> Technical Configuration Guide for Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 802.3ad and VLACP. Product Name Ethernet Routing Switch & Ethernet Switch
|
|
|
- Amy Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Product Name Ethernet Routing Switch & Ethernet Switch > Technical Configuration Guide for Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 802.3ad and VLACP Enterprise Solutions Engineering Document Version: 1.1
2 Copyright 2005 Nortel Networks All rights reserved. December 2005 The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks Inc. The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance with the terms of that license. Trademarks Nortel, the Nortel logo, the Globemark, Unified Networks, PASSPORT and BayStack are trademarks of Nortel Networks. Adobe and Acrobat Reader are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporate. All other Trademarks are the property of their respective owners. NORTEL External Distribution 1
3 Abstract The document provides an overview on how to configure 802.3ad Link Aggregation for the Nortel ERS and ES switches. Concepts will include 802.3ad, 802.3ad with SMLT, 802.3ad with Single Link SMLT, and VLACP. NORTEL External Distribution 2
4 Table of Contents 1. OVERVIEW: 802.3AD LINK AGGREGATION LACP AND LINK-LAYER FAILURE DETECTION VLACP USING VLACP OVER AN RPR LACP AND VLACP SUPPORT ON NORTEL PRODUCTS CONFIGURATION RULES AND GUIDELINES CONFIGURATION NOTES SMLT NETWORK DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS LACP AND SPANNING TREE INTERACTION ROUTING CONSIDERATIONS CONFIGURING LACP ERS ES SWITCH CONFIGURING VLACP ERS SWITCH ES SWITCH LACP CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE: BASE SCENARIO, POINT-TO-POINT CONFIGURATION STEPS VERIFICATION JDM LACP CONFIGURATION ERS8600A LACP INTEROPERABILITY BETWEEN A ES470 AND CISCO VERIFICATION LACP INTEROPERABILITY BETWEEN ERS8600 AND CISCO CATALYST CONFIGURATION STEPS SMLT WITH 802.3AD AND MLT WITH VLACP CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE SMLT TOPOLOGY CONFIG STEPS VERIFICATION VLACP EXAMPLE VIA LAN EXTENSION CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE VERIFICATION: REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION NORTEL External Distribution 3
5 1. Overview: 802.3ad Link Aggregation IEEE 802.3ad-based link aggregation allows you to aggregate two or more links together to form Link Aggregation Groups (LAG s) such that a MAC client can treat the Link Aggregation Group as if it were a single link. Although IEEE 802.3ad-based link aggregation and MultiLink Trunking (MLT) features provide similar services, MLT is statically defined, whereas IEEE 802.3ad-based link aggregation is dynamic and provides more functionality through the link aggregation control protocol (LACP). LACP dynamically detects whether links can be aggregated into a link aggregation group and does so when links become available. IEEE 802.3ad was designed for point-to-point link aggregation only. However, the ERS8600 has been implemented to provide extensions to support IEEE 802.3ad in Split MultiLink Trunking (SMLT) configurations, thereby allowing any IEEE 802.3ad-capable device to be connected to an SMLT aggregation pair. 1.1 LACP and Link-Layer Failure Detection Aside from automatic link aggregation, a side benefit of running LACP is its ability to detect linklayer failure within a service provider s network. LACP packets are exchanged end-to-end, thus if a link in the core were to fail and the local port(s) do not register the failure, LACP will time out and remove the port from the LAG - note that for the ERS8600 in release 3.7.x, the port s STP state is disabled whereas with an ES switch, the port is removed from the LAG and put into normal STP mode. The default settings, with the long timers, will remove the port from the LAG in 90 seconds. If short timers were used, the port can be removed in 3 seconds. VLACP Virtual LACP - can be used to speed up this process if necessary. Note that VLACP will also disable the port whereas LACP just removes a port from the LAG. 1.2 VLACP Virtual LACP (VLACP) is an extension to LACP, used to detect end-to-end failure. VLACP takes the point-to-point hello mechanism of LACP and uses it to periodically send hello packets to ensure end-to-end reachability and provide failure detection (across any L2 domain). When Hello packets are not received, VLACP transitions to a failure state and the port will be brought down. The benefit of this over LACP is that VLACP timers can be reduced to 400 milliseconds between a pair of ERS8600 switches. This will allow for approximately one second failure detection and switchover. Note that the lowest VLACP timer on an ES460/470 is 500ms. VLACP can also be used with Nortel s proprietary aggregation mechanism (MLT) to complement its capabilities and provide quick failure detection. VLACP is recommended for all SMLT links when the links are configured as MLT to ensure both end devices are able to communicate. By using VLACP over Single-Port SMLT, enhanced failure detection is extended beyond the limits of the number of SMLT or LACP instances that can be created on the ERS8600. NOTE: In the current implementation for the ERS8600, although either the CLI or JDM interface allows you to configure the short timers to less than 400ms, Nortel does not support this configuration. Changes will be made in the software to allow these short timers in a subsequent release (target release is ERS ). Although functions such as Remote fault indication (RFI) or Far-end fault indication (FEFI) can be used to indicate link failure, there are some limitations with these mechanisms. The first limitation is that with either of these mechanisms, they terminate at the next Ethernet hop. Hence, failures cannot be detected on an end-to-end basis over multiple hops such as LAN Extension services. The second limitation is both of these mechanisms required Auto-Negotiation to be enabled on the Ethernet interface. Hence, if an Ethernet interface does not support Auto-Negotiation; neither NORTEL External Distribution 4
6 of these mechanisms can be used. Finally, the third limitation is if an Ethernet interface should fail and still provide a transmit signal, RFI nor FEFI will be able to detect a failure. Hence, the far-end interface will still think the link up and continue to transmit traffic. VLACP will only work for port-to-port applications when there is a guarantee for a logical port-port match. It will not work in a port-to-multi-port scenario where there is no guarantee for a pointpoint match. 1.3 Using VLACP over an RPR As mentioned above, VLACP can be used across a LAN Extension service to provide end-to-end failure detection. In the case of using RPR, MLT is only supported on NNI links and not on UNI links. Hence, if MLT is used on a PRP ring via a UNI interface, by default, there is no mechanism to signal a remote link failure. For this application, providing Nortel switches are used at both ends, VLACP can configured on top of MLT to provide end-to-end failure detection. If the remote switch is not a Nortel switch, LACP can be used providing the switch supports 802.1ad. When setting up the OM3500, a separate TDI should be used for each link from the Nortel switch. If only one TDI is used, broadcasts would be flooded back to the end switch. As shown in the diagram above, two TDI s are used for this application. If you are using OEL2 mode, then configure the service type as point-to-point for more efficient use of bandwidth on RPR. NORTEL External Distribution 5
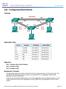
7 1.4 LACP and VLACP Support on Nortel Products Switch LACP Support VLACP Support Limitations ERS8600 Yes Yes 32 Link Aggregation Groups o A maximum of 8 active links are supported per LAG. Note 1 o A maximum of 8 standby links are supported per LAG. Note 1 o Up to 16 ports can be configured in a LAG (8 active and 8 standby ports) 383 Single-port SMLT LAG s (all ports minus IST port(s)) ERS8300 Release 2.2 Release Link Aggregation Groups o A maximum of 4 active links are supported per LAG ERS55x0 Release 5.0 Release Link Aggregation Groups o A maximum of 8 active links are support per LAG. 128 Single-port SMLT LAG s ERS1600 Release 2.1 Release Link Aggregation Groups o A maximum of 4 active links are supported per LAG All ports for Single-port SMLT ES460/470 Yes Yes 6 Link Aggregation Groups o Maximum of 4 active links are support per LAG o A fifth standby can be added to a trunk group. o The first four highest priority links form a trunk group while the 5 th lowest priority link remains in standby mode ES325/425 Release 3/7 (Q106) Yes 6 Link Aggregation Groups o Maximum of 4 active links are support per LAG Note 1: The maximum number of active links in a Link Aggregation group is 8; however, it is possible to configure up to 16 links in a LAG. The 8 links that are not active are in Standby mode. Should an active link be disable, the backup link with the lowest port number will immediately become active. Note 2: All links in a trunk group must have the same speed and must be full duplex. NORTEL External Distribution 6
8 2. Configuration Rules and Guidelines 2.1 Configuration Notes All ports in a link aggregation group must be operating in full-duplex mode (defined by the IEEE standard). All ports in a link aggregation group must be running same data rate (defined by the IEEE standard). All ports in a link aggregation group must be in the same VLAN or VLAN s. Ports in a LAG can be distributed over different modules. Link aggregation is compatible with the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP); STP normally should be disabled with on all SMLT ports. Link aggregation group(s) must be in the same STP group(s). If the NTSTG parameter is set to false, STP BPDU transmits only on one link. MTSTG is the default mode where ERS 8600 sends BPDUs on ALL links of an aggregation group MLT or 802.3ad group. To correctly enable tagging in LACP applications, you first need to disable LACP on the port, enable tagging on the port, and then re-enable LACP. LACP-enabled ports with the same key must have the same VLAN membership. On LACP-disabled ports with the same key, VLAN membership can be different. This usually happens when you add VLANs to or delete VLANs from these ports. But before LACP is re-enabled on these ports, VLAN membership must be the same for ports with the same key. In order to change the VLANs membership on a LAG, or the ports membership within the VLANs, LACP must be disabled on the ports. Once the changes are completed, LACP can be enabled again on all appropriate port members. 2.2 SMLT Network Design Considerations If you use LACP in an SMLT/Square configuration, the LACP ports must have the same keys for that SMLT/LAG; otherwise, the aggregation may fail if a switch failure occurs. LACP system priority should not be changed once LACP is enabled on one or more SMLTs and also enabled at port level. If some ports are joined into the desired MLT after dynamic configuration changes, enter the following CLI command: o ERS8610C:5# config mlt {1..32} lacp clear-link-aggrgate It is recommended to not enable LACP on the IST trunk to avoid unnecessary processing and to maintain simplicity. If a failure detection mechanism is required when there is an optical network between the SMLT core switches then use VLACP. 2.3 LACP and Spanning Tree Interaction The operation of the LACP module is only affected by the physical link state or its LACP peer status. When a link goes up and down, the LACP module will be notified. The STP forwarding state does not affect the operation of LACP module. LACPDU can be sent even if the port is in STP blocking state. NORTEL External Distribution 7
9 Unlike legacy MLTs, configuration changes (such as speed, duplex mode, and so on) to a LAG member port is not applied to all the member ports in this MLT. Instead, the changed port is taken out of the LAG and the corresponding aggregator and user is alerted when such a configuration is created. In contrast to MLT, IEEE 802.3ad-based link aggregation does not expect BPDUs to be replicated over all ports in the trunk group therefore you must enter the following command to disable the parameter on the spanning tree group for LACP-based link aggregation: Passport-8610:5# config stg x ntstg disable Be aware that this parameter is applicable to all trunk groups that are members of this spanning tree group. This is necessary when interworking with devices that only send BPDUs out one port of the LAG. 2.4 Routing Considerations If OSPF is enabled on the port, do not set the LACP periodic transmission timer to less than one second. NORTEL External Distribution 8
10 3. Configuring LACP Please take into consideration the following items when configuring LACP. LACP Priority LACP priority is configured at the system level and at the port level Port Priority used to determine which ports are aggregated into LAG as a standby-port configuration if more than the maximum numbers of ports supported in a LAG are configured. If the port priority is the same, then the lower MAC equals higher priority. System Priority used to generate the switch ID when communicating with other switches. For SMLT applications, this is used to determine a master/slave relationship between the SMLT switches. It is recommended to leave this value to default. If it is changed, it is recommended to disable LACP and then enabling it once the value is changed. LACP Keys LACP keys are used to determine which ports are eligible to be aggregated into a LAG. The LACP keys are defined when configuring the MLT and defined under the ports. The ports whose keys match the MLT s key will be able to be aggregated in that MLT. keys need not match between two LACP peers. keys must match on SMLT core switches when using LACP with SMLT. LACP Timers Customization of the failover times is achieved by changing the LACP timer attributes. Please note that these values are set by default to match the IEEE 802.3ad values, if they are changed, these values must match on the ports participating in aggregation between two DUTs. Any changes to these values at the global level, ERS8600 only, will be reflected on all ports. Or, these values can be changed on a per port level. The following displays the default timer settings. timeout: 3 fast-periodic-time: 1000 (ms) slow-periodic-time: (ms) The user can choose to use either the fast or slow timer, this is set on the port level. By default, the long timer is used. Hence, a link is determined ineligible to be aggregated if it does not receive an LACPDU for a period of: timeout x slow-periodic-time = 3 x 30s = 90s Should the user decide to use the fast-periodic-time instead, by default, the timeout period now becomes 3 x 1000 ms = 3 seconds. This change must be made to all ports participating in link aggregation, as well as the ports on the partnering node. NORTEL External Distribution 9
11 3.1 ERS Global LACP Parameters Via CLI LACP is configured globally by using the following command: Passport-8610:5# config lacp? Sub-Context: Current Context: aggr-wait-time milliseconds disable enable system-priority <integer> fast-periodic-time milliseconds slow-periodic-time milliseconds timeout-scale <integer> info where: Parameter Description info Displays current level parameter settings and next level directories. enable Enables LACP globally. disable Disables LACP globally. aggr-wait-time Sets the aggregator wait-time in milliseconds. The default wait-time is <milliseconds> 2,000 ms. The range is 200 to 2,000 ms. system-priority <integer> fast-periodic-time milliseconds slow-periodic-time milliseconds timeout-scale <integer> Sets LACP system priority globally. The default system-priority is 32,768. integer is the system priority value with range of Sets fast periodic time globally. The default fast-periodic-time is 1,000 ms. The range is 200 to 2,000 ms, however, Nortel recommends a value no lower than 400ms. milliseconds are the fast periodic time value. Sets slow periodic time globally. The default slow-periodic-time is 30,000 ms. The range is 10,000 to 30,000 ms milliseconds are the slow periodic time value. Sets a timeout scale globally. The default timeout-scale is 3. The range is 1 to 10. integer is the timeout scale value. NORTEL External Distribution 10
12 Via JDM Go to VLAN>MLT/LACP>LACP Global Check Enable to enable LACP globally Recommend keeping timers default LACP Interface Parameters Via CLI LACP must also be enabled on all desired ports by using the following command: where : Passport-8610:5# config ethernet <slot/port> lacp? Parameter info Sub-Context: Current Context: disable enable aggr-wait-time <miliseconds> fast-periodic-time <miliseconds> info key <integer> aggregation <true false> mode <active passive> partner-key <int> partner-port <int> partner-port-priority <int> partner-state <hex> partner-system-id <mac> partner-system-priority <int> port-priority <integer> slow-periodic-time <miliseconds> system-priority <integer> timeout <long short> timeout-scale <integer> Description Displays current level parameter settings and next level directories. NORTEL External Distribution 11
13 Parameter enable disable aggr-wait-time <milliseconds> fast-periodic-time <milliseconds> key <integer> aggregation <true false> mode <active passive> partner-key <int> partner-port <int> partner-port-priority <int> partner-state <hex> partner-system-id <mac> partner-system-priority <int> Description Enables LACP for a specific port-type. Disables LACP for a specific port-type. Sets the aggregation wait time (in milliseconds) for a specific porttype. milliseconds is the LACP aggregation wait time, an integer value in the range 200 and 2,000 ms Sets the fast periodic time (in milliseconds) for a specific port-type. The default value is 1,000 ms. milliseconds is the fast periodic time value; an integer value in the range 200 and 20,000 ms. Note: The fast periodic time value of 200 ms is not supported for this software release 3.7.x. The minimum supported fast periodic time value is 400 ms. Sets LACP aggregation key for a specific port-type. integer is an integer value in the range 1 and 32 for aggregatable ports. You can use a default key only for individual ports, an integer value in the range 0 and Sets individual port or aggregatable for a specific port type. true sets port as aggregatable. false sets port as individual. Sets the mode as active or passive for a specific port-type. Active Mode ports will initiate the aggregation process. Active mode ports will aggregate with other Active mode ports or Passive mode ports. Passive Mode ports will participate in LACP but will not initiate the aggregation process. Passive mode ports must be partnered with Active Mode ports for aggregation to occur. Sets the port partner s administration key value. int is the LACP partner s administrative key; an integer value in the range 0 and Sets the port partner s administration port value. int is the LACP partner s administrative port; an integer value in the range 0 and Sets the port partner s administration port priority value. int is the LACP partner s administrative port priority; an integer value in the range 0 and Sets the port partner s administration state. hex is the LACP partner s administrative state bitmap; (Exp,Def,Dis,Col,Syn,Agg,Time,Act). Example: Activity = true Aggregating = true val = (0x05) {0x0..0xff} Sets the port partner s administration system ID. mac is the LACP partner s administrative system ID; Mac address in the format: 0x00:0x00:0x00:0x00:0x00:0x00. Sets the port partner s administration system priority value. int is the LACP partner s administrative system priority; an integer value in the range 0 and NORTEL External Distribution 12
14 Parameter port-priority <integer> slow-periodic-time <milliseconds> Description Sets the LACP port priority to specific port type. The default value is integer is the port priority value; an integer value in the range 0 and Sets the slow periodic time (in milliseconds) for a specific port-type. The default value is 1,000 ms integer is the slow periodic time value, an integer value in the range 10,000 and 30,000 ms. Sets system-priority for a specific port-type. integer is system-priority value with range Sets the timeout value to either long or short for a specific port-type. system-priority <integer> timeout <long short> timeout-scale <integer> Sets a timeout scale for a specific port-type. The default value is 3. integer is the timeout scale value, an integer value in the range 1 and Via JDM Select the port where you wish to enable LACP, right-click it and select Edit. Go to the LACP window as shown below. NORTEL External Distribution 13
15 3.2 ES Switch Default LACP System-Priority The default lacp system-priority is set for and can be changed by using the following command: T(config)#lacp system-priority? < > priority LACP Interface Parameters Via CLI LACP must also be enabled on all desired ports by using the following command: T-PWR(config)#interface fastethernet all T-PWR(config-if)# lacp? Configure LACP port parameters aggregation Enable port aggregation mode clear-stats Clear LACP statistics key Set key value for ports mode Set LACP port mode priority Set port priority timeout-time Set port timeout where: Item aggregation clear-stats key mode priority timeout-time Description Enable or disable aggregation on this port Clears the LACP statistics Sets LACP aggregation key for a specific port-type. Value is in the range from 1 to 4095 Sets the LACP mode: Active = AdminEnabled + ActorAdminState(lacpActive) Passive = AdminEnabled Off = AdminDisabled The priority value assigned to this aggregation port. Value is in the range 0 to Set the timer for ether long or short. For example, to enable LACP aggregation on port 3, enter the following command: T-PWR(config)#interface fastethernet all T-PWR(config-if)# lacp aggregation port 3 enable NORTEL External Distribution 14
16 Via JDM Select the port where you wish to enable LACP, right-click it and select Edit. Go to the LACP window as shown below. NORTEL External Distribution 15
17 4. Configuring VLACP 4.1 ERS Switch Interface Level Via CLI VLACP is configured via the interface level using the command shown below. ERS8610C:5# config ethernet <slot/port> vlacp? Sub-Context: Current Context: disable enable fast-periodic-time <miliseconds> info slow-periodic-time <miliseconds> timeout <long short> timeout-scale <integer> ethertype <integer> macaddress <mac> where: Parameters and Variables info enable disable fast-periodic-time <milliseconds> slow-periodic-time <milliseconds> timeout <long short> timeout-scale <integer> Description Displays current level parameter settings and next level directories. Enables VLACP for a specific port-type. Disables VLACP for a specific port-type. Sets the fast periodic time value (in milliseconds) for a specific port-type. The default value is 200 ms milliseconds is the fast periodic time value, an integer value in the range 200 and 20,000 ms. Note: The fast periodic time value of 200 ms is not supported for this software release. The minimum supported fast periodic time value is 400 ms. Sets the slow periodic time value (in milliseconds) for a specific port-type. The default value is 30,000 ms milliseconds is the slow periodic time value, an integer value in the range 10,000 and 30,000 ms. Sets the port to use the long or short timeout value: long sets the port to use the timeout-scale value * the slowperiodic-time value. short sets the port to use the timeout-scale value * the fastperiodic-time value. For example, if you set the timeout-scale value to 3, and the fastperiodic-time value to 400 ms, the timer will expire within 1200 to 1400 ms. Sets a timeout scale for a specific port-type (where timeout-scale = periodic-time * timeout-scale). The default value is 3. integer is the timeout scale value, an integer value in the range 1 and 10. NORTEL External Distribution 16
18 Parameters and Variables ethertype <integer> macaddress <mac> Description Sets the VLACP protocol identification for this port. integer is the ethertype value, an integer value in the range 1 and Sets the Multicast MAC address used for the VLACPDU. Required parameters: mac is the MAC address in the following format: 0x00:0x00:0x00:0x00:0x00:0x Via JDM Select the port where you wish to enable VLACP, right-click it and select Edit. Go to the VLACP window as shown below Global Level Via CLI The following command enables VLACP globally: ERS8610C:5# config vlacp <enable disable info> NORTEL External Distribution 17
19 Via JDM Go to VLAN>MLT/LACP>VLACP Global 4.2 ES Switch Interface Level Via CLI VLACP is configured via the interface level using the command shown below T(config)#interface fastethernet all T(config-if)#vlacp port <port #>? enable Enable VLACP for the port(s) ethertype Set the ethertype value of VLACP fast-periodic-time Set the fast-periodic time interval funcmac-addr Set the mac-addr to exchange VLACPDU from end-to-end perspective slow-periodic-time Set the slow periodic time interval timeout Set the timeout type timeout-scale Set the timeout scale where: Parameters and Variables Description <port-type> Specifies the port type. In the current software release, port type must be Ethernet. <slot/port> enable disable Specifies the slot and port number. Enables or disables VLACP. timeout <long/short> Specifies whether the timeout control value for the port is a long or short timeout. long sets the port timeout value to: (timeout-scale value) x (slow-periodic-time value). short sets the port s timeout value to: (timeout-scale value) x (fast-periodic-time value). For example, if the timeout is set to short while the timeout-scale value is 3 and the fast-periodic-time value is 200 ms, the timer expires within 400 to 600 ms. Default is long. fast-periodic-time <integer> slow-periodic-time <integer> timeout-scale <integer> Specifies the number of milliseconds between periodic VLACPDU transmissions using short timeouts. The range is milliseconds. Default is 500. Specifies the number of milliseconds between periodic VLACPDU transmissions using long timeouts. The range is milliseconds. Default is Sets a timeout scale for the port, where timeout = (periodic time) x (timeout scale). The range is Default is 3. NORTEL External Distribution 18
20 Parameters and Variables Description funcmac-addr <mac> ethertype <integer> Specifies the address of the far-end switch/stack configured to be the partner of this switch/stack. If none is configured, any VLACPenabled switch communicating with the local switch through VLACP PDUs is considered to be the partner switch. Sets the VLACP protocol identification for this port. Defines the ethertype value of the VLACP frame. The range is 1 to Default is Via JDM Select the port where you wish to enable VLACP, right-click it and select Edit. Go to the VLACP window as shown below Global Level Via CLI The following command enables VLACP globally: T(config)#vlacp enable Via JDM Go to VLAN>MLT/LACP>VLACP Global NORTEL External Distribution 19
21 5. LACP Configuration Example: Base Scenario, Point-to-Point For this example, we will configure the following: Disable Spanning Tree on all LAG ports A Link Aggregation Group (LAG) is configured between ERS8600A and ERS8600B with 4 link members and the following items: o VLANs 10 and 20 will be tagged across the LAG o LACP key = 1 o MLT ID = 1 A LAG between ERS8600B and ES470A with 2 link members and the following items: o VLAN 10 will be tagged across the LAG o LACP key = 2 o MLT ID = 2 NOTE: In order to change the VLAN port membership or the VLAN tagged over the MLT. It is first required to disable LACP on the port, add the VLAN and associate it to the LACP ports, and then enable LACP on the ports. 5.1 Configuration Steps Perform the Following Steps on Switches ERS8600A 1. Create MLT 1 using key 1. Note: the key value must be the same as the port key. Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 lacp key 1 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 lacp enable 2. Disable Spanning Tree on ports 1/1-1/4 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 stg 1 stp disable 3. Configure LACP on ports 1/1-1/4 using key 1. The key used must be the same as that used in step 1 when setting up the MLT. Although the key must be same on all ports on the switch, they can be different on the remote switch. Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 lacp key 1 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 lacp aggregation true NORTEL External Distribution 20
22 4. Create VLANs and add port members Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 1 ports remove 1/1-1/4 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 10 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 10 ports add 1/1-1/4 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 20 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 20 ports add 1/1-1/4 5. Enable LACP on each port and globally Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 lacp enable Passport-8610:6# config lacp enable Perform the Following Steps on Switches ERS8600B 1. Create MLT 1 using key 1. Note: the key value must be the same as the port key Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 lacp key 1 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 lacp enable 2. Create MLT 2 using key 2 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 2 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 2 lacp key 2 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 2 lacp enable 3. Disable Spanning Tree on ports 1/1-1/4 and 1/33-1/34 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4,1/33-1/34 stg 1 stp disable 4. Configure LACP on ports 1/1-1/4 using key 1. The key used must be the same as that used in step 1 when setting up the MLT. Although the key must be same on all ports on the switch, they can be different on the remote switch. Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 lacp key 1 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4 lacp aggregation true 5. Configure LACP on ports 1/33-1/34 using key 2. The key used must be the same as that used in step 2 when setting up the MLT. Although the key must be same on all ports on the switch, they can be different on the remote switch. Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/33,1/34 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/33,1/34 lacp key 2 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/33,1/34 lacp aggregation true 6. Create VLANs and add port members Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 1 ports remove 1/1-1/4,1/34-1/35 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 10 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 10 ports add 1/1-1/4,1/33,1/34 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 20 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 20 ports add 1/1-1/4 7. Enable LACP on each port, enable LACP globally Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/4,1/33,1/34 lacp enable Passport-8610:6# config lacp enable NORTEL External Distribution 21
23 5.1.3 Perform the Following Steps on Switch ES470A 1. Go to configuration mode T >enable T# configure terminal 2. Enable tagging on ports 33 and 34, create VLAN 10, and add port members T(config)#vlan members remove 1 ALL T(config)#vlan ports 33,34 tagging tagall T(config)# vlan create 10 type port T(config)# vlan members add 10 33,34,35 3. Configure LACP on ports 33 an 34 using key 2. The key used must be the same as that used in step 1 when setting up the MLT. Although the key must be same on all ports on the switch, they can be different on the remote switch T(config)# interface fastethernet all T(config-if)#no spanning-tree port 18,19 stp T(config-if)# lacp key port 33, T(config-if)# lacp mode port 33,34 active T(config-if)# lacp aggregation port 33,34 enable T(config-if)# exit T(config)# 5.2 Verification ERS8600B LACP Passport-8610:6# show mlt info ===================================================================================== Mlt Info ===================================================================================== PORT SVLAN MLT MLT PORT VLAN MLTID IFINDEX NAME TYPE TYPE ADMIN CURRENT MEMBERS IDS MLT-1 trunk normal norm norm 1/1-1/ MLT-2 trunk normal norm norm 1/33-1/34 10 MULTICAST DESIGNATED LACP LACP MLTID IFINDEX DISTRIBUTION NT-STG PORTS ADMIN OPER disable disable 1/1 enable up disable disable 1/33 enable up NORTEL External Distribution 22
24 Passport-8610:6# show mlt lacp info 4097 ====================================================================== LACP Aggrgator Information ====================================================================== MAC COLLECTOR AGGR PORT MLTID IFINDEX ADDR MAXDELAY ORINDI MEMBERS :80:2d:36:14: aggr 1/33-1/ OPER OPERLAST MLTID IFINDEX STATE CHANGE up 10 day(s), 01:35: ACTOR ACTOR ACTOR ACTOR MLTID IFINDEX SYSPRIO SYSID ADMINKEY OPERKEY :80:2d:36:14: PARTNER PARTNER PARTNER MLTID IFINDEX SYSPRIO SYSID OPERKEY :09:97:49:a2: Passport-8610:6# show lacp info ======================================================================== Lacp Global Information ======================================================================== SystemId: 00:80:2d:36:14:00 Lacp: enable system-priority: timeout: 3 fast-periodic-time: 1000 slow-periodic-time: aggr-wait-time: ES470A LACP T#show mlt Trunk Name Members Bpdu Mode Status Trunk #1 NONE All Basic Disabled 2 Trunk #2 NONE All Basic Disabled 3 Trunk #3 NONE All Basic Disabled 4 Trunk #4 NONE All Basic Disabled 5 Trunk #5 NONE All Basic Disabled 6 Trunk # Single DynLag Enabled T#show lacp aggr Aggr ID Trunk Status Type Members Enabled LA T#show lacp port 33,34 Admin Oper Trunk Partner Port Priority Lacp A/I Timeout Key Key AggrId Id Port Status Active A Long Active Active A Long Active NORTEL External Distribution 23
25 470-48T#show lacp system System Priority : Collector Max Delay: T#show lacp port 33,34 Admin Oper Trunk Partner Port Priority Lacp A/I Timeout Key Key AggrId Id Port Status Active A Long Active Active A Long Active T#show lacp stats 33,34 Port LACPDUs Rx: 279 LACPDUs Tx: 334 MarkerPDUs Rx: 0 MarkerResponsePDUs Rx: 0 MarkerPDUs Tx: 0 MarkerResponsePDUs Tx: 0 UnknownPDUs Rx: 0 IllegalPDUs Rx: 0 Port LACPDUs Rx: 277 LACPDUs Tx: 333 MarkerPDUs Rx: 0 MarkerResponsePDUs Rx: 0 MarkerPDUs Tx: 0 MarkerResponsePDUs Tx: 0 UnknownPDUs Rx: 0 IllegalPDUs Rx: T#show lacp debug member 33,34 Port AggrId TrunkId Rx State Mux State Partner Port Current Ready Current Ready 97 NORTEL External Distribution 24
26 5.3 JDM LACP Configuration ERS8600A The following screenshots describe the configuration process for the above example using JDM. Assume the following: VLAN 10 and 20 have already been created. Ports 1/1-1/4 are tagging enabled and are members of VLAN 10 and 20. Both switches are mirror images of each other so the same commands can be entered in both. 1 Go to VLAN -> MLT/LACP>LACP Global Enabled by default Recommend keeping timers default 2 Go to VLAN -> MLT/LACP -> Multilink/LACP Trunks Click on Insert to create a new trunk group as shown below: NORTEL External Distribution 25
27 3 Go to VLAN -> MLT/LACP -> LACP and change the ActorAdminKey for the MLT to 1. This key must match the key on ports 1/1-1/4: NORTEL External Distribution 26
28 4 Next, start by clicking on each of the LAG ports (1/1 to 1/4), right-click the mouse key, and select Edit. Go to the LACP tab as shown below. Three fields need to be changed in the order as shown below. After each change, press Apply button. 1) ActorAdminKey = 1 2) ActorAdminState = aggregation 3) AdminEnable NORTEL External Distribution 27
29 Once the ports have been configured, the MLT should look like the following, note that ports 1/3-1/4 are not enabled thus do not show up as port members: NORTEL External Distribution 28
30 6. LACP Interoperability Between a ES470 and Cisco 3550 For this example, we will configure the following: A Link Aggregation Group (LAG) is configured between ES470A and a Cisco o VLANs 10 and 20 will be tagged across the LAG o LACP key = 3 o MLT ID = 2 o LACP Timeout = Long Perform the following steps on switch ES470A 1. Go to configuration mode T>enable T#config terminal 2. Enable tagging on ports 33 and 34, create VLAN 10 and 20, and add port members T(config)#vlan members remove 1 ALL T(config)#vlan ports 18,19 tagging tagall T(config)# vlan create 10 type port T(config)#vlan create 20 type port T(config)# vlan members add T(config)#vlan members add Configure LACP on ports 18 and 19 using key 3. The key used must be the same as that used in step 1 when setting up the MLT. Although the key must be same on all ports on the switch, they can be different on the remote switch T(config)# interface fastethernet all T(config-if)#no spanning-tree port 18,19 stp T(config-if)# lacp key port 18, T(config-if)# lacp mode port 18,19 active T(config-if)# lacp aggregation port 18,19 enable T(config-if)# exit T(config)# Cisco C3550 Configuration 1. Add VLANs 10 and 20 C3550#vlan data C3550(vlan)#vlan 10 state active C3550(vlan)#vlan 20 state active C3550(vlan)#exit NORTEL External Distribution 29
31 2. Configuration! spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id no spanning-tree vlan 2,4,10,20 spanning-tree vlan 4, priority 8192! vlan dot1q tag native! interface Port-channel3 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 switchport mode trunk!! interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 switchport mode trunk channel-group 3 mode active channel-protocol lacp! interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 switchport mode trunk channel-group 3 mode active channel-protocol lacp! interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access! 6.2 Verification C3550 C3550#show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 u - unsuitable for bundling U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator d - default port Number of channel-groups in use: 1 Number of aggregators: 1 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports Po3(SU) LACP Fa0/18(P) Fa0/19(P) NORTEL External Distribution 30
32 C3550#show lacp internal detail Flags: S - Device is requesting Slow LACPDUs F - Device is requesting Fast LACPDUs A - Device is in Active mode P - Device is in Passive mode Channel group 3 Actor (internal) information: Actor Actor Actor Port System ID Port Number Age Flags Fa0/ ,000b.5f02.f300 0x12 20s SA LACP Actor Actor Actor Port Priority Oper Key Port State x3 0x3D Port State Flags Decode: Activity: Timeout: Aggregation: Synchronization: Active Short Yes Yes Collecting: Distributing: Defaulted: Expired: Yes Yes No No Actor Actor Actor Port System ID Port Number Age Flags Fa0/ ,000b.5f02.f300 0x13 9s SA LACP Actor Actor Actor Port Priority Oper Key Port State x3 0x3D Port State Flags Decode: Activity: Timeout: Aggregation: Synchronization: Active Short Yes Yes Collecting: Distributing: Defaulted: Expired: Yes Yes No No C3550#show lacp neighbor detail Flags: S - Device is requesting Slow LACPDUs F - Device is requesting Fast LACPDUs A - Device is in Active mode P - Device is in Passive mode Channel group 3 neighbors Partner's information: Partner Partner Partner Port System ID Port Number Age Flags Fa0/ , a200 0x12 1s SA LACP Partner Partner Partner Port Priority Oper Key Port State x2003 0x3D Port State Flags Decode: Activity: Timeout: Aggregation: Synchronization: Active Short Yes Yes Collecting: Distributing: Defaulted: Expired: Yes Yes No No Partner Partner Partner Port System ID Port Number Age Flags Fa0/ , a200 0x13 20s SA LACP Partner Partner Partner Port Priority Oper Key Port State x2003 0x3D NORTEL External Distribution 31
33 Port State Flags Decode: Activity: Timeout: Aggregation: Synchronization: Active Short Yes Yes Collecting: Distributing: Defaulted: Expired: Yes Yes No No NORTEL External Distribution 32
34 7. LACP Interoperability between ERS8600 and Cisco Catalyst 6500 For this example, we will configure the following A Link Aggregation Group (LAG) is configured between ERS8600A and Cisco Catalyst o VLANs 10 and 20 will be tagged across the LAG o LACP key = 4 o MLT ID = 2 o o LACP Timeout = Long Configure ERS8600 to force it to only use the Cisco LACP port number and system id. 7.1 Configuration Steps Perform the following steps on switches ERS8600A 1. Create MLT 1 using key 1. Note: the key value must be the same as the port key. Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 2 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 2 lacp key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 2 lacp enable 2. Disable Spanning Tree on port 1/1-1/4 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 stg 1 stp disable 3. Configure LACP on ports 1/1-1/4 using key 4. The key used must be the same as that used in step 1 when setting up the MLT. In this case, we will configure the lacp partner key. We also need to configure the partner port. Note, to get the partner port on a Cisco Catalyst 6500, use the command show lacp internal detail and then convert the hexadecimal value from Cisco to the decimal value use by the ERS8600. To get the lacp partner-system-id, use the Cisco command show lacp sys-id to get the MAC address of the interface(s) you are connecting to. Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 lacp key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 lacp partner-key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1 lacp partner-port 773 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/2 lacp partner-port 774 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 lacp partner-port-priority Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 lacp partner-system-id 00:0f :35 :3b :89 :66 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 lacp aggregation true NORTEL External Distribution 33
35 4. Create VLANs and add port members Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 1 ports remove 1/1-1/2 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 10 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 10 ports add 1/1-1/2 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 20 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 20 ports add 1/1-1/2 5. Enable LACP on each port and globally Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 1/1-1/2 lacp enable Passport-8610:6# config lacp enable Cisco Catalyst 6500 Configuration In regards to the Cisco Catalyst 6500, configure LACP on port 3/5 and 3/6, disable Spanning Tree, and configure Port-Channel 4. Channel-group 4 on interface 3/5 and 3/6 automatically generates the LACP aggregate interface port-channel 4 with Key 4.! spanning-tree mode pvst no spanning-tree optimize bpdu transmission no spanning-tree vlan ! interface Port-channel4 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 switchport mode trunk! vlan internal allocation policy ascending vlan dot1q tag native vlan access-log ratelimit 2000! interface GigabitEthernet3/5 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 switchport mode trunk channel-protocol lacp channel-group 4 mode active! interface GigabitEthernet3/6 no ip address switchport switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q switchport trunk native vlan 10 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20 switchport mode trunk channel-protocol lacp channel-group 4 mode active NORTEL External Distribution 34
36 8. SMLT with 802.3ad and MLT with VLACP Configuration Example With the 3.7 release, the ERS8600 switch fully supports the IEEE 802.3ad Link aggregation control protocol; not only on MLT and DMLT links, but also extended to a pair of SMLT switches. With this extension, the ERS8600 switch now provides a standardized external link aggregation interface to third party vendor IEEE 802.3ad implementations. With previous software versions, interoperability was provided through a static configuration; now a dynamic link aggregation mechanism is provided. In this example, ES470A and ES470B are used as the SMLT Clients. ES470A will be configured with dynamic link aggregation using LACP. ES470B will be configured with static link aggregation using MLT. Note that any switch that supports LACP can be used as an LACP-enabled SMLT client. Likewise, any switch that support any form of static link aggregations such as MLT or EtherChannel can also be use as a SMLT client. Note: It is recommended to not run 802.3ad on the IST connection. The LACP keys on the SMLT core switches must match (ERS8600A, ERS8600B). Spanning is disabled by default on a port level when SMLT is enabled CP Limit should be disabled on all IST interface; this is the default setting If the SMLT client is a Nortel switch using MLT, VLACP should be enabled to provide end-to-end protection. The default VLACP setting should be fine for all direct connections. For LAN extension applications, fast timers should be used. 8.1 SMLT Topology NORTEL External Distribution 35
37 8.2 Config Steps ERS8600A Configuration 1. Create IST using VLAN 3999 using key 1. Note: the key value must be the same as the port key. Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 3999 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 add ports 1/1,2/1 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 add vlan 3999 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 3999 ip create /30 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 ist create ip vlan-id Create SMLT group Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 lacp key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 lacp enable Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 smlt create smlt-id 4 3. Enable VLAN Tagging on ports 3/13, 3/14, and 3/18 and remove VLAN 1 port membership Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14,3/18 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 1 ports remove 3/13-3/14,3/18 4. Configure LACP on ports 3/13-3/14 using key 4. The key must match on all ports in a LAG. The same key must be used on both SMLT core switches. Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14 lacp key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14 lacp aggregation true 5. Create SMLT VLAN 200 and add port members Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 200 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 200 ports add 3/13-3/15,3/18,1/1,1/2 6. Create VLAN 202 and Single-Port SMLT using SNMP ID 6 Passport-8610:5# config vlan 202 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# config vlan 202 ports add 3/13,3/14,3/18 Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 3/18 smlt 6 create 7. Add VLAN 202 to IST (MLT 1) Passport-8610:5# config mlt 1 add vlan Enable VLACP on port 3/18 Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 3/18 vlacp enable Passport-8610:6# config vlacp enable 9. Enable LACP on each port and globally Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14 lacp enable Passport-8610:6# config lacp enable NORTEL External Distribution 36
38 8.2.2 ERS8600B Configuration 1. Create IST using VLAN 3999 using key 1. Note: the key value must be the same as the port key. Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 3999 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 add ports 1/1,2/1 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 add vlan 3999 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 3999 ip create /30 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 1 ist create ip vlan-id Create SMLT group Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 create Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 lacp key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 lacp enable Passport-8610:5# conf mlt 4 smlt create smlt-id 4 3. Enable VLAN Tagging on ports 3/13, 3/14, and 3/18 and remove VLAN 1 port membership Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14,3/18 perform-tagging enable Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 1 ports remove 3/13-3/14,3/18 4. Configure LACP on ports 3/13-3/14 using key 4. The key must match on all ports in a LAG. The same key must be used on both SMLT core switches. Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14 lacp key 4 Passport-8610:5# conf Ethernet 3/13,3/14 lacp aggregation true 5. Create SMLT VLAN 200 and add port members Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 200 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# conf vlan 200 ports add 3/13-3/14,3/18,1/1,1/2 6. Create VLAN 202 and Single-Port SMLT using SNMP ID 6 Passport-8610:5# config vlan 202 create byport 1 Passport-8610:5# config vlan 202 ports add 3/18-3/19 Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 3/18 smlt 6 create 7. Add VLAN 202 to IST (MLT 1) Passport-8610:5# config mlt 1 add vlan Enable VLACP on port 3/18 and globally Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 3/18 vlacp enable Passport-8610:6# config vlacp enable 9. Enable LACP on each port and globally Passport-8610:5# conf ethernet 3/13,3/14 lacp enable Passport-8610:6# config lacp enable NORTEL External Distribution 37
39 8.2.3 ES470A configuration 1. Go to configuration mode T>enable T#config terminal 2. Enable tagging on ports 1/13, 1/14, 2/13, and 2/14, create VLAN 200 and 202, and add port members T(config)# vlan ports 1/13,1/14,2/13,2/14 tagging tagall T(config)# vlan create 200 type port T(config)# vlan members add 200 1/13-15,2/ T(config)# vlan create 202 type port T(config)# vlan members add 202 1/13-14,2/13-14,1/19,2/19 3. Configure LACP on ports 1/13, 1/14, 2/13, and 2/14 using key T(config)# interface fastethernet all T(config-if)# no spanning-tree port 1/13-14,2/13-14 stp T(config-if)# lacp key port 1/13-14,2/ T(config-if)# lacp mode port 1/13-14,2/13-14 active T(config-if)# lacp aggregation port 1/13-14,2/13-14 enable T(config-if)# exit T(config)# ES470B Configuration 1. Go to configuration mode T>enable T#config terminal 2. Enable tagging on ports 18 and 19, create VLAN 200 and 202, and add port members T(config)# vlan members remove 1 ALL T(config)# vlan ports 18,19 tagging tagall T(config)# vlan create 200 type port T(config)# vlan create 202 type port T(config)# vlan members add , T(config)# vlan members add Create MLT group for port 18 and T(config)# mlt 1 learning disable T(config)# mlt 1 member 18, T(config)# mlt 1 enable 4. Enable VLACP on port 18 and T(config)#interface fastethernet all T(config-if)#vlacp port 18,19 enable T(config-if)#exit 5. Enable VLACP Globally T(config)#vlacp enable NORTEL External Distribution 38
40 8.3 Verification ERS8600A and ERS8600B SMLT Verification ERS8610A:5# show mlt info ================================================================================ Mlt Info ================================================================================ PORT SVLAN MLT MLT PORT VLAN MLTID IFINDEX NAME TYPE TYPE ADMIN CURRENT MEMBERS IDS MLT-1 trunk normal ist ist 1/1-2/ MLT-4 trunk normal smlt smlt 3/13-3/ MULTICAST DESIGNATED LACP LACP MLTID IFINDEX DISTRIBUTION NT-STG PORTS ADMIN OPER disable enable 2/1 disable down disable disable 3/13 enable up ERS8610B:5# show mlt info ================================================================================ Mlt Info ================================================================================ PORT SVLAN MLT MLT PORT VLAN MLTID IFINDEX NAME TYPE TYPE ADMIN CURRENT MEMBERS IDS MLT-1 trunk normal ist ist 1/1-2/ MLT-4 trunk normal smlt smlt 3/13-3/ MULTICAST DESIGNATED LACP LACP MLTID IFINDEX DISTRIBUTION NT-STG PORTS ADMIN OPER disable disable 1/1 disable down disable disable 3/13 enable up ERS8600A and ERS8600B Single-Port SMLT Verification ERS8610A:5# show port info smlt port 3/18 =================================================== SMLT Info =================================================== PORT SMLT ADMIN CURRENT NUM ID TYPE TYPE /18 6 smlt smlt ERS8600B:6# show port info smlt port 3/18 =================================================== SMLT Info =================================================== PORT SMLT ADMIN CURRENT NUM ID TYPE TYPE /18 6 smlt smlt NORTEL External Distribution 39
41 8.3.3 ERS8600A and ERS8600B VLACP Verification ERS8610C:5# show port info vlacp port 3/18 ================================================================================ VLACP Information ================================================================================ INDEX ADMIN OPER PORT FAST SLOW TIMEOUT TIMEOUT ETHER MAC ENABLED ENABLED STATE TIME TIME TIME SCALE TYPE ADDR /18 true true UP long :80:c2:00:11:00 ERS8600D:6# show port info vlacp port 3/18 ================================================================================ VLACP Information ================================================================================ INDEX ADMIN OPER PORT FAST SLOW TIMEOUT TIMEOUT ETHER MAC ENABLED ENABLED STATE TIME TIME TIME SCALE TYPE ADDR /18 true true UP long :80:c2:00:11: ES470B - VLACP Verification T#show vlacp interface 18,19 ========================================================================= VLACP Information ========================================================================= INDEX ADMIN OPER FAST SLOW TIMEOUT TIMEOUT ETHER MAC ENABLED ENABLED TIME TIME TYPE SCALE TYPE ADDRESS /18 true true long :80:c2:00:11:00 0/19 true true long :80:c2:00:11:00 NORTEL External Distribution 40
42 9. VLACP Example via LAN Extension This example, we will configure VLACP between two ERS8600 s connected together via a service providers LAN extension service. The configuration below has two links going through a service provider cloud. VLACP can be used to detect failures within the service provider that normally would not be detected by the ERS8600 s using mechanisms such as RFI or Single Fiber Fault Detection (SFFD). Mechanisms such as RFI or SFFD will only work between directly connected interfaces on a pair of switches. In a LAN extension network, the switches are not directly connected; hence, a mechanism that is end-to-end such as VLACP must be deployed. In this example, we will configure VLACP for short timeout with a fast periodic time of 400ms. Note: when using the fast-periodic-time for detecting failure on an ERS8600, the minimum supported value is 400ms. This means that with a timeout-scale of 3 then failures should be detected in 400ms x 3 = 1.2 seconds. 9.1 Configuration Example 1. Enable VLACP on port 1/1 and 1/2 Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 1/1,1/2 vlacp fast-periodic-time 400 Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 1/1,1/2 vlacp timeout short Passport-8610:5# config ethernet 1/1,1/2 vlacp enable 2. Enable VLACP Globally Passport-8610:6# config vlacp enable 9.2 Verification: Passport-8610:6# show ports info vlacp port 1/1-1/2 ================================================================================ VLACP Information ================================================================================ INDEX ADMIN OPER PORT FAST SLOW TIMEOUT TIMEOUT ETHER MAC ENABLED ENABLED STATE TIME TIME TIME SCALE TYPE ADDR /1 true true UP short :80:c2:00:11:00 1/1 true true UP short :80:c2:00:11:00 Passport-8610:6# show vlacp info ================================================================================ Vlacp Global Information ================================================================================ SystemId: 00:80:2d:be:20:00 Vlacp: enable NORTEL External Distribution 41
Split Trunking Support with HP Auto Port Aggregation
 Split Trunking Support with HP Auto Port Aggregation Overview 2 When to Use Split Trunking 6 Examples 7 Setting up Split Trunks on Cisco Switches 7 Setting up Split Trunks on Nortel Switches 9 Conclusion
Split Trunking Support with HP Auto Port Aggregation Overview 2 When to Use Split Trunking 6 Examples 7 Setting up Split Trunks on Cisco Switches 7 Setting up Split Trunks on Nortel Switches 9 Conclusion
> Avaya / Cisco Interoperability Technical Configuration Guide. Ethernet Routing Switch
 Ethernet Routing Switch IP Phones Engineering > Avaya Data Solutions Document Date: April 6, 2010 Document Number: NN48500-588 Document Version: 2.0 Abstract The purpose of this TCG is to show some of
Ethernet Routing Switch IP Phones Engineering > Avaya Data Solutions Document Date: April 6, 2010 Document Number: NN48500-588 Document Version: 2.0 Abstract The purpose of this TCG is to show some of
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad LACP EtherChannels on the Cisco MWR 2941
 29 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.3ad LACP EtherChannels on the Cisco MWR 2941 Cisco MWR 2941 Release 3.5.1 and later supports IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) EtherChannels. Note The
29 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.3ad LACP EtherChannels on the Cisco MWR 2941 Cisco MWR 2941 Release 3.5.1 and later supports IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) EtherChannels. Note The
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card
 CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Administration Utilities
 NN47226-600 Document status: Standard Document version: 0301 Document date: 27 April 2010 All Rights Reserved Sourced in Canada and the United States of America The information in this document is subject
NN47226-600 Document status: Standard Document version: 0301 Document date: 27 April 2010 All Rights Reserved Sourced in Canada and the United States of America The information in this document is subject
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to use Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. REP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to use Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. REP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring EtherChannels
 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. It contains the following
This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. It contains the following
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
Configuring EtherChannels
 Configuring EtherChannels This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco
Configuring EtherChannels This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Abstract. GAK; Reviewed: WCH 8/14/2003. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2003 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Configuring Port Channels
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure port channels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of port channels in Cisco DCNM. For more information
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure port channels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of port channels in Cisco DCNM. For more information
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Configuring Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, page 1, page 9 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, page 16 Verifying the Load-Balancing Outgoing Port ID, page 17 Feature
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, page 1, page 9 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, page 16 Verifying the Load-Balancing Outgoing Port ID, page 17 Feature
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
 Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Ethernet Routing Switch 5000 Series Software Release 6.2.2
 Ethernet Routing Switch 5000 Series Software Release 6.2.2 1. Release Summary Release Date: 11-October-2011 Purpose: Software patch release to address customer and internally found software issues. 2.
Ethernet Routing Switch 5000 Series Software Release 6.2.2 1. Release Summary Release Date: 11-October-2011 Purpose: Software patch release to address customer and internally found software issues. 2.
IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges
 IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges First Published: April 19, 2010 Last Updated: May 26, 2011 Service provider bridges (also called provider bridges) allow switches in a service provider network
IEEE 802.1ad Support on Provider Bridges First Published: April 19, 2010 Last Updated: May 26, 2011 Service provider bridges (also called provider bridges) allow switches in a service provider network
Link Bundling Commands
 Link Bundling Commands This module provides command line interface (CLI) commands for configuring Link Bundle interfaces on the Cisco NCS 5000 Series Router. For detailed information about Link Bundle
Link Bundling Commands This module provides command line interface (CLI) commands for configuring Link Bundle interfaces on the Cisco NCS 5000 Series Router. For detailed information about Link Bundle
Configuring Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, on page 1, on page 8 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, on page 16 Verifying the Load-Balancing Outgoing Port ID, on page
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, on page 1, on page 8 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, on page 16 Verifying the Load-Balancing Outgoing Port ID, on page
Configuring Port Channels
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure port channels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of port channels using Cisco Data Center Network
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure port channels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of port channels using Cisco Data Center Network
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Interfaces for Firepower Threat Defense
 This chapter includes Firepower Threat Defense interface configuration including Ethernet settings, EtherChannels, VLAN subinterfaces, IP addressing, and more. About Firepower Threat Defense Interfaces,
This chapter includes Firepower Threat Defense interface configuration including Ethernet settings, EtherChannels, VLAN subinterfaces, IP addressing, and more. About Firepower Threat Defense Interfaces,
Configuring EtherChannels
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
Configuring Flex Links
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching
 Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
EtherChannel and Redundant Interfaces
 This chapter tells how to configure EtherChannels and redundant interfaces. Note For multiple context mode, complete all tasks in this section in the system execution space. To change from the context
This chapter tells how to configure EtherChannels and redundant interfaces. Note For multiple context mode, complete all tasks in this section in the system execution space. To change from the context
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 2 (GUI), page 4 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 5 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 2 (GUI), page 4 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 5 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
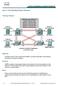 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Spanning Tree Protocol(STP)
 Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on the IEEE 802.1s standard.
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
Interfaces for Firepower Threat Defense
 This chapter includes Firepower Threat Defense interface configuration including Ethernet settings, EtherChannels, VLAN subinterfaces, IP addressing, and more. About Firepower Threat Defense Interfaces,
This chapter includes Firepower Threat Defense interface configuration including Ethernet settings, EtherChannels, VLAN subinterfaces, IP addressing, and more. About Firepower Threat Defense Interfaces,
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
Pass-Through Technology
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture,
CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture,
LACP Between Nexus 9000 and UCS Server
 LACP Between Nexus 9000 and UCS Server Document ID: 118851 Contributed by Viral Bhutta and Manuel Velasco, Cisco TAC Engineers. Mar 18, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
LACP Between Nexus 9000 and UCS Server Document ID: 118851 Contributed by Viral Bhutta and Manuel Velasco, Cisco TAC Engineers. Mar 18, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP)
 The is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). REP provides a way to control network loops, handle link failures, and improve convergence time. It
The is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). REP provides a way to control network loops, handle link failures, and improve convergence time. It
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
 This chapter describes Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP), REP configuration guidelines, VLAN load balancing, REP timers, and REP over EVC. This chapter also describes procedures to configure REP. Understanding
This chapter describes Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP), REP configuration guidelines, VLAN load balancing, REP timers, and REP over EVC. This chapter also describes procedures to configure REP. Understanding
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
Application Guide. VLANs for improved Q-SYS performance
 Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Configuring Interfaces and Circuits
 CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure the CSS interfaces and circuits and how to bridge interfaces to Virtual LANs (VLANs). Information in this chapter applies to all CSS models, except where
CHAPTER 5 This chapter describes how to configure the CSS interfaces and circuits and how to bridge interfaces to Virtual LANs (VLANs). Information in this chapter applies to all CSS models, except where
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLAN Trunks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt
 IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
Configuring the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch
 APPENDIXA Configuring the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch The Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch is an integrated Catalyst 3750 switch and Cisco 4400 series
APPENDIXA Configuring the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch The Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch is an integrated Catalyst 3750 switch and Cisco 4400 series
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Configuring MST Using Cisco NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
Describing the STP. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel
 Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
PracticeDump. Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam
 PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
Spanning Tree Protocol
 For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
Configuring Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, page 1, page 11 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, page 19 Triggering the Port Channel Membership Consistency Checker,
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, page 1, page 11 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, page 19 Triggering the Port Channel Membership Consistency Checker,
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
 CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
Configuring Cisco IP Phone Support
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure support for Cisco IP phones on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure support for Cisco IP phones on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
ETHERNET ROUTING SWITCH
 Table of Contents ETHERNET ROUTING SWITCH 1600...3 SOFTWARE RELEASE 2.1.4.0...3 1. Release Summary...3 2. Important Notes before Upgrading to This Release...3 3. Platforms Supported...3 4. Notes for Upgrade...3
Table of Contents ETHERNET ROUTING SWITCH 1600...3 SOFTWARE RELEASE 2.1.4.0...3 1. Release Summary...3 2. Important Notes before Upgrading to This Release...3 3. Platforms Supported...3 4. Notes for Upgrade...3
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Table of Contents 1 MSTP Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 MSTP Configuration 1-1 Overview 1-1 Introduction to STP 1-1 Why STP 1-1 Protocol Packets of STP 1-1 Basic Concepts in STP 1-2 How STP works 1-3 Introduction to RSTP 1-9 Introduction
Table of Contents 1 MSTP Configuration 1-1 Overview 1-1 Introduction to STP 1-1 Why STP 1-1 Protocol Packets of STP 1-1 Basic Concepts in STP 1-2 How STP works 1-3 Introduction to RSTP 1-9 Introduction
