Project BIOS Documentation EECS Fall 2012
|
|
|
- Byron Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Project BIOS Documentation EECS Fall 2012 TAs: Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College of Engineering, University of California, Berkeley Table of Contents Background... 1 Loading the BIOS... 2 Loading Your Own Programs... 2 The BIOS Program... 3 The UART... 4 Command List... 5 Adding Your Own Features... 5 Background For the first checkpoint we have provided you a BIOS written in C that your processor is instantiated with. BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System and forms the bare bones of the CPU system on initial boot up. The primary function of the BIOS is to locate, and initialize the system and peripheral devices essential to the PC operation such as memories, hard drives, and the CPU cores. Once these systems are online, the BIOS locates a boot loader that initializes the operating system loading process and passes control to it. For our project, we do not have to worry about loading the BIOS since the FPGA eliminates that problem for us. Furthermore, we will not deal too much with boot loaders, peripheral initialization, and device drivers as that is beyond the scope of this class. The BIOS for our project will simply allow you to get a taste of how the software and hardware layers come together. The reason why we instantiate the memory with the BIOS is to avoid the problem of bootstrapping the memory which is required on most computer systems today. Throughout the next few checkpoints we will be adding new memory mapped hardware that our BIOS will 1
2 interface with. This document is intended to explain the BIOS for checkpoint 1 and how it interfaces with the hardware. In addition, this document will provide you pointers if you wish to modify the BIOS at any point in the project. Loading the BIOS For the first checkpoint, the BIOS is loaded into the Instruction memory when you first build it. As shown in the Checkpoint 1 specification, this is made possible by instantiating your instruction memory to the BIOS file by building the block RAM with the biosv3.coe file. If you want to instantiate a modified BIOS you will have to change this.coe file in your block RAM directory and rebuild your design and the memory. To do this, simply cd to the /software/biosv3 directory and make the.coe file by running make. This should generate the.coe file using the compiler tailored to our ISA. Copy the resulting.coe file to the instruction memory block RAM directory and build the block RAM. The block RAM will then be built instantiated with the contents of the.coe file. When you get your design to synthesize and impact to the board, open up screen using the same command from Lab 4: screen $SERIALTTY Once you are in screen, if you CPU design is working correctly you should be able to hit Enter and a carrot prompt > will show up on the screen. If this doesn t work, try hitting the reset button on the FPGA which is the center compass switch and hit enter. If you can t get the BIOS carrot to come up, then your design is not working and you will have to fix it. Loading Your Own Programs The BIOS that we provide you is written so that you can actually load your own programs for testing purposes and benchmarking. Once you instantiate your BIOS block RAM with the biosv3.coe file and synthesize your design, you can transfer your own program files over the serial line. To load you own programs into the memory, you need to first have the.coe file for the program compiled. You can do this by copying the software directory of one of our C programs folders in /software directory and editing the files. You can write your own MIPS program by writing test code to the.s file or write your own c code by modifying the.c file. Once you have the.coe file for your program, impact your board with your design and run: coe_to_serial <file name> <target address> 2
3 The <file name> field corresponds to the.coe file that you are to uploading to the instruction memory. The <target address> field corresponds to the location in memory you want to write your program to. Once you have uploaded the file, you can fire up screen and run the command: jal <target hex address> Where the <target hex address> is where you stored the location of the coe file over serial. Note that our design does not implement memory protection so try to avoid storing your program over your BIOS memory. Also note that the instruction memory size for the first checkpoint is limited in address size so large programs may fail to load. The jal command will change the PC to where your program is stored in the instruction memory. The BIOS Program The BIOS itself is a fairly simple program and composes of a glorified infinite loop that waits for user input. If you open the biosv3.c file, you will see that the main method composes of a large for loop that prints a prompt and gets user input by calling the read_token method. If at any time your program execution or BIOS hangs or behaves unexpected, you can hit the reset button on your board to reset the program execution to the main method. The read_token method continuously polls the UART for user input from the keyboard until it sees the character specified by ds. In the case of the BIOS, the termination character read_token is called with is the \0xd character which corresponds to Enter. The read_token method will then return the values that it received from the user. Note that there is no backspace option so if you make a mistake you will have to wait until the next command to fix it. 3
4 Figure 1 BIOS Execution Flow The buffer returned from the read_token method with the user input is then parsed by comparing the returned buffer against commands that the BIOS recognizes. If the BIOS parses a command successfully it will execute the appropriate subroutine or commands. Otherwise it will tell you that the command you input is not recognized. If you want to add commands to the BIOS at any time in the project, you will have to add to the comparisons that follow after the read_token subroutine in the BIOS. The UART You will notice that some of the BIOS execution calls will call subroutines in the uart.c file which takes care of the transmission and reception of byte over the serial line. The uart.c file contains three subroutines. The first subroutine, uwrite_int8 executes a UART transmission for a single byte by writing to the output data register. The second subroutine uwrite_int8s allows you to process an array of type int8_t or chars and send 4
5 them over the serial line. The third routine uread_int8 polls the UART for valid data and reads a byte from the serial line. In essence, these three routines are operating the UART on your design from a software view using the memory mapped I/O. Therefore, in order for the software to operate the memory map correctly, the uart.c module must store and load from the correct addresses as defined by out memory map. You will find the necessary memory map addresses in the uart.h file that conforms to the design specification. Command List The following commands are built into the BIOS that we provide for you. All values are interpreted in hexadecimal and do not require any radix prefix (ex. 0x ). Note that there is not backspace command. jal <hexadecimal address> lw <hexadecimal address> lhu <hexadecimal address> lbu <hexadecimal address> Moves program execution to the specified address Displays word at specified address to screen Displays half at specified address to screen Displays byte at specified address to screen sw <value> <hexadecimal address> Stores specified word to address in memory sh <value> <hexadecimal address> Stores specified half to address in memory sb <value> <hexadecimal address> Stores specified byte to address in memory There is another command file in the main() method that is used only when you execute coe_to_serial. When you execute coe_to_serial, your workstation will initiate a byte transfer by calling this command in the BIOS. Therefore, don t mess with this command too much as it is one of the more critical components of your BIOS. Adding Your Own Features Feel free to modify the BIOS code if you want to add your own features during the project for fun or to make your life easier. If you do choose to modify the BIOS, make sure to preserve essential functionality such as the I/O and the ability to store programs. In order to add features, you can either add to the code in the biosv3.c file or create your own c source and header files. Note that you do not have access to standard c libraries so you will have to add them yourself if you need additional library functionality. 5
EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 2: Cache Integration
 Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 2: Cache Integration Prof. Kris Pister TAs: Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College
Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 2: Cache Integration Prof. Kris Pister TAs: Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College
EECS150 Lab Lecture 5 Introduction to the Project
 EECS150 Lab Lecture 5 Introduction to the Project Ian Juch Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/28/2012 1 Note on Lab4 You should augment the testbenches we
EECS150 Lab Lecture 5 Introduction to the Project Ian Juch Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/28/2012 1 Note on Lab4 You should augment the testbenches we
EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 2: Cache Integration
 Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 2: Cache Integration Prof. John Wawrzynek TAs: Vincent Lee, Shaoyi Cheng Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College of Engineering,
Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 2: Cache Integration Prof. John Wawrzynek TAs: Vincent Lee, Shaoyi Cheng Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College of Engineering,
EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 1: Pipelined MIPS Processor
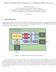 Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 1: Pipelined MIPS Processor Prof. Kris Pister TAs: Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2012 Checkpoint 1: Pipelined MIPS Processor Prof. Kris Pister TAs: Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 Project Introduction (I), Serial I/O. Announcements
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 Project Introduction (I), Serial I/O September 22, 2011 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs150
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 Project Introduction (I), Serial I/O September 22, 2011 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs150
Experiment 6: S-Record Loader
 Experiment 6 6-1 Fall 2004 Experiment 6: S-Record Loader Objectives: To study Motorola S-record format and the code necessary to download object files. To gain more understanding of D-Bug12 and similar
Experiment 6 6-1 Fall 2004 Experiment 6: S-Record Loader Objectives: To study Motorola S-record format and the code necessary to download object files. To gain more understanding of D-Bug12 and similar
EECS150 Lab Lecture 0
 EECS150 Lab Lecture 0 Kris Pister, Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 8/24/2012 EECS150-Fa12-Lab0 1 What is lab lecture?
EECS150 Lab Lecture 0 Kris Pister, Vincent Lee, Ian Juch, Albert Magyar Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 8/24/2012 EECS150-Fa12-Lab0 1 What is lab lecture?
EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification
 EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification Vincent Lee Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/7/2012 EECS150-Fa12-lab1 1 Lab Logistics T minus three weeks-ish
EECS150 Lab Lecture 2 Design Verification Vincent Lee Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley 9/7/2012 EECS150-Fa12-lab1 1 Lab Logistics T minus three weeks-ish
Laboratory Exercise 1: Machine Language Instructions
 Laboratory Exercise 1: Machine Language Instructions Jan Eric Larsson / janeric@eit.lth.se Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University November 26, 2012 Goals After this laboratory
Laboratory Exercise 1: Machine Language Instructions Jan Eric Larsson / janeric@eit.lth.se Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University November 26, 2012 Goals After this laboratory
Laboratory Exercise 3 Comparative Analysis of Hardware and Emulation Forms of Signed 32-Bit Multiplication
 Laboratory Exercise 3 Comparative Analysis of Hardware and Emulation Forms of Signed 32-Bit Multiplication Introduction All processors offer some form of instructions to add, subtract, and manipulate data.
Laboratory Exercise 3 Comparative Analysis of Hardware and Emulation Forms of Signed 32-Bit Multiplication Introduction All processors offer some form of instructions to add, subtract, and manipulate data.
An Introduction to Komodo
 An Introduction to Komodo The Komodo debugger and simulator is the low-level debugger used in the Digital Systems Laboratory. Like all debuggers, Komodo allows you to run your programs under controlled
An Introduction to Komodo The Komodo debugger and simulator is the low-level debugger used in the Digital Systems Laboratory. Like all debuggers, Komodo allows you to run your programs under controlled
Report on the USB Interface
 Report on the USB Interface Ian Coulter July 20, 2008 The USB interface, as it was before any changes were made, is found in c:\licas\tools as USB Control.exe. Changes were made using the c++ files in
Report on the USB Interface Ian Coulter July 20, 2008 The USB interface, as it was before any changes were made, is found in c:\licas\tools as USB Control.exe. Changes were made using the c++ files in
CS150 Fall 2012 Project Checkpoint 3 Version 1.3 Due 11/5/2012 by 5:00pm
 CS150 Fall 2012 Project Checkpoint 3 Version 1.3 Due 11/5/2012 by 5:00pm Prof. Kris Pister Albert Magyar, Vincent Lee, Ian Juch October 29, 2012 1 Interrupts! Interrupts provide a mechanism for devices
CS150 Fall 2012 Project Checkpoint 3 Version 1.3 Due 11/5/2012 by 5:00pm Prof. Kris Pister Albert Magyar, Vincent Lee, Ian Juch October 29, 2012 1 Interrupts! Interrupts provide a mechanism for devices
ECE260: Fundamentals of Computer Engineering
 Accessing and Addressing Memory James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy American
Accessing and Addressing Memory James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy American
ECE260: Fundamentals of Computer Engineering
 Accessing and Addressing Memory James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy American
Accessing and Addressing Memory James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy American
Codewarrior for ColdFire (Eclipse) 10.0 Setup
 Codewarrior for ColdFire (Eclipse) 10.0 Setup 1. Goal This document is designed to ensure that your Codewarrior for Coldfire v10.0 environment is correctly setup and to orient you to it basic functionality
Codewarrior for ColdFire (Eclipse) 10.0 Setup 1. Goal This document is designed to ensure that your Codewarrior for Coldfire v10.0 environment is correctly setup and to orient you to it basic functionality
AN HI-3200 Avionics Data Management Engine Evaluation Board Software Guide
 August 12, 2011 AN - 166 HI-3200 Avionics Data Management Engine Evaluation Board Software Guide Introduction This application note provides more detail on the HI-3200 demo software provided in the Holt
August 12, 2011 AN - 166 HI-3200 Avionics Data Management Engine Evaluation Board Software Guide Introduction This application note provides more detail on the HI-3200 demo software provided in the Holt
LAB C Translating Utility Classes
 LAB C Translating Utility Classes Perform the following groups of tasks: LabC1.s 1. Create a directory to hold the files for this lab. 2. Create and run the following two Java classes: public class IntegerMath
LAB C Translating Utility Classes Perform the following groups of tasks: LabC1.s 1. Create a directory to hold the files for this lab. 2. Create and run the following two Java classes: public class IntegerMath
EE475 Lab #3 Fall Memory Placement and Interrupts
 EE475 Lab #3 Fall 2005 Memory Placement and Interrupts In this lab you will investigate the way in which the CodeWarrior compiler and linker interact to place your compiled code and data in the memory
EE475 Lab #3 Fall 2005 Memory Placement and Interrupts In this lab you will investigate the way in which the CodeWarrior compiler and linker interact to place your compiled code and data in the memory
Homework #4 Processor Core Design
 Homework #4 Processor Core Design Last updated 2016-10-21, changes highlighted in yellow. For this homework, you will be building a single-cycle processor in Quartus II using Structural VHDL, downloading
Homework #4 Processor Core Design Last updated 2016-10-21, changes highlighted in yellow. For this homework, you will be building a single-cycle processor in Quartus II using Structural VHDL, downloading
Lecture 7: Examples, MARS, Arithmetic
 Lecture 7: Examples, MARS, Arithmetic Today s topics: More examples MARS intro Numerical representations 1 Dealing with Characters Instructions are also provided to deal with byte-sized and half-word quantities:
Lecture 7: Examples, MARS, Arithmetic Today s topics: More examples MARS intro Numerical representations 1 Dealing with Characters Instructions are also provided to deal with byte-sized and half-word quantities:
Final Project: LC-3 Simulator
 Final Project: LC-3 Simulator Due Date: Friday 4/27/2018 11:59PM; No late handins This is the final project for this course. It is a simulator for LC-3 computer from the Patt and Patel book. As you work
Final Project: LC-3 Simulator Due Date: Friday 4/27/2018 11:59PM; No late handins This is the final project for this course. It is a simulator for LC-3 computer from the Patt and Patel book. As you work
Memory Usage 0x7fffffff. stack. dynamic data. static data 0x Code Reserved 0x x A software convention
 Subroutines Why we use subroutines more modular program (small routines, outside data passed in) more readable, easier to debug code reuse i.e. smaller code space Memory Usage A software convention stack
Subroutines Why we use subroutines more modular program (small routines, outside data passed in) more readable, easier to debug code reuse i.e. smaller code space Memory Usage A software convention stack
ECE 353 Lab 3. (A) To gain further practice in writing C programs, this time of a more advanced nature than seen before.
 ECE 353 Lab 3 Motivation: The purpose of this lab is threefold: (A) To gain further practice in writing C programs, this time of a more advanced nature than seen before. (B) To reinforce what you learned
ECE 353 Lab 3 Motivation: The purpose of this lab is threefold: (A) To gain further practice in writing C programs, this time of a more advanced nature than seen before. (B) To reinforce what you learned
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 09: Processor / ISA 2
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 09: Processor / ISA 2 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 09: Processor / ISA 2 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
Lab 4 : MIPS Function Calls
 Lab 4 : MIPS Function Calls Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The objective of this lab
Lab 4 : MIPS Function Calls Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The objective of this lab
Operating Systems. Project #2: System Calls
 Operating Systems Project #2: System Calls Project #2: System Calls Objective Background Getting Started Using BIOS Routines Printing to the Screen via the BIOS (Interrupt 0x10) Reading from the Keyboard
Operating Systems Project #2: System Calls Project #2: System Calls Objective Background Getting Started Using BIOS Routines Printing to the Screen via the BIOS (Interrupt 0x10) Reading from the Keyboard
Macs don t have BIOS and some lower-end PCs use either emulated BIOS or the UEFI method. This project assumes an honest-to-goodness PC.
 O.S. Lab 1: Booting We will discuss it in more detail later, but a floppy disk is divided into sectors, each of which is 512 bytes. All reading and writing to the disk must be in whole sectors - it is
O.S. Lab 1: Booting We will discuss it in more detail later, but a floppy disk is divided into sectors, each of which is 512 bytes. All reading and writing to the disk must be in whole sectors - it is
Note that FLIP is an Atmel program supplied by Crossware with Atmel s permission.
 INTRODUCTION This manual will guide you through the first steps of getting the SE-8051ICD running with the Crossware 8051 Development Suite and the Atmel Flexible In-System Programming system (FLIP). The
INTRODUCTION This manual will guide you through the first steps of getting the SE-8051ICD running with the Crossware 8051 Development Suite and the Atmel Flexible In-System Programming system (FLIP). The
instructions aligned is little-endian
 MEMÓRIA Data Types These instructions load and store aligned data: Load word (lw) Load halfword (lh) Load halfword unsigned (lhu) Load byte (lb) Load byte unsigned (lbu) Store word (sw) Store halfword
MEMÓRIA Data Types These instructions load and store aligned data: Load word (lw) Load halfword (lh) Load halfword unsigned (lhu) Load byte (lb) Load byte unsigned (lbu) Store word (sw) Store halfword
Lecture 6: Assembly Programs
 Lecture 6: Assembly Programs Today s topics: Procedures Examples Large constants The compilation process A full example 1 Procedures Local variables, AR, $fp, $sp Scratchpad and saves/restores, $fp Arguments
Lecture 6: Assembly Programs Today s topics: Procedures Examples Large constants The compilation process A full example 1 Procedures Local variables, AR, $fp, $sp Scratchpad and saves/restores, $fp Arguments
Using the KD30 Debugger
 ELEC3730 Embedded Systems Tutorial 3 Using the KD30 Debugger 1 Introduction Overview The KD30 debugger is a powerful software tool that can greatly reduce the time it takes to develop complex programs
ELEC3730 Embedded Systems Tutorial 3 Using the KD30 Debugger 1 Introduction Overview The KD30 debugger is a powerful software tool that can greatly reduce the time it takes to develop complex programs
Experiment #5. Using BIOS Services and DOS functions Part 1: Text-based Graphics
 Experiment #5 Using BIOS Services and DOS functions Part 1: Text-based Graphics 5.0 Objectives: The objective of this experiment is to introduce BIOS and DOS interrupt service routines to be utilized in
Experiment #5 Using BIOS Services and DOS functions Part 1: Text-based Graphics 5.0 Objectives: The objective of this experiment is to introduce BIOS and DOS interrupt service routines to be utilized in
ECE260: Fundamentals of Computer Engineering. Supporting Procedures in Computer Hardware
 Supporting Procedures in Computer Hardware James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy
Supporting Procedures in Computer Hardware James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy
Lecture #6 Intro MIPS; Load & Store
 CS61C L6 Intro MIPS ; Load & Store (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #6 Intro MIPS; Load & Store 2007-7-3 Scott Beamer, Instructor Interesting Research on Social Sites
CS61C L6 Intro MIPS ; Load & Store (1) inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #6 Intro MIPS; Load & Store 2007-7-3 Scott Beamer, Instructor Interesting Research on Social Sites
Lab 4: List Processor and Chipscope
 Lab 4: List Processor and Chipscope University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems John Wawrzynek,
Lab 4: List Processor and Chipscope University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems John Wawrzynek,
EECS Computer Organization Fall Based on slides by the author and prof. Mary Jane Irwin of PSU.
 EECS 2021 Computer Organization Fall 2015 Based on slides by the author and prof. Mary Jane Irwin of PSU. Chapter Summary Stored-program concept Assembly language Number representation Instruction representation
EECS 2021 Computer Organization Fall 2015 Based on slides by the author and prof. Mary Jane Irwin of PSU. Chapter Summary Stored-program concept Assembly language Number representation Instruction representation
Patrick Murray 4/17/2012 EEL4713 Assignment 5
 Patrick Murray 4/17/2012 EEL4713 Assignment 5 Introduction For assignment 5 we were tasked with creating a fully functional pipelined MIPS processor. I used the code and general structure of assignment
Patrick Murray 4/17/2012 EEL4713 Assignment 5 Introduction For assignment 5 we were tasked with creating a fully functional pipelined MIPS processor. I used the code and general structure of assignment
Procedure Calling. Procedure Calling. Register Usage. 25 September CSE2021 Computer Organization
 CSE2021 Computer Organization Chapter 2: Part 2 Procedure Calling Procedure (function) performs a specific task and return results to caller. Supporting Procedures Procedure Calling Calling program place
CSE2021 Computer Organization Chapter 2: Part 2 Procedure Calling Procedure (function) performs a specific task and return results to caller. Supporting Procedures Procedure Calling Calling program place
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board
 Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board
 Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
Lab 0: Introduction to the FPGA Development Board University of California, Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS150 Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems
EXPERIMENT 1. FAMILIARITY WITH DEBUG, x86 REGISTERS and MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS
 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARITY WITH DEBUG, x86 REGISTERS and MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS Pre-lab: This lab introduces you to a software tool known as DEBUG. Before the lab session, read the first two sections of chapter
EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARITY WITH DEBUG, x86 REGISTERS and MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS Pre-lab: This lab introduces you to a software tool known as DEBUG. Before the lab session, read the first two sections of chapter
Spring 2017 :: CSE 506. Device Programming. Nima Honarmand
 Device Programming Nima Honarmand read/write interrupt read/write Spring 2017 :: CSE 506 Device Interface (Logical View) Device Interface Components: Device registers Device Memory DMA buffers Interrupt
Device Programming Nima Honarmand read/write interrupt read/write Spring 2017 :: CSE 506 Device Interface (Logical View) Device Interface Components: Device registers Device Memory DMA buffers Interrupt
CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design. Lab 3 Supplement
 CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design Due 11/13/2013 and 11/20/2013 Lab 3 Supplement Recall and follow the General notes from lab 1. You may work in groups of up to 2 (but no more
CSE/ESE 260M Introduction to Digital Logic and Computer Design Due 11/13/2013 and 11/20/2013 Lab 3 Supplement Recall and follow the General notes from lab 1. You may work in groups of up to 2 (but no more
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Strings and Func.ons. Anything can be represented as a number, i.e., data or instruc\ons
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Strings and Func.ons Instructor: Krste Asanovic, Randy H. Katz hdp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp12 Fall 2012 - - Lecture #7 1 New- School Machine Structures
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Strings and Func.ons Instructor: Krste Asanovic, Randy H. Katz hdp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/sp12 Fall 2012 - - Lecture #7 1 New- School Machine Structures
Slide Set 5. for ENCM 369 Winter 2014 Lecture Section 01. Steve Norman, PhD, PEng
 Slide Set 5 for ENCM 369 Winter 2014 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2014 ENCM 369 W14 Section
Slide Set 5 for ENCM 369 Winter 2014 Lecture Section 01 Steve Norman, PhD, PEng Electrical & Computer Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary Winter Term, 2014 ENCM 369 W14 Section
8032 MCU + Soft Modules. c = rcvdata; // get the keyboard scan code
 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 { 0x25, 0x66 }, // "4" { 0x2E, 0x6D }, // "5" { 0x36, 0x7D }, // "6" { 0x3D, 0x07 }, // "7" { 0x3E, 0x7F }, // "8" { 0x46,
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 { 0x25, 0x66 }, // "4" { 0x2E, 0x6D }, // "5" { 0x36, 0x7D }, // "6" { 0x3D, 0x07 }, // "7" { 0x3E, 0x7F }, // "8" { 0x46,
2.1 DOWNLOAD AND INSTALL MARS
 L a b # 2 T H E R U D I M E N T S O F M I P S A S S E M B L Y L A N G U A G E Instructor: I Putu Danu Raharja. Objectives: Describe the general structure of MIPS assembly language programs. Learn to read
L a b # 2 T H E R U D I M E N T S O F M I P S A S S E M B L Y L A N G U A G E Instructor: I Putu Danu Raharja. Objectives: Describe the general structure of MIPS assembly language programs. Learn to read
Computer Science and Engineering 331. Midterm Examination #1. Fall Name: Solutions S.S.#:
 Computer Science and Engineering 331 Midterm Examination #1 Fall 2000 Name: Solutions S.S.#: 1 41 2 13 3 18 4 28 Total 100 Instructions: This exam contains 4 questions. It is closed book and notes. Calculators
Computer Science and Engineering 331 Midterm Examination #1 Fall 2000 Name: Solutions S.S.#: 1 41 2 13 3 18 4 28 Total 100 Instructions: This exam contains 4 questions. It is closed book and notes. Calculators
Laboratory Exercise 6 Pipelined Processors 0.0
 Laboratory Exercise 6 Pipelined Processors 0.0 Goals After this laboratory exercise, you should understand the basic principles of how pipelining works, including the problems of data and branch hazards
Laboratory Exercise 6 Pipelined Processors 0.0 Goals After this laboratory exercise, you should understand the basic principles of how pipelining works, including the problems of data and branch hazards
Lecture 5: Procedure Calls
 Lecture 5: Procedure Calls Today s topics: Procedure calls and register saving conventions 1 Example Convert to assembly: while (save[i] == k) i += 1; i and k are in $s3 and $s5 and base of array save[]
Lecture 5: Procedure Calls Today s topics: Procedure calls and register saving conventions 1 Example Convert to assembly: while (save[i] == k) i += 1; i and k are in $s3 and $s5 and base of array save[]
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 08 - Project Introduction Part 1
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 08 - Project Introduction Part 1 Feb 9, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec08-proj1 Page 1 Project Overview A. Pipelined CPU review B.MIPS150 pipeline structure
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 08 - Project Introduction Part 1 Feb 9, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec08-proj1 Page 1 Project Overview A. Pipelined CPU review B.MIPS150 pipeline structure
EECS 150 Fall 2013 Checkpoint 1: Pipelined MIPS Processor
 Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2013 Checkpoint 1: Pipelined MIPS Processor Prof. John Wawrzynek TAs: Vincent Lee, Shaoyi Cheng Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College
Memory Arbiter Xilinx MIG EECS 150 Fall 2013 Checkpoint 1: Pipelined MIPS Processor Prof. John Wawrzynek TAs: Vincent Lee, Shaoyi Cheng Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences College
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology INPUT / OUTPUT
 Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture INPUT / OUTPUT Introduction Computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to outside
Eastern Mediterranean University School of Computing and Technology ITEC255 Computer Organization & Architecture INPUT / OUTPUT Introduction Computer system s I/O architecture is its interface to outside
Installing Oracle VirtualBox on Windows 10 and Creating a Starter Boot Disk for a Custom Operating System
 Installing Oracle VirtualBox on Windows 10 and Creating a Starter Boot Disk for a Custom Operating System David J. Walling Twitter: @davidjwalling September 14, 2016 This document describes steps for downloading
Installing Oracle VirtualBox on Windows 10 and Creating a Starter Boot Disk for a Custom Operating System David J. Walling Twitter: @davidjwalling September 14, 2016 This document describes steps for downloading
Assembly labs start this week. Don t forget to submit your code at the end of your lab section. Download MARS4_5.jar to your lab PC or laptop.
 CSC258 Week 10 Logistics Assembly labs start this week. Don t forget to submit your code at the end of your lab section. Download MARS4_5.jar to your lab PC or laptop. Quiz review A word-addressable RAM
CSC258 Week 10 Logistics Assembly labs start this week. Don t forget to submit your code at the end of your lab section. Download MARS4_5.jar to your lab PC or laptop. Quiz review A word-addressable RAM
NOTE: ESCAPE is not always being checked for when the Monitor is performing a selected function,
 Last Updated: December 21, 2018 VIP2K Monitor Program Ver. 1.4 NOTE: RCA Basic 3 by Ron Cenker Copyright 1981 NOTE: The VIP2K Membership Card Kit by Lee Hart, Copyright 2018 NOTE: VIP2K Monitor Program
Last Updated: December 21, 2018 VIP2K Monitor Program Ver. 1.4 NOTE: RCA Basic 3 by Ron Cenker Copyright 1981 NOTE: The VIP2K Membership Card Kit by Lee Hart, Copyright 2018 NOTE: VIP2K Monitor Program
MIPS R-format Instructions. Representing Instructions. Hexadecimal. R-format Example. MIPS I-format Example. MIPS I-format Instructions
 Representing Instructions Instructions are encoded in binary Called machine code MIPS instructions Encoded as 32-bit instruction words Small number of formats encoding operation code (opcode), register
Representing Instructions Instructions are encoded in binary Called machine code MIPS instructions Encoded as 32-bit instruction words Small number of formats encoding operation code (opcode), register
8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses:
 UNIT-III PART -A INTERRUPTS AND PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS Contents at a glance: 8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses Introduction to DOS and BIOS interrupts 8259A Priority Interrupt Controller
UNIT-III PART -A INTERRUPTS AND PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS Contents at a glance: 8086 Interrupts and Interrupt Responses Introduction to DOS and BIOS interrupts 8259A Priority Interrupt Controller
Course Administration
 Fall 2017 EE 3613: Computer Organization Chapter 2: Instruction Set Architecture 2/4 Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701 E-mail: kodi@ohio.edu
Fall 2017 EE 3613: Computer Organization Chapter 2: Instruction Set Architecture 2/4 Avinash Kodi Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701 E-mail: kodi@ohio.edu
CS 410/510. Mark P Jones Portland State University
 CS 41/51 Languages & Low-Level Programming Mark P Jones Portland State University Fall 21 Week 2: Bare Metal and the Boot Process 1 Copyright Notice These slides are distributed under the Creative Commons
CS 41/51 Languages & Low-Level Programming Mark P Jones Portland State University Fall 21 Week 2: Bare Metal and the Boot Process 1 Copyright Notice These slides are distributed under the Creative Commons
Small Computer Monitor User Guide
 Small Computer Monitor User Guide Monitor version 0.5 for the Z80 CPU Software and Documentation by Stephen C Cousins Edition 0.5.0 CONTENTS OVERVIEW...3 Conventions... 3 Serial port... 4 RC2014 systems...
Small Computer Monitor User Guide Monitor version 0.5 for the Z80 CPU Software and Documentation by Stephen C Cousins Edition 0.5.0 CONTENTS OVERVIEW...3 Conventions... 3 Serial port... 4 RC2014 systems...
Your File System Applications What s running on your machine It s own devices Networking. L07 - Getting to know your computer
 Getting to Know Your Computer Your File System Applications What s running on your machine It s own devices Networking Your File System My Computer Directories & Folders Hierarchy File Explorer (Rather
Getting to Know Your Computer Your File System Applications What s running on your machine It s own devices Networking Your File System My Computer Directories & Folders Hierarchy File Explorer (Rather
Special Topics for Embedded Programming
 1 Special Topics for Embedded Programming ETH Zurich Fall 2018 Reference: The C Programming Language by Kernighan & Ritchie 1 2 Overview of Topics Microprocessor architecture Peripherals Registers Memory
1 Special Topics for Embedded Programming ETH Zurich Fall 2018 Reference: The C Programming Language by Kernighan & Ritchie 1 2 Overview of Topics Microprocessor architecture Peripherals Registers Memory
FERGUSON BEAUREGARD. RTU-5000 Configurator User Manual
 FERGUSON BEAUREGARD RTU-5000 Configurator User Manual FERGUSON BEAUREGARD RTU-5000 Configurator User Manual The Ferguson Beauregard RTU-5000 Configurator program and manuals are Copyright 1997-2004 by
FERGUSON BEAUREGARD RTU-5000 Configurator User Manual FERGUSON BEAUREGARD RTU-5000 Configurator User Manual The Ferguson Beauregard RTU-5000 Configurator program and manuals are Copyright 1997-2004 by
NIOS CPU Based Embedded Computer System on Programmable Chip
 NIOS CPU Based Embedded Computer System on Programmable Chip 1 Lab Objectives EE8205: Embedded Computer Systems NIOS-II SoPC: PART-I This lab has been constructed to introduce the development of dedicated
NIOS CPU Based Embedded Computer System on Programmable Chip 1 Lab Objectives EE8205: Embedded Computer Systems NIOS-II SoPC: PART-I This lab has been constructed to introduce the development of dedicated
EECS 151/251 FPGA Project Report
 EECS 151/251 FPGA Project Report GSI: Vighnesh Iyer Team Number: 6 Partners: Ashwinlal Sreelal and Zhixin Alice Ye Due Date: Dec 9, 2016 Part I: Project Description The aims of this project were to develop
EECS 151/251 FPGA Project Report GSI: Vighnesh Iyer Team Number: 6 Partners: Ashwinlal Sreelal and Zhixin Alice Ye Due Date: Dec 9, 2016 Part I: Project Description The aims of this project were to develop
Computer Science 2500 Computer Organization Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring Topic Notes: MIPS Programming
 Computer Science 2500 Computer Organization Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring 2009 Topic Notes: MIPS Programming We spent some time looking at the MIPS Instruction Set Architecture. We will now consider
Computer Science 2500 Computer Organization Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Spring 2009 Topic Notes: MIPS Programming We spent some time looking at the MIPS Instruction Set Architecture. We will now consider
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL. Introduction. Projects. Design Entry
 EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
EE183 LAB TUTORIAL Introduction You will be using several CAD tools to implement your designs in EE183. The purpose of this lab tutorial is to introduce you to the tools that you will be using, Xilinx
Machine Language Instructions Introduction. Instructions Words of a language understood by machine. Instruction set Vocabulary of the machine
 Machine Language Instructions Introduction Instructions Words of a language understood by machine Instruction set Vocabulary of the machine Current goal: to relate a high level language to instruction
Machine Language Instructions Introduction Instructions Words of a language understood by machine Instruction set Vocabulary of the machine Current goal: to relate a high level language to instruction
EEM 486: Computer Architecture. Lecture 2. MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 EEM 486: Computer Architecture Lecture 2 MIPS Instruction Set Architecture EEM 486 Overview Instruction Representation Big idea: stored program consequences of stored program Instructions as numbers Instruction
EEM 486: Computer Architecture Lecture 2 MIPS Instruction Set Architecture EEM 486 Overview Instruction Representation Big idea: stored program consequences of stored program Instructions as numbers Instruction
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 11 SRAM (II), Caches. Announcements
 EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 11 SRAM (II), Caches September 29, 211 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http//www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs15 Fall
EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 11 SRAM (II), Caches September 29, 211 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http//www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs15 Fall
6.S195: Lab 6 6-Stage SMIPS Pipeline with Simple Branch Predictor
 6.S195: Lab 6 6-Stage SMIPS Pipeline with Simple Branch Predictor October 24, 2013 Due: Sunday November 3, 2013 Note: This lab uses a different infrastructure than the previous SMIPS lab in order to compile
6.S195: Lab 6 6-Stage SMIPS Pipeline with Simple Branch Predictor October 24, 2013 Due: Sunday November 3, 2013 Note: This lab uses a different infrastructure than the previous SMIPS lab in order to compile
Prerequisite Quiz January 23, 2007 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2007 John Kubiatowicz Prerequisite Quiz January 23, 2007 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering This
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Computer Science Division EECS Spring 2007 John Kubiatowicz Prerequisite Quiz January 23, 2007 CS252 Computer Architecture and Engineering This
Chapter 2 Operating-System Structures
 This chapter will discuss the following concepts: 2.1 Operating System Services 2.2 User Operating System Interface 2.3 System Calls 2.4 System Programs 2.5 Operating System Design and Implementation 2.6
This chapter will discuss the following concepts: 2.1 Operating System Services 2.2 User Operating System Interface 2.3 System Calls 2.4 System Programs 2.5 Operating System Design and Implementation 2.6
ECE251: Thursday September 27
 ECE251: Thursday September 27 Exceptions: Interrupts and Resets Chapter in text and Lab #6. READ ALL this material! This will NOT be on the mid-term exam. Lab Practical Exam #1 Homework # due today at
ECE251: Thursday September 27 Exceptions: Interrupts and Resets Chapter in text and Lab #6. READ ALL this material! This will NOT be on the mid-term exam. Lab Practical Exam #1 Homework # due today at
3. (3) Convert the following CUSP instruction into the appropriate bit pattern: ADS+! $103
 1. Given the binary bit string 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 (1) What is the Octal representation of this number? (1) What is the Hex representation of this number? What decimal number does it represent if it is: (1)
1. Given the binary bit string 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 (1) What is the Octal representation of this number? (1) What is the Hex representation of this number? What decimal number does it represent if it is: (1)
Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture
 Computer Science 220 Assembly Language & Comp. Architecture Siena College Fall 2011 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture.
Computer Science 220 Assembly Language & Comp. Architecture Siena College Fall 2011 Topic Notes: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture vonneumann Architecture Modern computers use the vonneumann architecture.
Operating Systems. Objective
 Operating Systems Project #1: Introduction & Booting Project #1: Introduction & Booting Objective Background Tools Getting Started Booting bochs The Bootloader Assembling the Bootloader Disk Images A Hello
Operating Systems Project #1: Introduction & Booting Project #1: Introduction & Booting Objective Background Tools Getting Started Booting bochs The Bootloader Assembling the Bootloader Disk Images A Hello
Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University.
 Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
Instructions: ti Language of the Computer Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Computer Hierarchy Levels Language understood
XC866 Getting Started on EasyKit & Toolkits
 March 2005 XC866 on EasyKit & Toolkits Page 1 N e v e r s t o p t h i n k i n g. Overview DAvE! This will get you started in using the XC866. KEIL HiTOP XC800_ FLOAD! You will be introduced to the following
March 2005 XC866 on EasyKit & Toolkits Page 1 N e v e r s t o p t h i n k i n g. Overview DAvE! This will get you started in using the XC866. KEIL HiTOP XC800_ FLOAD! You will be introduced to the following
Orange Coast College. Business Division. Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture. The Instructions
 Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Instructions 1 1 Topics: Assembly language, assemblers MIPS R2000 Assembly language Instruction set
Orange Coast College Business Division Computer Science Department CS 116- Computer Architecture The Instructions 1 1 Topics: Assembly language, assemblers MIPS R2000 Assembly language Instruction set
MIPS Lab Environment Reference 0.0
 MIPS Lab Environment Reference 0.0 The MIPS-Board The lab board (see Figure 1) is the 79S361 from Integrated Device Technology (IDT). It uses the IDT79R36100, a MIPS R3000 based processor, running at 25
MIPS Lab Environment Reference 0.0 The MIPS-Board The lab board (see Figure 1) is the 79S361 from Integrated Device Technology (IDT). It uses the IDT79R36100, a MIPS R3000 based processor, running at 25
MIPS Coding Snippets. Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University. Version of 9:32 PM 14-Feb-2016 Copyright 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved.
 MIPS Coding Snippets Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 9:32 PM 14-Feb-2016 Copyright 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. Loading a 32-bit constant into a register # Example loading
MIPS Coding Snippets Prof. James L. Frankel Harvard University Version of 9:32 PM 14-Feb-2016 Copyright 2016 James L. Frankel. All rights reserved. Loading a 32-bit constant into a register # Example loading
Disk Operating System
 Disk Operating System DOS stands for Disk Operating System. DOS controls the computer s hardware and provides an environment for programs to run. This system program must always be present when working
Disk Operating System DOS stands for Disk Operating System. DOS controls the computer s hardware and provides an environment for programs to run. This system program must always be present when working
Exceptions and Interrupts
 Exceptions and Interrupts Unexpected events (asynchronous interrupt) requiring change in flow of control (different ISAs use the terms differently) exception Arises within the CPU e.g., undefined opcode,
Exceptions and Interrupts Unexpected events (asynchronous interrupt) requiring change in flow of control (different ISAs use the terms differently) exception Arises within the CPU e.g., undefined opcode,
COMP2421 COMPUTER ORGANZATION. Lab 3
 Lab 3 Objectives: This lab shows you some basic techniques and syntax to write a MIPS program. Syntax includes system calls, load address instruction, load integer instruction, and arithmetic instructions
Lab 3 Objectives: This lab shows you some basic techniques and syntax to write a MIPS program. Syntax includes system calls, load address instruction, load integer instruction, and arithmetic instructions
Don t expect to be able to write and debug your code during the lab session.
 EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
EECS150 Spring 2002 Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Lab 4 Verilog Simulation Mapping
Lab 1: Setup 12:00 PM, Sep 10, 2017
 CS17 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Hughes Lab 1: Setup 12:00 PM, Sep 10, 2017 Contents 1 Your friendly lab TAs 1 2 Pair programming 1 3 Welcome to lab 2 4 The file system 2 5 Intro to terminal
CS17 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Hughes Lab 1: Setup 12:00 PM, Sep 10, 2017 Contents 1 Your friendly lab TAs 1 2 Pair programming 1 3 Welcome to lab 2 4 The file system 2 5 Intro to terminal
Roll Call. Erik Jonsson School of Engineering and Computer Science. The University of Texas at Dallas. Lecture #17: Final Session on SPIM; Bonus Set
 Roll Call 1 Requirements for Test #3 Exemption 1. No unexcused absences to end of semester (written excuse required must be MD-verified illness or work-related, with written excuse from supervisor). 2.
Roll Call 1 Requirements for Test #3 Exemption 1. No unexcused absences to end of semester (written excuse required must be MD-verified illness or work-related, with written excuse from supervisor). 2.
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring 2004 Instructor: Dan Garcia CS61C Midterm
 University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring 2004 Instructor: Dan Garcia 2004-03-08 CS61C Midterm Last Name First Name Student
University of California, Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring 2004 Instructor: Dan Garcia 2004-03-08 CS61C Midterm Last Name First Name Student
Experiment #0. PC Hardware and Operating Systems
 Experiment #0 PC Hardware and Operating Systems Objective: The objective of this experiment is to introduce the operating systems and different hardware components of a microcomputer. Equipment: Microcomputer
Experiment #0 PC Hardware and Operating Systems Objective: The objective of this experiment is to introduce the operating systems and different hardware components of a microcomputer. Equipment: Microcomputer
Pre-Lab due: at 3 p.m. Post-Lab due: at 5 p.m. Name:... Forename:... Initials:...
 151-0593-00 Embedded Control Systems (Fall 2018) Lab 1 Topic: Familiarization and Digital I/O Pre-Lab due: 10. 09. 18 at 3 p.m. Post-Lab due: 11. 09. 18 at 5 p.m. Name:... Forename:... Initials:... marianne.schmid@idsc.mavt.ethz.ch,
151-0593-00 Embedded Control Systems (Fall 2018) Lab 1 Topic: Familiarization and Digital I/O Pre-Lab due: 10. 09. 18 at 3 p.m. Post-Lab due: 11. 09. 18 at 5 p.m. Name:... Forename:... Initials:... marianne.schmid@idsc.mavt.ethz.ch,
CSE 351. GDB Introduction
 CSE 351 GDB Introduction Lab 2 Out either tonight or tomorrow Due April 27 th (you have ~12 days) Reading and understanding x86_64 assembly Debugging and disassembling programs Today: General debugging
CSE 351 GDB Introduction Lab 2 Out either tonight or tomorrow Due April 27 th (you have ~12 days) Reading and understanding x86_64 assembly Debugging and disassembling programs Today: General debugging
Week 2: Data and Output
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
CS 170 Java Programming 1 Week 2: Data and Output Learning to speak Java Types, Values and Variables Output Objects and Methods What s the Plan? Topic I: A little review IPO, hardware, software and Java
Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C C: A High-Level Language Gives symbolic names to values don t need to know which register or memory location Provides abstraction of underlying hardware operations
Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C C: A High-Level Language Gives symbolic names to values don t need to know which register or memory location Provides abstraction of underlying hardware operations
i ntel lee 8 Features 5 pecifications
 The widespread usage of low-cost microcomputer systems is made possible by Intel's development and volume production of the MCS-4 and MCS-8 microcomputer sets. To make it easier to use these sets, Intel
The widespread usage of low-cost microcomputer systems is made possible by Intel's development and volume production of the MCS-4 and MCS-8 microcomputer sets. To make it easier to use these sets, Intel
)8-,768'HY.LW 2YHUYLHZ. )XMLWVX0LNURHOHNWURQLN*PE+ Am Siebenstein Dreieich-Buchschlag, Germany
 )8-,768'HY.LW 2YHUYLHZ )XMLWVX0LNURHOHNWURQLN*PE+ Am Siebenstein 6-10 63303 Dreieich-Buchschlag, Germany Revision: V1.0 Date: 05.08.1999 Introduction to FUJITSU Development Kit for 16LX CPU family DevKit16
)8-,768'HY.LW 2YHUYLHZ )XMLWVX0LNURHOHNWURQLN*PE+ Am Siebenstein 6-10 63303 Dreieich-Buchschlag, Germany Revision: V1.0 Date: 05.08.1999 Introduction to FUJITSU Development Kit for 16LX CPU family DevKit16
OPERATING SYSTEM. Functions of Operating System:
 OPERATING SYSTEM Introduction: An operating system (commonly abbreviated to either OS or O/S) is an interface between hardware and user. OS is responsible for the management and coordination of activities
OPERATING SYSTEM Introduction: An operating system (commonly abbreviated to either OS or O/S) is an interface between hardware and user. OS is responsible for the management and coordination of activities
CP/M-86 Compatibility Guide For CP/M-80 Users
 CCGFCU.WS4 ---------- CP/M-86 Compatibility Guide For CP/M-80 Users (= CCGFCU...) Copyright (c) 1980 Digital Research Pacific Grove, California (Revision of 10/21/80) (= 21 October 1980) (Retyped by Emmanuel
CCGFCU.WS4 ---------- CP/M-86 Compatibility Guide For CP/M-80 Users (= CCGFCU...) Copyright (c) 1980 Digital Research Pacific Grove, California (Revision of 10/21/80) (= 21 October 1980) (Retyped by Emmanuel
