1. Mother vertex using BFS. A mother vertex in a graph G = (V,E) is a vertex v such that all other vertices in G can be reached by a path from v.
|
|
|
- Arabella Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Assignment(September 5 th 2017) Solutions (Hints) REMARK: The codes given below are just a guide, this is not the only way to write programs for these algorithms. What is important is that your program should implement the algorithm in the correct manner. 1. Mother vertex using BFS A mother vertex in a graph G = (V,E) is a vertex v such that all other vertices in G can be reached by a path from v. #include<iostream> #include<bits/stdc++.h> #include <list> using namespace std; int f=0; int par[20]; // This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list representation struct Graph int V; // No. of vertices list<int> *adj; ; // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists struct Graph* creategraph(int V) Graph* graph=new Graph; graph->v = V; graph->adj = new list<int>[v]; void addedge(struct Graph* graph,int v, int w) graph->adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v s list, if the graph is undirected,add v to w's list as well bool BFS(struct Graph* graph,int s) int d,flag=0; d=s;
2 bool *visited = new bool[graph->v]; for(int i = 0; i < graph->v; i++) visited[i] = false; // Create a queue for BFS list<int> queue; // Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it visited[s] = true; queue.push_back(s); // 'i' will be used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex list<int>::iterator i; while(!queue.empty()) // Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it s = queue.front(); cout << s << " "; f++; queue.pop_front(); // Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s // If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it visited // and enqueue it for(i = graph->adj[s].begin(); i!=graph-> adj[s].end(); ++i) if(!visited[*i]) visited[*i] = true; queue.push_back(*i); cout<<"\n"; for(int j=0;j<=6;j++) if(visited[j]!=true) flag=1; if(flag==0) cout<<"the vertex "<< d <<" is a mother vertex"; cout<<"\n";
3 int main() struct Graph* graph=creategraph(7); addedge(graph,0,1); addedge(graph,0,2); addedge(graph,1,3); addedge(graph,4,1); addedge(graph,6,4); addedge(graph,5,6); addedge(graph,5,2); addedge(graph,6,0); for(int i=0;i<=6;i++) cout<<"the BFS traversal from vertex "<< i << " is\n"; BFS(graph,i); cout<<"\n"; return 0; 2. Transitive Closure using Depth First Traversal Given a directed graph, find out if a vertex v is reachable from another vertex u for all vertex pairs (u, v) in the given graph. Here reachable mean that there is a path from vertex u to v. The reach-ability matrix is called transitive closure of a graph. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<iostream> #include<list> using namespace std; int tc[10][10]; struct Graph int V; list<int> *adj; ; struct Graph* creategraph(int V) Graph* graph=new Graph; graph->v = V; graph->adj = new list<int>[graph->v]; void addedge(struct Graph* graph,int v, int w)
4 graph->adj[v].push_back(w); // A recursive DFS traversal function that finds // all reachable vertices for s. void DFSUtil(struct Graph* graph,int s, int v) // Mark reachability from s to t as true. tc[s][v] = 1; // Find all the vertices reachable through v list<int>::iterator i; for (i =graph->adj[v].begin(); i!=graph->adj[v].end(); ++i) if (tc[s][*i] == 0) DFSUtil(graph,s, *i); // The function to find transitive closure. It uses // recursive DFSUtil() void transitiveclosure(struct Graph* graph) // Call the recursive helper function to print DFS // traversal starting from all vertices one by one for (int i=0; i<4; i++) for(int j=0;j<4;j++) tc[i][j]=0; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) DFSUtil(graph,i,i); // Every vertex is reachable from self. for (int i=0; i<4; i++) for (int j=0; j<4; j++) cout << tc[i][j] << " "; cout << endl; int main() struct Graph* graph= creategraph(4); addedge(graph,0, 1); addedge(graph,0, 2); addedge(graph,1, 2); addedge(graph,2, 0); addedge(graph,2, 3);
5 addedge(graph,3, 3); cout << "Transitive closure matrix is \n"; transitiveclosure(graph); return 0; 3. Connected components of undirected graph (Here DFS is used) #include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<iostream> #include<list> using namespace std; struct Graph int V; list<int> *adj; ; struct Graph* creategraph(int V)
6 Graph* graph=new Graph; graph->v = V; graph->adj = new list<int>[graph->v]; void addedge(struct Graph* graph,int v, int w) graph->adj[v].push_back(w); graph->adj[w].push_back(v); void DFSUtil(struct Graph* graph,int v, bool visited[]) // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; cout << v << " "; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex list<int>::iterator i; for (i = graph->adj[v].begin(); i!= graph->adj[v].end(); ++i) if (!visited[*i]) DFSUtil(graph,*i, visited); void connectedcomponents(struct Graph* graph) bool *visited = new bool[graph->v]; for(int i = 0; i < graph->v; i++) visited[i] = false; for (int j=0; j<graph->v; j++) if (visited[j] == false) // print all reachable vertices // from v DFSUtil(graph,j, visited); cout << "\n"; int main() // Create a graph given in the above diagram struct Graph* graph= creategraph(5); // 5 vertices numbered from 0 to 4 addedge(graph,1, 0); addedge(graph,1, 2);
7 addedge(graph,3, 4); cout << "Following are connected components \n"; connectedcomponents(graph); return 0; 4. Check whether directed graph is cyclic or not. Together with this,if we check connectivity as well, we know whether graph is tree or not. To check connectivity,check whether the dfs of a vertex reaches all other vertices, if not it is not connected. A graph has to connected and acyclic to be a tree. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<iostream> #include<list> using namespace std; struct Graph int V; list<int> *adj; ; struct Graph* creategraph(int V) Graph* graph=new Graph; graph->v = V; graph->adj = new list<int>[graph->v]; void addedge(struct Graph* graph,int v, int w) graph->adj[v].push_back(w); bool iscyclicutil(struct Graph* graph,int v,bool visited[],bool recstack[]) if(visited[v]==false) // Mark the current node as visited and part of recursion stack visited[v]=true; recstack[v]=true; list<int>::iterator i; for(i =graph->adj[v].begin(); i!=graph->adj[v].end(); ++i) if (!visited[*i] && iscyclicutil(graph,*i, visited,recstack) ) return true;
8 else if (recstack[*i]) return true; recstack[v] = false; // remove the vertex from recursion stack return false; bool iscyclic(struct Graph* graph) bool *visited = new bool[graph->v]; bool *recstack = new bool[graph->v]; for(int i = 0; i < graph->v; i++) visited[i] = false; recstack[i] = false; // Call the recursive helper function to detect cycle in different // DFS trees for(int i = 0; i < graph->v; i++) if (iscyclicutil(graph,i, visited, recstack)) return true; return false; int main() struct Graph* graph= creategraph(4); addedge(graph,1, 2); addedge(graph,2, 3); addedge(graph,3, 1); if(iscyclic(graph)) cout<<"the graph contains a cycle"; else cout<<"the graph does not contain a cycle";
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH
 CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Homework 5: Graphs, Minimum Spanning Trees, and Dijkstra Shortest-Path
 Homework 5: Graphs, Minimum Spanning Trees, and Dijkstra Shortest-Path 1. (4 points) A graph is Hamiltonian if there is a cycle in the graph visiting each vertex exactly once. Give an example of an Eulerian
Homework 5: Graphs, Minimum Spanning Trees, and Dijkstra Shortest-Path 1. (4 points) A graph is Hamiltonian if there is a cycle in the graph visiting each vertex exactly once. Give an example of an Eulerian
Graphs: Graph Data Structure:
 Graphs: A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links
Graphs: A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graph Traversals BFS & DFS 1 CS S-16
 CS-8S- BFS & DFS -: Visit every vertex, in an order defined by the topololgy of the graph. Two major traversals: Depth First Search Breadth First Search -: Depth First Search Starting from a specific node
CS-8S- BFS & DFS -: Visit every vertex, in an order defined by the topololgy of the graph. Two major traversals: Depth First Search Breadth First Search -: Depth First Search Starting from a specific node
Algorithm and Data Structures, Supplemental Solution 2010
 Algorithm and Data Structures, Supplemental Solution 00 Question ( marks) (a) marks class Stack { public: void push(int x); int pop(void); bool isempty(); Stack() { top = NULL; void display(); ; private:
Algorithm and Data Structures, Supplemental Solution 00 Question ( marks) (a) marks class Stack { public: void push(int x); int pop(void); bool isempty(); Stack() { top = NULL; void display(); ; private:
undirected graph 5 vertices 7 edges directed graph 6 vertices 8 edges
 ! "# $ % ' ( ) * * ## A A B B F E D C undirected graph 5 vertices 7 edges C D directed graph 6 vertices 8 edges E 1 , $ % # ' $ % ( $ %! * -* $ %. * #$/$' $' 0$ ( 0$! $ )*,1/$ * 2 3 "4!*!" 4 * # * 2 )
! "# $ % ' ( ) * * ## A A B B F E D C undirected graph 5 vertices 7 edges C D directed graph 6 vertices 8 edges E 1 , $ % # ' $ % ( $ %! * -* $ %. * #$/$' $' 0$ ( 0$! $ )*,1/$ * 2 3 "4!*!" 4 * # * 2 )
Chapter 16: Graphs and Digraphs
 Chapter 16: Graphs and Digraphs Exercises 16.1 1. adj: 2. adj: 3. adj: 4. adj: 5. E 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
Chapter 16: Graphs and Digraphs Exercises 16.1 1. adj: 2. adj: 3. adj: 4. adj: 5. E 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
UNIT Name the different ways of representing a graph? a.adjacencymatrix b. Adjacency list
 UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
Big O Notation and Graphs. CMSC Week 9
 Big O Notation and Graphs CMSC 132 - Week 9 Graphs API A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of nodes, called vertices E is a collection of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices and edges can be
Big O Notation and Graphs CMSC 132 - Week 9 Graphs API A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of nodes, called vertices E is a collection of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices and edges can be
國立清華大學電機工程學系. Outline
 國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE Data Structure Chapter Graph (Part I) Outline The Graph Abstract Data Type Introduction Definitions Graph Representations Elementary Graph Operations Minimum Cost Spanning Trees ch.- River
國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE Data Structure Chapter Graph (Part I) Outline The Graph Abstract Data Type Introduction Definitions Graph Representations Elementary Graph Operations Minimum Cost Spanning Trees ch.- River
DIRECTED GRAPHS BBM 201 DATA STRUCTURES DEPT. OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton University. BBM DAA SRUCURES DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING DIRECED GRAPHS Directed Graphs Digraph
Acknowledgement: he course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton University. BBM DAA SRUCURES DEP. O COMPUER ENGINEERING DIRECED GRAPHS Directed Graphs Digraph
Chapter 9 STACK, QUEUE
 Chapter 9 STACK, QUEUE 1 LIFO: Last In, First Out. Stacks Restricted form of list: Insert and remove only at front of list. Notation: Insert: PUSH Remove: POP The accessible element is called TOP. Stack
Chapter 9 STACK, QUEUE 1 LIFO: Last In, First Out. Stacks Restricted form of list: Insert and remove only at front of list. Notation: Insert: PUSH Remove: POP The accessible element is called TOP. Stack
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II DIRECTED GRAPHS Graphs slides are modified from COS 126 slides of Dr. Robert Sedgewick. 1 Directed graphs Digraph Set of vertices connected pairwise by directed
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II DIRECTED GRAPHS Graphs slides are modified from COS 126 slides of Dr. Robert Sedgewick. 1 Directed graphs Digraph Set of vertices connected pairwise by directed
Jordan University of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science CS 211 Exam #1 (23/10/2010) -- Form A
 Jordan University of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science CS 211 Exam #1 (23/10/2010) -- Form A Name: ID#: Section #: Day & Time: Instructor: Answer all questions as indicated. Closed book/closed
Jordan University of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science CS 211 Exam #1 (23/10/2010) -- Form A Name: ID#: Section #: Day & Time: Instructor: Answer all questions as indicated. Closed book/closed
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS5-5S-6 Graph Traversals BFS & DFS David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 6-: Graph Traversals Visit every vertex, in an order defined by
Data Structures and Algorithms CS5-5S-6 Graph Traversals BFS & DFS David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 6-: Graph Traversals Visit every vertex, in an order defined by
CSC 344 Algorithms and Complexity
 S 44 lgorithms and omplexity Lecture #1 Graphs (Extended) What is a Graph? graph consists of a set of nodes (or vertices) and a set of arcs (or edges). Each arc in a graphs is specified by a pair of nodes.
S 44 lgorithms and omplexity Lecture #1 Graphs (Extended) What is a Graph? graph consists of a set of nodes (or vertices) and a set of arcs (or edges). Each arc in a graphs is specified by a pair of nodes.
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June DATA STRUCTURES (Com. to ECE, CSE, EIE, IT, ECC)
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June - 2016 PART A 1. a) Write a procedure for the Tower of Hanoi problem? b) What you mean by enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue? c)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June - 2016 PART A 1. a) Write a procedure for the Tower of Hanoi problem? b) What you mean by enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue? c)
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
DC104 DATA STRUCTURE JUNE Q.2 a. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what pointer type will you use?
 Q.2 a. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what pointer type will you use? The heterogeneous linked list contains different data types in its nodes and we need a link
Q.2 a. If you are using C language to implement the heterogeneous linked list, what pointer type will you use? The heterogeneous linked list contains different data types in its nodes and we need a link
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 NPTEL MOOC,JAN-FEB 0 Week, Module DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Depth first search (DFS) MADHAVAN MUKUND, CHENNAI MATHEMATICAL INSTITUTE http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan Depth first search Start from
NPTEL MOOC,JAN-FEB 0 Week, Module DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Depth first search (DFS) MADHAVAN MUKUND, CHENNAI MATHEMATICAL INSTITUTE http://www.cmi.ac.in/~madhavan Depth first search Start from
This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science.
 Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 24 Notes Search in Graphs
 Lecture 24 Notes Search in Graphs 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will discuss the
Lecture 24 Notes Search in Graphs 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will discuss the
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
Homework 6 Solutions CS330 Discrete Structures, Fall 2017
 Homework 6 Solutions CS330 Discrete Structures, Fall 2017 Instructor: Professor Edward Reingold TA: Jiahui Hou, Haohua Du Solutions 1. 10 pts) Algorithm 1 Basic Euler Circuit Algorithm. procedure Euler(G
Homework 6 Solutions CS330 Discrete Structures, Fall 2017 Instructor: Professor Edward Reingold TA: Jiahui Hou, Haohua Du Solutions 1. 10 pts) Algorithm 1 Basic Euler Circuit Algorithm. procedure Euler(G
Graph traversal is a generalization of tree traversal except we have to keep track of the visited vertices.
 Traversal Techniques for Graphs Graph traversal is a generalization of tree traversal except we have to keep track of the visited vertices. Applications: Strongly connected components, topological sorting,
Traversal Techniques for Graphs Graph traversal is a generalization of tree traversal except we have to keep track of the visited vertices. Applications: Strongly connected components, topological sorting,
GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms?
 GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and discrete math. Hundreds
GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and discrete math. Hundreds
BE ISE 3 rd Semester
 Scheme of valuvation 1 What is a Binary tree? State its properties? How it is represented using array and linked list, give example. binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most
Scheme of valuvation 1 What is a Binary tree? State its properties? How it is represented using array and linked list, give example. binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Breadth First Search. cse2011 section 13.3 of textbook
 Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph.
 Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph. Motivating example: In a video game, you are searching for a path from a point in a maze to the exit. The maze can be modeled
Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph. Motivating example: In a video game, you are searching for a path from a point in a maze to the exit. The maze can be modeled
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Thoughts on how search algorithms work
 Thoughts on how search algorithms work Search algorithms play a prominent role in seach engines, path finding, and even in AI such as AlphaGo. I self-studied two fundamental search algorithms, DFS and
Thoughts on how search algorithms work Search algorithms play a prominent role in seach engines, path finding, and even in AI such as AlphaGo. I self-studied two fundamental search algorithms, DFS and
Mystery Algorithm! ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v )
 Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory
 CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory Dustin Tseng Mike Li Wednesday January 16, 2006 Dustin Tseng Mike Li: CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science, Lecture
CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science Lecture 6: Introductory Graph Theory Dustin Tseng Mike Li Wednesday January 16, 2006 Dustin Tseng Mike Li: CS490: Problem Solving in Computer Science, Lecture
Graphs. Motivations: o Networks o Social networks o Program testing o Job Assignment Examples: o Code graph:
 Graphs Motivations: o Networks o Social networks o Program testing o Job Assignment Examples: o Code graph: S1: int x S2: If x > 0 then S3: X = x + 2; Else S4: X =x -1; End if S5: While x > 1 do S6: Print
Graphs Motivations: o Networks o Social networks o Program testing o Job Assignment Examples: o Code graph: S1: int x S2: If x > 0 then S3: X = x + 2; Else S4: X =x -1; End if S5: While x > 1 do S6: Print
0 0 1/20 1/20 1/20 1/20 1/20
 CS 6212 October 2018 Youssef Homework 3 Due Date: November 7, 2018 Problem 1: (15 points) Let a1< a2< a3< a4< a5< a6 be 6 numbers accessible with the following probabilities: p1 = 4/20, p2 = 2/20, p3 =
CS 6212 October 2018 Youssef Homework 3 Due Date: November 7, 2018 Problem 1: (15 points) Let a1< a2< a3< a4< a5< a6 be 6 numbers accessible with the following probabilities: p1 = 4/20, p2 = 2/20, p3 =
Agenda. The main body and cout. Fundamental data types. Declarations and definitions. Control structures
 The main body and cout Agenda 1 Fundamental data types Declarations and definitions Control structures References, pass-by-value vs pass-by-references The main body and cout 2 C++ IS AN OO EXTENSION OF
The main body and cout Agenda 1 Fundamental data types Declarations and definitions Control structures References, pass-by-value vs pass-by-references The main body and cout 2 C++ IS AN OO EXTENSION OF
Data Structures and Algorithms Key to Homework Assignment 8
 Data Structures and Algorithms Key to Homework Assignment 8. Apply the strong components algorithm to the digraph that has the following adjacency matrix: 0 4 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Data Structures and Algorithms Key to Homework Assignment 8. Apply the strong components algorithm to the digraph that has the following adjacency matrix: 0 4 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graph Representations Graph G = (V,E) Directed Undirected Adjacency Lists Adjacency Matrix Graph Representations Adjacency List: Undirected Memory: Adjacency: Graph
Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graph Representations Graph G = (V,E) Directed Undirected Adjacency Lists Adjacency Matrix Graph Representations Adjacency List: Undirected Memory: Adjacency: Graph
Linked List using a Sentinel
 Linked List using a Sentinel Linked List.h / Linked List.h Using a sentinel for search Created by Enoch Hwang on 2/1/10. Copyright 2010 La Sierra University. All rights reserved. / #include
Linked List using a Sentinel Linked List.h / Linked List.h Using a sentinel for search Created by Enoch Hwang on 2/1/10. Copyright 2010 La Sierra University. All rights reserved. / #include
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS
 Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
CSE030 Fall 2012 Final Exam Friday, December 14, PM
 CSE030 Fall 2012 Final Exam Friday, December 14, 2012 3-6PM Write your name here and at the top of each page! Name: Select your lab session: Tuesdays Thursdays Paper. If you have any questions or need
CSE030 Fall 2012 Final Exam Friday, December 14, 2012 3-6PM Write your name here and at the top of each page! Name: Select your lab session: Tuesdays Thursdays Paper. If you have any questions or need
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Example Final Questions Instructions
 Example Final Questions Instructions This exam paper contains a set of sample final exam questions. It is for practice purposes only. You ll most likely need longer than three hours to answer all the questions.
Example Final Questions Instructions This exam paper contains a set of sample final exam questions. It is for practice purposes only. You ll most likely need longer than three hours to answer all the questions.
I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of. I Formally: G =(V, E), where V is a set and E V V.
 Directed and Undirected Graphs Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Directed and Undirected Graphs Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 10. Depth-First Search and Topological Sorting
 CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 10 Depth-First Search and Topological Sorting In this lecture, we will analyse the running time of DFS and discuss a few applications. 10.1 A recursive implementation
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 10 Depth-First Search and Topological Sorting In this lecture, we will analyse the running time of DFS and discuss a few applications. 10.1 A recursive implementation
Graphs. Data Structures 1 Graphs
 Graphs Graph Applications Definitions Graph Representations(adjacency matrix/list) Graph ADT Graph Traversals: BFS, DFS Shortest Path Algorithms Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms Data Structures Graphs
Graphs Graph Applications Definitions Graph Representations(adjacency matrix/list) Graph ADT Graph Traversals: BFS, DFS Shortest Path Algorithms Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms Data Structures Graphs
! Vertex = species. ! Edge = from prey to predator.
 irected Graphs irected Graphs igraph. Set of objects with oriented pairwise connections. x. One-way street, hyperlink. Reference: Chapter 19, Algorithms in Java, 3 rd dition, Robert Sedgewick. Robert Sedgewick
irected Graphs irected Graphs igraph. Set of objects with oriented pairwise connections. x. One-way street, hyperlink. Reference: Chapter 19, Algorithms in Java, 3 rd dition, Robert Sedgewick. Robert Sedgewick
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
Graph Traversal CSCI Algorithms I. Andrew Rosenberg
 Graph Traversal CSCI 700 - Algorithms I Andrew Rosenberg Last Time Introduced Graphs Today Traversing a Graph A shortest path algorithm Example Graph We will use this graph as an example throughout today
Graph Traversal CSCI 700 - Algorithms I Andrew Rosenberg Last Time Introduced Graphs Today Traversing a Graph A shortest path algorithm Example Graph We will use this graph as an example throughout today
Part I: Short Answer (12 questions, 65 points total)
 CSE 143 Sp01 Final Exam Sample Solution page 1 of 14 Part I: Short Answer (12 questions, 65 points total) Answer all of the following questions. READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. Answer each question in the
CSE 143 Sp01 Final Exam Sample Solution page 1 of 14 Part I: Short Answer (12 questions, 65 points total) Answer all of the following questions. READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. Answer each question in the
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
Computer Programming
 Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session: Recap of Arrays and Simultaneous Equations (S31 S35) Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr.
Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session: Recap of Arrays and Simultaneous Equations (S31 S35) Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr.
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Chapter 9. Priority Queue
 Chapter 9 Priority Queues, Heaps, Graphs Spring 2015 1 Priority Queue Priority Queue An ADT in which only the item with the highest priority can be accessed 2Spring 2015 Priority Depends on the Application
Chapter 9 Priority Queues, Heaps, Graphs Spring 2015 1 Priority Queue Priority Queue An ADT in which only the item with the highest priority can be accessed 2Spring 2015 Priority Depends on the Application
Section 1: True / False (2 points each, 30 pts total)
 Section 1: True / False (2 points each, 30 pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
Section 1: True / False (2 points each, 30 pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
Basic Graph Definitions
 CMSC 341 Graphs Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices, V, and a finite set of edges, E. Each edge is a pair (v,w) where v, w V. V and E are sets, so each vertex
CMSC 341 Graphs Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices, V, and a finite set of edges, E. Each edge is a pair (v,w) where v, w V. V and E are sets, so each vertex
Graphs. Part I: Basic algorithms. Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College
 Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
! A data type for which: ! An ADT may be implemented using various. ! Examples:
 Stacks and Queues Unit 6 Chapter 19.1-2,4-5 CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman 1 Abstract Data Type A data type for which: - only the properties of the data and the operations to be performed on the data are
Stacks and Queues Unit 6 Chapter 19.1-2,4-5 CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman 1 Abstract Data Type A data type for which: - only the properties of the data and the operations to be performed on the data are
CS Data Structure Spring Answer Key- Assignment #10
 CS300-201 Data Structure Spring 2012 2013 Answer Key- Assignment #10 Due Sunday, April 28 th. Q1): Write the following classes: - Class Vertex int id; String name; Vertex (int id, String name)... - Class
CS300-201 Data Structure Spring 2012 2013 Answer Key- Assignment #10 Due Sunday, April 28 th. Q1): Write the following classes: - Class Vertex int id; String name; Vertex (int id, String name)... - Class
CS 2412 Data Structures. Chapter 9 Graphs
 CS 2412 Data Structures Chapter 9 Graphs Some concepts A graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of lines (edges, arcs). A directed graph, or digraph, is a graph in which each line has a direction.
CS 2412 Data Structures Chapter 9 Graphs Some concepts A graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of lines (edges, arcs). A directed graph, or digraph, is a graph in which each line has a direction.
Separate Compilation and Namespaces Week Fall. Computer Programming for Engineers
 Separate Compilation and Namespaces Week 07 Fall Computer Programming for Engineers Problem Multiplied palindrome number Multiplied palindrome number A number is called as a palindrome when you can read
Separate Compilation and Namespaces Week 07 Fall Computer Programming for Engineers Problem Multiplied palindrome number Multiplied palindrome number A number is called as a palindrome when you can read
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
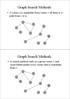 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Algorithms: Chapters Part 1: Introductory graph concepts
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Algorithms and Data Structures Graphs 3: Finding Connected Components Marius Kloft Content of this Lecture Finding Connected Components in Undirected Graphs Finding Strongly Connected Components in Directed
Algorithms and Data Structures Graphs 3: Finding Connected Components Marius Kloft Content of this Lecture Finding Connected Components in Undirected Graphs Finding Strongly Connected Components in Directed
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
To model real-world problems using graphs and explain the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem
 CHAPTER 24 Graphs and Applications Objectives To model real-world problems using graphs and explain the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem ( 24.1). To describe graph terminologies: vertices, edges, simple
CHAPTER 24 Graphs and Applications Objectives To model real-world problems using graphs and explain the Seven Bridges of Königsberg problem ( 24.1). To describe graph terminologies: vertices, edges, simple
Inf 2B: Graphs II - Applications of DFS
 Inf 2B: Graphs II - Applications of DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Reminder: Recursive DFS Algorithm dfs(g) 1. Initialise Boolean array visited by setting all entries
Inf 2B: Graphs II - Applications of DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Reminder: Recursive DFS Algorithm dfs(g) 1. Initialise Boolean array visited by setting all entries
ROOT: A node which doesn't have a parent. In the above tree. The Root is A.
 TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T 1, T 2...T k, each of whose roots are connected
TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T 1, T 2...T k, each of whose roots are connected
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Graphs II. Lecture 27. Prof.
 242 ata Structures and lgorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/242/ Graphs II Lecture 27 Prof. ric Polizzi Summary Previous Lecture omposed of vertices (nodes) and edges vertex or node edges
242 ata Structures and lgorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/242/ Graphs II Lecture 27 Prof. ric Polizzi Summary Previous Lecture omposed of vertices (nodes) and edges vertex or node edges
l Determine if a number is odd or even l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between a and z (inclusive)
 Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: l Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Final Exam Exercises Chapters 1-7 + 11 Write C++ code to: l Determine if a number is odd or even CS 2308 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman l Determine if a number/character is in a range - 1 to 10 (inclusive) - between
Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
UNIT 5 GRAPH. Application of Graph Structure in real world:- Graph Terminologies:
 UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
Review Questions for Final Exam
 CS 102 / ECE 206 Spring 11 Review Questions for Final Exam The following review questions are similar to the kinds of questions you will be expected to answer on the Final Exam, which will cover LCR, chs.
CS 102 / ECE 206 Spring 11 Review Questions for Final Exam The following review questions are similar to the kinds of questions you will be expected to answer on the Final Exam, which will cover LCR, chs.
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
[CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 9. Seungkyu Lee. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University
![[CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 9. Seungkyu Lee. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University [CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 9. Seungkyu Lee. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University](/thumbs/89/97777261.jpg) [CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 9 Seungkyu Lee Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University CHAPTER 9 Pointers #1~2 Pointer int main () { int a; int b; int c;
[CSE10200] Programming Basis ( 프로그래밍기초 ) Chapter 9 Seungkyu Lee Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering Kyung Hee University CHAPTER 9 Pointers #1~2 Pointer int main () { int a; int b; int c;
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 15. Dictionaries (1): A Key Table Class Prof. amr Goneid, AUC 1 Dictionaries(1): A Key Table Class Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 A Key Table
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 15. Dictionaries (1): A Key Table Class Prof. amr Goneid, AUC 1 Dictionaries(1): A Key Table Class Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 A Key Table
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
22.1 Representations of graphs
 22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
Announcements Problem Set 4 is out!
 CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
Data Structures Brett Bernstein
 Data Structures Brett Bernstein Final Review 1. Consider a binary tree of height k. (a) What is the maximum number of nodes? (b) What is the maximum number of leaves? (c) What is the minimum number of
Data Structures Brett Bernstein Final Review 1. Consider a binary tree of height k. (a) What is the maximum number of nodes? (b) What is the maximum number of leaves? (c) What is the minimum number of
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II. Shortest Paths
 CMSC 13: Object-Oriented Programming II Shortest Paths 1 Quiz 1 One advantage of adjacency list representation over adjacency matrix representation of a graph is that in adjacency list representation,
CMSC 13: Object-Oriented Programming II Shortest Paths 1 Quiz 1 One advantage of adjacency list representation over adjacency matrix representation of a graph is that in adjacency list representation,
Example Final Questions Instructions
 Example Final Questions Instructions This exam paper contains a set of sample final exam questions. It is for practice purposes only. You ll most likely need longer than three hours to answer all the questions.
Example Final Questions Instructions This exam paper contains a set of sample final exam questions. It is for practice purposes only. You ll most likely need longer than three hours to answer all the questions.
Lecture Notes. char myarray [ ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; The memory diagram associated with the array can be drawn like this
![Lecture Notes. char myarray [ ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; The memory diagram associated with the array can be drawn like this Lecture Notes. char myarray [ ] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } ; The memory diagram associated with the array can be drawn like this](/thumbs/80/81612702.jpg) Lecture Notes Array Review An array in C++ is a contiguous block of memory. Since a char is 1 byte, then an array of 5 chars is 5 bytes. For example, if you execute the following C++ code you will allocate
Lecture Notes Array Review An array in C++ is a contiguous block of memory. Since a char is 1 byte, then an array of 5 chars is 5 bytes. For example, if you execute the following C++ code you will allocate
A6-R3: DATA STRUCTURE THROUGH C LANGUAGE
 A6-R3: DATA STRUCTURE THROUGH C LANGUAGE NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF
A6-R3: DATA STRUCTURE THROUGH C LANGUAGE NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF
