Truth Functional Properties on Truth Trees
|
|
|
- Alannah Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Truth Functional Properties on Truth Trees
2 Truth-functional: Truth Falsity Indeterminacy Entailment Validity Equivalence Consistency
3 A set of sentences of SL is truth-functionally consistent if and only if there is at least one truth value assignment [of the constituents of the set of sentences] on which all the members of the set are true. We now know how to check for consistency using a tree, and can recover specific truthvalue assignments on which all members of a given set come out true (if the set is consistent).
4
5 A sentence of SL is truth-functionally false if and only if it is false on every possible truth-value assignment of its constituents. A sentences, is truthfunctionally false if and only if { } is truthfunctionally inconsistent. Since inconsistent sets are sets whose members can never all be true at the same time, and since { } has only one member, that member must never be true for the set to be inconsistent. Definition Explained via consistency
6 A sentence of SL is t.f. false if and only if { } has a closed truth tree (meaning { } is inconsistent). If the tree for { } closes, it means that it is impossible for to be true.
7 A sentence of SL is truth-functionally true if and only if it is true on every possible truth-value assignment of its constituents. Definition A sentence is truthfunctionally true if and only if {~ } is truthfunctionally inconsistent. Since inconsistent sets are sets whose members can never all be true, and since {~ } has only one member and is a negation, must be always true for ~ to be never true. Explained via Consistency
8 A sentence of SL is t.f. true if and only if {~ } has a closed truth tree (meaning {~ } is inconsistent). If the tree for {~ } closes, it means that it is impossible for ~ to be true, which in turn means it is impossible for to be false.
9 A sentence of SL is truth-functionally indeterminate if and only if it is neither truth-functionally true nor truthfunctionally false. A sentence is truthfunctionally indeterminate if and only if both {~ } and { } are truth-functionally consistent. Since is truth functionally true or false if one of the above sets is inconsistent. Definition Explained via consistency
10 A sentence of SL is t.f. indeterminate if and only if neither {~ } nor { } has a closed truth tree. If the tree for {~ } is open and the tree for { } is open, then it means that can be either true or false.
11 Sentences and of SL are truthfunctionally equivalent if and only if there is no truth value assignment [for the components of and ] on which and have different truth-values. Sentences and of SL are truth-functionally equivalent if and only if {~( )} is truthfunctionally inconsistent Since only truthfunctionally false sentences make sets of which they are sole members inconsistent, the negation of a sentence asserting that and have different truth-values being truth functionally false means that and must have the same truth-value. Definition Explained via consistency
12 Sentences and are equivalent if and only if {~( )} has a closed truth tree. If and are equivalent, then ( ) is truth functionally true because the two sentences always have the same truth-value. That would make ~( ) truth functionally false. So to check for equivalence of any two sentences of SL on a tree, join them with a biconditional, negate the biconditional, and check for consistency of the set with that negated biconditional as its only member.
13 A set of sentences of SL truthfunctionally entails a sentence if and only if there is no truthvalue assignment on which every member of is true and is false. if and only if {~ } is truthfunctionally inconsistent. Definition Explained via Consistency
14 A finite set entails a sentence if and only if the set {~ } has a closed tree (is inconsistent). So to check if some finite set entails some sentence, represent each member of the set along with the negation of what you re checking to see whether the set entails. If the table closes, then it is impossible for all members of the set to be true while false. is
15 Since validity is simply a special case of entailment, the same procedure can demonstrate that validity can be described in terms of consistency. If an argument is valid, then the union of the set of its premises and the negation of its conclusion will form a truth-functionally inconsistent set.
16 An argument with a finite number of premises is valid if and only if the set consisting of all and only its premises and the negation of the conclusion has a closed tree. A tree that closes when you include every premise and the negation of the conclusion means that the conclusion cannot be false while the premises are true.
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Fall
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday December 16 11:30am-2:30pm. Lecture A will take the exam in Lecture B will take the exam
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Fall 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/fa17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday December 16 11:30am-2:30pm. Lecture A will take the exam in Lecture B will take the exam
1. Logic as a subject matter is the study of logics, understood as models of acceptable inference patterns
 Lecture 9: Propositional Logic I Philosophy 130 23 & 28 October 2014 O Rourke I. Administrative A. Problem sets due Thursday, 30 October B. Midterm course evaluations C. Questions? II. Logic and Form A.
Lecture 9: Propositional Logic I Philosophy 130 23 & 28 October 2014 O Rourke I. Administrative A. Problem sets due Thursday, 30 October B. Midterm course evaluations C. Questions? II. Logic and Form A.
Class 8 - September 13 Indirect Truth Tables for Invalidity and Inconsistency ( 6.5)
 Philosophy 240: Symbolic Logic Fall 2010 Mondays, Wednesdays, Fridays: 9am - 9:50am Hamilton College Russell Marcus rmarcus1@hamilton.edu Class 8 - September 13 Indirect Truth Tables for Invalidity and
Philosophy 240: Symbolic Logic Fall 2010 Mondays, Wednesdays, Fridays: 9am - 9:50am Hamilton College Russell Marcus rmarcus1@hamilton.edu Class 8 - September 13 Indirect Truth Tables for Invalidity and
CS Bootcamp Boolean Logic Autumn 2015 A B A B T T T T F F F T F F F F T T T T F T F T T F F F
 1 Logical Operations 1.1 And The and operator is a binary operator, denoted as, &,, or sometimes by just concatenating symbols, is true only if both parameters are true. A B A B F T F F F F The expression
1 Logical Operations 1.1 And The and operator is a binary operator, denoted as, &,, or sometimes by just concatenating symbols, is true only if both parameters are true. A B A B F T F F F F The expression
Chapter 9 Deductive Arguments II Truth-Functional Logic. Tutorial: Truth Tables
 Chapter 9 Deductive Arguments II ruth-unctional Logic utorial: ruth ables ruth ables he aim of this tutorial is to help you learn to construct truth tables and use them to test the validity of arguments.
Chapter 9 Deductive Arguments II ruth-unctional Logic utorial: ruth ables ruth ables he aim of this tutorial is to help you learn to construct truth tables and use them to test the validity of arguments.
PHIL 240, Introduction to Logic, Sections Fall 2011 FINAL EXAM 14 December Name (5 points): Section (5 points):
 Section I True / False questions (2 points each) 1. TRUE Any argument that is sound is also valid. 2. FALSE_ If the premises of an argument are all true, then that argument is sound. 3. TRUE Every universal
Section I True / False questions (2 points each) 1. TRUE Any argument that is sound is also valid. 2. FALSE_ If the premises of an argument are all true, then that argument is sound. 3. TRUE Every universal
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH. Winter
 CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday March 18 8am-11am. Lecture A will take the exam in GH 242 Lecture B will take the exam
CSE 20 DISCRETE MATH Winter 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi17/cse20-ab/ Final exam The final exam is Saturday March 18 8am-11am. Lecture A will take the exam in GH 242 Lecture B will take the exam
Mathematical Logic Prof. Arindama Singh Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 9 Normal Forms
 Mathematical Logic Prof. Arindama Singh Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 9 Normal Forms In the last class we have seen some consequences and some equivalences,
Mathematical Logic Prof. Arindama Singh Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 9 Normal Forms In the last class we have seen some consequences and some equivalences,
Answer Key #1 Phil 414 JL Shaheen Fall 2010
 Answer Key #1 Phil 414 JL Shaheen Fall 2010 1. 1.42(a) B is equivalent to B, and so also to C, where C is a DNF formula equivalent to B. (By Prop 1.5, there is such a C.) Negated DNF meets de Morgan s
Answer Key #1 Phil 414 JL Shaheen Fall 2010 1. 1.42(a) B is equivalent to B, and so also to C, where C is a DNF formula equivalent to B. (By Prop 1.5, there is such a C.) Negated DNF meets de Morgan s
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Chapter p. 1/27
 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Chapter 2.1-2.7 p. 1/27 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Chapter 2.1-2.7 p. 1/27 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
Section 1.1 Logic LOGIC
 Section 1.1 Logic 1.1.1 1.1 LOGIC Mathematics is used to predict empirical reality, and is therefore the foundation of engineering. Logic gives precise meaning to mathematical statements. PROPOSITIONS
Section 1.1 Logic 1.1.1 1.1 LOGIC Mathematics is used to predict empirical reality, and is therefore the foundation of engineering. Logic gives precise meaning to mathematical statements. PROPOSITIONS
Propositional Logic. Andreas Klappenecker
 Propositional Logic Andreas Klappenecker Propositions A proposition is a declarative sentence that is either true or false (but not both). Examples: College Station is the capital of the USA. There are
Propositional Logic Andreas Klappenecker Propositions A proposition is a declarative sentence that is either true or false (but not both). Examples: College Station is the capital of the USA. There are
Figure-12 Membership Grades of x o in the Sets A and B: μ A (x o ) =0.75 and μb(xo) =0.25
 Membership Functions The membership function μ A (x) describes the membership of the elements x of the base set X in the fuzzy set A, whereby for μ A (x) a large class of functions can be taken. Reasonable
Membership Functions The membership function μ A (x) describes the membership of the elements x of the base set X in the fuzzy set A, whereby for μ A (x) a large class of functions can be taken. Reasonable
Logic Haskell Exercises
 Logic Haskell Exercises Young W. Lim 2018-09-15 Sat Young W. Lim Logic Haskell Exercises 2018-09-15 Sat 1 / 36 Outline 1 Based on 2 Logic Using TAMO.hs Young W. Lim Logic Haskell Exercises 2018-09-15 Sat
Logic Haskell Exercises Young W. Lim 2018-09-15 Sat Young W. Lim Logic Haskell Exercises 2018-09-15 Sat 1 / 36 Outline 1 Based on 2 Logic Using TAMO.hs Young W. Lim Logic Haskell Exercises 2018-09-15 Sat
Back to the knights and knaves island
 Back to the knights and knaves island During your Thanksgiving trip, you found another island with knights and knaves (you have a feeling that you may encounter many such islands this semester). Knights
Back to the knights and knaves island During your Thanksgiving trip, you found another island with knights and knaves (you have a feeling that you may encounter many such islands this semester). Knights
: Principles of Imperative Computation, Fall Written Homework 1 Solutions
 15-122 Written Homework 1 Page 1 of 9 15-122 : Principles of Imperative Computation, Fall 2013 Written Homework 1 Solutions Name: Andrew ID: Recitation: The theory portion of this week s homework will
15-122 Written Homework 1 Page 1 of 9 15-122 : Principles of Imperative Computation, Fall 2013 Written Homework 1 Solutions Name: Andrew ID: Recitation: The theory portion of this week s homework will
Lecture 5. Logic I. Statement Logic
 Ling 726: Mathematical Linguistics, Logic. Statement Logic V. Borschev and B. Partee, September 27, 2 p. Lecture 5. Logic I. Statement Logic. Statement Logic...... Goals..... Syntax of Statement Logic....2.
Ling 726: Mathematical Linguistics, Logic. Statement Logic V. Borschev and B. Partee, September 27, 2 p. Lecture 5. Logic I. Statement Logic. Statement Logic...... Goals..... Syntax of Statement Logic....2.
III SEMESTER B. A. PHILOSOPHY PHL3B04 - SYMBOLIC LOGIC AND INFORMATICS QUESTION BANK FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT. Multiple Choice Questions
 III SEMESTER B. A. PHILOSOPHY PHL3B04 - SYMBOLIC LOGIC AND INFORMATICS QUESTION BANK FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT Multiple Choice Questions MODULE - I 1. In Symbolic logic, do not change their value. a) Variables
III SEMESTER B. A. PHILOSOPHY PHL3B04 - SYMBOLIC LOGIC AND INFORMATICS QUESTION BANK FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT Multiple Choice Questions MODULE - I 1. In Symbolic logic, do not change their value. a) Variables
Propositional Logic. Part I
 Part I Propositional Logic 1 Classical Logic and the Material Conditional 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 The first purpose of this chapter is to review classical propositional logic, including semantic tableaux.
Part I Propositional Logic 1 Classical Logic and the Material Conditional 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 The first purpose of this chapter is to review classical propositional logic, including semantic tableaux.
1 Introduction to Logic
 1 Introduction to Logic Some Vocabulary Logic is the science of discursive reasoning.1 As a science, logic aims to discover general laws that apply to all discursive reasoning. Narrowly specific kinds
1 Introduction to Logic Some Vocabulary Logic is the science of discursive reasoning.1 As a science, logic aims to discover general laws that apply to all discursive reasoning. Narrowly specific kinds
Mathematical Logic Part Two
 Mathematical Logic Part Two Recap from Last Time Recap So Far A propositional variable a variable that either true or false. The propositional connectives are as follows: Negation: p Conjunction: p q Djunction:
Mathematical Logic Part Two Recap from Last Time Recap So Far A propositional variable a variable that either true or false. The propositional connectives are as follows: Negation: p Conjunction: p q Djunction:
Quantification. Using the suggested notation, symbolize the statements expressed by the following sentences.
 Quantification In this and subsequent chapters, we will develop a more formal system of dealing with categorical statements, one that will be much more flexible than traditional logic, allow a deeper analysis
Quantification In this and subsequent chapters, we will develop a more formal system of dealing with categorical statements, one that will be much more flexible than traditional logic, allow a deeper analysis
logic with quantifiers (informally)
 EDAA40 Discrete Structures in Computer Science 8: Quantificational logic Jörn W. Janneck, Dept. of Computer Science, Lund University logic with quantifiers (informally) Given a logical formula that depends
EDAA40 Discrete Structures in Computer Science 8: Quantificational logic Jörn W. Janneck, Dept. of Computer Science, Lund University logic with quantifiers (informally) Given a logical formula that depends
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4. Harper Langston New York University
 Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Discrete Mathematics Lecture 4 Harper Langston New York University Sequences Sequence is a set of (usually infinite number of) ordered elements: a 1, a 2,, a n, Each individual element a k is called a
Math Week in Review #5. A proposition, or statement, is a declarative sentence that can be classified as either true or false, but not both.
 Math 166 Fall 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 166 - Week in Review #5 Sections A.1 and A.2 - Propositions, Connectives, and Truth Tables A proposition, or statement, is a declarative sentence that can
Math 166 Fall 2006 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 166 - Week in Review #5 Sections A.1 and A.2 - Propositions, Connectives, and Truth Tables A proposition, or statement, is a declarative sentence that can
Truth Trees. Truth Tree Fundamentals
 Truth Trees 1 True Tree Fundamentals 2 Testing Grous of Statements for Consistency 3 Testing Arguments in Proositional Logic 4 Proving Invalidity in Predicate Logic Answers to Selected Exercises Truth
Truth Trees 1 True Tree Fundamentals 2 Testing Grous of Statements for Consistency 3 Testing Arguments in Proositional Logic 4 Proving Invalidity in Predicate Logic Answers to Selected Exercises Truth
Chapter 2 Homework Vocabulary Inductive reasoning - Conjecture - Counterexample - Conditional - Hypothesis - Conclusion - Truth value - Negation -
 Chapter 2 Homework Vocabulary Inductive reasoning - Conjecture - Counterexample - Conditional - Hypothesis - Conclusion - Truth value - Negation - Converse - Inverse - Contrapositive - Equivalent statements
Chapter 2 Homework Vocabulary Inductive reasoning - Conjecture - Counterexample - Conditional - Hypothesis - Conclusion - Truth value - Negation - Converse - Inverse - Contrapositive - Equivalent statements
NP-Completeness of 3SAT, 1-IN-3SAT and MAX 2SAT
 NP-Completeness of 3SAT, 1-IN-3SAT and MAX 2SAT 3SAT The 3SAT problem is the following. INSTANCE : Given a boolean expression E in conjunctive normal form (CNF) that is the conjunction of clauses, each
NP-Completeness of 3SAT, 1-IN-3SAT and MAX 2SAT 3SAT The 3SAT problem is the following. INSTANCE : Given a boolean expression E in conjunctive normal form (CNF) that is the conjunction of clauses, each
An Abductive Framework for General Logic Programs and other Nonmonotonic Systems
 An Abductive Framework for General Logic Programs and other Nonmonotonic Systems Gerhard Brewka Kurt Konolige GMD, Postfach 12 40 SRI International 5205 Sankt Augustin, Germany 333 Ravenswood Ave Menlo
An Abductive Framework for General Logic Programs and other Nonmonotonic Systems Gerhard Brewka Kurt Konolige GMD, Postfach 12 40 SRI International 5205 Sankt Augustin, Germany 333 Ravenswood Ave Menlo
STABILITY AND PARADOX IN ALGORITHMIC LOGIC
 STABILITY AND PARADOX IN ALGORITHMIC LOGIC WAYNE AITKEN, JEFFREY A. BARRETT Abstract. Algorithmic logic is the logic of basic statements concerning algorithms and the algorithmic rules of deduction between
STABILITY AND PARADOX IN ALGORITHMIC LOGIC WAYNE AITKEN, JEFFREY A. BARRETT Abstract. Algorithmic logic is the logic of basic statements concerning algorithms and the algorithmic rules of deduction between
Get my pizza right: Repairing missing is-a relations in ALC ontologies
 Get my pizza right: Repairing missing is-a relations in ALC ontologies Patrick Lambrix, Zlatan Dragisic and Valentina Ivanova Linköping University Sweden 1 Introduction Developing ontologies is not an
Get my pizza right: Repairing missing is-a relations in ALC ontologies Patrick Lambrix, Zlatan Dragisic and Valentina Ivanova Linköping University Sweden 1 Introduction Developing ontologies is not an
ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF
 CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.2 Direct Proof and Counterexample II: Rational Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All
CHAPTER 4 ELEMENTARY NUMBER THEORY AND METHODS OF PROOF Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 4.2 Direct Proof and Counterexample II: Rational Numbers Copyright Cengage Learning. All
How to Compute Halting
 2015-1-2 0 How to Compute Halting Eric C.R. Hehner Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto hehner@cs.utoronto.ca Abstract: A consistently specified halting function may be computed. Halting
2015-1-2 0 How to Compute Halting Eric C.R. Hehner Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto hehner@cs.utoronto.ca Abstract: A consistently specified halting function may be computed. Halting
G.CO.C.9: Compound Statements
 Regents Exam Questions G.CO.C.9: Compound Statements www.jmap.org Name: G.CO.C.9: Compound Statements 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 1) 9 2)
Regents Exam Questions G.CO.C.9: Compound Statements www.jmap.org Name: G.CO.C.9: Compound Statements 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 1) 9 2)
Relational Databases
 Relational Databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki () Relational databases 1 / 49 Plan of the course 1 Relational databases 2 Relational database design 3 Conceptual database design 4
Relational Databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki () Relational databases 1 / 49 Plan of the course 1 Relational databases 2 Relational database design 3 Conceptual database design 4
(More) Propositional Logic and an Intro to Predicate Logic. CSCI 3202, Fall 2010
 (More) Propositional Logic and an Intro to Predicate Logic CSCI 3202, Fall 2010 Assignments Next week: Guest lectures (Jim Martin and Nikolaus Correll); Read Chapter 9 (but you can skip sections on logic
(More) Propositional Logic and an Intro to Predicate Logic CSCI 3202, Fall 2010 Assignments Next week: Guest lectures (Jim Martin and Nikolaus Correll); Read Chapter 9 (but you can skip sections on logic
Practice Final. Read all the problems first before start working on any of them, so you can manage your time wisely
 PRINT your name here: Practice Final Print your name immediately on the cover page, as well as each page of the exam, in the space provided. Each time you are caught working on a page without your name
PRINT your name here: Practice Final Print your name immediately on the cover page, as well as each page of the exam, in the space provided. Each time you are caught working on a page without your name
Foundations of Computation
 Foundations of Computation Second Edition (Version 2.3.2, Summer 2011) Carol Critchlow and David Eck Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Hobart and William Smith Colleges Geneva, New York 14456
Foundations of Computation Second Edition (Version 2.3.2, Summer 2011) Carol Critchlow and David Eck Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Hobart and William Smith Colleges Geneva, New York 14456
Propositional Logic Formal Syntax and Semantics. Computability and Logic
 Propositional Logic Formal Syntax and Semantics Computability and Logic Syntax and Semantics Syntax: The study of how expressions are structured (think: grammar) Semantics: The study of the relationship
Propositional Logic Formal Syntax and Semantics Computability and Logic Syntax and Semantics Syntax: The study of how expressions are structured (think: grammar) Semantics: The study of the relationship
SINGLE VALUED NEUTROSOPHIC SETS
 Fuzzy Sets, Rough Sets and Multivalued Operations and pplications, Vol 3, No 1, (January-June 2011): 33 39; ISSN : 0974-9942 International Science Press SINGLE VLUED NEUTROSOPHIC SETS Haibin Wang, Yanqing
Fuzzy Sets, Rough Sets and Multivalued Operations and pplications, Vol 3, No 1, (January-June 2011): 33 39; ISSN : 0974-9942 International Science Press SINGLE VLUED NEUTROSOPHIC SETS Haibin Wang, Yanqing
CSE 215: Foundations of Computer Science Recitation Exercises Set #4 Stony Brook University. Name: ID#: Section #: Score: / 4
 CSE 215: Foundations of Computer Science Recitation Exercises Set #4 Stony Brook University Name: ID#: Section #: Score: / 4 Unit 7: Direct Proof Introduction 1. The statement below is true. Rewrite the
CSE 215: Foundations of Computer Science Recitation Exercises Set #4 Stony Brook University Name: ID#: Section #: Score: / 4 Unit 7: Direct Proof Introduction 1. The statement below is true. Rewrite the
Chapter 3. Set Theory. 3.1 What is a Set?
 Chapter 3 Set Theory 3.1 What is a Set? A set is a well-defined collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Here, well-defined means accurately and unambiguously stated or described. Any
Chapter 3 Set Theory 3.1 What is a Set? A set is a well-defined collection of objects called elements or members of the set. Here, well-defined means accurately and unambiguously stated or described. Any
SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION
 CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All
CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All
Resolution (14A) Young W. Lim 6/14/14
 Copyright (c) 2013-2014. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free
Copyright (c) 2013-2014. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free
(QiuXin Hui) 7.2 Given the following, can you prove that the unicorn is mythical? How about magical? Horned? Decide what you think the right answer
 (QiuXin Hui) 7.2 Given the following, can you prove that the unicorn is mythical? How about magical? Horned? Decide what you think the right answer is yourself, then show how to get the answer using both
(QiuXin Hui) 7.2 Given the following, can you prove that the unicorn is mythical? How about magical? Horned? Decide what you think the right answer is yourself, then show how to get the answer using both
CS 3512, Spring Instructor: Doug Dunham. Textbook: James L. Hein, Discrete Structures, Logic, and Computability, 3rd Ed. Jones and Barlett, 2010
 CS 3512, Spring 2011 Instructor: Doug Dunham Textbook: James L. Hein, Discrete Structures, Logic, and Computability, 3rd Ed. Jones and Barlett, 2010 Prerequisites: Calc I, CS2511 Rough course outline:
CS 3512, Spring 2011 Instructor: Doug Dunham Textbook: James L. Hein, Discrete Structures, Logic, and Computability, 3rd Ed. Jones and Barlett, 2010 Prerequisites: Calc I, CS2511 Rough course outline:
Topology I Test 1 Solutions October 13, 2008
 Topology I Test 1 Solutions October 13, 2008 1. Do FIVE of the following: (a) Give a careful definition of connected. A topological space X is connected if for any two sets A and B such that A B = X, we
Topology I Test 1 Solutions October 13, 2008 1. Do FIVE of the following: (a) Give a careful definition of connected. A topological space X is connected if for any two sets A and B such that A B = X, we
Publication Data. Reading Options. Licence and permissions ISBN Mark Jago, 2007
 Running Head The World is all that is the case http//www.humanities-ebooks.co.uk Philosophy Insights General Editor: Mark ddis Formal Logic Mark Jago What makes an argument valid? For advice on use of
Running Head The World is all that is the case http//www.humanities-ebooks.co.uk Philosophy Insights General Editor: Mark ddis Formal Logic Mark Jago What makes an argument valid? For advice on use of
DEFINITIONS DERIVED FROM NEUTROSOPHICS. Florentin Smarandache, University of New Mexico, Gallup Campus, USA
 DEFINITIONS DERIVED FROM NEUTROSOPHICS Florentin Smarandache, University of New Mexico, Gallup Campus, USA Abstract: Thirty-three new definitions are presented, derived from neutrosophic set, neutrosophic
DEFINITIONS DERIVED FROM NEUTROSOPHICS Florentin Smarandache, University of New Mexico, Gallup Campus, USA Abstract: Thirty-three new definitions are presented, derived from neutrosophic set, neutrosophic
Geometry Note-Sheet Overview
 Geometry Note-Sheet Overview 1. Logic a. A mathematical sentence is a sentence that states a fact or contains a complete idea. Open sentence it is blue x+3 Contains variables Cannot assign a truth variable
Geometry Note-Sheet Overview 1. Logic a. A mathematical sentence is a sentence that states a fact or contains a complete idea. Open sentence it is blue x+3 Contains variables Cannot assign a truth variable
Declarative Programming. 2: theoretical backgrounds
 Declarative Programming 2: theoretical backgrounds 1 Logic Systems: structure and meta-theoretical properties logic system syntax semantics proof theory defines which sentences are legal in the logical
Declarative Programming 2: theoretical backgrounds 1 Logic Systems: structure and meta-theoretical properties logic system syntax semantics proof theory defines which sentences are legal in the logical
CSL105: Discrete Mathematical Structures. Ragesh Jaiswal, CSE, IIT Delhi
 is another way of showing that an argument is correct. Definitions: Literal: A variable or a negation of a variable is called a literal. Sum and Product: A disjunction of literals is called a sum and a
is another way of showing that an argument is correct. Definitions: Literal: A variable or a negation of a variable is called a literal. Sum and Product: A disjunction of literals is called a sum and a
the Computability Hierarchy
 2013 0 the Computability Hierarchy Eric Hehner Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto hehner@cs.utoronto.ca Abstract A computability hierarchy cannot be constructed by halting oracles. Introduction
2013 0 the Computability Hierarchy Eric Hehner Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto hehner@cs.utoronto.ca Abstract A computability hierarchy cannot be constructed by halting oracles. Introduction
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WITH APPLICATIONS THIRD EDITION SUSANNA S. EPP DePaul University THOIVISON * BROOKS/COLE Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CONTENTS Chapter 1 The
DISCRETE MATHEMATICS WITH APPLICATIONS THIRD EDITION SUSANNA S. EPP DePaul University THOIVISON * BROOKS/COLE Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States CONTENTS Chapter 1 The
Maintaining Disjoint Sets
 Maintaining Disjoint Sets Ref: Chapter 21 of text. (Proofs in Section 21.4 omitted.) Given: A collection S 1, S 2,..., S k of pairwise disjoint sets. Each set has a name, its representative, which is an
Maintaining Disjoint Sets Ref: Chapter 21 of text. (Proofs in Section 21.4 omitted.) Given: A collection S 1, S 2,..., S k of pairwise disjoint sets. Each set has a name, its representative, which is an
Propositional logic (Ch. 7)
 Propositional logic (Ch. 7) Announcements Writing 2 graded - 2 weeks from today to resubmit Complete-state CSP So far we have been looking at incremental search (adding one value at a time) Complete-state
Propositional logic (Ch. 7) Announcements Writing 2 graded - 2 weeks from today to resubmit Complete-state CSP So far we have been looking at incremental search (adding one value at a time) Complete-state
Propositional logic (Ch. 7)
 Propositional logic (Ch. 7) Announcements Writing 3 due Sunday - ideally use for project - if you haven't decided project by then, you will have to redo this work Logic: definitions We say that two sentences
Propositional logic (Ch. 7) Announcements Writing 3 due Sunday - ideally use for project - if you haven't decided project by then, you will have to redo this work Logic: definitions We say that two sentences
Recursive Definitions
 Recursive Definitions Supplement to Chapter 7 of Steinhart, E. (2009) More Precisely: The Math You Need to Do Philosophy. Broadview Press. Copyright (C) 2009 Eric Steinhart. Non-commercial educational
Recursive Definitions Supplement to Chapter 7 of Steinhart, E. (2009) More Precisely: The Math You Need to Do Philosophy. Broadview Press. Copyright (C) 2009 Eric Steinhart. Non-commercial educational
Knowledge Representation
 Knowledge Representation References Rich and Knight, Artificial Intelligence, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, 1991 Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 Outline
Knowledge Representation References Rich and Knight, Artificial Intelligence, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill, 1991 Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 Outline
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Sections p.
 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Sections 10.1-10.3 p. 1/106 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Sections 10.1-10.3 p. 1/106 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
Lecture 5: Formation Tree and Parsing Algorithm
 Discrete Mathematics (II) Spring 2012 Lecture 5: Formation Tree and Parsing Algorithm Lecturer: Yi Li 1 Overview In this lecture, we completely focus on syntax of proposition. And the term proposition
Discrete Mathematics (II) Spring 2012 Lecture 5: Formation Tree and Parsing Algorithm Lecturer: Yi Li 1 Overview In this lecture, we completely focus on syntax of proposition. And the term proposition
A Look at Function Symbols and Planning
 From: AAAI Technical Report SS-93-03. Compilation copyright 1993, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. A Look at Function Symbols and Planning Eric Jacopin * Laforia, 4 place Jussieu, Bolte 169 France,
From: AAAI Technical Report SS-93-03. Compilation copyright 1993, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. A Look at Function Symbols and Planning Eric Jacopin * Laforia, 4 place Jussieu, Bolte 169 France,
CSC Discrete Math I, Spring Sets
 CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Sets Sets A set is well-defined, unordered collection of objects The objects in a set are called the elements, or members, of the set A set is said to contain its
CSC 125 - Discrete Math I, Spring 2017 Sets Sets A set is well-defined, unordered collection of objects The objects in a set are called the elements, or members, of the set A set is said to contain its
Lecture-12: Closed Sets
 and Its Examples Properties of Lecture-12: Dr. Department of Mathematics Lovely Professional University Punjab, India October 18, 2014 Outline Introduction and Its Examples Properties of 1 Introduction
and Its Examples Properties of Lecture-12: Dr. Department of Mathematics Lovely Professional University Punjab, India October 18, 2014 Outline Introduction and Its Examples Properties of 1 Introduction
Epimenides, Gödel, Turing: an Eternal Gölden Tangle [0]
![Epimenides, Gödel, Turing: an Eternal Gölden Tangle [0] Epimenides, Gödel, Turing: an Eternal Gölden Tangle [0]](/thumbs/89/99999765.jpg) 2014-10-6 0 Epimenides, Gödel, Turing: an Eternal Gölden Tangle [0] Eric C.R. Hehner Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto hehner@cs.utoronto.ca Abstract: The Halting Problem is a version
2014-10-6 0 Epimenides, Gödel, Turing: an Eternal Gölden Tangle [0] Eric C.R. Hehner Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto hehner@cs.utoronto.ca Abstract: The Halting Problem is a version
Definition MATH Benjamin V.C. Collins, James A. Swenson MATH 2730
 MATH 2730 Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson s and undefined terms The importance of definition s matter! may be more important in Discrete Math than in any math course that you have had previously.
MATH 2730 Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson s and undefined terms The importance of definition s matter! may be more important in Discrete Math than in any math course that you have had previously.
Propositional Logic:
 CS2209A 2017 Applied Logic for Computer Science Lecture 2 Propositional Logic: Syntax, semantics, truth table Instructor: Yu Zhen Xie Language of logic: building blocks Proposition: A sentence that can
CS2209A 2017 Applied Logic for Computer Science Lecture 2 Propositional Logic: Syntax, semantics, truth table Instructor: Yu Zhen Xie Language of logic: building blocks Proposition: A sentence that can
3.5 Indeterminate Forms. Consider the function given by the rule f(x) = Whenever direct substitution into lim x c f(x) yields a 0 0
 3.5 Indeterminate Forms Introduction; Consider the function given by the rule f() = ; its graph is shown below. 0 0 situations Clearly, = 3. Note, however, that if one merely tried to plug in 0 for when
3.5 Indeterminate Forms Introduction; Consider the function given by the rule f() = ; its graph is shown below. 0 0 situations Clearly, = 3. Note, however, that if one merely tried to plug in 0 for when
CS-171, Intro to A.I. Mid-term Exam Winter Quarter, 2014
 CS-171, Intro to A.I. Mid-term Exam Winter Quarter, 2014 YOUR NAME: YOUR ID: ID TO RIGHT: ROW: SEAT NO.: The exam will begin on the next page. Please, do not turn the page until told. When you are told
CS-171, Intro to A.I. Mid-term Exam Winter Quarter, 2014 YOUR NAME: YOUR ID: ID TO RIGHT: ROW: SEAT NO.: The exam will begin on the next page. Please, do not turn the page until told. When you are told
Propositional Calculus
 Propositional Calculus Proposition is a statement that is either or. Example 1 Propositions: It rains. Sun is shining and my coat is wet. If Ann plays with me, I give her a candy. x > 10 x = 1 and y
Propositional Calculus Proposition is a statement that is either or. Example 1 Propositions: It rains. Sun is shining and my coat is wet. If Ann plays with me, I give her a candy. x > 10 x = 1 and y
Flow Control. So Far: Writing simple statements that get executed one after another.
 Flow Control So Far: Writing simple statements that get executed one after another. Flow Control So Far: Writing simple statements that get executed one after another. Flow control allows the programmer
Flow Control So Far: Writing simple statements that get executed one after another. Flow Control So Far: Writing simple statements that get executed one after another. Flow control allows the programmer
IT 1033: Fundamentals of Programming Loops
 IT 1033: Fundamentals of Programming Loops Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Repetitions: Loops A loop is a sequence of instruction s that is continually repeated until a certain condition
IT 1033: Fundamentals of Programming Loops Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Repetitions: Loops A loop is a sequence of instruction s that is continually repeated until a certain condition
The strong chromatic number of a graph
 The strong chromatic number of a graph Noga Alon Abstract It is shown that there is an absolute constant c with the following property: For any two graphs G 1 = (V, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V, E 2 ) on the same
The strong chromatic number of a graph Noga Alon Abstract It is shown that there is an absolute constant c with the following property: For any two graphs G 1 = (V, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V, E 2 ) on the same
Softwaretechnik. Lecture 03: Types and Type Soundness. Peter Thiemann. University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2008
 Softwaretechnik Lecture 03: Types and Type Soundness Peter Thiemann University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2008 Peter Thiemann (Univ. Freiburg) Softwaretechnik SWT 1 / 35 Table of Contents Types and Type correctness
Softwaretechnik Lecture 03: Types and Type Soundness Peter Thiemann University of Freiburg, Germany SS 2008 Peter Thiemann (Univ. Freiburg) Softwaretechnik SWT 1 / 35 Table of Contents Types and Type correctness
Bertrand. A Symbolic Logic Problem Solver For The Macintosh Version 1.8
 Bertrand A Symbolic Logic Problem Solver For The Macintosh Version 1.8 CONTENTS 1) Contacting The Author 2) What Is Bertrand? 3) System Requirements 4) Paying For Your Copy Of Bertrand 5) Getting Started
Bertrand A Symbolic Logic Problem Solver For The Macintosh Version 1.8 CONTENTS 1) Contacting The Author 2) What Is Bertrand? 3) System Requirements 4) Paying For Your Copy Of Bertrand 5) Getting Started
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 6 Outline. Unary Relational Operations: SELECT and
 Chapter 6 The Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 6 Outline Unary Relational Operations: SELECT and PROJECT Relational
Chapter 6 The Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 6 Outline Unary Relational Operations: SELECT and PROJECT Relational
Truth Maintenance Systems. EECS 344 Winter 2008
 Truth Maintenance Systems EECS 344 Winter 2008 Outline What is a TMS? Basic TMS model Justification-based TMS What is a TMS? A useful problem-solver module Justifications, assumptions Inference Engine
Truth Maintenance Systems EECS 344 Winter 2008 Outline What is a TMS? Basic TMS model Justification-based TMS What is a TMS? A useful problem-solver module Justifications, assumptions Inference Engine
SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION
 CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 5 SEQUENCES, MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION, AND RECURSION Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. SECTION 5.5 Application: Correctness of Algorithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS
 THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS By: Sterling McKay APRIL 21, 2014 LONE STAR - MONTGOMERY Mentor: William R. Brown, MBA Mckay 1 In mathematics, truth is arguably the most essential of its components. Suppose
THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS By: Sterling McKay APRIL 21, 2014 LONE STAR - MONTGOMERY Mentor: William R. Brown, MBA Mckay 1 In mathematics, truth is arguably the most essential of its components. Suppose
1. A statement is a set of words and/or symbols that collectively make a claim that can be classified as true or false.
 Chapter 1 Line and Angle Relationships 1.1 Sets, Statements and Reasoning Definitions 1. A statement is a set of words and/or symbols that collectively make a claim that can be classified as true or false.
Chapter 1 Line and Angle Relationships 1.1 Sets, Statements and Reasoning Definitions 1. A statement is a set of words and/or symbols that collectively make a claim that can be classified as true or false.
Incomplete Information: Null Values
 Incomplete Information: Null Values Often ruled out: not null in SQL. Essential when one integrates/exchanges data. Perhaps the most poorly designed and the most often criticized part of SQL:... [this]
Incomplete Information: Null Values Often ruled out: not null in SQL. Essential when one integrates/exchanges data. Perhaps the most poorly designed and the most often criticized part of SQL:... [this]
for all x, the assertion P(x) is false. there exists x, for which the assertion P(x) is true.
 You can t prove a predicate is true because a predicate is not an assertion, you can t prove it is valid as it is not a deduction! If someone asks you to prove P(x), it is not totally clear what they mean.
You can t prove a predicate is true because a predicate is not an assertion, you can t prove it is valid as it is not a deduction! If someone asks you to prove P(x), it is not totally clear what they mean.
Institute of Southern Punjab, Multan
 Institute of Southern Punjab, Multan Mr. Muhammad Nouman Farooq BSC-H (Computer Science) MS (Telecomm. and Networks) Honors: Magna Cumm Laude Honors Degree Gold Medalist! Blog Url: noumanfarooqatisp.wordpress.com
Institute of Southern Punjab, Multan Mr. Muhammad Nouman Farooq BSC-H (Computer Science) MS (Telecomm. and Networks) Honors: Magna Cumm Laude Honors Degree Gold Medalist! Blog Url: noumanfarooqatisp.wordpress.com
Uncertain Data Models
 Uncertain Data Models Christoph Koch EPFL Dan Olteanu University of Oxford SYNOMYMS data models for incomplete information, probabilistic data models, representation systems DEFINITION An uncertain data
Uncertain Data Models Christoph Koch EPFL Dan Olteanu University of Oxford SYNOMYMS data models for incomplete information, probabilistic data models, representation systems DEFINITION An uncertain data
What is the study of logic?
 Chapter 2: The Representation of Knowledge Expert Systems: Principles and Programming, Fourth Edition What is the study of logic? Logic is the study of making inferences given a set of facts, we attempt
Chapter 2: The Representation of Knowledge Expert Systems: Principles and Programming, Fourth Edition What is the study of logic? Logic is the study of making inferences given a set of facts, we attempt
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Summary of Course Coverage
 CS-227, Discrete Structures I Spring 2006 Semester Summary of Course Coverage 1) Propositional Calculus a) Negation (logical NOT) b) Conjunction (logical AND) c) Disjunction (logical inclusive-or) d) Inequalities
CS-227, Discrete Structures I Spring 2006 Semester Summary of Course Coverage 1) Propositional Calculus a) Negation (logical NOT) b) Conjunction (logical AND) c) Disjunction (logical inclusive-or) d) Inequalities
CPSC 121: Models of Computation
 CPSC 121: Models of Computation Unit 1 Propositional Logic Based on slides by Patrice Belleville and Steve Wolfman Last Updated: 2017-09-09 12:04 AM Pre Lecture Learning Goals By the start of the class,
CPSC 121: Models of Computation Unit 1 Propositional Logic Based on slides by Patrice Belleville and Steve Wolfman Last Updated: 2017-09-09 12:04 AM Pre Lecture Learning Goals By the start of the class,
PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC (2)
 PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC (2) based on Huth & Ruan Logic in Computer Science: Modelling and Reasoning about Systems Cambridge University Press, 2004 Russell & Norvig Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach
PROPOSITIONAL LOGIC (2) based on Huth & Ruan Logic in Computer Science: Modelling and Reasoning about Systems Cambridge University Press, 2004 Russell & Norvig Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach
First-Order Logic Syntax
 First-Order Logic Syntax Reading: Chapter 8, 9.1-9.2, 9.5.1-9.5.5 FOL Syntax and Semantics read: 8.1-8.2 FOL Knowledge Engineering read: 8.3-8.5 FOL Inference read: Chapter 9.1-9.2, 9.5.1-9.5.5 (Please
First-Order Logic Syntax Reading: Chapter 8, 9.1-9.2, 9.5.1-9.5.5 FOL Syntax and Semantics read: 8.1-8.2 FOL Knowledge Engineering read: 8.3-8.5 FOL Inference read: Chapter 9.1-9.2, 9.5.1-9.5.5 (Please
Sams Teach Yourself Java 2 in 21 Days, Fourth Edition. Copyright 2004 by Sams Publishing. International Standard Book Number:
 Sams Teach Yourself Java 2 in 21 Days, Fourth Edition Copyright 2004 by Sams Publishing International Standard Book Number: 0-672-32628-0 Warning and Disclaimer Every effort has been made to make this
Sams Teach Yourself Java 2 in 21 Days, Fourth Edition Copyright 2004 by Sams Publishing International Standard Book Number: 0-672-32628-0 Warning and Disclaimer Every effort has been made to make this
Engineering 100 Midterm Exam Technical Part Fall 2010
 Engineering 100 Midterm Exam Technical Part Fall 2010 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: Page # Points
Engineering 100 Midterm Exam Technical Part Fall 2010 Name: unique name: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: Page # Points
Advanced features of the Calculate signal tool
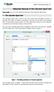 Advanced features of the Calculate signal tool Case study: how to us the advanced features of the Calculate signal tool? 1 The calculate signal tool The calculate signal tool is one of the most useful
Advanced features of the Calculate signal tool Case study: how to us the advanced features of the Calculate signal tool? 1 The calculate signal tool The calculate signal tool is one of the most useful
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Conditionals Janyl Jumadinova 10 October, 2018 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 10 October, 2018 1 / 16 Computational Thinking: a problem solving process Decomposition
Computational Expression Conditionals Janyl Jumadinova 10 October, 2018 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 10 October, 2018 1 / 16 Computational Thinking: a problem solving process Decomposition
Propositional Calculus: Boolean Algebra and Simplification. CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson
 Propositional Calculus: Boolean Algebra and Simplification CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson Propositional Calculus Topics Motivation: Simplifying Conditional Expressions
Propositional Calculus: Boolean Algebra and Simplification CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson Propositional Calculus Topics Motivation: Simplifying Conditional Expressions
Semantics via Syntax. f (4) = if define f (x) =2 x + 55.
 1 Semantics via Syntax The specification of a programming language starts with its syntax. As every programmer knows, the syntax of a language comes in the shape of a variant of a BNF (Backus-Naur Form)
1 Semantics via Syntax The specification of a programming language starts with its syntax. As every programmer knows, the syntax of a language comes in the shape of a variant of a BNF (Backus-Naur Form)
Situation Calculus and YAGI
 Situation Calculus and YAGI Institute for Software Technology 1 Progression another solution to the projection problem does a sentence hold for a future situation used for automated reasoning and planning
Situation Calculus and YAGI Institute for Software Technology 1 Progression another solution to the projection problem does a sentence hold for a future situation used for automated reasoning and planning
Sets. Mukulika Ghosh. Fall Based on slides by Dr. Hyunyoung Lee
 Sets Mukulika Ghosh Fall 2018 Based on slides by Dr. Hyunyoung Lee Sets Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects, called elements, without duplication. We write a A to denote that a is an element
Sets Mukulika Ghosh Fall 2018 Based on slides by Dr. Hyunyoung Lee Sets Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects, called elements, without duplication. We write a A to denote that a is an element
