D-Link Allocation in g Based Higher Bandwidth Mobile Adhoc
|
|
|
- Cory Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 D-Link Allocation in g Based Higher Bandwidth Mobile Adhoc Networks S.V. Vanitha 1, Dr.G.Mohankumar 2, 1Assistant Professor Department of ECE Park college of Engg and Technology Coimbatore 2 Principal Park college of Engg and Technology Coimbatore *** Abstract - D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide easy-to-use and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your home, business or public access wireless networks. D-Link wireless products will allow you access to the data you want, when and where you want it. You will be able to enjoy the freedom that wireless networking brings. In this paper we should analysis D-link analysis based mobile adhoc networks with simulation of NS-2. Mobility, Installation and Network Expansion and Scalability also considered. Key Words: Mobile wireless networks, IEEE802.11g,D link,throughput 1.INTRODUCTION ( Size 11, cambria font) The D-Link AirPlus G DI-524 High-Speed Wireless Router is an g high-performance, wireless router that supports high-speed wireless networking at home, at work or in public places. Unlike most routers, the DI-524 provides data transfers at up to 108 Mbps (compared to the standard 54 Mbps) when used with other D-Link AirPlus G products. The g standard is backwards compatible with b products. This means that you do not need to change your entire network to maintain connectivity. You may sacrifice some of g s speed when you mix b and g devices, but you will not lose the ability to communicate when you incorporate the g standard into your b network. You may choose to slowly change your network by gradually replacing the b devices with g devices. In order to provide QoS in a wireless network, the IEEE g MAC (Medium Access Control) protocol [3] is proposed. The IEEE g MAC protocol introduces the HCF (Hybrid Coordination Function), which defines two new MAC mechanisms namely, HCCA (HCF Controlled Channel Access) and EDCA (Enhanced Distributed Channel Access). EDCA achieves service differentiation by introducing different ACs (Access Categories) and their associated backoff entities. Although EDCA is designed to provide QoS assurance, it does not fit into multihop wireless environment because it has no notion of end-toend QoS guarantee. In addition to offering faster data transfer speeds when used with other g products, the DI-524 has the newest, strongest, most advanced security features available today. When used with other g WPA (WiFi Protected Access) and 802.1x compatible products in a network with a RADIUS server, the security features include: The multihop wireless environment is characterized by harsh propagation channels, interference, frequent and rapid changes in network topology, a lack of centralized network control, and the requirement of multihop communication from source to destination. Many of present wireless network applications will require that mission-critical data should be guaranteed to be delivered to their corresponding targets in time. However, end-to-end QoS (Quality of Service) assurance in multihop networks is a very challenging topic [1][2]. For home users that will not incorporate a RADIUS server in their network, the security for the DI-524, used in conjunction with other g products, will still be much stronger than ever before. Utilizing the Pre Shared Key mode of WPA, the DI- 524 will obtain a new security key every time it connects to the g network. You only need to input your encryption information once in the configuration menu. No longer will you have to manually input a new WEP key frequently to ensure security, with the DI-524, you will automatically receive a new key every time you connect, vastly increasing the safety of your communications. Fully compatible with the g standard to provide a wireless data rate of up to 54Mbps Backwards compatible with the b standard to provide a wireless data rate of up to 11Mbps WPA (Wi Fi Protected Access) authorizes and identifies users based on a secret key that changes automatically at a regular interval, for example: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), in conjunction with a RADIUS server, changes the temporal key every 10,000 packets, ensuring greater security 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 618
2 2.Features At present, the use of WLANs has been essentially focused on best e ort data transfer because the basic DCF and PCF access methods cannot provide delay guarantees to real-time multimedia ows. Recently, in order to support also delay-sensitive multimedia applications, such as real-time voice and video, the e working group has proposed innovative functionali- ties, which enable service di erentiation in WLANs. In particular, the e proposal introduces: (1) the Hybrid Coordination Function (HCF), which is an enhanced access method to distribute the limited rst-hop WLAN band- width among delay-insensitive and delay-sensitive ows; (2) a Call Admis sion Control (CAC) algorithm for preventing network overloads, which would drastically degrade the service o ered by the network; (3) speci c signaling messages for service request and Quality of Service (QoS) service level nego- tiation. - The e draft does not specify an e ective bandwidth allocation algorithm for providing the QoS required by real-time ows; it only suggests a simple scheduler that provides a Constant Bit Rate (CBR) service. This scheduler does not exploit any feedback information from mobile stations in order to dynamically assign the WLAN bandwidth. Thus, it is not well suited for bursty media ows An improved bandwidth allocation algorithm has been proposed in, which schedules transmission opportunities by taking into account both the average and the maximum source rates declared by each data source. However, also this scheme does not consider the dynamic behav- ior of multimedia ows. An adaptive version of the simple scheduler, which is based on the Delay-Earliest Due-Date algorithm, has been proposed in This algorithm implements a trial and error procedure to discover the optimal bandwidth assignment to each station. Active measurement methods inject specific probes into the network and estimate the available bandwidth from measurements of the probing traffic at the ingress and at the egress of the network. The majority of the methods uses packet pairs, i.e. two packets sent with a defined spacing in time referred to as gap, or packet trains, i.e. a larger number of packets sent at a defined constant rate. The rate of a packet train can be converted into a certain spacing of the train s packets, showing a direct relation to the gap model of packet pairs. Packet are specific packet trains. that are sent at a geometrically increasing rate respectively with a geometrically decreasinggap. FCFS multiplexing is usually 3. Related Work In this section, IEEE g protocol and the EDCA mechanism are described. In addition, the existing research works on dynamic traffic prioritization schemes in multihop wireless networks are discussed. 3.1 IEEE g Mechanism Assumed, where flows share the capacity of a link proportionally to their offered rates. For constant rate probes an expression referred to as rate response curve can be derived as where ri and ro are the input and output rates of probes respectively and λ is the input rate of crosstraffic. If λ C the available bandwidth follows as AB = C λ and otherwise AB = 0. Based on this model the task of available bandwidth estimation is to select the rate of probing traffic such that (2) can be solved for C and λ or C λ. While (2) is usually used for packet train probes, an equivalent gap response curve can be derived for packet pairs, where the gap g is linked to the rate r by the packet size l resulting in gi = l/ri and go = l/ro [2]. In [1] measurement methods are classified by their inference technique as either direct or iterative probing schemes. Direct probing schemes assume that the capacity of the link C is known in advance. In this case (2) can be solved for the rate of the cross-traffic if the probing rate is larger than the available bandwidth 4 Relevant Wireless Link Characteristics In this section we discuss relevant characteristics of wireless links that are of vital importance for bandwidth estimation. We show how these aspects , IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 619
3 affect current fluid rate and gap models from Sect. 2 and reason which quantity we expect to be estimated by known methods for bandwidth estimation in wireless 318 M. Bredel and M. Fidler systems. We use the term wireless link meaning a wireless broadcast channel with Medium Access Control (MAC) and Radio Link Control (RLC) protocols. Fading and interference: As opposed to wired links the characteristics of wireless channels are highly variable due to fading. Other potentially hidden stations, which may even include stations that implement different radio standards using the same frequency band, create interference on the wireless broadcast medium. These effects can cause rapid fluctuations of the signal-tonoise ratio and may lead to high bit error rates. Different modulation and coding schemes combined with rate adaptation may be used for compensation. As a consequence, the capacity and the availability of the channel may vary drastically. The task of available bandwidth estimation is to infer the portion of the capacity of a link or a network path that remains unused by cross-traffic. The scheme is an efficient way to improve the channel utilization because the contention overhead is shared among all the frames transmitted in a burst. Moreover, it enables service differentiation between multiple traffic classes by virtue of various Transmission limits. The available bandwidth of a link with index i can be defined as [12] ABi(τ, t) = Ci(1 ui(τ, t)) (1) where Ci is the capacity and ui [0, 1] is the utilization by cross-traffic in the interval [τ, t). The available bandwidth of a network path is determined by the available bandwidth of the tight link as AB(τ, t) = mini {ABi(τ, t)} [1]. IEEE e [3] was proposed to supplement IEEE g [5] by providing service differentiation in WLAN. The IEEE e defines a set of QoS enhancements for WLAN applications through modifications to the MAC layer. The standard is considered of critical importance for delay sensitive applications, such as voice over WLAN and streaming multimedia. The IEEE e MAC protocol introduces the HCF, which defines two new MAC mechanisms namely, HCCA and EDCA. EDCA achieves service differentiation by introducing different ACs (Access Categories) and their associated backoff entities. Fig1 : Dlink of Transmission To mitigate the impact of the overheads and improve the system efficiency, the TXOP scheme has been proposed in the IEEE e protocol. Different from IEEE where a station can transmit only one frame after winning the channel, the TXOP scheme allows a station gaining the channel to transmit the frames available in its buffer successively provided that the duration of transmission does not exceed a certain threshold, namely the TXOP limit. As shown in Fig. 3, each frame is acknowledged by an ACK after a SIFS interval. The next frame is transmitted immediately after it waits for an SIFS upon receiving this ACK. If the transmission of any frame fails the burst is terminated and the station contends again for the channel to retransmit the failed frame. To mitigate the impact of the overheads and improve the system efficiency, the scheme has been proposed in the IEEE g protocol. Different from IEEE where a station can transmit only one frame after winning the channel, the TXOP scheme allows a station gaining the channel to transmit the frames available in its buffer successively provided that the duration of transmission does not exceed a certain threshold, namely the limit. As shown in Fig. 1 each frame is acknowledged by an ACK after a SIFS interval. The next frame is transmitted immediately after it waits for an SIFS upon receiving this ACK. If the transmission of any frame fails the burst is terminated and the station contends again for the channel to retransmit the failed frame. 4.1 Penetrating wall For this experiment, we put one laptop indoor, and the other laptop outdoor, then we fixed the indoor laptop s 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 620
4 position, moved the outdoor laptop so that the distance between them is changing with distance: 5m, 10m, 15m, and 20m. In between them there is a wall as the obstruction, the wireless signal has to penetrate the wall. 5. Experimental Results and Analysis 5.1Indoor without Obstructions Fig 2 depicts the results of TCP experiment performed in the indoor environment. The achieved throughput performance is indeed affected by the size of messages communicated with the two hosts. With the increasing message sizes, the throughput has been improved accordingly. For instances, with the message size of 32- Kbyte (i.e., 2^5-Kbytes in Fig 2), TCP only achieves in the range of 11 Mbps (i.e., 19% of the theoretica results indicate the opposite trend. We expected the performance should be best with the distance less than 5 meters away. But it turns out the ad-hoc mode performs the worst compared to the distance [5m, 10m] and [10m, 20m]. The observed performance trend demonstrates that increasing the distance does improve the achieved throughput performance. There are perhaps a number of reasons for causing this unique performance trend. One of the reasons can be related to the multi-path propagation of the radio frequency in the physical layer. When the distance is less than 5 meters, the transmitted signal for LOS (line of sight) transmission is affected by the other reflection, diffraction and scattering radio frequencies [K85]. Though the LOS signal arrives quickly, the signal timing and strength from the multi-path signals can be quite different. Therefore in the MAC Layer, the delay differences can be great enough that bit errors occur. Thus, the receiver can not distinguish the symbols and interpret the corresponding bits correctly. When the distance is increased, the multi-path interference is reduced because the timing and strength difference between LOS and non-los signals. 6. Proposed Schemes and Protocols Fig4-Mbpspeakbandwidth). With the message size of 4-Mbyte (i.e., 2^12-Kbytes in Fig 5), the throughput can be achieved to 13 Mbps. The 2-Mbps performance improvement represents the 18% increase from 32-Kbyte message size. Just like the wire-line networks, larger messages cause smaller software overhead. Thus, the results are considered reasonable. However, an interesting observation has been found related to the distance factor. Unlike the wire-line networks, the communication pair in ad-hoc networks can move their position more freely. It is the conventional thinking that the throughput performance should be better when the distance is shorter. The reason behind the expectation is that the time to propagate the messages to the destination is shorter. Interestingly, our measured performance The discovery of IEEE g s throughput-distance relationships in its ad-hoc act in QOS routing. Since the bandwidth allocation is the top priority of the routing decision, the baseline performance results indicate that proper paths should be chosen with the consideration of the distance between any two routing nodes. However, the majority of the existing schemes seem to be lack of the joint consideration with the distance factor. For instances, many assumed the bandwidth is uniformly identical within the distance limit, thus the routing decisions favor the minimal number of hop counts. We believe, given the solid evidences from the baseline experiments, the routing decisions within the (multi-hop) ad-hoc networks should be different.we Applied this algorithm Algorithm MaxThroughput(u) Initialization: N = {u}.v 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 621
5 for all nodes v if v is a neighbor of u then B(v) = bw(u, v) else B(v) = 0 Loop Find w not in N such that B(w) is a maximum add w to N (Beacon neighbour) update B(v) for each neighbor v of w and not in N : B(v) = max( B(v), min( B(w), bw(w, v) ) ) 3.[FML03] Z. Fu, X. Meng and S. Lu, A Transport Protocol for Supporting Multimedia Streaming in Mobile Ad- Hoc Networks, IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, Vol. 22, No. 10, Dec [GPLRS95] A. Guha, A. Pavan, J. Liu, A. Rastogi and T. Steeves, "Supporting Real-time and Multimedia Applications on the MERCURI Testbed", IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, Vol. 13, No. 4, May until N = N Return all B(u,v) where v. N and v u 7. Conclusion In this paper, we propose the higher bnawidth scheme for mobile wireless networks. First, we propose d link scheme that dynamically assigns priorities to traffic according to network status and delay requirement, in order to achieve guaranteed end-to-end d link wireless networks. In order to calculate per class delay more accurately, the proposed scheme employs reliability of the link. In addition, the proposed scheme performs priority resetting when the burst collision is occurred. Through priority resetting, it can satisfy the end-to-end delay requirement of mission-critical data by sacrificing QoS for non-mission-critical data along the path for the delivery of those mission-critical data. References 1.[DLS01] B. Daines, J. Liu and K. Sivalingam, Supporting Multimedia Communication over A Gigabit Ethernet Network, International Journal of Parallel and Distributed Systems and Networks, Vol. 4, No. 2, Jun [FKFB05] W. Feng, E. Kaiser, W. Feng, M. Baillif, Panoptes: Scalable Low-power Video Sensor Networking Technologies, ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications, Vol. 1, No. 9,May , IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 622
CHAPTER 4 CALL ADMISSION CONTROL BASED ON BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION (CACBA)
 92 CHAPTER 4 CALL ADMISSION CONTROL BASED ON BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION (CACBA) 4.1 INTRODUCTION In our previous work, we have presented a cross-layer based routing protocol with a power saving technique (CBRP-PS)
92 CHAPTER 4 CALL ADMISSION CONTROL BASED ON BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION (CACBA) 4.1 INTRODUCTION In our previous work, we have presented a cross-layer based routing protocol with a power saving technique (CBRP-PS)
PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION
 PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION Phuc Khanh KIEU, Shinichi MIYAMOTO Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University 2-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka, 565-871 JAPAN
PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION Phuc Khanh KIEU, Shinichi MIYAMOTO Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University 2-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka, 565-871 JAPAN
Dynamic Traffic Prioritization and TXOP Allocation in e Based Multihop Wireless Networks
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.12 No.2, February 2012 33 Dynamic Traffic Prioritization and TXOP Allocation in 802.11e Based Multihop Wireless Networks Dongho
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.12 No.2, February 2012 33 Dynamic Traffic Prioritization and TXOP Allocation in 802.11e Based Multihop Wireless Networks Dongho
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Analysis of IEEE e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs
 Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
Wireless Networked Systems
 Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #6: Medium Access Control QoS and Service Differentiation, and Power Management Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Quality of Service (802.11e)
Wireless Networked Systems CS 795/895 - Spring 2013 Lec #6: Medium Access Control QoS and Service Differentiation, and Power Management Tamer Nadeem Dept. of Computer Science Quality of Service (802.11e)
D-Link AirPlus G DI-524
 D-Link AirPlus G DI-524 802.11g/ 2.4 GHz Wireless Router TM Manual Building Networks for People Contents Package Contents... 3 Introduction... 4 Wireless Basics... 8 Getting Started...11 Using the Configuration
D-Link AirPlus G DI-524 802.11g/ 2.4 GHz Wireless Router TM Manual Building Networks for People Contents Package Contents... 3 Introduction... 4 Wireless Basics... 8 Getting Started...11 Using the Configuration
A Novel Framework for Radio Resource Management in IEEE Wireless LANs
 Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Conference papers Communications Network Research Institute 2005-01-01 A Novel Framework for Radio Resource Management in IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Mark Davis Dublin
Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Conference papers Communications Network Research Institute 2005-01-01 A Novel Framework for Radio Resource Management in IEEE 802.11 Wireless LANs Mark Davis Dublin
Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) PW Chapter Medium Access. Chapter 8 Overview
 Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) PW0-105 Chapter 8 802.11 Medium Access Chapter 8 Overview CSMA/CA vs. CSMA/CD Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) Point Coordination Function (PCF) Hybrid
Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) PW0-105 Chapter 8 802.11 Medium Access Chapter 8 Overview CSMA/CA vs. CSMA/CD Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) Point Coordination Function (PCF) Hybrid
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE
 3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Lecture 9. Quality of Service in ad hoc wireless networks
 Lecture 9 Quality of Service in ad hoc wireless networks Yevgeni Koucheryavy Department of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology yk@cs.tut.fi Lectured by Jakub Jakubiak QoS statement
Lecture 9 Quality of Service in ad hoc wireless networks Yevgeni Koucheryavy Department of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology yk@cs.tut.fi Lectured by Jakub Jakubiak QoS statement
Wireless LANs. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs)) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Computer Networks: Wireless Networks 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices
Exam4Tests. Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily
 Exam4Tests http://www.exam4tests.com Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily Exam : PW0-300 Title : Certified Wireless Network Expert Vendors : CWNP Version : DEMO Get Latest
Exam4Tests http://www.exam4tests.com Latest exam questions & answers help you to pass IT exam test easily Exam : PW0-300 Title : Certified Wireless Network Expert Vendors : CWNP Version : DEMO Get Latest
. 14 Byte for Acks. Due to this fact, the overhead is more relevant if the data contained in packets is sent to high rates:
 QoS in IEEE 802.11 Issues Some issues are important for quality of service: the first one mentioned is the difference of performances expired by nodes based on their position in the network. Indeed, considering
QoS in IEEE 802.11 Issues Some issues are important for quality of service: the first one mentioned is the difference of performances expired by nodes based on their position in the network. Indeed, considering
Qos support and adaptive video
 Qos support and adaptive video QoS support in ad hoc networks MAC layer techniques: 802.11 e - alternation of contention based and contention free periods; differentiated (per class) Interframe Spacing
Qos support and adaptive video QoS support in ad hoc networks MAC layer techniques: 802.11 e - alternation of contention based and contention free periods; differentiated (per class) Interframe Spacing
Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering
 Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Technical Report MECSE-6-2006 Medium Access Control (MAC) Schemes for Quality of Service (QoS) provision of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Technical Report MECSE-6-2006 Medium Access Control (MAC) Schemes for Quality of Service (QoS) provision of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
Lecture 16: QoS and "
 Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
Efficient Transmission of H.264 Video over WLANs
 Efficient Transmission of H.264 Video over WLANs Yaser P. Fallah March 2007 UBC 1 Multimedia Communications Multimedia applications are becoming increasingly popular Video on mobile devices (cell phones,
Efficient Transmission of H.264 Video over WLANs Yaser P. Fallah March 2007 UBC 1 Multimedia Communications Multimedia applications are becoming increasingly popular Video on mobile devices (cell phones,
Performance Improvement of Wireless Network Using Modern Simulation Tools
 Performance Improvement of Wireless Network Using Modern Simulation Tools Ms. Nimisha Dinesh Deval 1, Prof. Mrs. S. P. Pawar 2 1ME student CSE Dept, SVERIs college of Engineering, Pandharpur, Maharashtra,
Performance Improvement of Wireless Network Using Modern Simulation Tools Ms. Nimisha Dinesh Deval 1, Prof. Mrs. S. P. Pawar 2 1ME student CSE Dept, SVERIs college of Engineering, Pandharpur, Maharashtra,
Performance evaluation of Cooperative MAC and ZRP in Cooperative Communication Networking Environment
 Performance evaluation of Cooperative MAC and ZRP in Cooperative Communication Networking Environment N Charan 1, Dr. Sreerangaraju M.N 2, Nagesh R 3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics & Communication
Performance evaluation of Cooperative MAC and ZRP in Cooperative Communication Networking Environment N Charan 1, Dr. Sreerangaraju M.N 2, Nagesh R 3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics & Communication
CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation for IEEE WLANs. Presented by Eric Wang
 CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation for IEEE 802.11 WLANs Presented by Eric Wang 1 Outline Introduction Related Work Preliminaries CARA Performance Evaluation Conclusion and Future Work 2 Basic CSMA/CA
CARA: Collision-Aware Rate Adaptation for IEEE 802.11 WLANs Presented by Eric Wang 1 Outline Introduction Related Work Preliminaries CARA Performance Evaluation Conclusion and Future Work 2 Basic CSMA/CA
Strategies and Guidelines for Improving Wireless Local Area Network Performance
 Strategies and Guidelines for Improving Wireless Local Area Network Performance Dr Nurul Sarkar Associate Professor School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences nurul.sarkar@aut.ac.nz 2 Outline of Talk
Strategies and Guidelines for Improving Wireless Local Area Network Performance Dr Nurul Sarkar Associate Professor School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences nurul.sarkar@aut.ac.nz 2 Outline of Talk
ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks
 ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks Husheng Li Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring, 2014 Wireless Local Networks 1 A WLAN links two or more devices using
ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks Husheng Li Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring, 2014 Wireless Local Networks 1 A WLAN links two or more devices using
A Tool for Simulating IEEE e Contention-based Access
 A Tool for Simulating IEEE 802.11e Contention-based Access Andreas Floros 1 and Theodore Karoubalis 2 1 Dept. of Informatics, Ionian University, Plateia Tsirigoti 7, 49 100 Corfu, Greece floros@ionio.gr
A Tool for Simulating IEEE 802.11e Contention-based Access Andreas Floros 1 and Theodore Karoubalis 2 1 Dept. of Informatics, Ionian University, Plateia Tsirigoti 7, 49 100 Corfu, Greece floros@ionio.gr
CSE 461: Wireless Networks
 CSE 461: Wireless Networks Wireless IEEE 802.11 A physical and multiple access layer standard for wireless local area networks (WLAN) Ad Hoc Network: no servers or access points Infrastructure Network
CSE 461: Wireless Networks Wireless IEEE 802.11 A physical and multiple access layer standard for wireless local area networks (WLAN) Ad Hoc Network: no servers or access points Infrastructure Network
Quality of Service (QoS) Settings on AP541N Access Point
 Quality of Service (QoS) Settings on AP541N Access Point Objective Quality of Service (QoS) is a technique used to achieve better performance for a computer network and is also used to enhance the quality
Quality of Service (QoS) Settings on AP541N Access Point Objective Quality of Service (QoS) is a technique used to achieve better performance for a computer network and is also used to enhance the quality
An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE WLANs
 An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE 802.11 WLANs Juki Wirawan Tantra, Chuan Heng Foh, and Bu Sung Lee Centre of Muldia and Network Technology School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological
An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE 802.11 WLANs Juki Wirawan Tantra, Chuan Heng Foh, and Bu Sung Lee Centre of Muldia and Network Technology School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological
Notes on the Inefficiency of e HCCA
 Notes on the Inefficiency of 802.e HCCA C. Casetti, C.-F. Chiasserini, M. Fiore and M. Garetto Dipartimento di Elettronica, Politecnico di Torino - Italy E-mail: {casetti,chiasserini,fiore,garetto}@polito.it
Notes on the Inefficiency of 802.e HCCA C. Casetti, C.-F. Chiasserini, M. Fiore and M. Garetto Dipartimento di Elettronica, Politecnico di Torino - Italy E-mail: {casetti,chiasserini,fiore,garetto}@polito.it
D-Link AirPlus G DWL-G700AP
 TM D-Link AirPlus G DWL-G700AP 2.4GHz Wireless Access Point Manual Building Networks for People Contents Package Contents...3 Introduction...4 Wireless Basics...6 Getting Started...8 Using the Configuration
TM D-Link AirPlus G DWL-G700AP 2.4GHz Wireless Access Point Manual Building Networks for People Contents Package Contents...3 Introduction...4 Wireless Basics...6 Getting Started...8 Using the Configuration
2. LITERATURE REVIEW. Performance Evaluation of Ad Hoc Networking Protocol with QoS (Quality of Service)
 2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
2. LITERATURE REVIEW I have surveyed many of the papers for the current work carried out by most of the researchers. The abstract, methodology, parameters focused for performance evaluation of Ad-hoc routing
Wireless Local Area Networks. Networks: Wireless LANs 1
 Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Wireless Local Area Networks Networks: Wireless LANs 1 Wireless Local Area Networks The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones) created an obvious application
Fairness and Transmission Opportunity Limit in IEEE802.11e Enhanced Distributed Channel Access
 Fairness and Transmission Opportunity Limit in IEEE802.11e Enhanced Distributed Channel Access by Anni Matinlauri Instructor: Jouni Karvo Supervisor: Professor Raimo Kantola Agenda Background Research
Fairness and Transmission Opportunity Limit in IEEE802.11e Enhanced Distributed Channel Access by Anni Matinlauri Instructor: Jouni Karvo Supervisor: Professor Raimo Kantola Agenda Background Research
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AF IN CONSIDERING LINK
 I.J.E.M.S., VOL.2 (3) 211: 163-171 ISSN 2229-6X PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AF IN CONSIDERING LINK UTILISATION BY SIMULATION Jai Kumar and U.C. Jaiswal Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Madan
I.J.E.M.S., VOL.2 (3) 211: 163-171 ISSN 2229-6X PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AF IN CONSIDERING LINK UTILISATION BY SIMULATION Jai Kumar and U.C. Jaiswal Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Madan
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control
 Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Table of Contents 1 WLAN QoS Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 WLAN QoS Configuration 1-1 WLAN QoS Overview 1-1 Terminology 1-1 WMM Protocol Overview 1-2 Protocols and Standards 1-4 WMM Configuration 1-4 Configuration Prerequisites 1-4 Configuring
Table of Contents 1 WLAN QoS Configuration 1-1 WLAN QoS Overview 1-1 Terminology 1-1 WMM Protocol Overview 1-2 Protocols and Standards 1-4 WMM Configuration 1-4 Configuration Prerequisites 1-4 Configuring
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS)
 Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
QoS issues in Wi-Fi-WMM based triple play home networks
 QoS issues in Wi-Fi-WMM based triple play home networks Yun Tao Shi Jean-Marie Bonnin Gilles Straub Thomson, France INRIA/IRISA, France Thomson, France yun-tao.shi@thomson.net jm.bonnin@enst-bretagne.fr
QoS issues in Wi-Fi-WMM based triple play home networks Yun Tao Shi Jean-Marie Bonnin Gilles Straub Thomson, France INRIA/IRISA, France Thomson, France yun-tao.shi@thomson.net jm.bonnin@enst-bretagne.fr
User Guide. For TP-Link Auranet Access Points
 User Guide For TP-Link Auranet Access Points EAP110 / EAP115 / EAP225 / EAP245 / EAP320 / EAP330 / EAP115-Wall / EAP110-Outdoor 1910012276 REV 2.0.2 October 2017 CONTENTS About this User Guide... 1 Overview...
User Guide For TP-Link Auranet Access Points EAP110 / EAP115 / EAP225 / EAP245 / EAP320 / EAP330 / EAP115-Wall / EAP110-Outdoor 1910012276 REV 2.0.2 October 2017 CONTENTS About this User Guide... 1 Overview...
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Topic 2b Wireless MAC. Chapter 7. Wireless and Mobile Networks. Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach
 Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
Topic 2b Wireless MAC Chapter 7 Wireless and Mobile Networks Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 7-1 Ch. 7: Background: # wireless
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless 802.11 1 Topics 802 Standard MAC and LLC Sublayers Review of MAC in Ethernet MAC in 802.11 Wireless 2 IEEE Standards In 1985, Computer
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 7 Ethernet and Wireless 802.11 1 Topics 802 Standard MAC and LLC Sublayers Review of MAC in Ethernet MAC in 802.11 Wireless 2 IEEE Standards In 1985, Computer
On the Performance Enhancement of Wireless LAN - A Multi-polling Mechanism with Hidden Terminal Solution
 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com On the Performance Enhancement of Wireless LAN - A Multi-polling Mechanism with Hidden Terminal Solution Yue Fang, Daqing Gu, A. Bruce McDonald,
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com On the Performance Enhancement of Wireless LAN - A Multi-polling Mechanism with Hidden Terminal Solution Yue Fang, Daqing Gu, A. Bruce McDonald,
University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series. Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks
 University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks Rastin Pries and Klaus Heck Report No. 339 September 2004
University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks Rastin Pries and Klaus Heck Report No. 339 September 2004
Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 7: Wireless LAN
 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 7: Wireless LAN [Schiller, Section 7.3] [Reader, Part 6] [Optional: "IEEE 802.11n Development: History, Process, and Technology", Perahia, IEEE Communications
Call Admission Control for IEEE Contention Access Mechanism
 Call Admission Control for IEEE 82.11 Contention Access Mechanism Dennis Pong and Tim Moors School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications, The University of New South Wales, Australia Email:
Call Admission Control for IEEE 82.11 Contention Access Mechanism Dennis Pong and Tim Moors School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications, The University of New South Wales, Australia Email:
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AF IN CONSIDERING LINK UTILISATION BY SIMULATION WITH DROP-TAIL
 I.J.E.M.S., VOL.2 (4) 2011: 221-228 ISSN 2229-600X PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AF IN CONSIDERING LINK UTILISATION BY SIMULATION WITH DROP-TAIL Jai Kumar, Jaiswal Umesh Chandra Department of Computer Science
I.J.E.M.S., VOL.2 (4) 2011: 221-228 ISSN 2229-600X PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AF IN CONSIDERING LINK UTILISATION BY SIMULATION WITH DROP-TAIL Jai Kumar, Jaiswal Umesh Chandra Department of Computer Science
Multiple Access Links and Protocols
 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Simulating coexistence between y and h systems in the 3.65 GHz band An amendment for e
 Simulating coexistence between 802.11y and 802.16h systems in the 3.65 GHz band An amendment for 802.11e IEEE 802.16 Presentation Submission Template (Rev. 8.3) Document Number: C802.16h-07/050 Date Submitted:
Simulating coexistence between 802.11y and 802.16h systems in the 3.65 GHz band An amendment for 802.11e IEEE 802.16 Presentation Submission Template (Rev. 8.3) Document Number: C802.16h-07/050 Date Submitted:
Prioritization scheme for QoS in IEEE e WLAN
 Prioritization scheme for QoS in IEEE 802.11e WLAN Yakubu Suleiman Baguda a, Norsheila Fisal b a,b Department of Telematics & Communication Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi
Prioritization scheme for QoS in IEEE 802.11e WLAN Yakubu Suleiman Baguda a, Norsheila Fisal b a,b Department of Telematics & Communication Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi
CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS
 28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
CSMA based Medium Access Control for Wireless Sensor Network
 CSMA based Medium Access Control for Wireless Sensor Network H. Hoang, Halmstad University Abstract Wireless sensor networks bring many challenges on implementation of Medium Access Control protocols because
CSMA based Medium Access Control for Wireless Sensor Network H. Hoang, Halmstad University Abstract Wireless sensor networks bring many challenges on implementation of Medium Access Control protocols because
Mohamed Khedr.
 Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 Overview Packet Switching IP addressing
Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 Overview Packet Switching IP addressing
Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology
 Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology Prashant Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Scholar, Computer Networks, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.), India
Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology Prashant Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Scholar, Computer Networks, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.), India
Multi-Hop Simulator for Ad-Hoc IEEE e
 Multi-Hop Simulator for Ad-Hoc IEEE 802.11e João M. Ferro, Fernando J. Velez, Member, IAENG Abstract This work addresses the development of a cross-layer wireless network simulator for IEEE 802.11e in
Multi-Hop Simulator for Ad-Hoc IEEE 802.11e João M. Ferro, Fernando J. Velez, Member, IAENG Abstract This work addresses the development of a cross-layer wireless network simulator for IEEE 802.11e in
Wireless Router at Home
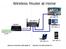 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Final Exam: Mobile Networking (Part II of the course Réseaux et mobilité )
 Final Exam: Mobile Networking (Part II of the course Réseaux et mobilité ) Prof. J.-P. Hubaux February 12, 2004 Duration: 2 hours, all documents allowed Please write your answers on these sheets, at the
Final Exam: Mobile Networking (Part II of the course Réseaux et mobilité ) Prof. J.-P. Hubaux February 12, 2004 Duration: 2 hours, all documents allowed Please write your answers on these sheets, at the
Supporting Service Differentiation for Real-Time and Best-Effort Traffic in Stateless Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks (SWAN)
 Supporting Service Differentiation for Real-Time and Best-Effort Traffic in Stateless Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks (SWAN) G. S. Ahn, A. T. Campbell, A. Veres, and L. H. Sun IEEE Trans. On Mobile Computing
Supporting Service Differentiation for Real-Time and Best-Effort Traffic in Stateless Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks (SWAN) G. S. Ahn, A. T. Campbell, A. Veres, and L. H. Sun IEEE Trans. On Mobile Computing
Mobile Communications. Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks
 Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
On the Performance Characteristics of WLANs: Revisited
 On the Performance Characteristics of WLANs: Revisited S. Choi,, K. Park and C.K. Kim Sigmetrics 2005 Banff, Canada Presenter - Bob Kinicki Advanced Computer Networks Fall 2007 Outline Introduction System
On the Performance Characteristics of WLANs: Revisited S. Choi,, K. Park and C.K. Kim Sigmetrics 2005 Banff, Canada Presenter - Bob Kinicki Advanced Computer Networks Fall 2007 Outline Introduction System
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Improving the Data Scheduling Efficiency of the IEEE (d) Mesh Network
 Improving the Data Scheduling Efficiency of the IEEE 802.16(d) Mesh Network Shie-Yuan Wang Email: shieyuan@csie.nctu.edu.tw Chih-Che Lin Email: jclin@csie.nctu.edu.tw Ku-Han Fang Email: khfang@csie.nctu.edu.tw
Improving the Data Scheduling Efficiency of the IEEE 802.16(d) Mesh Network Shie-Yuan Wang Email: shieyuan@csie.nctu.edu.tw Chih-Che Lin Email: jclin@csie.nctu.edu.tw Ku-Han Fang Email: khfang@csie.nctu.edu.tw
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Media Access Control (MAC) Sub-layer and Ethernet
 Media Access Control (MAC) Sub-layer and Ethernet Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF MAC Sub-layer The MAC sub-layer is a sub-layer
Media Access Control (MAC) Sub-layer and Ethernet Dr. Sanjay P. Ahuja, Ph.D. Fidelity National Financial Distinguished Professor of CIS School of Computing, UNF MAC Sub-layer The MAC sub-layer is a sub-layer
Medium Access Control. MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols
 Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
Medium Access Control MAC protocols: design goals, challenges, contention-based and contention-free protocols 1 Why do we need MAC protocols? Wireless medium is shared Many nodes may need to access the
CHAPTER 4 CROSS LAYER INTERACTION
 38 CHAPTER 4 CROSS LAYER INTERACTION The cross layer interaction techniques used in the lower layers of the protocol stack, solve the hidden and exposed terminal problems of wireless and ad hoc networks.
38 CHAPTER 4 CROSS LAYER INTERACTION The cross layer interaction techniques used in the lower layers of the protocol stack, solve the hidden and exposed terminal problems of wireless and ad hoc networks.
EVALUATION OF EDCF MECHANISM FOR QoS IN IEEE WIRELESS NETWORKS
 MERL A MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORY http://www.merl.com EVALUATION OF EDCF MECHANISM FOR QoS IN IEEE802.11 WIRELESS NETWORKS Daqing Gu and Jinyun Zhang TR-2003-51 May 2003 Abstract In this paper,
MERL A MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORY http://www.merl.com EVALUATION OF EDCF MECHANISM FOR QoS IN IEEE802.11 WIRELESS NETWORKS Daqing Gu and Jinyun Zhang TR-2003-51 May 2003 Abstract In this paper,
MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users
 MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users Static Channel Allocation: Frequency Division Multiplexing
MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users Static Channel Allocation: Frequency Division Multiplexing
Media Access Control in Ad Hoc Networks
 Media Access Control in Ad Hoc Networks The Wireless Medium is a scarce precious resource. Furthermore, the access medium is broadcast in nature. It is necessary to share this resource efficiently and
Media Access Control in Ad Hoc Networks The Wireless Medium is a scarce precious resource. Furthermore, the access medium is broadcast in nature. It is necessary to share this resource efficiently and
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Improving the quality of H.264 video transmission using the Intra-Frame FEC over IEEE e networks
 Improving the quality of H.264 video transmission using the Intra-Frame FEC over IEEE 802.11e networks Seung-Seok Kang 1,1, Yejin Sohn 1, and Eunji Moon 1 1Department of Computer Science, Seoul Women s
Improving the quality of H.264 video transmission using the Intra-Frame FEC over IEEE 802.11e networks Seung-Seok Kang 1,1, Yejin Sohn 1, and Eunji Moon 1 1Department of Computer Science, Seoul Women s
Empirical Study of Mobility effect on IEEE MAC protocol for Mobile Ad- Hoc Networks
 Empirical Study of Mobility effect on IEEE 802.11 MAC protocol for Mobile Ad- Hoc Networks Mojtaba Razfar and Jane Dong mrazfar, jdong2@calstatela.edu Department of Electrical and computer Engineering
Empirical Study of Mobility effect on IEEE 802.11 MAC protocol for Mobile Ad- Hoc Networks Mojtaba Razfar and Jane Dong mrazfar, jdong2@calstatela.edu Department of Electrical and computer Engineering
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer. Computer Networks: Wireless LANs
 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) Primer 1 Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) The proliferation of laptop computers and other mobile devices (PDAs and cell phones)
Medium Access Control Sublayer
 Wireless (WLAN) Medium Access Control Sublayer Mahalingam Mississippi State University, MS October 20, 2014 Outline Medium Access Protocols Wireless (WLAN) 1 Medium Access Protocols ALOHA Slotted ALOHA
Wireless (WLAN) Medium Access Control Sublayer Mahalingam Mississippi State University, MS October 20, 2014 Outline Medium Access Protocols Wireless (WLAN) 1 Medium Access Protocols ALOHA Slotted ALOHA
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Reliable Multicast Scheme Based on Busy Signal in Wireless LANs
 Journal of Modern Science and Technology Vol.2 No.1 March 2014. Pp.18-25 Reliable Multicast Scheme Based on Busy Signal in Wireless LANs Sunmyeng For unicast transmissions, the IEEE 802.11 WLAN MAC (Medium
Journal of Modern Science and Technology Vol.2 No.1 March 2014. Pp.18-25 Reliable Multicast Scheme Based on Busy Signal in Wireless LANs Sunmyeng For unicast transmissions, the IEEE 802.11 WLAN MAC (Medium
IEEE s ESS Mesh Networking
 IEEE 802.11s ESS Mesh Networking Prof. Young-Bae Ko (youngko@ajou.ac.kr) Ubiquitous Networked Systems (UbiNeS) Lab (http://uns.ajou.ac.kr) KRnet 2006 Contents Introduction - Wireless Mesh Networks IEEE
IEEE 802.11s ESS Mesh Networking Prof. Young-Bae Ko (youngko@ajou.ac.kr) Ubiquitous Networked Systems (UbiNeS) Lab (http://uns.ajou.ac.kr) KRnet 2006 Contents Introduction - Wireless Mesh Networks IEEE
STUDY AND COMPARISION OF PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK
 STUDY AND COMPARISION OF PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK 1 Arpita Singh, 2 Navendu Nitin, 3 Neelesh Agrawal, 4 Arvind Kumar Jaiswal 1 PG student, SHIATS-DU,
STUDY AND COMPARISION OF PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK 1 Arpita Singh, 2 Navendu Nitin, 3 Neelesh Agrawal, 4 Arvind Kumar Jaiswal 1 PG student, SHIATS-DU,
Impulse Radio Ultra Wide Band Based Mobile Adhoc Network Routing Performance Analysis
 American Journal of Applied Sciences, 10 (4): 361-366, 2013 ISSN: 1546-9239 2013 Sreedhar and Venkatesh, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
American Journal of Applied Sciences, 10 (4): 361-366, 2013 ISSN: 1546-9239 2013 Sreedhar and Venkatesh, This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 3.0 license
Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router
 Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router Objective A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) utilizes radio communication to connect wireless devices to a LAN. An example is a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe.
Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router Objective A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) utilizes radio communication to connect wireless devices to a LAN. An example is a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe.
Advanced Computer Networks WLAN
 Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
Advanced Computer Networks 263 3501 00 WLAN Patrick Stuedi Spring Semester 2014 1 Oriana Riva, Department of Computer Science ETH Zürich Last week Outlook Medium Access COPE Short Range Wireless Networks:
IEEE Ad Hoc Networks: Performance Measurements
 IEEE 8.11 Ad Hoc Networks: Performance Measurements Giuseppe Anastasi Dept. of Information Engineering University of Pisa Via Diotisalvi - 561 Pisa, Italy Email: g.anastasi@iet.unipi.it Eleonora Borgia,
IEEE 8.11 Ad Hoc Networks: Performance Measurements Giuseppe Anastasi Dept. of Information Engineering University of Pisa Via Diotisalvi - 561 Pisa, Italy Email: g.anastasi@iet.unipi.it Eleonora Borgia,
Investigating MAC-layer Schemes to Promote Doze Mode in based WLANs
 Investigating MAC-layer Schemes to Promote Doze Mode in 802.11-based WLANs V. Baiamonte and C.-F. Chiasserini CERCOM - Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino Torino, Italy Email: baiamonte,chiasserini
Investigating MAC-layer Schemes to Promote Doze Mode in 802.11-based WLANs V. Baiamonte and C.-F. Chiasserini CERCOM - Dipartimento di Elettronica Politecnico di Torino Torino, Italy Email: baiamonte,chiasserini
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide
 Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
DVA-G3340S High-Speed 2.4 GHz Wireless ADSL VOIP Router. Manual
 DVA-G3340S High-Speed 2.4 GHz Wireless ADSL VOIP Router Manual Contents Package Contents...4 Introduction...5 Features...8 Using the Web Interface...9 Home > Wizard...9 Home > Wireless...10 Home > Wireless
DVA-G3340S High-Speed 2.4 GHz Wireless ADSL VOIP Router Manual Contents Package Contents...4 Introduction...5 Features...8 Using the Web Interface...9 Home > Wizard...9 Home > Wireless...10 Home > Wireless
An Implementation of Cross Layer Approach to Improve TCP Performance in MANET
 An Implementation of Cross Layer Approach to Improve TCP Performance in MANET 1 Rajat Sharma Pursuing M.tech(CSE) final year from USIT(GGSIPU), Dwarka, New Delhi E-mail address: rajatfit4it@gmail.com 2
An Implementation of Cross Layer Approach to Improve TCP Performance in MANET 1 Rajat Sharma Pursuing M.tech(CSE) final year from USIT(GGSIPU), Dwarka, New Delhi E-mail address: rajatfit4it@gmail.com 2
LP-2396K Outdoor 2.4GHz Wireless AP/CPE/Bridge
 User Manual LP-2396K Outdoor 2.4GHz Wireless AP/CPE/Bridge 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Product Introduction... 4 1.2 Package Content... 5 1.3 Product Features... 6 1.4 Application... 6
User Manual LP-2396K Outdoor 2.4GHz Wireless AP/CPE/Bridge 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Product Introduction... 4 1.2 Package Content... 5 1.3 Product Features... 6 1.4 Application... 6
Announcements : Wireless Networks Lecture 11: * Outline. Power Management. Page 1
 Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 11: 802.11* Please mail survey team information» Can include topic preferences now if you have them Submit project designs through blackboard Homework 2
Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 11: 802.11* Please mail survey team information» Can include topic preferences now if you have them Submit project designs through blackboard Homework 2
Adaptive Channel Occupation for Wireless Video Delivery
 Adaptive Channel Occupation for Wireless Video Delivery Ismail Djama and Toufik Ahmed CNRS-LaBRI Lab, University of Bordeaux-1. 351 Cours de la Libération, F-3345 Talence - France Tel: +33 5 4 35 47, Fax:
Adaptive Channel Occupation for Wireless Video Delivery Ismail Djama and Toufik Ahmed CNRS-LaBRI Lab, University of Bordeaux-1. 351 Cours de la Libération, F-3345 Talence - France Tel: +33 5 4 35 47, Fax:
ICE 1332/0715 Mobile Computing (Summer, 2008)
 ICE 1332/0715 Mobile Computing (Summer, 2008) Medium Access Control Prof. Chansu Yu http://academic.csuohio.edu/yuc/ Simplified Reference Model Application layer Transport layer Network layer Data link
ICE 1332/0715 Mobile Computing (Summer, 2008) Medium Access Control Prof. Chansu Yu http://academic.csuohio.edu/yuc/ Simplified Reference Model Application layer Transport layer Network layer Data link
UAMAC: Unidirectional-Link Aware MAC Protocol for Heterogeneous Ad Hoc Networks
 UAMAC: Unidirectional-Link Aware MAC Protocol for Heterogeneous Ad Hoc Networks Sung-Hee Lee, Jong-Mu Choi, and Young-Bae Ko College of Information and Communication, Ajou University, South Korea shlee@dmc.ajou.ac.kr,
UAMAC: Unidirectional-Link Aware MAC Protocol for Heterogeneous Ad Hoc Networks Sung-Hee Lee, Jong-Mu Choi, and Young-Bae Ko College of Information and Communication, Ajou University, South Korea shlee@dmc.ajou.ac.kr,
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
There are 10 questions in total. Please write your SID on each page.
 Name: SID: Department of EECS - University of California at Berkeley EECS122 - Introduction to Communication Networks - Spring 2005 to the Final: 5/20/2005 There are 10 questions in total. Please write
Name: SID: Department of EECS - University of California at Berkeley EECS122 - Introduction to Communication Networks - Spring 2005 to the Final: 5/20/2005 There are 10 questions in total. Please write
