Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel
|
|
|
- Joseph Wood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex 200-Mb link. The uplink from the distribution layer switch to the access layer switch has been saturated with bandwidth-intensive applications. The users in VLAN 20 that are served by the access layer switches need more bandwidth. Instead of purchasing new switches with gigabit Ethernet capability, Fast EtherChannel (FEC) will be configured. FEC is the Cisco method of scaling bandwidth for 100-Mb Ethernet links. A second 100-Mb Ethernet link will be added between the distribution layer and the access layer switches. The switches will then be configured to operate as one logical link. The network design is as follows: Catalyst Type Switch VTP Domain VTP Mode 3550 DLSwitch CORP Server 2950 ALSwitch1 CORP Client 2950 ALSwitch2 CORP Client 1-12 CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
2 VLAN configuration information: VLAN ID VLAN Name VLAN Subnet DLSwitch ALSwitch1 ALSwitch2 1 Native /24 All Ports Gb0/1-2 Fa0/1-4 Gb0/1-2 Fa0/ Accounting /24 Fa0/5-8 Fa0/ Marketing /24 Fa0/9-12 FA0/9-12 Trunk 802.1Q 802.1Q 802.1Q Step 1 Wait until all switch configurations and vlan.dat files have been erased and then cable the lab. If the vlan database exists, delete it on all switches and clear the configuration. Switch#delete flash:vlan.dat Delete filename [vlan.dat]? Delete flash:vlan.dat? [confirm] Switch# Switch#erase startup-config Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Switch#reload System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]:n Proceed with reload? [confirm] Cable the lab according to the diagram. Crossover Cat 5 cables must be used since the devices are similar. Configure the hostname, passwords, and Telnet access on all the switches. Configure the interface VLAN 1 IP address on each switch and configure the IP address on each host. Switch(config)#hostname DLSwitch DLSwitch(config)#enable secret cisco DLSwitch(config)#line console 0 DLSwitch(config-line)#password cisco DLSwitch(config-line)#login DLSwitch(config-line)#line vty 0 15 DLSwitch(config-line)#password cisco DLSwitch(config-line)#login DLSwitch(config-line)#interface vlan 1 DLSwitch(config-if)#ip address DLSwitch(config-if)#no shutdown DLSwitch(config-if)#^Z Switch(config)#hostname ALSwitch1 ALSwitch1(config)#enable secret cisco ALSwitch1(config)#line console 0 ALSwitch1(config-line)#password cisco ALSwitch1(config-line)#login ALSwitch1(config-line)#line vty 0 15 ALSwitch1(config-line)#password cisco ALSwitch1(config-line)#login 2-12 CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3 ALSwitch1(config-line)#login ALSwitch1(config-line)#interface vlan 1 ALSwitch1(config-if)#ip address ALSwitch1(config-if)#no shutdown ALSwitch1(config-if)#^Z Switch(config)#hostname ALSwitch2 ALSwitch2(config)#enable secret cisco ALSwitch2(config)#line console 0 ALSwitch2(config-line)#password cisco ALSwitch2(config-line)#login ALSwitch2(config-line)#line vty 0 15 ALSwitch2(config-line)#password cisco ALSwitch2(config-line)#login ALSwitch2(config-line)#interface vlan 1 ALSwitch2(config-if)#ip address ALSwitch2(config-if)#no shutdown ALSwitch2(config-if)#^Z Step 2 Configure the vtp domain CORP and create and name VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 on the DLSwitch. The 3550 switch defaults to the VTP server mode so it does not need to be configured. However if necessary, the command to enable the server mode is vtp server in the vlan database configuration mode. DLSwitch#vlan database DLSwitch(vlan)#vtp domain CORP DLSwitch(vlan)#vlan 10 name Accounting DLSwitch(vlan)#vlan 20 name Marketing DLSwitch(vlan)#exit Configure ALSwitch1 and ALSwitch2 as VTP clients and assign ports to the respective VLANs in each switch as shown in the configuration table above. The interface range command can be used to configure several interfaces at the same time. They must be configured to join the domain in client mode. ALSwitch1#vlan database ALSwitch1(vlan)#vtp client ALSwitch1(vlan)#exit ALSwitch1(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/5-8 ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10 ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#exit ALSwitch1(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/9-12 ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20 ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#^z Configure the VLAN database on ALSwitch2. ALSwitch2#vlan database ALSwitch2(vlan)#vtp client ALSwitch2(vlan)#exit Place the ports on ALSwitch2 into the proper VLAN CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
4 ALSwitch2(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/5-8 ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10 ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#exit ALSwitch2(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/9-12 ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20 ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#^Z DLSwitch#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 1 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 7 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : CORP VTP Pruning Mode VTP V2 Mode VTP Traps Generation MD5 digest : 0x78 0x22 0xAC 0x9E 0xD0 0x20 0x93 0x02 Configuration last modified by at :55:36 Local updater ID is on interface Vl1 (lowest numbered VLAN interface found) DLSwitch#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports default active Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12 Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16 Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20 Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24 Gi0/1, Gi0/2 10 Accounting active 20 Marketing active 1002 fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans enet enet enet fddi tr VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans fdnet ieee trnet ibm Remote SPAN VLANs Primary Secondary Type Ports ALSwitch1#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 1 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 250 Number of existing VLANs : 7 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : CORP 4-12 CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
5 VTP Pruning Mode VTP V2 Mode VTP Traps Generation MD5 digest : 0x78 0x22 0xAC 0x9E 0xD0 0x20 0x93 0x02 Configuration last modified by at :55:36 ALSwitch1#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports default active Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/13, Fa0/14 Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18 Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22 Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2 10 Accounting active Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 20 Marketing active Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/ fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans enet enet enet fddi tr srb fdnet ieee trnet ibm Remote SPAN VLANs Primary Secondary Type Ports ALSwitch2#show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 1 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 250 Number of existing VLANs : 7 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : CORP VTP Pruning Mode VTP V2 Mode VTP Traps Generation MD5 digest : 0x78 0x22 0xAC 0x9E 0xD0 0x20 0x93 0x02 Configuration last modified by at :55:36 ALSwitch2#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports default active Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/13, Fa0/14 Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18 Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22 Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2 10 Accounting active Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 20 Marketing active Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/ fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
6 1 enet enet enet fddi tr srb fdnet ieee trnet ibm Remote SPAN VLANs Step 3 Primary Secondary Type Ports Configure the ports connecting the switches to trunk mode. Configure ports FastEthernet 0/1, 0/2, 0/3, and 0/4 on the DLSwitch. Note: The encapsulation in some IOS versions may be set to auto, which will not allow the user to set the switchport mode to trunking. If this is the case, the encapsulation will need to be configured first. DLSwitch(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1 4 DLSwitch(config-if-range)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q DLSwitch(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk DLSwitch(config-if-range)#^Z Configure ports FastEthernet 0/1 and FastEthernet 0/2 on ALSwitch1. ALSwitch1(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1 2 ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#^Z Configure ports FastEthernet 0/1 and FastEthernet 0/2 on ALSwitch2. ALSwitch2(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1 2 ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#^Z DLSwitch#show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/2 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/3 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/4 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/ Fa0/ Fa0/ Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 1,10,20 Fa0/2 1,10,20 Fa0/3 1,10,20 Fa0/4 1,10,20 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 1,10,20 Fa0/2 1,10,20 Fa0/3 1,10, CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
7 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/4 1,10,20 ALSwitch1#show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/2 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/ Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 1,10,20 Fa0/2 1,10,20 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 1,10,20 Fa0/2 none ALSwitch2#show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/2 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/ Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 1,10,20 Fa0/2 1,10,20 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 1,10,20 Fa0/2 none Step 4 An EtherChannel is composed of individual Fast EtherChannel (FEC) or Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) links, which are bundled into a single logical link, as shown in the graphic. GEC provides fullduplex bandwidth of up to 16 Gbps between a switch and another switch or host. FEC provides the ability to combine eight 100-Mbps full duplex links for a 1.6-Gbps full duplex link. The Ethernet switches must be configured to treat two physical links as one logical link. Configure DLSwitch to combine ports FastEthernet 0/1 and 0/2 into one logical channel. DLSwitch(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1 2 DLSwitch(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 DLSwitch(config-if-range)# 01:05:51: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, 01:05:51: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, 01:05:59: %EC-5-L3DONTBNDL1: Fa0/1 suspended: PAgP not enabled on the remote port. 01:05:59: %EC-5-L3DONTBNDL1: Fa0/2 suspended: PAgP not enabled on the remote port. DLSwitch(config-if-range)#exit 7-12 CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
8 Configure DLSwitch to combine ports FastEthernet 0/3 and 0/4 into another logical channel. DLSwitch(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/3 4 DLSwitch(config-if-range)#channel-group 2 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2 DLSwitch(config-if-range)# 01:07:24: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/3, 01:07:24: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/4, 01:07:24: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan1, changed state to down DLSwitch(config-if-range)# 01:07:33: %EC-5-L3DONTBNDL1: Fa0/4 suspended: PAgP not enabled on the remote port. 01:07:33: %EC-5-L3DONTBNDL1: Fa0/3 suspended: PAgP not enabled on the remote port. DLSwitch(config-if-range)#^Z Configure ALSwitch1 to combine ports 0/1 and 0/2 into one logical channel. ALSwitch1(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1 2 ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 01:08:30: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, 01:08:30: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, 01:08:32: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up 01:08:32: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up 01:08:33: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Port-channel1, changed state to up 01:08:34: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel1, changed state to up ALSwitch1(config-if-range)#^Z Configure the ALSwitch2 to combine ports 0/1 and 0/2 into one logical channel. ALSwitch2(config)#interface range fastethernet 0/1 2 ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 01:11:19: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, 01:11:19: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, 01:11:22: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up 01:11:22: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/2, changed state to up 01:11:23: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Port-channel1, changed state to up 01:11:24: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel1, changed state to up ALSwitch2(config-if-range)#^Z Step 5 The disadvantage of using FEC is that up to eight FastEthernet ports would be unavailable for clients. When GEC is available, Fast EtherChannel is an expensive way to increase bandwidth. FEC technology can be used with Gigabit links to create multi-megabit logical links. Use the show etherchannel summary command to verify the fast EtherChannel connection CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
9 DLSwitch#show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 u - unsuitable for bundling U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator d - default port Number of channel-groups in use: 2 Number of aggregators: 2 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports Po1(SU) PAgP Fa0/1(P) Fa0/2(P) 2 Po2(SU) PAgP Fa0/3(P) Fa0/4(P) DLSwitch#show etherchannel brief Channel-group listing: Group: Group state = L2 Ports: 2 Maxports = 8 Port-channels: 1 Max Port-channels = 1 Protocol: PAgP Group: Group state = L2 Ports: 2 Maxports = 8 Port-channels: 1 Max Port-channels = 1 Protocol: PAgP DLSwitch# ALSwitch1#show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 u - unsuitable for bundling U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator d - default port Number of channel-groups in use: 1 Number of aggregators: 1 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports Po1(SU) PAgP Fa0/1(P) Fa0/2(Pd) ALSwitch1#show etherchannel brief % This command is an unreleased and unsupported feature Channel-group listing: Group: Group state = L2 Ports: 2 Maxports = 8 Port-channels: 1 Max Port-channels = 1 Protocol: PAgP 9-12 CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
10 ALSwitch1# ALSwitch2#show etherchannel brief % This command is an unreleased and unsupported feature Channel-group listing: Group: Group state = L2 Ports: 2 Maxports = 8 Port-channels: 1 Max Port-channels = 1 Protocol: PAgP ALSwitch2# Step 6 Verify the port aggregation protocol (PAgP) operation. The PAgP facilitates the automatic creation of EtherChannels by exchanging packets between Ethernet interfaces. By using PAgP, the switch learns the identity of partners capable of supporting PAgP and learns the capabilities of each interface. It then dynamically groups similarly configured interfaces into a single logical link, channel, or aggregate port. These interfaces are grouped based on hardware, administrative, and port parameter constraints. For example, PAgP groups the interfaces with the same speed, duplex, native VLAN, VLAN range, trunking status, and trunking type. After grouping the links into an EtherChannel, PAgP adds the group to the spanning tree as a single switch port. Use the show pagp neighbor command on DLSwitch to verify PagP operation. DLSwitch#show pagp neighbor Flags: S - Device is sending Slow hello. C - Device is in Consistent state. A - Device is in Auto mode. P - Device learns on physical port. Channel group 1 neighbors Partner Partner Partner Partner Group Port Name Device ID Port Age Flags Cap. Fa0/1 ALSwitch1 000a.8afc.dd80 Fa0/1 27s SC Fa0/2 ALSwitch1 000a.8afc.dd80 Fa0/2 7s SC Channel group 2 neighbors Partner Partner Partner Partner Group Port Name Device ID Port Age Flags Cap. Fa0/3 ALSwitch e8e3.f340 Fa0/1 14s SC Fa0/4 ALSwitch e8e3.f340 Fa0/2 20s SC How is it shown that PAgP is operational? Use show pagp? and some of the other show commands for EtherChannel and PAgP. DLSwitch#show pagp? <1-64> Channel group number counters Traffic information internal Internal information neighbor Neighbor information CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
11 DLSwitch#show etherchannel? <1-64> Channel group number brief Brief information detail Detail information load-balance Load-balance/frame-distribution scheme among ports in port-channel port Port information port-channel Port-channel information summary One-line summary per channel-group Step 7 Configure and monitor EtherChannel load balancing. EtherChannel balances the traffic load across the links in a channel. This is accomplished by reducing part of the binary pattern formed from the addresses in the frame to a numerical value that selects one of the links in the channel. EtherChannel load balancing can use either source MAC or destination MAC address forwarding. Execute the show etherchannel load-balance command on the DLSwitch. DLSwitch#show etherchannel load-balance Source MAC address The load balancing decision is based on source MAC address by default. The remainder of this step requires the transfer of files between hosts to observe the load balancing. View the port lights on DLSwitch to determine which source MAC address is used. Verify the default behavior by transferring a TFTP file from Host A to Host C. 1. Observe the lights on the DLSwitch. Which links were used? 2. Transfer a file from Host B to Host C. Were the same links used as in the previous question between the two hosts? a. Transfer a file from Host C to Host A. Which links did the file transfer use? b. Transfer a file from Host C to Host B. Were the same links used as in the previous file transfer? Step 8 Configure and monitor destination MAC address load balancing. Configure the DLSwitch for load balancing based on the destination MAC address CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
12 DLSwitch(config)#port-channel load-balance dst-mac Verify destination MAC address load balancing with the show etherchannel load-balance command. DLSwitch#show etherchannel load-balance Destination MAC address Verify the default behavior by transferring a TFTP file from Host A to Host C. 1. Observe the lights on the switch. Which link did the file transfer over? a. Transfer a file from Host B to Host C. Was the file transferred over the same link as in the previous file transfer? b. Transfer a file from Host C to Host A. Which link did the file transfer use? c. Transfer a file from Host C to Host B. Were the same links used as in the previous file transfer? CCNP 3: Multilayer Switching v Lab Copyright 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
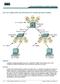 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch
 Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Question 5.1. Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain.
 Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
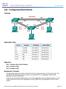 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
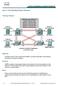 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
PT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
Lab Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
RealCiscoLAB.com. Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012
 Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches
 Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches Document ID: 118736 Contributed by Meghana Tandon, Sumanth Srinath, and Vishnu Asok, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 06, 2015 Contents Introduction
Behavior of Cisco Discovery Protocol between Routers and Switches Document ID: 118736 Contributed by Meghana Tandon, Sumanth Srinath, and Vishnu Asok, Cisco TAC Engineers. May 06, 2015 Contents Introduction
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
 Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
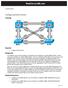 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Lab Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test
 Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
VLAN. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 3850 Switches) 1
 clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
clear vtp counters, page 2 debug platform vlan, page 3 debug sw-vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 6 debug sw-vlan notification, page 7 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 9 interface vlan, page 11 private-vlan,
ISP /24. Fas0/0. Fas1/0/1. Fas1/0/22 NYCORE1. Cisco PS. Fas0/1. Lab Nic /24
 Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Introduction The Configuring VLANs and Trunks module provides you with the instructions and Cisco hardware to develop your hands on skills in configuring layer 2 technologies VLANs and trunking. This module
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
VLAN Commands. Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Denali 16.3.x (Catalyst 3650 Switches) 1
 client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
client vlan, page 2 clear vtp counters, page 3 debug platform vlan, page 4 debug sw-vlan, page 5 debug sw-vlan ifs, page 7 debug sw-vlan notification, page 8 debug sw-vlan vtp, page 10 interface vlan,
Lab Catalyst 2950 and 3550 Series Intra-VLAN Security
 Lab 7.2.5.1 Catalyst 2950 and 3550 Series Intra-VLAN Security Objective Scenario Configure intra-vlan security with Access Control Lists (ACLs) using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. This lab will
Lab 7.2.5.1 Catalyst 2950 and 3550 Series Intra-VLAN Security Objective Scenario Configure intra-vlan security with Access Control Lists (ACLs) using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. This lab will
Lab 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Configuring EtherChannels
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers.
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco 7600 Series
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP)
 Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98155 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP Configure VTP VTP Troubleshooting and Caveats Unable
Troubleshooting VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) Document ID: 98155 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Understand VTP Configure VTP VTP Troubleshooting and Caveats Unable
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Pruning
 Lab 2.3.7.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Pruning Objective Configure VTP pruning between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch using the command-line
Lab 2.3.7.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Pruning Objective Configure VTP pruning between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch using the command-line
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Lab Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses
 Lab 6.2.6 Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Move a PC from one switch port to another and add a new PC to the switch. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.6 Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Move a PC from one switch port to another and add a new PC to the switch. Background/Preparation
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH
 BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
BASIC CONFIGURATION CISCO SWITCH switch#show running-config ( prikaz trenutne konfiguracije ) switch#show startup-config ( prikaz startne konfiguracije ) switch#configure terminal ( ulaz u global config
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Pruning
 Lab 2.9.3 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Pruning Objective Configure VTP pruning between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch using the command-line
Lab 2.9.3 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Pruning Objective Configure VTP pruning between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch using the command-line
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
 Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
CCNA Layer 2 switching. Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03
 CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Lab Troubleshooting VTP Configuration
 Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Lecture (04) VTP Ports Security
 Lecture (04) VTP Ports Security By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2015, Practical App. Networks II VTP VLAN Trucking Protocol (VTP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that propagates
Lecture (04) VTP Ports Security By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2015, Practical App. Networks II VTP VLAN Trucking Protocol (VTP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that propagates
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
SWITCH Lab Guide Labs powered by
 SWITCH Lab Guide 300-115 ii SWITCH 300-115 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please
SWITCH Lab Guide 300-115 ii SWITCH 300-115 Lab Guide LM20170908/BV1.0 iii 25 C e n tur y Blvd., S te. 5 0 0, N a s hvill e, T N 37214 B o s o n.c o m To perform the labs referenced in this book, please
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0
 Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring EtherChannels
 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. It contains the following
This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. It contains the following
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad LACP EtherChannels on the Cisco MWR 2941
 29 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.3ad LACP EtherChannels on the Cisco MWR 2941 Cisco MWR 2941 Release 3.5.1 and later supports IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) EtherChannels. Note The
29 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.3ad LACP EtherChannels on the Cisco MWR 2941 Cisco MWR 2941 Release 3.5.1 and later supports IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) EtherChannels. Note The
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
Configuring Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, page 1, page 9 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, page 16 Verifying the Load-Balancing Outgoing Port ID, page 17 Feature
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Port Channels, page 1, page 9 Verifying Port Channel Configuration, page 16 Verifying the Load-Balancing Outgoing Port ID, page 17 Feature
