Formal Methods. Seminar 2
|
|
|
- Hector Hall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Formal Methods Seminar 2 1
2 First Part of the Programming Assignment Design in Ocaml the Abstract Syntax Tree for a small object-oriented language called CoreJava. The syntax of CoreJava is described in the following slides. 2
3 A CoreJava program P consists of a list of class declarations as follows: P ::= def+ def+ ::= def def1; def2;...;defn The program contains at least one class declaration. The last class declaration must contain a method called main which is the starting execution point for the CoreJava program. 3
4 A class declaration def consists of the following: def ::= class cn1 extends cn2 { field* # meth*} where cn1 is the current class name and cn2 is the name of the parent class The body of the class consists of a list of fields declarations followed by a list of methods declarations. The fields list is separated by # from the methods list. The fields list is either empty or field+ ::= field1;field2;...;fieldn. The methods list is either empty or meth+ ::= meth1;meth2;...;methn. 4
5 A field declaration consists of the following: field ::= typ fn where typ is the type of the field and fn is the name of the field A type typ can be either a primitive type, or a class name or the bottom (the type of null). typ ::= prim cn _ _ prim ::= int float bool void 5
6 A method declaration consists of the following: meth ::= typ1 mn((typ pn)*) {e} where typ1 is the type of the method result, mn is the method name, (typ pn)* is the list of method parameters. The list of method parameters can be either empty or (typ pn)+ ::= typ1 pn1, typ2 pn2,...,typn pnn The body of the method is given by the expression e. 6
7 An expression is defined as follows: e ::= null (null value) kint (a constant value) kfloat true false () ( a value of type void) v (a variable name) v.f ( a field f of an object denoted by v) 7
8 An expression is defined as follows: e ::=... v=e (variable assignment) v.f=e (object field assignment) { (typ v) e1} (local variable declaration such that v has type typ and its scope is the expression e1) e1;e2 ( a sequence such that e2 is executed only after e1 is executed) if v then {e1} else {e2} (conditional where the condition is a variable) 8
9 An expression is defined as follows: e ::=... e1 opint e2 (arithmetic expressions for ints where opint ::= + - * /) e1 opfloat e2 (arithmetic expressions for floats where opfloat ::= *. /.) e1 && e2 (logical expressions) e1 e2!e (negation) 9
10 An expression is defined as follows: e ::=... new cn(v*) (creation of an instance object of the class cn. The fields of the new object are initialized by the list of variables v*. The fields are intialized in the order defined in the declaration of class cn) v.mn(v*) (method call where v is the method receiver and the list of variables v* are the current arguments initializing the method parameters) while v {e} (loop where the condition is a variable) 10
11 An expression can also be e ::=... e1 opcmp e2 (relational expressions where opcm ::= < <= ==!= > >=) (cn) v (cast expression) v instanceof cn 11
12 Discussion on the Ocaml implementation The following slides show how you can represent the Abstract Syntax Tree of CoreJava in Ocaml. 12
13 A program can be represented as a dictionary of classes (association list or you may want to consult Chapter 13 from realworldocaml.org): type progr= (string*classdecl) list type classdecl = (string*string*flddecllist*mthdecllist) type flddecllist = flddecl list type flddecl = typ * string type mthdecllist = mthdecl list type mthdecl =(typ*string*fprmlist*blkexp) type fprmlist = fprm list type fprm = (typ*string) 13
14 type typ = Tprim of tprim Tclass of string Tbot type tprim = Tint Tfloat Tbool Tvoid type blkexp = Bvar of typ*string*exp Bnvar of exp type val = Vnull Int of int Float of float Bool of bool Vvoid type exp = Value of val Var of string Vfld of string*string...(see next slide) 14
15 type exp =... AsgnV of string*exp AsgnF of string*string*exp Blk of blkexp Seq of exp*exp If of string*blkexp*blkexp AddInt of exp*exp MulInt of exp*exp... (please continue yourself the first assignment) 15
(Not Quite) Minijava
 (Not Quite) Minijava CMCS22620, Spring 2004 April 5, 2004 1 Syntax program mainclass classdecl mainclass class identifier { public static void main ( String [] identifier ) block } classdecl class identifier
(Not Quite) Minijava CMCS22620, Spring 2004 April 5, 2004 1 Syntax program mainclass classdecl mainclass class identifier { public static void main ( String [] identifier ) block } classdecl class identifier
Lecture 4 Abstract syntax
 Lecture 4 Abstract syntax Abstract syntax examples for various languages: A simple expression language OCaml MiniJava (a subset of Java) CS 421 Class 4, 1/26/12 1 Ex: Abstract syntax of simple expressions
Lecture 4 Abstract syntax Abstract syntax examples for various languages: A simple expression language OCaml MiniJava (a subset of Java) CS 421 Class 4, 1/26/12 1 Ex: Abstract syntax of simple expressions
Static Checking and Type Systems
 1 Static Checking and Type Systems Chapter 6 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2009 2 The Structure of our Compiler Revisited Character stream Lexical
1 Static Checking and Type Systems Chapter 6 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2009 2 The Structure of our Compiler Revisited Character stream Lexical
Homework 3 COSE212, Fall 2018
 Homework 3 COSE212, Fall 2018 Hakjoo Oh Due: 10/28, 24:00 Problem 1 (100pts) Let us design and implement a programming language called ML. ML is a small yet Turing-complete functional language that supports
Homework 3 COSE212, Fall 2018 Hakjoo Oh Due: 10/28, 24:00 Problem 1 (100pts) Let us design and implement a programming language called ML. ML is a small yet Turing-complete functional language that supports
Project 2 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, Mar 7, 2012
 Project 2 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, Mar 7, 2012 Updates Feb 29. Added reflexivity for is subtype. Clarified lca class and castable behavior when given the same class/type. Feb 27. Typo fix (replaced lub with
Project 2 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, Mar 7, 2012 Updates Feb 29. Added reflexivity for is subtype. Clarified lca class and castable behavior when given the same class/type. Feb 27. Typo fix (replaced lub with
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
CS1622. Semantic Analysis. The Compiler So Far. Lecture 15 Semantic Analysis. How to build symbol tables How to use them to find
 CS1622 Lecture 15 Semantic Analysis CS 1622 Lecture 15 1 Semantic Analysis How to build symbol tables How to use them to find multiply-declared and undeclared variables. How to perform type checking CS
CS1622 Lecture 15 Semantic Analysis CS 1622 Lecture 15 1 Semantic Analysis How to build symbol tables How to use them to find multiply-declared and undeclared variables. How to perform type checking CS
Project 6 Due 11:59:59pm Thu, Dec 10, 2015
 Project 6 Due 11:59:59pm Thu, Dec 10, 2015 Updates None yet. Introduction In this project, you will add a static type checking system to the Rube programming language. Recall the formal syntax for Rube
Project 6 Due 11:59:59pm Thu, Dec 10, 2015 Updates None yet. Introduction In this project, you will add a static type checking system to the Rube programming language. Recall the formal syntax for Rube
CVO103: Programming Languages. Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions
 CVO103: Programming Languages Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions Hakjoo Oh 2018 Spring Hakjoo Oh CVO103 2018 Spring, Lecture 5 April 3, 2018 1 / 23 Plan Part 1 (Preliminaries):
CVO103: Programming Languages Lecture 5 Design and Implementation of PLs (1) Expressions Hakjoo Oh 2018 Spring Hakjoo Oh CVO103 2018 Spring, Lecture 5 April 3, 2018 1 / 23 Plan Part 1 (Preliminaries):
OCaml. ML Flow. Complex types: Lists. Complex types: Lists. The PL for the discerning hacker. All elements must have same type.
 OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
OCaml The PL for the discerning hacker. ML Flow Expressions (Syntax) Compile-time Static 1. Enter expression 2. ML infers a type Exec-time Dynamic Types 3. ML crunches expression down to a value 4. Value
COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification
 COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification Vincent Foley February 26, 2015 1 Declarations Declarations are the primary means of introducing new identifiers in the symbol table. In Go, top-level declarations
COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification Vincent Foley February 26, 2015 1 Declarations Declarations are the primary means of introducing new identifiers in the symbol table. In Go, top-level declarations
COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification
 COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification Vincent Foley March 5, 2017 1 Introduction This document presents the typing rules for all the language constructs (i.e. declarations, statements, expressions)
COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification Vincent Foley March 5, 2017 1 Introduction This document presents the typing rules for all the language constructs (i.e. declarations, statements, expressions)
Midterm 1. CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Spring Instructions Total 100. Name: March 14, 2012
 Name: Midterm 1 CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Spring 2012 March 14, 2012 Instructions This exam contains 8 pages, including this one. Make sure you have all the pages. Write your name on the top of
Name: Midterm 1 CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Spring 2012 March 14, 2012 Instructions This exam contains 8 pages, including this one. Make sure you have all the pages. Write your name on the top of
Motivation was to facilitate development of systems software, especially OS development.
 A History Lesson C Basics 1 Development of language by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs culminated in the C language in 1972. Motivation was to facilitate development of systems software, especially OS development.
A History Lesson C Basics 1 Development of language by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs culminated in the C language in 1972. Motivation was to facilitate development of systems software, especially OS development.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Operational Semantics CMSC 330 Summer 2018 1 Formal Semantics of a Prog. Lang. Mathematical description of the meaning of programs written in that language
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Operational Semantics CMSC 330 Summer 2018 1 Formal Semantics of a Prog. Lang. Mathematical description of the meaning of programs written in that language
Key Differences Between Python and Java
 Python Python supports many (but not all) aspects of object-oriented programming; but it is possible to write a Python program without making any use of OO concepts. Python is designed to be used interpretively.
Python Python supports many (but not all) aspects of object-oriented programming; but it is possible to write a Python program without making any use of OO concepts. Python is designed to be used interpretively.
Motivation was to facilitate development of systems software, especially OS development.
 A History Lesson C Basics 1 Development of language by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs culminated in the C language in 1972. Motivation was to facilitate development of systems software, especially OS development.
A History Lesson C Basics 1 Development of language by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs culminated in the C language in 1972. Motivation was to facilitate development of systems software, especially OS development.
Decaf Language Reference Manual
 Decaf Language Reference Manual C. R. Ramakrishnan Department of Computer Science SUNY at Stony Brook Stony Brook, NY 11794-4400 cram@cs.stonybrook.edu February 12, 2012 Decaf is a small object oriented
Decaf Language Reference Manual C. R. Ramakrishnan Department of Computer Science SUNY at Stony Brook Stony Brook, NY 11794-4400 cram@cs.stonybrook.edu February 12, 2012 Decaf is a small object oriented
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Functional Programming with Lists
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as
COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification
 COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification Vincent Foley April 8, 2018 1 Introduction This document presents the typing rules for all the language constructs (i.e. declarations, statements, expressions)
COMP520 - GoLite Type Checking Specification Vincent Foley April 8, 2018 1 Introduction This document presents the typing rules for all the language constructs (i.e. declarations, statements, expressions)
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Formal Semantics of a Prog. Lang. Specifying Syntax, Semantics
 Recall Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Source Scanner Parser Static Analyzer Operational Semantics Intermediate Representation Front End Back End
Recall Architecture of Compilers, Interpreters CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Source Scanner Parser Static Analyzer Operational Semantics Intermediate Representation Front End Back End
Mid-Term 2 Grades
 Mid-Term 2 Grades 100 46 1 HW 9 Homework 9, in untyped class interpreter: Add instanceof Restrict field access to local class Implement overloading (based on argument count) Due date is the same as for
Mid-Term 2 Grades 100 46 1 HW 9 Homework 9, in untyped class interpreter: Add instanceof Restrict field access to local class Implement overloading (based on argument count) Due date is the same as for
Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Tuesday, April 25, 2017
 Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Tuesday, April 25, 2017 Introduction In this project, you will write a compiler for a programming language called Rube, which is a small objectoriented programming language with
Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Tuesday, April 25, 2017 Introduction In this project, you will write a compiler for a programming language called Rube, which is a small objectoriented programming language with
Introduction to Programming (Java) 2/12
 Introduction to Programming (Java) 2/12 Michal Krátký Department of Computer Science Technical University of Ostrava Introduction to Programming (Java) 2008/2009 c 2006 2008 Michal Krátký Introduction
Introduction to Programming (Java) 2/12 Michal Krátký Department of Computer Science Technical University of Ostrava Introduction to Programming (Java) 2008/2009 c 2006 2008 Michal Krátký Introduction
Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421)
 Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421) #3: Closures, evaluation of function applications, order of evaluation #4: Evaluation and Application rules using symbolic rewriting Madhusudan Parthasarathy
Programming Languages and Compilers (CS 421) #3: Closures, evaluation of function applications, order of evaluation #4: Evaluation and Application rules using symbolic rewriting Madhusudan Parthasarathy
JavaScript Syntax. Web Authoring and Design. Benjamin Kenwright
 JavaScript Syntax Web Authoring and Design Benjamin Kenwright Milestone Dates Demonstrate Coursework 1 Friday (15 th December) 10 Minutes Each Coursework 2 (Group Project) Website (XMAS) Javascript Game
JavaScript Syntax Web Authoring and Design Benjamin Kenwright Milestone Dates Demonstrate Coursework 1 Friday (15 th December) 10 Minutes Each Coursework 2 (Group Project) Website (XMAS) Javascript Game
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Functional Programming with Lists
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as a linked data structure
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with Lists 1 Lists in OCaml The basic data structure in OCaml Lists can be of arbitrary length Implemented as a linked data structure
Standard Version of Starting Out with C++, 4th Edition. Chapter 6 Functions. Copyright 2003 Scott/Jones Publishing
 Standard Version of Starting Out with C++, 4th Edition Chapter 6 Functions Copyright 2003 Scott/Jones Publishing Topics 6.1 Modular Programming 6.2 Defining and Calling Functions 6.3 Function Prototypes
Standard Version of Starting Out with C++, 4th Edition Chapter 6 Functions Copyright 2003 Scott/Jones Publishing Topics 6.1 Modular Programming 6.2 Defining and Calling Functions 6.3 Function Prototypes
Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, Nov 25, 2015 (no late submissions)
 Introduction Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, Nov 25, 2015 (no late submissions) In this project, you will write a compiler for a programming language called Rube, which is a small objectoriented programming
Introduction Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, Nov 25, 2015 (no late submissions) In this project, you will write a compiler for a programming language called Rube, which is a small objectoriented programming
CA4003 Compiler Construction Assignment Language Definition
 CA4003 Compiler Construction Assignment Language Definition David Sinclair 2017-2018 1 Overview The language is not case sensitive. A nonterminal, X, is represented by enclosing it in angle brackets, e.g.
CA4003 Compiler Construction Assignment Language Definition David Sinclair 2017-2018 1 Overview The language is not case sensitive. A nonterminal, X, is represented by enclosing it in angle brackets, e.g.
CS4120/4121/5120/5121 Spring 2018 Xi Type System Specification Cornell University Version of February 18, 2018
 CS4120/4121/5120/5121 Spring 2018 Xi Type System Specification Cornell University Version of February 18, 2018 0 Changes 2/16: Added typing rule for empty blocks 1 Types The Xi type system uses a somewhat
CS4120/4121/5120/5121 Spring 2018 Xi Type System Specification Cornell University Version of February 18, 2018 0 Changes 2/16: Added typing rule for empty blocks 1 Types The Xi type system uses a somewhat
Comp 311: Sample Midterm Examination
 Comp 311: Sample Midterm Examination October 29, 2007 Name: Id #: Instructions 1. The examination is closed book. If you forget the name for a Scheme operation, make up a name for it and write a brief
Comp 311: Sample Midterm Examination October 29, 2007 Name: Id #: Instructions 1. The examination is closed book. If you forget the name for a Scheme operation, make up a name for it and write a brief
Outline. More optimizations for our interpreter. Types for objects
 Outline More optimizations for our interpreter Types for objects Optimization Eliminate tree walks: object creation, method calls fish initialize get_ grow eat colorfish color set_color get_color pickyfish
Outline More optimizations for our interpreter Types for objects Optimization Eliminate tree walks: object creation, method calls fish initialize get_ grow eat colorfish color set_color get_color pickyfish
Computer Science II (20082) Week 1: Review and Inheritance
 Computer Science II 4003-232-08 (20082) Week 1: Review and Inheritance Richard Zanibbi Rochester Institute of Technology Review of CS-I Syntax and Semantics of Formal (e.g. Programming) Languages Syntax
Computer Science II 4003-232-08 (20082) Week 1: Review and Inheritance Richard Zanibbi Rochester Institute of Technology Review of CS-I Syntax and Semantics of Formal (e.g. Programming) Languages Syntax
Functional Programming. Pure Functional Programming
 Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
The Substitution Model. Nate Foster Spring 2018
 The Substitution Model Nate Foster Spring 2018 Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language abstract syntax tree (AST) evaluation based on single steps parser and lexer (in lab)
The Substitution Model Nate Foster Spring 2018 Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language abstract syntax tree (AST) evaluation based on single steps parser and lexer (in lab)
Begin at the beginning
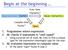 Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Begin at the beginning Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set of
Recap. Recap. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions. If-then-else expressions
 Recap Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types (Semantics) Recap Integers: +,-,* floats: +,-,* Booleans: =,
Recap Epressions (Synta) Compile-time Static Eec-time Dynamic Types (Semantics) Recap Integers: +,-,* floats: +,-,* Booleans: =,
Scheme in Scheme: The Metacircular Evaluator Eval and Apply
 Scheme in Scheme: The Metacircular Evaluator Eval and Apply CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Brandeis University Spring Term, 2015 The metacircular evaluator is A rendition of Scheme,
Scheme in Scheme: The Metacircular Evaluator Eval and Apply CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Brandeis University Spring Term, 2015 The metacircular evaluator is A rendition of Scheme,
Module 8: Local and functional abstraction
 Module 8: Local and functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18); Sections 19-23. We will cover material on functional abstraction in a somewhat different order than the text. We will
Module 8: Local and functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18); Sections 19-23. We will cover material on functional abstraction in a somewhat different order than the text. We will
egrapher Language Reference Manual
 egrapher Language Reference Manual Long Long: ll3078@columbia.edu Xinli Jia: xj2191@columbia.edu Jiefu Ying: jy2799@columbia.edu Linnan Wang: lw2645@columbia.edu Darren Chen: dsc2155@columbia.edu 1. Introduction
egrapher Language Reference Manual Long Long: ll3078@columbia.edu Xinli Jia: xj2191@columbia.edu Jiefu Ying: jy2799@columbia.edu Linnan Wang: lw2645@columbia.edu Darren Chen: dsc2155@columbia.edu 1. Introduction
Principles of Programming Languages
 Principles of Programming Languages Lesson 14 Type Checking Collaboration and Management Dana Fisman www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172 1 Type Checking We return to the issue of type safety we discussed informally,
Principles of Programming Languages Lesson 14 Type Checking Collaboration and Management Dana Fisman www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172 1 Type Checking We return to the issue of type safety we discussed informally,
Fall Lecture 3 September 4. Stephen Brookes
 15-150 Fall 2018 Lecture 3 September 4 Stephen Brookes Today A brief remark about equality types Using patterns Specifying what a function does equality in ML e1 = e2 Only for expressions whose type is
15-150 Fall 2018 Lecture 3 September 4 Stephen Brookes Today A brief remark about equality types Using patterns Specifying what a function does equality in ML e1 = e2 Only for expressions whose type is
CS558 Programming Languages
 CS558 Programming Languages Winter 2018 Lecture 7b Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2018 Dynamic Type Checking Static type checking offers the great advantage of catching errors early And
CS558 Programming Languages Winter 2018 Lecture 7b Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2018 Dynamic Type Checking Static type checking offers the great advantage of catching errors early And
A Third Look At ML. Chapter Nine Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1
 A Third Look At ML Chapter Nine Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline More pattern matching Function values and anonymous functions Higher-order functions and currying Predefined higher-order
A Third Look At ML Chapter Nine Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline More pattern matching Function values and anonymous functions Higher-order functions and currying Predefined higher-order
The SPL Programming Language Reference Manual
 The SPL Programming Language Reference Manual Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington Arlington, TX 76019 fegaras@cse.uta.edu February 27, 2018 1 Introduction The SPL language is a Small Programming
The SPL Programming Language Reference Manual Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington Arlington, TX 76019 fegaras@cse.uta.edu February 27, 2018 1 Introduction The SPL language is a Small Programming
Operators. Java operators are classified into three categories:
 Operators Operators are symbols that perform arithmetic and logical operations on operands and provide a meaningful result. Operands are data values (variables or constants) which are involved in operations.
Operators Operators are symbols that perform arithmetic and logical operations on operands and provide a meaningful result. Operands are data values (variables or constants) which are involved in operations.
Programming Languages
 CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
CSE 130: Fall 2009 Programming Languages Lecture 2: A Crash Course in ML News On webpage: Suggested HW #1 PA #1 (due next Fri 10/9) Technical issues installing Ocaml - should be resolved soon! Ranjit Jhala
Dialects of ML. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Dialects of ML (cont.) Features of ML. Functional Languages. Features of ML (cont.
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 1 Functional Programming Dialects of ML ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh,1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml 1 Functional Programming Dialects of ML ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh,1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
CITS3211 FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING. 13. Interpretation
 CITS3211 FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING 13. Interpretation Summary: This lecture discusses the construction of a simple interpreter for Haskell. R.L. While, 1997 2002, R. Davies 2003 7 Interpretation The simplest
CITS3211 FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING 13. Interpretation Summary: This lecture discusses the construction of a simple interpreter for Haskell. R.L. While, 1997 2002, R. Davies 2003 7 Interpretation The simplest
The Substitution Model
 The Substitution Model Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Substitute by The Who Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language abstract syntax tree (AST) evaluation based on
The Substitution Model Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Substitute by The Who Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language abstract syntax tree (AST) evaluation based on
The Environment Model
 The Environment Model Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Selections from Doctor Who soundtracks by Murray Gold Review Previously in 3110: Interpreters: ASTs, evaluation, parsing Formal syntax: BNF
The Environment Model Prof. Clarkson Fall 2017 Today s music: Selections from Doctor Who soundtracks by Murray Gold Review Previously in 3110: Interpreters: ASTs, evaluation, parsing Formal syntax: BNF
Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward. 2. Rewind. 3. Slow motion. Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml. Go over the pieces individually
 Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Rewind 3. Slow motion Go over the pieces individually History, Variants Meta Language Designed by Robin Milner @ Edinburgh Language
Plan (next 4 weeks) 1. Fast forward Rapid introduction to what s in OCaml 2. Rewind 3. Slow motion Go over the pieces individually History, Variants Meta Language Designed by Robin Milner @ Edinburgh Language
CS558 Programming Languages
 CS558 Programming Languages Fall 2017 Lecture 7b Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2017 Type Inference Some statically typed languages, like ML (and to a lesser extent Scala), offer alternative
CS558 Programming Languages Fall 2017 Lecture 7b Andrew Tolmach Portland State University 1994-2017 Type Inference Some statically typed languages, like ML (and to a lesser extent Scala), offer alternative
Functions. Arizona State University 1
 Functions CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 6 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Functions CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 6 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State University
Study Guide for Test 2
 Study Guide for Test 2 Topics: decisions, loops, arrays, c-strings, linux Material Selected from: Chapters 4, 5, 6, 7, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4 Examples 14 33 Assignments 4 8 Any syntax errors are unintentional
Study Guide for Test 2 Topics: decisions, loops, arrays, c-strings, linux Material Selected from: Chapters 4, 5, 6, 7, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4 Examples 14 33 Assignments 4 8 Any syntax errors are unintentional
Decaf Language Reference
 Decaf Language Reference Mike Lam, James Madison University Fall 2016 1 Introduction Decaf is an imperative language similar to Java or C, but is greatly simplified compared to those languages. It will
Decaf Language Reference Mike Lam, James Madison University Fall 2016 1 Introduction Decaf is an imperative language similar to Java or C, but is greatly simplified compared to those languages. It will
FRAC: Language Reference Manual
 FRAC: Language Reference Manual Justin Chiang jc4127 Kunal Kamath kak2211 Calvin Li ctl2124 Anne Zhang az2350 1. Introduction FRAC is a domain-specific programming language that enables the programmer
FRAC: Language Reference Manual Justin Chiang jc4127 Kunal Kamath kak2211 Calvin Li ctl2124 Anne Zhang az2350 1. Introduction FRAC is a domain-specific programming language that enables the programmer
Types, Variables, and Constants
 , Variables, and Constants What is a Type The space in which a value is defined Space All possible allowed values All defined operations Integer Space whole numbers +, -, x No divide 2 tj Why Types No
, Variables, and Constants What is a Type The space in which a value is defined Space All possible allowed values All defined operations Integer Space whole numbers +, -, x No divide 2 tj Why Types No
Background. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Useful Information on OCaml language. Dialects of ML. ML (Meta Language) Standard ML
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with OCaml 1 Background ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh, 1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Functional Programming with OCaml 1 Background ML (Meta Language) Univ. of Edinburgh, 1973 Part of a theorem proving system LCF The Logic of Computable Functions
Object oriented programming. Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: Ch: 3
 Object oriented programming Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: http://www.masses.ir/lectures/oops2017sut Ch: 3 1 In this slide We follow: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Trail: Learning
Object oriented programming Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: http://www.masses.ir/lectures/oops2017sut Ch: 3 1 In this slide We follow: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Trail: Learning
Hoare Logic and Model Checking
 Hoare Logic and Model Checking Kasper Svendsen University of Cambridge CST Part II 2016/17 Acknowledgement: slides heavily based on previous versions by Mike Gordon and Alan Mycroft Pointers Pointers and
Hoare Logic and Model Checking Kasper Svendsen University of Cambridge CST Part II 2016/17 Acknowledgement: slides heavily based on previous versions by Mike Gordon and Alan Mycroft Pointers Pointers and
Lecture 3: Expressions
 CS 7400 September 23 30, 2009 Dr. Wand Readings: EOPL3, Secs. 3.1 3.5 Lecture 3: Expressions Key Concepts: syntax and semantics expressed and denoted values expressions environment specifying the behavior
CS 7400 September 23 30, 2009 Dr. Wand Readings: EOPL3, Secs. 3.1 3.5 Lecture 3: Expressions Key Concepts: syntax and semantics expressed and denoted values expressions environment specifying the behavior
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Lets, Tuples, Records
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lets, Tuples, Records CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Let Expressions Enable binding variables in other expressions These are different from the let definitions we
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Lets, Tuples, Records CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 Let Expressions Enable binding variables in other expressions These are different from the let definitions we
InterprocStack analyzer for recursive programs with finite-type and numerical variables
 InterprocStack analyzer for recursive programs with finite-type and numerical variables Bertrand Jeannet Contents 1 Invoking InterprocStack 1 2 The Simple language 2 2.1 Syntax and informal semantics.........................
InterprocStack analyzer for recursive programs with finite-type and numerical variables Bertrand Jeannet Contents 1 Invoking InterprocStack 1 2 The Simple language 2 2.1 Syntax and informal semantics.........................
The Pyth Language. Administrivia
 Administrivia The Pyth Language Lecture 5 Please make sure you have registered your team, created SSH keys as indicated on the admin page, and also have electronically registered with us as well. Prof.
Administrivia The Pyth Language Lecture 5 Please make sure you have registered your team, created SSH keys as indicated on the admin page, and also have electronically registered with us as well. Prof.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. OCaml Imperative Programming
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory
The Design of Core C++ (Notes)
 The Design of Core C++ (Notes) Uday Reddy May 13, 1994 This note is to define a small formal language called Core C++ which reflects the essential structure of C++. As the name implies, the design only
The Design of Core C++ (Notes) Uday Reddy May 13, 1994 This note is to define a small formal language called Core C++ which reflects the essential structure of C++. As the name implies, the design only
The Warhol Language Reference Manual
 The Warhol Language Reference Manual Martina Atabong maa2247 Charvinia Neblett cdn2118 Samuel Nnodim son2105 Catherine Wes ciw2109 Sarina Xie sx2166 Introduction Warhol is a functional and imperative programming
The Warhol Language Reference Manual Martina Atabong maa2247 Charvinia Neblett cdn2118 Samuel Nnodim son2105 Catherine Wes ciw2109 Sarina Xie sx2166 Introduction Warhol is a functional and imperative programming
The Environment Model. Nate Foster Spring 2018
 The Environment Model Nate Foster Spring 2018 Review Previously in 3110: Interpreters: ASTs, evaluation, parsing Formal syntax: BNF Formal semantics: dynamic: small-step substitution model static semantics
The Environment Model Nate Foster Spring 2018 Review Previously in 3110: Interpreters: ASTs, evaluation, parsing Formal syntax: BNF Formal semantics: dynamic: small-step substitution model static semantics
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
CSE 130 : Winter 2009 Programming Languages News PA 2 out, and due Mon 1/26 5pm Lecture 5: Functions and Datatypes t UC San Diego Recap: Environments Phone book Variables = names Values = phone number
Formal Semantics. Prof. Clarkson Fall Today s music: Down to Earth by Peter Gabriel from the WALL-E soundtrack
 Formal Semantics Prof. Clarkson Fall 2015 Today s music: Down to Earth by Peter Gabriel from the WALL-E soundtrack Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language: abstract syntax
Formal Semantics Prof. Clarkson Fall 2015 Today s music: Down to Earth by Peter Gabriel from the WALL-E soundtrack Review Previously in 3110: simple interpreter for expression language: abstract syntax
By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program
 1 By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program variables. Apply C++ syntax rules to declare variables, initialize
1 By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program variables. Apply C++ syntax rules to declare variables, initialize
COMP 250: Java Programming I. Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette
 COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
COMP 250: Java Programming I Carlos G. Oliver, Jérôme Waldispühl January 17-18, 2018 Slides adapted from M. Blanchette Variables and types [Downey Ch 2] Variable: temporary storage location in memory.
Lecture 09: Data Abstraction ++ Parsing is the process of translating a sequence of characters (a string) into an abstract syntax tree.
 Lecture 09: Data Abstraction ++ Parsing Parsing is the process of translating a sequence of characters (a string) into an abstract syntax tree. program text Parser AST Processor Compilers (and some interpreters)
Lecture 09: Data Abstraction ++ Parsing Parsing is the process of translating a sequence of characters (a string) into an abstract syntax tree. program text Parser AST Processor Compilers (and some interpreters)
CSC Web Programming. Introduction to JavaScript
 CSC 242 - Web Programming Introduction to JavaScript JavaScript JavaScript is a client-side scripting language the code is executed by the web browser JavaScript is an embedded language it relies on its
CSC 242 - Web Programming Introduction to JavaScript JavaScript JavaScript is a client-side scripting language the code is executed by the web browser JavaScript is an embedded language it relies on its
SEMANTIC ANALYSIS TYPES AND DECLARATIONS
 SEMANTIC ANALYSIS CS 403: Type Checking Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2015 Parsing only verifies that the program consists of tokens arranged in a syntactically valid combination now we move to check whether
SEMANTIC ANALYSIS CS 403: Type Checking Stefan D. Bruda Winter 2015 Parsing only verifies that the program consists of tokens arranged in a syntactically valid combination now we move to check whether
PostgreSQL: Decoding Partition
 PostgreSQL: Decoding Partition Beena Emerson February 14, 2019 1 INTRODUCTION 2 What is Partitioning? Why partition? When to Partition? What is Partitioning? Subdividing a database table into smaller parts.
PostgreSQL: Decoding Partition Beena Emerson February 14, 2019 1 INTRODUCTION 2 What is Partitioning? Why partition? When to Partition? What is Partitioning? Subdividing a database table into smaller parts.
Case Study: Undefined Variables
 Case Study: Undefined Variables CS 5010 Program Design Paradigms Bootcamp Lesson 7.4 Mitchell Wand, 2012-2017 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Case Study: Undefined Variables CS 5010 Program Design Paradigms Bootcamp Lesson 7.4 Mitchell Wand, 2012-2017 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Outline. What is semantics? Denotational semantics. Semantics of naming. What is semantics? 2 / 21
 Semantics 1 / 21 Outline What is semantics? Denotational semantics Semantics of naming What is semantics? 2 / 21 What is the meaning of a program? Recall: aspects of a language syntax: the structure of
Semantics 1 / 21 Outline What is semantics? Denotational semantics Semantics of naming What is semantics? 2 / 21 What is the meaning of a program? Recall: aspects of a language syntax: the structure of
Variables. Substitution
 Variables Elements of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Variables, binding and substitution James Cheney University of Edinburgh October 6, 2015 A variable is a symbol that can stand for another expression.
Variables Elements of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Variables, binding and substitution James Cheney University of Edinburgh October 6, 2015 A variable is a symbol that can stand for another expression.
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 3 September 18, 2017 1 / 44 Why learn ML? Learning ML is a good way of
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 3 Functional Programming in OCaml Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 3 September 18, 2017 1 / 44 Why learn ML? Learning ML is a good way of
Recap: Functions as first-class values
 Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values, bindings What are the benefits? Parameterized, similar functions (e.g. Testers) Creating, (Returning) Functions Iterator, Accumul, Reuse
Recap: Functions as first-class values Arguments, return values, bindings What are the benefits? Parameterized, similar functions (e.g. Testers) Creating, (Returning) Functions Iterator, Accumul, Reuse
Introduction to Programming (Java) 4/12
 Introduction to Programming (Java) 4/12 Michal Krátký Department of Computer Science Technical University of Ostrava Introduction to Programming (Java) 2008/2009 c 2006 2008 Michal Krátký Introduction
Introduction to Programming (Java) 4/12 Michal Krátký Department of Computer Science Technical University of Ostrava Introduction to Programming (Java) 2008/2009 c 2006 2008 Michal Krátký Introduction
CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages
![CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages](/thumbs/85/92581372.jpg) CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages Introduction to OCaml (Continued) Ravi Chugh! Jan 14 Announcements HW #1 due Mon Jan 20 Post questions/discussion to Piazza Check Piazza for TA/Tutor lab hours
CSE 130 [Winter 2014] Programming Languages Introduction to OCaml (Continued) Ravi Chugh! Jan 14 Announcements HW #1 due Mon Jan 20 Post questions/discussion to Piazza Check Piazza for TA/Tutor lab hours
All the operations used in the expression are over integers. a takes a pair as argument. (a pair is also a tuple, or more specifically, a 2-tuple)
 Weekly exercises in INF3110 week 41 6-10.10.2008 Exercise 1 Exercise 6.1 in Mitchell's book a) fun a(x,y) = x+2*y; val a = fn : int * int -> int All the operations used in the expression are over integers.
Weekly exercises in INF3110 week 41 6-10.10.2008 Exercise 1 Exercise 6.1 in Mitchell's book a) fun a(x,y) = x+2*y; val a = fn : int * int -> int All the operations used in the expression are over integers.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. OCaml Imperative Programming
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Fall 2017 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory All
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Fall 2017 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory All
Lecture 7: Type Systems and Symbol Tables. CS 540 George Mason University
 Lecture 7: Type Systems and Symbol Tables CS 540 George Mason University Static Analysis Compilers examine code to find semantic problems. Easy: undeclared variables, tag matching Difficult: preventing
Lecture 7: Type Systems and Symbol Tables CS 540 George Mason University Static Analysis Compilers examine code to find semantic problems. Easy: undeclared variables, tag matching Difficult: preventing
CSE 130, Winter 2011: Final Examination
 Name: ID : CSE 130, Winter 2011: Final Examination March 15, 2011 Do not start the exam until you are told to. This is a open-book, open-notes exam, but with no computational devices allowed (such as calculators/cellphones/laptops).
Name: ID : CSE 130, Winter 2011: Final Examination March 15, 2011 Do not start the exam until you are told to. This is a open-book, open-notes exam, but with no computational devices allowed (such as calculators/cellphones/laptops).
Welcome Back. CSCI 262 Data Structures. Hello, Let s Review. Hello, Let s Review. How to Review 8/19/ Review. Here s a simple C++ program:
 Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Welcome Back CSCI 262 Data Structures 2 - Review What you learned in CSCI 261 (or equivalent): Variables Types Arrays Expressions Conditionals Branches & Loops Functions Recursion Classes & Objects Streams
Java Primer 1: Types, Classes and Operators
 Java Primer 1 3/18/14 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Java Primer 1: Types,
Java Primer 1 3/18/14 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Java Primer 1: Types,
M/s. Managing distributed workloads. Language Reference Manual. Miranda Li (mjl2206) Benjamin Hanser (bwh2124) Mengdi Lin (ml3567)
 1 M/s Managing distributed workloads Language Reference Manual Miranda Li (mjl2206) Benjamin Hanser (bwh2124) Mengdi Lin (ml3567) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Lexical elements 2.1 Comments 2.2
1 M/s Managing distributed workloads Language Reference Manual Miranda Li (mjl2206) Benjamin Hanser (bwh2124) Mengdi Lin (ml3567) Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Lexical elements 2.1 Comments 2.2
SECTION II: LANGUAGE BASICS
 Chapter 5 SECTION II: LANGUAGE BASICS Operators Chapter 04: Basic Fundamentals demonstrated declaring and initializing variables. This chapter depicts how to do something with them, using operators. Operators
Chapter 5 SECTION II: LANGUAGE BASICS Operators Chapter 04: Basic Fundamentals demonstrated declaring and initializing variables. This chapter depicts how to do something with them, using operators. Operators
Implemen'ng a Func'onal Language. A Basic Func2onal Language. Goal: illustrate and understand the features of the run-2me support
 Implemen'ng a Func'onal Language 1 A Basic Func2onal Language Goal: illustrate and understand the features of the run-2me support 2 1 Environment Environments record what value is associated with a given
Implemen'ng a Func'onal Language 1 A Basic Func2onal Language Goal: illustrate and understand the features of the run-2me support 2 1 Environment Environments record what value is associated with a given
C Basics. Chapter 2: C Basics. C Programming Language. v3.3 February 6, 2017
 Chapter 2: C Programming Language Šimon Řeřucha v3.3 February 6, 2017 There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always bitch about and those nobody uses. Bjarne Stroustrup. General
Chapter 2: C Programming Language Šimon Řeřucha v3.3 February 6, 2017 There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always bitch about and those nobody uses. Bjarne Stroustrup. General
Language Proposal: tail
 Language Proposal: tail A tail recursion optimization language Some Wise Gal Team Roles Team Members UNIs Roles Sandra Shaefer Jennifer Lam Serena Shah Simpson Fiona Rowan sns2153 jl3953 ss4354 fmr2112
Language Proposal: tail A tail recursion optimization language Some Wise Gal Team Roles Team Members UNIs Roles Sandra Shaefer Jennifer Lam Serena Shah Simpson Fiona Rowan sns2153 jl3953 ss4354 fmr2112
Tools : The Java Compiler. The Java Interpreter. The Java Debugger
 Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Meeting14:Denotations
 Meeting14:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Reminder: 5-minute feedback discussion with Sean is part of the assignment ("interview light") Talk (with me, with the class
Meeting14:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Reminder: 5-minute feedback discussion with Sean is part of the assignment ("interview light") Talk (with me, with the class
Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, July 16, 2014
 Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, July 16, 2014 Updates Apr 1. Clarified that built-in methods can t be overridden, and that the evaluation order for send is slightly different than normal method call. Mar
Project 5 Due 11:59:59pm Wed, July 16, 2014 Updates Apr 1. Clarified that built-in methods can t be overridden, and that the evaluation order for send is slightly different than normal method call. Mar
Lesson 06 Arrays. MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL
 Lesson 06 Arrays MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Array An array is a group of variables (called elements or components) containing
Lesson 06 Arrays MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Array An array is a group of variables (called elements or components) containing
