Types, Universes and Everything
|
|
|
- Edith Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Types, Universes and Everything Andres Löh Dept. of Information and Computing Sciences, Utrecht University P.O. Box , 3508 TB Utrecht, The Netherlands Web pages: May 26, 2010
2 This talk The importance of strong type systems for programming. Current research topic: dependently typed programming. 2
3 Example (C#) stolen from Tim Sweeney s POPL 2006 talk Given a vertex array and an index array, let us read the indexed vertices, transform them, and write the result into a new array. 3
4 Example (C#) stolen from Tim Sweeney s POPL 2006 talk Given a vertex array and an index array, let us read the indexed vertices, transform them, and write the result into a new array. Vertex[ ] Transform (Vertex[ ] Vertices, int[ ] Indices, Matrix m) { } Vertex[ ] Result = new Vertex[Indices.length]; for (int i = 0; i < Indices.length; i +) Result[i] = Transform (m, Vertices[Indices[i]]); return Result; 3
5 Example (C#) stolen from Tim Sweeney s POPL 2006 talk Given a vertex array and an index array, let us read the indexed vertices, transform them, and write the result into a new array. Vertex[ ] Transform (Vertex[ ] Vertices, int[ ] Indices, Matrix m) { } Vertex[ ] Result = new Vertex[Indices.length]; for (int i = 0; i < Indices.length; i +) Result[i] = Transform (m, Vertices[Indices[i]]); return Result; Can anything go wrong? 3
6 Example (C#) stolen from Tim Sweeney s POPL 2006 talk Given a vertex array and an index array, let us read the indexed vertices, transform them, and write the result into a new array. Vertex[ ] Transform (Vertex[ ] Vertices, int[ ] Indices, Matrix m) { } Vertex[ ] Result = new Vertex[Indices.length]; for (int i = 0; i < Indices.length; i +) Result[i] = Transform (m, Vertices[Indices[i]]); return Result; Can anything go wrong? can be null can be null can be null 3
7 Example (C#) stolen from Tim Sweeney s POPL 2006 talk Given a vertex array and an index array, let us read the indexed vertices, transform them, and write the result into a new array. Vertex[ ] Transform (Vertex[ ] Vertices, int[ ] Indices, Matrix m) { can dereference null pointer } Vertex[ ] Result = new Vertex[Indices.length]; for (int i = 0; i < Indices.length; i +) Result[i] = Transform (m, Vertices[Indices[i]]); return Result; Can anything go wrong? can be null can be null can be null 3
8 Example (C#) stolen from Tim Sweeney s POPL 2006 talk Given a vertex array and an index array, let us read the indexed vertices, transform them, and write the result into a new array. Vertex[ ] Transform (Vertex[ ] Vertices, int[ ] Indices, Matrix m) { can dereference null pointer } can be null can be null can be null Vertex[ ] Result = new Vertex[Indices.length]; for (int i = 0; i < Indices.length; i +) Result[i] = Transform (m, Vertices[Indices[i]]); return Result; unnecessary bounds check can be out of bounds Can anything go wrong? 3
9 The problem Types often cannot express the properties of programs sufficiently well. 4
10 Potential solutions (Lots of) Testing 5
11 Potential solutions (Lots of) Testing Assertions and Contracts 5
12 Potential solutions (Lots of) Testing Assertions and Contracts External verification 5
13 Potential solutions (Lots of) Testing Assertions and Contracts External verification... 5
14 The problem in the real world The CWE/SANS Top 25 Most Dangerous Programming Errors Failure to Preserve Web Page Structure ( Cross-site Scripting ) Failure to Preserve SQL Query Structure ( SQL Injection ) Failure to Preserve OS Command Structure Buffer Copy without Checking Size of Input ( Buffer Overflow ) Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory Improper Check for Unusual or Exceptional Conditions Improper Validation of Array Index Integer Overflow or Wraparound Missing Encryption of Sensitive Data 6...
15 Better types? Vertex[ ] Transform (Vertex[ ] Vertices, int[ ] Indices, Matrix m) { Vertex[ ] Result = new Vertex[Indices.length]; for (int i = 0; i < Indices.length; i +) Result[i] = Transform (m, Vertices[Indices[i]]); return Result; } 7
16 Better types! Transform {n : Nat} (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] 8
17 Better types! types do not admit null values Transform {n : Nat} (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] 8
18 Better types! quantification over a natural number types do not admit null values Transform {n : Nat} (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] 8
19 Better types! quantification over a natural number types do not admit null values vector has an explicit length Transform {n : Nat} (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] 8
20 Better types! quantification over a natural number types do not admit null values vector has an explicit length Transform {n : Nat} indices must be in range (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] 8
21 Better types! quantification over a natural number types do not admit null values vector has an explicit length Transform {n : Nat} indices must be in range (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) length of result is known : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] 8
22 Better types! quantification over a natural number types do not admit null values vector has an explicit length Transform {n : Nat} indices must be in range (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) length of result is known : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] result constructed using a vector comprehension 8
23 Better types! quantification over a natural number types do not admit null values vector has an explicit length Transform {n : Nat} indices must be in range (Vertices : Vector Vertex n) (Indices : Buffer (m : Nat where m < n)) (m : Matrix) length of result is known : Vector Vertex (Indices.length) = [Transform (m, Vertices[i]) where i Indices] result constructed using a vector comprehension Note that we mix terms (here: natural numbers) with types. 8
24 Dependent types A B 9
25 Dependent types A B (x : A) B(x) {x : A} B(x) 9
26 Dependent types A B (x : A) B(x) {x : A} B(x) (Indices : Buffer Nat) Vector Vertex (Indices.length) 9
27 Type checking with dependent types Type checker must perform evaluation. 10
28 Type checking with dependent types Type checker must perform evaluation. Is Vector Vertex (2 + 2) the same as Vector Vertex 4? 10
29 Type checking with dependent types Type checker must perform evaluation. Is Vector Vertex (2 + 2) the same as Vector Vertex 4? Is Vector Vertex (n + 2) the same as Vector Vertex (2 + n)? 10
30 The power of dependent types We can add near-arbitrary properties and restrictions to our types: 11
31 The power of dependent types We can add near-arbitrary properties and restrictions to our types: Vectors of a certain length Numbers in a certain range 11
32 The power of dependent types We can add near-arbitrary properties and restrictions to our types: Vectors of a certain length Numbers in a certain range Sorted lists; lists of even numbers; lists without duplicates 11
33 The power of dependent types We can add near-arbitrary properties and restrictions to our types: Vectors of a certain length Numbers in a certain range Sorted lists; lists of even numbers; lists without duplicates Associative and commutative binary operators 11
34 The power of dependent types We can add near-arbitrary properties and restrictions to our types: Vectors of a certain length Numbers in a certain range Sorted lists; lists of even numbers; lists without duplicates Associative and commutative binary operators Properly escaped OS commands Well-formed SQL queries... 11
35 Strong types are helpful We can make illegal configurations impossible to represent. We can preserve information we obtain from run-time testing. With a suitable development environment, types can guide the programming process. 12
36 Curry-Howard correspondence Programming is like reasoning in (intuitionistic) logic property proof type program 13
37 Curry-Howard correspondence Programming is like reasoning in (intuitionistic) logic property proof truth falsity conjunction disjunction implication negation universal quantification existential quantification type program inhabited type uninhabited type pair union type function function to the uninhabited type dependent function dependent pair 13
38 Universe constructions A particular strength of dependently typed systems is that we can compute types from values. 14
39 Universe constructions A particular strength of dependently typed systems is that we can compute types from values. A type of codes together with an interpretation function mapping codes to types is called a universe. 14
40 Universe constructions A particular strength of dependently typed systems is that we can compute types from values. A type of codes together with an interpretation function mapping codes to types is called a universe. Because we can analyze the codes as normal values, we can write functions that are extremely generic by using a universe. 14
41 Simple universe example: C-style printf Codes Format strings such as "Test(%s): %d". Interpretation function Function that maps a format string to the type of the corresponding printf function, such as (String, Int) String. Using the universe We can define printf as an ordinary function. 15
42 Advanced universe example: databases The untyped approach Construct SQL queries as strings and send them to the database. The (E)DSL approach Have a special language mechanism or library to construct syntactically correct SQL queries. The model-driven approach Take the schema of a database and generate suitable datatypes and interface code from it. Then use the generated code. 16
43 The databases universe Code The database schemas. Interpretation function Takes schemas and computes suitable datatypes. Using the universe Together with an EDSL, we can write type-safe queries that are guaranteed to adhere to the schema, and can adapt when the schema changes. 17
44 Does it work yet? Dependently typed programming languages are currently in an experimental stage: Good enough to write smaller programs. Lack of libraries. Not yet very optimized for performance. Quite a number of interesting and challenging problems that we can solve. If you want to try a language: check out Agda. Haskell allows a limited encoding of dependent types. 18
Programming with Universes, Generically
 Programming with Universes, Generically Andres Löh Well-Typed LLP 24 January 2012 An introduction to Agda Agda Functional programming language Static types Dependent types Pure (explicit effects) Total
Programming with Universes, Generically Andres Löh Well-Typed LLP 24 January 2012 An introduction to Agda Agda Functional programming language Static types Dependent types Pure (explicit effects) Total
Universes. Universes for Data. Peter Morris. University of Nottingham. November 12, 2009
 for Data Peter Morris University of Nottingham November 12, 2009 Introduction Outline 1 Introduction What is DTP? Data Types in DTP Schemas for Inductive Families 2 of Data Inductive Types Inductive Families
for Data Peter Morris University of Nottingham November 12, 2009 Introduction Outline 1 Introduction What is DTP? Data Types in DTP Schemas for Inductive Families 2 of Data Inductive Types Inductive Families
Dependent types and program equivalence. Stephanie Weirich, University of Pennsylvania with Limin Jia, Jianzhou Zhao, and Vilhelm Sjöberg
 Dependent types and program equivalence Stephanie Weirich, University of Pennsylvania with Limin Jia, Jianzhou Zhao, and Vilhelm Sjöberg What are dependent types? Types that depend on values of other types
Dependent types and program equivalence Stephanie Weirich, University of Pennsylvania with Limin Jia, Jianzhou Zhao, and Vilhelm Sjöberg What are dependent types? Types that depend on values of other types
Example of a Demonstration that a Problem is NP-Complete by reduction from CNF-SAT
 20170926 CNF-SAT: CNF-SAT is a problem in NP, defined as follows: Let E be a Boolean expression with m clauses and n literals (literals = variables, possibly negated), in which - each clause contains only
20170926 CNF-SAT: CNF-SAT is a problem in NP, defined as follows: Let E be a Boolean expression with m clauses and n literals (literals = variables, possibly negated), in which - each clause contains only
Introduction to dependent types in Coq
 October 24, 2008 basic use of the Coq system In Coq, you can play with simple values and functions. The basic command is called Check, to verify if an expression is well-formed and learn what is its type.
October 24, 2008 basic use of the Coq system In Coq, you can play with simple values and functions. The basic command is called Check, to verify if an expression is well-formed and learn what is its type.
Modal Logic: Implications for Design of a Language for Distributed Computation p.1/53
 Modal Logic: Implications for Design of a Language for Distributed Computation Jonathan Moody (with Frank Pfenning) Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Modal Logic: Implications for
Modal Logic: Implications for Design of a Language for Distributed Computation Jonathan Moody (with Frank Pfenning) Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Modal Logic: Implications for
Typed Lambda Calculus
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University Sept. 8, 2016 The Two Sides of A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a system of notation for functions
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University Sept. 8, 2016 The Two Sides of A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a system of notation for functions
CS 161 Computer Security
 Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security 1/27 Reasoning About Code Often functions make certain assumptions about their arguments, and it is the caller s responsibility to make sure those assumptions
Uncertain Data Models
 Uncertain Data Models Christoph Koch EPFL Dan Olteanu University of Oxford SYNOMYMS data models for incomplete information, probabilistic data models, representation systems DEFINITION An uncertain data
Uncertain Data Models Christoph Koch EPFL Dan Olteanu University of Oxford SYNOMYMS data models for incomplete information, probabilistic data models, representation systems DEFINITION An uncertain data
Programming Proofs and Proving Programs. Nick Benton Microsoft Research, Cambridge
 Programming Proofs and Proving Programs Nick Benton Microsoft Research, Cambridge Coffee is does Greek 1. To draw a straight line from any point to any point. 2. To produce a finite straight line continuously
Programming Proofs and Proving Programs Nick Benton Microsoft Research, Cambridge Coffee is does Greek 1. To draw a straight line from any point to any point. 2. To produce a finite straight line continuously
Dependent Types and Irrelevance
 Dependent Types and Irrelevance Christoph-Simon Senjak Technische Universität München Institut für Informatik Boltzmannstraße 3 85748 Garching PUMA Workshop September 2012 Dependent Types Dependent Types
Dependent Types and Irrelevance Christoph-Simon Senjak Technische Universität München Institut für Informatik Boltzmannstraße 3 85748 Garching PUMA Workshop September 2012 Dependent Types Dependent Types
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Chapter p. 1/27
 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Chapter 2.1-2.7 p. 1/27 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer Science (Arkoudas and Musser) Chapter 2.1-2.7 p. 1/27 CSCI.6962/4962 Software Verification Fundamental Proof Methods in Computer
Structural polymorphism in Generic Haskell
 Structural polymorphism in Generic Haskell Andres Löh andres@cs.uu.nl 5 February 2005 Overview About Haskell Genericity and other types of polymorphism Examples of generic functions Generic Haskell Overview
Structural polymorphism in Generic Haskell Andres Löh andres@cs.uu.nl 5 February 2005 Overview About Haskell Genericity and other types of polymorphism Examples of generic functions Generic Haskell Overview
Theorem proving. PVS theorem prover. Hoare style verification PVS. More on embeddings. What if. Abhik Roychoudhury CS 6214
 Theorem proving PVS theorem prover Abhik Roychoudhury National University of Singapore Both specification and implementation can be formalized in a suitable logic. Proof rules for proving statements in
Theorem proving PVS theorem prover Abhik Roychoudhury National University of Singapore Both specification and implementation can be formalized in a suitable logic. Proof rules for proving statements in
Lessons Learned in Static Analysis Tool Evaluation. Providing World-Class Services for World-Class Competitiveness
 Lessons Learned in Static Analysis Tool Evaluation 1 Overview Lessons learned in the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Topics Licensing Performance Measurement Limitations
Lessons Learned in Static Analysis Tool Evaluation 1 Overview Lessons learned in the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Topics Licensing Performance Measurement Limitations
The Truth about Types. Bartosz Milewski
 The Truth about Types Bartosz Milewski Truth Truth Logic Types Categories Truth intro Unit type Terminal object true I () : () Proofs Logic Types Categories Proof of proposition A Type A is inhabited Morphism
The Truth about Types Bartosz Milewski Truth Truth Logic Types Categories Truth intro Unit type Terminal object true I () : () Proofs Logic Types Categories Proof of proposition A Type A is inhabited Morphism
Propositional Calculus. Math Foundations of Computer Science
 Propositional Calculus Math Foundations of Computer Science Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus so that they can use it to
Propositional Calculus Math Foundations of Computer Science Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus so that they can use it to
CIS 194: Homework 8. Due Wednesday, 8 April. Propositional Logic. Implication
 CIS 194: Homework 8 Due Wednesday, 8 April Propositional Logic In this section, you will prove some theorems in Propositional Logic, using the Haskell compiler to verify your proofs. The Curry-Howard isomorphism
CIS 194: Homework 8 Due Wednesday, 8 April Propositional Logic In this section, you will prove some theorems in Propositional Logic, using the Haskell compiler to verify your proofs. The Curry-Howard isomorphism
Hoare logic. A proof system for separation logic. Introduction. Separation logic
 Introduction Hoare logic Lecture 6: Examples in separation logic In the previous lecture, we saw how reasoning about pointers in Hoare logic was problematic, which motivated introducing separation logic.
Introduction Hoare logic Lecture 6: Examples in separation logic In the previous lecture, we saw how reasoning about pointers in Hoare logic was problematic, which motivated introducing separation logic.
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification
 VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
Lecture 3 Notes Arrays
 Lecture 3 Notes Arrays 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Summer 1 2015) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer 1 Introduction So far we have seen how to process primitive data like integers in imperative
Lecture 3 Notes Arrays 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Summer 1 2015) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer 1 Introduction So far we have seen how to process primitive data like integers in imperative
Type Theory meets Effects. Greg Morrisett
 Type Theory meets Effects Greg Morrisett A Famous Phrase: Well typed programs won t go wrong. 1. Describe abstract machine: M ::= 2. Give transition relation: M 1 M 2
Type Theory meets Effects Greg Morrisett A Famous Phrase: Well typed programs won t go wrong. 1. Describe abstract machine: M ::= 2. Give transition relation: M 1 M 2
The three faces of homotopy type theory. Type theory and category theory. Minicourse plan. Typing judgments. Michael Shulman.
 The three faces of homotopy type theory Type theory and category theory Michael Shulman 1 A programming language. 2 A foundation for mathematics based on homotopy theory. 3 A calculus for (, 1)-category
The three faces of homotopy type theory Type theory and category theory Michael Shulman 1 A programming language. 2 A foundation for mathematics based on homotopy theory. 3 A calculus for (, 1)-category
Dependent types and program equivalence. Stephanie Weirich, University of Pennsylvania with Limin Jia, Jianzhou Zhao, and Vilhelm Sjöberg
 Dependent types and program equivalence Stephanie Weirich, University of Pennsylvania with Limin Jia, Jianzhou Zhao, and Vilhelm Sjöberg Doing dependent types wrong without going wrong Stephanie Weirich,
Dependent types and program equivalence Stephanie Weirich, University of Pennsylvania with Limin Jia, Jianzhou Zhao, and Vilhelm Sjöberg Doing dependent types wrong without going wrong Stephanie Weirich,
Hiding local state in direct style: a higher-order anti-frame rule
 1 / 65 Hiding local state in direct style: a higher-order anti-frame rule François Pottier January 28th, 2008 2 / 65 Contents Introduction Basics of the type system A higher-order anti-frame rule Applications
1 / 65 Hiding local state in direct style: a higher-order anti-frame rule François Pottier January 28th, 2008 2 / 65 Contents Introduction Basics of the type system A higher-order anti-frame rule Applications
 https://lambda.mines.edu Evaluating programming languages based on: Writability: How easy is it to write good code? Readability: How easy is it to read well written code? Is the language easy enough to
https://lambda.mines.edu Evaluating programming languages based on: Writability: How easy is it to write good code? Readability: How easy is it to read well written code? Is the language easy enough to
Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell. Anish Tondwalkar
 Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell Anish Tondwalkar Overview Motivation Liquid Haskell Fault Localization Fault Localization Evaluation Predicate Discovery Predicate Discovery Evaluation Conclusion
Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell Anish Tondwalkar Overview Motivation Liquid Haskell Fault Localization Fault Localization Evaluation Predicate Discovery Predicate Discovery Evaluation Conclusion
Generic Programming for Domain Reasoners
 Generic Programming for Domain Reasoners José Pedro Magalhães 1 joint work with Johan Jeuring 1,2 Bastiaan Heeren 2 1 Department of Information and Computing Sciences, Utrecht University 2 School of Computer
Generic Programming for Domain Reasoners José Pedro Magalhães 1 joint work with Johan Jeuring 1,2 Bastiaan Heeren 2 1 Department of Information and Computing Sciences, Utrecht University 2 School of Computer
Lecture Notes on Ints
 Lecture Notes on Ints 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 2 August 26, 2010 1 Introduction Two fundamental types in almost any programming language are booleans and integers.
Lecture Notes on Ints 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 2 August 26, 2010 1 Introduction Two fundamental types in almost any programming language are booleans and integers.
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 16: Building Secure Software Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Review A large number of software vulnerabilities various
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 16: Building Secure Software Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Review A large number of software vulnerabilities various
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 22
 ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 22 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 31 October 2018 Don t forget HW#7 Announcements 1 Computer Security and why it matters for embedded
ECE 471 Embedded Systems Lecture 22 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 31 October 2018 Don t forget HW#7 Announcements 1 Computer Security and why it matters for embedded
18-642: Code Style for Compilers
 18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/25/2017 1 Anti-Patterns: Coding Style: Language Use Code compiles with warnings Warnings are turned off or over-ridden Insufficient warning level set Language safety
18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/25/2017 1 Anti-Patterns: Coding Style: Language Use Code compiles with warnings Warnings are turned off or over-ridden Insufficient warning level set Language safety
Verification & Validation of Open Source
 Verification & Validation of Open Source 2011 WORKSHOP ON SPACECRAFT FLIGHT SOFTWARE Gordon Uchenick Coverity, Inc Open Source is Ubiquitous Most commercial and proprietary software systems have some open
Verification & Validation of Open Source 2011 WORKSHOP ON SPACECRAFT FLIGHT SOFTWARE Gordon Uchenick Coverity, Inc Open Source is Ubiquitous Most commercial and proprietary software systems have some open
An Introduction to Programming and Proving in Agda (incomplete draft)
 An Introduction to Programming and Proving in Agda (incomplete draft) Peter Dybjer January 29, 2018 1 A first Agda module Your first Agda-file is called BoolModule.agda. Its contents are module BoolModule
An Introduction to Programming and Proving in Agda (incomplete draft) Peter Dybjer January 29, 2018 1 A first Agda module Your first Agda-file is called BoolModule.agda. Its contents are module BoolModule
18-642: Code Style for Compilers
 18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/6/2018 2017-2018 Philip Koopman Programming can be fun, so can cryptography; however they should not be combined. Kreitzberg and Shneiderman 2017-2018 Philip Koopman
18-642: Code Style for Compilers 9/6/2018 2017-2018 Philip Koopman Programming can be fun, so can cryptography; however they should not be combined. Kreitzberg and Shneiderman 2017-2018 Philip Koopman
Multi-paradigm Declarative Languages
 Michael Hanus (CAU Kiel) Multi-paradigm Declarative Languages ICLP 2007 1 Multi-paradigm Declarative Languages Michael Hanus Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel Programming Languages and Compiler Construction
Michael Hanus (CAU Kiel) Multi-paradigm Declarative Languages ICLP 2007 1 Multi-paradigm Declarative Languages Michael Hanus Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel Programming Languages and Compiler Construction
Software Verification for Java 5
 Software Verification for Java 5 KeY Symposium 2007 Mattias Ulbrich June 14, 2007 Content KeY + Java 5 Typesafe Enumeration Datatypes Enhanced For Loops Generic Classes 1. Keep pace with the progress of
Software Verification for Java 5 KeY Symposium 2007 Mattias Ulbrich June 14, 2007 Content KeY + Java 5 Typesafe Enumeration Datatypes Enhanced For Loops Generic Classes 1. Keep pace with the progress of
Propositional Calculus. CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson
 Propositional Calculus CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus
Propositional Calculus CS 270: Mathematical Foundations of Computer Science Jeremy Johnson Propositional Calculus Objective: To provide students with the concepts and techniques from propositional calculus
Mixed Integer Linear Programming
 Mixed Integer Linear Programming Part I Prof. Davide M. Raimondo A linear program.. A linear program.. A linear program.. Does not take into account possible fixed costs related to the acquisition of new
Mixed Integer Linear Programming Part I Prof. Davide M. Raimondo A linear program.. A linear program.. A linear program.. Does not take into account possible fixed costs related to the acquisition of new
Secure Programming Techniques
 Secure Programming Techniques Meelis ROOS mroos@ut.ee Institute of Computer Science Tartu University spring 2014 Course outline Introduction General principles Code auditing C/C++ Web SQL Injection PHP
Secure Programming Techniques Meelis ROOS mroos@ut.ee Institute of Computer Science Tartu University spring 2014 Course outline Introduction General principles Code auditing C/C++ Web SQL Injection PHP
Lecture 8 Data Structures
 Lecture 8 Data Structures 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Iliano Cervesato In this lecture we introduce the idea of imperative data
Lecture 8 Data Structures 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Iliano Cervesato In this lecture we introduce the idea of imperative data
Query optimization. Elena Baralis, Silvia Chiusano Politecnico di Torino. DBMS Architecture D B M G. Database Management Systems. Pag.
 Database Management Systems DBMS Architecture SQL INSTRUCTION OPTIMIZER MANAGEMENT OF ACCESS METHODS CONCURRENCY CONTROL BUFFER MANAGER RELIABILITY MANAGEMENT Index Files Data Files System Catalog DATABASE
Database Management Systems DBMS Architecture SQL INSTRUCTION OPTIMIZER MANAGEMENT OF ACCESS METHODS CONCURRENCY CONTROL BUFFER MANAGER RELIABILITY MANAGEMENT Index Files Data Files System Catalog DATABASE
SQL Injection. EECS Introduction to Database Management Systems
 SQL Injection EECS3421 - Introduction to Database Management Systems Credit "Foundations of Security: What Every Programmer Needs To Know" (Chapter 8) by Neil Daswani, Christoph Kern, and Anita Kesavan
SQL Injection EECS3421 - Introduction to Database Management Systems Credit "Foundations of Security: What Every Programmer Needs To Know" (Chapter 8) by Neil Daswani, Christoph Kern, and Anita Kesavan
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 15: Software Security II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Vulnerabilities Buffer overflow vulnerabilities account
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 15: Software Security II Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Software Vulnerabilities Buffer overflow vulnerabilities account
Alonzo a Compiler for Agda
 Alonzo a Compiler for Agda Marcin Benke Institute of Informatics, Warsaw University, ben@mimuw.edu.pl 1 Introduction Agda [Norell, 2007] is an interactive system for developing constructive proofs in a
Alonzo a Compiler for Agda Marcin Benke Institute of Informatics, Warsaw University, ben@mimuw.edu.pl 1 Introduction Agda [Norell, 2007] is an interactive system for developing constructive proofs in a
Lecture 8: Summary of Haskell course + Type Level Programming
 Lecture 8: Summary of Haskell course + Type Level Programming Søren Haagerup Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense October 31, 2017 Principles from Haskell
Lecture 8: Summary of Haskell course + Type Level Programming Søren Haagerup Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense October 31, 2017 Principles from Haskell
Engineering Your Software For Attack
 Engineering Your Software For Attack Robert A. Martin Senior Principal Engineer Cyber Security Center Center for National Security The MITRE Corporation 2013 The MITRE Corporation. All rights reserved.
Engineering Your Software For Attack Robert A. Martin Senior Principal Engineer Cyber Security Center Center for National Security The MITRE Corporation 2013 The MITRE Corporation. All rights reserved.
Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis
 Computer Security Course. Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis Program Verification Program Verification How to prove a program free of buffer overflows? Precondition Postcondition Loop invariants
Computer Security Course. Software Security: Vulnerability Analysis Program Verification Program Verification How to prove a program free of buffer overflows? Precondition Postcondition Loop invariants
COMP SCI 3EA3 Specifications and Correctness Duration of Examination: 50 minutes
 Best of luck! McMaster University Department of Computing and Software Musa Al-hassy CONTENTS CompSci 3EA3 January 30, 2018 iday Class COMP SCI 3EA3 Specifications and Correctness Duration of Examination:
Best of luck! McMaster University Department of Computing and Software Musa Al-hassy CONTENTS CompSci 3EA3 January 30, 2018 iday Class COMP SCI 3EA3 Specifications and Correctness Duration of Examination:
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
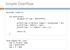 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS
 LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS A Computer Science Perspective WINFRIED KARL GRASSMANN Department of Computer Science University of Saskatchewan JEAN-PAUL TREMBLAY Department of Computer Science University
LOGIC AND DISCRETE MATHEMATICS A Computer Science Perspective WINFRIED KARL GRASSMANN Department of Computer Science University of Saskatchewan JEAN-PAUL TREMBLAY Department of Computer Science University
Hardware versus software
 Logic 1 Hardware versus software 2 In hardware such as chip design or architecture, designs are usually proven to be correct using proof tools In software, a program is very rarely proved correct Why?
Logic 1 Hardware versus software 2 In hardware such as chip design or architecture, designs are usually proven to be correct using proof tools In software, a program is very rarely proved correct Why?
Section Notes - Week 1 (9/17)
 Section Notes - Week 1 (9/17) Why do we need to learn bits and bitwise arithmetic? Since this class is about learning about how computers work. For most of the rest of the semester, you do not have to
Section Notes - Week 1 (9/17) Why do we need to learn bits and bitwise arithmetic? Since this class is about learning about how computers work. For most of the rest of the semester, you do not have to
Program Verification & Testing; Review of Propositional Logic
 8/24: p.1, solved; 9/20: p.5 Program Verification & Testing; Review of Propositional Logic CS 536: Science of Programming, Fall 2018 A. Why Course guidelines are important. Active learning is the style
8/24: p.1, solved; 9/20: p.5 Program Verification & Testing; Review of Propositional Logic CS 536: Science of Programming, Fall 2018 A. Why Course guidelines are important. Active learning is the style
Madhya Pradesh Bhoj (Open) University, Bhopal
 Subject-I- Data Structure through C Maximum Marks: 30 funz s'k& Q3 Q4 Q5 Q3 Describe the methods of parallel processing. What do you mean by Instruction? Describe the computer instructions in brief. How
Subject-I- Data Structure through C Maximum Marks: 30 funz s'k& Q3 Q4 Q5 Q3 Describe the methods of parallel processing. What do you mean by Instruction? Describe the computer instructions in brief. How
Lecture Notes for 04/04/06: UNTRUSTED CODE Fatima Zarinni.
 Lecture Notes for 04/04/06 UNTRUSTED CODE Fatima Zarinni. Last class we started to talk about the different System Solutions for Stack Overflow. We are going to continue the subject. Stages of Stack Overflow
Lecture Notes for 04/04/06 UNTRUSTED CODE Fatima Zarinni. Last class we started to talk about the different System Solutions for Stack Overflow. We are going to continue the subject. Stages of Stack Overflow
CS131 Typed Lambda Calculus Worksheet Due Thursday, April 19th
 CS131 Typed Lambda Calculus Worksheet Due Thursday, April 19th Name: CAS ID (e.g., abc01234@pomona.edu): I encourage you to collaborate. collaborations below. Please record your Each question is worth
CS131 Typed Lambda Calculus Worksheet Due Thursday, April 19th Name: CAS ID (e.g., abc01234@pomona.edu): I encourage you to collaborate. collaborations below. Please record your Each question is worth
Lecture 4 September Required reading materials for this class
 EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
EECS 261: Computer Security Fall 2007 Lecture 4 September 6 Lecturer: David Wagner Scribe: DK Moon 4.1 Required reading materials for this class Beyond Stack Smashing: Recent Advances in Exploiting Buffer
COS 320. Compiling Techniques
 Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
C Refresher, Advance C, Coding Standard, Misra C Compliance & Real-time Programming
 C Refresher, Advance C, Coding Standard, Misra C Compliance & Real-time Programming Course Overview This course transforms an IT-Professional or a Student into an expert C Programming Person with concepts
C Refresher, Advance C, Coding Standard, Misra C Compliance & Real-time Programming Course Overview This course transforms an IT-Professional or a Student into an expert C Programming Person with concepts
Runtime Checking for Program Verification Systems
 Runtime Checking for Program Verification Systems Karen Zee, Viktor Kuncak, and Martin Rinard MIT CSAIL Tuesday, March 13, 2007 Workshop on Runtime Verification 1 Background Jahob program verification
Runtime Checking for Program Verification Systems Karen Zee, Viktor Kuncak, and Martin Rinard MIT CSAIL Tuesday, March 13, 2007 Workshop on Runtime Verification 1 Background Jahob program verification
Programming Languages Lecture 14: Sum, Product, Recursive Types
 CSE 230: Winter 200 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Sum, Product, Recursive Types The end is nigh HW 3 No HW 4 (= Final) Project (Meeting + Talk) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap Goal: Relate
CSE 230: Winter 200 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 4: Sum, Product, Recursive Types The end is nigh HW 3 No HW 4 (= Final) Project (Meeting + Talk) Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Recap Goal: Relate
Testing. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 2. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]
![Testing. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 2. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences] Testing. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 2. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]](/thumbs/89/100566300.jpg) Testing Advanced functional programming - Lecture 2 Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano 1 Program Correctness 2 Testing and correctness When is a program correct? 3 Testing and correctness When is a
Testing Advanced functional programming - Lecture 2 Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano 1 Program Correctness 2 Testing and correctness When is a program correct? 3 Testing and correctness When is a
Gaps in Static Analysis Tool Capabilities. Providing World-Class Services for World-Class Competitiveness
 Gaps in Static Analysis Tool Capabilities 1 Overview Gaps in Static Analysis tools as identified during the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Collaborative effort between
Gaps in Static Analysis Tool Capabilities 1 Overview Gaps in Static Analysis tools as identified during the evaluation of five (5) commercially available static analysis tools Collaborative effort between
The Prolog to Mercury transition guide
 The Prolog to Mercury transition guide Version 14.01.1 Thomas Conway Zoltan Somogyi Fergus Henderson Copyright c 1995 2014 The University of Melbourne. Permission is granted to make and distribute verbatim
The Prolog to Mercury transition guide Version 14.01.1 Thomas Conway Zoltan Somogyi Fergus Henderson Copyright c 1995 2014 The University of Melbourne. Permission is granted to make and distribute verbatim
Symmetry in Type Theory
 Google May 29th, 2012 What is Symmetry? Definition Symmetry: Two or more things that initially look distinct, may actually be instances of a more general underlying principle. Why do we care? Simplicity.
Google May 29th, 2012 What is Symmetry? Definition Symmetry: Two or more things that initially look distinct, may actually be instances of a more general underlying principle. Why do we care? Simplicity.
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages. Lecture 17 Recursive Types. Dan Grossman 2012
 CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 17 Recursive Types Dan Grossman 2012 Where are we System F gave us type abstraction code reuse strong abstractions different from real languages (like ML),
CS-XXX: Graduate Programming Languages Lecture 17 Recursive Types Dan Grossman 2012 Where are we System F gave us type abstraction code reuse strong abstractions different from real languages (like ML),
Prepared Statement. Always be prepared
 Prepared Statement Always be prepared The problem with ordinary Statement The ordinary Statement was open to SQL injections if fed malicious data. What would the proper response to that be? Filter all
Prepared Statement Always be prepared The problem with ordinary Statement The ordinary Statement was open to SQL injections if fed malicious data. What would the proper response to that be? Filter all
Other array problems. Integer overflow. Outline. Integer overflow example. Signed and unsigned
 Other array problems CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 4: Low-level attacks Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Missing/wrong bounds check One unsigned
Other array problems CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 4: Low-level attacks Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Missing/wrong bounds check One unsigned
CS61C : Machine Structures
 Get your clickers ready...! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1)!!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia
Get your clickers ready...! inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 3 Introduction to the C Programming Language (pt 1)!!Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia!!!www.cs.berkeley.edu/~ddgarcia
Relational Databases
 Relational Databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki () Relational databases 1 / 49 Plan of the course 1 Relational databases 2 Relational database design 3 Conceptual database design 4
Relational Databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki () Relational databases 1 / 49 Plan of the course 1 Relational databases 2 Relational database design 3 Conceptual database design 4
Notes. Notes. Introduction. Notes. Propositional Functions. Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry.
 Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry Spring 2006 1 / 1 Computer Science & Engineering 235 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Sections 1.3 1.4 of Rosen cse235@cse.unl.edu Introduction
Slides by Christopher M. Bourke Instructor: Berthe Y. Choueiry Spring 2006 1 / 1 Computer Science & Engineering 235 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Sections 1.3 1.4 of Rosen cse235@cse.unl.edu Introduction
Critical Analysis of Computer Science Methodology: Theory
 Critical Analysis of Computer Science Methodology: Theory Björn Lisper Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University bjorn.lisper@mdh.se http://www.idt.mdh.se/ blr/ March 3, 2004 Critical
Critical Analysis of Computer Science Methodology: Theory Björn Lisper Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University bjorn.lisper@mdh.se http://www.idt.mdh.se/ blr/ March 3, 2004 Critical
Functional Logic Design Patterns
 FLOPS 2002 Functional Logic Design Patterns Michael Hanus Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel joint work with Sergio Antoy Portland State University 1 SOME HISTORY AND MOTIVATION 1993 ([POPL 94, JACM
FLOPS 2002 Functional Logic Design Patterns Michael Hanus Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel joint work with Sergio Antoy Portland State University 1 SOME HISTORY AND MOTIVATION 1993 ([POPL 94, JACM
Secure Coding, some simple steps help. OWASP EU Tour 2013
 Secure Coding, some simple steps help. OWASP EU Tour 2013 About Me Steven van der Baan - Dutch - 7Safe, part of PA Consulting Group - Developer - Pentester - Consultant - CISSP, OSCP It's amazing how
Secure Coding, some simple steps help. OWASP EU Tour 2013 About Me Steven van der Baan - Dutch - 7Safe, part of PA Consulting Group - Developer - Pentester - Consultant - CISSP, OSCP It's amazing how
CSE 127 Computer Security
 CSE 127 Computer Security Fall 2015 Web Security I: SQL injection Stefan Savage The Web creates new problems Web sites are programs Partially implemented in browser» Javascript, Java, Flash Partially implemented
CSE 127 Computer Security Fall 2015 Web Security I: SQL injection Stefan Savage The Web creates new problems Web sites are programs Partially implemented in browser» Javascript, Java, Flash Partially implemented
CMSC 414 Computer and Network Security
 CMSC 414 Computer and Network Security Buffer Overflows Dr. Michael Marsh August 30, 2017 Trust and Trustworthiness You read: Reflections on Trusting Trust (Ken Thompson), 1984 Smashing the Stack for Fun
CMSC 414 Computer and Network Security Buffer Overflows Dr. Michael Marsh August 30, 2017 Trust and Trustworthiness You read: Reflections on Trusting Trust (Ken Thompson), 1984 Smashing the Stack for Fun
Outline. Introduction Concepts and terminology The case for static typing. Implementing a static type system Basic typing relations Adding context
 Types 1 / 15 Outline Introduction Concepts and terminology The case for static typing Implementing a static type system Basic typing relations Adding context 2 / 15 Types and type errors Type: a set of
Types 1 / 15 Outline Introduction Concepts and terminology The case for static typing Implementing a static type system Basic typing relations Adding context 2 / 15 Types and type errors Type: a set of
CS 261 Fall Mike Lam, Professor Integer Encodings
 CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor https://xkcd.com/571/ Integer Encodings Integers Topics C integer data types Unsigned encoding Signed encodings Conversions Integer data types in C99 1 byte 2 bytes
CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor https://xkcd.com/571/ Integer Encodings Integers Topics C integer data types Unsigned encoding Signed encodings Conversions Integer data types in C99 1 byte 2 bytes
Syntax of Eiffel: a Brief Overview
 Syntax of Eiffel: a Brief Overview EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Escape Sequences Escape sequences are special characters to be placed in your program text. In Java, an escape sequence
Syntax of Eiffel: a Brief Overview EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Escape Sequences Escape sequences are special characters to be placed in your program text. In Java, an escape sequence
C-LANGUAGE CURRICULAM
 C-LANGUAGE CURRICULAM Duration: 2 Months. 1. Introducing C 1.1 History of C Origin Standardization C-Based Languages 1.2 Strengths and Weaknesses Of C Strengths Weaknesses Effective Use of C 2. C Fundamentals
C-LANGUAGE CURRICULAM Duration: 2 Months. 1. Introducing C 1.1 History of C Origin Standardization C-Based Languages 1.2 Strengths and Weaknesses Of C Strengths Weaknesses Effective Use of C 2. C Fundamentals
Programming Languages Third Edition
 Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Commands, and Queries, and Features. Syntax of Eiffel: a Brief Overview. Escape Sequences. Naming Conventions
 Commands, and Queries, and Features Syntax of Eiffel: a Brief Overview EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG In a Java class: Attributes: Data Mutators: Methods that change attributes without
Commands, and Queries, and Features Syntax of Eiffel: a Brief Overview EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG In a Java class: Attributes: Data Mutators: Methods that change attributes without
Databases. Jörg Endrullis. VU University Amsterdam
 Databases Jörg Endrullis VU University Amsterdam The Relational Model Overview 1. Relational Model Concepts: Schema, State 2. Null Values 3. Constraints: General Remarks 4. Key Constraints 5. Foreign Key
Databases Jörg Endrullis VU University Amsterdam The Relational Model Overview 1. Relational Model Concepts: Schema, State 2. Null Values 3. Constraints: General Remarks 4. Key Constraints 5. Foreign Key
Boolean Representations and Combinatorial Equivalence
 Chapter 2 Boolean Representations and Combinatorial Equivalence This chapter introduces different representations of Boolean functions. It then discusses the applications of these representations for proving
Chapter 2 Boolean Representations and Combinatorial Equivalence This chapter introduces different representations of Boolean functions. It then discusses the applications of these representations for proving
Semantic Errors in Database Queries
 Semantic Errors in Database Queries 1 Semantic Errors in Database Queries Stefan Brass TU Clausthal, Germany From April: University of Halle, Germany Semantic Errors in Database Queries 2 Classification
Semantic Errors in Database Queries 1 Semantic Errors in Database Queries Stefan Brass TU Clausthal, Germany From April: University of Halle, Germany Semantic Errors in Database Queries 2 Classification
Analysis of Software Artifacts
 Analysis of Software Artifacts Properties with ESC/Java Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic specifications Expressed in Java
Analysis of Software Artifacts Properties with ESC/Java Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic specifications Expressed in Java
Formal C semantics: CompCert and the C standard
 Formal C semantics: CompCert and the C standard Robbert Krebbers 1, Xavier Leroy 2, and Freek Wiedijk 1 1 ICIS, Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands 2 Inria Paris-Rocquencourt, France Abstract.
Formal C semantics: CompCert and the C standard Robbert Krebbers 1, Xavier Leroy 2, and Freek Wiedijk 1 1 ICIS, Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands 2 Inria Paris-Rocquencourt, France Abstract.
Outline. Classic races: files in /tmp. Race conditions. TOCTTOU example. TOCTTOU gaps. Vulnerabilities in OS interaction
 Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Outline CSci 5271 Introduction to Computer Security Day 3: Low-level vulnerabilities Stephen McCamant University of Minnesota, Computer Science & Engineering Race conditions Classic races: files in /tmp
Depending on Types. Stephanie Weirich University of Pennsylvania
 Depending on Types Stephanie Weirich University of Pennsylvania TDD Type- Driven Development with Dependent Types The Agda Experience On 2012-01- 11 03:36, Jonathan Leivent wrote on the Agda mailing list:
Depending on Types Stephanie Weirich University of Pennsylvania TDD Type- Driven Development with Dependent Types The Agda Experience On 2012-01- 11 03:36, Jonathan Leivent wrote on the Agda mailing list:
4. Jump to *RA 4. StackGuard 5. Execute code 5. Instruction Set Randomization 6. Make system call 6. System call Randomization
 04/04/06 Lecture Notes Untrusted Beili Wang Stages of Static Overflow Solution 1. Find bug in 1. Static Analysis 2. Send overflowing input 2. CCured 3. Overwrite return address 3. Address Space Randomization
04/04/06 Lecture Notes Untrusted Beili Wang Stages of Static Overflow Solution 1. Find bug in 1. Static Analysis 2. Send overflowing input 2. CCured 3. Overwrite return address 3. Address Space Randomization
Promela and SPIN. Mads Dam Dept. Microelectronics and Information Technology Royal Institute of Technology, KTH. Promela and SPIN
 Promela and SPIN Mads Dam Dept. Microelectronics and Information Technology Royal Institute of Technology, KTH Promela and SPIN Promela (Protocol Meta Language): Language for modelling discrete, event-driven
Promela and SPIN Mads Dam Dept. Microelectronics and Information Technology Royal Institute of Technology, KTH Promela and SPIN Promela (Protocol Meta Language): Language for modelling discrete, event-driven
COMP3441 Lecture 7: Software Vulnerabilities
 COMP3441 Lecture 7: Software Vulnerabilities Ron van der Meyden (University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia) April 22, 2013 Overview Buffer overflow attacks SQL injection attacks Defensive measures
COMP3441 Lecture 7: Software Vulnerabilities Ron van der Meyden (University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia) April 22, 2013 Overview Buffer overflow attacks SQL injection attacks Defensive measures
Typed Lambda Calculus for Syntacticians
 Department of Linguistics Ohio State University January 12, 2012 The Two Sides of Typed Lambda Calculus A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a
Department of Linguistics Ohio State University January 12, 2012 The Two Sides of Typed Lambda Calculus A typed lambda calculus (TLC) can be viewed in two complementary ways: model-theoretically, as a
CSc 520. Principles of Programming Languages 25: Types Introduction
 CSc 520 Principles of Programming Languages 25: Types Introduction Christian Collberg Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@cs.arizona.edu Copyright c 2005 Christian Collberg April
CSc 520 Principles of Programming Languages 25: Types Introduction Christian Collberg Department of Computer Science University of Arizona collberg@cs.arizona.edu Copyright c 2005 Christian Collberg April
Lecture 4 Searching Arrays
 Lecture 4 Searching Arrays 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is to find elements in collections,
Lecture 4 Searching Arrays 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2018) Frank Pfenning One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is to find elements in collections,
Lecture Notes on Linear Search
 Lecture Notes on Linear Search 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 5 January 28, 2014 1 Introduction One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is
Lecture Notes on Linear Search 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 5 January 28, 2014 1 Introduction One of the fundamental and recurring problems in computer science is
Detecting Logical Errors in SQL Queries
 Detecting Logical Errors in SQL Queries Stefan Brass Christian Goldberg Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg, Institut für Informatik, Von-Seckendorff-Platz 1, D-06099 Halle (Saale), Germany (brass
Detecting Logical Errors in SQL Queries Stefan Brass Christian Goldberg Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg, Institut für Informatik, Von-Seckendorff-Platz 1, D-06099 Halle (Saale), Germany (brass
Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages
 Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Lecture 24 Thursday, April 19, 2018 1 Error-propagating semantics For the last few weeks, we have been studying type systems.
Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences CS 152: Programming Languages Lecture 24 Thursday, April 19, 2018 1 Error-propagating semantics For the last few weeks, we have been studying type systems.
What happens. 376a. Database Design. Execution strategy. Query conversion. Next. Two types of techniques
 376a. Database Design Dept. of Computer Science Vassar College http://www.cs.vassar.edu/~cs376 Class 16 Query optimization What happens Database is given a query Query is scanned - scanner creates a list
376a. Database Design Dept. of Computer Science Vassar College http://www.cs.vassar.edu/~cs376 Class 16 Query optimization What happens Database is given a query Query is scanned - scanner creates a list
