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 United States License You are free: to Share to copy, distribute, display, and perform the work to Remix to make derivative works Under the following conditions: Attribution. You must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work). Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same, similar or a compatible license. For any reuse or distribution, you must make clear to others the license terms of this work. The best way to do this is with a link to: Any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder. Apart from the remix rights granted under this license, nothing in this license impairs or restricts the author's moral rights. 2
3 Who Cares About Spatial Safety, Anyway? June 2, 2009: itunes-8.2 Open URL, stack overflow May 12, 2009: libxml, Safari-3.2.3, Visit website, heap overflow Feb 20, 2009: Acrobat Reader Open PDF, overflow Jan 22, 2009: Windows, RPC packet, overflow (Conficker worm) These buffer overflows are security vulnerabilities 3
4 SoftBound: Spatial Safety for C Compiler transformation to enforce spatial safety Inspired by fat pointer schemes and HardBound Compatible no source code modifications Key: disjoint fat pointers memory layout unchanged Simple analysis intra-procedural Separate compilation, creation of safe libraries Effective observed no false positives/negatives Low overhead All loads and stores 67% overhead Only stores 21% overhead 4
5 memory acctid bal id memory a b c x10 Spatial Violation Example registers p reg 0x12 0x13 0x10 0x17 0x11 struct BankAccount { } b; char acctid[3]; int balance; b.balance = 0; char* id = &(b.acctid); char* p = id; do { char ch = readchar(); *p = ch; p++; } while(ch); 5
6 Preventing Spatial Violations treat the symptoms address space randomization use a safe language add bounds non-executable stack/heap write perfect code protect return addresses checking to C all incomplete what about (existing) C code? 6
7 Background: Bounds Checking for C Prior work: [Hastings92, Austin94, Jones97, Jim02, Necula02, Yong03, Eigler03, Ruwase04, Nethercote04, Xu04, Dhurjati06, Criswell07, ] Tripwires e.g., Purify, Valgrind Few bits of state for each byte in memory A red-zone block between objects Pointer based e.g., SafeC, Cyclone, CCured, MSCC, Pointer becomes a fat pointer (ptr, base, bound) Pointer dereferences are checked Object based e.g., Jones & Kelly, CRED, SafeCode, SVA, Checks pointer manipulations Must point within same object All have one or more challenges: High runtime overheads Incompleteness, handling arbitrary casts Incompatible pointer representations, code incompatibilities 7
8 memory acctid bal id Background: Fat Pointer Approach memory a b c 0 id_bse 0x10 0x10 id_bnd 0x13 registers p_bse 0x10 p reg 0x11 0x10 0x12 p_bnd 0x13 0x13 struct BankAccount { } b; char acctid[3]; int balance; b.balance = 0; char* id = &(b.acctid); char* id_bse = &(b.acctid); char* id_bnd = &(b.acctid) + 3; char* p = id; char* p_bse = id_bse; char* p_bnd = id_bnd; do { char ch = readchar(); check(p, p_bse, p_bnd);*p = ch; p++; } while(ch); 8
9 Background: Object Based Approach memory acctid bal memory a b c p table registers reg 0x12 0x17 0x16 0x10 0x13 0x11 object table 10,11 11,12 12,13 16,17 Obj id 0x10 10 to 16 struct BankAccount { } b; char acctid[3]; int balance; insert(b, &b, &b+sizeof(b)); b.balance = 0; char* id = &(b.acctid); char* p = id; do { char ch = readchar(); *p = ch; p++; p = lookup(p, p + 1); } while(ch); 9
10 Object based Comparison of Approaches + Disjoint metadata memory layout unchanged high source compatibility Cannot detect sub-object overflows, range lookup Fat pointer + Detects sub-objects overflows Inline metadata memory layout changes low source compatibility HardBound [Devietti08] + Hardware to reduce overhead & improve compatibility Requires new hardware 10
11 memory acctid bal id memory a b c 0 SoftBound Approach data 38 registers p_bse 0x10 p reg 0x13 0x10 0x12 0x11 p_bnd 0x13 metadata Meta 0x13 0x10 struct BankAccount { } b; char acctid[3]; int balance; b.balance = 0; char* id = &(b.acctid); lookup(&id)->bse = &(b.acctid); lookup(&id)->bnd = &(b.acctid) + 3; char* p = id; char* p_bse = lookup(&id)->bse; char* p_bnd = lookup(&id)->bnd; do { char ch = readchar(); check(p, p_bse, p_bnd);*p=ch; p++; } while(ch); 11
12 memory SoftBound Approach registers memory acctid bal id a b c 0 data 38 p.bse 0x10 p reg 0x13 p.bnd 0x13 metadata Meta 0x13 0x10 Pointer based Disjoint metadata Unchanged memory layout Safe with arbitrary casts 12
13 Rest of Talk SoftBound handling of base/bound metadata Storage Checking on pointer dereference Creation Propagation SoftBound prototype Experiments 13
14 SoftBound Base/Bound Storage Registers For memory: hash table Tagged, open hashing Fast hash function (bitmask) Nine x86 instructions Shift, mask, multiply, add, three loads, cmp, branch Alternative: shadow space No collisions eliminates tag Reduce memory footprint Five x86 instructions Shift, mask, add, two loads Table Space base Hash tag base bound Shadow bound 14
15 Pointer Dereference Checks All pointer dereferences are checked if (p < p_base) abort(); if (p + size > p_bound) abort(); value = *p; Five x86 instructions (cmp, br, add, cmp, br) Bounds check elimination not focus Intra-procedural dominator based Previous techniques would help a lot 15
16 Pointer Creation Heap Objects Stack and Global Objects p = malloc(size); p_base = p; p_bound = p + size; int array[100]; p = &array; p_base = p; p_bound = p + sizeof(array); 16
17 Base/Bound Metadata Propagation Pointer assignments and casts Just propagate pointer base and bound Loading/storing a pointer from memory Loads/stores base and bound from metadata space Pointer arguments to a function Bounds passed as extra arguments (in registers) int f(char* p) { } int _f(char* p, void* p_base, void* p_bound) { } 17
18 Pointers to Structure Fields struct { char acctid[3]; int balance; } *ptr; char* id = &(ptr->acctid); option #1 Entire Structure id_base = ptr_base; id_bound = ptr_bound; option #2 Shrink to Field Only id_base = &(ptr->acctid); id_bound = &(ptr->acctid) + 3; Programmer intent ambiguous; optional shrinking of bounds 18
19 See Paper For Proof of spatial safety guarantees Region delineated by pointer metadata is always valid Formalized a rich subset of C Includes arbitrary casts, recursive structures, etc Mechanized proof in Coq Online at: Handling various aspects of C Separate compilation and library code memcpy() Function pointers Variable argument functions Etc 19
20 SoftBound Prototype Source LLVM as its foundation Typed IR helps in pointer identification Typed IR Optimize ~7K lines of code SoftBound Optimize Binary 20
21 Experiments Three questions Can SoftBound detect overflows? Does SoftBound work with existing C code? Does SoftBound have low overhead? 21
22 Spatial Violation Detection Can SoftBound detect overflows? Synthetic attacks [Wilander et al] Prevented all these attacks Bugbench [Lu05]: overflows from real applications Benchmark SoftBound Mudflap Valgrind Go Yes No No Compress Yes Yes Yes Polymorph Yes Yes No Gzip Yes Yes Yes No false negatives encountered 22
23 Source Compatibility Experiments Does SoftBound work with existing C code? 272K lines of code total 23 benchmarks from Spec, Olden BugBench Multithreaded HTTP Server with CGI support FTP server No false positives encountered 23
24 Percent Runtime Overhead: Shadow Space Full Checking Store Only Checking 67% 21% Check only stores [Yong03, Castro06] Full Checking: default for development & testing Attacks predominantly use stores Store-only: for security critical apps, production code 24
25 Experiments Recap Can SoftBound detect overflows? Yes Does SoftBound work with existing C code? Yes Does SoftBound have low overhead? Yes Full checking overhead - 67% Store only checking overhead - 21% 25
26 Conclusions SoftBound provides spatial safety for C Fat pointer approach, but with disjoint metadata Provides spatial safety guarantees SoftBound is: Compatible (no false positives, no source changes) Effective (no false negatives) Fast enough for Debugging & testing: full checking Security-critical software: store only checking Future work More optimizations, temporal safety (dangling pointers) 26
27 Want to try it out? 27
28
Secure Low-Level Programming via Hardware-Assisted Memory-Safe C
 Secure Low-Level Programming via Hardware-Assisted Memory-Safe C Prof. Milo Martin Santosh Nagarakatte, Joe Devietti, Jianzhou Zhao, Colin Blundell Prof. Steve Zdancewic University of Pennsylvania Please
Secure Low-Level Programming via Hardware-Assisted Memory-Safe C Prof. Milo Martin Santosh Nagarakatte, Joe Devietti, Jianzhou Zhao, Colin Blundell Prof. Steve Zdancewic University of Pennsylvania Please
HardBound: Architectural Support for Spatial Safety of the C Programming Language
 HardBound: Architectural Support for Spatial Safety of the C Programming Language Joe Devietti *, Colin Blundell, Milo Martin, Steve Zdancewic * University of Washington, University of Pennsylvania devietti@cs.washington.edu,
HardBound: Architectural Support for Spatial Safety of the C Programming Language Joe Devietti *, Colin Blundell, Milo Martin, Steve Zdancewic * University of Washington, University of Pennsylvania devietti@cs.washington.edu,
CS-527 Software Security
 CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
CS-527 Software Security Memory Safety Asst. Prof. Mathias Payer Department of Computer Science Purdue University TA: Kyriakos Ispoglou https://nebelwelt.net/teaching/17-527-softsec/ Spring 2017 Eternal
CS527 Software Security
 Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Security Policies Purdue University, Spring 2018 Security Policies A policy is a deliberate system of principles to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent, and
Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++
 Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier, Richard Eisenberg, Peter-Michael Osera, Santosh Nagarakatte*, Milo M. K. Martin, and Steve Zdancewic October 30, 2013 University
Ironclad C++ A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier, Richard Eisenberg, Peter-Michael Osera, Santosh Nagarakatte*, Milo M. K. Martin, and Steve Zdancewic October 30, 2013 University
SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Memory Safety for C
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Technical Reports (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science January 2009 SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Memory Safety for C Santosh
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Technical Reports (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science January 2009 SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Memory Safety for C Santosh
SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Memory Safety for C
 SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Memory Safety for C Santosh Nagarakatte Jianzhou Zhao Milo M. K. Martin Steve Zdancewic Computer and Information Sciences Department, University of Pennsylvania
SoftBound: Highly Compatible and Complete Spatial Memory Safety for C Santosh Nagarakatte Jianzhou Zhao Milo M. K. Martin Steve Zdancewic Computer and Information Sciences Department, University of Pennsylvania
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur:
 A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
A program execution is memory safe so long as memory access errors never occur: Buffer overflows, null pointer dereference, use after free, use of uninitialized memory, illegal free Memory safety categories
HardBound: Architectural Support for Spatial Safety of the C Programming Language
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 3-1-2008 HardBound: Architectural Support for Spatial Safety of the C Programming Language
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 3-1-2008 HardBound: Architectural Support for Spatial Safety of the C Programming Language
Heriot-Watt University
 Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Tag-Protector: An Effective and Dynamic Detection of Illegal Memory Accesses Through Compile-time Code Instrumentation Saeed, Ahmed; Ahmadinia,
Heriot-Watt University Heriot-Watt University Research Gateway Tag-Protector: An Effective and Dynamic Detection of Illegal Memory Accesses Through Compile-time Code Instrumentation Saeed, Ahmed; Ahmadinia,
Runtime Defenses against Memory Corruption
 CS 380S Runtime Defenses against Memory Corruption Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Reading Assignment Cowan et al. Buffer overflows: Attacks and defenses for the vulnerability of the decade (DISCEX 2000). Avijit,
CS 380S Runtime Defenses against Memory Corruption Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Reading Assignment Cowan et al. Buffer overflows: Attacks and defenses for the vulnerability of the decade (DISCEX 2000). Avijit,
Baggy bounds checking. Periklis Akri5dis, Manuel Costa, Miguel Castro, Steven Hand
 Baggy bounds checking Periklis Akri5dis, Manuel Costa, Miguel Castro, Steven Hand C/C++ programs are vulnerable Lots of exis5ng code in C and C++ More being wrieen every day C/C++ programs are prone to
Baggy bounds checking Periklis Akri5dis, Manuel Costa, Miguel Castro, Steven Hand C/C++ programs are vulnerable Lots of exis5ng code in C and C++ More being wrieen every day C/C++ programs are prone to
SAFECODE: A PLATFORM FOR DEVELOPING RELIABLE SOFTWARE IN UNSAFE LANGUAGES DINAKAR DHURJATI
 SAFECODE: A PLATFORM FOR DEVELOPING RELIABLE SOFTWARE IN UNSAFE LANGUAGES BY DINAKAR DHURJATI B.Tech., Indian Institute of Technology - Delhi, 2000 DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the
SAFECODE: A PLATFORM FOR DEVELOPING RELIABLE SOFTWARE IN UNSAFE LANGUAGES BY DINAKAR DHURJATI B.Tech., Indian Institute of Technology - Delhi, 2000 DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the
CCured. One-Slide Summary. Lecture Outline. Type-Safe Retrofitting of C Programs
 CCured Type-Safe Retrofitting of C Programs [Necula, McPeak,, Weimer, Condit, Harren] #1 One-Slide Summary CCured enforces memory safety and type safety in legacy C programs. CCured analyzes how you use
CCured Type-Safe Retrofitting of C Programs [Necula, McPeak,, Weimer, Condit, Harren] #1 One-Slide Summary CCured enforces memory safety and type safety in legacy C programs. CCured analyzes how you use
Secure Virtual Architecture: Using LLVM to Provide Memory Safety to the Entire Software Stack
 Secure Virtual Architecture: Using LLVM to Provide Memory Safety to the Entire Software Stack John Criswell, University of Illinois Andrew Lenharth, University of Illinois Dinakar Dhurjati, DoCoMo Communications
Secure Virtual Architecture: Using LLVM to Provide Memory Safety to the Entire Software Stack John Criswell, University of Illinois Andrew Lenharth, University of Illinois Dinakar Dhurjati, DoCoMo Communications
Stack Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers
 Stack Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers Gregory J. Duck, Roland H.C. Yap, and Lorenzo Cavallaro NDSS 2017 Overview Heap Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers, CC 2016 Stack New method for detecting
Stack Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers Gregory J. Duck, Roland H.C. Yap, and Lorenzo Cavallaro NDSS 2017 Overview Heap Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers, CC 2016 Stack New method for detecting
Preventing Use-after-free with Dangling Pointers Nullification
 Preventing Use-after-free with Dangling Pointers Nullification Byoungyoung Lee, Chengyu Song, Yeongjin Jang Tielei Wang, Taesoo Kim, Long Lu, Wenke Lee Georgia Institute of Technology Stony Brook University
Preventing Use-after-free with Dangling Pointers Nullification Byoungyoung Lee, Chengyu Song, Yeongjin Jang Tielei Wang, Taesoo Kim, Long Lu, Wenke Lee Georgia Institute of Technology Stony Brook University
AHEMS: Asynchronous Hardware-Enforced Memory Safety
 Submitted for publication. Author copy - do not redistribute. AHEMS: Asynchronous Hardware-Enforced Memory Safety Kuan-Yu Tseng, Dao Lu, Zbigniew Kalbarczyk, Ravishankar Iyer Coordinated Science Laboratory
Submitted for publication. Author copy - do not redistribute. AHEMS: Asynchronous Hardware-Enforced Memory Safety Kuan-Yu Tseng, Dao Lu, Zbigniew Kalbarczyk, Ravishankar Iyer Coordinated Science Laboratory
CMPSC 497 Execution Integrity
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Execution Integrity
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Execution Integrity
Cling: A Memory Allocator to Mitigate Dangling Pointers. Periklis Akritidis
 Cling: A Memory Allocator to Mitigate Dangling Pointers Periklis Akritidis --2010 Use-after-free Vulnerabilities Accessing Memory Through Dangling Pointers Techniques : Heap Spraying, Feng Shui Manual
Cling: A Memory Allocator to Mitigate Dangling Pointers Periklis Akritidis --2010 Use-after-free Vulnerabilities Accessing Memory Through Dangling Pointers Techniques : Heap Spraying, Feng Shui Manual
Securing Software Applications Using Dynamic Dataflow Analysis. OWASP June 16, The OWASP Foundation
 Securing Software Applications Using Dynamic Dataflow Analysis Steve Cook OWASP June 16, 2010 0 Southwest Research Institute scook@swri.org (210) 522-6322 Copyright The OWASP Foundation Permission is granted
Securing Software Applications Using Dynamic Dataflow Analysis Steve Cook OWASP June 16, 2010 0 Southwest Research Institute scook@swri.org (210) 522-6322 Copyright The OWASP Foundation Permission is granted
DieHard: Probabilistic Memory Safety for Unsafe Programming Languages
 DieHard: Probabilistic Memory Safety for Unsafe Programming Languages Emery Berger University of Massachusetts Amherst Ben Zorn Microsoft Research Problems with Unsafe Languages C, C++: pervasive apps,
DieHard: Probabilistic Memory Safety for Unsafe Programming Languages Emery Berger University of Massachusetts Amherst Ben Zorn Microsoft Research Problems with Unsafe Languages C, C++: pervasive apps,
Effective Memory Protection Using Dynamic Tainting
 Effective Memory Protection Using Dynamic Tainting James Clause Alessandro Orso (software) and Ioanis Doudalis Milos Prvulovic (hardware) College of Computing Georgia Institute of Technology Supported
Effective Memory Protection Using Dynamic Tainting James Clause Alessandro Orso (software) and Ioanis Doudalis Milos Prvulovic (hardware) College of Computing Georgia Institute of Technology Supported
SoK: Eternal War in Memory Laszlo Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, and Dawn Song In: Oakland 14
 SoK: Eternal War in Memory Laszlo Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, and Dawn Song In: Oakland 14 Presenter: Mathias Payer, EPFL http://hexhive.github.io 1 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes
SoK: Eternal War in Memory Laszlo Szekeres, Mathias Payer, Tao Wei, and Dawn Song In: Oakland 14 Presenter: Mathias Payer, EPFL http://hexhive.github.io 1 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes
Memory Safety for Embedded Devices with nescheck
 Memory Safety for Embedded Devices with nescheck Daniele MIDI, Mathias PAYER, Elisa BERTINO Purdue University AsiaCCS 2017 Ubiquitous Computing and Security Sensors and WSNs are pervasive Small + cheap
Memory Safety for Embedded Devices with nescheck Daniele MIDI, Mathias PAYER, Elisa BERTINO Purdue University AsiaCCS 2017 Ubiquitous Computing and Security Sensors and WSNs are pervasive Small + cheap
in memory: an evolution of attacks Mathias Payer Purdue University
 in memory: an evolution of attacks Mathias Payer Purdue University Images (c) MGM, WarGames, 1983 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes according to CVE Memory
in memory: an evolution of attacks Mathias Payer Purdue University Images (c) MGM, WarGames, 1983 Memory attacks: an ongoing war Vulnerability classes according to CVE Memory
Fast, precise dynamic checking of types and bounds in C
 Fast, precise dynamic checking of types and bounds in C Stephen Kell stephen.kell@cl.cam.ac.uk Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge p.1 Tool wanted if (obj >type == OBJ COMMIT) { if (process commit(walker,
Fast, precise dynamic checking of types and bounds in C Stephen Kell stephen.kell@cl.cam.ac.uk Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge p.1 Tool wanted if (obj >type == OBJ COMMIT) { if (process commit(walker,
Heap Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers
 Heap Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers Gregory J. Duck Roland H. C. Yap Department of Computer Science National University of Singapore, Singapore {gregory,ryap}@comp.nus.edu.sg Abstract Heap buffer
Heap Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers Gregory J. Duck Roland H. C. Yap Department of Computer Science National University of Singapore, Singapore {gregory,ryap}@comp.nus.edu.sg Abstract Heap buffer
7. Optimization! Prof. O. Nierstrasz! Lecture notes by Marcus Denker!
 7. Optimization! Prof. O. Nierstrasz! Lecture notes by Marcus Denker! Roadmap > Introduction! > Optimizations in the Back-end! > The Optimizer! > SSA Optimizations! > Advanced Optimizations! 2 Literature!
7. Optimization! Prof. O. Nierstrasz! Lecture notes by Marcus Denker! Roadmap > Introduction! > Optimizations in the Back-end! > The Optimizer! > SSA Optimizations! > Advanced Optimizations! 2 Literature!
Memory Safety for Low- Level Software/Hardware Interactions
 Safety for Low- Level Software/Hardware Interactions John Criswell Nicolas Geoffray Montreal or Bust! Vikram Adve Safety Future is Bright User-space memory safety is improving Safe languages SAFECode,
Safety for Low- Level Software/Hardware Interactions John Criswell Nicolas Geoffray Montreal or Bust! Vikram Adve Safety Future is Bright User-space memory safety is improving Safe languages SAFECode,
Boundless Memory Blocks
 Boundless Memory Blocks Cristian Cadar Massachusetts Institute of Technology (now Stanford University) M. Rinard, D. Dumitran D. Roy, T. Leu Massachusetts Institute of Technology Annual Computer Security
Boundless Memory Blocks Cristian Cadar Massachusetts Institute of Technology (now Stanford University) M. Rinard, D. Dumitran D. Roy, T. Leu Massachusetts Institute of Technology Annual Computer Security
An Efficient and Backwards-Compatible Transformation to Ensure Memory Safety of C Programs
 An Efficient and Backwards-Compatible Transformation to Ensure Memory Safety of C Programs Wei Xu, Daniel C. DuVarney, and R. Sekar Department of Computer Science, Stony Brook University Stony Brook, NY
An Efficient and Backwards-Compatible Transformation to Ensure Memory Safety of C Programs Wei Xu, Daniel C. DuVarney, and R. Sekar Department of Computer Science, Stony Brook University Stony Brook, NY
CMPSC 497 Other Memory Vulnerabilities
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Other Memory
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA CMPSC 497 Other Memory
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE. The University of Tokyo
 Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
Information Flow Analysis and Type Systems for Secure C Language (VITC Project) Jun FURUSE The University of Tokyo furuse@yl.is.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp e-society MEXT project toward secure and reliable software
CS 430 Spring Mike Lam, Professor. Data Types and Type Checking
 CS 430 Spring 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Data Types and Type Checking Type Systems Type system Rules about valid types, type compatibility, and how data values can be used Benefits of a robust type system
CS 430 Spring 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Data Types and Type Checking Type Systems Type system Rules about valid types, type compatibility, and how data values can be used Benefits of a robust type system
5. Semantic Analysis!
 5. Semantic Analysis! Prof. O. Nierstrasz! Thanks to Jens Palsberg and Tony Hosking for their kind permission to reuse and adapt the CS132 and CS502 lecture notes.! http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~palsberg/! http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/hosking/!
5. Semantic Analysis! Prof. O. Nierstrasz! Thanks to Jens Palsberg and Tony Hosking for their kind permission to reuse and adapt the CS132 and CS502 lecture notes.! http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~palsberg/! http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/hosking/!
Fast Byte-Granularity Software Fault Isolation
 Fast Byte-Granularity Software Fault Isolation Manuel Costa Microsoft Research, Cambridge Joint work with: Miguel Castro, Jean-Philippe Martin, Marcus Peinado, Periklis Akritidis, Austin Donnelly, Paul
Fast Byte-Granularity Software Fault Isolation Manuel Costa Microsoft Research, Cambridge Joint work with: Miguel Castro, Jean-Philippe Martin, Marcus Peinado, Periklis Akritidis, Austin Donnelly, Paul
Watchdog: Hardware for Safe and Secure Manual Memory Management and Full Memory Safety
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 6-2012 Watchdog: Hardware for Safe and Secure Manual Memory Management and Full Memory
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 6-2012 Watchdog: Hardware for Safe and Secure Manual Memory Management and Full Memory
Undefined Behaviour in C
 Undefined Behaviour in C Report Field of work: Scientific Computing Field: Computer Science Faculty for Mathematics, Computer Science and Natural Sciences University of Hamburg Presented by: Dennis Sobczak
Undefined Behaviour in C Report Field of work: Scientific Computing Field: Computer Science Faculty for Mathematics, Computer Science and Natural Sciences University of Hamburg Presented by: Dennis Sobczak
Checked C. Michael Hicks The University of Maryland joint work with David Tarditi (MSR), Andrew Ruef (UMD), Sam Elliott (UW)
 Checked C Michael Hicks The University of Maryland joint work with David Tarditi (MSR), Andrew Ruef (UMD), Sam Elliott (UW) UM Motivation - Lots of C/C++ code out there. - One open source code indexer
Checked C Michael Hicks The University of Maryland joint work with David Tarditi (MSR), Andrew Ruef (UMD), Sam Elliott (UW) UM Motivation - Lots of C/C++ code out there. - One open source code indexer
Týr: A Dependent Type System for Spatial Memory Safety in LLVM
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 324 (2016) 3 13 www.elsevier.com/locate/entcs Týr: A Dependent Type System for Spatial Memory Safety in LLVM Vítor
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 324 (2016) 3 13 www.elsevier.com/locate/entcs Týr: A Dependent Type System for Spatial Memory Safety in LLVM Vítor
Stack Overflow COMP620
 Stack Overflow COMP620 There are two kinds of people in America today: those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and know it, and those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and don t know
Stack Overflow COMP620 There are two kinds of people in America today: those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and know it, and those who have experienced a foreign cyber attack and don t know
Code Injection Attacks Buffer Overflows
 CSE 5095 & ECE 4451 & ECE 5451 Spring 2017 System Security Lecture 1 Code Injection Attacks Buffer Overflows Based on and extracted from Nickolai Zeldovitch, Computer System Security, course material at
CSE 5095 & ECE 4451 & ECE 5451 Spring 2017 System Security Lecture 1 Code Injection Attacks Buffer Overflows Based on and extracted from Nickolai Zeldovitch, Computer System Security, course material at
Defeating Code Reuse Attacks with Minimal Tagged Architecture. Samuel Fingeret. B.S., Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2014)
 Defeating Code Reuse Attacks with Minimal Tagged Architecture by Samuel Fingeret B.S., Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2014) Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Defeating Code Reuse Attacks with Minimal Tagged Architecture by Samuel Fingeret B.S., Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2014) Submitted to the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Heap Arrays. Steven R. Bagley
 Heap Arrays Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index a[42] = 35; Variables and arrays have a type int, char, double,
Heap Arrays Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index a[42] = 35; Variables and arrays have a type int, char, double,
Decoupling Dynamic Information Flow Tracking with a Dedicated Coprocessor
 Decoupling Dynamic Information Flow Tracking with a Dedicated Coprocessor Hari Kannan, Michael Dalton, Christos Kozyrakis Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University Motivation Dynamic analysis help
Decoupling Dynamic Information Flow Tracking with a Dedicated Coprocessor Hari Kannan, Michael Dalton, Christos Kozyrakis Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University Motivation Dynamic analysis help
Heap Arrays and Linked Lists. Steven R. Bagley
 Heap Arrays and Linked Lists Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index Variables and arrays have a type Create our
Heap Arrays and Linked Lists Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index Variables and arrays have a type Create our
System Assertions. Andreas Zeller
 System Assertions Andreas Zeller System Invariants Some properties of a program must hold over the entire run: must not access data of other processes must handle mathematical exceptions must not exceed
System Assertions Andreas Zeller System Invariants Some properties of a program must hold over the entire run: must not access data of other processes must handle mathematical exceptions must not exceed
Type Checking Systems Code
 Type Checking Systems Code Greg Morrisett Cornell University Abstract. Our critical computing systems are coded in low-level, typeunsafe languages such as C, and it is unlikely that they will be re-coded
Type Checking Systems Code Greg Morrisett Cornell University Abstract. Our critical computing systems are coded in low-level, typeunsafe languages such as C, and it is unlikely that they will be re-coded
PtrSplit: Supporting General Pointers in Automatic Program Partitioning
 PtrSplit: Supporting General Pointers in Automatic Program Partitioning Shen Liu Gang Tan Trent Jaeger Computer Science and Engineering Department The Pennsylvania State University 11/02/2017 Motivation
PtrSplit: Supporting General Pointers in Automatic Program Partitioning Shen Liu Gang Tan Trent Jaeger Computer Science and Engineering Department The Pennsylvania State University 11/02/2017 Motivation
Decoupling Dynamic Information Flow Tracking with a Dedicated Coprocessor
 1 Decoupling Dynamic Information Flow Tracking with a Dedicated Coprocessor Hari Kannan, Michael Dalton, Christos Kozyrakis Presenter: Yue Zheng Yulin Shi Outline Motivation & Background Hardware DIFT
1 Decoupling Dynamic Information Flow Tracking with a Dedicated Coprocessor Hari Kannan, Michael Dalton, Christos Kozyrakis Presenter: Yue Zheng Yulin Shi Outline Motivation & Background Hardware DIFT
Outline. Classic races: files in /tmp. Race conditions. TOCTTOU example. TOCTTOU gaps. Vulnerabilities in OS interaction
 Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Stack Overflow. Faculty Workshop on Cyber Security May 23, 2012
 Stack Overflow Faculty Workshop on Cyber Security May 23, 2012 Goals Learn to hack into computer systems using buffer overflow Steal sensitive data Crash computer programs Lay waste to systems throughout
Stack Overflow Faculty Workshop on Cyber Security May 23, 2012 Goals Learn to hack into computer systems using buffer overflow Steal sensitive data Crash computer programs Lay waste to systems throughout
Program Security and Vulnerabilities Class 2
 Program Security and Vulnerabilities Class 2 CEN-5079: 28.August.2017 1 Secure Programs Programs Operating System Device Drivers Network Software (TCP stack, web servers ) Database Management Systems Integrity
Program Security and Vulnerabilities Class 2 CEN-5079: 28.August.2017 1 Secure Programs Programs Operating System Device Drivers Network Software (TCP stack, web servers ) Database Management Systems Integrity
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security. Spring 2007 Lecture 2
 CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 2 Announcements First project is on the web Due: Feb. 1st at midnight Form groups of 2 or 3 people If you need help finding a group,
CIS 551 / TCOM 401 Computer and Network Security Spring 2007 Lecture 2 Announcements First project is on the web Due: Feb. 1st at midnight Form groups of 2 or 3 people If you need help finding a group,
Short Notes of CS201
 #includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
#includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
CNIT 127: Exploit Development. Ch 18: Source Code Auditing. Updated
 CNIT 127: Exploit Development Ch 18: Source Code Auditing Updated 4-10-17 Why Audit Source Code? Best way to discover vulnerabilities Can be done with just source code and grep Specialized tools make it
CNIT 127: Exploit Development Ch 18: Source Code Auditing Updated 4-10-17 Why Audit Source Code? Best way to discover vulnerabilities Can be done with just source code and grep Specialized tools make it
Types II. Hwansoo Han
 Types II Hwansoo Han Arrays Most common and important composite data types Homogeneous elements, unlike records Fortran77 requires element type be scalar Elements can be any type (Fortran90, etc.) A mapping
Types II Hwansoo Han Arrays Most common and important composite data types Homogeneous elements, unlike records Fortran77 requires element type be scalar Elements can be any type (Fortran90, etc.) A mapping
Ironclad C++: A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Technical Reports (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 3-28-2013 Ironclad C++: A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier University
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Technical Reports (CIS) Department of Computer & Information Science 3-28-2013 Ironclad C++: A Library-Augmented Type-Safe Subset of C++ Christian DeLozier University
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By
 CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
Real-World Buffer Overflow Protection in User & Kernel Space
 Real-World Buffer Overflow Protection in User & Kernel Space Michael Dalton, Hari Kannan, Christos Kozyrakis Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University http://raksha.stanford.edu 1 Motivation Buffer
Real-World Buffer Overflow Protection in User & Kernel Space Michael Dalton, Hari Kannan, Christos Kozyrakis Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University http://raksha.stanford.edu 1 Motivation Buffer
Bounds-Checking for C++
 Outsourcing Report Bounds-Checking for C++ Alexander Lamaison Department of Computing Imperial College London Supervisor: Paul H. J. Kelly 12 th January 2007 Contents
Outsourcing Report Bounds-Checking for C++ Alexander Lamaison Department of Computing Imperial College London Supervisor: Paul H. J. Kelly 12 th January 2007 Contents
Compiler Construction: LLVMlite
 Compiler Construction: LLVMlite Direct compilation Expressions X86lite Input Output Compile directly from expression language to x86 Syntax-directed compilation scheme Special cases can improve generated
Compiler Construction: LLVMlite Direct compilation Expressions X86lite Input Output Compile directly from expression language to x86 Syntax-directed compilation scheme Special cases can improve generated
Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone
 Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone Dan Grossman Cornell University June 2002 Joint work with: Greg Morrisett, Trevor Jim (AT&T), Michael Hicks, James Cheney, Yanling Wang Cyclone A safe C-level
Region-Based Memory Management in Cyclone Dan Grossman Cornell University June 2002 Joint work with: Greg Morrisett, Trevor Jim (AT&T), Michael Hicks, James Cheney, Yanling Wang Cyclone A safe C-level
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security. Lecture 16 Buffer Overflow Attacks
 ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security Lecture 16 Buffer Overflow Attacks Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park Buffer overflow
ENEE 457: Computer Systems Security Lecture 16 Buffer Overflow Attacks Charalampos (Babis) Papamanthou Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park Buffer overflow
Lecture 10. Pointless Tainting? Evaluating the Practicality of Pointer Tainting. Asia Slowinska, Herbert Bos. Advanced Operating Systems
 Lecture 10 Pointless Tainting? Evaluating the Practicality of Pointer Tainting Asia Slowinska, Herbert Bos Advanced Operating Systems December 15, 2010 SOA/OS Lecture 10, Pointer Tainting 1/40 Introduction
Lecture 10 Pointless Tainting? Evaluating the Practicality of Pointer Tainting Asia Slowinska, Herbert Bos Advanced Operating Systems December 15, 2010 SOA/OS Lecture 10, Pointer Tainting 1/40 Introduction
Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues
 Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Lecture 9 Assertions and Error Handling CS240
 Lecture 9 Assertions and Error Handling CS240 The C preprocessor The C compiler performs Macro expansion and directive handling Preprocessing directive lines, including file inclusion and conditional compilation,
Lecture 9 Assertions and Error Handling CS240 The C preprocessor The C compiler performs Macro expansion and directive handling Preprocessing directive lines, including file inclusion and conditional compilation,
Inference of Memory Bounds
 Research Review 2017 Will Klieber, software security researcher Joint work with Will Snavely public release and unlimited distribution. 1 Copyright 2017 Carnegie Mellon University. All Rights Reserved.
Research Review 2017 Will Klieber, software security researcher Joint work with Will Snavely public release and unlimited distribution. 1 Copyright 2017 Carnegie Mellon University. All Rights Reserved.
Low level security. Andrew Ruef
 Low level security Andrew Ruef What s going on Stuff is getting hacked all the time We re writing tons of software Often with little regard to reliability let alone security The regulatory environment
Low level security Andrew Ruef What s going on Stuff is getting hacked all the time We re writing tons of software Often with little regard to reliability let alone security The regulatory environment
Light-weight Bounds Checking
 Light-weight Bounds Checking Niranjan Hasabnis, Ashish Misra and R. Sekar Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 11794 ABSTRACT Memory errors in C and C++ programs continue to be one of the dominant sources
Light-weight Bounds Checking Niranjan Hasabnis, Ashish Misra and R. Sekar Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 11794 ABSTRACT Memory errors in C and C++ programs continue to be one of the dominant sources
Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 CSE 5095 & ECE 6095 Spring 2016 Instructor Marten van Dijk System Security Lecture 1 Buffer Overflows Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut Email:
CSE 5095 & ECE 6095 Spring 2016 Instructor Marten van Dijk System Security Lecture 1 Buffer Overflows Syed Kamran Haider Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Connecticut Email:
Identifying Memory Corruption Bugs with Compiler Instrumentations. 이병영 ( 조지아공과대학교
 Identifying Memory Corruption Bugs with Compiler Instrumentations 이병영 ( 조지아공과대학교 ) blee@gatech.edu @POC2014 How to find bugs Source code auditing Fuzzing Source Code Auditing Focusing on specific vulnerability
Identifying Memory Corruption Bugs with Compiler Instrumentations 이병영 ( 조지아공과대학교 ) blee@gatech.edu @POC2014 How to find bugs Source code auditing Fuzzing Source Code Auditing Focusing on specific vulnerability
Computer System and programming in C
 Computer System and programming in C 1 C structures: aggregate, yet scalar aggregate in that they hold multiple data items at one time named members hold data items of various types like the notion of
Computer System and programming in C 1 C structures: aggregate, yet scalar aggregate in that they hold multiple data items at one time named members hold data items of various types like the notion of
SoK: Sanitizing for Security
 SoK: Sanitizing for Security Dokyung Song, Julian Lettner, Prabhu Rajasekaran, Yeoul Na, Stijn Volckaert, Per Larsen, Michael Franz University of California, Irvine {dokyungs,jlettner,rajasekp,yeouln,stijnv,perl,franz}@uci.edu
SoK: Sanitizing for Security Dokyung Song, Julian Lettner, Prabhu Rajasekaran, Yeoul Na, Stijn Volckaert, Per Larsen, Michael Franz University of California, Irvine {dokyungs,jlettner,rajasekp,yeouln,stijnv,perl,franz}@uci.edu
Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08
 Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08 For your solutions you should submit a hard copy; either hand written pages stapled together or a print out of a typeset document
Homework 3 CS161 Computer Security, Fall 2008 Assigned 10/07/08 Due 10/13/08 For your solutions you should submit a hard copy; either hand written pages stapled together or a print out of a typeset document
Software Security Buffer Overflows more countermeasures. Erik Poll. Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen
 Software Security Buffer Overflows more countermeasures Erik Poll Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen Recap last week Recurring security problems in C(++) code buffer overflows bugs with pointers
Software Security Buffer Overflows more countermeasures Erik Poll Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen Recap last week Recurring security problems in C(++) code buffer overflows bugs with pointers
Putting the Checks into Checked C. Archibald Samuel Elliott Quals - 31st Oct 2017
 Putting the Checks into Checked C Archibald Samuel Elliott Quals - 31st Oct 2017 Added Runtime Bounds Checks to the Checked C Compiler 2 C Extension for Spatial Memory Safety Added Runtime Bounds Checks
Putting the Checks into Checked C Archibald Samuel Elliott Quals - 31st Oct 2017 Added Runtime Bounds Checks to the Checked C Compiler 2 C Extension for Spatial Memory Safety Added Runtime Bounds Checks
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
Fundamentals of Computer Security
 Fundamentals of Computer Security Spring 2015 Radu Sion Software Errors Buffer Overflow TOCTTOU 2005-15 Portions copyright by Bogdan Carbunar and Wikipedia. Used with permission Why Security Vulnerabilities?
Fundamentals of Computer Security Spring 2015 Radu Sion Software Errors Buffer Overflow TOCTTOU 2005-15 Portions copyright by Bogdan Carbunar and Wikipedia. Used with permission Why Security Vulnerabilities?
SoK: Sanitizing for Security
 SoK: Sanitizing for Security Dokyung Song, Julian Lettner, Prabhu Rajasekaran, Yeoul Na, Stijn Volckaert, Per Larsen, Michael Franz University of California, Irvine {dokyungs,jlettner,rajasekp,yeouln,stijnv,perl,franz}@uci.edu
SoK: Sanitizing for Security Dokyung Song, Julian Lettner, Prabhu Rajasekaran, Yeoul Na, Stijn Volckaert, Per Larsen, Michael Franz University of California, Irvine {dokyungs,jlettner,rajasekp,yeouln,stijnv,perl,franz}@uci.edu
Module: Program Vulnerabilities. Professor Trent Jaeger. CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security
 CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CSE543 - Introduction to Computer and Network Security Module: Program Vulnerabilities Professor Trent Jaeger 1 Programming Why do we write programs? Function What functions do we enable via our programs?
CNIT 127: Exploit Development. Ch 1: Before you begin. Updated
 CNIT 127: Exploit Development Ch 1: Before you begin Updated 1-14-16 Basic Concepts Vulnerability A flaw in a system that allows an attacker to do something the designer did not intend, such as Denial
CNIT 127: Exploit Development Ch 1: Before you begin Updated 1-14-16 Basic Concepts Vulnerability A flaw in a system that allows an attacker to do something the designer did not intend, such as Denial
Baggy bounds with LLVM
 Baggy bounds with LLVM Anton Anastasov Chirantan Ekbote Travis Hance 6.858 Project Final Report 1 Introduction Buffer overflows are a well-known security problem; a simple buffer-overflow bug can often
Baggy bounds with LLVM Anton Anastasov Chirantan Ekbote Travis Hance 6.858 Project Final Report 1 Introduction Buffer overflows are a well-known security problem; a simple buffer-overflow bug can often
Architectural Support for Low Overhead Detection of Memory Violations
 Architectural Support for Low Overhead Detection of Memory Violations Saugata Ghose, Latoya Gilgeous, Polina Dudnik, Aneesh Aggarwal, Corey Waxman State University of New York, Binghamton, NY 13902 aneesh@binghamtonedu
Architectural Support for Low Overhead Detection of Memory Violations Saugata Ghose, Latoya Gilgeous, Polina Dudnik, Aneesh Aggarwal, Corey Waxman State University of New York, Binghamton, NY 13902 aneesh@binghamtonedu
Limitations of the stack
 The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
The heap hic 1 Limitations of the stack int *table_of(int num, int len) { int table[len+1]; for (int i=0; i
CSci 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems. Programs in C/Unix
 CSci 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems Programs in C/Unix Today Basic C programming Follow on to recitation Structure of a C program A C program consists of a collection of C functions, structs, arrays,
CSci 4061 Introduction to Operating Systems Programs in C/Unix Today Basic C programming Follow on to recitation Structure of a C program A C program consists of a collection of C functions, structs, arrays,
Run-time Environments - 3
 Run-time Environments - 3 Y.N. Srikant Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Principles of Compiler Design Outline of the Lecture n What is run-time
Run-time Environments - 3 Y.N. Srikant Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Principles of Compiler Design Outline of the Lecture n What is run-time
Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures
 Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures David Brumley, James Newsome, Dawn Song, Hao Wang, and Somesh Jha (presented by Boniface Hicks) Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security
Towards Automatic Generation of Vulnerability- Based Signatures David Brumley, James Newsome, Dawn Song, Hao Wang, and Somesh Jha (presented by Boniface Hicks) Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security
Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui
 Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui Projects 1 Information flow analysis for mobile applications 2 2 Machine-learning-guide typestate analysis for UAF vulnerabilities 3 3 Preventing
Honours/Master/PhD Thesis Projects Supervised by Dr. Yulei Sui Projects 1 Information flow analysis for mobile applications 2 2 Machine-learning-guide typestate analysis for UAF vulnerabilities 3 3 Preventing
Stack Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers
 Stack Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers Gregory J. Duck and Roland H. C. Yap Department of Computer Science National University of Singapore {gregory, ryap}@comp.nus.edu.sg Lorenzo Cavallaro Information
Stack Bounds Protection with Low Fat Pointers Gregory J. Duck and Roland H. C. Yap Department of Computer Science National University of Singapore {gregory, ryap}@comp.nus.edu.sg Lorenzo Cavallaro Information
System Assertions. Your Submissions. Oral Exams FEBRUARY FEBRUARY FEBRUARY
 System Assertions Andreas Zeller 1 Your Submissions Program must behave exactly as specified (i.e., input, output, flags, etc.) Program must use recent Python 2 version (i.e., Python 2.6 installed in CIP
System Assertions Andreas Zeller 1 Your Submissions Program must behave exactly as specified (i.e., input, output, flags, etc.) Program must use recent Python 2 version (i.e., Python 2.6 installed in CIP
CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College October 2, 2018
 CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory Kevin Webb Swarthmore College October 2, 2018 Overview How to reference the location of a variable in memory Where variables are placed in memory How to make
CS 31: Intro to Systems Pointers and Memory Kevin Webb Swarthmore College October 2, 2018 Overview How to reference the location of a variable in memory Where variables are placed in memory How to make
CSE409, Rob Johnson, Alin Tomescu, November 11 th, 2011 Buffer overflow defenses
 Buffer overflow defenses There are two categories of buffer-overflow defenses: - Make it hard for the attacker to exploit buffer overflow o Address space layout randomization o Model checking to catch
Buffer overflow defenses There are two categories of buffer-overflow defenses: - Make it hard for the attacker to exploit buffer overflow o Address space layout randomization o Model checking to catch
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
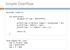 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Software security, secure programming
 Software security, secure programming Lecture 4: Protecting your code against software vulnerabilities? (overview) Master on Cybersecurity Master MoSiG Academic Year 2017-2018 Preamble Bad news several
Software security, secure programming Lecture 4: Protecting your code against software vulnerabilities? (overview) Master on Cybersecurity Master MoSiG Academic Year 2017-2018 Preamble Bad news several
Homework I - Solution
 CS 426 Fall 2017 1 Homework I - Solution Homework I - Solution CS 426 Compiler Construction Fall Semester 2017 1. (50 points) Intermediate representations: (a) (25 points) Construct a Control-Flow Graph
CS 426 Fall 2017 1 Homework I - Solution Homework I - Solution CS 426 Compiler Construction Fall Semester 2017 1. (50 points) Intermediate representations: (a) (25 points) Construct a Control-Flow Graph
Shuntaint: Emulation-based Security Testing for Formal Verification
 Shuntaint: Emulation-based Security Testing for Formal Verification Bruno Luiz ramosblc@gmail.com Abstract. This paper describes an emulated approach to collect traces of program states, in order to verify
Shuntaint: Emulation-based Security Testing for Formal Verification Bruno Luiz ramosblc@gmail.com Abstract. This paper describes an emulated approach to collect traces of program states, in order to verify
HA2lloc: Hardware-Assisted Secure Allocator
 HA2lloc: Hardware-Assisted Secure Allocator Orlando Arias, Dean Sullivan, Yier Jin {oarias,dean.sullivan}@knights.ucf.edu yier.jin@ece.ufl.edu University of Central Florida University of Florida June 25,
HA2lloc: Hardware-Assisted Secure Allocator Orlando Arias, Dean Sullivan, Yier Jin {oarias,dean.sullivan}@knights.ucf.edu yier.jin@ece.ufl.edu University of Central Florida University of Florida June 25,
LibsafeXP: A Practical & Transparent Tool for Run-time Buffer Overflow Preventions
 The 7th Annual IEEE Information Assurance Workshop LibsafeXP: A Practical & Transparent Tool for Run-time Buffer Overflow Preventions Zhiqiang Lin, Bing Mao and Li Xie Dept. of Computer Science Nanjing
The 7th Annual IEEE Information Assurance Workshop LibsafeXP: A Practical & Transparent Tool for Run-time Buffer Overflow Preventions Zhiqiang Lin, Bing Mao and Li Xie Dept. of Computer Science Nanjing
