How to improve in-home performance for DOCSIS 3.1
|
|
|
- Buck Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to improve in-home performance for DOCSIS 3.1
2 How to improve in-home performance for DOCSIS 3.1 When international telecommunications standard Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) 3.1 was initiated in late 2013, it targeted greater capacity and increased speed for HFC broadband networks, while remaining compatible with earlier technologies. Delivering DOCSIS services, whether 64 QAM upstream (3.0) or orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) 1024 (3.1), is often possible with minimal investment and network changes. However, to maximize delivery quality with the highest data speeds requires an in-home network resilient against interference and noise contributors. Where is your performance for the next generation of services? There are several obstacles to delivering DOCSIS technologies, including the common effects of loose connectors, signal level discrepancies and ingress/ egress. In addition, the peripheral wireless technology long term evolution (LTE) is present in homes within the same spectrum (regionally specific) as broadband cable systems. Negative effects from, for example, ingress and egress from coaxial cable shielding deficiencies and/or loose connectors with the presence of LTE transmissions can generate service calls, degrade the customer experience, and are increasingly monitored regularly. To achieve the capacity demands required by the exploding adoption of data services, there is a natural evolution towards the deployment of more complex modulation techniques over DOCSIS platforms. This has always been a leading indication that the overall network performance needs to improve. The transitions from QPSK to 16 / 32 / 64 QAM over the years presented additional challenges that gave rise to common phrases, such as drop hardening, home integrity check, proactive network maintenance and line conditioning. q There is a natural evolution towards the deployment of more complex modulation techniques over DOCSIS platforms. Network architectures are evolving to include fewer homes per node, creating increased capacity per subscriber and delivering higher speeds. Fewer homes per node will improve performance through reduced return path noise funneling. The actual bandwidth considerations vary geographically around the globe, and any modification to the network frequency allocation split between the forward and return path can come with a significant capital and operational cost. DOCSIS
3 DOCSIS 3.1, utilizing OFDM modulation techniques and LDPC (low-density paritycheck) error correction, offers additional capacity per subscriber for a robust performing network - but maximizing the return on investment may require some efforts within the transmission medium. The question that cannot be avoided today is: Can we consistently reach the DOCSIS 3.1 performance required while meeting the growing capacity demands? This white paper details common network issues that plague operational budgets and serve as obstacles to delivering the most recent DOCSIS technology standards. It will also suggest network enhancements and daily installation tactics to improve network performance. Reliable network performance improvements, along with proactive network maintenance (PNM) efforts and monitoring systems, create the in-home service integrity that drives up customer satisfaction and reduces churn. The In-Home Network Threshold Experience over the past few decades has proven that in-home architectural issues, typical installation errors and in-home connectivity components contribute significantly to overall network performance falling below acceptable threshold levels. These issues have been inherited from legacy operators, the inhome DIYs, and common craft errors that are simply down to human nature. There is a performance threshold for every major electronic component in the network. Installation errors, as well as the increased number of passive devices, affect performance making it challenging to effectively deliver to the DOCSIS 3.1 standard. Improving the network performance for increased data capacity is also challenged by the growing number of customer premise equipment (CPE) devices online. Furthermore, these CPE devices, in the form of modems, routers and set-top devices, are often installed by the subscribers themselves. Because of this there are more installation errors in this sector, resulting in a higher number of service calls. In addition, multiple wireless devices using LTE frequencies in close proximity to the coax network are increasing the risk of interference. The diagram above shows the area where the cable TV and LTE spectrums coexist. The left side of the diagram, where the F connectors on installed CPE devices are tight, shows no interference in LTE phone transmissions. The right, where connectors are loose, shows transmissions with a high resistance to ground. Note that the cable TV spectrum where LTE coexists has been left vacant - in this case, perhaps to avoid interference issues in the short term. As data demands increase with service adoption and competitive offerings, the desire to deploy more sophisticated modulation techniques over DOCSIS platforms indicates the need for overall network performance improvements or raising the threshold for DOCSIS 3.1 performance. q Installation errors, as well as the increased number of passive devices, affect performance making it challenging to effectively deliver to the DOCSIS 3.1 standard. 02
4 Common Sources of In-Home Network Performance Issues In-home network radio frequency (RF) performance plays a lead role in delivering services that meet service quality demands. There are three main areas impacting today s in-home network performance: 1. Quantity of Products With the increasing number of revenue generating units (RGUs) per home come additional components in the form of connectors, passive splitters, drop amplifiers, coaxial cables, as well as modems and set-top devices. Additional RGUs typically require passives to reduce signal carrier strength, which allows the infiltration of noise. It also increases the total cost of ownership (TCO) through more service calls - a systemic problem that is difficult to track for a single component. There is a cumulative effect whereby more devices installed create additional noise, thus a greater funneling effect in the return path. 2. Quality of Components The quality of the components used to connect multiple home devices impacts performance with respect to electrical integrity and component reliability. RF ingress and egress from components that have poor RF shielding enable interference and noise that funnels in the return path to the head-end or cable modem termination system (CMTS). This RF noise degrades performance, increases error rates and diminishes the integrity of data flow. 3. Quality of Installation The greater the number of components requiring installation, the greater the chance for installation errors. For example, when connectors are left loose or are improperly installed, the RF performance is negatively impacted. Again, with the increase in self-installations comes an increase in craft errors resulting in service calls. Loose connections are also very susceptible to moisture ingress. The loss of continuity from loose connectors can significantly degrade signal return loss and insertion loss, creating reflections that generate data transmission errors and hinder performance. Perhaps the most common service call condition is caused by loose connectors. Over 50 percent of all indoor connectors are less than finger-tight. Often a connector may be loose with no continuity to ground, such that the connector post and nut are floating or un-coupled. This causes very high resistance and generates immediate signal level degradation, as well as ingress and egress. This paper addresses this challenge further in subsequent sections. Another common source of in-home performance degradation is low signal level. The overall signal level as a result of increased passives and associated passive loss may not be sufficient to deliver adequate performance, thus the need for amplification. The removal of these obstacles, combined with architectural improvements, creates a path to and beyond the current DOCSIS 3.1 threshold requirement to competitively deliver services that exceed consumer demand. It has been demonstrated that with a few simple network investments you can have a successful deployment. q Perhaps the most common service call condition is caused by loose connectors. Over 50 percent of all indoor connectors are less than finger-tight. 03
5 Discovery to Solution To control and increase in-home performance requires a focus on, and evaluation of, the components in place today. It is vital to be cognizant of the current performance of all components, specifically the integrity of the F connectors, coaxial cable, passives (such as splitters), and F-81 line splices. Let s review these individual components. F Connectors By far the most critical component in the home is the F connector. It is also the highest volume component in the network. For example, there are approximately 250 million CPE devices deployed in North American networks. These devices contain over 3 billion F connectors. The F connector is also the most common failure point, responsible for a significant operational cost burden that is magnitudes above the initial capital cost. The high operational burden has become a focus of attention, with significant efforts being made to improve the technology and quality while reducing the associated installation craft errors. The technology of the F connector has progressed over the years from a hex crimp design to a 360 degree compression design. Furthermore, the physical design enhancements have created connector technology with a dynamic range of function. This covers varying braid content from 60 percent coverage through to quad shield, with performance parameters exceeding recommended industry standards in some cases. Proven field observations around craft errors and connectors that generate service calls have delivered further advancements in connectors over the past ten years. However, it is still common to find older technology connector devices within the walls - i.e., located behind wall plates. With connector improvements in mind, service offerings are placing more stringent requirements on this component within the in-home network. With our field research showing over 50 percent of the indoor connections less than finger-tight or loose, the problem of loss of continuity to ground has gained high visibility with operators and installers. In the one-way analog networks of previous years loose connections had minimal to no impact. This is not the case in today s networks. Loss of continuity occurs through loose connections where the connector hex nut is physically separated or intermittently disconnected from the connector post that extends within the grounding braid in the coaxial cable. The loss of continuity creates an impedance mismatch, ingress / egress, high insertion loss and reflections that impede the data transfer. In fact, a single connector without continuity to ground can result in service calls at numerous homes within a single optical service area or node. q The F connector is the most common failure point, responsible for a significant operational cost burden that is magnitudes above the initial capital cost. 04
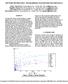
6 To minimize network impairments and service calls, it is essential to select an F connector that easily installs on all common cables in every environment and seals out moisture 100 percent of the time. While there are many components contributing to in-home performance issues, the connector is often most vulnerable due to subscriber self-installs, device movement and common vibrations. To address this operational burden, extensive research and monitoring of in-home networks worldwide resulted in the development of a connector that maintains continuity to ground even when loose. When left loose, the continuity connector performs to a level near that of a fully tightened connector, minimally impeding network performance. It has been widely adopted by the largest global operators and recognized as an enabler to better customer experiences and lower operational costs. It has become a standard migration and is in millions of homes. The figure below is a graph exhibiting a single loose connector with no continuity to ground. It shows the Before, affecting 200 homes in the return path and the resulting noise reduction in After, when the single suspect connector was tightened. Deployment of continuity connectors is increasing, resulting in fewer service calls. In the example here, tracking code word error rates (CER) improved when loose connectors were replaced with continuity connectors that were also left loose. The difference here is conclusive: immediate performance improvements were noted for the upstream CER and service calls were reduced. Coaxial Cable Today s networks are demanding coax cable performance to 1.2 GHz, but legacy installed coax may only have adequate performance at a frequency specified below 1 GHz. Older coaxial cables should be verified as performing adequately. The ingress effects caused by poor or damaged coaxial cable and poor or loose coaxial connectors within the home can generate service calls and service disruption affecting numerous subscribers. q The connector is often most vulnerable due to subscriber self-installs, device movement and common vibrations. 05
7 Passive Devices When it comes to passive devices, specific parameters (electrical, bandwidth and physical) are designed into every solution. These parameters, however, have changed over the years to evolve with the network demands. This section observes various passive devices and their performance threshold parameters. Passive Splitters Splitters may perform to adequate specifications (which include insertion loss and return loss) per their specified bandwidth. However, the bandwidth requirements may have expanded since installation and these components may not perform well beyond 1 GHz or even to lower frequencies in the typical frequency range of 5 MHz to 860 MHz. Due to inadequate performance at higher and lower frequencies than originally designed to, the bandwidth edges in which the network operates will be significantly degraded. Passive Line Splices F-81 splices, such as those located in wall plates, may be older and specified to a limited operating frequency. With often more than five in every home (in wall plates and splices - that ALL look alike but with different specifications), it is difficult to identify the weaker links. Return loss and center-conductor contacts are often not specified to current operating frequencies, again hindering performance for impedance, return loss and insertion loss. Passives in General Shielding effectiveness is another area where older or poor-quality passives may be installed but not be obvious during routine visits. It is not generally desirable for technicians to replace poor coax within the walls of homes because of the operational cost burden. However, the network parameters and certification techniques within the home are starting to demand this. Operators are now providing a home integrity checklist of performance parameters for service technicians and installers prior to closing out the service call or installation. The checklist is becoming key in helping ensure that the vital parameters around signal integrity and data performance are met or exceeded. These checklist parameters are a subset of the proactive network maintenance systems or standard operational practices (SOP) and have an overall positive impact on future home services and cumulative network performance improvement. Finally, with the growing number of CPE devices and televisions per household, signal levels may require amplification due to the increase in the number of passives required. The initial network build may not have considered the high level of passive loss or the loss increase due to higher bandwidth needs over time. The signal levels at each CPE device may not be adequate to offer acceptable performance. The situation may need amplification. q With the growing number of CPE devices and televisions per household, signal levels may require amplification due to the increase in the number of passives required. 06
8 Passive MoCA Filters There is also rising deployment of wholehouse DVR services as their adoption continues to grow. This uses a technology standard known as Multimedia over Coax Alliance (MoCA). MoCA operates at a much higher frequency and must be blocked via a low pass filter at the point of entry to the home. Since strict inhome MoCA networks provide a secure transmission from DVR to client devices, it is a requirement to contain these signals in the subscriber s home network and to prevent connection overlap with DVRs of neighboring homes. Unfortunately, these low-pass MoCA filters add additional insertion loss, weakening the primary signal. Drop Amplifiers Drop amplifiers continue to be used to counter the effects of passive loss. Technicians must be sure to use the amplifier gain wisely and not attempt to cover other issues within the drop plant, such as excessive loss due to poor quality passives or damaged devices. These issues could include damaged coax, loose connectors or passives that simply do not meet current bandwidth requirements. Secondly, the bandwidth and the location within the in-home network of the drop amplifiers themselves are critical to overall system performance. Finally, we should consider a passive port on the amplifier, also known as a bypass port. This maintains VoIP and data transmission via the DOCSIS modem when there is no power in the home and ensures that the DOCSIS carrier remains above the noise floor. Line Conditioning There are passive and active devices to enhance signal levels over a broad frequency spectrum in the forward and return path bands. These offer improvements by either filtering noise, blocking unwanted carriers that create interference, or switching the return path on and off to reduce the cumulative noise effects in the return path. CPE devices require a signal level window to operate properly. When the signal levels exceed, fall below or both due to excessive tilt, the CPE fails to perform at optimum levels. Frequencyspecific devices, such as equalizers, cable simulators, attenuators, gain devices (drop amplifiers), and high / low pass filters, groom signals for optimum CPE performance. Another recent technology introduced is a noise mitigation technology that switches the return path on / off. The switching speed does not affect data transfer and the circuit is closed only when data is transmitted (or polled). To prevent noise funneling in the network, the circuit is in an open position when no upstream data is transferred. Major operators are currently conducting further studies on the positive effects surrounding network performance and customer satisfaction. q MoCA networks provide a secure transmission from DVR to client devices. 07
9 Improving In-Home Network Performance Through Drop Hardening Drop hardening improves signal-tonoise ratio, reduces impulse noise, and minimizes ingress and egress, all of which decrease service calls. Initial service calls often create follow-up service calls, and approximately 20 percent of repeat / follow-up service calls result in customer churn. The operational cost of a service call almost always exceeds the capital cost, which is why the drop hardening procedure should be efficiently conducted at every visit. Drop hardening involves three vital steps: 1. Identifying Root Causes Root cause identification is important as it leads to product and process improvements. To control, stabilize and improve in-home performance requires a focus and evaluation of the components in place today. These vary greatly from one home to another as a result of the initial installation, architecture required at the time of installation(s), and the variation of craft and component quality installed by operators and home owners. Today s advanced PNM systems can often direct technicians to root causes, identifying loose connectors, moisture damage, inadequate or damaged coax, and passive components, to name a few. Knowing the root cause provides valuable insight to drop hardening / performance improvements. 2. Benchmarking a Performance Threshold An SOP, outlining architectural guidelines and test parameters ensures a uniform approach is taken in order to reach the desired threshold. Signal levels at the CPE, to include both forward and return, should be in the desired range. DOCSIS levels from the cable modem should also be within the desired range as these vary greatly based on the passive loss variations in the return path. Signal to noise ratio (SNR) and modulation error ratio (MER) are also commonly tested. Many of today s PNM systems are constantly monitoring all network devices via DOCSIS parameters. Using logic, the operator is directed to issue areas that when repaired provide a cumulative performance improvement for numerous subscribers. An integrity check can now be registered within the management system and monitoring continues automatically. Evolving the Quality of Components It is imperative to use quality components that meet or exceed current and future performance requirements. This involves upgrading devices with bandwidth limitations and ensuring that electrical / mechanical performance specifications are verified in accordance with network requirements. Bandwidth limitations may vary greatly within the home from hidden components, such as the coax within the walls, to the simple splitters installed by the home owners to add additional devices (routers or TVs, for example). The component quality must take into account the craft sensitivity of initial installations and reconnections commonly conducted by subscribers. It is essential that products meet or exceed mechanical and electrical performance recommendations, not to exclude the areas of bandwidth (upper and lower frequency limits), RF shielding effectiveness, return loss, insertion loss and stability in varying environmental conditions. q Initial service calls often create followup service calls, and approximately 20 percent of repeat / follow-up service calls result in customer churn. 08
10 Conclusion The current state of in-home networks will likely need to be enhanced or improved to meet increasingly stringent demands. Often the transmission medium has been neglected over time and the operational cost burden of service calls results in reduced profit and a loss of subscribers. Regardless of the physical plant changes and the modulation schemes that provide us with increased data capacity, it is the daily, routine installation practices that can be the greatest contributor of success to network performance and the user experience. Without following these best practices investigating the drop plant to discover root causes of issues and selecting the best available technology within components planned for future requirements service calls due to plant network issues will continue. Improving the drop plant significantly increases the likelihood of a successful DOCSIS 3.1 launch and a more profitable future. q The current state of in-home networks will likely need to be enhanced or improved to meet the increasingly stringent demands. 09
11 About PPC PPC is a global leader in connective technology with a worldwide reputation for technical leadership. We have developed many industry firsts including pushable fiber, universal crimp and compression connectors, continuity connectors, integrated weather sealing connectors, among our many innovations. As a Belden brand, PPC also accesses Belden s powerful position within the signal transmission solutions space to offer a very unique end-to-end solution to its customers. If you would like to discuss your DOCSIS 3.1 challenge or any of the topics in this ebook, please contact us directly. We d be delighted to hear from you. Krista Tysco Global Marketing +1 (315) krista.tysco@ppc-online.com ppc@ppc-online.com Sign up to the PPC newsletter, Connections SUBSCRIBE NOW All rights reserved. You are free to share this publication with others. However, no part of it may be reproduced in any form or by any means, electronic or manual, without prior written permission from the publisher PPC - A BELDEN BRAND
How to Improve In-Home Performance Thresholds for DOCSIS 3.1 DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper
 How to Improve In-Home Performance Thresholds for DOCSIS 3.1 DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper Rick Haube Director of Global Marketing, PPC Broadband, Inc. a Belden Company When international telecommunications standard
How to Improve In-Home Performance Thresholds for DOCSIS 3.1 DOCSIS 3.1 White Paper Rick Haube Director of Global Marketing, PPC Broadband, Inc. a Belden Company When international telecommunications standard
Passive optical LAN explained
 Understanding the technology for a more advanced enterprise network Strategic White Paper Network architects have used local area network (LAN) switches to manage the volume of traffic in enterprise networks
Understanding the technology for a more advanced enterprise network Strategic White Paper Network architects have used local area network (LAN) switches to manage the volume of traffic in enterprise networks
MOVING BEYOND THE STANDARD: CREATING ADDITIONAL BANDWIDTH THROUGH EXTENDING DOCSIS 2.0. Jack Moran, Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff
 MOVING BEYOND THE STANDARD: CREATING ADDITIONAL BANDWIDTH THROUGH EXTENDING DOCSIS 2.0 Jack Moran, Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Abstract Advanced
MOVING BEYOND THE STANDARD: CREATING ADDITIONAL BANDWIDTH THROUGH EXTENDING DOCSIS 2.0 Jack Moran, Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Abstract Advanced
Cisco Prisma D-PON: Your DOCSIS-Based Fiber-to-the-Home Solution
 Cisco Prisma D-PON: Your DOCSIS-Based Fiber-to-the-Home Solution Introduction Today s consumers live in a brave new world of media technology. They channel surf program guides, not channels; they pause,
Cisco Prisma D-PON: Your DOCSIS-Based Fiber-to-the-Home Solution Introduction Today s consumers live in a brave new world of media technology. They channel surf program guides, not channels; they pause,
ZCorum s Ask a Broadband Expert Series:
 ZCorum s Ask a Broadband Expert Series: DOCSIS 3.1 and the PNM Toolbox: The Future Of Plant Maintenance Is Here A Technical Paper presented by Marsha Hemmerich, Marketing Specialist, ZCorum 1.800.909.9441
ZCorum s Ask a Broadband Expert Series: DOCSIS 3.1 and the PNM Toolbox: The Future Of Plant Maintenance Is Here A Technical Paper presented by Marsha Hemmerich, Marketing Specialist, ZCorum 1.800.909.9441
Optimizing PON architectures maximizes electronics efficiencies. White paper
 Optimizing PON architectures maximizes electronics efficiencies White paper When deploying a passive optical network (PON), the FTTH architecture chosen directly affects the cost of active equipment. Placement
Optimizing PON architectures maximizes electronics efficiencies White paper When deploying a passive optical network (PON), the FTTH architecture chosen directly affects the cost of active equipment. Placement
PathTrak Return Path Monitoring System. HFC Upstream Monitoring Solution
 PathTrak Return Path Monitoring System HFC Upstream Monitoring Solution Key Benefits/Features y Speed troubleshooting with essential spectrum and cable-modem upstream analysis and monitoring in one solution
PathTrak Return Path Monitoring System HFC Upstream Monitoring Solution Key Benefits/Features y Speed troubleshooting with essential spectrum and cable-modem upstream analysis and monitoring in one solution
Five Challenges of Configuring an HD Interactive Coaxial Network. By Tom Robinson and Brad Niems, Holland Electronics
 Five Challenges of Configuring an HD Interactive Coaxial Network By Tom Robinson and Brad Niems, Holland Electronics (May 3, 2011) There has been much debate and deliberation over the last ten years concerning
Five Challenges of Configuring an HD Interactive Coaxial Network By Tom Robinson and Brad Niems, Holland Electronics (May 3, 2011) There has been much debate and deliberation over the last ten years concerning
Real-World LTE Performance for Public Safety
 WHITE PAPER Real-World LTE Performance for Public Safety Relating Technical Capabilities to User Experience Executive Summary Government and public safety organizations are watching the fast pace of technological
WHITE PAPER Real-World LTE Performance for Public Safety Relating Technical Capabilities to User Experience Executive Summary Government and public safety organizations are watching the fast pace of technological
Proactive Network Maintenance (PNM) 4º Workshop America Movil - Painel B3
 Proactive Network Maintenance (PNM) 4º Workshop America Movil - Painel B3 Tim Fike Business Development Manager Cisco Systems, Inc. fiket@cisco.com May 9, 2017 What if you could pro-actively identify and
Proactive Network Maintenance (PNM) 4º Workshop America Movil - Painel B3 Tim Fike Business Development Manager Cisco Systems, Inc. fiket@cisco.com May 9, 2017 What if you could pro-actively identify and
802.11n in the Outdoor Environment
 POSITION PAPER 802.11n in the Outdoor Environment How Motorola is transforming outdoor mesh networks to leverage full n advantages Municipalities and large enterprise customers are deploying mesh networks
POSITION PAPER 802.11n in the Outdoor Environment How Motorola is transforming outdoor mesh networks to leverage full n advantages Municipalities and large enterprise customers are deploying mesh networks
HST-3000 Handheld Services Tester Platform Overview
 Provided by www.aaatesters.com HST-3000 Handheld Services Tester Platform Overview Experience the Power of One The growth of converged services has changed the landscape of the telecommunications industry,
Provided by www.aaatesters.com HST-3000 Handheld Services Tester Platform Overview Experience the Power of One The growth of converged services has changed the landscape of the telecommunications industry,
Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Using Technology. Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager
 White Paper Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager Cable Broadband Communications Group, Texas Instruments Introduction Wireless home networking has emerged
White Paper Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager Cable Broadband Communications Group, Texas Instruments Introduction Wireless home networking has emerged
Deploying Distributed Access Architecture - Facts and experiences with R-PHY & DOCSIS 3.1
 Deploying Distributed Access Architecture - Facts and experiences with R-PHY & DOCSIS 3.1 DISTRIBUTED ACCESS ARCHITECTURE (DAA) PRE-CONFERENCE SESSION CABLE-TEC EXPO 2018, ATLANTA GA KJELD BALMER DIRECTOR,
Deploying Distributed Access Architecture - Facts and experiences with R-PHY & DOCSIS 3.1 DISTRIBUTED ACCESS ARCHITECTURE (DAA) PRE-CONFERENCE SESSION CABLE-TEC EXPO 2018, ATLANTA GA KJELD BALMER DIRECTOR,
Cable Operator Deploys World s First
 Case Study Commercial DOCSIS 3.0 Implementation Cable Operator Deploys World s First Commercial DOCSIS 3.0 Implementation Motorola s DOCSIS 3.0-Qualified CMTS and DOCSIS 3.0-Certified SURFboard Cable Modem
Case Study Commercial DOCSIS 3.0 Implementation Cable Operator Deploys World s First Commercial DOCSIS 3.0 Implementation Motorola s DOCSIS 3.0-Qualified CMTS and DOCSIS 3.0-Certified SURFboard Cable Modem
Broadband & VOD Deployment Trend for MSO
 2010/TEL41/LSG/IR/004 Agenda Item: 5 Broadband & VOD Deployment Trend for MSO Purpose: Information Submitted by: Chinese Taipei Industry Roundtable: National Broadband Networks and Fibre to the Premises
2010/TEL41/LSG/IR/004 Agenda Item: 5 Broadband & VOD Deployment Trend for MSO Purpose: Information Submitted by: Chinese Taipei Industry Roundtable: National Broadband Networks and Fibre to the Premises
Distribute or Die: Hybrid Fiber Coax Hanging by a Cable. Samir Parikh Gainspeed, Inc.
 Distribute or Die: Hybrid Fiber Coax Hanging by a Cable Samir Parikh Gainspeed, Inc. Abstract The hybrid fiber coax (HFC) networks currently in place were designed to carry broadcast analog video, not
Distribute or Die: Hybrid Fiber Coax Hanging by a Cable Samir Parikh Gainspeed, Inc. Abstract The hybrid fiber coax (HFC) networks currently in place were designed to carry broadcast analog video, not
Physical Layer Part 3
 Physical Layer Part 3 Transmission Media Computer Networks: Transmission Media 1 Transmission Media Transmission medium:: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Repeaters or amplifiers may
Physical Layer Part 3 Transmission Media Computer Networks: Transmission Media 1 Transmission Media Transmission medium:: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Repeaters or amplifiers may
WHITE PAPER ULTRA LOW LATENCY MICROWAVE THE NEED FOR SPEED: BEST PRACTICES FOR BUILDING ULTRA-LOW LATENCY MICROWAVE NETWORKS
 THE NEED FOR SPEED: BEST PRACTICES FOR BUILDING ULTRA-LOW LATENCY MICROWAVE NETWORKS JULY 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 MICROWAVE: THE NEW DEFAULT TRANSPORT FOR LOW LATENCY APPLICATIONS... 3
THE NEED FOR SPEED: BEST PRACTICES FOR BUILDING ULTRA-LOW LATENCY MICROWAVE NETWORKS JULY 2012 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 MICROWAVE: THE NEW DEFAULT TRANSPORT FOR LOW LATENCY APPLICATIONS... 3
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management
 Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management This chapter describes the spectrum management features supported for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) routers. Spectrum management support
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management This chapter describes the spectrum management features supported for the Cisco Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) routers. Spectrum management support
WHEN RF AND IP CLASH THE REALM OF DOCSIS & VOIP TROUBLESHOOTING BY BRADY VOLPE, THE VOLPE FIRM FORMALLY OF SUNRISE TELECOM
 WHEN RF AND IP CLASH THE REALM OF DOCSIS & VOIP BY BRADY VOLPE, THE VOLPE FIRM FORMALLY OF SUNRISE TELECOM Contemporary troubleshooting of Data over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS ) requires
WHEN RF AND IP CLASH THE REALM OF DOCSIS & VOIP BY BRADY VOLPE, THE VOLPE FIRM FORMALLY OF SUNRISE TELECOM Contemporary troubleshooting of Data over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS ) requires
SMALL CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION Strategic White Paper
 SMALL CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION Strategic White Paper Small cells is an umbrella term for a genre of low-powered wireless access points capable of using both licensed and unlicensed spectrum. Small cells
SMALL CELLS: AN INTRODUCTION Strategic White Paper Small cells is an umbrella term for a genre of low-powered wireless access points capable of using both licensed and unlicensed spectrum. Small cells
Maintaining The Power Advantage In HFC Networks
 Maintaining The Power Advantage In HFC Networks A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by John Chamberlain Director, Office of the CTO CommScope 1100 CommScope Place SE, Hickory, NC 28603 828.431.9800
Maintaining The Power Advantage In HFC Networks A Technical Paper prepared for SCTE/ISBE by John Chamberlain Director, Office of the CTO CommScope 1100 CommScope Place SE, Hickory, NC 28603 828.431.9800
Physical Layer Part 3
 Physical Layer Part 3 Transmission Media Networks: Transmission Media 1 Transmission Media Transmission medium:: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Repeaters or amplifiers may be used
Physical Layer Part 3 Transmission Media Networks: Transmission Media 1 Transmission Media Transmission medium:: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Repeaters or amplifiers may be used
Proxim Wireless. All rights reserved.
 Wireless Network Design Best Practices Regardless of the application, today wireless broadband is the order of the day, providing fiber like connectivity and reliability in a matter of hours. However,
Wireless Network Design Best Practices Regardless of the application, today wireless broadband is the order of the day, providing fiber like connectivity and reliability in a matter of hours. However,
Passive Optical Neworks Optical Distribution Network. White Paper. Northforge Innovations Inc.
 Passive Optical Neworks Optical Distribution Network White Paper Northforge Innovations Inc. February 2018 1 Introduction Passive Optical Networks (PON) are broadly deployed to provide high-bandwidth Fiber
Passive Optical Neworks Optical Distribution Network White Paper Northforge Innovations Inc. February 2018 1 Introduction Passive Optical Networks (PON) are broadly deployed to provide high-bandwidth Fiber
White Paper. Defining the Future of Multi-Gigabit Wireless Communications. July 2010
 White Paper Defining the Future of Multi-Gigabit Wireless Communications July 2010 2 Introduction The widespread availability and use of digital multimedia content has created a need for faster wireless
White Paper Defining the Future of Multi-Gigabit Wireless Communications July 2010 2 Introduction The widespread availability and use of digital multimedia content has created a need for faster wireless
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS
 Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS First Published: February 14, 2008 Last Updated: June 20, 2011 Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SCA integrates support for this feature
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS First Published: February 14, 2008 Last Updated: June 20, 2011 Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SCA integrates support for this feature
Extending Ethernet over 2-wire Copper Networks
 Extending Ethernet over 2-wire Copper Networks Eleanor Huang Product Manager Mark Wu Technical Writer Executive Summary To improve the efficiency of industrial automation systems, many operators are considering
Extending Ethernet over 2-wire Copper Networks Eleanor Huang Product Manager Mark Wu Technical Writer Executive Summary To improve the efficiency of industrial automation systems, many operators are considering
Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS
 17 CHAPTER Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS Revised: March 30, 2009 This chapter describes the spectrum management features supported by the Cisco Cable Modem Termination
17 CHAPTER Spectrum Management and Advanced Spectrum Management for the Cisco CMTS Revised: March 30, 2009 This chapter describes the spectrum management features supported by the Cisco Cable Modem Termination
3 Chapter Introduction. 3.2 Copper Cable
 3 Chapter 3 3.1 Introduction The Network Media is the device that physically carries the data from computer to computer. The three major types of network media are: Copper Cable Fiber-Optic Cable Wireless
3 Chapter 3 3.1 Introduction The Network Media is the device that physically carries the data from computer to computer. The three major types of network media are: Copper Cable Fiber-Optic Cable Wireless
DYNAMIC LINE MANAGEMENT FOR VECTORING SCENARIOS
 DYNAMIC LINE MANAGEMENT FOR VECTORING SCENARIOS STRATEGIC WHITE PAPER Operators are embracing vectoring technology as a means to extend and protect their legacy investments in copper access. However, the
DYNAMIC LINE MANAGEMENT FOR VECTORING SCENARIOS STRATEGIC WHITE PAPER Operators are embracing vectoring technology as a means to extend and protect their legacy investments in copper access. However, the
NEXT GENERATION CMTS CHARACTERISTICS INCLUDING IP MULTICAST. Doug Jones YAS Broadband Ventures
 NEXT GENERATION CMTS CHARACTERISTICS INCLUDING IP MULTICAST Doug Jones YAS Broadband Ventures Abstract The cable industry is currently faced with upgrading from DOCSIS v1.0 CMTS equipment to DOCSIS v1.1
NEXT GENERATION CMTS CHARACTERISTICS INCLUDING IP MULTICAST Doug Jones YAS Broadband Ventures Abstract The cable industry is currently faced with upgrading from DOCSIS v1.0 CMTS equipment to DOCSIS v1.1
Business Case for the Cisco ASR 5500 Mobile Multimedia Core Solution
 Business Case for the Cisco ASR 5500 Mobile Multimedia Core Solution Executive Summary The scale, use and technologies of mobile broadband networks are changing rapidly. Mobile broadband growth continues
Business Case for the Cisco ASR 5500 Mobile Multimedia Core Solution Executive Summary The scale, use and technologies of mobile broadband networks are changing rapidly. Mobile broadband growth continues
DOCSIS FOR LTE SMALL CELL BACKHAUL ADDRESSING PERFORMANCE AND THROUGHPUT REQUIREMENTS FOR MOBILE BACKHAUL
 DOCSIS FOR LTE SMALL CELL BACKHAUL ADDRESSING PERFORMANCE AND THROUGHPUT REQUIREMENTS FOR MOBILE BACKHAUL WHITE PAPER Small cells can be used to increase wireless network capacity, provide coverage in
DOCSIS FOR LTE SMALL CELL BACKHAUL ADDRESSING PERFORMANCE AND THROUGHPUT REQUIREMENTS FOR MOBILE BACKHAUL WHITE PAPER Small cells can be used to increase wireless network capacity, provide coverage in
innovative technology to keep you a step ahead In-Home Leakage Evaluation System
 Dual-Band Leakage Receiver for Both Aeronautical and LTE Frequencies Sensitivity Up to 0.1 uv/m at 138 MHz and 0.4 uv/m at 757.5 MHz Tagged Signal Source Combined with a Discriminating Leakage Receiver
Dual-Band Leakage Receiver for Both Aeronautical and LTE Frequencies Sensitivity Up to 0.1 uv/m at 138 MHz and 0.4 uv/m at 757.5 MHz Tagged Signal Source Combined with a Discriminating Leakage Receiver
ADC CORPORATE CAPABILITIES
 building global connections ADC CORPORATE CAPABILITIES Building Global Connections We live in a highly connected world. Fueled by applications such as IPTV, video-on-demand (VoD), and the widespread use
building global connections ADC CORPORATE CAPABILITIES Building Global Connections We live in a highly connected world. Fueled by applications such as IPTV, video-on-demand (VoD), and the widespread use
Casa Systems Distributed Access (DA500, DA1000 and DA2000)
 Data Sheet Casa Systems Distributed Access (, and ) Winning and keeping residential and enterprise video and Internet services customers has never been tougher. Service providers face a range of competition
Data Sheet Casa Systems Distributed Access (, and ) Winning and keeping residential and enterprise video and Internet services customers has never been tougher. Service providers face a range of competition
New Same-Band Combining Technology Improves LTE Deployment
 White Paper New Same-Band Combining Technology Improves LTE Deployment Juan Irola, Engineer Principal, Electrical www.commscope.com Contents New same-band combining technology improves LTE deployment 3
White Paper New Same-Band Combining Technology Improves LTE Deployment Juan Irola, Engineer Principal, Electrical www.commscope.com Contents New same-band combining technology improves LTE deployment 3
WHAT YOU LL NEED TO BEGIN:
 W ipnet INSTALLATION GUIDE v1.1 WHAT YOU LL NEED TO BEGIN: THE PARTS WiPNET or WiPNET WiFi* WiPLOCK Filter (as needed) OR WiPNET MoCA Amplifier-Splitter (suggested) Surface Mount (as needed) Low Voltage
W ipnet INSTALLATION GUIDE v1.1 WHAT YOU LL NEED TO BEGIN: THE PARTS WiPNET or WiPNET WiFi* WiPLOCK Filter (as needed) OR WiPNET MoCA Amplifier-Splitter (suggested) Surface Mount (as needed) Low Voltage
Extending Ethernet over 2-wire Copper Networks
 Extending Ethernet over 2-wire Copper Networks Executive Summary To improve the efficiency of industrial automation systems, many operators are considering the possibility of IP upgrades to provide centralised
Extending Ethernet over 2-wire Copper Networks Executive Summary To improve the efficiency of industrial automation systems, many operators are considering the possibility of IP upgrades to provide centralised
MOTOROLA EXPEDIENCE TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
 MOTOROLA EXPEDIENCE TECHNICAL OVERVIEW EXPEDIENCE TECHNICAL OVERVIEW a) Introduction Motorola s EXPEDIENCE Platform is an Indoor NLOS (Non Line Of Sight) Wireless Broadband platform specifically optimized
MOTOROLA EXPEDIENCE TECHNICAL OVERVIEW EXPEDIENCE TECHNICAL OVERVIEW a) Introduction Motorola s EXPEDIENCE Platform is an Indoor NLOS (Non Line Of Sight) Wireless Broadband platform specifically optimized
Adaptive Coding and Modulation: Enhance Operational Efficiency of Wireless Backhaul
 Adaptive Coding and Modulation: Enhance Operational Efficiency of Wireless Backhaul WHITE PAPER With the advent of newer data services and increase in usage of smart phones, there is an increased demand
Adaptive Coding and Modulation: Enhance Operational Efficiency of Wireless Backhaul WHITE PAPER With the advent of newer data services and increase in usage of smart phones, there is an increased demand
Troubleshooting. Troubleshooting Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides basic installation troubleshooting information. The chapter includes the following sections: Overview Initialization and Self-Test Problems Subsystems Using the Reset Switch
CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides basic installation troubleshooting information. The chapter includes the following sections: Overview Initialization and Self-Test Problems Subsystems Using the Reset Switch
Increasing Bandwidth while Reducing Costs with the AOI Remote PHY Solution
 Increasing Bandwidth while Reducing Costs with the AOI Remote PHY Solution Executive Summary This paper introduces the concept a Remote PHY Device (RPD) in cable operator (MSO) networks and describes how
Increasing Bandwidth while Reducing Costs with the AOI Remote PHY Solution Executive Summary This paper introduces the concept a Remote PHY Device (RPD) in cable operator (MSO) networks and describes how
Anatomy of a HFC network
 Anatomy of a HFC network 1 Everything you wanted to know and were afraid to ask about how HFC networks work and deliver data services. Outside plant primer 2 What the heck are those things on the pole
Anatomy of a HFC network 1 Everything you wanted to know and were afraid to ask about how HFC networks work and deliver data services. Outside plant primer 2 What the heck are those things on the pole
CABLE NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO CABLE NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES AND PROTOCOLS
 CABLE NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO CABLE NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES AND PROTOCOLS Peter R. Egli 1/15 Contents 1. Cable network architecture 2. Relevant cable network standards 3. DOCSIS 2/15 1. Cable Network architecture
CABLE NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO CABLE NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES AND PROTOCOLS Peter R. Egli 1/15 Contents 1. Cable network architecture 2. Relevant cable network standards 3. DOCSIS 2/15 1. Cable Network architecture
Physical Layer Part 3
 Physical Layer Part 3 Transmission Media Networks: Transmission Media 1 Transmission Media Transmission medium:: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Repeaters or amplifiers may be used
Physical Layer Part 3 Transmission Media Networks: Transmission Media 1 Transmission Media Transmission medium:: the physical path between transmitter and receiver. Repeaters or amplifiers may be used
Connect to wavelength management
 Connect to wavelength management As consumers purchase more and more devices (cell phones, televisions, laptops, etc.) communication networks supporting these devices need to evolve to supply enough bandwidth
Connect to wavelength management As consumers purchase more and more devices (cell phones, televisions, laptops, etc.) communication networks supporting these devices need to evolve to supply enough bandwidth
Metro Ethernet for Government Enhanced Connectivity Drives the Business Transformation of Government
 Metro Ethernet for Government Enhanced Connectivity Drives the Business Transformation of Government Why You Should Choose Cox Metro Ethernet To meet the critical demands of better supporting local emergency
Metro Ethernet for Government Enhanced Connectivity Drives the Business Transformation of Government Why You Should Choose Cox Metro Ethernet To meet the critical demands of better supporting local emergency
Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (ETSI Markets)
 Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (ETSI Markets) The Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (MPR) provides cost-effective IP transformation for seamless microwave transport of TDM, ATM, IP
Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (ETSI Markets) The Alcatel-Lucent 9500 Microwave Packet Radio (MPR) provides cost-effective IP transformation for seamless microwave transport of TDM, ATM, IP
innovative technology to keep you a step ahead
 Dual-Mode & Dual-Frequency In-Home Leakage Detector that Accurately Monitors Leakage in an All-Digital System or Mixed Digital and Analog Systems Provides a Cost-Effective Solution for In- Home Leakage
Dual-Mode & Dual-Frequency In-Home Leakage Detector that Accurately Monitors Leakage in an All-Digital System or Mixed Digital and Analog Systems Provides a Cost-Effective Solution for In- Home Leakage
DDoS MITIGATION BEST PRACTICES
 DDoS MITIGATION BEST PRACTICES DDoS ATTACKS ARE INCREASING EXPONENTIALLY Organizations are becoming increasingly aware of the threat that Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can pose. According
DDoS MITIGATION BEST PRACTICES DDoS ATTACKS ARE INCREASING EXPONENTIALLY Organizations are becoming increasingly aware of the threat that Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can pose. According
One Release. One Architecture. One OS. High-Performance Networking for the Enterprise with JUNOS Software
 Solution Brochure High-Performance Networking for the Enterprise with JUNOS Software Using the Network to Achieve Higher Availability, Lower OPEX and Improved Productivity for Your Business Core Branch
Solution Brochure High-Performance Networking for the Enterprise with JUNOS Software Using the Network to Achieve Higher Availability, Lower OPEX and Improved Productivity for Your Business Core Branch
Connector and Cable Specifications
 APPENDIX B This appendix describes the pinouts and cabling requirements for the interfaces and cables used on the Cisco ubr925 cable access router. All connectors for these interfaces are on the rear-panel,
APPENDIX B This appendix describes the pinouts and cabling requirements for the interfaces and cables used on the Cisco ubr925 cable access router. All connectors for these interfaces are on the rear-panel,
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology
 LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
LTE : The Future of Mobile Broadband Technology Erick Setiawan tukangbajaksawah@gmail.com 1 Become a necessity today, where the wireless broadband technology needed to meet increasing expectations in terms
WHITE PAPER. Expert Tips for Planning an Industrial Wireless Network. Mike Werning Field Application Engineer, Moxa Americas
 Expert Tips for Planning an Industrial Wireless Network Mike Werning Field Application Engineer, Moxa Americas Executive Summary Wi-Fi is now present everywhere and people have become comfortable using
Expert Tips for Planning an Industrial Wireless Network Mike Werning Field Application Engineer, Moxa Americas Executive Summary Wi-Fi is now present everywhere and people have become comfortable using
eclipse packet node aviat networks transforming networks to all-ip
 eclipse packet node aviat networks ANSI transforming networks to all-ip 4G Wireless Backhaul for 4G/LTE Networks 2 AVIAT NETWORKS 4G/LTE Ready Wireless Backhaul Enabling the mobile broadband future The
eclipse packet node aviat networks ANSI transforming networks to all-ip 4G Wireless Backhaul for 4G/LTE Networks 2 AVIAT NETWORKS 4G/LTE Ready Wireless Backhaul Enabling the mobile broadband future The
Mission Critical Mobile Broadband:
 Critical communications for all professional users Follow us on @TCCAcritcomms February 2013 CRITICAL COMMUNICATIONS BROADBAND GROUP WHITE PAPER Mission Critical Mobile Broadband: Important Note The opinions
Critical communications for all professional users Follow us on @TCCAcritcomms February 2013 CRITICAL COMMUNICATIONS BROADBAND GROUP WHITE PAPER Mission Critical Mobile Broadband: Important Note The opinions
An ADTRAN White Paper. Defining Broadband Speeds: Estimating Capacity in Access Network Architectures
 An ADTRAN White Paper Defining Broadband Speeds: Estimating Capacity in Access Network Architectures Defining Broadband Speeds: Estimating Capacity in Access Network Architectures Executive Summary This
An ADTRAN White Paper Defining Broadband Speeds: Estimating Capacity in Access Network Architectures Defining Broadband Speeds: Estimating Capacity in Access Network Architectures Executive Summary This
MA R K E TING R E PORT. The Future of Passive Optical Networking is Here NG-PON2
 MA R K E TING R E PORT The Future of Passive Optical Networking is Here NG-PON2 NG-PON2 The future of Passive Optical Networking is Here Introduction...3 The Evolution of Passive Optical Networking...4
MA R K E TING R E PORT The Future of Passive Optical Networking is Here NG-PON2 NG-PON2 The future of Passive Optical Networking is Here Introduction...3 The Evolution of Passive Optical Networking...4
Chapter 1: introduction
 Chapter 1: introduction our goal: v get feel and terminology v more depth, detail later in course v approach: use Internet as example overview: v what s the Internet? v what s a protocol? v edge; hosts,
Chapter 1: introduction our goal: v get feel and terminology v more depth, detail later in course v approach: use Internet as example overview: v what s the Internet? v what s a protocol? v edge; hosts,
REDUCING CAPEX AND OPEX THROUGH CONVERGED OPTICAL INFRASTRUCTURES. Duane Webber Cisco Systems, Inc.
 REDUCING CAPEX AND OPEX THROUGH CONVERGED OPTICAL INFRASTRUCTURES Duane Webber Cisco Systems, Inc. Abstract Today's Cable Operator optical infrastructure designs are becoming more important as customers
REDUCING CAPEX AND OPEX THROUGH CONVERGED OPTICAL INFRASTRUCTURES Duane Webber Cisco Systems, Inc. Abstract Today's Cable Operator optical infrastructure designs are becoming more important as customers
Air4G Innovative. Compact. All-outdoor. Integrated WiMAX and LTE multi-platform base station exceeding the extremes in cost-efficiency
 Air4G Innovative. Compact. All-outdoor. Integrated WiMAX and LTE multi-platform base station exceeding the extremes in cost-efficiency Air4G Air4G A 4G network revolution in a compact, efficient package
Air4G Innovative. Compact. All-outdoor. Integrated WiMAX and LTE multi-platform base station exceeding the extremes in cost-efficiency Air4G Air4G A 4G network revolution in a compact, efficient package
Mobile Network Evolution
 ANSI Mobile Network Evolution Eclipse Packet Node, enabling the 4G mobile broadband future The explosive demand for the next-generation mobile user experience is forcing operators to quickly implement
ANSI Mobile Network Evolution Eclipse Packet Node, enabling the 4G mobile broadband future The explosive demand for the next-generation mobile user experience is forcing operators to quickly implement
The 5G consumer business case. An economic study of enhanced mobile broadband
 The 5G consumer business case An economic study of enhanced mobile broadband Enhancing today s services for tomorrow 5G has the potential to drive new revenue streams. Much focus has been on the innovative
The 5G consumer business case An economic study of enhanced mobile broadband Enhancing today s services for tomorrow 5G has the potential to drive new revenue streams. Much focus has been on the innovative
Title of Presentation
 Improve the productivity, efficiency and safety of your remote operations Title of Presentation Presenter MM/DD/YYYY COMPANY OVERVIEW Overview RigNet (NASDAQ: RNET) provides technology solutions around
Improve the productivity, efficiency and safety of your remote operations Title of Presentation Presenter MM/DD/YYYY COMPANY OVERVIEW Overview RigNet (NASDAQ: RNET) provides technology solutions around
Distributed PON Architectures for North American MSO s Next-Generation Access
 FEATURED TOPIC Distributed PON Architectures for North American MSO s Next-Generation Access Keiichi TSUJIMOTO*, Yohei HAMADA, Howard ABRAMSON, and Kazuya MATSUMOTO ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FEATURED TOPIC Distributed PON Architectures for North American MSO s Next-Generation Access Keiichi TSUJIMOTO*, Yohei HAMADA, Howard ABRAMSON, and Kazuya MATSUMOTO ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core
 Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Inter? 1.2 work edge end systems, works, links 1.3 work core packet switching, circuit switching, work structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in works 1.5 protocol layers,
Troubleshooting. Troubleshooting Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides basic installation troubleshooting information. The chapter includes the following sections: Overview Initialization and Self-Test Problems Subsystems Further Contacts This
CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides basic installation troubleshooting information. The chapter includes the following sections: Overview Initialization and Self-Test Problems Subsystems Further Contacts This
Medianet for Cable Operators. Transitioning Service Providers to Experience Providers
 Medianet for Cable Operators Transitioning Service Providers to Experience Providers 1 Driving the Technology Revolution 1 Delivery Technology Revolution 2 3 Fiber Deep All Digital Video IP Convergence
Medianet for Cable Operators Transitioning Service Providers to Experience Providers 1 Driving the Technology Revolution 1 Delivery Technology Revolution 2 3 Fiber Deep All Digital Video IP Convergence
Driving Gigabit Speeds: From Lab to Consumer
 Driving Gigabit Speeds: From Lab to Consumer FALL 2018 About About CableLabs As the leading Innovation and R&D lab for the cable industry, CableLabs creates global impact through its 60+ cable-network-operator
Driving Gigabit Speeds: From Lab to Consumer FALL 2018 About About CableLabs As the leading Innovation and R&D lab for the cable industry, CableLabs creates global impact through its 60+ cable-network-operator
WHITE PAPER. The 450 MHz Band Ecosystem
 WHITE PAPER The 450 MHz Band Ecosystem Introduction M2M communications, in which everyday objects and devices are online and able to interact with each other, have seen significant growth in recent years.
WHITE PAPER The 450 MHz Band Ecosystem Introduction M2M communications, in which everyday objects and devices are online and able to interact with each other, have seen significant growth in recent years.
Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter 3.3
 Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter 3.3 Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter is an easy-to-use tool with a GUI that helps network administrators and technicians to streamline RF problem resolution. The tool dynamically
Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter 3.3 Cisco Broadband Troubleshooter is an easy-to-use tool with a GUI that helps network administrators and technicians to streamline RF problem resolution. The tool dynamically
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Siemon 10G ip Solutions
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Siemon 10G ip Solutions The world of enterprise cabling is evolving rapidly. Emerging, high-bandwidth services and the adoption of higher speed Ethernet standards, like
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Siemon 10G ip Solutions The world of enterprise cabling is evolving rapidly. Emerging, high-bandwidth services and the adoption of higher speed Ethernet standards, like
Outside plant solutions for multisystem operators
 Outside plant solutions for multisystem operators MSO: outside plant solutions Leading innovation in fiber connectivity and cable management solutions CommScope offers a unique and diverse product line
Outside plant solutions for multisystem operators MSO: outside plant solutions Leading innovation in fiber connectivity and cable management solutions CommScope offers a unique and diverse product line
RELIABLE CONNECTIONS FOR A CONNECTED WORLD
 RELIABLE CONNECTIONS FOR A CONNECTED WORLD AlphaGateway The Enabling Technology AlphaGateway Family With over 40 years of broadband cable TV powering expertise and over 1 million hardened modems in operation
RELIABLE CONNECTIONS FOR A CONNECTED WORLD AlphaGateway The Enabling Technology AlphaGateway Family With over 40 years of broadband cable TV powering expertise and over 1 million hardened modems in operation
Broadband and Last Mile Networks
 Broadband and Last Mile Networks Last-Mile Network Design Concerns Infrastructure Cost Throughput: Upstream and Downstream Packet or Circuit Switching Congestion Control Latency History: Dial-up First
Broadband and Last Mile Networks Last-Mile Network Design Concerns Infrastructure Cost Throughput: Upstream and Downstream Packet or Circuit Switching Congestion Control Latency History: Dial-up First
wi4 Fixed Point-to-Multipoint Canopy Solutions
 wi4 Fixed Point-to-Multipoint Canopy Solutions Canopy Technology is as Simple as it is Powerful The wi4 Fixed Point-to-Multipoint Canopy solution is streamlined, powerful and simple, with built-in installation
wi4 Fixed Point-to-Multipoint Canopy Solutions Canopy Technology is as Simple as it is Powerful The wi4 Fixed Point-to-Multipoint Canopy solution is streamlined, powerful and simple, with built-in installation
Delivering next-generation fibre throughout every building
 Delivering next-generation fibre throughout every building Linking the future As the worldwide leader in the cable industry, Prysmian Group believes in the effective, efficient and sustainable supply of
Delivering next-generation fibre throughout every building Linking the future As the worldwide leader in the cable industry, Prysmian Group believes in the effective, efficient and sustainable supply of
4G Mobile Communications
 4G Mobile Communications Welcome to 4G The term 4G is used broadly to include several types of broadband wireless access communication systems, not only cellular telephone systems. One of the terms to
4G Mobile Communications Welcome to 4G The term 4G is used broadly to include several types of broadband wireless access communication systems, not only cellular telephone systems. One of the terms to
Preparing for a 5G Future
 Preparing for a 5G Future RF Planning of Millimeter Wave Frequencies for RAN Evolution SOLUTION BRIEF Orchestrating Network Performance Expectations for 5G According to the Global mobile Supplier s Association
Preparing for a 5G Future RF Planning of Millimeter Wave Frequencies for RAN Evolution SOLUTION BRIEF Orchestrating Network Performance Expectations for 5G According to the Global mobile Supplier s Association
Delivering copper-based broadband access services at 100 Mbps. George Ginis February 12 th, 2014
 Delivering copper-based broadband access services at 100 Mbps George Ginis February 12 th, 2014 1 Vectored VDSL Needs More than Copper Network Operations Support Systems DSL monitoring and optimization
Delivering copper-based broadband access services at 100 Mbps George Ginis February 12 th, 2014 1 Vectored VDSL Needs More than Copper Network Operations Support Systems DSL monitoring and optimization
White Paper Power and Its Connection to Network Reliability
 White Paper Power and Its Connection to Network Reliability ALPHA TECHNOLOGIES Power and Its Connection to Network Reliability By Eric Wentz from Alpha Technologies, Inc. Reliability continues to be the
White Paper Power and Its Connection to Network Reliability ALPHA TECHNOLOGIES Power and Its Connection to Network Reliability By Eric Wentz from Alpha Technologies, Inc. Reliability continues to be the
02/15/01 1 T1E1.4/ Contact: J. Cioffi, Dept of EE, Stanford U., Stanford, CA , F:
 02/15/01 1 T1E1.4/2001-088 Project: T1E1.4: Spectrum Management II Title: Unbundled DSL Evolution (088) Contact: J. Cioffi, Dept of EE, Stanford U., Stanford, CA 94305 cioffi@stanford.edu, 1-650-723-2150,
02/15/01 1 T1E1.4/2001-088 Project: T1E1.4: Spectrum Management II Title: Unbundled DSL Evolution (088) Contact: J. Cioffi, Dept of EE, Stanford U., Stanford, CA 94305 cioffi@stanford.edu, 1-650-723-2150,
The Value of Content at the Edge
 The Value of Content at the Edge Executive Summary The way we use the Internet has changed, and the result has been exploding traffic growth that is projected to increase at a 30 to 50 percent compound
The Value of Content at the Edge Executive Summary The way we use the Internet has changed, and the result has been exploding traffic growth that is projected to increase at a 30 to 50 percent compound
An ADTRAN White Paper. Distributed Access Solutions for the Local Loop
 An ADTRAN White Paper Distributed Access Solutions for the Local Loop Executive Summary ADTRAN s Total Access System is a distributed access solution that enables carriers to strategically plan and design
An ADTRAN White Paper Distributed Access Solutions for the Local Loop Executive Summary ADTRAN s Total Access System is a distributed access solution that enables carriers to strategically plan and design
SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS
 SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS Erik L. Org (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA; erik@bitwave.com ); Russell J. Cyr (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA;
SOFTWARE DEFINED RADIO PROGRAMMABLE TRANSCEIVERS FOR FEMTOCELLS Erik L. Org (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA; erik@bitwave.com ); Russell J. Cyr (BitWave Semiconductor, Inc., Lowell, MA, USA;
CAN EMTC IOT BE SUPPORTED OVER THE HFC NETWORK
 CAN EMTC IOT BE SUPPORTED OVER THE HFC NETWORK A Constructional Proposal of MOVING IOT into HFC A Technical Paper Prepared for SCTE/ISBE by Shengbo Ge Shanghai, China Cable HFC/CRDC CHG/ Cisco Systems
CAN EMTC IOT BE SUPPORTED OVER THE HFC NETWORK A Constructional Proposal of MOVING IOT into HFC A Technical Paper Prepared for SCTE/ISBE by Shengbo Ge Shanghai, China Cable HFC/CRDC CHG/ Cisco Systems
Networking. Prof. Abdul Hameed
 Networking Prof. Abdul Hameed http://informationtechnology.pk http://informationtechnology.pk 0 Chapter Topics Networking Fundamentals Network Architectures and Components Connecting to the Internet Installing
Networking Prof. Abdul Hameed http://informationtechnology.pk http://informationtechnology.pk 0 Chapter Topics Networking Fundamentals Network Architectures and Components Connecting to the Internet Installing
200-micron Fiber Enables New Cable Designs
 White Paper 200-micron Fiber Enables New Cable Designs Since single-mode fiber was first introduced in the early 1980 s, little has changed in its basic geometric parameters. The core size has remained
White Paper 200-micron Fiber Enables New Cable Designs Since single-mode fiber was first introduced in the early 1980 s, little has changed in its basic geometric parameters. The core size has remained
Transform your bottom line: 5G Fixed Wireless Access
 Transform your bottom line: 5G Fixed Wireless Access Transform Your Bottom Line: 5G Fixed Wireless Access 1 Seizing the opportunity of 5G with Fixed Wireless Access To get a sense of the future of broadband,
Transform your bottom line: 5G Fixed Wireless Access Transform Your Bottom Line: 5G Fixed Wireless Access 1 Seizing the opportunity of 5G with Fixed Wireless Access To get a sense of the future of broadband,
Network Access Technology Consideration in Europe. By Helge Tiainen of InCoax and Chair of the MoCA Access Work Group
 Network Access Technology Consideration in Europe By Helge Tiainen of InCoax and Chair of the MoCA Access Work Group Introduction There is no shortage of networking alternatives to reach multi-dwelling
Network Access Technology Consideration in Europe By Helge Tiainen of InCoax and Chair of the MoCA Access Work Group Introduction There is no shortage of networking alternatives to reach multi-dwelling
Nokia Passive Optical LAN solution
 As businesses contemplate how to introduce a new generation of services, improve productivity, lower costs and build a competitive advantage, they are faced with tough decisions about the performance and
As businesses contemplate how to introduce a new generation of services, improve productivity, lower costs and build a competitive advantage, they are faced with tough decisions about the performance and
White Paper. Re-enterable Plug and Play Fiber Access Terminals. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION COMMON TYPES OF FIBER ACCESS TERMINALS
 Re-enterable Plug and Play Fiber Access Terminals Will Miller, Product Line Manager OSP Connectivity, AFL ABSTRACT In modern FTTx builds, connectorized fiber access terminals are commonly the last point
Re-enterable Plug and Play Fiber Access Terminals Will Miller, Product Line Manager OSP Connectivity, AFL ABSTRACT In modern FTTx builds, connectorized fiber access terminals are commonly the last point
Addressing issues in the local area network
 Addressing issues in the local area network Enabling the digital enterprise with passive optical LAN Strategic White Paper For more than 30 years, the local area networks (LANs) that enable enterprise
Addressing issues in the local area network Enabling the digital enterprise with passive optical LAN Strategic White Paper For more than 30 years, the local area networks (LANs) that enable enterprise
A New Approach to Outdoor DAS Network Physical Layer Using E-Line Technology
 A New Approach to Outdoor DAS Network Physical Layer Using E-Line Technology A white paper describing a new physical layer technology for wireless mobile networks with dramatically lower cost. Corridor
A New Approach to Outdoor DAS Network Physical Layer Using E-Line Technology A white paper describing a new physical layer technology for wireless mobile networks with dramatically lower cost. Corridor
With the publication. Make the right connection: Bonding a shielded system. installation
 Make the right connection: Bonding a shielded system installation With the publication of the IEEE 802.3an 10GBase-T standard in 2006, Augmented Category 6 (i.e., Category 6A) cabling systems are being
Make the right connection: Bonding a shielded system installation With the publication of the IEEE 802.3an 10GBase-T standard in 2006, Augmented Category 6 (i.e., Category 6A) cabling systems are being
Computer Networks and the internet. Daniel Graham Ph.D
 Computer Networks and the internet Daniel Graham Ph.D 1.1 What Is the Internet? The Internet is a computer network that interconnects hundreds of millions of computing devices throughout the world. As
Computer Networks and the internet Daniel Graham Ph.D 1.1 What Is the Internet? The Internet is a computer network that interconnects hundreds of millions of computing devices throughout the world. As
LIGHTS! Broadband Basics
 LIGHTS! Broadband Basics Presented by: Tom Robinson, President 73 Chestnut Rd, Suite 301 Paoli, PA 19301 Phone (610) 889-7470 robinson@cbgcommunications.com NATOA ANNUAL CONFERENCE SEPTEMBER 17, 2013 2013
LIGHTS! Broadband Basics Presented by: Tom Robinson, President 73 Chestnut Rd, Suite 301 Paoli, PA 19301 Phone (610) 889-7470 robinson@cbgcommunications.com NATOA ANNUAL CONFERENCE SEPTEMBER 17, 2013 2013
