Technical evaluation of EIZO RadiForce RX850 8MP monitor
|
|
|
- Pearl Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technical evaluation of EIZO RadiForce RX850 8MP monitor NCCPM Technical Report 1801 June 2018 Cecilia J Strudley, Lucy M Warren and Kenneth C Young
2 2
3 Acknowledgements The authors are grateful to the staff at the Jarvis Breast Screening Centre, Guildford, for their assistance with the evaluation of this equipment. Funding This study was funded for the NHS Breast Screening Programme by Public Health England. One of the authors (LMW) works on the OPTIMAM 2 research programme funded by Cancer Research UK (C30682/A17321). 3
4 Contents Executive summary 5 1. Introduction Testing procedures and performance standards for image display Objectives 6 2. Methods System tested Physics QC tests Observer study 8 3. Results Physics QC tests Observer study Discussion Physics QC tests Comparison of observer performance between monitors The effect of using quadrant view in addition to full field view Study design Summary Conclusions 19 References 20 Appendix 1: Manufacturer s comments 21 Appendix 2: Jack-knife alternative free-response receiver operating characteristic 22 Appendix 3: Results for individual observers 23 4
5 Executive summary The objective of this evaluation was to determine whether use of the EIZO 8MP monitor would make any difference to cancer detection in breast screening if used as an alternative to a pair of conventional 5MP monitors. A study was carried out where seven observers assessed three hundred cases using a pair of 5MP monitors and a single 8MP monitor. No significant difference was found between the monitors when quadrant view was used in addition to full field view. When only the full field view was used, observers perform marginally better in detecting malignant calcifications using the pair of 5MP monitors. When readers are generalised to the population, this difference becomes non-significant. Therefore, if only the full field view is used to view subtle or very subtle calcification clusters, without zooming, then the 8MP monitor may not be a suitable replacement for the pair of 5MP monitors. However, provided that all images are magnified at least to the extent that image pixels are mapped 1:1 to the monitor pixels, no significant disadvantage in using the 8MP monitor has been demonstrated. The 8MP monitor is also able to display colour images, which were not assessed during this evaluation. Performance in detecting calcifications was considerably improved by using quadrant view in addition to full field view when using either the pair of 5MP monitors or the 8MP monitor. 5
6 1. Introduction It is current practice in the NHSBSP that a pair of 5MP monitors is used to display mammograms when reporting screening mammograms. Recent innovations in display technology have made available larger format monitors allowing display of a pair of mammograms on a single monitor at a similar resolution. This evaluation is of an EIZO 8MP colour monitor, which approximates to a pair of 4MP displays on a single screen. 1.1 Testing procedures and performance standards for image display Current guidelines for the testing of pairs of 5MP mammography displays are given in NHSBSP Equipment Report , and include measurements of the dynamic range of the display, the matching and uniformity of luminance of the pair of monitors, a test of the resolution of the display and conformance to the DICOM greyscale standard. These tests were carried out on the 8MP monitor. However, additional tests were needed to determine the effect, if any, of using a single 8MP display instead of the conventional pair of 5MP monitors. A study was carried out to compare the performance of observers using a conventional pair of 5MP monochrome EIZO monitors to that when using the EIZO 8MP colour monitor to display mammograms. There was no assessment of the colour performance. 1.2 Objectives The objectives of this evaluation were: to evaluate the performance of the EIZO 8MP monitor to determine whether use of the EIZO 8MP monitor would make any difference to cancer detection in breast screening, if used as an alternative to a pair of conventional 5MP monitors. 6
7 2. Methods 2.1 System tested The equipment tested was an EIZO RadiForce RX850 8MP colour monitor which is an LED backlit LCD display. For comparison, tests were also carried out on a pair of EIZO 5MP monochrome monitors. Details of the monitors used in this evaluation are given in Table 1 and Figure 1. Table 1. Details of the monitors used in this evaluation 8MP monitor Pair of 5MP monitors Model RadiForce RX 850 GX540-CL Serial number(s) and Date of manufacture November 2014 September 2009 Format 4096 pixels x 2160 pixels Each: 2048 pixels x 2560 pixels Pixel pitch mm x mm mm x mm Viewable image size mm x mm Each: mm x mm 4096 pixels 4096 (2x 2048) pixels 2160 pixels 2560 pixels Figure 1. Dimensions of the two monitor types used in this evaluation. The 8MP monitor is shown on the left and the pair of 5MP monitors on the right The width of the 8MP monitor in pixels is equivalent to the combined width of the two 5MP monitors (4096 pixels versus 2 x 2048 pixels), though the physical width of the viewable image is slightly greater (by 3%) for the 8MP monitor (698 mm versus 2 x 338 mm) due to the increased pixel pitch. The height of the 8MP monitor in pixels is significantly less than the height of the 5MP monitors (2160 pixels versus 2560 pixels) and the physical height of the viewable image is 87% of the viewable image height for the 5MP (368 mm versus 422 mm). 7
8 2.2 Physics QC tests Physics tests were carried out on the 8MP monitor and on the pair of 5MP monitors used for comparison in the observer study. Measurements were made using an external light-meter. Ambient lighting for the observer study was measured at the centre of each screen with the sensor pointing outwards under various conditions. As recommended in NHSBSP 0604, test patterns designed by the American Association of Physics in Medicine (AAPM) were used in this evaluation. These test patterns are available at euref.com. AAPM TG18-QC was displayed on each monitor and the visibility of the resolution gratings, difference between adjacent greyscale squares and corner patches within each greyscale square and sharpness of high and low contrast lines and borders were assessed. Further assessment of the resolution was made using the TG18-LPV-50 and LPH-50 line pair patterns. To measure luminance uniformity and to compare central luminance of the two halves of the 8MP display and of the two 5MP displays, use was made of the AAPM TG18-UN80 test pattern. Greyscale DICOM conformance was measured using the AAPM TG18 greyscale steps. The ambient luminance was measured with the sensor facing each monitor at a distance of 30cm with the monitors off. 2.3 Observer study Seven observers (4 radiologists and 3 radiographers), with an average of 8.8 years of experience (range one to twenty four years) were enrolled for the observer study. They had read an average of 6700 mammograms per annum (range 3200 to 12000), 300 clinical cases, imaged using Hologic Selenia mammography systems, were selected from the pool of mammograms in the OPTIMAM image database 2,3. The cases comprised 100 normal cases and 200 cases with biopsy proven cancers of subtle or very subtle appearance. Of these, 100 cases included calcifications and 100 cases included non-calcified lesions. The women whose cases were normal had since returned for the next screening episode and the screening images were found to be still normal. The cases containing calcifications included 111 malignant clusters and 8 benign clusters. The cases containing non-calcified lesions included 101 lesions, of which 45 appeared as a mass, as opposed to a focal asymmetry or distortion. Seven of these were spiculated and 38 were ill-defined. The locations and conspicuity of the cancers were recorded by experienced radiologists in advance of the study and the diagnosis for each cancer was confirmed by checking the pathology data records. Although each case included two views of each breast, only one view per breast was used for the study. For cases including a cancer, the view where the cancer was least obvious was selected, provided that it was judged to be visible. For normal cases the view to be used was randomly selected. Thus, for the study, each case consisted of a pair of CC or MLO views. Two thirds of the cases included a cancer of subtle or very subtle appearance, and some cases included more than one cancer in which case one of 8
9 the cancers may have been of obvious appearance. The least conspicuous cancers were used for this study in order to maximise the sensitivity of the study to any differences in cancer detection. The study was conducted using MedXViewer software 4, which allows the observer to mark suspected cancers on the images and record answers to questions about each mark. It was expected that any difference in the visibility of cancers between the two types of monitor would be greatest when entire images were viewed, due to the smaller screen size and reduced number of pixels for those displayed on the 8MP monitor. However in clinical practice readers normally use quadrant view and zoom as well, which may overcome any effect due to these differences between the two display types. It was therefore decided to make the assessment of each case a two stage process. Each case was first displayed full field and the observers were asked to mark any cancers and give their overall assessment of the case. Next the same case was made available in quadrant view (1:1 pixel in image to pixel on monitor), and the observers were able to cycle through the quadrant views and the full field view, change, remove or add marks made in the first stage, and then reassess the case. Cases were divided into five sets of 60 cases and each set was read by each observer on each monitor type, alternating between the two types of monitor. The sets were sequenced differently for each observer and the order in which cases within each set were presented was randomised for each observer. Restrictions were placed on the pace of the study, such that there was a minimum of two weeks before observers saw any case for the second time, to reduce any risk of cases being remembered. Observers were also restricted to a maximum of two sets of cases per day to avoid fatigue. Prior to the main study a set of 15 cases containing more obvious cancers were used for training purposes to familiarise the observers with the software and to test the study setup. Observers were instructed to work in ambient light conditions conforming to the NHSBSP standard, as described in section 3.1. Observers were first presented with a pair of MLO or CC images for each case, displayed full field, with quadrant view and magnification controls disabled, and asked to mark any possible cancers they could see. Cancers were marked electronically using the mouse pointer and a right click to indicate the position of the possible cancer. A box was then displayed on the screen asking the following three questions about that mark. The responses available for selection are shown in brackets after each question below: 1. What type of cancer is this? (Calcification cluster / Calcified lesion / Non-calcified lesion) 2. How confident are you that this is a cancerous calcification cluster / calcified lesion / noncalcified lesion? (Slider bar to indicate 1% to 100%) 3. Would you recall on the basis of this lesion? (Yes / No) 9
10 When the observer had finished marking any cancers they could see they were instructed to press enter on the keyboard. For the second stage of the assessment of each case the views retained any marks made in the first stage. Quadrant view was enabled allowing the observers to step through the four quadrant views as well as the full field view. Observers were asked to review any marks already made and to look for any further cancers. Options were available to change responses given to questions regarding each mark made in the first stage, to delete marks and to add further marks. When the observers had finished the second stage they were instructed to again press enter in order to move on to the next case. Reader marks for both stages of each case were recorded in a database and retrieved for later analysis. The data recorded included date and time information so that case reading speeds could be compared for the two monitor types. Each mark made was compared to the ground truth data stored for each image. If the position of the mark fell within the boundary of a recorded cancer the mark was designated a true positive. Where more than one mark was made within a single recorded cancer then the mark with the highest confidence rating was used and the others discarded. Marks, on the basis of which observers had indicated that they would recall a case for further assessment, were classified as either true positives or false positives. These, together with data on all the cases in the study, were fed into JAFROC analysis software. Analysis was carried out using Chakraborty s JAFROC analysis software (version 4) 5. A brief explanation of JAFROC analysis is found at Appendix 2. 10
11 3. Results 3.1 Physics QC tests The results of the Physics QC tests are summarised in Table 2 below. Measurements of ambient illuminance were found to be within the 10 lux limit providing the overhead lights were dimmed to the minimum setting and the light-box turned off. The visual assessment of greyscale contrast steps indicated satisfactory contrast across the greyscale range. For both the 8MP and the pair of 5MP monitors, the steps in contrast between adjacent squares were noticeable, contrasts of 5% on 0% and 95% on 100% luminance were visible and +/-1.6% corner patches on each of the contrast squares were just discernible, with the exception of the black for both monitor types. High contrast borders appeared sharp with no smearing or artefacts for either monitor type. When viewing the TG18-QC test pattern, the high contrast resolution gratings of 2 pixel and 1 pixel line width were resolved with the naked eye at all positions on both monitor types, as were the 2 pixel low contrast lines. Using a magnifying glass, low contrast single pixel line pairs were seen on the 5MP monitors, but not on the 8MP monitor. The assessment was repeated using the TG18-LPV-50 and LPH-50 test patterns to display the narrow low contrast resolution grating over a larger area. It was possible to resolve these test patterns on both monitor types. When a uniform 10% luminance was displayed on the two monitor types, a slight difference in the shade of grey was noticed. The 5MP monitor had a slightly pinkish hue with some angular dependence, whereas the 8MP monitor displayed a colder blue shade of grey. Both monitor types conformed to the uniformity standard, which stipulates a maximum deviation of 30% from the luminance at the centre of the screen. The matching of luminance between the two 5MP monitors conformed to the standard which stipulates a maximum difference of 5%. This limit was also satisfied when applied to the left and right halves of the 8MP monitor. Measurements showed that both monitor types conformed to within 10% of the DICOM greyscale standard. 11
12 Table 2. Summary of physics QC test results Test Limiting value Left 5MP Right 5MP 8MP Lmin <1.5 cd/m Lmax >450 cd/m Luminance ratio (Lmax/Lmin) > Ambient luminance <0.4*Lmin 0.27*Lmin 0.24*Lmin 0.17*Lmin Visual Noticeable difference between 0% Yes Yes Yes assessment of greyscale steps and 5% and between 95% and 100% luminance Sharpness No artefacts, smearing OK OK OK Resolution All contrast line pairs seen OK OK Partially OK Luminance uniformity Max 30% difference from centre 3% 2% 3% (3% & 2%)* Matching Max 5% difference in white luminance between centres of left & right displays 2.5% 3% DICOM greyscale Max deviation of 10% 3.1% 3.9% 5.6% standard *For the 8MP monitor results are shown treating it both as a single display and in brackets as two adjacent displays, left and right 3.2 Observer study Comparison of two monitor types: Detection rates Detection rates were calculated in terms of the proportion of confirmed cancers that each reader correctly located and would recall. The mean detection rates for viewing calcification clusters or non-calcified lesions on each monitor type using full field view only or full field plus quadrant views are shown in Figures 2 and 3 below. 12
13 1.0 Full field view Full field + quadrant view Detection rate x5MP 8MP 2x5MP 8MP 50% 44% 65% 64% Figure 2. Mean cancer detection rates for calcification clusters viewed on each monitor type using full field view only or full field view plus quadrant views 1.0 Full field view Full field + quadrant view Detection rate x5MP 8MP 2x5MP 8MP 56% 55% 63% 61% Figure 3. Mean cancer detection rates for non-calcified lesions viewed on each monitor type using full field view only or full field view plus quadrant views Comparison of two monitor types: JAFROC analysis The JAFROC analysis used has greater statistical power than ROC analysis because true positives are only generated when the location of a cancer is correctly identified. JAFROC analysis results are in terms of a figure of merit, which is the area under the curve in the plot of lesion localisation fraction versus false positive fraction. The mean figures of merit for the seven readers were obtained for calcification clusters and for non-calcified lesions. These figures of merit are presented in Table 3. 13
14 Table 3. Mean figures of merit for calcification clusters and non-calcified lesions when cases are viewed full field, and full field plus quadrant view FOM (full field view) FOM (full field plus quadrant view) 2x 5MP 8MP 2x 5MP 8MP Calcifications Non-calcified lesions * Result indicating statistically significant difference between the two monitor types The differences between the two monitor types and the p values for these differences resulting from two analyses: Analysis 1 (random reader and random case) and Analysis 2 (fixed reader and random case) are shown in Figures 4 and 5. In each graph the differences in the figures of merit are presented with error bars showing the 95% confidence limits on these differences. In each case the figure of merit for the 8MP monitor is subtracted from that for the pair of 5MP monitors such that a positive difference indicates a better performance for the pair of 5MP monitors and a negative difference indicates better performance for the 8MP monitor. Where the error bars straddle the x axis, the difference calculated is not statistically significant. C a lc ific a tio n c lu s te rs F u ll fie ld v ie w N o n -c a lc ifie d le s io n s F u ll fie ld v ie w F O M d iffe re n c e (2 x 5 M P - 8 M P ) A n a ly s is 1 A n a ly s is 2 Figure 4. Difference in figure of merit between pair of 5MP monitors and 8MP monitor when calcification clusters or non-calcified lesions are viewed full field. The error bars indicate the 95% confidence limits for Analysis 1 (random reader and random case) and Analysis 2 (fixed reader and random case). F O M d iffe re n c e (2 x 5 M P - 8 M P ) A n a ly s is 1 A n a ly s is 2 14
15 C a lc ific a tio n c lu s te rs F u ll fie ld + q u a d ra n t v ie w N o n -c a lc ifie d le s io n s F u ll fie ld + q u a d ra n t v ie w F O M d iffe re n c e (2 x 5 M P - 8 M P ) A n a ly s is 1 A n a ly s is 2 Figure 5. Difference in figure of merit between pair of 5MP monitors and 8MP monitor when calcification clusters or non-calcified lesions are viewed using quadrant view in addition to full field. The error bars indicate the 95% confidence limits for Analysis 1 (random reader and random case) and Analysis 2 (fixed reader and random case). F O M d iffe re n c e (2 x 5 M P - 8 M P ) A n a ly s is 1 A n a ly s is Effect of using quadrant view in addition to full field view An improvement in cancer detection was noted when quadrant view was used in addition to full field view. Tables 4 and 5 show the differences in figure of merit between full field view and full field plus quadrant view for the pair of 5MP monitors and for the 8MP monitor, together with the p values for Analysis 1 and Analysis 2. Table 4. Mean figures of merit for pair of 5MP monitors, with p values calculated for Analysis 1 (random reader and random case) and Analysis 2 (fixed reader and random case) FOM (2 x 5MP) p value Full field view Full field + quadrant view Difference Analysis 1 Analysis 2 Calcifications * 0.000* Non-calcified lesions * Result indicating statistically significant difference between the two monitor types 15
16 Table 5. Mean figures of merit for 8MP monitor, with p values calculated for Analysis 1 (random reader and random case) and Analysis 2 (fixed reader and random case) FOM (8MP) p value Full field view Full field + quadrant view Difference Analysis 1 Analysis 2 Calcifications * 0.000* Non-calcified lesions * Result indicating statistically significant difference between the two monitor types The results shown in Tables 4 and 5 (Analysis 2) is also presented graphically in Figure 6. A difference greater than zero indicates better performance when using quadrant view in addition to full field view. C a lc ific a tio n c lu s te rs N o n -c a lc ifie d le s io n s F O M d iffe re n c e (F F + Q - F F ) x 5 M P 8 M P Figure 6. Difference in figure of merit between full field view only and full field plus quadrant views for the pair of 5MP and for 8MP monitors when viewing calcification clusters or non-calcified lesions. The error bars indicate the 95% confidence limits for Analysis 2 (fixed reader and random case). F O M d iffe re n c e (F F + Q - F F ) x 5 M P 8 M P 16
17 4. Discussion 4.1 Physics QC tests Tests carried out on the pair of 5MP monitors and on the 8MP monitor showed that they mostly met the NHSBSP standards for digital mammography. It was more difficult to see the low contrast narrow (single pixel) line pairs on the 8MP monitor than on the pair of 5MP monitors. They were only visible when displayed full-screen on the 8MP monitor. 4.2 Comparison of observer performance between monitors The greatest difference in detection (recall) rate between the two monitor types was found when viewing calcification clusters using full field view only. (50% for the pair of 5MP monitors and 44% for the 8MP monitor). When using quadrant view in addition to full field view, or when viewing non-calcified lesions, the differences in detection rates for the two monitor types were reduced to one or two percent JAFROC analysis software was used to generate figures of merit indicating the mean performance of the observers, taking account of false positives as well as correct lesion localisations. This statistical analysis includes an estimate of the significance of differences in figures of merit between modalities. When mammograms were displayed using full field view only, the mean JAFROC figure of merit for the pair of 5MP monitors was significantly better (p=0.05) when viewing calcification clusters and using Analysis 2 (fixed reader, random case). Differences when viewing non-calcified lesions, or using Analysis 1 (random reader, random case) for any lesion type, were not statistically significant. When quadrant view was used in addition to full field view, JAFROC analysis showed no statistically significant differences between the two types of display. 4.3 The effect of using quadrant view in addition to full field view Detection rates when using quadrant view in addition to full field view were in all cases greater than when using full field view only, and the observed differences were greatest when viewing calcification clusters. For example, when using a pair of 5MP monitors to view calcification clusters, the use of quadrant view improved the detection rate from 50% to 65%. JAFROC figures of merit were used to test the effect of using quadrant view in addition to full field view. The additional use of quadrant view gave statistically significant improvements in performance (p<0.001) when viewing calcification clusters on either type of display, using either 17
18 Analysis 1 or Analysis 2. Differences in performance when viewing non-calcified lesions were not statistically significant. It should be noted that the observer study was designed to compare the two types of display rather than the effect of using quadrant view in addition to full field view. As each case was assessed using full field view, immediately followed by additional use of the quadrant views, the two modalities were not independent and the validity of the statistical analysis in this regard is therefore questionable. The magnitude of the effect of using quadrant views may be actually be less than that measured in this study, but this study does illustrate the considerable advantage that one may expect from using magnified views in addition to full field views for the detection of calcification clusters. 4.4 Study design In this study all the cancers used were subtle or very subtle, assuming that the detection of more obvious cancers would be less sensitive to the monitor used. In the screening environment, a much wider range in visibility of cancer is present. Calculating the proportion of malignant cancers detected through screening which have the same characteristics as the cancers used in this study would allow us to calculate the expected change in cancer detection in a screening environment, which corresponds to the change in cancer detection found in this study. 4.5 Summary This study has demonstrated the clear advantage of using magnified views in addition to the full field view in detecting calcification clusters, regardless of whether one is using a pair of 5MP monitors or the single 8MP monitor. It has also shown that if only the full field view is used to view subtle or very subtle calcification clusters, without zooming, then the 8MP monitor may not be a suitable replacement for the pair of 5MP monitors. However, provided that all images are magnified at least to the extent that image pixels are mapped 1:1 to the monitor pixels, no significant disadvantage in using the 8MP monitor has been demonstrated. The 8MP monitor is also able to display colour images, which were not assessed during this evaluation. 18
19 5. Conclusions Physics QC tests conducted on the 8MP mammography display demonstrated compliance with all the requirements of the NHSBSP standards for primary displays, except one, which failed (visibility of low-contrast line pairs on the TG-18 QC pattern). The low contrast line pairs were only visible when displayed full screen on the 8MP monitor. When quadrant view was used in addition to full field view there was no significant difference between using the pair of 5MP monitors and using the 8MP monitor to detect malignant calcifications or non-calcified lesions. When only the full field view was used, observers perform marginally better (p=0.050) in detecting malignant calcifications using the pair of 5MP monitors. When readers are generalised to the population, this difference becomes non-significant. There was no significant difference between the monitors for the detection of malignant non-calcified lesions when only full field view was used. Performance in detecting calcifications was improved by using quadrant view in addition to full field view when using either the pair of 5MP monitors or the 8MP monitor. 19
20 References 1. Kulama E, Burch A, Castellano I et al. Commissioning and routine testing of full field digital mammography systems (NHSBSP Equipment Report 0604, Version 3). Sheffield: NHS Cancer Screening Programmes, Halling-Brown MD, Looney PT, Patela MN et al. The Oncology Medical Image Database (OMI-DB). Proceedings of SPIE 9039 (2014) 3 Halling-Brown MD, Looney PT, Patela MN et al. Mammographic image database (MIDB) and associated web-enabled software for research. In: Fujita H, Hara T, Muramatsu C, editors. Breast imaging, 12 th international workshop, IWDM 2014, vol LNCS; p Looney P T, Young K C, Mackenzie A et al. MedXViewer: An extensible web-enabled software package for medical imaging. Proceedings of SPIE 9037 (2014) 5. Chakraborty D P and Berbaum K. S. Observer studies involving detection and localization: Modelling, analysis, and validation. Med. Phys. 31, (2004). 20
21 Appendix 1: Manufacturer s comments EIZO are pleased with the finding that an 8MP does not reduce the ability of a reader to diagnose breast images in quadrant view (see section 5). The goal of the product is to make a workstation more flexible by having colour while not reducing the viewer s ability to read breast images. As colour becomes a greater part of radiological imaging in the future, the ability to show colour in an image will become more important. The viewer should also find that they experience less eye fatigue using a single display instead of two separate units as they eye does not have to sweep across the dark section in the centre of the field of view due to the two separate displays having wide bezels. Any reduction in bezel width should allow the user to see more of the important radiological images and less of the unimportant plastic of the bezel. EIZO felt that the testing was very well thought out and conducted to give fair results. 21
22 Appendix 2: Jack-knife alternative freeresponse receiver operating characteristic In Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis, cases are assessed for disease probability and rated according to the risk of malignancy. Comparing assessments against the truth for each case allows each assessment to be categorised as a true positive (TP) or true negative (TN). The true positive fraction (TPF) is obtained by dividing the number of TPs by the total number of malignant cases. The false positive fraction (FPF) is obtained by dividing the number of FPs by the total number of normal cases. TPF is plotted against FPF, with multiple points corresponding to different operating points as denoted by the confidence rating level selected. The area under the curve is used as a figure of merit. The maximum area under the curve is one, corresponding to a perfect diagnostic system. Guessing the diagnosis, where half of the cases are malignant, would give an area under the curve of 0.5. ROC analysis takes no account of the location of any detected lesion, whereas in free-response ROC (FROC) the location of each suspected lesion is recorded and is only counted as a TP if there is actually a lesion at that location, regardless of the presence of any further lesions elsewhere in the images for that case. The number of correct lesion localisations is divided by the total number of lesions to obtain the lesion localisation fraction (LLF). In alternative FROC (AFROC) analysis the figure of merit is the area under the curve when LLF is plotted against FPF. Jack-knife AFROC (JAFROC) analysis is a method of calculating the area under the curve for FROC data obtained from multiple readers assessing multiple cases. The figure of merit (area under the curve) is the probability that a malignant lesion is rated as more suspicious than a false positive on a normal image. Chakraborty s JAFROC software, which was used to analyse the data for this study, generates p values relating to differences in figures of merit for pairs of modalities. A p value of 0.05 or less indicates a confidence of 95% or more that there is a real difference between the two modalities. For each pair of modalities two analyses are carried out: Analysis 1 (random reader, random case) and Analysis 2 (fixed reader, random case). The fixed reader is an average of the observers employed in the study. The random readers and random cases are restricted to those used in the study, and may or may not be representative of the general population of readers. 22
23 Appendix 3: Results for individual observers JAFROC figures of merit for individual observers detecting calcification clusters using full field view only and using full field and quadrant views are shown in Figures A1 and A2. There is a variation in results between observers, which is typical for these types of observer study. 1.0 Calcification clusters Full field view only 2 x 5MP 8MP 0.8 Figure of Merit A B C D E F G Observers Figure A1. Figures of merit for individual observers when viewing calcifications on the two monitor types, using full field view only 1.0 Calcification clusters Full field +quadrant view 2 x 5MP 8MP 0.8 Figure of Merit A B C D E F G Observers Figure A2. Figures of merit for individual observers when viewing calcifications on the two monitor types, using full field plus quadrant views 23
Learning Objectives. Outline. Lung Cancer Workshop VIII 8/2/2012. Nicholas Petrick 1. Methodologies for Evaluation of Effects of CAD On Users
 Methodologies for Evaluation of Effects of CAD On Users Nicholas Petrick Center for Devices and Radiological Health, U.S. Food and Drug Administration AAPM - Computer Aided Detection in Diagnostic Imaging
Methodologies for Evaluation of Effects of CAD On Users Nicholas Petrick Center for Devices and Radiological Health, U.S. Food and Drug Administration AAPM - Computer Aided Detection in Diagnostic Imaging
4/19/2016. Deborah Thames R.T. (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT
 Deborah Thames R.T. (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT 1 Three manufacturers approved for Tomo Hologic and GE, and Siemens Why 2D Digital Mammography 2D FFDM it appears to
Deborah Thames R.T. (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT 1 Three manufacturers approved for Tomo Hologic and GE, and Siemens Why 2D Digital Mammography 2D FFDM it appears to
CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS
 130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
Evaluating computer-aided detection algorithms
 Evaluating computer-aided detection algorithms Hong Jun Yoon and Bin Zheng Department of Radiology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15261 Berkman Sahiner Department of Radiology, University
Evaluating computer-aided detection algorithms Hong Jun Yoon and Bin Zheng Department of Radiology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15261 Berkman Sahiner Department of Radiology, University
Computer-aided detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms.
 Computer-aided detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms. Stelios Halkiotis, John Mantas & Taxiarchis Botsis. University of Athens Faculty of Nursing- Health Informatics Laboratory.
Computer-aided detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms. Stelios Halkiotis, John Mantas & Taxiarchis Botsis. University of Athens Faculty of Nursing- Health Informatics Laboratory.
Limitations of Projection Radiography. Stereoscopic Breast Imaging. Limitations of Projection Radiography. 3-D Breast Imaging Methods
 Stereoscopic Breast Imaging Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. Chief, Physics Section Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Limitations of Projection Radiography Mammography is a projection imaging
Stereoscopic Breast Imaging Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. Chief, Physics Section Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Limitations of Projection Radiography Mammography is a projection imaging
algorithms ISSN
 Algorithms 2009, 2, 828-849; doi:10.3390/a2020828 OPEN ACCESS algorithms ISSN 1999-4893 www.mdpi.com/journal/algorithms Review Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Mammography Using Content- Based Image Retrieval
Algorithms 2009, 2, 828-849; doi:10.3390/a2020828 OPEN ACCESS algorithms ISSN 1999-4893 www.mdpi.com/journal/algorithms Review Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Mammography Using Content- Based Image Retrieval
Mass Classification Method in Mammogram Using Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbour Equality
 Mass Classification Method in Mammogram Using Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbour Equality Abstract: Mass classification of objects is an important area of research and application in a variety of fields. In this
Mass Classification Method in Mammogram Using Fuzzy K-Nearest Neighbour Equality Abstract: Mass classification of objects is an important area of research and application in a variety of fields. In this
Design Considerations in Optimizing a Breast Tomosynthesis System
 Design Considerations in Optimizing a Breast Tomosynthesis System Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Science, Hologic Introduction Breast tomosynthesis, also referred to as three-dimensional
Design Considerations in Optimizing a Breast Tomosynthesis System Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Science, Hologic Introduction Breast tomosynthesis, also referred to as three-dimensional
Cluster-oriented Detection of Microcalcifications in Simulated Low-Dose Mammography
 Cluster-oriented Detection of Microcalcifications in Simulated Low-Dose Mammography Hartmut Führ 1, Oliver Treiber 1, Friedrich Wanninger 2 GSF Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit 1 Institut für
Cluster-oriented Detection of Microcalcifications in Simulated Low-Dose Mammography Hartmut Führ 1, Oliver Treiber 1, Friedrich Wanninger 2 GSF Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit 1 Institut für
Pattern recognition (4)
 Pattern recognition (4) 1 Things we have discussed until now Statistical pattern recognition Building simple classifiers Supervised classification Minimum distance classifier Bayesian classifier (1D and
Pattern recognition (4) 1 Things we have discussed until now Statistical pattern recognition Building simple classifiers Supervised classification Minimum distance classifier Bayesian classifier (1D and
Automated Lesion Detection Methods for 2D and 3D Chest X-Ray Images
 Automated Lesion Detection Methods for 2D and 3D Chest X-Ray Images Takeshi Hara, Hiroshi Fujita,Yongbum Lee, Hitoshi Yoshimura* and Shoji Kido** Department of Information Science, Gifu University Yanagido
Automated Lesion Detection Methods for 2D and 3D Chest X-Ray Images Takeshi Hara, Hiroshi Fujita,Yongbum Lee, Hitoshi Yoshimura* and Shoji Kido** Department of Information Science, Gifu University Yanagido
MIXTURE MODELING FOR DIGITAL MAMMOGRAM DISPLAY AND ANALYSIS 1
 MIXTURE MODELING FOR DIGITAL MAMMOGRAM DISPLAY AND ANALYSIS 1 Stephen R. Aylward, Bradley M. Hemminger, and Etta D. Pisano Department of Radiology Medical Image Display and Analysis Group University of
MIXTURE MODELING FOR DIGITAL MAMMOGRAM DISPLAY AND ANALYSIS 1 Stephen R. Aylward, Bradley M. Hemminger, and Etta D. Pisano Department of Radiology Medical Image Display and Analysis Group University of
WorkstationOne. - a diagnostic breast imaging workstation. User Training Presentation. doc #24 (v2.0) Let MammoOne Assist You in Digital Mammography
 WorkstationOne - a diagnostic breast imaging workstation User Training Presentation WorkstationOne Unique streamlined workflow for efficient digital mammography reading Let MammoOne Let MammoOne Assist
WorkstationOne - a diagnostic breast imaging workstation User Training Presentation WorkstationOne Unique streamlined workflow for efficient digital mammography reading Let MammoOne Let MammoOne Assist
Detection of microcalcification clusters by 2D-mammography and narrow and wide angle digital breast tomosynthesis
 Detection of microcalcification clusters by 2D-mammography and narrow and wide angle digital breast tomosynthesis Andria Hadjipanteli a, Premkumar Elangovan b, Padraig T Looney a, Alistair Mackenzie a,
Detection of microcalcification clusters by 2D-mammography and narrow and wide angle digital breast tomosynthesis Andria Hadjipanteli a, Premkumar Elangovan b, Padraig T Looney a, Alistair Mackenzie a,
10/9/2018. Deborah Thames BSRS RT (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT
 Deborah Thames BSRS RT (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT 1 Mammography Five FFDM approved for Tomo Hologic, Ge Senoclair and GE Pristina, Siemens, and Fujifilm 2 Why 2D Digital
Deborah Thames BSRS RT (R)(M)(QM) Theory & Technology and advancement in 3D imaging DBT 1 Mammography Five FFDM approved for Tomo Hologic, Ge Senoclair and GE Pristina, Siemens, and Fujifilm 2 Why 2D Digital
MD215MG Calibrator User's Manual
 MD215MG Calibrator User's Manual Version 1.0 Contents 1 Introduction...3 1.1 Overview...3 1.2 Operating Environment...4 2 Installation...5 2.1 Installing the Display...5 2.2 Installing MD215MG Calibrator...6
MD215MG Calibrator User's Manual Version 1.0 Contents 1 Introduction...3 1.1 Overview...3 1.2 Operating Environment...4 2 Installation...5 2.1 Installing the Display...5 2.2 Installing MD215MG Calibrator...6
TITLE: Computer Aided Detection of Breast Masses in Digital Tomosynthesis
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0293 TITLE: Computer Aided Detection of Breast Masses in Digital Tomosynthesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Swatee Singh Joseph Lo Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Duke University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0293 TITLE: Computer Aided Detection of Breast Masses in Digital Tomosynthesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Swatee Singh Joseph Lo Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Duke University
Things you ll know (or know better to watch out for!) when you leave in December: 1. What you can and cannot infer from graphs.
 1 2 Things you ll know (or know better to watch out for!) when you leave in December: 1. What you can and cannot infer from graphs. 2. How to construct (in your head!) and interpret confidence intervals.
1 2 Things you ll know (or know better to watch out for!) when you leave in December: 1. What you can and cannot infer from graphs. 2. How to construct (in your head!) and interpret confidence intervals.
A ranklet-based CAD for digital mammography
 A ranklet-based CAD for digital mammography Enrico Angelini 1, Renato Campanini 1, Emiro Iampieri 1, Nico Lanconelli 1, Matteo Masotti 1, Todor Petkov 1, and Matteo Roffilli 2 1 Physics Department, University
A ranklet-based CAD for digital mammography Enrico Angelini 1, Renato Campanini 1, Emiro Iampieri 1, Nico Lanconelli 1, Matteo Masotti 1, Todor Petkov 1, and Matteo Roffilli 2 1 Physics Department, University
Ontario Cancer Profiles User Help File
 Ontario Cancer Profiles User Help File Contents Introduction... 2 Module 1 Tool Overview and Layout... 3 Overview of the tool... 3 Highlights vs. selections... 6 Data suppression or unreliable estimates...
Ontario Cancer Profiles User Help File Contents Introduction... 2 Module 1 Tool Overview and Layout... 3 Overview of the tool... 3 Highlights vs. selections... 6 Data suppression or unreliable estimates...
7/30/2018. QC Considerations for Mobile Devices. Outline. No disclosures.
 QC Considerations for Mobile Devices Alisa Walz-Flannigan, PhD (DABR) Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota AAPM Annual Meeting July 30, 2018 2017 MFMER slide-1 No disclosures. Any commercial products referenced
QC Considerations for Mobile Devices Alisa Walz-Flannigan, PhD (DABR) Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota AAPM Annual Meeting July 30, 2018 2017 MFMER slide-1 No disclosures. Any commercial products referenced
Classification of Hyperspectral Breast Images for Cancer Detection. Sander Parawira December 4, 2009
 1 Introduction Classification of Hyperspectral Breast Images for Cancer Detection Sander Parawira December 4, 2009 parawira@stanford.edu In 2009 approximately one out of eight women has breast cancer.
1 Introduction Classification of Hyperspectral Breast Images for Cancer Detection Sander Parawira December 4, 2009 parawira@stanford.edu In 2009 approximately one out of eight women has breast cancer.
Applications of multi-resolution neural networks to mammography
 Applications of multi-resolution neural networks to mammography Clay D. Spence and Paul Sajda Sarnoff Corporation CN5300 Princeton, NJ 08543-5300 {cspence, psajda }@sarnoff.com Abstract We have previously
Applications of multi-resolution neural networks to mammography Clay D. Spence and Paul Sajda Sarnoff Corporation CN5300 Princeton, NJ 08543-5300 {cspence, psajda }@sarnoff.com Abstract We have previously
Classification of Breast Mass Abnormalities using Denseness and Architectural Distortion
 Electronic Letters on Computer Vision and Image Analysis ():-0, 00 Classification of Breast Mass Abnormalities using Denseness and Architectural Distortion S. Baeg * and N. Kehtarnavaz + * Texas Instruments,
Electronic Letters on Computer Vision and Image Analysis ():-0, 00 Classification of Breast Mass Abnormalities using Denseness and Architectural Distortion S. Baeg * and N. Kehtarnavaz + * Texas Instruments,
Perception and Computer Vision with Alternate Sensors
 Perception and Computer Vision with Alternate Sensors Dave Tahmoush tahmoush@cs.umd.edu Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition The computer vision algorithms for visible range sensors in day and office-like
Perception and Computer Vision with Alternate Sensors Dave Tahmoush tahmoush@cs.umd.edu Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition The computer vision algorithms for visible range sensors in day and office-like
2. On classification and related tasks
 2. On classification and related tasks In this part of the course we take a concise bird s-eye view of different central tasks and concepts involved in machine learning and classification particularly.
2. On classification and related tasks In this part of the course we take a concise bird s-eye view of different central tasks and concepts involved in machine learning and classification particularly.
Synthesized 2D Mammographic Imaging
 Synthesized 2D Mammographic Imaging Theory and Clinical Performance Synthesized 2D Mammographic Imaging Theory and Clinical Performance Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President, Image Research Hologic, Inc.,
Synthesized 2D Mammographic Imaging Theory and Clinical Performance Synthesized 2D Mammographic Imaging Theory and Clinical Performance Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President, Image Research Hologic, Inc.,
SVM-based CBIR of Breast Masses on Mammograms
 SVM-based CBIR of Breast Masses on Mammograms Lazaros Tsochatzidis, Konstantinos Zagoris, Michalis Savelonas, and Ioannis Pratikakis Visual Computing Group, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
SVM-based CBIR of Breast Masses on Mammograms Lazaros Tsochatzidis, Konstantinos Zagoris, Michalis Savelonas, and Ioannis Pratikakis Visual Computing Group, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
FEATURE EXTRACTION FROM MAMMOGRAPHIC MASS SHAPES AND DEVELOPMENT OF A MAMMOGRAM DATABASE
 FEATURE EXTRACTION FROM MAMMOGRAPHIC MASS SHAPES AND DEVELOPMENT OF A MAMMOGRAM DATABASE G. ERTAŞ 1, H. Ö. GÜLÇÜR 1, E. ARIBAL, A. SEMİZ 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Bogazici University, Istanbul,
FEATURE EXTRACTION FROM MAMMOGRAPHIC MASS SHAPES AND DEVELOPMENT OF A MAMMOGRAM DATABASE G. ERTAŞ 1, H. Ö. GÜLÇÜR 1, E. ARIBAL, A. SEMİZ 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Bogazici University, Istanbul,
Rare Event Detection Algorithm. User s Guide
 Rare Event Detection Algorithm User s Guide Copyright 2008 Aperio Technologies, Inc. Part Number/Revision: MAN 0123, Revision A Date: September 2, 2008 This document applies to software versions Release
Rare Event Detection Algorithm User s Guide Copyright 2008 Aperio Technologies, Inc. Part Number/Revision: MAN 0123, Revision A Date: September 2, 2008 This document applies to software versions Release
Development of an Automated Method for Detecting Mammographic Masses With a Partial Loss of Region
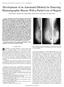 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2001 1209 Development of an Automated Method for Detecting Mammographic Masses With a Partial Loss of Region Yuji Hatanaka*, Takeshi Hara,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2001 1209 Development of an Automated Method for Detecting Mammographic Masses With a Partial Loss of Region Yuji Hatanaka*, Takeshi Hara,
TexRAD Research Version Client User Guide Version 3.9
 Imaging tools for medical decision makers Cambridge Computed Imaging Ltd Grange Park Broadway Bourn Cambridge CB23 2TA UK TexRAD Research Version Client User Guide Version 3.9 Release date 23/05/2016 Number
Imaging tools for medical decision makers Cambridge Computed Imaging Ltd Grange Park Broadway Bourn Cambridge CB23 2TA UK TexRAD Research Version Client User Guide Version 3.9 Release date 23/05/2016 Number
Digital image processing
 Digital image processing Image enhancement algorithms: grey scale transformations Any digital image can be represented mathematically in matrix form. The number of lines in the matrix is the number of
Digital image processing Image enhancement algorithms: grey scale transformations Any digital image can be represented mathematically in matrix form. The number of lines in the matrix is the number of
Keywords: Thresholding, Morphological operations, Image filtering, Adaptive histogram equalization, Ceramic tile.
 Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Blobs and Cracks
Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Blobs and Cracks
A web app for guided and interactive generation of multimarker panels (www.combiroc.eu)
 COMBIROC S TUTORIAL. A web app for guided and interactive generation of multimarker panels (www.combiroc.eu) Overview of the CombiROC workflow. CombiROC delivers a simple workflow to help researchers in
COMBIROC S TUTORIAL. A web app for guided and interactive generation of multimarker panels (www.combiroc.eu) Overview of the CombiROC workflow. CombiROC delivers a simple workflow to help researchers in
ISSN: (Online) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2015 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Survey Paper / Case Study Available online
RITtrend allows you to effectively manage all your physics QA data in one powerful and customizable package.
 So much is asked of medical physicists these days We Can Help Automated Radiation Therapy Phantom Analysis in Seconds QC for Therapy OBI s and CT simulators. Radia s Catphan/OBI module performs analysis
So much is asked of medical physicists these days We Can Help Automated Radiation Therapy Phantom Analysis in Seconds QC for Therapy OBI s and CT simulators. Radia s Catphan/OBI module performs analysis
Naïve Bayes Classification. Material borrowed from Jonathan Huang and I. H. Witten s and E. Frank s Data Mining and Jeremy Wyatt and others
 Naïve Bayes Classification Material borrowed from Jonathan Huang and I. H. Witten s and E. Frank s Data Mining and Jeremy Wyatt and others Things We d Like to Do Spam Classification Given an email, predict
Naïve Bayes Classification Material borrowed from Jonathan Huang and I. H. Witten s and E. Frank s Data Mining and Jeremy Wyatt and others Things We d Like to Do Spam Classification Given an email, predict
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA
 FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
FINDING THE TRUE EDGE IN CTA by: John A. Rumberger, PhD, MD, FACC Your patient has chest pain. The Cardiac CT Angiography shows plaque in the LAD. You adjust the viewing window trying to evaluate the stenosis
MEDICAL IMAGE NOISE REDUCTION AND REGION CONTRAST ENHANCEMENT USING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 MEDICAL IMAGE NOISE REDUCTION AND REGION CONTRAST ENHANCEMENT USING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Miguel Alemán-Flores, Luis Álvarez-León Departamento de Informática y Sistemas, Universidad de Las Palmas
MEDICAL IMAGE NOISE REDUCTION AND REGION CONTRAST ENHANCEMENT USING PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Miguel Alemán-Flores, Luis Álvarez-León Departamento de Informática y Sistemas, Universidad de Las Palmas
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks
 Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
SPRINGFIELD SOLUTIONS BARCODE GUIDELINES
 SPRINGFIELD SOLUTIONS BARCODE GUIDELINES The development of any artwork intended to include a barcode should always take into account the guidelines set down in the GS1 UK document entitled Bar Coding
SPRINGFIELD SOLUTIONS BARCODE GUIDELINES The development of any artwork intended to include a barcode should always take into account the guidelines set down in the GS1 UK document entitled Bar Coding
Quality Management Software. Version User's Manual
 Quality Management Software Version 4.13 User's Manual Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Operating Environment... 3 2 Installation... 5 2.1 Installing the Display... 5 2.2 Installing Medivisor
Quality Management Software Version 4.13 User's Manual Contents 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Overview... 3 1.2 Operating Environment... 3 2 Installation... 5 2.1 Installing the Display... 5 2.2 Installing Medivisor
Naïve Bayes Classification. Material borrowed from Jonathan Huang and I. H. Witten s and E. Frank s Data Mining and Jeremy Wyatt and others
 Naïve Bayes Classification Material borrowed from Jonathan Huang and I. H. Witten s and E. Frank s Data Mining and Jeremy Wyatt and others Things We d Like to Do Spam Classification Given an email, predict
Naïve Bayes Classification Material borrowed from Jonathan Huang and I. H. Witten s and E. Frank s Data Mining and Jeremy Wyatt and others Things We d Like to Do Spam Classification Given an email, predict
An approach for classification of malignant and benign microcalcification clusters
 Sådhanå (2018) 43:39 Ó Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-0805-2sadhana(0123456789().,-volv)ft3 ](0123456789().,-volV) An approach for classification of malignant and benign
Sådhanå (2018) 43:39 Ó Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-018-0805-2sadhana(0123456789().,-volv)ft3 ](0123456789().,-volV) An approach for classification of malignant and benign
TITLE: Stereoscopic Digital Mammography: Improving Cancer Diagnosis. CONTRACTNG ORGANIZATION: BBN Systems and Technologies,
 AD Contract' NUMBER DAMD17-96-C-6079 TITLE: Stereoscopic Digital Mammography: Improving Cancer Diagnosis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATION: David J. Getty, Ph.D. CONTRACTNG ORGANIZATION: BBN Systems and Technologies,
AD Contract' NUMBER DAMD17-96-C-6079 TITLE: Stereoscopic Digital Mammography: Improving Cancer Diagnosis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATION: David J. Getty, Ph.D. CONTRACTNG ORGANIZATION: BBN Systems and Technologies,
Product information. Hi-Tech Electronics Pte Ltd
 Product information Introduction TEMA Motion is the world leading software for advanced motion analysis. Starting with digital image sequences the operator uses TEMA Motion to track objects in images,
Product information Introduction TEMA Motion is the world leading software for advanced motion analysis. Starting with digital image sequences the operator uses TEMA Motion to track objects in images,
Linescan System Design for Robust Web Inspection
 Linescan System Design for Robust Web Inspection Vision Systems Design Webinar, December 2011 Engineered Excellence 1 Introduction to PVI Systems Automated Test & Measurement Equipment PC and Real-Time
Linescan System Design for Robust Web Inspection Vision Systems Design Webinar, December 2011 Engineered Excellence 1 Introduction to PVI Systems Automated Test & Measurement Equipment PC and Real-Time
EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Industrially Focused Mathematical Modelling
 EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Industrially Focused Mathematical Modelling More Accurate Optical Measurements of the Cornea Raquel González Fariña Contents 1. Introduction... 2 Background... 2 2.
EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Industrially Focused Mathematical Modelling More Accurate Optical Measurements of the Cornea Raquel González Fariña Contents 1. Introduction... 2 Background... 2 2.
Extensions of One-Dimensional Gray-level Nonlinear Image Processing Filters to Three-Dimensional Color Space
 Extensions of One-Dimensional Gray-level Nonlinear Image Processing Filters to Three-Dimensional Color Space Orlando HERNANDEZ and Richard KNOWLES Department Electrical and Computer Engineering, The College
Extensions of One-Dimensional Gray-level Nonlinear Image Processing Filters to Three-Dimensional Color Space Orlando HERNANDEZ and Richard KNOWLES Department Electrical and Computer Engineering, The College
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
Computer Science 474 Spring 2010 Viewing Transformation
 Viewing Transformation Previous readings have described how to transform objects from one position and orientation to another. One application for such transformations is to create complex models from
Viewing Transformation Previous readings have described how to transform objects from one position and orientation to another. One application for such transformations is to create complex models from
doi: /
 Yiting Xie ; Anthony P. Reeves; Single 3D cell segmentation from optical CT microscope images. Proc. SPIE 934, Medical Imaging 214: Image Processing, 9343B (March 21, 214); doi:1.1117/12.243852. (214)
Yiting Xie ; Anthony P. Reeves; Single 3D cell segmentation from optical CT microscope images. Proc. SPIE 934, Medical Imaging 214: Image Processing, 9343B (March 21, 214); doi:1.1117/12.243852. (214)
1. Classification Map
 GEO 426 : Choropleth Maps Tanita Suepa 1. Classification Map All of my classification maps use red sequential scheme because the intensity of red can identify the severity of breast cancer in each area
GEO 426 : Choropleth Maps Tanita Suepa 1. Classification Map All of my classification maps use red sequential scheme because the intensity of red can identify the severity of breast cancer in each area
By choosing to view this document, you agree to all provisions of the copyright laws protecting it.
 Copyright 2009 IEEE. Reprinted from 31 st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Sept. 2009. This material is posted here with permission
Copyright 2009 IEEE. Reprinted from 31 st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2009. EMBC 2009. Sept. 2009. This material is posted here with permission
Foveal Algorithm for the Detection of Microcalcification Clusters: a FROC Analysis
 Foveal Algorithm for the Detection of Microcalcification Clusters: a FROC Analysis Marius George Linguraru a,b, Michael Brady a and Ruth English c a Medical Vision Laboratory, University of Oxford, Ewert
Foveal Algorithm for the Detection of Microcalcification Clusters: a FROC Analysis Marius George Linguraru a,b, Michael Brady a and Ruth English c a Medical Vision Laboratory, University of Oxford, Ewert
Crop Counting and Metrics Tutorial
 Crop Counting and Metrics Tutorial The ENVI Crop Science platform contains remote sensing analytic tools for precision agriculture and agronomy. In this tutorial you will go through a typical workflow
Crop Counting and Metrics Tutorial The ENVI Crop Science platform contains remote sensing analytic tools for precision agriculture and agronomy. In this tutorial you will go through a typical workflow
Segmentation of the pectoral muscle edge on mammograms by tunable parametric edge detection
 Segmentation of the pectoral muscle edge on mammograms by tunable parametric edge detection R CHANDRASEKHAR and Y ATTIKIOUZEL Australian Research Centre for Medical Engineering (ARCME) The University of
Segmentation of the pectoral muscle edge on mammograms by tunable parametric edge detection R CHANDRASEKHAR and Y ATTIKIOUZEL Australian Research Centre for Medical Engineering (ARCME) The University of
EyeView Functional Vision Analysis Software
 EyeView Functional Vision Analysis Software Software customized for Stereo Optical Corporation for use with the Optec 6500 Instruction Manual Vision Sciences Research Corporation 130 Ryan Industrial Court,
EyeView Functional Vision Analysis Software Software customized for Stereo Optical Corporation for use with the Optec 6500 Instruction Manual Vision Sciences Research Corporation 130 Ryan Industrial Court,
ABSTRACT. Similarity Classification and Retrieval in Cancer Images and Informatics
 ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: Similarity Classification and Retrieval in Cancer Images and Informatics David Alan Tahmoush, Doctor of Philosophy, 2008 Dissertation directed by: Professor Hanan Samet
ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: Similarity Classification and Retrieval in Cancer Images and Informatics David Alan Tahmoush, Doctor of Philosophy, 2008 Dissertation directed by: Professor Hanan Samet
Monte Carlo simulation of scatter field for calculation of contrast of discs in synthetic CDMAM images
 Monte Carlo simulation of scatter field for calculation of contrast of discs in synthetic CDMAM images Oliver Díaz 1, Mary Yip 1, Jorge Cabello 1, David R. Dance 2,3, Kenneth C. Young 2,3, and Kevin Wells
Monte Carlo simulation of scatter field for calculation of contrast of discs in synthetic CDMAM images Oliver Díaz 1, Mary Yip 1, Jorge Cabello 1, David R. Dance 2,3, Kenneth C. Young 2,3, and Kevin Wells
Dual-Frame Sample Sizes (RDD and Cell) for Future Minnesota Health Access Surveys
 Dual-Frame Sample Sizes (RDD and Cell) for Future Minnesota Health Access Surveys Steven Pedlow 1, Kanru Xia 1, Michael Davern 1 1 NORC/University of Chicago, 55 E. Monroe Suite 2000, Chicago, IL 60603
Dual-Frame Sample Sizes (RDD and Cell) for Future Minnesota Health Access Surveys Steven Pedlow 1, Kanru Xia 1, Michael Davern 1 1 NORC/University of Chicago, 55 E. Monroe Suite 2000, Chicago, IL 60603
Medical Image Feature, Extraction, Selection And Classification
 Medical Image Feature, Extraction, Selection And Classification 1 M.VASANTHA *, 2 DR.V.SUBBIAH BHARATHI, 3 R.DHAMODHARAN 1. Research Scholar, Mother Teresa Women s University, KodaiKanal, and Asst.Professor,
Medical Image Feature, Extraction, Selection And Classification 1 M.VASANTHA *, 2 DR.V.SUBBIAH BHARATHI, 3 R.DHAMODHARAN 1. Research Scholar, Mother Teresa Women s University, KodaiKanal, and Asst.Professor,
Improving Positron Emission Tomography Imaging with Machine Learning David Fan-Chung Hsu CS 229 Fall
 Improving Positron Emission Tomography Imaging with Machine Learning David Fan-Chung Hsu (fcdh@stanford.edu), CS 229 Fall 2014-15 1. Introduction and Motivation High- resolution Positron Emission Tomography
Improving Positron Emission Tomography Imaging with Machine Learning David Fan-Chung Hsu (fcdh@stanford.edu), CS 229 Fall 2014-15 1. Introduction and Motivation High- resolution Positron Emission Tomography
Evaluation of Fourier Transform Coefficients for The Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis From Diffuse Optical Tomography Images
 Evaluation of Fourier Transform Coefficients for The Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis From Diffuse Optical Tomography Images Ludguier D. Montejo *a, Jingfei Jia a, Hyun K. Kim b, Andreas H. Hielscher
Evaluation of Fourier Transform Coefficients for The Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis From Diffuse Optical Tomography Images Ludguier D. Montejo *a, Jingfei Jia a, Hyun K. Kim b, Andreas H. Hielscher
Insight: Measurement Tool. User Guide
 OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide - 1 - October 2007 Insight: Measurement Tool User Guide Open Microscopy Environment: http://www.openmicroscopy.org OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide
OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide - 1 - October 2007 Insight: Measurement Tool User Guide Open Microscopy Environment: http://www.openmicroscopy.org OMERO Beta v2.2: Measurement Tool User Guide
doi: /
 Shuang Liu ; Mary Salvatore ; David F. Yankelevitz ; Claudia I. Henschke ; Anthony P. Reeves; Segmentation of the whole breast from low-dose chest CT images. Proc. SPIE 9414, Medical Imaging 2015: Computer-Aided
Shuang Liu ; Mary Salvatore ; David F. Yankelevitz ; Claudia I. Henschke ; Anthony P. Reeves; Segmentation of the whole breast from low-dose chest CT images. Proc. SPIE 9414, Medical Imaging 2015: Computer-Aided
A. Overview of the CAD System In this paper, the classification is performed in four steps. Initially the mammogram image is smoothened using median
 Ant Colony Optimization and a New Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm for Classification of Microcalcifications in Mammograms M.Karnan #1 K.Thangavel *2 P.Ezhilarasu *3 #1 Tamilnadu College of Engg.,
Ant Colony Optimization and a New Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm for Classification of Microcalcifications in Mammograms M.Karnan #1 K.Thangavel *2 P.Ezhilarasu *3 #1 Tamilnadu College of Engg.,
Minimizing Noise and Bias in 3D DIC. Correlated Solutions, Inc.
 Minimizing Noise and Bias in 3D DIC Correlated Solutions, Inc. Overview Overview of Noise and Bias Digital Image Correlation Background/Tracking Function Minimizing Noise Focus Contrast/Lighting Glare
Minimizing Noise and Bias in 3D DIC Correlated Solutions, Inc. Overview Overview of Noise and Bias Digital Image Correlation Background/Tracking Function Minimizing Noise Focus Contrast/Lighting Glare
A Method for Producing Simulated Mammograms: Observer Study
 A Method for Producing Simulated Mammograms: Observer Study Payam Seifi M.Sc. Michael R. Chinander Ph.D. Robert M. Nishikawa Ph.D., FAAPM Carl J. Vyborny Translational Laboratory for Breast Imaging Research
A Method for Producing Simulated Mammograms: Observer Study Payam Seifi M.Sc. Michael R. Chinander Ph.D. Robert M. Nishikawa Ph.D., FAAPM Carl J. Vyborny Translational Laboratory for Breast Imaging Research
Validation of a digital mammography image simulation chain with automated scoring of CDMAM images
 Validation of a digital mammography image simulation chain with automated scoring of CDMAM images Mary Yip 1, Abdulaziz Alsager 2, Emma Lewis 1, Kevin Wells 1, and Kenneth C. Young 3 1 Centre for Vision,
Validation of a digital mammography image simulation chain with automated scoring of CDMAM images Mary Yip 1, Abdulaziz Alsager 2, Emma Lewis 1, Kevin Wells 1, and Kenneth C. Young 3 1 Centre for Vision,
Using DataQuest on a Handheld
 Using DataQuest on a Handheld Appendix B This appendix gives an overview of using the Vernier DataQuest application on a TI-Nspire handheld. It includes information on accessing the common tools in the
Using DataQuest on a Handheld Appendix B This appendix gives an overview of using the Vernier DataQuest application on a TI-Nspire handheld. It includes information on accessing the common tools in the
1.Some Basic Gray Level Transformations
 1.Some Basic Gray Level Transformations We begin the study of image enhancement techniques by discussing gray-level transformation functions.these are among the simplest of all image enhancement techniques.the
1.Some Basic Gray Level Transformations We begin the study of image enhancement techniques by discussing gray-level transformation functions.these are among the simplest of all image enhancement techniques.the
A new interface for manual segmentation of dermoscopic images
 A new interface for manual segmentation of dermoscopic images P.M. Ferreira, T. Mendonça, P. Rocha Faculdade de Engenharia, Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade do Porto, Portugal J. Rozeira Hospital Pedro
A new interface for manual segmentation of dermoscopic images P.M. Ferreira, T. Mendonça, P. Rocha Faculdade de Engenharia, Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade do Porto, Portugal J. Rozeira Hospital Pedro
Medical images, segmentation and analysis
 Medical images, segmentation and analysis ImageLab group http://imagelab.ing.unimo.it Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia Medical Images Macroscopic Dermoscopic ELM enhance the features of
Medical images, segmentation and analysis ImageLab group http://imagelab.ing.unimo.it Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio Emilia Medical Images Macroscopic Dermoscopic ELM enhance the features of
Unique Features of the GE Senoclaire Tomosynthesis System. Tyler Fisher, M.S., DABR Therapy Physics, Inc.
 Unique Features of the GE Senoclaire Tomosynthesis System Tyler Fisher, M.S., DABR Therapy Physics, Inc. Conflict of Interest Disclosure I have no conflicts to disclose. Learning Objectives Overview of
Unique Features of the GE Senoclaire Tomosynthesis System Tyler Fisher, M.S., DABR Therapy Physics, Inc. Conflict of Interest Disclosure I have no conflicts to disclose. Learning Objectives Overview of
Feature Space Scaling Of 2D Segmented Psoriasis Skin Images
 Feature Space Scaling Of 2D Segmented Psoriasis Skin Images Anuradha Balasubramaniam 1, Anbu Selvi 2 Student,Computer Science & Engineering, Meenakshi College of Engineering,India 1 Asst.Professor,Computer
Feature Space Scaling Of 2D Segmented Psoriasis Skin Images Anuradha Balasubramaniam 1, Anbu Selvi 2 Student,Computer Science & Engineering, Meenakshi College of Engineering,India 1 Asst.Professor,Computer
COMBINED WARNING EDITING GUIDANCE DOCUMENT. European Commission Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General
 COMBINED WARNING EDITING GUIDANCE DOCUMENT European Commission Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General CONTENTS > INTRODUCTION 2 he longest line reaches the e > TYPOGRAPHY 3 FONT > THE COMBINED
COMBINED WARNING EDITING GUIDANCE DOCUMENT European Commission Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General CONTENTS > INTRODUCTION 2 he longest line reaches the e > TYPOGRAPHY 3 FONT > THE COMBINED
TotalLab TL100 Quick Start
 TotalLab TL100 Quick Start Contents of thetl100 Quick Start Introduction to TL100 and Installation Instructions The Control Centre Getting Started The TL100 Interface 1D Gel Analysis Array Analysis Colony
TotalLab TL100 Quick Start Contents of thetl100 Quick Start Introduction to TL100 and Installation Instructions The Control Centre Getting Started The TL100 Interface 1D Gel Analysis Array Analysis Colony
In this section you will learn some simple data entry, editing, formatting techniques and some simple formulae. Contents
 In this section you will learn some simple data entry, editing, formatting techniques and some simple formulae. Contents Section Topic Sub-topic Pages Section 2 Spreadsheets Layout and Design S2: 2 3 Formulae
In this section you will learn some simple data entry, editing, formatting techniques and some simple formulae. Contents Section Topic Sub-topic Pages Section 2 Spreadsheets Layout and Design S2: 2 3 Formulae
The Impact of Diffuse Illumination on Iris Recognition
 The Impact of Diffuse Illumination on Iris Recognition Amanda Sgroi, Kevin W. Bowyer, and Patrick J. Flynn University of Notre Dame asgroi kwb flynn @nd.edu Abstract Iris illumination typically causes
The Impact of Diffuse Illumination on Iris Recognition Amanda Sgroi, Kevin W. Bowyer, and Patrick J. Flynn University of Notre Dame asgroi kwb flynn @nd.edu Abstract Iris illumination typically causes
A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model
 A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model Mohammadhosein Amooshahi a and Abbas Samani abc a Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model Mohammadhosein Amooshahi a and Abbas Samani abc a Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
Breast Cancer Detection and Classification Using Ultrasound and Ultrasound Elastography Images
 Breast Cancer Detection and Classification Using Ultrasound and Ultrasound Elastography Images Ramya S. 1, Nanda S. 2 1IV Sem, M.Tech, Biomedical Signal Processing & Instrumentation, SJCE, Mysuru, Karnataka,
Breast Cancer Detection and Classification Using Ultrasound and Ultrasound Elastography Images Ramya S. 1, Nanda S. 2 1IV Sem, M.Tech, Biomedical Signal Processing & Instrumentation, SJCE, Mysuru, Karnataka,
2011 Clinical. Breast Imaging. Superior Image Quality. FREE SYLLABUS with purchase of entire set 16 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) tm
 A DVD Teaching Program 2011 Clinical Breast Imaging Digital Mammography 1.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Breast Ultrasound 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Breast MR 1.75 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)
A DVD Teaching Program 2011 Clinical Breast Imaging Digital Mammography 1.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Breast Ultrasound 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Breast MR 1.75 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)
Parameter optimization of a computer-aided diagnosis scheme for the segmentation of microcalcification clusters in mammograms
 Parameter optimization of a computer-aided diagnosis scheme for the segmentation of microcalcification clusters in mammograms Marios A. Gavrielides a) Department of Biomedical Engineering, Duke University,
Parameter optimization of a computer-aided diagnosis scheme for the segmentation of microcalcification clusters in mammograms Marios A. Gavrielides a) Department of Biomedical Engineering, Duke University,
A New Fourier-Based Approach to Measure Irregularity of Breast Masses in Mammograms
 A New Fourier-Based Approach to Measure Irregularity of Breast Masses in Mammograms Gensheng Zhang, Sung Shin, Wei Wang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science South Dakota State University
A New Fourier-Based Approach to Measure Irregularity of Breast Masses in Mammograms Gensheng Zhang, Sung Shin, Wei Wang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science South Dakota State University
Chapter 7 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES FOR MAMMOGRAM CLASSIFICATION
 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES FOR MAMMOGRAM CLASSIFICATION Supervised and unsupervised learning are the two prominent machine learning algorithms used in pattern recognition and classification. In this
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES FOR MAMMOGRAM CLASSIFICATION Supervised and unsupervised learning are the two prominent machine learning algorithms used in pattern recognition and classification. In this
Evolutionary Algorithms in the Classification of Mammograms
 Evolutionary Algorithms in the Classification of Mammograms D. C. Hope E. Munday S. L. Smith Department of Electronics The University of York Heslington, York YO10 5DD, UK {dch104, sls5, em24}@ohm.york.ac.uk
Evolutionary Algorithms in the Classification of Mammograms D. C. Hope E. Munday S. L. Smith Department of Electronics The University of York Heslington, York YO10 5DD, UK {dch104, sls5, em24}@ohm.york.ac.uk
XnView Image Viewer. a ZOOMERS guide
 XnView Image Viewer a ZOOMERS guide Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...14 Printing... 22 Image Editing...26 Configuration... 34 Note that this guide is for XnView version 1.8. The current
XnView Image Viewer a ZOOMERS guide Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...14 Printing... 22 Image Editing...26 Configuration... 34 Note that this guide is for XnView version 1.8. The current
extracted from the input image. Moreover, the pixels on the edges (edge pixels) are extracted by using the Canny method [4] (Fig. 2).
![extracted from the input image. Moreover, the pixels on the edges (edge pixels) are extracted by using the Canny method [4] (Fig. 2). extracted from the input image. Moreover, the pixels on the edges (edge pixels) are extracted by using the Canny method [4] (Fig. 2).](/thumbs/73/68674809.jpg) Proceedings of the IIEEJ Image Electronics and Visual Computing Workshop 2012 Kuching, Malaysia, November 21-24, 2012 FACE DETECTION AND FACE ECOGNITION OF CATOON CHAACTES USING FEATUE EXTACTION Kohei
Proceedings of the IIEEJ Image Electronics and Visual Computing Workshop 2012 Kuching, Malaysia, November 21-24, 2012 FACE DETECTION AND FACE ECOGNITION OF CATOON CHAACTES USING FEATUE EXTACTION Kohei
Measurement of display transfer characteristic (gamma, )
 Measurement of display transfer characteristic (gamma, ) A. Roberts (BBC) EBU Sub group G4 (Video origination equipment) has recently completed a new EBU publication setting out recommended procedures
Measurement of display transfer characteristic (gamma, ) A. Roberts (BBC) EBU Sub group G4 (Video origination equipment) has recently completed a new EBU publication setting out recommended procedures
ENGLISH. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 ENGLISH Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Medical imaging excellence Planmed is strongly committed to improving the early detection of breast cancer. Our mission is to provide top quality imaging systems for
ENGLISH Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Medical imaging excellence Planmed is strongly committed to improving the early detection of breast cancer. Our mission is to provide top quality imaging systems for
Future is Effortless
 AQUATM Radiology is a machine Quality Assurance management solution that standardizes, streamlines and automates QA procedures throughout rediology department and across multiple sites. AQUATM Radiology
AQUATM Radiology is a machine Quality Assurance management solution that standardizes, streamlines and automates QA procedures throughout rediology department and across multiple sites. AQUATM Radiology
Forensic Image Recognition using a Novel Image Fingerprinting and Hashing Technique
 Forensic Image Recognition using a Novel Image Fingerprinting and Hashing Technique R D Neal, R J Shaw and A S Atkins Faculty of Computing, Engineering and Technology, Staffordshire University, Stafford
Forensic Image Recognition using a Novel Image Fingerprinting and Hashing Technique R D Neal, R J Shaw and A S Atkins Faculty of Computing, Engineering and Technology, Staffordshire University, Stafford
PSA-Manager Version 3 User Manual
 PSA-Manager Version 3 User Manual CONTENTS 1 Introduction...2 2 File Types and Locations...3 3 PSA-Manager Windows...4 4 Viewing Trace Files...7 4.1.1 The Trace Memo sub-window...8 4.1.2 Printing Trace
PSA-Manager Version 3 User Manual CONTENTS 1 Introduction...2 2 File Types and Locations...3 3 PSA-Manager Windows...4 4 Viewing Trace Files...7 4.1.1 The Trace Memo sub-window...8 4.1.2 Printing Trace
k-nn Disgnosing Breast Cancer
 k-nn Disgnosing Breast Cancer Prof. Eric A. Suess February 4, 2019 Example Breast cancer screening allows the disease to be diagnosed and treated prior to it causing noticeable symptoms. The process of
k-nn Disgnosing Breast Cancer Prof. Eric A. Suess February 4, 2019 Example Breast cancer screening allows the disease to be diagnosed and treated prior to it causing noticeable symptoms. The process of
Evaluation Measures. Sebastian Pölsterl. April 28, Computer Aided Medical Procedures Technische Universität München
 Evaluation Measures Sebastian Pölsterl Computer Aided Medical Procedures Technische Universität München April 28, 2015 Outline 1 Classification 1. Confusion Matrix 2. Receiver operating characteristics
Evaluation Measures Sebastian Pölsterl Computer Aided Medical Procedures Technische Universität München April 28, 2015 Outline 1 Classification 1. Confusion Matrix 2. Receiver operating characteristics
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
2015 User Satisfaction Survey Final report on OHIM s User Satisfaction Survey (USS) conducted in autumn 2015
 2015 User Satisfaction Survey Final report on OHIM s User Satisfaction Survey (USS) conducted in autumn 2015 Alicante 18 December 2015 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 SUMMARY OF SURVEY RESULTS... 4 2. METHODOLOGY
2015 User Satisfaction Survey Final report on OHIM s User Satisfaction Survey (USS) conducted in autumn 2015 Alicante 18 December 2015 Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 SUMMARY OF SURVEY RESULTS... 4 2. METHODOLOGY
