VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter
|
|
|
- Josephine McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 4.1, VMware vcenter 4.1, and related products
2 VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter Copyright 2009, 2010 by ESXLab.com All rights reserved. Published by: Larry Karnis, ESXLab.com 15 Claypine Trail Brampton, Ontario Canada L6V 3L8 Phone: Toll Free: Facsimile: Web: (905) (888) (905) First edition published October 2009 Fully updated for vsphere 4.1, October 2010 To find out more about our products and services including consulting services, renting access to our remote lab facilities, running your own VMware class or custom training and content solutions, please visit our website or This document was prepared in its entirety using the open source OpenOffice 3 office suite. OpenOffice can be freely downloaded for free from Microsoft Visio 2007 was used to create some of the slide graphics. Final PDF assembly was performed with PDFFactory Pro available at Screen grabs were captured with Screen Grab Pro from Traction software. This free tool is available from This document, the images, screen grabs, etc. are original works. This document is copyright 2009 by ESXLab.com. All rights reserved. No reproduction by any means including photo-copying or electronic imaging is permitted without prior written authorization from the copyright holder. This training material is provided 'as is', without any warranty either expressed or implied. ESXLab.com prepared this material with due care for accuracy and completeness, but does not warrant that the content is either error free or suitable for any specific use. By using this courseware, customer agrees to accept responsibility for all results desirable or otherwise. Customer agrees that all lab exercises are for illustration purposes only, and assumes all risk of data damage or loss resulting from such use. Microsoft, Microsoft Windows, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows 2003 Server, Microsoft Exchange 5.5, Microsoft Exchange 2000, Microsoft Exchange 2003 and Microsoft Exchange 2007 are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. GroupWise and NetMail are trademarks of Novell Inc. Lotus Domino is a trademark of IBM Corporation. RedHat and Fedora Core are trademarks of RedHat Inc. VMware, VMware Workstation, VMware Server, VMware Player, VMware ESX, VMotion, etc. are registered trademarks of VMware Corporation. All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners. ESXLab.com is an independent training and content development company that is in no way affiliated with or in any way related to VMware Inc. In no case is any such relationship either implied or intended.
3 Time Line & Table of Contents Get Certified Now! ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist Day 1 Topics Chapter 0 - Overview Chapter 1 VMware vsphere Overview Chapter 2 Standalone ESXi Chapter 3 Virtual & Physical Networking Chapter 4 NAS Shared Storage Day 2 Topics Chapter 5 Virtual Machines Chapter 6 vcenter Chapter 7 Virtual Machine Rapid Deployment Day 3 Topics Chapter 8 Permission Model Chapter 9 Advanced Virtual Networking Chapter 10 Using Fibre and iscsi Shared Storage Chapter 11 VMware File System Chapter 12 Resource Management 2010 ESXLab.com. All rights reserved. - i - October, 2010 Photocopying this document in whole or in part is not permitted.
4 Day 4 Topics Chapter 13 Virtual Machine Cold and Hot Migration Chapter 14 Distributed Resource Scheduler Chapter 15 VMware High Availability Clusters Chapter 16 Guided Consolidation Chapter 17 VMware Data Recovery Day 5 Topics Chapter 18 Server Consolidation with vcenter Converter Chapter 19 vcenter Alarms Chapter 20 VMware Update Manager Chapter 21 Performance Monitoring Chapter 22 Final Thoughts Appendix Appendix 1 Definitions & Acronyms 2010 ESXLab.com. All rights reserved. - ii - October, 2010 Photocopying this document in whole or in part is not permitted.
5 Chapter 0 - Overview ESXLab.com VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-1 Module 0 Introduction
6 Introduction to Virtualization Introduction to vsphere Class Overview Virtualization Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-2 Module 0 Introduction
7 Virtualization App O/S App O/S App O/S App O/S App O/S App O/S App O/S App O/S VMware vsphere App O/S A software abstraction that creates virtual hardware & maps it to physical hardware Is completely transparent to guest OS and applications Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-3 Traditional PC Server Deployments One O/S and Application per server Captive local disk Workloads locked to server Virtual Deployment Require fewer physical servers Can run many workloads as Virtual Machines Workloads not locked to server (cold migration, VMotion, Storage VMotion) Load balancing and high availability options depend on shared disk Higher hardware utilization rates Lower marginal cost to deploy new workloads (just make a new VM) Better reliability and performance due to more capable hardware New options for Disaster Recovery, Back Up Module 0 Introduction
8 Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. VMware vsphere VMware ESXi Enterprise class server virtualization software Management, Performance, Monitoring vcenter Load Balancing VMotion, Storage VMotion and DRS Clusters High Availability HA Clusters Planning, Deployment and Back Up Capacity Planner, vcenter Converter, VMware Data Recovery Continuous Availability VMware Fault Tolerance 0-4 VMware provides a complete suite of products both for virtualization as well as for management, back up, disaster recovery, testing, replication and much more. These products make mitigating to virtualization very beneficial. The primary risk of virtualization is too many eggs in one basket... That is, if you consolidate workloads into virtual machines but lack the ability to: - Load balance your VMs across servers - Rapidly recover VMs that fail when a physical host fails - Easily manage and monitor VMs - Deploy VMs from known good images then you are creating risk... If you cannot load balance, then you run the risk of poor VM performance (due to host resource over-commit). If you cannot automatically place and restart VMs due to a physical server failure, then you may have critical production VMs down for hours if a host fails. Furthermore, if a physical host that supports a large VM population fails catastrophically, then your VMs might be down for days (until the hardware can be repaired). VMware Virtual Infrastructure provides all of the above features. Other products are maturing but do not yet offer the same breadth or depth of functionality as VMware. Module 0 Introduction
9 Key Topics Virtualization Overview Stand Alone ESXi Virtual & Physical Networking vsphere Management Virtual Machines, Rapid Deployment Shared Storage VM Migration & Load Balancing High Availability Physical to Virtual Conversions Back Up, Recovery & Disaster Recovery Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-5 The above items are key topics in this class but not a complete list of topics. For a complete list of topics, please consult the table of contents. Module 0 Introduction
10 Public Class Daily Timetable Schedule 09:00 a.m. Start 10:30 a.m. Break 12:00 p.m. Lunch 01:00 p.m. Resume 03:00 p.m. Break 05:00 p.m. End of Day Informal Ask questions any time Cell phones on vibrate please Take calls outside class Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-6 The above schedule is for public classes based on our standard timetable. Your training company/partner may set a different schedule. Module 0 Introduction
11 Problems & Opportunities Business or IT problem we face Identify common pain points. E.g. Provisioning Deployment Management Imaging Back Up & DR Etc. Virtual Solution Explain how Virtual Infrastructure addresses the problem New methods Streamlined procedures Less risk Faster results Reduced costs Simplify Etc. Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-7 Virtualization addresses most of the common pain points experienced by modern PC server deployments. As we go through this class you will learn how virtualization delivers the above benefits and much more. Module 0 Introduction
12 Introductions Who Name and current job Why are you here? Official reason Honest reason Experience with Windows Linux/UNIX VMware hosted products (Player, Server, etc.) VMware ESXi 3.x, VirtualCenter 2.x 3 rd party Virtualization (Xen/Hyper-V) Favorite vacation spot? Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-8 Experience with virtualization is not a prerequisite for this class... If you do have prior virtualization experience either with VMware products or other products please feel free to share them with the class. Module 0 Introduction
13 Vendor Neutral Certification ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist, Technician Exam based certifications for virtualization professionals Score 80%+ and earn ECVS Score 60-79% and earn ECVT About the exam Available at the end of class 75 questions in 90 minutes Multiple choice or True/False For more information see the brochure at the back of this book Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 0-9 VMware will not award certification to candidates unless you sit their class and then pass the VCP-410 exam. In response, ESXLab.com has created verifiable, vendor neutral VMware vsphere certifications so that attendees of ESXLab vsphere classes can achieve certification. Our exam fully tests a candidates knowledge and skill with VMware's vsphere products. There are two certifications you can earn. ECVS is awarded to high scoring candidates who, through their exam score, clearly demonstrate a superior level of knowledge and experience. ECVT is awarded to candidates who pass the exam and who demonstrate a solid understanding of the skills needed to effectively manage vsphere. The ECVS exam is free to any one who sits an ESXLab.com class. Your instructor should make the exam available to you on Friday afternoon at the end of the lecture/lab portion of the class. If you cannot stay for the exam (or if it is not offered), you can make arrangements with your local training center to sit the exam at a later time (note: a fee may apply). To be successful in the exam, we strongly suggest you: - Review the course book daily giving extra time to topics you found challenging - Review and/or redo the labs so that you fully understand the mechanics - Ask questions in class - Review VMware official product documentation available at Module 0 Introduction
14 Module 0 Introduction
15 Chapter 1 - Introduction Introduction to VMware vsphere Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-1 Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
16 VMware vsphere Introduction to vsphere Common IT problems vsphere solutions vsphere deployment options Storage, Network and server cloud computing Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-2 Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
17 Problems & Opportunities Low server resource utilization Data center costs, space, power, cooling Application, OS deployment Back Up & Recovery Server Refresh Remote access and support Hardware maintenance Operating system license costs Disaster Recovery Test, Development, Training, QA Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-3 Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
18 Server Resource Utilization Pre-virtualization server utilization rates are very low One OS/application per server Fortune 1,000; 8% avg. utilization Typical utilization % Usually one critical resource Other sub-systems mostly idle Why 1 OS, application/server? Political, administrative isolation Application, DLL isolation Simplify backup, recovery, DR Perception is that PC servers are cheap to buy, license, run Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-4 The most common method of deploying PC serves is one application per server. The reason for this is many-fold but is based on the belief that the complexities, risks and inflexibility of running many applications on a single server and operating system are simply not worth the cost savings of running many applications or services on a single PC server. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
19 App O/S App O/S App O/S vsphere App O/S App O/S Server Consolidation Many VM's/physical server VMs compete for available host CPU, RAM, Disk, Network VMs get needed resources Not declared resources Idling VMs may give up CPU, RAM Ensures active VMs run well under CPU, memory over commit (when vcpu count > physical core count) Share network, storage bandwidth Administrators can tune VMs Weighted scheduling, memory management and disk I/O Ensures critical VMs get resources when, as needed Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-5 Virtualization solves the one-workload/server problem without the traditional costs, risks or complexities of installing many applications on a single server. A PC server running VMware ESXi is capable of running many virtual machines concurrently. Each virtual machine is an independent software entity that functions as a complete, generic PC server. Each virtual machine has: - A virtual hardware layer that includes a generic motherboard, chipset, keyboard, mouse, video controller, IDE controller, CD/DVD device, NIC, PCI bus, SCSI controller, SCSI disk(s), CPU(s) and memory sized appropriately for the intended operating system and application - An operating system that recognizes and can drive virtual hardware - One or more applications Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
20 OS, Apps Tied to PC Server Problems OS, application health, availability, speed, scalability tied to PC server Server outage means application outage MSCS clustering is complex, expensive Resource contention reduces application performance E.g.: app(s) demand more CPU than available Virtual Solutions Virtual machines Many to one P2V consolidation Load balance VMs to improve performance Migrate VMs to less busy ESXi hosts Automate with DRS If an ESXi host fails Restart or continue VMs on another ESXi host Manual or automated VM, OS back in service in 0-3 minutes VMware HA Fault Tolerance Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-6 Traditional PC server deployment strategies result in a functional, but less than optimal environment... To ensure that we have sufficient resources to ensure acceptable performance for our application, we over-provision physical servers with CPU, memory, NICs and storage. Even so, it is possible that, during busy periods, our application may slow down due to a scarcity of some critical resource. If our server fails, our application becomes unavailable even though the operating system and application disk image on the failed machine are healthy. Our application remains unavailable until the server is repaired something that may take many hours or days. To defend against prolonged outages, we may be tempted to deploy traditional application level clusters (such as Microsoft Cluster Services). This usually requires us to duplicate our application, operating system and hardware on a machine that will spend most of it's time waiting (e.g.: stand by node of a 2 node active/stand-by cluster). Not only is this expensive, but the increased complexity of running a cluster may actually increase risk of down time. Virtualization addresses these problems in new ways. Because VMs are free to migrate to other ESXi hosts, we can rebalance ESXi clusters to address performance issues. And, with High Availability clusters, we can place and boot failed VMs on healthy ESXi hosts. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
21 Problems Power, cooling costs Square foot costs Out of rack space Expensive to build out Additional concerns Networking costs Shared SAN storage Back up procedures, time, costs Disaster Recovery Administrator time Config. consistency Datacenter Issues Virtual Solutions Consolidation rates of VMs/ESXi Relieves rack space congestion Reduces power, cooling costs Leverages existing networking, storage resources (SAN switches) Fewer physical servers to administer, back up, network, etc. Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-7 Data center power and cooling costs are substantial and are expected to continue to rise. Here are some sobering facts about what it takes to power a server in a data center: - A 1U PC Server can draw 300W to 1,200W of power - A 2U PC Server can draw W of power on each of its power supplies - A rack of 1U servers at 400W/server will consume 135 amps of power per hour - Many data centers double their power consumption every 3 years - As servers become more powerful, the power draw per server increases - Data centers often run out of power/cooling before running out of rack space - Idle servers often consume more than 50% of their maximum power draw - Cooling servers consumes as much to twice as much energy to operate them - Servers with 32+GB of RAM use more power to run RAM than they do to run CPUs (especially true of servers that run high frequency FB memory) Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
22 OS, Application Imaging Problems Bare metal installs Complex Drivers, agents, etc. Time consuming Introduce needless variation, risk Imaging solutions not universal Tied to manufacturer, hardware components Images may not help if maker changes hardware configuration Virtual Solutions VMs get generic hardware, not physical hardware Easy to create VM master images Clones, Templates Copy & customize... Easy to create a VM Image Library Easy to maintain Not tied to hardware Easy to change H/W vendors Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-8 OS and application imaging solutions ease the task of deploying operating systems and their applications. Typically an administrator installs their preferred OS and apps onto a PC server and then uses an imaging tool to harvest a deployment image for future use. This works great if you need to deploy the same image onto the same hardware but can cause problems if: - Your vendor changes underlying hardware (chipsets, storage controllers, etc.) - Your images require frequent maintenance - You change hardware vendors Virtual machines don't suffer from these problems because their virtual hardware is independent from the physical hardware seen by ESXi. So, even if you change hardware (or hardware vendors), you can still deploy VMs from your pre-build VM images. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
23 Problems Backup tools are expensive, complex Backup, recovery, application, open file agents Speed limited by network bandwidth Limited back up windows Virtual networking not as fast as physical networking Back Up & Recovery Virtual Solutions Most LAN backup tools are supported File system back ups VM snapshots Data synchronized Disk image backup VMware Consolidated Backup (VCB) Based on snapshots Data Recovery VM back up, recovery File level recovery Virtual appliance Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 1-9 VMs work with traditional LAN based back up tools so you can continue to use these if you like. However, VM networking is not as efficient as pure physical networking, so you should expect your back up windows (time to complete a back up) to increase when using network based back up tools in a VM. There are a number of solutions to this problem... VMware Consolidated Backup uses a physical back up proxy server and direct SAN connectivity to snapshot and back up your running VM with no network dependency (Fibre SAN only). Since Fibre SAN networks run at 4Gb or 8GB and they were designed for high volume storage traffic, your back ups should complete much faster than LAN based back ups. VMware Data Recovery (DR) performs snapshot based back ups with full virtual disk deduplication, so backups are fast and complete. And Data Recovery provides you with the ability to do both file level and full virtual machine level recoveries. Third party back up tools such as VRanger Pro ( PHD Virtual Back Up ( or Veeam Backup & Replication ( leverage ESXi storage APIs to quickly and safely back up VMs. These tools are easy to install and use, are (relatively) low in cost (unlike traditional network back up tools) and make it easy to recover individual files or complete VMs. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
24 Problems PC servers have a short life span 3-5 yrs depending on available maintenance support contracts OS, application migrations are time consuming, risky Workload down during migration Done off hours Hard to do remotely Inherently risky Server Refresh Virtual Solution Virtual hardware VM H/W is independent of physical hardware Easy to migrate VMs to another ESXi host Hot, cold VM migration Limits down time 4 simple steps... Provision new server Install ESXi, join cluster Migrate VMs to new host Shut down, wipe server Can be performed remotely Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Virtual Machine hardware is a software abstraction that is independent of physical PC server hardware. ESXi maps virtual hardware operations to physical hardware activity. Virtual machines see: A virtual motherboard with a chipset, keyboard, mouse, IDE, floppy controller A virtual PCI video controller One to four virtual IDE CD/DVD devices One to two virtual floppy drives A virtual PCI bus Up to 8 virtual Network Interface Cards (NICs) One to 4 virtual SCSI Host Bus Adapters (SCSI HBAs) Up to 15 virtual SCSI disks per SCSI HBA Up to 8 virtual CPUs that map to physical CPU cores Virtual memory that is indistinguishable from physical memory Virtual hardware presented to VMs is the same regardless of the underlying physical hardware. Therefore a VM can migrate from ESXi host to ESXi host (even if the ESXi hosts are different makes or models of hardware) without issue. T H The only exception is CPU. The make, model and stepping, but not cores or hyperthreading, of the physical CPU is exposed to the Guest OS at boot time. These properties should not change (due to VM migration) as the VM runs. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
25 Problems HW maintenance requires down time Short maintenance windows Weekend vendor support is costly Must be on site 7x24 4hr response Expensive Often no guarantee of a fix within 4hr window Without top tier contract, hardware issues may keep a server down for days Hardware Maintenance Virtual Solutions To perform H/W tasks on ESXi host Evacuate ESXi host of Virtual Machines VMotion, cold migrate VMs to other ESXi hosts Patch, upgrade, repair, reconfigure host No VM down time during maintenance If ESXi capacity permits, maintenance can be done during production hours Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Before virtualization, server hardware maintenance was a costly and risky task that was usually performed on weekends. With virtualization, server hardware maintenance is greatly simplified and risk is eliminated. To perform physical server maintenance on ESXi hosts: - VMotion all VMs off the host that will be maintained - Shut down and power off the host when all fully evacuated of VMs - Add, upgrade, fix hardware - Power on the server - Rejoin clusters - Migrate VMs back to the fixed host Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
26 High Windows OS Costs Problems Windows 2003, 2008 Server licenses are expensive Host licenses, CALs May have to buy more expensive editions for needed features E.g. Microsoft Cluster Services not available on Windows Server Standard Editions Solution Windows Enterprise, Datacenter have VM friendly pricing Enterprise 4 VM at no additional charge Datacenter unlimited VMs at no additional charge Check your License agreement for entitled instance count Volume purchase agreements Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Microsoft may grant you the right to run additional instances of Windows 2003/2008 Server depending on the base license installed... Windows 2003/2008 Standard does not permit additional VM instances so every VM would require a unique Windows Standard license. Windows 2003/2008 Enterprise permits a limited number of Windows VMs (up to 4) to be run on the same machine running the original license without additional charge. Windows 2003/2008 Datacenter permits an unlimited number of Windows VMs to run on the same host running the original Windows license at no additional cost. As VM consolidation rates go up (more VMs/ESXi host), the cost to license Windows per VM can go down dramatically if you select the appropriate Windows edition (Enterprise or Datacenter). You also get the added benefit of the enhanced features (e.g.: Clustering) offered by premium Windows editions). Windows Datacenter simplifies license compliance, because you are entitled to run an unlimited number of VMs/server. You are also entitled to downgrade your Windows editions in the same family (e.g.: If you have W2k3 Datacenter, you can deploy W2k3 Standard or Enterprise in your VMs). Note: Posted prices are accurate retail prices as of September, Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
27 MS Virtualization Calculator Part A License cost by average VM/s per server Part B License cost by actual VMs per server Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class This calculator, published on Microsoft's web site shows the US Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) of Microsoft Windows Server operating system licenses (both Windows Server 2008 and 2003) and Virtual Machine instance counts as permitted by the three Windows Server editions; Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter. This calculator shows that, under certain conditions, substantial savings can be had by purchasing either Windows Enterprise or Windows Datacenter editions over individual Windows Standard editions. With the premium Windows editions, the higher base cost is offset by the lower marginal cost per Windows VM. To gain the lowest cost per Windows VM, you must have high Virtual Machine to physical machine ratios (e.g.: VMs per physical server). With today's high core count CPUs (i.e.: CPUs with 4, 6, 8 or 12 cores per physical CPU) and relatively low RAM costs, such consolidation rates are not just attainable, but actually reasonable. In the example above, there are 2 ways to calculate license costs; Average VMs per host and actual VM's per host. The example was worked so that both methods correlate (i.e.: actual VMs in the Blue part match the average VMs in the Green part), and prices mostly match as a result. Please check your own volume license agreements before changing your licensing strategy! Note: Posted prices are accurate retail prices as of September, Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
28 Disaster Recovery Problems Ensure business continuity Replication is costly Duplicate all HW, SW at remote site Complex DR procedures must be tested, reviewed, refined, retested Risky Failure of DR plan puts business at extreme risk Virtual Solutions ESXi + SAN Shadow SAN LUNS to DR site ESXi host(s) at DR site set to run VMs ESXi only solution Snapshot VM, copy to DR site Can be scripted and scheduled Snapshot guest OS sync ensures valid, consistent, reliable virtual disk image Use 3 rd party tools Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The traditional approach to disaster recovery is to duplicate all of your expensive hardware and software at a second datacenter. This is costly and must be carefully planned and tested before being trusted. With virtualization, you can simplify disaster planning by replicating VMs and storage at your DR site. If you have SANs that support LUN shadowing, you could shadow critical LUNs from your production SAN to your DR SAN. If you have a primary site failure, just boot the VMs at your DR site's ESXi hosts and SAN If you don't have LUN shadowing capabilities, you can still replicate VMs at a DR site. In this case, you need to decide how you are going to replicate your VMs. You could either: - Perform off line replication of VMs from nightly back up images. This works and can Efficient but you risk loosing up to one day's work - Use VMware Consolidated Back Up to snapshot and copy running VMs to your DR site - Use 3 rd party tools to do on-the-fly VM replication at your DR site. A number of 3 rd party tools are available to perform VM hot replication including: - Veeam Backup & Replication ( - Vizioncore vreplicator ( Check out a comparison of these two products here: Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
29 Test, Development & QA Problems Development, test environments don't match production environment Too costly to deploy an exact match Differences introduce variation, risk Hard to validate changes, test software, catch errors if production, test/development environments differ Virtual Solutions Clone production VMs Clone - Exact copy of original VM Test changes on clone Configuration changes OS patches Application upgrades Validate procedures VM snapshots let you back out of changes Saves VM state No need to re-image if problems encountered Revert back to original Try again! Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
30 IT Technical Career Benefits Indeed VMware job tracking graph According to Dice ( Candidates with one completed virtualization project are considered experienced Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Having ESXi and vcenter skills is good for your career as a IT technical practicioner! Virtualization skills remain in demand even though many aspects of IT are flat. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
31 vsphere Components VMware ESXi/ESX with Virtual SMP ESXi 4.1 or ESX 4.1 VSMP Virtual Symmetric Multi-Processing 1-8 vcpus (cores) per VM VMware VMFS high performance file systems VMware vcenter management VMotion hot VM migration Storage VMotion hot relocates VM disk Distributed Resource Scheduler (load balance) High Availability clusters (failure recovery) Guided Consolidation (plan your consolidation) Converter (physical/virtual migrations) Update Manager (patch, update ESXi) Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
32 VMware ESXi Enterprise class virtualization Bare metal install Lean hypervisor Dynamically load balances VMs Assigns CPU, RAM resources when needed, as needed If resources are scarce, idling VMs get little service Dynamically tunable Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi is a bare metal hypervisor. It is bare-metal because ESXi is installed upon and owns the physical PC server. A hypervisor is an operating system whose primary task is running virtual machines rather than normal operating system tasks. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
33 VMware vsphere 4.1 Editions vsphere vsphere vsphere vsphere ESXi Standard Advanced Enterprise Enterprise+ ESX + VSMP + VMFS P P P P P vsphere Client P P P P P Consolidated Back Up P P P P Update Manager P P P P High Availability P P P P Thin Provisioning P P P P VMotion P P P P Hot Add Hardware P P P Data Recovery P P P Fault Tolerance P P P vshield Zones P P P Virt. Serial Port Concentrator P P P DRS Load Balancing P P Distributed Power Mgt P P Storage VMotion P P Distributed vswitches P Host Profiles Storage I/O QoS Network I/O QoS P P P Price per CPU Socket $0 $995 $2,245 $2,875 $3,495 Subscription & Support Basic $273 $472 $604 $734 Subscription & Support Production $323 $561 $719 $874 Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class VMware licenses are expensive. To get the best value out of them, you should plan for high server consolidation rates. Consolidating 10 legacy physical PC servers onto one ESXi host is very reasonable (the author has seen 35 VMs on an ESXi host on a number of occasions). By consolidating many workloads onto a single PC server you avoid: - The cost of refreshing older PC servers - The cost of maintenance contracts for these PC servers - The labor cost of physically migrating the OS and apps to a new server - Administrative and power costs running more PC servers - Reduced network switch and SAN switch port use VMware now licenses ESXi by the socket so a two physical CPU machine would require two licenses (2 x the price shown above). Subscription and Support (SnS) is mandatory at the time of purchase. vcenter is also needed to take advantage of many advanced features such as VMotion, Storage VMotion, Update Manager, High Availability, DRS, Fault Tolerance, Distributed Power Management, Distributed vswitches and Host Profiles. vsphere pricing is explained here and is current for the USA as of Sept, Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
34 vsphere Hardware Limits vsphere vsphere vsphere vsphere ESXi Standard Advanced Enterprise Enterprise+ Max Cores per Physical CPU Max RAM per Physical ESX Server 256GB 256GB 256GB 256GB unlimited Max Virtual CPUs per VM VMware has license imposed hardware limits on physical servers and VMs Physical servers Max 256GB RAM (2TB for Enterprise +) Max 6 core physical CPUs (12 for Advanced and Enterprise+) Virtual Machines Max 4 Virtual CPUs per VM on most editions Exception - Enterprise + allows 8 vcpu VMs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class VMware imposes limits on: - The maximum number of physical CPU cores per physical CPU - The maximum physical RAM that can be used in a physical PC server - The maximum number of virtual CPUs you can add to a VM For physical servers, you need to determine if you want to use 6-core or 8-12 core physical processors. You also need to decide if you want to put more than 256GB of RAM in your physical PC servers. For Virtual Machines, you should select the VMware vsphere edition based (in part) on the number of virtual CPUs (vcpus)you need to present to your biggest VMs (i.e.: can you get by with up to 4 vcpus/vm or will your enterprise workloads, such as SQL and MS Exchange need 5-8 vcpus per VM). All vsphere editions have the same VM RAM limit, which is 256GB/VM. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
35 Small Business Bundles vsphere vsphere Essentials Essentials Plus ESX Servers (2 sockets) 3 3 ESX Cores (6 cores max) 6 6 vcenter Server Nodes 3 3 VSMP (Max vcpus/vm) 4 4 Update Manager P P VMware HA P Data Recovery P VMotion P Package Price $495 $3,495 Support and Subscription Basic $116 $734 Support and Subscription Production $874 Per Incident Support Price $299 Prices from as of September, Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class VMware has created special license bundles that are targeted at small business. These license bundles provide smaller customers with virtualization and management capabilities for less than the cost of one (competent) PC server. The Essentials Plus bundle adds hot migration (VMotion) rapid VMware failure recovery (VMware HA), automated patching and updating capability for ESXi hosts and Windows (Update Manager) and simple back up and recovery (Data Recovery). These added features make Essentials Plus a compelling offering. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
36 VMware vcenter Management Console for vsphere Manage host, VM, network, storage Administer, monitor, tune, review Schedule jobs, review activity, resource maps Host Profiles and VM specifications P2V migrations Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
37 Single Host Deployment Single ESXi host VMs share host CPU, RAM, Disk, Network of the host system Manage with vsphere Client Low-cost or free ESXi or vsphere Standard Edition Benefits Lower capital cost Lowers power use Faster deployments Easier upgrades Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The primary benefit that moves most organizations to virtualization is server consolidation (replacing physically deployed servers/workloads with virtual machines). While there are many benefits to consolidating onto ESXi there is one major risk you have many workloads now dependent on the health of a single machine. In the past, if a server failed, only one group of users were inconvenienced. With virtualization, a physical server failure has the potential to impact many more users. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
38 Multiple ESXi w. Shared Storage Migrated VMs onto shared SAN storage VMs still run on single host No VMotion, DRS, HA without vcenter Some fault tolerance If an ESXi host fails Use Datastore Browser to import VMs onto surviving host(s) Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class By moving your VMs onto shared storage, you untie your VMs from a single physical host. You also break the storage limits that may be imposed on you by your server platform. But, best of all, you now have a simple way to recover VMs that fail due to a server failure. As we will see later, VMware provides a piece of software called the Datastore Browser. The Datastore Browser has the ability to reassign ownership of powered off VMs to other hosts. So, if a server does fail... - Log into a surviving ESXi host - Launch the Datastore Browser - Identify the VMs that failed when the ESXi host failed - Take ownership of these VMs using the Datastore Browser by adding them to the surviving ESXi host's inventory - Power on these VMs on the new host While this approach is somewhat labor intensive, it does solve the problem of VMs being down because a host is down. You can automate VM recovery with VMware HA. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
39 Full vsphere Add vcenter ESXi and VM management Includes Cold migration Consolidation Converter Enables VMotion Storage VMotion High Availability Load balancing Fault Tolerance Back Up etc. Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
40 Cloud Computing Dynamically provision hardware on demand Provision what's needed, when needed Physical hardware abstracted, shared Storage Shared Storage Appliances (SANs) Provision, grow LUNs on demand LUNs visible to many ESXi hosts PC Servers run ESXi to deploy, run VMs Size for reasonable VM workload Provision more as VM population grows Dynamically load balance to maintain performance Networking VMware Distributed vswitches Virtual switches that span ESXi hosts Add physical uplinks to improve ESXi LAN speed Consistent configuration, metrics across ESXi hosts Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
41 Storage Cloud Storage Area Networks (SANs) Aggregate physical disks into LUNs Presents LUNs to ESXi VMFS cluster filesystem Safe concurrent access Grow LUNs as needed Provision LUNs on demand Snapshot, back up LUNs Shadow (replicate) LUNs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
42 Server Cloud Provision PC Servers to meet growth, performance needs Buy a new PC server Install ESXi, join vcenter Add to DRS cluster VMs rebalance onto new server Reduces CPU, memory use on other servers Add to HA cluster Restarts VMs if an ESXi host fails Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
43 Network Cloud Distributed vswitches span ESXi hosts Unified view of all Port, Port Group settings Simple consistent, VMotion compatible configuration Common MAC address table Supports internal Private VLANs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Distributed vswitches are software objects that emulate a standard layer 2 switch. Distributed vswitches span two or more ESXi hosts and provide consistent network functionality across all VMs, etc. that are plugged into the distributed vswitch. A distributed vswitch has a single common MAC table and a unified set of performance counters. Because a vnetwork Distributed Switch configuration spans all ESXi hosts, they are especially helpful for VMotion because VMs will find exactly the same Port Group (configured exactly the same way) on any ESXi host that shares the distributed vswitch. Distributed vswitches are created and managed with the vsphere Client. You must have vcenter to create a distributed vswitch. You must have VMware vsphere Enterprise + to create and use vnetwork Distributed Switches. For organizations that run Cisco enterprise networking products, VMware offers the Cisco Nexus 1000V distributed switch. This is an upgrade to VMware's default vnetwork Distributed Switch. The Nexus 1000V offers full Cisco IOS compatibility and can be managed and monitored with standard Cisco tools. Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
44 Module 1 - Introduction to vsphere
45 Chapter 2 VMware ESXi VMware ESXi 4.1 Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-1 Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
46 Stand Alone ESXi ESXi Overview ESXi Installation Procedures Best Practices Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-2 Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
47 Project Plan By the end of this chapter, we will have Installed ESXi onto a stand alone server Partitioned local storage for ESXi and VMs Connected to ESXi using the vsphere Client and Secure Shell Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-3 Our first step in this class is to install ESXi onto stand alone PC servers and then connect to those newly installed ESXi hosts using the vsphere Client and SSH. In future chapters we will add to our original implementation. Our ultimate objective is a, scalable, highly redundant, load balanced Virtual Infrastructure implementation that supports a large community of Windows 2000, Windows 2003, Windows 2008, desktop and Linux VMs. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
48 Problems & Opportunities Problems Server consolidation DNS, DHCP, Web, File & Print, AD, DC Reduce costs Capital $ Hardware support $ IT staff admin time Free up rack space Increase server utilization rates Position for future growth, flexibility Virtual Solution Low cost vsphere Standard Edition supports 256GB physical RAM 1-6 core CPUs 1-32 GB NICs GB NICs Local, shared storage volumes, file shares Consolidate many VMs onto one host Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-4 vsphere Standard Edition is a low cost version of VMware ESXi especially intended for entry level virtualization deployments that offer the following hardware capabilities One or more physical CPUs 4 or 6 core CPUs supported (up to 12 core CPUs on vsphere Enterprise(+)) Will use up all available physical memory up to 256GB Local disks or RAID volumes on supported SATA, SCSI or SAS controllers Up to 32, 1GB NICs including dual and quad NICs Up to 4, 10GB NICs iscsi hardware and software initiators Fibre host bus adapter support Use of NFS shares With the ability to run up to 8 light duty or 2-4 medium duty VMs per CPU core, ESXi or vsphere Standard Editions are excellent choices for entry level server consolidation projects. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
49 ESXi Block Diagram Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-5 VMware ESXi is a bare-metal virtualization hypervisor solution. As such, it must install on an industry standard PC server. Please check VMware's Hardware Compatibility Guide (portal on web site) for the most up to date list of supported PC servers. Because it owns the hardware, ESXi is in full control of resource assignments to running VMs. The VMkernel, allocates hardware resources on an as-needed basis. In this way, the VMkernel can prevent idling VMs from wasting CPU cycles that could otherwise be used by busy VMs. Likewise, the VMkernel keeps track of needed RAM, not just requested or allocated RAM. It can dynamically re-assign RAM to memory starved VMs, thereby ensuring that VMs get the memory they need to run. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
50 Scalable ESXi Deployment SAN advantages Local storage for High performance Higher availability Boot, SC, VM paging Capacity management SAN LUNs ESXi boot, swap, VM use LUN Backup, replication Disaster Recovery Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-6 As your ESXi deployment matures (technically) you will want to introduce: Different LAN (virtual) segments to isolate network traffic. You could different LAN segments for things like IP Storage, Management and production systems Shared storage solutions including iscsi, Fibre SAN and NFS shares Hardware redundancy in the form of multipath storage solutions and teamed NIC configurations. You may even wish to consider a Boot From SAN solution so you don't need to configure servers with local storage. Boot from SAN is available on supported Fibre SAN controllers and also with iscsi SAN controllers (using iscsi hardware initiators). Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
51 CPUs 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 or 12 core CPUs Max 128 cores/host Intel 64-bit Xeon only Hyperthreading AMD Opteron NUMA local memory All Opteron CPUs supported Memory Min 2GB to boot 256GB 2TB on Enterprise + ESXi Server Hardware Network 1-32 GB NICs GB NICs VLAN, NIC Teams Storage Local volumes SCSI, SAS, SATA RAID, non-raid iscsi SANs Fibre SANs File Shares NFS only No SMB support Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-7 ESXi is capable of using the largest PC server hardware platforms. Apart from what is stated above, ESXi is limited to: No more than 192 CPU cores (or Hyperthreaded logical processors) for CPU scheduling purposes All available RAM (ESXi Standard/Enterprise) Furthermore the following implementation limitations need to be considered: Very limited selection of supported 10GB Ethernet controllers Jumbo Frame now supported, which will dramatically improve software iscsi performance Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
52 ESXi Installable: loaded onto disk or onto a USB thumb drive Embedded: burned into flash on the motherboard No Service Console OS More secure Available for free Per incident support available ESXi vs. ESX ESX Installed onto a storage volume Local or SAN storage Includes a full Console OS based on CentOS 5.2 Linux Larger memory foot print Retired after ESX 4.1 VMware recommends deploying ESXi only for current and future installs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-8 VMware has officially stated that ESX will be retired at the end of the ESX 4.1 release. That is, VMware will no longer release ESX for future releases of their software just ESXi. For this reason, VMware recommends that all current and future hypervisor deployments, be ESXi, not ESX. ESXi comes in two forms Embedded and Installable. Embedded is baked into firmware on the motherboard of select PC servers. This lets you boot your server without any local storage. ESXi Installable is a version of ESXi that can be installed onto local storage, USB memory keys or SAN storage. It is installed from CD media that you can download from ESXi does away with the Service Console. This provides a smaller, leaner hypervisor than full ESX. It is also more secure because there is less software (to exploit) and fewer services running on ESXi than there is on ESX. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
53 ESXi Install Steps Install steps... Boot your server from ESXi install media Accept the EULA Select target disk for installation Agree to partition and format disk Reboot server when install complete Post install steps... Log in and change root password Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class. 2-9 Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
54 ESXi Boot Screen To begin your ESXi install, boot from CD Hit ENTER to launch the installer Customized installs Serve media from HTTP or NFS Scripted installs simplify deployment Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi is installed in text mode so your PC server doesn't need to have graphics capability. VMware makes it possible to set up an install server for ESXi so you can perform network based installs. Using Linux' KickStart capabilities, ESXi installations can be automated/scripted so you can install and configure new servers hands-off. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
55 Accept the VMware EULA You must accept the VMware End User License Agreement before you install ESXi Hit F11 to proceed to the next step Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The ESXi installer uses your Video Card's VESA mode for hardware independent graphics. The good news is that VESA is almost universally supported (and consequently should work). The bad news is that VESA is the slowest mode of operation. The overall sluggishness of VESA mode is exacerbated by the use of remote management cards such as: HP Integrated Lights Out (ilo) IBM Remote Server Assistant (RSA) Dell Dell Remote Access Controller (DRAC) While useful, remote graphics consoles over slower WAN links will require patience and a steady hand. To minimize the sluggish (drunk) mouse behavior, use key sequences like Tab move to the next clickable region Enter invoke a clickable action Space select a clickable option In fairness to ESXi, graphics mode is only used during installation so graphics performance (or lack of it) is an installation time only issue. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
56 Select the Target Volume Installer displays available storage volumes Categorized as Local or Remote Local volumes are visible to just your host and consist of local RAID or physical volumes Remote volumes are visible SAN LUNs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Normal ESXi installations occur in graphics mode. Consequently, the installer must get your preferences/settings for the install language, keyboard and mouse. These settings are used only during installation. Since, once it is in service, ESXi runs in text mode (with no native graphics capabilities), your language, keyboard and mouse preferences are discarded once the installation has completed. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
57 Install Custom Storage Drivers The installer is ready to proceed... Selected volume is re-partitioned, formatted All existing partitions on the selected volume are deleted Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The installer will now install ESXi onto your selected storage volume. To do this, the installer: - Wipes all partitions on the selected target storage volume - Creates partitions as needed (normally 8 partitions are created) Useful information about the installation disk: - ESXi consumes about 6GB of disk space in overhead. The rest is for VM use - partition 4 is the boot partition and is located at the front of the disk (behind the Master Boot Record and partition table) - partitions 2 and 4, 5, 6 & 8 are for ESXi use and occupy the front of the disk - partition 7 is a vmkcore partition (partition code 0xfc) and is a ESXi partition used to hold crash dumps - partition 3 consumes all remaining disk space and is partitioned and formatted as a VMware File System (VMFS) Note: ESXi has an known issue installing onto local disk of > 2TB in size. If you have a very large local RAID array the installer will report but not use all available space. You will have to manually extend the size of the VMFS volume to claim all space. A great community article on how to fix this issue can be found here: Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
58 Installation Completed Once your installation has completed, hit Enter to reboot to ESXi Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class It only takes about 3-5 minutes to install ESXi onto your PC server. The install proceeds non-interactively. A status indicator updates a percent completed horizontal bar. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
59 ESXi Small footprint, bare metal hypervisor Use F2 at the boot screen to set up your ESXi 4.1 host Simple BIOS like interface Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi has a simple, BIOS like interface that makes it very easy to configure. To configure your ESX host, simply hit F2 at the greeter screen. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
60 Log In for the First Time The administrator account for ESXi is root By default, no root password is set Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The ESXi administrator account is root (the traditional Linux administrator account). When you install ESXi, the system defaults to: - no root password - IP properties set via DHCP - no command line access (either locally or remotely) In the next few slides, we will discuss how to change these values. Since there is no default password, just hit Enter to proceed to the ESXi configuration screens. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
61 ESXi Configuration Menu Configure ESXi through a simple text menu Hit Enter to activate a menu function Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The ESXi configuration menu is a simple text interface where you complete your server's customizations. Use the up/down arrows to move to a function. When a function is highlighted, its properties and the command keys used to modify that function are displayed on the right. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
62 Set the Root Password The first thing you should do is set the root account password Prevents unauthorized access to your server Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
63 Default Management IP Settings By default your ESXi host uses DHCP Host name and IP address assigned using an IP address out of your lease pool Example above reclaims a desktop PC lease! Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class You must set the IP properties of your ESXi host before you can manage it. Select Configure Management Network to set the: - Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) - IP address - Netmask - Default Gateway and other properties. You can set these values statically or dynamically using DHCP. DHCP servers can send static properties to a host. To do this, configure your DHCP server with the MAC address of your ESXi host management NIC and then set the static properties to server whenever that NIC broadcasts for a DHCP lease. Be sure to Restart Management Network after all changes to ensure your updates take effect. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
64 Configure Management Network The Configure Management Network submenu let's you set key network properties Management NIC IP properties DNS settings Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class It is a best practice to use static network settings for your ESXi host. To complete this task, you must: 1. Select the correct NIC for management networking 2. Set a static IP address and Netmask and Default Gateway values 3. Identify your local DNS server(s) and the default DNS search domains Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
65 Select Management NIC(s) Physical NICs is used to carry mgt. traffic Select Network Adapters to view/change NICs Select 2 or more NICs to automatically create a NIC team Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class You manage your ESXi host through your network. To communicate with your ESXi host (using either the vsphere Client directly or vcenter indirectly), you must have network connectivity to it. Since modern PC servers may have many NICs and these NICs may be connected into different physical and/or virtual LAN segments, you may have to select the correct physical NIC (rather than the default NIC) before you can manage your machine. NIC Teams The Network Adapters screen lets you review and select the NIC or NICs you wish to use to carry network traffic. If you select more than one physical NIC, you automatically create a NIC team. NIC teams afford better speed and redundancy. Tip It can be difficult (or impossible) to tell which RJ45 jack is associated with which MAC address. A simple way of selecting the correct physical NIC(s) is to unplug all NICs from their switch except for the NICs you wish to use for management. Then use the Status column (Connected means the NIC has a link to the switch) to determine which NICs you should for management. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
66 IP Configuration Best to use Static IP properties No chance your server could loose its IP lease and therefore it's IP address Static IPs are needed for vcenter Management Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Complete this form to set your ESXi host management NIC IP properties. vcenter cannot manage an ESXi host whose IP address changes. For this reason it is best to give all of your ESXi, ESXi hosts fixed IP properties. You must select Set static IP addresses... and complete all three fields to complete your static IP address properties assignment. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
67 DNS Configuration You must set DNS and FQDN properties Enter the IP of your DNS server(s) You MUST enter the FQDN of your ESXi host Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi and vcenter require DNS services to function properly. So it is critical that you have DNS name servers set up and accessible from your local LAN segment. It is a best practice to have both primary and secondary DNS servers available... but ESXi will function with just primary DNS. You must set a fully qualified domain name for your ESXi host. The ESXi FQDN must be resolvable forward (host name IP address) and backward (IP address FQDN). Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
68 Custom DNS Suffixes DNS suffixes are help resolve host names DNS look ups that contain only a host name have suffixes from this list appended before a DNS look up is attempted Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class DNS Suffixes are used to enable DNS to look up the IP address of a host specified only by it's host name (and not qualified with a domain name). An example might be a look up request for a host called esxi5. DNS needs a full domain name. Custom Suffixes will append domain names from the list set on this screen to simple host names and then perform a DNS query. This continues until either: - a matching FQDN is found and it's IP address is returned - no matching FQDN is found and all suffix Domain names have been tried It is a good practice to add at last one domain name to this list! Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
69 Apply Network Changes Network changes are applied en mass NIC, IP and DNS changes are activated by restarting Management Network services Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class All network changes are applied at one time when you leave the Configure Management Network sub-menu. First the new settings are applied to the appropriate configuration files, and then the ESXi hosts' management network is brought down and back up again. For this reason, it is best to be at the physical server's console when updating management networking properties. You should be brought back to the System Customization menu. Your network changes should be visible. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
70 Test Management Network Basic connectivity test with Ping, DNS Pings gateway, DNS server Tries to resolve the server's FQDN Each test reports OK or Fail Do not proceed until all tests pass! Verify your DNS server is ping-able Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
71 Local/Remote Tech Support Tech Support mode enables command line access to your ESXi host Local must be on the physical server's console Remote can Secure Shell to your server Default is OFF for both services May need to turn on for VMware/partner access Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Tech Support Mode enables functions used by support providers who are comfortable working on the ESXi command line. By default, all local and remote command line access to your ESXi host is disabled so you can only access your ESXi host through: - the vsphere client pointed directly at your ESXi host - vcenter if vcenter has management control over your ESXi host - The VMware Management Assistant service (VMA), if installed Enabling Local Tech Support allows physical console command line access. Support personnel who have access to the physical console (directly or via remote console services such as Dell DRAC, HP ILO or IBM RSA) would be able to log in to your server. Enabling Remote Tech Support enables the Secure Shell Daemon (sshd) and supports network based administrator access to your box without the need for remote console services. Warning Enabling Remote tech support enables direct root access to your ESXi host through a TCP/IP connection. This is a potential security threat. Turn on this feature only if needed. If this feature is turned on, set a strong root password. Never expose your machine to an untrusted network like the Internet if Remote Tech Support is turned on! Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
72 Restart Management Agents ESXi uses agents (services) to communicate with vcenter and the vsphere client If agents fail, your server is unmanageable Use this feature to reset management agents Does not interfere with running VMs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class It may happen that the management agents (services) on your ESXi host become unstable or crash. If this occurs, your ESXi host will not respond to vcenter or the vsphere client. In vcenter your host will grey out and report as disconnected. You could reboot the ESXi host but that would bring down all running VMs. A more acceptable option is to simply restart the management agents on your ESXi host. This function can be done at any time. Any connected vsphere Client sessions will be closed. Once this function completes, your host should become active in vcenter and should accept direct vsphere Client login requests. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
73 ESXi Ready for Service ESXi server is ready for use Additional hot keys are active Use the vsphere Client to manage ESXi Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Once ESXi has rebooted, it is managed with through the web or via VMware's vsphere Client. You can download the vsphere Client from There are additional hot keys active on the ESXi console: Alt-F1 first command line log in screen Alt-F2 the ESXi greeter screen (screen shot above) Alt-F3 to Alt-F10 no function Alt-F11 Grey scale status screen/greeter screen with no F-key prompts Alt-F12 VMkernel log dump Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
74 Alt-F12 VMkernel Log Entries Hit Alt-F12 at any time to view the VMkernel log contents Displays the most recent VMkernel log contents Look here to see detailed error messages Or, look at /var/log/messages on the cmd line Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The VMkernel records detailed log entries into a file called /var/log/messages. You can view this file by logging into the Local/Remote tech support prompts (as root) and issuing the command: # less /var/log/messages You can see the most recent entries by hitting the Alt-F12 keys on your machine's console. This display shows one screen full of the most current additions to the VMkernel log file. You should check this file if you are troubleshooting problems and need more information than is available in the vsphere client. Hit Alt-F2 to go back to the ESXi greeter screen when done. Note All command line commands entered using Local or Remote tech support are logged to /var/log messages. In this way, it is possible to reproduce the activities of prior command line sessions. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
75 Login with vsphere Client Launch vsphere Client Use ESXi IP or FQDN ESXi User name (root) ESXi Password Chatty, but low bandwidth application Runs well over corporate LAN, WAN Can run over Internet Selectable session time out values Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class You manage your ESXi host directly with the vsphere Client. This is a separate download and install available from VMware ( All VMware client to server connections are encrypted using strong encryption. The encrypted link is set up before any data is exchanged between the client and the back end server. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
76 Security Warning All VMware client/server connections use 256-bit AES symmetric key encryption ESXi uses self-signed Digital Certificates No Certificate Granting Authority to verify authenticity Since host is local, ignore warning Check Install this certificate... Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi uses self-signed digital certificates to support end-to-end encryption. All communications between VMware client and VMware server software is encrypted using strong encryption. Since the digital certificate cannot be independently verified by a 3 rd party Certificate Granting Authority, a warning is issued. It is (usually) safe to permanently disregard this warning. It is possible to purchase an SSL certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA) and then install that certificate onto your ESXi host. This would eliminate the warning messages because a trusted can verify the host is who it says it is. Normally trusted certificates are used on Internet facing hosts to ensure the integrity of web requests (e.g.: for secure banking/payment systems, etc.). Since your ESXi hosts won't be directly on the Internet, there is no need (and no benefit) to purchasing a trusted certificate for your machine. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
77 vsphere Client ESXi VSphere Client presents a task launch page Inventory work with your ESXi host Roles define user categories System Logs review, save log files Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
78 vsphere Client Menu,Button Bars Tabbed Interface Items being Managed Recent Actions 4 Sections: Menus, Inventory, Tabs, Recent Tasks Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
79 ESXi Configuration Hardware links to review/set HW settings Software links to review/customize ESXi Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Most ESXi hardware and software configuration is done using the vsphere Client. Use the Configuration tab and the appropriate boxes (Hardware, Software) to review and/or configure your server. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
80 Review/Set Time Configuration Navigation: Software Time Configuration ESXi owns the hardware clock Provides clock services to VMs Use Network Time Protocol to ensure a very accurate clock Not configured by default Use Properties... to enable/configure NTP Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi uses Network Time Protocol to ensure that it's clock remains accurate. This is important because the ESXi host provides clock services to all VMs it runs. So, any clock drift in the ESXi host will result in clock drift in VMs. If VM clocks drift by more than 5 minutes they may not be able to join or remain members of Active Directory domains. Click the Properties... link to review and configure NTP. Best Practice Always set your server's BIOS clock to UTC and ensure you select Server Clock is UTC when you install ESXi. That way, VMs will get a UTC clock and can then set their local time zone to any region they like. If you set the hardware clock to your local time, then VMs must all operate in your local time zone only (because they cannot calculate time zone offsets from any time zone other than UTC). Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
81 Local ESXi Users & Groups Users & Groups Tab Define ESXi users Right click on background, Select Add... Set user login, password and group (optional) Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class You can create local ESXi user accounts with passwords to allow for local authentication (for both the vsphere client and Local/Remote Troubleshooting if enabled). To do this click on the Users & Groups tab and then right-click the back ground and select Add... You can make new groups by clicking the Groups button and then rightclicking the background. Best Practice You would create local accounts only if you do not have an Active Directory service available. Otherwise, it is a best practice to join an AD domain and use domain accounts. Tip To command line log into ESXi over the network (from Windows, ESXi Remote Troubleshooting Mode must be enabled) download the putty Secure Shell terminal emulator at Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
82 Joining a Domain ESXi can join an Active Directory domain Navigation: Software Authentication Services Properties... Specify domain, then domain user/password with rights to add hosts to a domain Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi 4.1 can now join an Active Directory domain. AD authentication allows you to set up access rules for ESXi login without having to create local user accounts on ESXi. FYI Joining an AD domain is the first step to allowing AD defined users to access ESXi directly. The second step is to select inventory items (your ESXi host, folders, VMs, Resource Pools) and assign these users rights on these items. Without specific permission assignments, AD based users will not be able to interact with ESXi. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
83 Licensing ESXi 4.1 License options Evaluation Mode 60-day evaluation Cannot be extended All features available Serial Number 25 character code Get from VMware Enables entitled licensed features Click Edit... to add an ESXi license License entitlements can also be obtained from vcenter Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi now ships with an unrestricted use 60-day evaluation license. This eliminates the need to contact VMware for temporary evaluation licenses. ESXi can be activated using a stand alone host license. A host license is issued on a host by host basis and unlocks access to feature entitlements purchased for that host. Alternatively, ESXi can draw a license entitlement for needed features from vcenter. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
84 Lab 2 Install ESXi 4.1 In this lab we will perform an install of ESXi 4.1 onto a physical PC server Install onto dedicated HP DL365 servers Use RDP to access our kit central server From there, use Remote ILO console to power on and install ESXi Our server pod Is located in a remote Class-A data center Accessed by Microsoft Terminal Services Has one server/student Uses real PC server hardware Not simulation, emulation or PCs running ESXi in a VM Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
85 Sizing ESXi CPU, Memory Physical CPUs service Virtual CPUs About 2-5% CPU virtualization overhead Plan for between 2-8 vcpus per CPU core Maximize CPU cores, speed & cache size Don't expect Intel Hyperthreading to help Only vsphere Advanced, Enterprise + support 8 and 12 core CPUs Memory Must have 2GB RAM to install/boot ESXi VMkernel uses 400+MB of RAM All remaining RAM free for VM use VMs given RAM as needed, not declared x memory over commit is reasonable Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
86 Sizing ESXi Storage, NICs Storage Controllers ESXi is inherently multipath aware 3 rd party multipath solutions now supported Use native or 3 rd party multipathing for Better I/O performance to LUNs, improved reliability NICs Virtual Switches use physical NICs Physical NIC uplinks vswitch to physical LAN segments Virtual NIC traffic consumes CPU cycles Faster ESXi CPUs give faster virtual network speed Benchmark network performance before deploying network heavy production workloads Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
87 System Health Status Click Configuration > Health Status to review host hardware health Uses CIM to poll hardware Reports back issues found Issues propagate up to the host Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The vsphere Client can report on most aspects of your system's hardware health including: - CPU sockets, cores and cache size - Power supply, motherboard, CPU and add on card temperatures - Fan location, health and speed - Hardware firmware and driver health including chipset, NIC, storage controller, BIOS functionality - Power supply count and health (connected, disconnected, missing, etc.) - System boards Use this view to get a quick assessment of your server's physical health. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
88 Physical CPU Properties Click Configuration Processors to review host CPU properties. Verify: CPU socket, core and Hyperthreading status matches expectations Click Properties... to enable Hyperthreading Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi reports on the properties of the CPUs found in your server, including: - The make/model of the machine - Make/model and speed of the CPUs - Number of populated sockets - Number of cores in the CPU - Number of Logical Processors (sockets * cores * HT logical processors) - Presence/Absence of Hyperthreading (Intel CPUs only) - Presence/Absence of power management capabilities (newer CPUs only) If you have Intel CPUs and Hyperthreading is reporting N/A you should check to see if Hyperthreading is active. To do this, click: Properties > Hyperthreading > Enabled This will turn on Hyperthreading support even if the machine's BIOS is set to disable it. You will need to reboot ESXi for this change to take effect. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
89 Physical Memory Properties Click Configuration Memory to review host RAM configuration. Note: System (VMkernel) RAM is reserved All remaining RAM available for VM use Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class ESXi uses memory in 2 ways: 1. For the VMkernel hypervisor (approximately 400MB) 2. For virtual machines (all remaining RAM). ESXi needs a minimum of 2GB of RAM or it will refuse to run. Adding more RAM means more room for VMs to run which should result in good performance as your VM population and RAM requirements grow. ESXi is very frugal and hands out memory to VMs only when needed and only for as long as needed. We will explore ESXi memory scavenging techniques later in this class. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
90 Network Adapters All recognized NICs displayed in the Network Adapters view Speed, Assigned vswitch, physical MAC address and Observed IP ranges reported Observed IP range - helps you determine which sub-net a physical NIC can see and consequently what traffic is should carry Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Observed IP Ranges This value displays the IP address range observed by ESXi as frames flow through each physical NIC. Here's what it's used for. In most corporate networks, different physical LAN segments are used to isolate different types of traffic such as Production traffic, storage traffic, management traffic, back up traffic, etc. It is a common practice to use different sub-net address blocks for each physical segment. For example, your company may subnet it's network traffic as follows: /16 Production traffic including servers /16 Desktop PCs and printers /16 Management LAN segment for direct PC server management /24 Back Up LAN /24 IP Storage LAN (for iscsi servers) In the above scheme, if a physical NIC reported Observed IPs in the 10.1/16 range, you would know it was physically connected to the management LAN. If another physical NIC reported Observed IPs in the /24 range, then it should be used to carry back up traffic. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
91 Network Properties Click Configuration > DNS and Routing to review ESXi Service Console settings: Verify Host, Fully Qualified Domain Name, IP address, DNS IP and Gateway Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Click Properties... to make any changes It is important that your Service Console OS network settings are correct. After installation, it is a good idea to review these settings and fix any errors you find. Click Properties... to edit network settings for the Service Console. You will need to reboot your ESXi host befor these changes take effect. Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
92 Module 2 - Stand Alone ESXi
93 Chapter 12 Resource Pools Resource Management and Resource Pools Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 12 Resource Pools
94 Resource Administration When consolidating onto ESXi, we must ensure that resources are delegated in a predictable manner Resource Pools are containers that compete for ESXi or cluster CPU, memory resources Resource Pools can be used to delegate resources Resource Pool settings can limit the host resources consumed by a pool Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class It is usually more important to allocate scarce resources such as CPU and RAM in a predictable manner than in a fair manner. Fairness usually implies that all VMs get a fair (or equal) access to host resources. While this sounds nice, the reality is that some VMs (e.g.: Production VMs) are likely much more important to us than other VMs (e.g.: test, development, quality assurance and training VMs). Predictable resource allocation implies that you know and have control over how resources are allocated. There are two aspects to predictable resource allocation: If resources are not fully committed (i.e.: there are more physical resources available than all VMs demand) then the VMkernel will ensure that VMs get all the resources (either CPU or memory) that they request and perhaps resources for idling (allocated but unneeded CPU, RAM). If resources are over committed (i.e.: VMs currently demand more memory or CPU cycles than the ESXi host can deliver) then the VMkernel allocates scarce resources to the most important VMs. The VMkernel has a number of strategies it uses to determine who is most important when experiencing resource contention. Some of these strategies are built into the VMkernel and others are under your control. We will explore these in this chapter. Module 12 Resource Pools
95 Project Plan Fine tune VMs and VM containers Create resource containers Ensure important VMs run well under load Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class More important VMs (indicated above by more stars), need preferential resource scheduling priority when a host resource (CPU or Memory) is over committed As an administrator, our job is to ensure that our VMs run in a predictable manner and that our most important VMs continue to provide a minimally acceptable level of service. We can accomplish this task by resource tuning VMs individually or collectively by placing them into a Resource Pool. Module 12 Resource Pools
96 CPU Resource Tunables Default - a VM gets all the CPU it needs If VMware Tools is installed, the VMkernel knows if the VM is idling or if it is doing useful work The VMkernel may not allow a VM to idle if CPU resources are scarce Needed by VMs with work to do VMs will be allowed to accumulate idle time if spare CPU resources are available Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Whenever the VMkernel has more CPU resources than VMs demand, the VMkernel gives all running VMs get all of the CPU cycles they require. On its own, the VMkernel has no way of knowing what the VM guest OS is doing with the CPU cycles it is allocated. If the guest OS wastes these cycles running its idle task (because it has nothing to do) then those cycles accomplish nothing in the VM and are not available for use by VMs that have real work to do. If you install VMware Tools into your VMs (a best practice), then VMware Tools will report back to the VMkernel whenever the guest OS in a VM runs its idle task. By doing this, the VMkernel always knows which VMs truly need CPU service and which VMs would waste CPU by idling. The VMkernel CPU scheduler automatically treats VMs that need to run as high priority VMs and VMs that want to idle as lower priority VMs. In this way, the VMkernel allocates CPU resources to where they are needed. If the VMkernel has more physical CPU resources than are needed to run all non-idling VMs, then the VMkernel CPU scheduler will allow idling VMs to accumulate idle time. Module 12 Resource Pools
97 Physical to Virtual CPU Service Server CPUs run at fixed frequencies vcpus compete with other VMs for service If no CPU contention vcpus gets all the cycles of a core (e.g.: 2.6ghz) With CPU contention vcpus share a core VM gets limited cycles 0Mhz vcpu 2.6Ghz Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Physical CPUs always cycle at full (rated) frequency. However, because (potentially many) VMs compete for a physical CPU resource (socket or core), a VM may not receive a full core of cycles in any given second of time. If the host is over-provisioned with CPU resources, ESXi will allow a VM to use all of the CPU it wants. In this situation, the maximum number of cycles a uni-processor VM can use is the number of cycles a single CPU core can deliver (2.6ghz in the above example). If the host is severely CPU over-committed, then the VMkernel must select which VMs run and which VMs wait. Under severe CPU stress, a low value VM could loose its turn at the CPU. It could receive as few as zero MHZ in a given second in time. It is more likely that a VM will receive at least some cycles each second. How much depends on many factors including: - Has it received it's declared reservation. If not, it will get additional cycles - Has it reached it's user-defined limit? If it has, the VM will get no more cycles - How many CPU shares does the VM holds? VMs with more shares win access to CPU resources more frequently than VMs with fewer shares Module 12 Resource Pools
98 CPU Resource Tunables CPU - a critical machine resource Tunables exist to control VM CPU use Limit max Mhz/sec a CPU can get Default is total mhz available across all of a VMs vcpu(s) Can be lowered to reduce VM claim on CPU Too low and the VM may become non-viable Typically used to Restrict low-value VMs from competing aggressively for CPU Limit CPU on VMs that would just waste it (e.g.: old NT4 apps that burn CPU) Test VMs to see how they would behave under extreme CPU contention Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class When the VMkernel determines that it is time to run a VM, the VMkernel allocates physical CPU resources (usually CPU cores) to the VM equal to the number of Virtual CPUs in the VM). That is, if the VM has 1 vcpu it will run with one core of resources. A dual vcpu VM runs with two CPU cores and a 4 vcpu VM runs with 4 CPU cores. Each vcpu can be no faster than the frequency of the physical CPU core that runs the vcpu. So if you have a physical CPU that runs at 2.6ghz, then a vcpu cannot run any faster than 2.6Ghz. This is the absolute upper limit of CPU cycles that can be allocated to the VM (on a per VCPU basis). If you like, you can lower this limit to a lesser value by setting a CPU limit to some number of MHZ less than the frequency of the physical CPU core. For example, you can set a limit of 1ghz for very low value VMs. If you did this, the VMkernel CPU scheduler would never allocate more than 1ghz of cycles to the VM, even if there were spare CPU resources available. One good example for the use of CPU limits is legacy NT4 applications. Some old NT4 based applications waste CPU by polling the keyboard rather than giving up the CPU when they are idle. If you migrated this workload to a VM, it would try to burn a full physical CPU core (of a modern, high speed CPU, not the 300-1,000mhz that an old Pentium 3 CPU could deliver). By setting a limit, you could control how much CPU this badly behaving application could consume perhaps limiting it to no more cycles than it had when it was physically deployed. Module 12 Resource Pools
99 CPU Resource Tunables Reservation a guaranteed allocation of CPU cycles VM always gets its declared Mhz reservation Provided even if the VM is idling VMs won't power on if reservation can't be met Reservations are aggregate values A dual vcpu VM with a 500 Mhz reservation would get 250 Mhz/vCPU Shares a weighted scheduling value Default is 1,000 CPU shares/vcpu VMs are scheduled in proportion to shares held relative to the total outstanding shares Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class You can also assign CPU reservations. A reservation is a guaranteed allocation of CPU cycles (in mhz) to a VM. This allocation is delivered to the VM every second by the VMkernel CPU scheduler and is provided regardless whether the VM needs the cycles or would waste the cycles running its idle task. An example of a VM that could benefit from a CPU reservation is a busy VM that runs an interactive network application such as Microsoft Terminal Services or Citrix servers. Normally, under CPU load, the interactive VM may lose its CPU to other VMs. If that were to happen, then users working with the VM might experience lag or jerkiness in their interactive sessions. If you assign a CPU reservation, then the VM will hold onto the CPU even if starts to idle. This would allow the interactive VM to appear more responsive (smoother) under load as the VM can respond instantly to any keyboard or mouse events from the client. Reservations are guaranteed commitments of resources. Once you declare a reservation, the VMkernel will honor it, even if it means penalizing other VMs. Excessive use of reservations could lead to artificial contention as the VMkernel is no longer free to pull CPU away from idling VMs and redirect it to busy VMs. Module 12 Resource Pools
100 Dynamic Memory Balancing VMs can use up to their declared RAM Any shortfall is made up through OS paging Windows uses pagefile.sys Linux would page to it's swap partition May happen if you undersize a VM VMware Tools reports active Guest OS RAM VMkernel compares to allocated RAM Can take back any over-allocations. E.g.: 1. VM declares 1GB RAM, but only uses/gets 500MB 2. VM temporarily spikes to 900 MB 3. VMkernel gives the VM 400 MB more RAM 4. After spike, VM has a 400 MB over-allocation 5. VMkernel takes back some/all excess RAM to give to other VMs Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class When a VM boots, the VMs BIOS reports the declared amount of RAM to the VMs guest OS. The guest OS will then treat this declaration as the total physical RAM available to the VM. If the VM needs more RAM than it was provisioned with, the VM will use it's native memory management capabilities (paging). Paging transfers less important memory pages to disk to free up memory for more important pages. The VMkernel allocates RAM to a VM as the VM attempts to use memory, not on boot. So, if a VM boots with a 1GB memory declaration but only loads 500MB of pages into RAM, the VMkernel will only provide the VM with 500MB. In this way, the VMkernel prevents memory waste by allocating RAM to VMs that don't need it. If a VM clearly demonstrates an ongoing need for more RAM than it was given (through persistent guest OS paging), you should increase the declared memory for the VM the next time you can power cycle it (power down, dial up RAM, power on). It is possible that the VM could spike on memory (thereby gaining more RAM from the VMkernel) and then later have the application that needed the memory release it. When this happens, the VM ends up with an over allocation of physical RAM. The VMkernel will learn about this over allocation through VMware tools (who reports unused memory back to the VMkernel) and can steal back any over allocation through the Ballooning memory management technique (more later). Module 12 Resource Pools
101 VM Memory Tunables VM Memory is virtual, not physical VM thinks all declared RAM is present If no memory over commit VM gets all needed RAM With memory over commit Some/all of VM RAM can be stolen via paging Share value determines if VM wins/loses RAM Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class When a VM runs, it believes it has it's full memory allocation (as set in the Edit Settings... > Memory). In reality, the VMkernel assigns the VM physical memory only when the VM attempts to read/write a given page. The VM can never receive more physical RAM that it was assigned (Edit Settings > Memory). And, it will only receive a full allocation if it actually tries to use each and every page. Under memory contention, the VMkernel employs various memory management techniques to ensure that memory is used efficiently. The technique of last resort is VMkernel paging. Under extreme memory stress, the VMkernel will page out some/all of the VM's memory and re-assign that memory to other (more important) VMs. However, the VMkernel will never page out any declared reserved memory or the memory used to hold the VMs virtual hardware. Memory shares are used to determine which VMs hold on to memory and which VMs have their memory paged (which VMs win or loose memory competitions). In a nutshell, the more memory shares held by the VM, the more likely it is to hold on to its memory under memory stress. The standard formula used to calculate memory shares is 10 shares for each MB of RAM declared by the VM. Module 12 Resource Pools
102 Memory Resource Tunables Memory - a critical machine resource Tunables similar to CPU tunables Limit max RAM that a VM can get Any shortfall is made up through OS paging Custom Limit max RAM that can be allocated to a VM Must be less than declared RAM Used to force the VM to live with less than declared RAM Attempts to use more than Custom Limit RAM results in VM paging Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Memory is a critical ESXi resource and the one most likely to become exhausted (although this is changing as memory prices for PC servers continue to fall). Managing ESXi server memory starts with a change in attitude toward memory. In physical PC server deployment, the practice was to over provision the PC server with RAM because physically opening the PC server to add RAM in the future meant acquiring memory, finding a maintenance window and then powering down the server to add memory. Over provisioning is one of the habits we want to break. With VMs, changing the memory allocation is simple. Find a 5 minute maintenance window, shutdown the VM and increase the memory setting. Then, simply power on the VM and it has more RAM. The guest OS will automatically see and use the larger allocation. So, the first best-practice you should adopt to conserve memory is to not over provision your VMs with RAM. If you cannot take a VM down, you can reduce it's memory demands by reducing the Memory Limit assigned to the VM. Normally the memory limit is the amount of RAM assigned. However, you can drop this value, and the VM will be forced to give up any allocation over this new limit. If the VM needs more RAM that this new, lower limit, it will be made up through paging. Module 12 Resource Pools
103 Memory Resource Tunables Reservation a guaranteed memory allocation Once provided, it cannot be stolen Not provided in advance The VM must use the RAM to get its reservation Reservations used to keep VM viable E.g: if excess VMkernel paging would unacceptably reduce performance Shares a weighted scheduling value Default is 10 shares/mb assigned Under memory contention, the VMkernel favors VM with more shares and pages out VMs with fewer shares Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Under memory stress ESXi can page some or all of the VMs memory to disk (a VMkernel swap file allocated to the VM for this possibility). If too much of the VMs memory is paged to disk, the VMs performance will suffer noticeably. If the VMkernel continues to page more and more of the VM to disk, the VMs performance will continue to degrade until the VMs performance becomes unacceptable (or non-existent if 100% of the VM is paged to disk). You use memory reservations to guarantee that high value VMs retain an acceptable minimum allocation of RAM. This helps to ensure that critical VMs maintain a tolerable level of level of performance even during periods of extreme memory starvation. The ESXi memory manager guarantees that a VM always gets its reservation and never receives more than its limit. If memory is scarce, the VMkernel will dynamically shuffle memory between VMs in real time using a number of techniques (transparent page sharing, ballooning and VMkernel swapping). The VMkernel uses Share allocations to decide which VMs retain memory (or receive RAM) and which VMs are forced to give up memory (under stress). By default, a VM receives 10 memory shares for each 1MB of declared RAM. That way VMs with more declared memory are more likely to retain RAM than smaller VMs (if a big VM didn't need the RAM why was it assigned?). Module 12 Resource Pools
104 Shares A weight used for CPU, Memory scheduling Determines relative importance of VM Scenario: Single vcpu VM-A has 1,000 CPU shares All VMs combined have 10,000 CPU shares CPU is over-committed so VMs must compete for CPU service CPU resources available for VM-A: Number of ESX Host Percent of % of a CPU Physical CPU Cores Shares Held Core for VM-A 1 10% % % % % 100 Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The VMkernel uses a weighted scheduling algorithm called Shares to decide how to hand out scarce resources. Shares apply to the delegation of CPU cycles, memory and disk/lun I/O bandwidth. The idea behind share based allocation is very simple. In a nutshell, the more shares you have (relative to other VMs) the proportionally greater service you receive, for that resource, from the VMkernel. Shares are handled as a magnitude or weight and share assignments are always relative to the outstanding total. For example, suppose you had 4 VMs with 1,000 shares each. The total number of outstanding shares is 4,000 and each VM holds ¼ of these shares so under CPU contention, each VM would get 25% of available CPU resources. If a VM were critical, you could increase its share assignment; say to 3,000 shares. Now there is a total of 6,000 outstanding shares, and one VM holds ½ of the total. Consequently, it would receive 50% of all CPU and the remaining three VMs would compete for the remaining half. If two more VMs were to power on with 1,000 CPU shares each, then the total shares would increase to 8,000 and our important VM would hold 3/8 of all shares. The remaining 5 VMs would compete for the remaining 5/8. Module 12 Resource Pools
105 Resource Pools A folder with resource assignments Create on ESXi hosts or clusters Available on standalone ESX, ESXi or vcenter Claims resources from its parent By default, gets all the CPU, RAM that the parent can deliver Subject to custom limits Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class A Resource Pool is an inventory item that is only available under the Hosts and Clusters view. A Resource Pool functions nominally like a folder in that it can contain sub-items including VMs and sub-resource Pools. Unlike a folder, a Resource Pool support CPU and Memory assignments. The Resource Pool draws CPU and Memory resources from its parent host, resource pool, or cluster and then divides whatever it receives amongst its members according to their individual Share, Reservation and Limit settings. In the example above, the Production Resource Pool competes with other Resource Pools at the same level for an allocation of ESXi CPU and RAM from the esx1.esxlab.com ESXi host. Whatever resources it gets are then delegated to the Resource Pool members (the three powered on VMs). Resource Pools act as resource containers and make it easy for ESXi administrators to assign specific resource settings to a Resource Pool as required. Module 12 Resource Pools
106 Resource Pool Settings Resource Pool settings: Shares, Reservations, Limits for CPU, RAM 3 standard Share settings High (8,000) Normal (4,000) Low (2,000) Custom - Set fixed value Virtual hardware gets a guaranteed memory reservation Expandable Reservations Borrow from parent if allowed and needed Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Resource delegations make it easy to sub-divide the resources of your ESXi host or cluster without having to worry about how the Resource Pool owner will use the resources. For example, suppose you have a (internal) customer who, in exchange for budget, requests a guaranteed allocation of 4Ghz of CPU and 4GB of RAM. Here is how you meet this request: - Create a new Resource Pool for the customer - Edit the Resource Pool's properties. Assign a 4Ghz CPU reservation and a 4 GB memory reservation. - If the allocation is strict (e.g. the customer can have 4Ghz/4GB and no more), assign a Limit of 4Ghz CPU and 4GB of RAM - Assign the customer the role of Resource Pool Administrator (see the Permissions chapter on how to do this) Now, the customer 'owns' their own Resource Pool. The can create one VM or many VMs in their Resource Pool. They can set individual VM resource assignments (Reservations, Shares, Limits) for both CPU and Memory. Because of the Resource Pool reservations, the customer receives a guaranteed allocation of CPU and RAM. If you set Limits, the customer also is constrained with a hard cap on the amount of resources their VMs can collectively consume. Module 12 Resource Pools
107 Expandable Reservations Reservations guaranteed commitment of CPU or Memory resources VM cannot power on if it's reservation cannot be met Expandable reservations let a resource pool 'borrow' resources if it cannot meet a reservation request itself If a resource pools' CPU or RAM reservation is fully delegated, any short fall is requested from the parent If parent has free resources, and Expandable Reservations set, the resource pool get it Cannot be forced to give it back! Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class One option available to VMs and Resource Pools is Expandable Reservations... A Reservation is a guaranteed allocation of resources. That is, once a VM or Resource Pool claims a Reservation, there is no way (other than de-tuning the VM or RP, or powering off the VM) to reclaim the resource. ESXi will to honor all Reservation requests. On VM boot, if ESXi cannot meet a VM reservation request, then that VM will not be allowed to power on. This could happen if (for example) a Resource Pool had a total declared reservation of 2GB and this reservation was fully allocated to other powered on VM (in the RP). Any attempt to power on a new VM that wanted its own memory reservation, would fail. Normally the RP Administrator would have to reduce the reservation settings of other VMs to free up memory for the VM to boot. Another alternative is to use Expandable Reservations. Expandable Reservations give a VM or sub-rp permission to borrow resources directly from the parent Resource Pool's parent an ESXi host or cluster rather than from just the Resource Pool itself. The good news with Expandable Reservations is that the VM can get is reservation and boot. The bad news is that there is no way to force a VM to give back any expandable reservation it has acquired. Also, once Expandable Reservations are enabled, there is no way to cap how much resources a RP borrows from it's parent's parent. USE EXPANDABLE RESERVATIONS WITH CAUTION! Module 12 Resource Pools
108 Why use Resource Pools Delegate resources from host or cluster to a pool or sub-pool Resource Pool settings control delegation to VMs and sub-pools in the pool Resource pools can have permission assignments Resource Pool example: We have a resource SLA with a user User must gets resources as per their SLA Solution Create resource pool Give user Resource Pool Admin rights Adjust settings to deliver resources within agreed range (e.g.: Reservation: 2ghz, Limit: 4ghz) Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class As previously discussed, Resource Pools are a great way to meet any resource commitments you have with your user community. They allow ESXi administrators to delegate a fraction of host CPU/Memory without having to worry about how those resources will be used. If the customer powers on too many VMs or if the VMs attempt to use more resources than their Resource Pool has, then the customer's VMs will exhibit poor performance even though the ESXi host may have uncommitted resources. If the customer wishes to increase their resource allocation, then they would need to negotiate a higher resource delegation, presumably in exchange for more budget or other consideration. Module 12 Resource Pools
109 Auto-Update Resource Pools Scheduled Tasks can update RP settings Use to adjust RP settings at some future date/time View > Management > Scheduled Tasks Right click > New Scheduled Task Complete wizard Set CPU properties Set Memory properties Set date/time to change Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class vcenter has a Scheduled Tasks feature that lets you complete a wizard (to perform some function) and then set a future time/date for that wizard to run. New to ESXi 4/vCenter 4 is the ability to schedule resource changes to VMs and Resource Pools. To invoke this function, please do the following from the vsphere Client: - Click View > Management > Scheduled Tasks - On the background click New Scheduled Task - Select Change Resource Settings from a Resource Pool or Virtual Machine - Give the task a name (so you can use it again) - Set the task frequency (it can auto-repeat) - Set the tasks date/time to run - Optionally send a notification when the task completes - Complete the wizard making the resource changes you require Module 12 Resource Pools
110 CPU Resource Allocations You can review CPU settings via the Resource Allocation tab, CPU button The selected ESXi host has 2 Resource pools with High, Normal shares 8000 and 4000 CPU shares respectively Under contention, Production VMs get 66% of available CPU, Web Servers get 33% Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The Resource Allocation tab gives you a tabular view of the resource settings and allocations for your VMs and Resource pools under a datacenter, folder, cluster or host. In this tab, you can easily see how the resources of an inventory object are allocated to VMs and Resource Pools. You can also edit some settings (Reservations, Limits, Shares) directly in this view by simply placing your mouse over the item you'd like to change, clicking it to invoke a drop down or an edit box and then making the necessary adjustments. Module 12 Resource Pools
111 Memory Resource Allocations Review Memory settings via the Resource Allocation tab, Memory button The selected ESXi host has 2 resource pools with High, Normal shares Share Value and % Shares not displayed Note Memory > Reserved Capacity This is RAM needed to run VM virtual hardware Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Click the Memory button to see details of Resource Pool and VM memory resource allocations. Note that resource pools set to Normal shares get substantially more shares than VMs that are also set to Normal share allocations. Again, you can edit key fields simply by clicking on the Reservations, Shares or Limits values for a VM or Resource Pool. Module 12 Resource Pools
112 Storage Resource Allocations Review Storage settings via the Resource Allocation tab, Storage button VMs on the selected ESXi host have High, Normal and Low storage shares Get 57%, 28% and 14% of I/O bandwidth respectively Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 12 Resource Pools
113 Virtual Hardware Resources VM virtual hardware consumes memory RAM used for virtual hardware visible here Reserved RAM use grows as you add more virtual H/W components vcpus, NICs, Disks, SCSI HBAs RAM use ranges from 100MB to 900+MB Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class VMware virtual machines run on top of virtual hardware. Virtual hardware is software that behaves, to the Guest OS, like and is indistinguishable from physical hardware. ESXi uses memory to hold the data structures that make up virtual hardware. A VM with one vcpu, one NIC, one SCSI HBA and one virtual SCSI disk consumes about 100MB of RAM (depending on virtual hardware version in use). As you add more hardware, the amount of memory consumed to support the VM's virtual hardware grows. In the extreme case, a VM with 4 vcpus, 4 NICs, multiple virtual SCSI HBAs and many virtual SCSI disks may consume 900+MB of RAM before any physical memory is allocated for virtual machine operating system and program use. Memory allocated for VM virtual hardware is never paged out to disk and so is best viewed as an implied memory reservation over and above any reservations set for the VM. So, to ensure the most efficient memory use possible; don't oversize a VM's virtual hardware. Module 12 Resource Pools
114 Resource Pool Summary Tab RP Summary tab displays RP properties Collective CPU and Memory reported Resource Settings Reservation is total VM h/w reservation + VM declared reservations Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class The Resource Pool Summary tab contains useful information on the resource settings and resource consumption of your pool. You should periodically review the resource settings of all of your resource pools individually, and then collectively, to ensure that resources continue to be allocated in a way that makes sense for your system. Module 12 Resource Pools
115 Lab 12 To complete this lab, you will Create a resource pool Place VMs in the Pool Generate a CPU load in a VM Use Resource Pool settings to limit VM performance Get Certified now. Sit the ESXLab Certified Virtualization Specialist exam at the end of your class Module 12 Resource Pools
116 Module 12 Resource Pools
VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter
 Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 4.1, VMware
Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 4.1 with ESXi and vcenter A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 4.1, VMware
By the end of the class, attendees will have learned the skills, and best practices of virtualization. Attendees
 Course Name Format Course Books 5-day instructor led training 735 pg Study Guide fully annotated with slide notes 244 pg Lab Guide with detailed steps for completing all labs vsphere Version Covers uses
Course Name Format Course Books 5-day instructor led training 735 pg Study Guide fully annotated with slide notes 244 pg Lab Guide with detailed steps for completing all labs vsphere Version Covers uses
VMware vsphere 5.0 with ESXi and vcenter
 Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 5.0 with ESXi and vcenter A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 5.0, VMware
Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 5.0 with ESXi and vcenter A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 5.0, VMware
VMware vsphere 6.5 Boot Camp
 Course Name Format Course Books 5-day, 10 hour/day instructor led training 724 pg Study Guide fully annotated with slide notes 243 pg Lab Guide with detailed steps for completing all labs 145 pg Boot Camp
Course Name Format Course Books 5-day, 10 hour/day instructor led training 724 pg Study Guide fully annotated with slide notes 243 pg Lab Guide with detailed steps for completing all labs 145 pg Boot Camp
VMware vsphere 5 with ESXi and vcenter - Boot Camp
 Boot Camp VMware vsphere 5 with ESXi and vcenter - Boot Camp A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 5, VMware
Boot Camp VMware vsphere 5 with ESXi and vcenter - Boot Camp A step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with VMware ESXi 5, VMware
VMware vsphere with ESX 4 and vcenter
 VMware vsphere with ESX 4 and vcenter This class is a 5-day intense introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular vsphere suite including VMware ESX 4 and vcenter. Assuming no prior virtualization
VMware vsphere with ESX 4 and vcenter This class is a 5-day intense introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular vsphere suite including VMware ESX 4 and vcenter. Assuming no prior virtualization
VMware vsphere with ESX 4.1 and vcenter 4.1
 QWERTYUIOP{ Overview VMware vsphere with ESX 4.1 and vcenter 4.1 This powerful 5-day class is an intense introduction to virtualization using VMware s vsphere 4.1 including VMware ESX 4.1 and vcenter.
QWERTYUIOP{ Overview VMware vsphere with ESX 4.1 and vcenter 4.1 This powerful 5-day class is an intense introduction to virtualization using VMware s vsphere 4.1 including VMware ESX 4.1 and vcenter.
VMware vsphere 5.5 Advanced Administration
 Format 4-day instructor led training Course Books 630+ pg Study Guide with slide notes 180+ pg Lab Guide with detailed steps for completing labs vsphere Version This class covers VMware vsphere 5.5 including
Format 4-day instructor led training Course Books 630+ pg Study Guide with slide notes 180+ pg Lab Guide with detailed steps for completing labs vsphere Version This class covers VMware vsphere 5.5 including
Virtualization with VMware ESX and VirtualCenter SMB to Enterprise
 Virtualization with VMware ESX and VirtualCenter SMB to Enterprise This class is an intense, five-day introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular Virtual Infrastructure suite including
Virtualization with VMware ESX and VirtualCenter SMB to Enterprise This class is an intense, five-day introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular Virtual Infrastructure suite including
VMware vsphere with ESX 6 and vcenter 6
 VMware vsphere with ESX 6 and vcenter 6 Course VM-06 5 Days Instructor-led, Hands-on Course Description This class is a 5-day intense introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular vsphere
VMware vsphere with ESX 6 and vcenter 6 Course VM-06 5 Days Instructor-led, Hands-on Course Description This class is a 5-day intense introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular vsphere
"Charting the Course... VMware vsphere 6.7 Boot Camp. Course Summary
 Description Course Summary This powerful 5-day, 10 hour per day extended hours class is an intensive introduction to VMware vsphere including VMware ESXi 6.7 and vcenter 6.7. This course has been completely
Description Course Summary This powerful 5-day, 10 hour per day extended hours class is an intensive introduction to VMware vsphere including VMware ESXi 6.7 and vcenter 6.7. This course has been completely
Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional (CVP) VMware vsphere 6.0 Level 2 Exam CVP2-110
 Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional (CVP) VMware vsphere 6.0 Level 2 Exam CVP2-110 Exam Information Candidate Eligibility: The Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional
Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional (CVP) VMware vsphere 6.0 Level 2 Exam CVP2-110 Exam Information Candidate Eligibility: The Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional
Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional (CVP) VMware vsphere 6.0 Level 1 Exam CVP1-110
 Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional (CVP) VMware vsphere 6.0 Level 1 Exam CVP1-110 Exam Information Candidate Eligibility: The Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional
Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional (CVP) VMware vsphere 6.0 Level 1 Exam CVP1-110 Exam Information Candidate Eligibility: The Logical Operations Certified Virtualization Professional
Overview. Prerequisites. VMware vsphere 6.5 Optimize, Upgrade, Troubleshoot
 VMware vsphere 6.5 Optimize, Upgrade, Troubleshoot Course Name Format Course Books vsphere Version Delivery Options Remote Labs Max Attendees Requirements Lab Time Availability May, 2017 Suggested Price
VMware vsphere 6.5 Optimize, Upgrade, Troubleshoot Course Name Format Course Books vsphere Version Delivery Options Remote Labs Max Attendees Requirements Lab Time Availability May, 2017 Suggested Price
Virtualization with VMware ESX and VirtualCenter SMB to Enterprise
 Virtualization with VMware ESX and VirtualCenter SMB to Enterprise This class is an intense, four-day introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular Virtual Infrastructure suite including
Virtualization with VMware ESX and VirtualCenter SMB to Enterprise This class is an intense, four-day introduction to virtualization using VMware s immensely popular Virtual Infrastructure suite including
VMware Join the Virtual Revolution! Brian McNeil VMware National Partner Business Manager
 VMware Join the Virtual Revolution! Brian McNeil VMware National Partner Business Manager 1 VMware By the Numbers Year Founded Employees R&D Engineers with Advanced Degrees Technology Partners Channel
VMware Join the Virtual Revolution! Brian McNeil VMware National Partner Business Manager 1 VMware By the Numbers Year Founded Employees R&D Engineers with Advanced Degrees Technology Partners Channel
EVALUATION COPY. VMware vsphere 5.5 with ESXi and vcenter Boot Camp. Unauthorized reproduction or distribution is prohibited. Study Guide.
 Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 5.5 with ESXi and vcenter Boot Camp A in depth, step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with
Study Guide 5 Day VMware vsphere 5.5 with ESXi and vcenter Boot Camp A in depth, step by step approach to successful virtualization planning, deployment and administration. Featuring VMware vsphere with
VMware Overview VMware Infrastructure 3: Install and Configure Rev C Copyright 2007 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved.
 VMware Overview Kontakt: jens.soeldner@netlogix.de 1-1 You Are Here Virtual Infrastructure VMware Overview ESX Server Installation ESX Server Installation Networking Networking Storage Storage ESX Server
VMware Overview Kontakt: jens.soeldner@netlogix.de 1-1 You Are Here Virtual Infrastructure VMware Overview ESX Server Installation ESX Server Installation Networking Networking Storage Storage ESX Server
"Charting the Course... VMware vsphere 6.5 Optimize, Upgrade, Troubleshoot. Course Summary
 Course Summary Description This powerful 5-day class provides an in-depth look at vsphere 6.5. In this course, cover how to deploy vsphere 6.5, how to optimize it including VMs, ESXi hosts, vcenter Server
Course Summary Description This powerful 5-day class provides an in-depth look at vsphere 6.5. In this course, cover how to deploy vsphere 6.5, how to optimize it including VMs, ESXi hosts, vcenter Server
VMware vsphere Administration Training. Course Content
 VMware vsphere Administration Training Course Content Course Duration : 20 Days Class Duration : 3 hours per day (Including LAB Practical) Fast Track Course Duration : 10 Days Class Duration : 8 hours
VMware vsphere Administration Training Course Content Course Duration : 20 Days Class Duration : 3 hours per day (Including LAB Practical) Fast Track Course Duration : 10 Days Class Duration : 8 hours
VI3 to vsphere 4.0 Upgrade and New Technology Ultimate Bootcamp
 VI3 to vsphere 4.0 Upgrade and New Technology Ultimate Bootcamp Course Length: 2 Days Course Overview This instructor-led course covers everything the student needs to know to upgrade from VMware 3.x to
VI3 to vsphere 4.0 Upgrade and New Technology Ultimate Bootcamp Course Length: 2 Days Course Overview This instructor-led course covers everything the student needs to know to upgrade from VMware 3.x to
VMware vsphere: Taking Virtualization to the Next Level
 About this research note: Product Evaluation notes provide an analysis of the market position of a specific product and its vendor through an in-depth exploration of their relative capabilities. VMware
About this research note: Product Evaluation notes provide an analysis of the market position of a specific product and its vendor through an in-depth exploration of their relative capabilities. VMware
Microsoft E xchange 2010 on VMware
 : Microsoft E xchange 2010 on VMware Availability and R ecovery Options This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws. This product is covered by one or more
: Microsoft E xchange 2010 on VMware Availability and R ecovery Options This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws. This product is covered by one or more
VMware vsphere 5.5 Professional Bootcamp
 VMware vsphere 5.5 Professional Bootcamp Course Overview Course Objectives Cont. VMware vsphere 5.5 Professional Bootcamp is our most popular proprietary 5 Day course with more hands-on labs (100+) and
VMware vsphere 5.5 Professional Bootcamp Course Overview Course Objectives Cont. VMware vsphere 5.5 Professional Bootcamp is our most popular proprietary 5 Day course with more hands-on labs (100+) and
Red Hat enterprise virtualization 3.1 feature comparison
 Red Hat enterprise virtualization 3.1 feature comparison at a glance Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization 3.1 is first fully open source, enterprise ready virtualization platform Compare functionality of
Red Hat enterprise virtualization 3.1 feature comparison at a glance Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization 3.1 is first fully open source, enterprise ready virtualization platform Compare functionality of
A Dell Technical White Paper Dell Virtualization Solutions Engineering
 Dell vstart 0v and vstart 0v Solution Overview A Dell Technical White Paper Dell Virtualization Solutions Engineering vstart 0v and vstart 0v Solution Overview THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES
Dell vstart 0v and vstart 0v Solution Overview A Dell Technical White Paper Dell Virtualization Solutions Engineering vstart 0v and vstart 0v Solution Overview THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES
Installing VMware vsphere 5.1 Components
 Installing VMware vsphere 5.1 Components Module 14 You Are Here Course Introduction Introduction to Virtualization Creating Virtual Machines VMware vcenter Server Configuring and Managing Virtual Networks
Installing VMware vsphere 5.1 Components Module 14 You Are Here Course Introduction Introduction to Virtualization Creating Virtual Machines VMware vcenter Server Configuring and Managing Virtual Networks
WHITE PAPER SEPTEMBER VMWARE vsphere AND vsphere WITH OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT. Licensing, Pricing and Packaging
 WHITE PAPER SEPTEMBER 2017 VMWARE vsphere AND vsphere WITH OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Licensing, Pricing and Packaging Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 VMware vsphere with Operations Management Overview
WHITE PAPER SEPTEMBER 2017 VMWARE vsphere AND vsphere WITH OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Licensing, Pricing and Packaging Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 VMware vsphere with Operations Management Overview
Administering VMware vsphere and vcenter 5
 Administering VMware vsphere and vcenter 5 Course VM-05 5 Days Instructor-led, Hands-on Course Description This 5-day class will teach you how to master your VMware virtual environment. From installation,
Administering VMware vsphere and vcenter 5 Course VM-05 5 Days Instructor-led, Hands-on Course Description This 5-day class will teach you how to master your VMware virtual environment. From installation,
PassTest. Bessere Qualität, bessere Dienstleistungen!
 PassTest Bessere Qualität, bessere Dienstleistungen! Q&A Exam : VCP-510 Title : VMware Certified Professional on VSphere 5 Version : Demo 1 / 7 1.Which VMware solution uses the security of a vsphere implementation
PassTest Bessere Qualität, bessere Dienstleistungen! Q&A Exam : VCP-510 Title : VMware Certified Professional on VSphere 5 Version : Demo 1 / 7 1.Which VMware solution uses the security of a vsphere implementation
Red Hat enterprise virtualization 3.0
 Red Hat enterprise virtualization 3.0 feature comparison at a glance Red Hat Enterprise is the first fully open source, enterprise ready virtualization platform Compare the functionality of RHEV to VMware
Red Hat enterprise virtualization 3.0 feature comparison at a glance Red Hat Enterprise is the first fully open source, enterprise ready virtualization platform Compare the functionality of RHEV to VMware
vsphere Installation and Setup Update 2 Modified on 10 JULY 2018 VMware vsphere 6.5 VMware ESXi 6.5 vcenter Server 6.5
 vsphere Installation and Setup Update 2 Modified on 10 JULY 2018 VMware vsphere 6.5 VMware ESXi 6.5 vcenter Server 6.5 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware website at:
vsphere Installation and Setup Update 2 Modified on 10 JULY 2018 VMware vsphere 6.5 VMware ESXi 6.5 vcenter Server 6.5 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware website at:
Directions in Data Centre Virtualization and Management
 Directions in Data Centre Virtualization and Management Peter West Product Marketing Manager, Product Marketing EMEA, VMware, Inc. New Approach To Data Centre Scalability Simplify the containers Add Hardware
Directions in Data Centre Virtualization and Management Peter West Product Marketing Manager, Product Marketing EMEA, VMware, Inc. New Approach To Data Centre Scalability Simplify the containers Add Hardware
VMware vsphere 6.0 / 6.5 Infrastructure Deployment Boot Camp
 Title: Summary: Length: Overview: VMware vsphere 6.0 / 6.5 Infrastructure Deployment Boot Camp Class formats available: Live In-Classroom Training (LICT) Mixed class with Classroom and Online Instruction
Title: Summary: Length: Overview: VMware vsphere 6.0 / 6.5 Infrastructure Deployment Boot Camp Class formats available: Live In-Classroom Training (LICT) Mixed class with Classroom and Online Instruction
Exploring Options for Virtualized Disaster Recovery
 Exploring Options for Virtualized Disaster Recovery Ong, Kok Leong Senior Systems Consultant, VMware ASEAN Email: klong@vmware.com Mobile: +60-12-4706070 16 th October 2008 Recovery Time Objective Building
Exploring Options for Virtualized Disaster Recovery Ong, Kok Leong Senior Systems Consultant, VMware ASEAN Email: klong@vmware.com Mobile: +60-12-4706070 16 th October 2008 Recovery Time Objective Building
Introduction to Virtualization. From NDG In partnership with VMware IT Academy
 Introduction to Virtualization From NDG In partnership with VMware IT Academy www.vmware.com/go/academy Why learn virtualization? Modern computing is more efficient due to virtualization Virtualization
Introduction to Virtualization From NDG In partnership with VMware IT Academy www.vmware.com/go/academy Why learn virtualization? Modern computing is more efficient due to virtualization Virtualization
VMware vsphere Storage Appliance Installation and Configuration
 VMware vsphere Storage Appliance Installation and Configuration vsphere Storage Appliance 1.0 vsphere 5.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions
VMware vsphere Storage Appliance Installation and Configuration vsphere Storage Appliance 1.0 vsphere 5.0 This document supports the version of each product listed and supports all subsequent versions
VMware vsphere 4. The Best Platform for Building Cloud Infrastructures
 Table of Contents Get the efficiency and low cost of cloud computing with uncompromising control over service levels and with the freedom of choice................ 3 Key Benefits........................................................
Table of Contents Get the efficiency and low cost of cloud computing with uncompromising control over service levels and with the freedom of choice................ 3 Key Benefits........................................................
Cisco HyperFlex Hyperconverged Infrastructure Solution for SAP HANA
 Cisco HyperFlex Hyperconverged Infrastructure Solution for SAP HANA Learn best practices for running SAP HANA on the Cisco HyperFlex hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) solution. 2018 Cisco and/or its
Cisco HyperFlex Hyperconverged Infrastructure Solution for SAP HANA Learn best practices for running SAP HANA on the Cisco HyperFlex hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) solution. 2018 Cisco and/or its
Managing VMware ESXi in the Datacenter. Dwarakanath P Rao Sr Partner consultant 6 th November 2008
 Managing VMware ESXi in the Datacenter Dwarakanath P Rao Sr Partner consultant 6 th November 2008 Agenda VMware ESXi Overview ESXi Getting Started Case Studies VMware ESXi Overview Next What generation
Managing VMware ESXi in the Datacenter Dwarakanath P Rao Sr Partner consultant 6 th November 2008 Agenda VMware ESXi Overview ESXi Getting Started Case Studies VMware ESXi Overview Next What generation
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introducing VMware Infrastructure 3. Chapter 1
 Mccain c01.tex V3-04/16/2008 5:22am Page 1 Chapter 1 Introducing VMware Infrastructure 3 VMware Infrastructure 3 (VI3) is the most widely used virtualization platform available today. The lineup of products
Mccain c01.tex V3-04/16/2008 5:22am Page 1 Chapter 1 Introducing VMware Infrastructure 3 VMware Infrastructure 3 (VI3) is the most widely used virtualization platform available today. The lineup of products
ATTACHMENT A SCOPE OF WORK IMPLEMENTATION SERVICES. Cisco Server and NetApp Storage Implementation
 ATTACHMENT A SCOPE OF WORK IMPLEMENTATION SERVICES I. Executive Summary Superior Court of California, County of Orange (Court) is in the process of conducting a large enterprise hardware refresh. This
ATTACHMENT A SCOPE OF WORK IMPLEMENTATION SERVICES I. Executive Summary Superior Court of California, County of Orange (Court) is in the process of conducting a large enterprise hardware refresh. This
VMware vsphere 4.0 The best platform for building cloud infrastructures
 VMware vsphere 4.0 The best platform for building cloud infrastructures VMware Intelligence Community Team Rob Amos - Intelligence Programs Manager ramos@vmware.com (703) 209-6480 Harold Hinson - Intelligence
VMware vsphere 4.0 The best platform for building cloud infrastructures VMware Intelligence Community Team Rob Amos - Intelligence Programs Manager ramos@vmware.com (703) 209-6480 Harold Hinson - Intelligence
V.I.B.E. Virtual. Integrated. Blade. Environment. Harveenpal Singh. System-x PLM
 V.I.B.E. Virtual. Integrated. Blade. Environment. Harveenpal Singh System-x PLM x86 servers are taking on more demanding roles, including high-end business critical applications x86 server segment is the
V.I.B.E. Virtual. Integrated. Blade. Environment. Harveenpal Singh System-x PLM x86 servers are taking on more demanding roles, including high-end business critical applications x86 server segment is the
How it can help your organisation
 How it can help your organisation History Types of Virtualisation & Hypervisors Virtualisation Features Why Virtualisation? Virtualising Oracle Performance Licensing Support Cloud 1998 VMware founded by
How it can help your organisation History Types of Virtualisation & Hypervisors Virtualisation Features Why Virtualisation? Virtualising Oracle Performance Licensing Support Cloud 1998 VMware founded by
The vsphere 6.0 Advantages Over Hyper- V
 The Advantages Over Hyper- V The most trusted and complete virtualization platform SDDC Competitive Marketing 2015 Q2 VMware.com/go/PartnerCompete 2015 VMware Inc. All rights reserved. v3b The Most Trusted
The Advantages Over Hyper- V The most trusted and complete virtualization platform SDDC Competitive Marketing 2015 Q2 VMware.com/go/PartnerCompete 2015 VMware Inc. All rights reserved. v3b The Most Trusted
VMware vstorage APIs FOR ARRAY INTEGRATION WITH EMC VNX SERIES FOR SAN
 White Paper VMware vstorage APIs FOR ARRAY INTEGRATION WITH EMC VNX SERIES FOR SAN Benefits of EMC VNX for Block Integration with VMware VAAI EMC SOLUTIONS GROUP Abstract This white paper highlights the
White Paper VMware vstorage APIs FOR ARRAY INTEGRATION WITH EMC VNX SERIES FOR SAN Benefits of EMC VNX for Block Integration with VMware VAAI EMC SOLUTIONS GROUP Abstract This white paper highlights the
Potpuna virtualizacija od servera do desktopa. Saša Hederić Senior Systems Engineer VMware Inc.
 Potpuna virtualizacija od servera do desktopa Saša Hederić Senior Systems Engineer VMware Inc. VMware ESX: Even More Reliable than a Mainframe! 2 The Problem Where the IT Budget Goes 5% Infrastructure
Potpuna virtualizacija od servera do desktopa Saša Hederić Senior Systems Engineer VMware Inc. VMware ESX: Even More Reliable than a Mainframe! 2 The Problem Where the IT Budget Goes 5% Infrastructure
VMware vsphere 6.0 / 6.5 Advanced Infrastructure Deployment (AID)
 Title: Summary: Length: Overview: VMware vsphere 6.0 / 6.5 Advanced Infrastructure Deployment (AID) Class formats available: Online Learning (OLL) Live In-Classroom Training (LICT) Mixed class with Classroom
Title: Summary: Length: Overview: VMware vsphere 6.0 / 6.5 Advanced Infrastructure Deployment (AID) Class formats available: Online Learning (OLL) Live In-Classroom Training (LICT) Mixed class with Classroom
EXAM - VCP5-DCV. VMware Certified Professional 5 Data Center Virtualization (VCP5-DCV) Exam. Buy Full Product.
 VMware EXAM - VCP5-DCV VMware Certified Professional 5 Data Center Virtualization (VCP5-DCV) Exam Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/vcp5-dcv.html Examskey VMware VCP5-DCV exam demo product is here
VMware EXAM - VCP5-DCV VMware Certified Professional 5 Data Center Virtualization (VCP5-DCV) Exam Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/vcp5-dcv.html Examskey VMware VCP5-DCV exam demo product is here
Availability & Resource
 Achieving Cost-effective High Availability & Resource Management Agenda Virtual Infrastructure Stack How Vmware helps in the Data Center Availability and Resource Management 2 The VMware Virtual Infrastructure
Achieving Cost-effective High Availability & Resource Management Agenda Virtual Infrastructure Stack How Vmware helps in the Data Center Availability and Resource Management 2 The VMware Virtual Infrastructure
VMware Exam VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 Version: 11.3 [ Total Questions: 288 ]
![VMware Exam VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 Version: 11.3 [ Total Questions: 288 ] VMware Exam VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 Version: 11.3 [ Total Questions: 288 ]](/thumbs/91/107356849.jpg) s@lm@n VMware Exam VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 Version: 11.3 [ Total Questions: 288 ] VMware VCP-511 : Practice Test Question No : 1 Click the Exhibit button. An administrator has
s@lm@n VMware Exam VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 Version: 11.3 [ Total Questions: 288 ] VMware VCP-511 : Practice Test Question No : 1 Click the Exhibit button. An administrator has
VCP410 VMware vsphere Cue Cards
 VMware ESX 4.0 will only install and run on servers with 64-bit x86 CPUs. ESX 4.0 Requires 2GB RAM minimum ESX 4.0 requires 1 or more network adapters ESX 4.0 requires a SCSI disk, Fibre Channel LUN, or
VMware ESX 4.0 will only install and run on servers with 64-bit x86 CPUs. ESX 4.0 Requires 2GB RAM minimum ESX 4.0 requires 1 or more network adapters ESX 4.0 requires a SCSI disk, Fibre Channel LUN, or
VMware Virtual SAN. Technical Walkthrough. Massimiliano Moschini Brand Specialist VCI - vexpert VMware Inc. All rights reserved.
 VMware Virtual SAN Technical Walkthrough Massimiliano Moschini Brand Specialist VCI - vexpert 2014 VMware Inc. All rights reserved. VMware Storage Innovations VI 3.x VMFS Snapshots Storage vmotion NAS
VMware Virtual SAN Technical Walkthrough Massimiliano Moschini Brand Specialist VCI - vexpert 2014 VMware Inc. All rights reserved. VMware Storage Innovations VI 3.x VMFS Snapshots Storage vmotion NAS
Using EonStor DS Series iscsi-host storage systems with VMware vsphere 5.x
 Using EonStor DS Series iscsi-host storage systems with VMware vsphere 5.x Application notes Abstract These application notes explain configuration details for using Infortrend EonStor DS Series iscsi-host
Using EonStor DS Series iscsi-host storage systems with VMware vsphere 5.x Application notes Abstract These application notes explain configuration details for using Infortrend EonStor DS Series iscsi-host
Virtualizing Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 with NetApp and VMware
 Virtualizing Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 with NetApp and VMware Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 in a virtualized environment that leverages VMware virtualization and NetApp unified storage
Virtualizing Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 with NetApp and VMware Deploying Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 in a virtualized environment that leverages VMware virtualization and NetApp unified storage
VMware Infrastructure Update 1 for Dell PowerEdge Systems. Deployment Guide. support.dell.com
 VMware Infrastructure 3.0.2 Update 1 for Dell PowerEdge Systems Deployment Guide www.dell.com support.dell.com Notes and Notices NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better
VMware Infrastructure 3.0.2 Update 1 for Dell PowerEdge Systems Deployment Guide www.dell.com support.dell.com Notes and Notices NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better
Exploring Options for Virtualized Disaster Recovery. Ranganath GK Solution Architect 6 th Nov 2008
 Exploring Options for Virtualized Disaster Recovery Ranganath GK Solution Architect 6 th Nov 2008 Defining Disaster Recovery What is a disaster? Extended outage that requires an organization to recover
Exploring Options for Virtualized Disaster Recovery Ranganath GK Solution Architect 6 th Nov 2008 Defining Disaster Recovery What is a disaster? Extended outage that requires an organization to recover
VMware vsphere 4. Architecture VMware Inc. All rights reserved
 VMware vsphere 4 Architecture 2010 VMware Inc. All rights reserved VMware vsphere Architecture vsphere Client vcenter Converter plug-in Update Manager plug-in vcenter Database vcenter Server vcenter Linked
VMware vsphere 4 Architecture 2010 VMware Inc. All rights reserved VMware vsphere Architecture vsphere Client vcenter Converter plug-in Update Manager plug-in vcenter Database vcenter Server vcenter Linked
Exam Name: VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 (Private Beta)
 Vendor: VMware Exam Code: VCP-511 Exam Name: VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 (Private Beta) Version: DEMO QUESTION 1 The VMware vcenter Server Appliance has been deployed using default settings.
Vendor: VMware Exam Code: VCP-511 Exam Name: VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 (Private Beta) Version: DEMO QUESTION 1 The VMware vcenter Server Appliance has been deployed using default settings.
AB Drives. T4 - Process Control: Virtualization for Manufacturing. Insert Photo Here Anthony Baker. PlantPAx Characterization & Lab Manager
 T4 - Process Control: Virtualization for Manufacturing Insert Photo Here Anthony Baker PlantPAx Characterization & Lab Manager Rockwell Automation Rockwell Automation Process Solutions User Group (PSUG)
T4 - Process Control: Virtualization for Manufacturing Insert Photo Here Anthony Baker PlantPAx Characterization & Lab Manager Rockwell Automation Rockwell Automation Process Solutions User Group (PSUG)
Adobe Acrobat Connect Pro 7.5 and VMware ESX Server
 White Paper Table of contents 2 Tested environments 3 Benchmarking tests 3 Performance comparisons 7 Installation requirements 7 Installing and configuring the VMware environment 1 Supported virtual machine
White Paper Table of contents 2 Tested environments 3 Benchmarking tests 3 Performance comparisons 7 Installation requirements 7 Installing and configuring the VMware environment 1 Supported virtual machine
VMware vsphere Customized Corporate Agenda
 VMware vsphere Customized Corporate Agenda It's not just VMware Install, Manage, Configure (Usual VCP Course). For working professionals, just VCP is not enough, below is the custom agenda. At the outset,
VMware vsphere Customized Corporate Agenda It's not just VMware Install, Manage, Configure (Usual VCP Course). For working professionals, just VCP is not enough, below is the custom agenda. At the outset,
Vmware VCP-310. VMware Certified Professional on VI3.
 Vmware VCP-310 VMware Certified Professional on VI3 http://killexams.com/exam-detail/vcp-310 D. Only one VLAN can be specified in a port group. Answer: B, D Question: 423 What is a characteristic of a
Vmware VCP-310 VMware Certified Professional on VI3 http://killexams.com/exam-detail/vcp-310 D. Only one VLAN can be specified in a port group. Answer: B, D Question: 423 What is a characteristic of a
Exam4Tests. Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily
 Exam4Tests http://www.exam4tests.com Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily Exam : VCP510PSE Title : VMware Certified Professional 5 - Data Center Virtualization PSE Vendor
Exam4Tests http://www.exam4tests.com Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily Exam : VCP510PSE Title : VMware Certified Professional 5 - Data Center Virtualization PSE Vendor
vsphere Upgrade Guide
 ESX 4.0 ESXi 4.0 vcenter Server 4.0 vsphere Client 4.0 EN-000112-00 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at: http://www.vmware.com/support/ The VMware Web site
ESX 4.0 ESXi 4.0 vcenter Server 4.0 vsphere Client 4.0 EN-000112-00 You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at: http://www.vmware.com/support/ The VMware Web site
Securing the Data Center against
 Securing the Data Center against vulnerabilities & Data Protection Agenda Virtual Virtualization Technology How Virtualization affects the Datacenter Security Keys to a Secure Virtualized Deployment and
Securing the Data Center against vulnerabilities & Data Protection Agenda Virtual Virtualization Technology How Virtualization affects the Datacenter Security Keys to a Secure Virtualized Deployment and
VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage (vsphere ICM 6.7)
 VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage (vsphere ICM 6.7) COURSE OVERVIEW: This five-day course features intensive hands-on training that focuses on installing, configuring, and managing VMware vsphere
VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage (vsphere ICM 6.7) COURSE OVERVIEW: This five-day course features intensive hands-on training that focuses on installing, configuring, and managing VMware vsphere
New Features in VMware vsphere (ESX 4)
 New Features in VMware vsphere (ESX 4) VMware vsphere Fault Tolerance FT VMware Fault Tolerance or FT is a new HA solution from VMware for VMs. It is only available in vsphere 4 and above and provides
New Features in VMware vsphere (ESX 4) VMware vsphere Fault Tolerance FT VMware Fault Tolerance or FT is a new HA solution from VMware for VMs. It is only available in vsphere 4 and above and provides
Vblock Architecture. Andrew Smallridge DC Technology Solutions Architect
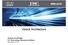 Vblock Architecture Andrew Smallridge DC Technology Solutions Architect asmallri@cisco.com Vblock Design Governance It s an architecture! Requirements: Pretested Fully Integrated Ready to Go Ready to Grow
Vblock Architecture Andrew Smallridge DC Technology Solutions Architect asmallri@cisco.com Vblock Design Governance It s an architecture! Requirements: Pretested Fully Integrated Ready to Go Ready to Grow
IBM Emulex 16Gb Fibre Channel HBA Evaluation
 IBM Emulex 16Gb Fibre Channel HBA Evaluation Evaluation report prepared under contract with Emulex Executive Summary The computing industry is experiencing an increasing demand for storage performance
IBM Emulex 16Gb Fibre Channel HBA Evaluation Evaluation report prepared under contract with Emulex Executive Summary The computing industry is experiencing an increasing demand for storage performance
VMware - VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage [V6.7]
![VMware - VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage [V6.7] VMware - VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage [V6.7]](/thumbs/93/112437773.jpg) VMware - VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage [V6.7] Code: Length: URL: EDU-VSICM67 5 days View Online This five-day course features intensive hands-on training that focuses on installing, configuring,
VMware - VMware vsphere: Install, Configure, Manage [V6.7] Code: Length: URL: EDU-VSICM67 5 days View Online This five-day course features intensive hands-on training that focuses on installing, configuring,
1V Number: 1V0-621 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min. 1V0-621
 1V0-621 Number: 1V0-621 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min 1V0-621 VMware Certified Associate 6 - Data Center Virtualization Fundamentals Exam Exam A QUESTION 1 Which tab in the vsphere Web Client
1V0-621 Number: 1V0-621 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min 1V0-621 VMware Certified Associate 6 - Data Center Virtualization Fundamentals Exam Exam A QUESTION 1 Which tab in the vsphere Web Client
Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007
 Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007 Enabled by EMC Celerra Unified Storage and Microsoft Hyper-V Reference Architecture Copyright 2010 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published May, 2010 EMC
Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007 Enabled by EMC Celerra Unified Storage and Microsoft Hyper-V Reference Architecture Copyright 2010 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published May, 2010 EMC
Virtual Server Agent for VMware VMware VADP Virtualization Architecture
 Virtual Server Agent for VMware VMware VADP Virtualization Architecture Published On: 11/19/2013 V10 Service Pack 4A Page 1 of 18 VMware VADP Virtualization Architecture - Virtual Server Agent for VMware
Virtual Server Agent for VMware VMware VADP Virtualization Architecture Published On: 11/19/2013 V10 Service Pack 4A Page 1 of 18 VMware VADP Virtualization Architecture - Virtual Server Agent for VMware
VMware vsphere Beginner s Guide
 The latest version of VMware s virtualization platform, vsphere 5, builds on the already solid foundation of. With the growth of cloud computing and the move from ESX to ESXi, it s imperative for IT pros
The latest version of VMware s virtualization platform, vsphere 5, builds on the already solid foundation of. With the growth of cloud computing and the move from ESX to ESXi, it s imperative for IT pros
VMware ESX Server 3i. December 2007
 VMware ESX Server 3i December 2007 ESX Server 3i Exec Summary What is it? What does it do? What is unique? Who can use it? How do you use it? Next generation, thin hypervisor integrated in server hardware
VMware ESX Server 3i December 2007 ESX Server 3i Exec Summary What is it? What does it do? What is unique? Who can use it? How do you use it? Next generation, thin hypervisor integrated in server hardware
The Future of Virtualization. Jeff Jennings Global Vice President Products & Solutions VMware
 The Future of Virtualization Jeff Jennings Global Vice President Products & Solutions VMware From Virtual Infrastructure to VDC- Windows Linux Future Future Future lication Availability Security Scalability
The Future of Virtualization Jeff Jennings Global Vice President Products & Solutions VMware From Virtual Infrastructure to VDC- Windows Linux Future Future Future lication Availability Security Scalability
What s New in VMware vsphere 5.1 Platform
 vsphere 5.1 Platform VMware vsphere 5.1 TECHNICAL MARKETING DOCUMENTATION V 2.0 / UPDATED JUNE 2012 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 vsphere Platform Enhancements... 3 User Access... 3 Auditing....
vsphere 5.1 Platform VMware vsphere 5.1 TECHNICAL MARKETING DOCUMENTATION V 2.0 / UPDATED JUNE 2012 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 vsphere Platform Enhancements... 3 User Access... 3 Auditing....
Virtualizing SQL Server 2008 Using EMC VNX Series and VMware vsphere 4.1. Reference Architecture
 Virtualizing SQL Server 2008 Using EMC VNX Series and VMware vsphere 4.1 Copyright 2011, 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published March, 2012 EMC believes the information in this publication
Virtualizing SQL Server 2008 Using EMC VNX Series and VMware vsphere 4.1 Copyright 2011, 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Published March, 2012 EMC believes the information in this publication
Exam : VMWare VCP-310
 Exam : VMWare VCP-310 Title : VMware Certified Professional on VI3 Update : Demo 1. Which of the following files are part of a typical virtual machine? Select 3 response(s). A. Virtual Disk File (.vmdk)
Exam : VMWare VCP-310 Title : VMware Certified Professional on VI3 Update : Demo 1. Which of the following files are part of a typical virtual machine? Select 3 response(s). A. Virtual Disk File (.vmdk)
IOmark- VM. HP HP ConvergedSystem 242- HC StoreVirtual Test Report: VM- HC b Test Report Date: 27, April
 IOmark- VM HP HP ConvergedSystem 242- HC StoreVirtual Test Report: VM- HC- 150427- b Test Report Date: 27, April 2015 Copyright 2010-2015 Evaluator Group, Inc. All rights reserved. IOmark- VM, IOmark-
IOmark- VM HP HP ConvergedSystem 242- HC StoreVirtual Test Report: VM- HC- 150427- b Test Report Date: 27, April 2015 Copyright 2010-2015 Evaluator Group, Inc. All rights reserved. IOmark- VM, IOmark-
EXAM - VCP550. VMware Certified Professional - Data Center Virtualization. Buy Full Product.
 VMware EXAM - VCP550 VMware Certified Professional - Data Center Virtualization Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/vcp550.html Examskey VMware VCP550 exam demo product is here for you to test the
VMware EXAM - VCP550 VMware Certified Professional - Data Center Virtualization Buy Full Product http://www.examskey.com/vcp550.html Examskey VMware VCP550 exam demo product is here for you to test the
VMware vsphere 6.5: Install, Configure, Manage (5 Days)
 www.peaklearningllc.com VMware vsphere 6.5: Install, Configure, Manage (5 Days) Introduction This five-day course features intensive hands-on training that focuses on installing, configuring, and managing
www.peaklearningllc.com VMware vsphere 6.5: Install, Configure, Manage (5 Days) Introduction This five-day course features intensive hands-on training that focuses on installing, configuring, and managing
Detail the learning environment, remote access labs and course timings
 Course Duration: 4 days Course Description This course has been designed as an Introduction to VMware for IT Professionals, but assumes that some labs have already been developed, with time always at a
Course Duration: 4 days Course Description This course has been designed as an Introduction to VMware for IT Professionals, but assumes that some labs have already been developed, with time always at a
Configuration Maximums VMware Infrastructure 3: ESX Server 3.5 Update 2, ESX Server 3i version 3.5 Update 2, VirtualCenter 2.
 Topic Configuration s VMware Infrastructure 3: ESX Server 3.5 Update 2, ESX Server 3i version 3.5 Update 2, VirtualCenter 2.5 Update 2 When you are selecting and configuring your virtual and physical equipment,
Topic Configuration s VMware Infrastructure 3: ESX Server 3.5 Update 2, ESX Server 3i version 3.5 Update 2, VirtualCenter 2.5 Update 2 When you are selecting and configuring your virtual and physical equipment,
EMC Integrated Infrastructure for VMware. Business Continuity
 EMC Integrated Infrastructure for VMware Business Continuity Enabled by EMC Celerra and VMware vcenter Site Recovery Manager Reference Architecture Copyright 2009 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved.
EMC Integrated Infrastructure for VMware Business Continuity Enabled by EMC Celerra and VMware vcenter Site Recovery Manager Reference Architecture Copyright 2009 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved.
The Future of Virtualization Desktop to the Datacentre. Raghu Raghuram Vice President Product and Solutions VMware
 The Future of Virtualization Desktop to the Datacentre Raghu Raghuram Vice President Product and Solutions VMware Virtualization- Desktop to the Datacentre VDC- vcloud vclient With our partners, we are
The Future of Virtualization Desktop to the Datacentre Raghu Raghuram Vice President Product and Solutions VMware Virtualization- Desktop to the Datacentre VDC- vcloud vclient With our partners, we are
Vmware VCP-511. VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 (Private Beta) Download Full Version :
 Vmware VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 (Private Beta) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/vcp-511 in RAM. A virtual machine running completely in RAM performs
Vmware VCP-511 VMware Certified Professional on vsphere 5 (Private Beta) Download Full Version : http://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/vcp-511 in RAM. A virtual machine running completely in RAM performs
1 Quantum Corporation 1
 1 Tactics and Tips for Protecting Virtual Servers Mark Eastman Director, Solutions Marketing April 2008 VMware Changing the Way Data Protection is Done No longer 1 server, 1 backup paradigm App Virtual
1 Tactics and Tips for Protecting Virtual Servers Mark Eastman Director, Solutions Marketing April 2008 VMware Changing the Way Data Protection is Done No longer 1 server, 1 backup paradigm App Virtual
70-414: Implementing an Advanced Server Infrastructure Course 01 - Creating the Virtualization Infrastructure
 70-414: Implementing an Advanced Server Infrastructure Course 01 - Creating the Virtualization Infrastructure Slide 1 Creating the Virtualization Infrastructure Slide 2 Introducing Microsoft System Center
70-414: Implementing an Advanced Server Infrastructure Course 01 - Creating the Virtualization Infrastructure Slide 1 Creating the Virtualization Infrastructure Slide 2 Introducing Microsoft System Center
Microsoft Virtualization Delivers More Capabilities, Better Value than VMware
 It s clear that virtualization can help you save money and operate more effi ciently. However, what may not be so apparent at fi rst glance, is which virtualization approach makes the most sense. VMware
It s clear that virtualization can help you save money and operate more effi ciently. However, what may not be so apparent at fi rst glance, is which virtualization approach makes the most sense. VMware
IOmark- VM. HP MSA P2000 Test Report: VM a Test Report Date: 4, March
 IOmark- VM HP MSA P2000 Test Report: VM- 140304-2a Test Report Date: 4, March 2014 Copyright 2010-2014 Evaluator Group, Inc. All rights reserved. IOmark- VM, IOmark- VDI, VDI- IOmark, and IOmark are trademarks
IOmark- VM HP MSA P2000 Test Report: VM- 140304-2a Test Report Date: 4, March 2014 Copyright 2010-2014 Evaluator Group, Inc. All rights reserved. IOmark- VM, IOmark- VDI, VDI- IOmark, and IOmark are trademarks
IOmark- VM. IBM IBM FlashSystem V9000 Test Report: VM a Test Report Date: 5, December
 IOmark- VM IBM IBM FlashSystem V9000 Test Report: VM- 151205- a Test Report Date: 5, December 2015 Copyright 2010-2015 Evaluator Group, Inc. All rights reserved. IOmark- VM, IOmark- VDI, VDI- IOmark, and
IOmark- VM IBM IBM FlashSystem V9000 Test Report: VM- 151205- a Test Report Date: 5, December 2015 Copyright 2010-2015 Evaluator Group, Inc. All rights reserved. IOmark- VM, IOmark- VDI, VDI- IOmark, and
vstart 50 VMware vsphere Solution Overview
 vstart 50 VMware vsphere Solution Overview Release 1.3 for 12 th Generation Servers Dell Virtualization Solutions Engineering Revision: A00 March 2012 THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY,
vstart 50 VMware vsphere Solution Overview Release 1.3 for 12 th Generation Servers Dell Virtualization Solutions Engineering Revision: A00 March 2012 THIS WHITE PAPER IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY,
VCAP5-DCD. Vmware. VMware Certified Advanced Professional 5 - Data Center Design
 Vmware VCAP5-DCD VMware Certified Advanced Professional 5 - Data Center Design Download Full Version : https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/vcap5-dcd QUESTION: 262 A multitier website has an RTO
Vmware VCAP5-DCD VMware Certified Advanced Professional 5 - Data Center Design Download Full Version : https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/vcap5-dcd QUESTION: 262 A multitier website has an RTO
Symantec NetBackup PureDisk Compatibility Matrix Created August 26, 2010
 Symantec NetBackup PureDisk 6.6.1 Compatibility Matrix Created August 26, 2010 Copyright 2010 Symantec Corporation. All rights reserved. Symantec, the Symantec Logo, and Backup Exec are trademarks or registered
Symantec NetBackup PureDisk 6.6.1 Compatibility Matrix Created August 26, 2010 Copyright 2010 Symantec Corporation. All rights reserved. Symantec, the Symantec Logo, and Backup Exec are trademarks or registered
Vendor: VMware. Exam Code: VCP550PSE. Exam Name: VMware Certified Professional - Data Center Virtualization (PSE) Version: Demo
 Vendor: VMware Exam Code: VCP550PSE Exam Name: VMware Certified Professional - Data Center Virtualization (PSE) Version: Demo QUESTION 1 An administrator is planning a vsphere infrastructure with the following
Vendor: VMware Exam Code: VCP550PSE Exam Name: VMware Certified Professional - Data Center Virtualization (PSE) Version: Demo QUESTION 1 An administrator is planning a vsphere infrastructure with the following
VMware vsphere 5.0 STORAGE-CENTRIC FEATURES AND INTEGRATION WITH EMC VNX PLATFORMS
 VMware vsphere 5.0 STORAGE-CENTRIC FEATURES AND INTEGRATION WITH EMC VNX PLATFORMS A detailed overview of integration points and new storage features of vsphere 5.0 with EMC VNX platforms EMC Solutions
VMware vsphere 5.0 STORAGE-CENTRIC FEATURES AND INTEGRATION WITH EMC VNX PLATFORMS A detailed overview of integration points and new storage features of vsphere 5.0 with EMC VNX platforms EMC Solutions
Stellar performance for a virtualized world
 IBM Systems and Technology IBM System Storage Stellar performance for a virtualized world IBM storage systems leverage VMware technology 2 Stellar performance for a virtualized world Highlights Leverages
IBM Systems and Technology IBM System Storage Stellar performance for a virtualized world IBM storage systems leverage VMware technology 2 Stellar performance for a virtualized world Highlights Leverages
