Prime Factorization. Jane Alam Jan. 1 P a g e Document prepared by Jane Alam Jan
|
|
|
- Antonia Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prime Factorization by Jane Alam Jan 1 P a g e
2 Prime Factorization Introduction Sometimes we need to prime factorize numbers. So, what is prime factorization? Actually prime factorization means finding the prime factors of a number. That means the primes that divide the number, should be listed and how many times a prime divides the number should also be listed. For example, 40 = 2 3 * = 2 3 * 3 * = 3 * = = 2 5 * 3 3 * 5 * 7 2 * 19 Now, how to generate the prime factorization of a number? So, obviously the first task is - we have to generate primes. You can read the paper for "Sieve of Eratosthenes" to know how to find primes. From now on, we will think that we have an array named prime[] which contains all the primes. So, prime[0] = 2, prime [1] = 3, prime [2] = 5, 2 P a g e
3 Idea 1 The first idea that comes into mind is, we can check all the primes and try to divide the number. If we can divide the number by a prime, we will try to divide as many times as we can. We will continue our work until the number becomes 1. For example, we want to prime factorize 40. At first, we take an empty list; it will contain the primes we have used for factorization (that's how we can find the primes we have used). The steps are given below. Initially we have 40 List: (empty) Step 1) 40 is divisible by 2 (the 1 st prime), so, we divide 40 by 2 (and get 20) and add 2 in the list, we get 20 List: 2 Step 2) 20 is divisible by 2, so, we divide 20 by 2 (and get 10) and add 2 in the list, we get 10 List: 2 2 Step 3) 10 is divisible by 2, so, we divide 10 by 2 (and get 5) and add 2 in the list, we get 5 List: Step 4) 5 is not divisible by 3 (the 2 nd prime), so the list remains unchanged Step 5) 5 is divisible by 5 (the 3 rd prime), so, we divide 5 by 5 (and get 1) and add 5 in the list, we get 1 List: Now if we go further it will be unnecessary, because 1 can't be factorized further. So, we are sure that 40 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 5 = 2 3 * 5. This way we can prime factorize any number. 3 P a g e
4 The following code implements the same idea as described. int List[128]; // saves the List int listsize; // saves the size of List void primefactorize( int n ) { listsize = 0; // Initially the List is empty, we denote that size = 0 for( int i = 0; prime[i] <= n; i++ ) { if( n % prime[i] == 0 ) { // So, n is a multiple of the ith prime // So, we continue dividing n by prime[i] as long as possible while( n % prime[i] == 0 ) { n /= prime[i]; // we have divided n by prime[i] List[listSize] = prime[i]; // added the ith prime in the list listsize++; // added a prime, so, size should be increased int main() { primefactorize( 40 ); for( int i = 0; i < listsize; i++ ) // traverse the List array printf("%d ", List[i]); return 0; If we analyze the code a bit, we will find that, the condition should be n!= 1, but here, the condition is given as prime[i] <= n. Do they have any difference? Idea 2 The idea described in the previous section is not quite good, since if a prime number is given, say the th prime, we have to check all the primes up to it and then we can find the factorization. For example, if we want to find the prime factorization of 19 (the 9 th prime), then the code will try to divide 19 by 2, then 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 15, 17, and finally 19. So, only 19 divides 19, then we will find the prime factorization of 19. So, it takes 9 operations. The better idea is check primes up to sqrt(n). This idea is described in the paper for Sieve of Eratosthenes. As we have stated there - an integer n, which is not a prime, will have a divisor (a prime divisor, too) less than or equal to sqrt(n). So, this way can divide n by its prime divisor, thus reducing it. But if we follow this way, can there be any problems? At first, we try to factorize 40. The integer part (or floor) of sqrt(40) = 6. So, we will take primes up to 6. Now see that the largest prime used for 40 is 5 (in Idea 1). So, we will have the same steps as in Idea 1. 4 P a g e
5 Now we try to factorize 114. The integer part (or floor) of sqrt(114) = 10. So, we will take primes up to 10. Initially we have 114 List: (empty) Step 1) 114 is divisible by 2, so, we divide 114 by 2 (and get 57) and add 2 in the list, we get 57 List: 2 Step 2) 57 is divisible by 3, so, we divide 57 by 3 (and get 19) and add 3 in the list, we get 19 List: 2 3 Step 3) 19 is not divisible by 5 or 7. We will stop here, because the next prime is 11, but we assumed that we will check primes up to 10. So, we are sure that 19 doesn't have any prime divisor less than or equal to 10. So, as we have mentioned already, 19 must be a prime. Thus we add 19 in the list. 1 List: So, to find the prime factorization of a given number, this method will check primes up to sqrt(n), which is far better than the previous one. So, the necessary prime numbers to factorize n is the primes numbers less than or equal to sqrt(n). So, when we generate primes, we can only generate the important primes checking the limit of the test data. For example if the maximum number in the input is , we need to generate primes up to sqrt( ) = So, primes up to 1000 are required only! 5 P a g e
6 The following code implements the idea, which we have just described. int List[128]; // saves the List int listsize; // saves the size of List void primefactorize( int n ) { listsize = 0; // Initially the List is empty, we denote that size = 0 int sqrtn = int( sqrt(n) ); // find the sqrt of the number for( int i = 0; prime[i] <= sqrtn; i++ ) { // we check up to the sqrt if( n % prime[i] == 0 ) { // n is multiple of prime[i] // So, we continue dividing n by prime[i] as long as possible while( n % prime[i] == 0 ) { n /= prime[i]; // we have divided n by prime[i] List[listSize] = prime[i]; // added the ith prime in the list listsize++; // added a prime, so, size should be increased // we can add some optimization by updating sqrtn here, since n // is decreased. think why it's important and how it can be added if( n > 1 ) { // n is greater than 1, so we are sure that this n is a prime List[listSize] = n; // added n (the prime) in the list listsize++; // increased the size of the list int main() { primefactorize( 114 ); for( int i = 0; i < listsize; i++ ) // traverse the List array printf("%d ", List[i]); return 0; Discussion How many primes do we generate? We need the primes to the sqrt(max number in the input). But there can be a problem. In the above algorithm we have used the condition prime[i] <= sqrtn. So, when prime[i] is greater than sqrtn then the loop will terminate, but if we generate primes exactly up to sqrtn, a problem may occur. For example, say we are about to prime factorize 29, and so, we have generated primes 2, 3, 5 only (up to integer part of sqrt(29) = 5). So, prime[0] = 2, prime[1] = 3 and prime[2] = 5. Now in the loop when i becomes 2, so prime[i] = 5 which is less than or equal to square root of 29 and thus the loop will move further. But in the next turn, i increases and becomes 3. But as we have generated only 3 primes (prime[0 to 2]), prime[3] (invalid value) will be compared to sqrt(29). So, when generating primes, be sure that at least one extra prime is generated for safety. 6 P a g e
CHAPTER 5 Pipelined Computations
 CHAPTER 5 Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming.
CHAPTER 5 Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming.
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/85/92778785.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
COP 4516: Math for Programming Contest Notes
 COP 4516: Math for Programming Contest Notes Euclid's Algorithm Euclid's Algorithm is the efficient way to determine the greatest common divisor between two integers. Given two positive integers a and
COP 4516: Math for Programming Contest Notes Euclid's Algorithm Euclid's Algorithm is the efficient way to determine the greatest common divisor between two integers. Given two positive integers a and
Pipelined Computations
 Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming. Each
Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming. Each
UCT Algorithm Circle: Number Theory
 UCT Algorithm Circle: 7 April 2011 Outline Primes and Prime Factorisation 1 Primes and Prime Factorisation 2 3 4 Some revision (hopefully) What is a prime number? An integer greater than 1 whose only factors
UCT Algorithm Circle: 7 April 2011 Outline Primes and Prime Factorisation 1 Primes and Prime Factorisation 2 3 4 Some revision (hopefully) What is a prime number? An integer greater than 1 whose only factors
// initialize array to true. for (i = 0; i < s; i++) f[i] = true; // get rid of known non-primes f[0] = f[1] = false;
![// initialize array to true. for (i = 0; i < s; i++) f[i] = true; // get rid of known non-primes f[0] = f[1] = false; // initialize array to true. for (i = 0; i < s; i++) f[i] = true; // get rid of known non-primes f[0] = f[1] = false;](/thumbs/73/68432618.jpg) Listing 1: GeneratePrimes.java This class Generates prime numbers up to a user specified maximum. The algorithm used is the Sieve of Eratosthenes. Eratosthenes of Cyrene, b. c. 276 BC, Cyrene, Libya
Listing 1: GeneratePrimes.java This class Generates prime numbers up to a user specified maximum. The algorithm used is the Sieve of Eratosthenes. Eratosthenes of Cyrene, b. c. 276 BC, Cyrene, Libya
Other operators. Some times a simple comparison is not enough to determine if our criteria has been met.
 Lecture 6 Other operators Some times a simple comparison is not enough to determine if our criteria has been met. For example: (and operation) If a person wants to login to bank account, the user name
Lecture 6 Other operators Some times a simple comparison is not enough to determine if our criteria has been met. For example: (and operation) If a person wants to login to bank account, the user name
Integers are whole numbers; they include negative whole numbers and zero. For example -7, 0, 18 are integers, 1.5 is not.
 What is an INTEGER/NONINTEGER? Integers are whole numbers; they include negative whole numbers and zero. For example -7, 0, 18 are integers, 1.5 is not. What is a REAL/IMAGINARY number? A real number is
What is an INTEGER/NONINTEGER? Integers are whole numbers; they include negative whole numbers and zero. For example -7, 0, 18 are integers, 1.5 is not. What is a REAL/IMAGINARY number? A real number is
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Math 302 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory. Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus)
 Math 30 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus) March 30, 009 Contents 1 The Integers 3 1.1 Axioms of Z...................................... 3 1.
Math 30 Introduction to Proofs via Number Theory Robert Jewett (with small modifications by B. Ćurgus) March 30, 009 Contents 1 The Integers 3 1.1 Axioms of Z...................................... 3 1.
CSC 1051 Villanova University. CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I. Course website:
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
2-D Arrays. Of course, to set each grid location to 0, we have to use a loop structure as follows (assume i and j are already defined):
 2-D Arrays We define 2-D arrays similar to 1-D arrays, except that we must specify the size of the second dimension. The following is how we can declare a 5x5 int array: int grid[5][5]; Essentially, this
2-D Arrays We define 2-D arrays similar to 1-D arrays, except that we must specify the size of the second dimension. The following is how we can declare a 5x5 int array: int grid[5][5]; Essentially, this
How many positive 3-digit integers from have an odd number of divisors?
 Jan. 4, 2006 How many positive 3-digit integers from have an odd number of divisors? Why is it true that only perfect squares have an odd number of divisors? If a number has an odd number of divisors,
Jan. 4, 2006 How many positive 3-digit integers from have an odd number of divisors? Why is it true that only perfect squares have an odd number of divisors? If a number has an odd number of divisors,
INFO Object-Oriented Programming
 INFO0062 - Object-Oriented Programming Exercise session #1 - Basic Java programs Jean-François Grailet University of Liège Faculty of Applied Sciences Academic Year 2017-2018 Creating a simple Java program
INFO0062 - Object-Oriented Programming Exercise session #1 - Basic Java programs Jean-François Grailet University of Liège Faculty of Applied Sciences Academic Year 2017-2018 Creating a simple Java program
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fifth Edition. Chapter 6: User-Defined Functions I
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fifth Edition Chapter 6: User-Defined Functions I In this chapter, you will: Objectives Learn about standard (predefined) functions and discover
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fifth Edition Chapter 6: User-Defined Functions I In this chapter, you will: Objectives Learn about standard (predefined) functions and discover
Local and Global Variables
 Lecture 10 Local and Global Variables Nearly every programming language has a concept of local variable. As long as two functions mind their own data, as it were, they won t interfere with each other.
Lecture 10 Local and Global Variables Nearly every programming language has a concept of local variable. As long as two functions mind their own data, as it were, they won t interfere with each other.
3. Priority Queues. ADT Stack : LIFO. ADT Queue : FIFO. ADT Priority Queue : pick the element with the lowest (or highest) priority.
 3. Priority Queues 3. Priority Queues ADT Stack : LIFO. ADT Queue : FIFO. ADT Priority Queue : pick the element with the lowest (or highest) priority. Malek Mouhoub, CS340 Winter 2007 1 3. Priority Queues
3. Priority Queues 3. Priority Queues ADT Stack : LIFO. ADT Queue : FIFO. ADT Priority Queue : pick the element with the lowest (or highest) priority. Malek Mouhoub, CS340 Winter 2007 1 3. Priority Queues
Function. Mathematical function and C+ + function. Input: arguments. Output: return value
 Lecture 9 Function Mathematical function and C+ + function Input: arguments Output: return value Sqrt() Square root function finds the square root for you It is defined in the cmath library, #include
Lecture 9 Function Mathematical function and C+ + function Input: arguments Output: return value Sqrt() Square root function finds the square root for you It is defined in the cmath library, #include
Lab 1: Cipher Fundamentals
 Lab 1: Cipher Fundamentals Objective: The key objective of this lab is to be introduced to some of the fundamental principles involved in cryptography, including the usage of Base-64, hexadecimal, the
Lab 1: Cipher Fundamentals Objective: The key objective of this lab is to be introduced to some of the fundamental principles involved in cryptography, including the usage of Base-64, hexadecimal, the
Sorting. CSE 143 Java. Insert for a Sorted List. Insertion Sort. Insertion Sort As A Card Game Operation. CSE143 Au
 CSE 43 Java Sorting Reading: Ch. 3 & Sec. 7.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list
CSE 43 Java Sorting Reading: Ch. 3 & Sec. 7.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list
Streams. CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Spring Term, 2004
 Streams CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Spring Term, 2004 We ve already seen how evaluation order can change behavior when we program with state. Now we want to investigate how
Streams CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Spring Term, 2004 We ve already seen how evaluation order can change behavior when we program with state. Now we want to investigate how
Lesson 4.02: Operations with Radicals
 Lesson 4.02: Operations with Radicals Take a Hike! Sheldon is planning on taking a hike through a state park. He has mapped out his route carefully. He plans to hike 3 miles to the scenic overlook, and
Lesson 4.02: Operations with Radicals Take a Hike! Sheldon is planning on taking a hike through a state park. He has mapped out his route carefully. He plans to hike 3 miles to the scenic overlook, and
Topic 8: Lazy Evaluation
 Topic 8: Lazy Evaluation 1 Recommended Exercises and Readings From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 17.1, 17.2, 17.4, 17.8, 17.23, 17.25, 17.28, 17.29 Readings: Chapter
Topic 8: Lazy Evaluation 1 Recommended Exercises and Readings From Haskell: The craft of functional programming (3 rd Ed.) Exercises: 17.1, 17.2, 17.4, 17.8, 17.23, 17.25, 17.28, 17.29 Readings: Chapter
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Algorithms and Data Structures Dr. Malek Mouhoub Department of Computer Science University of Regina Fall 2002 Malek Mouhoub, CS3620 Fall 2002 1 6. Priority Queues 6. Priority Queues ffl ADT Stack : LIFO.
Algorithms and Data Structures Dr. Malek Mouhoub Department of Computer Science University of Regina Fall 2002 Malek Mouhoub, CS3620 Fall 2002 1 6. Priority Queues 6. Priority Queues ffl ADT Stack : LIFO.
Applied Cryptography and Network Security
 Applied Cryptography and Network Security William Garrison bill@cs.pitt.edu 6311 Sennott Square Lecture #8: RSA Didn t we learn about RSA last time? During the last lecture, we saw what RSA does and learned
Applied Cryptography and Network Security William Garrison bill@cs.pitt.edu 6311 Sennott Square Lecture #8: RSA Didn t we learn about RSA last time? During the last lecture, we saw what RSA does and learned
Number System. Introduction. Natural Numbers (N) Whole Numbers (W) Integers (Z) Prime Numbers (P) Face Value. Place Value
 1 Number System Introduction In this chapter, we will study about the number system and number line. We will also learn about the four fundamental operations on whole numbers and their properties. Natural
1 Number System Introduction In this chapter, we will study about the number system and number line. We will also learn about the four fundamental operations on whole numbers and their properties. Natural
Sorting. CSC 143 Java. Insert for a Sorted List. Insertion Sort. Insertion Sort As A Card Game Operation CSC Picture
 CSC 43 Java Sorting Reading: Sec. 9.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list in sorted
CSC 43 Java Sorting Reading: Sec. 9.3 Sorting Binary search is a huge speedup over sequential search But requires the list be sorted Slight Problem: How do we get a sorted list? Maintain the list in sorted
A lot of people make repeated mistakes of not calling their functions and getting errors. Make sure you're calling your functions.
 Handout 2 Functions, Lists, For Loops and Tuples [ ] Functions -- parameters/arguments, "calling" functions, return values, etc. Please make sure you understand this example: def square(x): return x *
Handout 2 Functions, Lists, For Loops and Tuples [ ] Functions -- parameters/arguments, "calling" functions, return values, etc. Please make sure you understand this example: def square(x): return x *
There are three questions on this exam. You have 2 hours to complete it. Please indent your program so that it is easy for the grader to read.
 There are three questions on this exam. You have 2 hours to complete it. Please indent your program so that it is easy for the grader to read. 1. Write a function named largestadjacentsum that iterates
There are three questions on this exam. You have 2 hours to complete it. Please indent your program so that it is easy for the grader to read. 1. Write a function named largestadjacentsum that iterates
Definition MATH Benjamin V.C. Collins, James A. Swenson MATH 2730
 MATH 2730 Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson s and undefined terms The importance of definition s matter! may be more important in Discrete Math than in any math course that you have had previously.
MATH 2730 Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson s and undefined terms The importance of definition s matter! may be more important in Discrete Math than in any math course that you have had previously.
CSci 1113, Fall 2015 Lab Exercise 4 (Week 5): Write Your Own Functions. User Defined Functions
 CSci 1113, Fall 2015 Lab Exercise 4 (Week 5): Write Your Own Functions User Defined Functions In previous labs, you've encountered useful functions, such as sqrt() and pow(), that were created by other
CSci 1113, Fall 2015 Lab Exercise 4 (Week 5): Write Your Own Functions User Defined Functions In previous labs, you've encountered useful functions, such as sqrt() and pow(), that were created by other
36 Modular Arithmetic
 36 Modular Arithmetic Tom Lewis Fall Term 2010 Tom Lewis () 36 Modular Arithmetic Fall Term 2010 1 / 10 Outline 1 The set Z n 2 Addition and multiplication 3 Modular additive inverse 4 Modular multiplicative
36 Modular Arithmetic Tom Lewis Fall Term 2010 Tom Lewis () 36 Modular Arithmetic Fall Term 2010 1 / 10 Outline 1 The set Z n 2 Addition and multiplication 3 Modular additive inverse 4 Modular multiplicative
The four laws of programs
 Statements 1 2 The four laws of programs 3 These are like Isaac Asimov's 4 laws of robotics: 0: programs must work properly 1: programs must be readable, provided this does not conflict with the previous
Statements 1 2 The four laws of programs 3 These are like Isaac Asimov's 4 laws of robotics: 0: programs must work properly 1: programs must be readable, provided this does not conflict with the previous
3.4. FOR-LOOPS 65. for <v a r i a b l e > in < sequence >:
 3.4. FOR-LOOPS 65 3.4 For-loops In the previous section we looked at while-loops, Python s basic looping structure. There is a second loop construct in Python called a for-loop. This is more specialized.
3.4. FOR-LOOPS 65 3.4 For-loops In the previous section we looked at while-loops, Python s basic looping structure. There is a second loop construct in Python called a for-loop. This is more specialized.
C++ for Everyone, 2e, Cay Horstmann, Copyright 2012 John Wiley and Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Using a Debugger WE5.
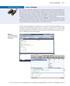 Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Using a Debugger WE5 W o r k E D E x a m p l e 5.2 Using a Debugger As you have undoubtedly realized by now, computer programs rarely run perfectly the first time. At times, it can be quite frustrating
Homework 1: Solution (Sieve of Eratosthenes) 50 Points
 September 24, 2018 Homework 1: Solution (Sieve of Eratosthenes) 50 Points Consider the algorithm named Sieve of Eratosthenes: Sieve Input: an integer n > 1. Let A be an array of Boolean values, indexed
September 24, 2018 Homework 1: Solution (Sieve of Eratosthenes) 50 Points Consider the algorithm named Sieve of Eratosthenes: Sieve Input: an integer n > 1. Let A be an array of Boolean values, indexed
CS102: Standard I/O. %<flag(s)><width><precision><size>conversion-code
 CS102: Standard I/O Our next topic is standard input and standard output in C. The adjective "standard" when applied to "input" or "output" could be interpreted to mean "default". Typically, standard output
CS102: Standard I/O Our next topic is standard input and standard output in C. The adjective "standard" when applied to "input" or "output" could be interpreted to mean "default". Typically, standard output
Casting in C++ (intermediate level)
 1 of 5 10/5/2009 1:14 PM Casting in C++ (intermediate level) Casting isn't usually necessary in student-level C++ code, but understanding why it's needed and the restrictions involved can help widen one's
1 of 5 10/5/2009 1:14 PM Casting in C++ (intermediate level) Casting isn't usually necessary in student-level C++ code, but understanding why it's needed and the restrictions involved can help widen one's
Computer Programming
 Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session: Recap of Arrays and Simultaneous Equations (S31 S35) Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr.
Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak Dr. Supratik Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Session: Recap of Arrays and Simultaneous Equations (S31 S35) Dr. Deepak B. Phatak & Dr.
Repetition Through Recursion
 Fundamentals of Computer Science I (CS151.02 2007S) Repetition Through Recursion Summary: In many algorithms, you want to do things again and again and again. For example, you might want to do something
Fundamentals of Computer Science I (CS151.02 2007S) Repetition Through Recursion Summary: In many algorithms, you want to do things again and again and again. For example, you might want to do something
Python Numbers. Learning Outcomes 9/19/2012. CMSC 201 Fall 2012 Instructor: John Park Lecture Section 01 Discussion Sections 02-08, 16, 17
 Python Numbers CMSC 201 Fall 2012 Instructor: John Park Lecture Section 01 Discussion Sections 02-08, 16, 17 1 (adapted from Meeden, Evans & Mayberry) 2 Learning Outcomes To become familiar with the basic
Python Numbers CMSC 201 Fall 2012 Instructor: John Park Lecture Section 01 Discussion Sections 02-08, 16, 17 1 (adapted from Meeden, Evans & Mayberry) 2 Learning Outcomes To become familiar with the basic
Lab 1: Cipher Fundamentals
 Lab 1: Cipher Fundamentals Objective: The key objective of this lab is to be introduced to some of the fundamental principles involved in cryptography, including the usage of Base-64, hexadecimal, the
Lab 1: Cipher Fundamentals Objective: The key objective of this lab is to be introduced to some of the fundamental principles involved in cryptography, including the usage of Base-64, hexadecimal, the
Q1: Functions / 33 Q2: Arrays / 47 Q3: Multiple choice / 20 TOTAL SCORE / 100 Q4: EXTRA CREDIT / 10
 EECE.2160: ECE Application Programming Spring 2018 Exam 2 March 30, 2018 Name: Lecture time (circle 1): 8-8:50 (Sec. 201) 12-12:50 (Sec. 202) For this exam, you may use only one 8.5 x 11 double-sided page
EECE.2160: ECE Application Programming Spring 2018 Exam 2 March 30, 2018 Name: Lecture time (circle 1): 8-8:50 (Sec. 201) 12-12:50 (Sec. 202) For this exam, you may use only one 8.5 x 11 double-sided page
Discrete Structures Lecture The Basics of Counting
 Introduction Good morning. Combinatorics is the study of arrangements of objects. Perhaps, the first application of the study of combinatorics was in the study of gambling games. Understanding combinatorics
Introduction Good morning. Combinatorics is the study of arrangements of objects. Perhaps, the first application of the study of combinatorics was in the study of gambling games. Understanding combinatorics
3x - 5 = 22 4x - 12 = 2x - 9
 3. Algebra Solving Equations ax + b = cx + d Algebra is like one big number guessing game. I m thinking of a number. If you multiply it by 2 and add 5, you get 21. 2x + 5 = 21 For a long time in Algebra
3. Algebra Solving Equations ax + b = cx + d Algebra is like one big number guessing game. I m thinking of a number. If you multiply it by 2 and add 5, you get 21. 2x + 5 = 21 For a long time in Algebra
Physics 3620/6620 Test # 1-1 -
 Physics 3620/6620 Test # 1-1 - The test is worth 100 points, but a maximum of 120 points are available Problems 1-3 are worth a maximum of 20 points each, and problem #4, with the VI, is worth a maximum
Physics 3620/6620 Test # 1-1 - The test is worth 100 points, but a maximum of 120 points are available Problems 1-3 are worth a maximum of 20 points each, and problem #4, with the VI, is worth a maximum
ECE G205 Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Fall Exercises in Preparation to the Midterm
 ECE G205 Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Fall 2003 Exercises in Preparation to the Midterm The following problems can be solved by either providing the pseudo-codes of the required algorithms or the
ECE G205 Fundamentals of Computer Engineering Fall 2003 Exercises in Preparation to the Midterm The following problems can be solved by either providing the pseudo-codes of the required algorithms or the
Lecture 3. Review. CS 141 Lecture 3 By Ziad Kobti -Control Structures Examples -Built-in functions. Conditions: Loops: if( ) / else switch
 Lecture 3 CS 141 Lecture 3 By Ziad Kobti -Control Structures Examples -Built-in functions Review Conditions: if( ) / else switch Loops: for( ) do...while( ) while( )... 1 Examples Display the first 10
Lecture 3 CS 141 Lecture 3 By Ziad Kobti -Control Structures Examples -Built-in functions Review Conditions: if( ) / else switch Loops: for( ) do...while( ) while( )... 1 Examples Display the first 10
Loop Invariant Examples
 Loop Invariant Examples Page 1 Problems Page 3 Help (Code) Page 5 Solutions (to Help Code) Problems: Exercise 0 @return the average of the list average(double[ ] a) // Yes, this should be as easy as it
Loop Invariant Examples Page 1 Problems Page 3 Help (Code) Page 5 Solutions (to Help Code) Problems: Exercise 0 @return the average of the list average(double[ ] a) // Yes, this should be as easy as it
17. [Exploring Numbers]
![17. [Exploring Numbers] 17. [Exploring Numbers]](/thumbs/92/111022017.jpg) . [Exploring Numbers] Skill. Comparing whole numbers. Compare the size of the digits in the same place, one at a time. Work from left to right across each number. Q. Which number is the A ) 06 B ) 60 C
. [Exploring Numbers] Skill. Comparing whole numbers. Compare the size of the digits in the same place, one at a time. Work from left to right across each number. Q. Which number is the A ) 06 B ) 60 C
A.4 Rationalizing the Denominator
 A.4 Rationalizing the Denominator RATIONALIZING THE DENOMINATOR A.4 Rationalizing the Denominator If a radical expression contains an irrational denominator, such as,, or 0, then it is not considered to
A.4 Rationalizing the Denominator RATIONALIZING THE DENOMINATOR A.4 Rationalizing the Denominator If a radical expression contains an irrational denominator, such as,, or 0, then it is not considered to
6. Asymptotics: The Big-O and Other Notations
 Chapter 7 SEARCHING 1. Introduction, Notation 2. Sequential Search 3. Binary Search 4. Comparison Trees 5. Lower Bounds 6. Asymptotics: The Big-O and Other Notations Outline Transp. 1, Chapter 7, Searching
Chapter 7 SEARCHING 1. Introduction, Notation 2. Sequential Search 3. Binary Search 4. Comparison Trees 5. Lower Bounds 6. Asymptotics: The Big-O and Other Notations Outline Transp. 1, Chapter 7, Searching
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008 Laziness For this lecture, I want to return to something that came up during the last homework, the third homework where
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 13 CSU 370 Fall 2008 (Pucella) Friday, Oct 31, 2008 Laziness For this lecture, I want to return to something that came up during the last homework, the third homework where
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/80/82301067.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. O(logn) 2. O(n) 3. O(nlogn) 4. O(n 2 ) 5. O(2 n ) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. O(logn) 2. O(n) 3. O(nlogn) 4. O(n 2 ) 5. O(2 n ) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Computer Science. INVITATION TO Computer Science 1
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Computer Science INVITATION TO Computer Science 1 Q8. Under what conditions would the well-known quadratic formula not be effectively computable? (Assume that you are working
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Computer Science INVITATION TO Computer Science 1 Q8. Under what conditions would the well-known quadratic formula not be effectively computable? (Assume that you are working
D - Tic Tac Toe. Let's use our 9 sparkles to build a tic tac toe game! 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page 1 of 9
 D - Tic Tac Toe Let's use our 9 sparkles to build a tic tac toe game! 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page 1 of 9 INTRODUCTION Let's use our 9 sparkles to build a tic tac toe game! Step 1 Assemble the Robot
D - Tic Tac Toe Let's use our 9 sparkles to build a tic tac toe game! 2017 courses.techcamp.org.uk/ Page 1 of 9 INTRODUCTION Let's use our 9 sparkles to build a tic tac toe game! Step 1 Assemble the Robot
CSC-140 Assignment 5
 CSC-140 Assignment 5 Please do not Google a solution to these problems, cause that won t teach you anything about programming - the only way to get good at it, and understand it, is to do it! 1 Introduction
CSC-140 Assignment 5 Please do not Google a solution to these problems, cause that won t teach you anything about programming - the only way to get good at it, and understand it, is to do it! 1 Introduction
11.3 Function Prototypes
 11.3 Function Prototypes A Function Prototype contains the function s return type, name and parameter list Writing the function prototype is declaring the function. float square (float x); In a function
11.3 Function Prototypes A Function Prototype contains the function s return type, name and parameter list Writing the function prototype is declaring the function. float square (float x); In a function
Array Elements as Function Parameters
 Arrays Class 26 Array Elements as Function Parameters we have seen that array elements are simple variables they can be used anywhere a normal variable can unsigned values [] {10, 15, 20}; unsigned quotient;
Arrays Class 26 Array Elements as Function Parameters we have seen that array elements are simple variables they can be used anywhere a normal variable can unsigned values [] {10, 15, 20}; unsigned quotient;
In this section we take an aside from the normal discussion in algebra.
 1.5 Set Notation In this section we take an aside from the normal discussion in algebra. We want to take a look at the topic of sets and set notation. The reason we want to do this is so that as we encounter
1.5 Set Notation In this section we take an aside from the normal discussion in algebra. We want to take a look at the topic of sets and set notation. The reason we want to do this is so that as we encounter
CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I
 Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Repetition CSC 1051 Data Structures and Algorithms I Dr. Mary-Angela Papalaskari Department of Computing Sciences Villanova University Course website: www.csc.villanova.edu/~map/1051/ Some slides in this
Object Oriented Programming Using C++ Mathematics & Computing IET, Katunayake
 Assigning Values // Example 2.3(Mathematical operations in C++) float a; cout > a; cout
Assigning Values // Example 2.3(Mathematical operations in C++) float a; cout > a; cout
RBI PHASE 1 RECAP 2 ND JULY 18 QUANT NUMBER SYSTEM
 RBI PHASE 1 RECAP 2 ND JULY 18 QUANT NUMBER SYSTEM Relative primes Two numbers are said to be relative or co-prime if they do not have any common factor other than 1. As 15 and 16 do not have any common
RBI PHASE 1 RECAP 2 ND JULY 18 QUANT NUMBER SYSTEM Relative primes Two numbers are said to be relative or co-prime if they do not have any common factor other than 1. As 15 and 16 do not have any common
>>> * *(25**0.16) *10*(25**0.16)
 #An Interactive Session in the Python Shell. #When you type a statement in the Python Shell, #the statement is executed immediately. If the #the statement is an expression, its value is #displayed. #Lines
#An Interactive Session in the Python Shell. #When you type a statement in the Python Shell, #the statement is executed immediately. If the #the statement is an expression, its value is #displayed. #Lines
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Rational Numbers: Multiply and Divide
 Rational Numbers: Multiply and Divide Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers You know that when you multiply a positive number by a positive number, the result is positive. Multiplication with negative
Rational Numbers: Multiply and Divide Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers You know that when you multiply a positive number by a positive number, the result is positive. Multiplication with negative
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES PART ONE: Problem-Solving Techniques
 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES PART ONE: Problem-Solving Techniques 1 Principles of Programming and Software Engineering 1 const CENTS_PER_DOLLAR = 100; void computechange(int dollarcost, int centscost, int& d,
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES PART ONE: Problem-Solving Techniques 1 Principles of Programming and Software Engineering 1 const CENTS_PER_DOLLAR = 100; void computechange(int dollarcost, int centscost, int& d,
CS 455 Midterm 2 Spring 2018 [Bono] Apr. 3, 2018
![CS 455 Midterm 2 Spring 2018 [Bono] Apr. 3, 2018 CS 455 Midterm 2 Spring 2018 [Bono] Apr. 3, 2018](/thumbs/95/123664282.jpg) Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Midterm 2 Spring 2018 [Bono] Apr. 3, 2018 There are 7 problems on the exam, with 59 points total available. There are 10 pages to the exam (5 pages double-sided),
Name: USC NetID (e.g., ttrojan): CS 455 Midterm 2 Spring 2018 [Bono] Apr. 3, 2018 There are 7 problems on the exam, with 59 points total available. There are 10 pages to the exam (5 pages double-sided),
CS2110 Assignment 2 Lists, Induction, Recursion and Parsing, Summer
 CS2110 Assignment 2 Lists, Induction, Recursion and Parsing, Summer 2008 Due Thursday July 3, 2008, 6:00PM 0 General Instructions 0.1 Purpose This assignment will help you solidify your knowledge of Java
CS2110 Assignment 2 Lists, Induction, Recursion and Parsing, Summer 2008 Due Thursday July 3, 2008, 6:00PM 0 General Instructions 0.1 Purpose This assignment will help you solidify your knowledge of Java
16.216: ECE Application Programming Spring 2015 Exam 2 Solution
 16.216: ECE Application Programming Spring 2015 Exam 2 Solution 1. (20 points, 5 points per part) Multiple choice For each of the multiple choice questions below, clearly indicate your response by circling
16.216: ECE Application Programming Spring 2015 Exam 2 Solution 1. (20 points, 5 points per part) Multiple choice For each of the multiple choice questions below, clearly indicate your response by circling
Programming for Electrical and Computer Engineers. Loops
 Programming for Electrical and Computer Engineers Loops Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 6-1 Iteration Statements C s iteration statements are used to set up loops. A loop is a statement whose job is to repeatedly
Programming for Electrical and Computer Engineers Loops Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 6-1 Iteration Statements C s iteration statements are used to set up loops. A loop is a statement whose job is to repeatedly
Greedy Algorithms. Previous Examples: Huffman coding, Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms
 Greedy Algorithms A greedy algorithm is one where you take the step that seems the best at the time while executing the algorithm. Previous Examples: Huffman coding, Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms Coin
Greedy Algorithms A greedy algorithm is one where you take the step that seems the best at the time while executing the algorithm. Previous Examples: Huffman coding, Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms Coin
Algorithmic Thinking: Computing with Lists
 Algorithmic Thinking: Computing with Lists So Far in Python Data types: int, float, Boolean, string Assignments, function definitions Control structures: For loops, while loops, conditionals Last Lecture
Algorithmic Thinking: Computing with Lists So Far in Python Data types: int, float, Boolean, string Assignments, function definitions Control structures: For loops, while loops, conditionals Last Lecture
Computer Science 136 Spring 2004 Professor Bruce. Final Examination May 19, 2004
 Computer Science 136 Spring 2004 Professor Bruce Final Examination May 19, 2004 Question Points Score 1 10 2 8 3 15 4 12 5 12 6 8 7 10 TOTAL 65 Your name (Please print) I have neither given nor received
Computer Science 136 Spring 2004 Professor Bruce Final Examination May 19, 2004 Question Points Score 1 10 2 8 3 15 4 12 5 12 6 8 7 10 TOTAL 65 Your name (Please print) I have neither given nor received
COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math Prime Numbers January 24, / 15
 COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math January 24, 2017 COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math Prime Numbers January 24, 2017 1 / 15 Outline 1 Prime Numbers The Sieve of Eratosthenes Python Implementations GCD and Co-Primes COMPSCI
COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math January 24, 2017 COMPSCI 230 Discrete Math Prime Numbers January 24, 2017 1 / 15 Outline 1 Prime Numbers The Sieve of Eratosthenes Python Implementations GCD and Co-Primes COMPSCI
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering\ Lecture No. #02 Introduction: GCD
 Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering\ Lecture No. #02 Introduction: GCD In this session, we will write another algorithm to solve a mathematical problem. If you
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering\ Lecture No. #02 Introduction: GCD In this session, we will write another algorithm to solve a mathematical problem. If you
ECE15: Introduction to Computer Programming Using the C Language. Lecture Unit 4: Flow of Control
 ECE15: Introduction to Computer Programming Using the C Language Lecture Unit 4: Flow of Control Outline of this Lecture Examples of Statements in C Conditional Statements The if-else Conditional Statement
ECE15: Introduction to Computer Programming Using the C Language Lecture Unit 4: Flow of Control Outline of this Lecture Examples of Statements in C Conditional Statements The if-else Conditional Statement
Sanjay Rajopadhye Colorado State University
 Sanjay Rajopadhye Colorado State University n Find all the prime numbers up to a given number n n By filtering out the multiples of known primes n Many strategies n Start with a sequential algorithm and
Sanjay Rajopadhye Colorado State University n Find all the prime numbers up to a given number n n By filtering out the multiples of known primes n Many strategies n Start with a sequential algorithm and
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
Building Java Programs Chapter 5 Lecture 5-1: while Loops, Fencepost Loops, and Sentinel Loops reading: 4.1, 5.1 self-check: Ch. 4 #2; Ch. 5 # 1-10 exercises: Ch. 4 #2, 4, 5, 8; Ch. 5 # 1-2 Copyright 2009
1 / 20 2 / 20 3 / 20 4 / 20 5 / 20
 CSC 207 (17fa) Exam 2 Practice Page 1 of 12 Exam 2 Practice (November 10, 2017) This exam is closed-book, notes, and technology. Please do not open the test until the instructor says time has begun. Please
CSC 207 (17fa) Exam 2 Practice Page 1 of 12 Exam 2 Practice (November 10, 2017) This exam is closed-book, notes, and technology. Please do not open the test until the instructor says time has begun. Please
Linked lists (6.5, 16)
 Linked lists (6.5, 16) Linked lists Inserting and removing elements in the middle of a dynamic array takes O(n) time (though inserting at the end takes O(1) time) (and you can also delete from the middle
Linked lists (6.5, 16) Linked lists Inserting and removing elements in the middle of a dynamic array takes O(n) time (though inserting at the end takes O(1) time) (and you can also delete from the middle
Pointers and scanf() Steven R. Bagley
 Pointers and scanf() Steven R. Bagley Recap Programs are a series of statements Defined in functions Can call functions to alter program flow if statement can determine whether code gets run Loops can
Pointers and scanf() Steven R. Bagley Recap Programs are a series of statements Defined in functions Can call functions to alter program flow if statement can determine whether code gets run Loops can
Section A Arithmetic ( 5) Exercise A
 Section A Arithmetic In the non-calculator section of the examination there might be times when you need to work with quite awkward numbers quickly and accurately. In particular you must be very familiar
Section A Arithmetic In the non-calculator section of the examination there might be times when you need to work with quite awkward numbers quickly and accurately. In particular you must be very familiar
UNIT 1: INTEGERS Definition Absolute Value of an integer How to compare integers
 UNIT 1: INTEGERS 1.1. Definition Integers are the set of whole numbers and their opposites. The number line is used to represent integers. This is shown below. The number line goes on forever in both directions.
UNIT 1: INTEGERS 1.1. Definition Integers are the set of whole numbers and their opposites. The number line is used to represent integers. This is shown below. The number line goes on forever in both directions.
Q1: Multiple choice / 20 Q2: Arrays / 40 Q3: Functions / 40 TOTAL SCORE / 100 EXTRA CREDIT / 10
 EECE.2160: ECE Application Programming Spring 2017 Exam 2 March 29, 2017 Name: Section (circle 1): 201 (Dr. Li, MWF 8-8:50) 202 (Dr. Geiger, MWF 12-12:50) For this exam, you may use only one 8.5 x 11 double-sided
EECE.2160: ECE Application Programming Spring 2017 Exam 2 March 29, 2017 Name: Section (circle 1): 201 (Dr. Li, MWF 8-8:50) 202 (Dr. Geiger, MWF 12-12:50) For this exam, you may use only one 8.5 x 11 double-sided
Organizing and Summarizing Data
 Section 2.2 9 Organizing and Summarizing Data Section 2.2 C H A P T E R 2 4 Example 2 (pg. 72) A Histogram for Discrete Data To create a histogram, you have two choices: 1): enter all the individual data
Section 2.2 9 Organizing and Summarizing Data Section 2.2 C H A P T E R 2 4 Example 2 (pg. 72) A Histogram for Discrete Data To create a histogram, you have two choices: 1): enter all the individual data
Administrivia. Last modified: Fri Aug 25 10:59: CS61B: Lecture #2 1
 Administrivia Please make sure you have obtained a Unix account. If you are a concurrent enrollment student not yet on our lists, please tell a TA sothatwecanhaveyouaddedtothoseeligibletoreceiveanaccount.
Administrivia Please make sure you have obtained a Unix account. If you are a concurrent enrollment student not yet on our lists, please tell a TA sothatwecanhaveyouaddedtothoseeligibletoreceiveanaccount.
CS 360 Programming Languages Interpreters
 CS 360 Programming Languages Interpreters Implementing PLs Most of the course is learning fundamental concepts for using and understanding PLs. Syntax vs. semantics vs. idioms. Powerful constructs like
CS 360 Programming Languages Interpreters Implementing PLs Most of the course is learning fundamental concepts for using and understanding PLs. Syntax vs. semantics vs. idioms. Powerful constructs like
Prime Generating Algorithms by Skipping Composite Divisors
 Prime Generating Algorithms by Skipping Composite Divisors Neeraj Anant Pande Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics & Statistics Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya (College), Nanded-431602 Maharashtra, INDIA
Prime Generating Algorithms by Skipping Composite Divisors Neeraj Anant Pande Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics & Statistics Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya (College), Nanded-431602 Maharashtra, INDIA
Scheme Quick Reference
 Scheme Quick Reference COSC 18 Fall 2003 This document is a quick reference guide to common features of the Scheme language. It is not intended to be a complete language reference, but it gives terse summaries
Scheme Quick Reference COSC 18 Fall 2003 This document is a quick reference guide to common features of the Scheme language. It is not intended to be a complete language reference, but it gives terse summaries
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 7 January 30, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 7 1/44 Public-key cryptography RSA Factoring Assumption Computing with Big Numbers Fast Exponentiation
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 7 January 30, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 7 1/44 Public-key cryptography RSA Factoring Assumption Computing with Big Numbers Fast Exponentiation
OPTICAL ERATOSTHENES SIEVE
 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume LVI, Number 1, 2011 OPTICAL ERATOSTHENES SIEVE LIVIU ŞTIRB Abstract. The sieve of Eratosthenes is a simple algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a
STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume LVI, Number 1, 2011 OPTICAL ERATOSTHENES SIEVE LIVIU ŞTIRB Abstract. The sieve of Eratosthenes is a simple algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a
CpSc 421 Final Solutions
 CpSc 421 Final Solutions Do any eight of the ten problems below. If you attempt more than eight problems, please indicate which ones to grade (otherwise we will make a random choice). This allows you to
CpSc 421 Final Solutions Do any eight of the ten problems below. If you attempt more than eight problems, please indicate which ones to grade (otherwise we will make a random choice). This allows you to
Arrays in Functions!
 Arrays in Functions! 1E3! Topic 12! 12 Arrays in Functions 1 Objectives! n This topic should allow students to! n Pass array elements to functions! n Pass whole arrays to functions! n Write functions that
Arrays in Functions! 1E3! Topic 12! 12 Arrays in Functions 1 Objectives! n This topic should allow students to! n Pass array elements to functions! n Pass whole arrays to functions! n Write functions that
The First Real Bug. gdb. Computer Organization I McQuain
 The First Real Bug 1 Debugging vs Testing 2 Software testing is any activity aimed at evaluating an attribute or capability of a program and determining whether it meets its specified results All about
The First Real Bug 1 Debugging vs Testing 2 Software testing is any activity aimed at evaluating an attribute or capability of a program and determining whether it meets its specified results All about
Binary, Hexadecimal and Octal number system
 Binary, Hexadecimal and Octal number system Binary, hexadecimal, and octal refer to different number systems. The one that we typically use is called decimal. These number systems refer to the number of
Binary, Hexadecimal and Octal number system Binary, hexadecimal, and octal refer to different number systems. The one that we typically use is called decimal. These number systems refer to the number of
What is a Fraction? Fractions. One Way To Remember Numerator = North / 16. Example. What Fraction is Shaded? 9/16/16. Fraction = Part of a Whole
 // Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
// Fractions Pages What is a Fraction? Fraction Part of a Whole Top Number? Bottom Number? Page Numerator tells how many parts you have Denominator tells how many parts are in the whole Note: the fraction
Arithmetic Expressions in C
 Arithmetic Expressions in C Arithmetic Expressions consist of numeric literals, arithmetic operators, and numeric variables. They simplify to a single value, when evaluated. Here is an example of an arithmetic
Arithmetic Expressions in C Arithmetic Expressions consist of numeric literals, arithmetic operators, and numeric variables. They simplify to a single value, when evaluated. Here is an example of an arithmetic
For Module 2 SKILLS CHECKLIST. Fraction Notation. George Hartas, MS. Educational Assistant for Mathematics Remediation MAT 025 Instructor
 Last Updated: // SKILLS CHECKLIST For Module Fraction Notation By George Hartas, MS Educational Assistant for Mathematics Remediation MAT 0 Instructor Assignment, Section. Divisibility SKILL: Determine
Last Updated: // SKILLS CHECKLIST For Module Fraction Notation By George Hartas, MS Educational Assistant for Mathematics Remediation MAT 0 Instructor Assignment, Section. Divisibility SKILL: Determine
Recursion. James Brucker
 Recursion James Brucker What is Recursion? Recursion means for a function or method to call itself. A typical example of this is computing factorials: n! = n * (n-1)! Using recursion, we can compute n!
Recursion James Brucker What is Recursion? Recursion means for a function or method to call itself. A typical example of this is computing factorials: n! = n * (n-1)! Using recursion, we can compute n!
