Data Structures Lecture 6
|
|
|
- Neil Harvey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 6
2 Announcement Project Proposal due on Nov. 9 Remember to bring a hardcopy of your project proposal to the class next week Also submit your project proposal file to your TAs Discuss potential difficulties of your project We can select some topics and explain in the lab
3 Announcement We will have programming lectures and tests on Nov. 6 in 逸仙樓 5F. HWs Review BMI Generic Progression Keyword Counting The Ordered List HTML Tag Matching Web Site Score
4 Abstract Non-linear Data Structures Trees and their variations
5 Abstract Data Type (ADT) An abstract data type (ADT) is an abstraction of a data structure An ADT specifies: Data stored Operations on the data Error conditions associated with operations We have discussed Array ADT, List ADT, Stack ADT, and Queue ADT All of them are linear ADT
6 A Hierarchical Structure
7 Linux/Unix file systems
8 Tree: A Hierarchical ADT A tree (upside down) is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure Computers R Us A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child relation Sales Manufacturing R&D Each element (except the top element) has a parent and zero or more children elements US International Laptops Europe Asia Canada Desktops
9 Tree Terminology Root: a node without any parent (A) Internal node: a node with at least one child (A, B, C, F) A External node (a.k.a. leaf ): a node without children (E, I, J, K, G, H, D) B C D Subtree: tree consisting of a node and its descendants E F G H I J K subtree
10 Tree Terminology Ancestors of a node: parent, grandparent, grand-grandparent, etc. A Depth of a node: number of ancestors B C D Height of a tree: maximum depth of any node (3) Descendant of a node: child, grandchild, grand-grandchild, etc. E F G H I J K
11 Tree ADT We use positions to define the tree ADT The positions in a tree are its nodes and neighboring positions satisfy the parent-child relationships method root() parent(v) children(v) isroot(v) isexternal(v) isinternal(v) description Return the tree s root; error if tree is empty Return v s parent; error if v is a root Return v s children (an iterable collection of nodes) Test whether v is a root Test whether v is an external node Test whether v is an internal node
12 Tree ADT Generic methods (not necessarily related to a tree structure): method isempty() size() iterator() positions() replace(v,e) description Test whether the tree has any node or not Return the number of nodes in the tree Return an iterator of all the elements stored in the tree Return an iterable collection of all the nodes of the tree Replace with e and return the element stored at node v
13 A Linked Structure for Tree A node is represented by an object storing Element A parent node A sequence of children nodes (parent node) (a list of children) (element) (child node)
14 A Linked Structure for Tree Node objects implement the Position ADT B B A D F A D F C E C E
15 Tree Traversal Visit all nodes in a tree Do some operations during the visit Computers R Us Sales Manufacturing R&D US International Laptops Desktops Europe Asia Canada
16 Preorder Traversal A node is visited (so is the operation) before its descendants Application: Print a structured document Algorithm preorder(v) visit(v) for each child w of v preorder (w)
17 Preorder Traversal 1 Make Money Fast! 2 1. Motivations 2. Methods References Greedy 1.2 Avidity Stock Fraud 2.2 Ponzi Scheme 2.3 Bank Robbery For your project, you can print a structured web site with its sub links using preorder traversal
18 Postorder Traversal A node is visited after its descendants Application: Compute space used by files in a directory and its subdirectories Algorithm postorder(v) for each child w of v postorder (w) visit(v)
19 Postorder Traversal 9 cs16/ 3 homeworks/ 7 programs/ 8 todo.txt 1K h1c.doc 3K h1nc.doc 2K DDR.java 10K Stocks.java 25K Robot.java 20K For your project, you can compute the score of a web site and its sub links Using postorder traversal
20 Binary Tree A binary tree is a tree with the following properties: A Each internal node has at most two children B C The children of a node are an ordered pair (left and right) We call the children of an internal node left child and right child D E F G H I
21 Binary Tree Alternative recursive definition: a binary tree is either A a tree consisting of a single node, or a tree whose root has an ordered pair of children, each of which is a binary tree B C D E F G H I
22 Arithmetic Expression Tree Binary tree associated with an arithmetic expression internal nodes: operators + external nodes: operands Example: arithmetic expression tree for the expression: 2-3 b (2 (a - 1) + (3 b)) a 1
23 Decision Tree Binary tree associated with a decision process internal nodes: questions with yes/no answer external nodes: decisions Example: dining decision Want a fast meal? Yes No On a diet? On expense account? Yes No Yes No Subway Mc Donald s 王品台塑我家牛排
24 Proper Binary Trees Each internal node has exactly 2 children
25 Proper Binary Trees n :number of total nodes e :number of external nodes i :number of internal nodes h :height (maximum depth of a node) Properties: 1. e = i n = 2e h i 4. h (n - 1)/2 5. e 2 h 6. h log 2 e 7. h log 2 (n + 1) - 1
26 Properties 1. e = i+1 2. n = e+i = 2e-1 = 2i+1
27 Properties 3. h <= i 4. h<= (n-1)/2
28 Properties 5. e <= 2 h 6. h >= log 2 e 7. h >= log 2 ((n+1)/2) = log 2 (n+1) -1
29 BinaryTree ADT The BinaryTree ADT extends the Tree ADT, i.e., it inherits all the methods of the Tree ADT Additional methods: position left(p) position right(p) boolean hasleft(p) boolean hasright(p) Update methods may be defined by data structures implementing the BinaryTree ADT
30 Inorder Traversal A node is visited after its left subtree and before its right subtree Algorithm inorder(v) if hasleft (v) inorder (left (v)) visit(v) if hasright (v) inorder (right (v))
31 Print Arithmetic Expressions Specialization of an inorder traversal print operand or operator when visiting node print ( before traversing left subtree print ) after traversing right subtree Algorithm printexpression(v) if hasleft (v) print( ( ) printexpression (left(v)) print(v.element ()) if hasright (v) printexpression (right(v)) print ( ) ) a 1 ((2 (a - 1)) + (3 b)) b
32 Evaluate Arithmetic Expressions Specialization of a postorder traversal recursive method returning the value of a subtree when visiting an internal node, combine the values of the subtrees Algorithm evalexpr(v) if isexternal (v) return v.element () else x evalexpr(leftchild (v)) y evalexpr(rightchild (v)) operator stored at v return x y
33 Euler Tour Traversal Generic traversal of a binary tree Walk around the tree and visit each node three times: + on the left (preorder) from below (inorder) on the right (postorder) 2 L B R
34 A template method pattern A generic computation mechanism Specialized for an application by redefining the visit actions Algorithm eulartour(t,v) Perform the action for visiting node v on the left If v has a left child u in T then eulartour(t, u) Perform the action for visiting node v from below If v has a right child w in T then eulartour(t, w) Perform the action for visiting node v on the right
35 An application of EularTour printexpression On the left action: print ( From below action: print v On the right action: print ) Algorithm printexpression(t,v) if T.isInternal(v) then print ( If v has a left child u in T then printexpression(t, u) print(v) If v has a right child w in T then printexpression(t, w) if T.isInternal(v) then print )
36 A Linked Structure for Binary Trees A node is represented by an object storing Element Parent node Left child node Right child node Parent node Element Left child Right child
37 A Linked Structure for Binary Trees B B A D C E A D C E
38 An Array-Based Representation Nodes are stored in an array A Node v is stored at A[rank(v)] rank(root) = 1 Left in even: if node is the left child of parent(node), rank(node) = 2 rank(parent(node)) Right in odd: if node is the right child of parent(node), rank(node) = 2 rank(parent(node)) + 1 A[0] is always empty A[i] is empty if there is no node in the ith position The array size N is 2 (h+1)
39 An Array-Based Representation 1 A 2 3 B D E F 4 5 C J 6 7 G H A B D G H
40 HW 6 (Due on 11/16) Compute the score of a website! Construct a tree and its nodes according to a given website An element (referred by a node) represents one web page and has three fields: (name, url, score) Given a keyword and its weight, compute the score of each node Score = number of appearance * weight The score of a node = the score of the content of its url + the scores of its children This can be done by a postorder traversal of a tree Output the hierarchy of the website (with names and scores) using parentheses This can be done by an eular tour
41 An example input You will be given a website like: Soslab, Publication, Projects, AppBeach, Stranger, Member, Course,
42 An example output Given a set of keywords, (Yu,1.2), (Fang, 1.8) you shall output something like ( Soslab, 56.6 (Publication, 18) (Projects, 15.6 (AppBeach, 2.6) (Stranger, 8.8) ) (Member, 9.2) (Course, 4.8) ) Fang Yu, 56.6 indicates that the sum of the score in the content of the given url ( and its sub links
43 Coming Up We will have a programming test in the lab on Nov. 6 The project proposal is due on Nov. 9 We will talk about heap (some kind of a tree) on Nov. 9. Read Chapter 8
Trees. Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud. Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Trees Goodrich, Tamassia
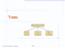 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Stock Fraud. Ponzi Scheme Goodrich, Tamassia. Trees 1
 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Stock Fraud. Ponzi Scheme. Trees Goodrich, Tamassia
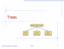 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Trees 1 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parent-child
Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees
 Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Tree Example Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A
Data Structures and Algorithms Trees Tree Example Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2 What is a Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A
Trees. 9/21/2007 8:11 AM Trees 1
 Trees 9/21/2007 8:11 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 6.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 6.2.3) BinaryTree ADT ( 6.3.1) Inorder traversal ( 6.3.4) Euler Tour traversal ( 6.3.4) Template
Trees 9/21/2007 8:11 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 6.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 6.2.3) BinaryTree ADT ( 6.3.1) Inorder traversal ( 6.3.4) Euler Tour traversal ( 6.3.4) Template
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Stock Fraud Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees
 Part 4: Trees Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 2 Example: Family Tree 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 3 Example: Unix File
Part 4: Trees Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 2 Example: Family Tree 2013 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser Trees 3 Example: Unix File
Trees 3/19/14. Mammal. Dog Pig Cat
 Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
Presentation for use with the textbook ata Structures and lgorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 014 Trees Mammal og Pig at Trees 1 What is a Tree
OUTLINE. General Trees (Ch. 7.1) Binary Trees (Ch. 7.3) Tree Traversals (Ch. 7.2)
 CH 7 : TREE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO 1 OUTLINE
CH 7 : TREE ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO 1 OUTLINE
Outline. Definitions Traversing trees Binary trees
 Trees Chapter 8 Outline Definitions Traversing trees Binary trees Outline Definitions Traversing trees Binary trees Graph a b Node ~ city or computer Edge ~ road or data cable c Undirected or Directed
Trees Chapter 8 Outline Definitions Traversing trees Binary trees Outline Definitions Traversing trees Binary trees Graph a b Node ~ city or computer Edge ~ road or data cable c Undirected or Directed
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Stock Fraud. 02/06/2006 Trees 1
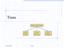 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 02/06/2006 Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 7.1.2) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 7.2.2-3) BinaryTree ADT ( 7.3.1) Inorder traversal
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 02/06/2006 Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 7.1.2) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 7.2.2-3) BinaryTree ADT ( 7.3.1) Inorder traversal
Trees and Binary Trees
 Trees and Binary Trees Become Rich Force Others to be Poor Rob Banks Stock Fraud The class notes are a compilation and edition from many sources. The instructor does not claim intellectual property or
Trees and Binary Trees Become Rich Force Others to be Poor Rob Banks Stock Fraud The class notes are a compilation and edition from many sources. The instructor does not claim intellectual property or
Trees. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Ponzi Scheme. Stock Fraud. 1/18/2005 4:17 AM Trees 1
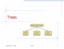 Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 1/18/2005 4:17 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 2.3.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 2.3.2) BinaryTree ADT ( 2.3.3) Inorder traversal
Trees Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery 1/18/2005 4:17 AM Trees 1 Outline and Reading Tree ADT ( 2.3.1) Preorder and postorder traversals ( 2.3.2) BinaryTree ADT ( 2.3.3) Inorder traversal
Data Structures. Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees
 Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
Data Structures Trees, Binary trees & Binary Search Trees Tree In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes with a parentchild relation Applications:
Trees. Trees. CSE 2011 Winter 2007
 Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Trees CSE 2011 Winter 2007 2/5/2007 10:00 PM 1 Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search,
Stock Fraud. Nancy Amato. Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University
 Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Chapter 7: Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures
Make Money Fast! Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Chapter 7: Nancy Amato Parasol Lab, Dept. CSE, Texas A&M University Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures
What is a Tree. Trees. Tree ADT ( 6.1.2) Tree Terminology. subtree. In computer science, a tree is an abstract model
 What is a Tree Trees Stock raud Make Money ast! Ponzi Scheme ank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model omputers R Us of a hierarchical structure tree consists of with a parent-child
What is a Tree Trees Stock raud Make Money ast! Ponzi Scheme ank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model omputers R Us of a hierarchical structure tree consists of with a parent-child
Unit 1 (9Hrs) Trees. Mahesh Sanghavi & Deepali Pawar Department of Computer Engineering, SNJB s KBJ College of Engineering, Chandwad, India
 Unit 1 (9Hrs) Trees Mahesh Sanghavi & Deepali Pawar Department of Computer Engineering, SNJB s KBJ College of Engineering, Chandwad, India The class notes are a compilation and edition from many sources.
Unit 1 (9Hrs) Trees Mahesh Sanghavi & Deepali Pawar Department of Computer Engineering, SNJB s KBJ College of Engineering, Chandwad, India The class notes are a compilation and edition from many sources.
Elementary Data Structures. Stacks, Queues, & Lists Amortized analysis Trees
 Elementary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, & Lists Amortized analysis Trees The Stack ADT ( 2.1.1) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Insertions and deletions follow the last-in first-out scheme Think
Elementary Data Structures Stacks, Queues, & Lists Amortized analysis Trees The Stack ADT ( 2.1.1) The Stack ADT stores arbitrary objects Insertions and deletions follow the last-in first-out scheme Think
Trees. Data structures and Algorithms. Make Money Fast! Bank Robbery. Stock Fraud. Ponzi Scheme
 Make Money Fast! Trees Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich,
Make Money Fast! Trees Stock Fraud Ponzi Scheme Bank Robbery Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich,
Ch02 Data Structures
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Binary trees. Binary trees. Binary trees
 Binary trees March 23, 2018 1 Binary trees A binary tree is a tree in which each internal node has at most two children. In a proper binary tree, each internal node has exactly two children. Children are
Binary trees March 23, 2018 1 Binary trees A binary tree is a tree in which each internal node has at most two children. In a proper binary tree, each internal node has exactly two children. Children are
A Hierarchical Structure. Lecture11: Trees I. Tree Data Structures. Unix/Linux file systems. Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH
 Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2013F) Lecture11: Trees I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2013F) Lecture11: Trees I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Ch02 Data Structures
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Ch02 Data Structures xkcd Seven http://xkcd.com/1417/ Used with permission under
In a postorder traversal, a node is visited after its descendants Application: compute space used by files in a directory and its subdirectories 9 1
 What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
What is a Tree Trees Stock Fraud Make Money Fast! Winning Lotto / Bank Robbery In computer science, a tree is an abstract model of a hierarchical structure A tree consists of nodes ith a parent-child relation
Binary Tree. Binary tree terminology. Binary tree terminology Definition and Applications of Binary Trees
 Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
Binary Tree (Chapter 0. Starting Out with C++: From Control structures through Objects, Tony Gaddis) Le Thanh Huong School of Information and Communication Technology Hanoi University of Technology 11.1
COSC 2011 Section N. Trees: Terminology and Basic Properties
 COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
COSC 2011 Tuesday, March 27 2001 Overview Trees and Binary Trees Quick review of definitions and examples Tree Algorithms Depth, Height Tree and Binary Tree Traversals Preorder, postorder, inorder Binary
DataStruct 7. Trees. Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011.
 2013-2 DataStruct 7. Trees Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011. November 6, 2013 Advanced Networking Technology Lab. (YU-ANTL) Dept.
2013-2 DataStruct 7. Trees Michael T. Goodrich, et. al, Data Structures and Algorithms in C++, 2 nd Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2011. November 6, 2013 Advanced Networking Technology Lab. (YU-ANTL) Dept.
Tree. A path is a connected sequence of edges. A tree topology is acyclic there is no loop.
 Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
A Hierarchical Structure. Lecture11: Tree I. Tree Data Structures. Unix/Linux file systems. Bohyung Han CSE, POSTECH
 Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2015F) Lecture11: Tree I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Unix/Linux file systems Hierarchical Structure (2015F) Lecture11: Tree I ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr 2 Tree ata Structures n abstract model of a hierarchical structure 2 dimensional structure
Outline. Preliminaries. Binary Trees Binary Search Trees. What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications
 Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
Trees 1 Outline Preliminaries What is Tree? Implementation of Trees using C++ Tree traversals and applications Binary Trees Binary Search Trees Structure and operations Analysis 2 What is a Tree? A tree
CSC148 Week 6. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
The tree data structure. Trees COL 106. Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal. Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo
 The tree data structure 1 Trees COL 106 Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo 1 Trees The tree data structure 3 A rooted tree data structure stores
The tree data structure 1 Trees COL 106 Amit Kumar Shweta Agrawal Acknowledgement :Many slides are courtesy Douglas Harder, UWaterloo 1 Trees The tree data structure 3 A rooted tree data structure stores
Section 5.5. Left subtree The left subtree of a vertex V on a binary tree is the graph formed by the left child L of V, the descendents
 Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming. Lecture 1 Trees
 COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming Lecture 1 Trees Lecture outline n Motivation n Definitions n Ordered trees n Generic methods for tree operations n Tree traversal (preorder, postorder,
COMP26120: Algorithms and Imperative Programming Lecture 1 Trees Lecture outline n Motivation n Definitions n Ordered trees n Generic methods for tree operations n Tree traversal (preorder, postorder,
Topics on the Midterm
 Midterm Review Topics on the Midterm Data Structures & Object-Oriented Design Run-Time Analysis Linear Data Structures The Java Collections Framework Recursion Trees Priority Queues & Heaps Maps, Hash
Midterm Review Topics on the Midterm Data Structures & Object-Oriented Design Run-Time Analysis Linear Data Structures The Java Collections Framework Recursion Trees Priority Queues & Heaps Maps, Hash
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree
 CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
CSE 230 Intermediate Programming in C and C++ Binary Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu Introduction to Tree Tree is a non-linear data structure
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Tree Traversal. Lecture12: Tree II. Preorder Traversal
 Tree Traersal (0F) Lecture: Tree II Process of isiting nodes in a tree systematically Some algorithms need to isit all nodes in a tree. Example: printing, counting nodes, etc. Implementation Can be done
Tree Traersal (0F) Lecture: Tree II Process of isiting nodes in a tree systematically Some algorithms need to isit all nodes in a tree. Example: printing, counting nodes, etc. Implementation Can be done
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms
 CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
CE 221 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 4: Trees (Binary) Text: Read Weiss, 4.1 4.2 Izmir University of Economics 1 Preliminaries - I (Recursive) Definition: A tree is a collection of nodes. The
csci 210: Data Structures Trees
 csci 210: Data Structures Trees 1 Summary Topics general trees, definitions and properties interface and implementation tree traversal algorithms depth and height pre-order traversal post-order traversal
csci 210: Data Structures Trees 1 Summary Topics general trees, definitions and properties interface and implementation tree traversal algorithms depth and height pre-order traversal post-order traversal
CSC148H Week 8. Sadia Sharmin. July 12, /29
 CSC148H Week 8 Sadia Sharmin July 12, 2017 1/29 Motivating Trees I A data structure is a way of organizing data I Stacks, queues, and lists are all linear structures I They are linear in the sense that
CSC148H Week 8 Sadia Sharmin July 12, 2017 1/29 Motivating Trees I A data structure is a way of organizing data I Stacks, queues, and lists are all linear structures I They are linear in the sense that
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Topic 14. The BinaryTree ADT
 Topic 14 The BinaryTree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree
Topic 14 The BinaryTree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree
Why Do We Need Trees?
 CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
CSE 373 Lecture 6: Trees Today s agenda: Trees: Definition and terminology Traversing trees Binary search trees Inserting into and deleting from trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Why Do We Need Trees?
Trees Algorhyme by Radia Perlman
 Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
tree nonlinear Examples
 The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
7.1 Introduction. A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w
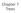 Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
BBM 201 Data structures
 BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
BBM 201 Data structures Lecture 11: Trees 2018-2019 Fall Content Terminology The Binary Tree The Binary Search Tree Data Structures and Problem Solving with C++: Walls and Mirrors, Carrano and Henry, 2013
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson
 Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
Lecture Notes 16 - Trees CSS 501 Data Structures and Object-Oriented Programming Professor Clark F. Olson Reading: Carrano, Chapter 15 Introduction to trees The data structures we have seen so far to implement
DATA STRUCTURES USING C
 DATA STRUCTURES USING C The British Constitution Crown Church of England Cabinet House of Commons House of Lords Supreme Court Ministers County Metropolitan Council police Rural District County Borough
DATA STRUCTURES USING C The British Constitution Crown Church of England Cabinet House of Commons House of Lords Supreme Court Ministers County Metropolitan Council police Rural District County Borough
Binary Trees. Reading: Lewis & Chase 12.1, 12.3 Eck Programming Course CL I
 inary Trees Reading: Lewis & hase 12.1, 12.3 Eck 9.4.1 Objectives Tree basics Learn the terminology used when talking about trees iscuss methods for traversing trees iscuss a possible implementation of
inary Trees Reading: Lewis & hase 12.1, 12.3 Eck 9.4.1 Objectives Tree basics Learn the terminology used when talking about trees iscuss methods for traversing trees iscuss a possible implementation of
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University
 Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Data Structure Lecture#10: Binary Trees (Chapter 5) U Kang Seoul National University U Kang (2016) 1 In This Lecture The concept of binary tree, its terms, and its operations Full binary tree theorem Idea
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-12-01 09:30:53 1/54 Chapter-11.pdf (#13) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or
Chapter 11.!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1
 Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
Chapter 11!!!!Trees! 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 11 A-1 2015-03-25 21:47:41 1/53 Chapter-11.pdf (#4) Terminology Definition of a general tree! A general tree T is a set of one or more
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Trees Kostas Alexis Trees List, stacks, and queues are linear in their organization of data. Items are one after another In this section, we organize data in a
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Trees Kostas Alexis Trees List, stacks, and queues are linear in their organization of data. Items are one after another In this section, we organize data in a
INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1
 Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
Universitetet i Oslo Institutt for Informatikk A. Maus, R.K. Runde, I. Yu INF2220: algorithms and data structures Series 1 Topic Trees & estimation of running time (Exercises with hints for solution) Issued:
TREES Lecture 12 CS2110 Fall 2016
 TREES Lecture 12 CS2110 Fall 2016 Prelim 1 tonight! 2 5:30 prelim is very crowded. You HAVE to follow these directions: 1. Students taking the normal 5:30 prelim (not the quiet room) and whose last names
TREES Lecture 12 CS2110 Fall 2016 Prelim 1 tonight! 2 5:30 prelim is very crowded. You HAVE to follow these directions: 1. Students taking the normal 5:30 prelim (not the quiet room) and whose last names
CS 234. Module 5. October 18, CS 234 Module 5 ADTS with items related by structure 1 / 25
 CS 234 Module 5 October 18, 2018 CS 234 Module 5 ADTS with items related by structure 1 / 25 ADTs representing structure We have seen ADTs where: There is no relation among items. Items are orderable types
CS 234 Module 5 October 18, 2018 CS 234 Module 5 ADTS with items related by structure 1 / 25 ADTs representing structure We have seen ADTs where: There is no relation among items. Items are orderable types
Tree. Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11. Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni. Sep 3,2010
 SE-286: Data Structures t and Programming Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Trees Nature Lover sviewofatree leaves branches root 3 Computer
SE-286: Data Structures t and Programming Tree Virendra Singh Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture 11 Courtesy: Prof. Sartaj Sahni 1 Trees Nature Lover sviewofatree leaves branches root 3 Computer
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 10 / 10 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? A few comments about Doubly Linked Lists w/ dummy head/tail Trees Binary trees
TREES. Tree Overview 9/28/16. Prelim 1 tonight! Important Announcements. Tree terminology. Binary trees were in A1!
 //16 Prelim 1 tonight! :3 prelim is very crowded. You HAVE to follow these directions: 1. Students taking the normal :3 prelim (not the quiet room) and whose last names begin with A through Da MUST go
//16 Prelim 1 tonight! :3 prelim is very crowded. You HAVE to follow these directions: 1. Students taking the normal :3 prelim (not the quiet room) and whose last names begin with A through Da MUST go
Recursive Data Structures and Grammars
 Recursive Data Structures and Grammars Themes Recursive Description of Data Structures Grammars and Parsing Recursive Definitions of Properties of Data Structures Recursive Algorithms for Manipulating
Recursive Data Structures and Grammars Themes Recursive Description of Data Structures Grammars and Parsing Recursive Definitions of Properties of Data Structures Recursive Algorithms for Manipulating
Computer Science 210 Data Structures Siena College Fall Topic Notes: Trees
 Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Computer Science 0 Data Structures Siena College Fall 08 Topic Notes: Trees We ve spent a lot of time looking at a variety of structures where there is a natural linear ordering of the elements in arrays,
Tree Structures. A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node
 Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Binary Trees 1 Tree Structures A tree is A hierarchical data structure whose point of entry is the root node This structure can be partitioned into disjoint subsets These subsets are themselves trees and
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
CSCI-401 Examlet #5. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science. Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department
 Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department HL Topics 1-7, D1-4 1: System design 2: Computer Organisation 3: Networks 4: Computational
Abstract Data Structures IB Computer Science Content developed by Dartford Grammar School Computer Science Department HL Topics 1-7, D1-4 1: System design 2: Computer Organisation 3: Networks 4: Computational
Chapter 4 Trees. Theorem A graph G has a spanning tree if and only if G is connected.
 Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 8/15 Hua Lu
 Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 8/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Trees Basics Rooted trees Binary trees Binary tree ADT Tree traversal
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 8/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Trees Basics Rooted trees Binary trees Binary tree ADT Tree traversal
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 13, 2017 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Outline C++ Supplement.1: Trees 1 C++ Supplement.1: Trees Uses
Data Structures Lecture 5
 Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 5 Announcement Project Proposal due on Nov. 9 Remember to bring a hardcopy
Fall 2017 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. Dept. Management Information Systems, National Chengchi University Data Structures Lecture 5 Announcement Project Proposal due on Nov. 9 Remember to bring a hardcopy
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Lesson 3: trees and visits Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by Dr. Gabriele D Angelo) International
Lesson 3: trees and visits Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by Dr. Gabriele D Angelo) International
Section Summary. Introduction to Trees Rooted Trees Trees as Models Properties of Trees
 Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data type. Topic 17. "A tree may grow a. its leaves will return to its roots." Properties of Trees
 Topic 17 Introduction ti to Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data t d internal type nodes one
Topic 17 Introduction ti to Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data t d internal type nodes one
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Trees. Tree Structure Binary Tree Tree Traversals
 Trees Tree Structure Binary Tree Tree Traversals The Tree Structure Consists of nodes and edges that organize data in a hierarchical fashion. nodes store the data elements. edges connect the nodes. The
Trees Tree Structure Binary Tree Tree Traversals The Tree Structure Consists of nodes and edges that organize data in a hierarchical fashion. nodes store the data elements. edges connect the nodes. The
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, Prof. Zadia Codabux
 CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
CS 231 Data Structures and Algorithms Fall 2018 Recursion and Binary Trees Lecture 21 October 24, 2018 Prof. Zadia Codabux 1 Agenda ArrayQueue.java Recursion Binary Tree Terminologies Traversal 2 Administrative
Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 -
 Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park Basic Tree Concepts Logical structures Chap. 2~4 Chap. 5 Chap. 6 Linear list Tree Graph Linear structures Non-linear structures Linear Lists
Data Structure - Binary Tree 1 - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park Basic Tree Concepts Logical structures Chap. 2~4 Chap. 5 Chap. 6 Linear list Tree Graph Linear structures Non-linear structures Linear Lists
Upcoming ACM Events Linux Crash Course Date: Time: Location: Weekly Crack the Coding Interview Date:
 Upcoming ACM Events Linux Crash Course Date: Oct. 2nd and 3rd Time: 1:15 pm - 3:15 pm Location: UW1-210 (10/02) and UW1-221 (10/03) Weekly Crack the Coding Interview Date: Weekly Fridays from Oct. 5th
Upcoming ACM Events Linux Crash Course Date: Oct. 2nd and 3rd Time: 1:15 pm - 3:15 pm Location: UW1-210 (10/02) and UW1-221 (10/03) Weekly Crack the Coding Interview Date: Weekly Fridays from Oct. 5th
Topic 18 Binary Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb
 Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
Binary Trees Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
Binary Trees 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Trees Fall 2018 15-121 (Reid-Miller) 2 Binary Trees A binary tree is either empty or it contains a root node and left- and right-subtrees that are also
Data Structures. Trees. By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini. M.A. Eljinini, PhD
 Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
Data Structures Trees By Dr. Mohammad Ali H. Eljinini Trees Are collections of items arranged in a tree like data structure (none linear). Items are stored inside units called nodes. However: We can use
Terminology. The ADT Binary Tree. The ADT Binary Search Tree
 Terminology The ADT Binary Tree The ADT Binary Search Tree 1 Terminology 3 A general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: o A single node
Terminology The ADT Binary Tree The ADT Binary Search Tree 1 Terminology 3 A general tree A general tree T is a set of one or more nodes such that T is partitioned into disjoint subsets: o A single node
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
About This Lecture. Trees. Outline. Recursive List Definition slide 1. Recursive Tree Definition. Recursive List Definition slide 2
 Revised 21-Mar-05 About This Lecture 2 Trees In this lecture we study a non-linear container called a Tree and a special kind of Tree called a Binary Tree. CMPUT 115 - Lecture 18 Department of Computing
Revised 21-Mar-05 About This Lecture 2 Trees In this lecture we study a non-linear container called a Tree and a special kind of Tree called a Binary Tree. CMPUT 115 - Lecture 18 Department of Computing
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree
 CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
CSE 214 Computer Science II Introduction to Tree Fall 2017 Stony Brook University Instructor: Shebuti Rayana shebuti.rayana@stonybrook.edu http://www3.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse214/sec02/ Tree Tree is a non-linear
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Course Review for. Cpt S 223 Fall Cpt S 223. School of EECS, WSU
 Course Review for Midterm Exam 1 Cpt S 223 Fall 2011 1 Midterm Exam 1 When: Friday (10/14) 1:10-2pm Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & in-class
Course Review for Midterm Exam 1 Cpt S 223 Fall 2011 1 Midterm Exam 1 When: Friday (10/14) 1:10-2pm Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & in-class
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 19, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Uses Of Trees Chapter 7: Trees
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College October 19, 2016 Outline Outline 1 Chapter 7: Trees Outline Chapter 7: Trees 1 Chapter 7: Trees Uses Of Trees Chapter 7: Trees
Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers
 04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
04-630 Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers David Vernon Carnegie Mellon University Africa vernon@cmu.edu www.vernon.eu Data Structures and Algorithms for Engineers 1 Carnegie Mellon University
TREES Lecture 10 CS2110 Spring2014
 TREES Lecture 10 CS2110 Spring2014 Readings and Homework 2 Textbook, Chapter 23, 24 Homework: A thought problem (draw pictures!) Suppose you use trees to represent student schedules. For each student there
TREES Lecture 10 CS2110 Spring2014 Readings and Homework 2 Textbook, Chapter 23, 24 Homework: A thought problem (draw pictures!) Suppose you use trees to represent student schedules. For each student there
Lecture 26. Introduction to Trees. Trees
 Lecture 26 Introduction to Trees Trees Trees are the name given to a versatile group of data structures. They can be used to implement a number of abstract interfaces including the List, but those applications
Lecture 26 Introduction to Trees Trees Trees are the name given to a versatile group of data structures. They can be used to implement a number of abstract interfaces including the List, but those applications
