Computer networks for the home
|
|
|
- Julia Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technical paper Computer networks for the home Computer networks for the home An overview This paper gives information about current and emerging technologies for networking computers in the home. It is worth noting that much of the information here would also be relevant to schools wishing to create a small network or add a small number of devices to their existing network. In recent years, there has been an upsurge in the use of computers and computer devices in the home and a rise in owning multiple devices. It is thus anticipated that the need for computer networks in the home is likely to increase. Creating a computer network at home provides many of the same advantages that a school or a small enterprise network would gain. Depending on the sort of network chosen, these gains can include: increased flexibility of internet access from various locations in the home internet access from two or more devices using a single internet access point. sharing peripheral devices such as printers sharing files between devices sharing applications from a main computer to other devices attached to the network using the network for home entertainment, such as gaming or accessing centrally stored music files. What types of home networks are there? There are many types of solutions to networking in the home. Some options include: wire your house or a room in your house with data cables install some form of wireless networking link your computers through the existing power cables link your computers through the existing telephone cable. How does a home network work? In general, the principle of a home network is no different to that of a network in an educational establishment. That is, two or more devices need to be able to interact with each other over a wired or wireless connection. The interaction between the devices could be simply to share the same internet connection or to share files and computer peripherals. Wireless networks There are a number of wireless (radio) technologies currently available. The family is widely promoted but a range of alternatives also exists. Wireless family many educational establishments now use equipment and this same technology could be used in the home. In brief, a wireless access card is needed for each device in order for it to be connected to the network. An 'access point' may also be needed if more than two devices want to share a peripheral or the same internet access. There are a number of different standards, which are covered in depth in Becta s Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) technical information sheet [ Becta page 1 of 10
2 Infrared networks this technology uses infrared light to maintain a connection between devices. It is a convenient technology as many devices, especially portable devices, have infrared ports built into them. There are two types of infrared networks: direct infrared and diffuse infrared. Direct networks Direct infrared networks need a clear line of sight between devices to make a connection. As most laptops already have infrared ports, a basic peer-to-peer network for such tasks as file sharing could be established by simply pointing the infrared devices towards each other. Diffuse networks Diffuse infrared technology operates by flooding an area with infrared light. The infrared signal bounces off the walls and ceiling so that a receiver in a device can pick up the signal regardless of the position of the device. This makes it more suitable than direct infrared for tasks where mobility of devices is an issue, and where multiple devices need to share the same network for tasks such as sharing peripherals and files. Unlike direct infrared, the data rates are contended and thus are shared between the number of devices needing simultaneous network access. Wireless touch screen a wireless touch screen is a wireless computer display screen that is sensitive to human touch allowing a user to interact with the computer by touching pictures or words on the screen. Recently this technology has been taken a stage further and now the touch screen can be carried from room to room while interacting with the main base PC via a wireless network link. This allows access to files stored on the home s main PC and the internet via the main PC when the wireless touch screen in located elsewhere in the home. Currently, wireless touch screens use Microsoft s technology and are marketed as Smart Displays. They are only available for use with Microsoft s XP operating system and only one touch screen can be used at a time with the base PC. It is important to note that currently if the smart display is in use, the base PC cannot be used independently. Personal area networks a personal area network (PAN) in a home networking context is the interconnection of devices within the range of an individual person and it typically uses wireless technology. (The use of short-range wireless technology is what distinguishes PANs from LANs.) For example, a person travelling with a laptop, a personal digital assistant (PDA), and a mobile phone could interconnect them via a short-range radio link. This kind of PAN could also be connected to the internet or other networks. There are several types of PAN solutions available one of the most widely available is based on the 'Bluetooth' specification. Bluetooth can be found built into many devices such as PDAs and laptops, but external adapters can also be purchased. It is possible to connect devices using a Bluetooth access point in a similar way to the technology, although data rates are much slower. HomeRF (home radio frequency) this technology doesn t require an access point. Each device needs a HomeRF card. This can either be attached via a USB cable or integrated into the device. Future development work on HomeRF products has now stopped and whilst it may be still be possible to buy these products in the UK it is unlikely that they will feature strongly in future home networks. Wired networks Wired networks obviously require some sort of wiring between devices. Those wishing to network devices at home using a wired network can either introduce new cables into their homes using technologies such as Ethernet or use their existing cabling or wiring as with technologies such as Powerline. Ethernet this technology is used extensively by large schools, companies and other institutions that network their computers. It currently offers the fastest data rates of any home networking solution and it is very reliable and robust. However Ethernet networks generally require a higher degree of Becta page 2 of 10
3 technical knowledge to install than the two other solutions covered below and new cabling is obviously more expensive than the alternative of using the existing wiring in the home. Powerline this technology uses the existing electricity cabling in the home to form the wiring for a network. Data is thus transported via the electricity cables to a computer device. The computer device could be installed with a Powerline Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) card and thus it could interface directly with the electricity cables, or the computer device could be a Powerline switch or hub. As most rooms in a typical house have one or more power outlets, a network can easily be set up with one or more devices in each room if necessary. The data transfer rates for the latest Powerline standard (PowerPlug 1.0) are now comparable with networks such as b, and Powerline equipment is becoming less expensive and more widely available. Phoneline the concept of a Phoneline network (often referred to as HomePNA) is similar to that of a Powerline network. The existing wiring inside the home (in this case twisted copper telephone cable) is used to form the wiring of the network. As many homes have more than one telephone socket to service a single telephone line, a network can be formed. Where only a single socket is available, extra telephone wiring would have to be installed. Phoneline technology allows voice calls and the transportation of data from one computer to the next to be made simultaneously. There is some concern about this type of technology when it is used with an Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) as the internet access technology. The concern is about interference between the Phoneline signal and the ADSL signal. Phoneline equipment is still available in the UK, and it may still be a viable home networking option provided access to the internet is not via ADSL. Network interface cards For all of the technologies outlined above a network interface card (NIC) or a network adapter will be needed for each device so that the interface to the network can be established and maintained. In some cases this NIC or network adapter may be built in to the device already (such as with Bluetooth enabled devices) but in others a card or adapter for each networked device will need to be purchased. Table 1 typical costs for home networking technologies Typical costs Ethernet NIC 15 Ethernet category 5 cabling 2 per metre Powerline PCI card 120; switch 250 Phoneline 60 for a two-device starter kit products NIC 60 Access points PANs Bluetooth access points Bluetooth adapters 50 Infrared Direct infrared adapters 45 Wireless touch screen 1,000 Becta page 3 of 10
4 Accessing the internet via a home network While many people may want to network the devices in their home for activities such as file sharing, others may simply wish to share an internet connection between multiple devices. There are two main ways to achieve this. It is possible to use one of the home s computers to act as a proxy server for all other devices that want access to the internet. Many current computer systems have the functionality to allow a computer to act as a proxy server for all other devices via application software functionality. While this is a cost-effective solution, it does mean that the computer acting as a proxy server has to be stationary and switched on for other devices to be able to use the internet. A hardware router could be installed. This router would be connected to the internet access point and then all other devices would be connected to the router. In a typical home network, the router would have to have proxy server functionality as well so that it could identify the correct individual devices on the network to send the incoming data to. There are many such routers on the market today and both wired (for example, Linksys Etherfast Router) and wireless (Apple s Airport Extreme and Cisco s Aironet) versions are available. Many of the routers on the market are multi-functioned, for example, many wireless routers have ADSL modems built in and are also wireless access points. It is worth noting that most routers connect to the internet access point via an Ethernet connection and not via the universal serial bus (USB) port typically used by ADSL modems. If simultaneous access to the internet is needed, then a high-speed access technology such as ADSL would be worth considering. For example, with multiple devices simultaneously accessing the internet via a modem connected to the public switched telephone network (PSTN), the 56Kbps would, in theory, become shared between the devices. There may also be a need to clarify whether the contract with the internet service provider (ISP) allows multiple devices to access to the internet. For both solutions, the same considerations would have to be given to the NICs that would be needed, and whether connecting to the hardware router or proxy server would be via a wireless or wired connection. What content/applications can home networking deliver? There are two main considerations that need some advanced planning when referring to delivering content and applications across home networks. Firstly, whether it is possible to share the content or applications across multiple devices or whether the content and applications are limited to a single device (as in the case of Smart Displays). The second consideration is whether the data rates for a particular networking technology are suitable for the sort of content and applications that are to be shared. Table 2 maximum theoretical data rates for home networking technologies Related standard Maximum theoretical data rates Ethernet IEEE Mbps (10baseT) 100Mbps (100baseT) Powerline HomePlug (version 1.0) 14Mbps (NB earlier competing standards had significantly slower data rates) Becta page 4 of 10
5 Phoneline HomePNA version 1.1 1Mbps HomePNA version Mbps products IEEE b 11Mbps IEEE a 54Mbps PANs Bluetooth v Kbps Infrared IrDA - version 1.1 (Infrared Data Association) 9.6Kbps 4Mbps Wireless touch screen Smart Display (uses IEEE b) 11Mbps The advantages and disadvantages of different home networking technologies While some of the advantages and disadvantages between home networking technologies will already be apparent, some will only become apparent when thought is given to such issues as the use of the planned network, the number of devices in the network, and the available funds. These issues are discussed later in this paper. Below is a table that sets out some of the advantages and disadvantages of the technologies already discussed. Table 3 advantages and disadvantages of home networking technologies Ethernet Powerline Advantages Disadvantages Potential best usage Fast data rates Very reliable There is a great deal of technical support and information available Robust Uses existing electrical wiring Every room of a typical house has several electrical outlets Easy to install New cables need to be fitted More expensive to install than other networking technologies Requires a higher degree of technical knowledge to install Current number of suppliers are limited Not as fast as Ethernet Excellent for shared internet access, and where high speed file and peripheral sharing are needed and where mobility is not required Good for shared internet access, file sharing and peripheral sharing and where mobility is not required Becta page 5 of 10
6 Phoneline Inexpensive Quality of service is built into the network Reliable Operates at a constant 10Mbps, even when the phone is in use Easy to install family Many devices have NICs built in PANs Infrared Wireless touch screen Networks between devices can be formed dynamically Devices can be portable and still be connected to the network Many devices now shipped with short-range wireless as standard Easy to install Many devices shipped with infrared Useful for PANs Security better than some other wireless technologies Work from anywhere in the home via a portable screen Typically lighter than carrying a laptop Damage whilst moving around the home is limited to the screen and not to other hardware Extra phone line extensions may be needed if multiple devices are required on a network Need a phone jack close to each computer to avoid additional cabling Not as fast as Fast Ethernet (100Mbps) Possible interference issues with internet access technology Not as fast as Fast Ethernet May be interference issues with other wireless devices Signal may not be able to carry through several thick walls in a house Some products not backwards compatible Limited range Limited data rates Compatibility issues between different standards and occasionally between devices using the same standard Limited data rates in many products Limited range in many products Devices have to be located in same room and can be limited by line of sight Data rates vary significantly between infrared units At present only one touch screen can access the main PC at any one time If touch screen in use, the main PC cannot be used independently Currently similar price to b enabled entry level laptop Good for shared internet access, file sharing and peripheral sharing and where mobility is not required Good for laptops, desktops and handheld connected organisers inside and outside home where mobility is required Good for shared internet access Good for creating small personal networks between devices in an adhoc manner or networks where power usage needs to be kept to a minimum Direct infrared: good for ad-hoc networks where line of sight and fast data rates are not an issue Diffuse infrared: good for networks where a single room is used Good for gaining access to the main PC whilst on the move and where simultaneous access to multiple network devices is not required Becta page 6 of 10
7 Where is home networking used? It is not yet particularly common for computer networks to be installed in the home although the technologies that are used in home networking are the same or very similar to those used by small businesses in the commercial sector. According to Young People and ICT 2002 (a survey published by Becta on behalf of the DfES), 81per cent of households surveyed had access to a computer in the home (an increase from 78 per cent in 2001). Of the 68 per cent of households that owned computers, 32 per cent had two or more. In addition, access to portable devices such as laptops and palmtops steadily increased. The above figures show that access to a computer or even multiple computers is on the increase. Thus, it is possible to identify several scenarios where networking devices in the home may be useful. 1. It is presumed that the desire to access the internet from a single mobile device from various locations in the house will become increasingly common. Several of the solutions discussed above would enable this to happen. 2. With the use of the internet on the increase, and 44 per cent of those surveyed (Young People and ICT 2002) responding that a computer was located in a non-communal room of the house, it is presumed that access to the internet from multiple devices will increase and thus a way of simultaneously connecting multiple devices to the internet (as discussed above) will be needed. 3. It is also possible to buy hardware that allows simultaneous connection to the internet via advanced set-top boxes acting as home gateways for multiple devices such as televisions, computers and gaming consoles. These internet connections are likely to be realised by access technologies that allow fast data rates, such as broadband via twisted copper, cable or satellite. 4. Sharing and exchanging information from one device to the next or sharing of peripheral devices such as printers. 5. According to the previously mentioned survey, the majority of young people used a computer to play games, and a high percentage used a computer for listening to music. A home network of multimedia and gaming devices would allow interactive gaming between devices in the home and the sharing of music files. Issues about buying and installing home networking equipment Many issues need to be considered when buying equipment to provide a home network. Use of the network There are many different ways of using a network. It may be that a network is only needed occasionally to swap files from one device to another. Alternatively, the devices on the network may need to share the applications that are based on the main home computer. While a cheaper network solution with a slower data rate may be perfectly adequate for the first scenario, it is unlikely that it would be the best for the latter. Number of networked devices Giving consideration to the number of devices that need to be networked is crucial. If a home has many devices located in different rooms, then technologies such as Ethernet may well be inappropriate or costly as new cables will have to be laid and safely secured. Alternatively, if all the devices are in one room it may be practical and cost effective to use an Ethernet network. Becta page 7 of 10
8 Further, attention should be paid to the possibility of adding devices to the network later. This would be relatively easy with a Powerline network for example, but it might be a problem if a Phoneline network was chosen and the network needed to be extended to a room in the house that had no telephone point. Layout of the home All networking equipment has a limited range, although when using such technologies such as Ethernet in the home this is unlikely to be an issue technologies also have a considerable range (typically metres) but the data transfer rates lessen the further the networked device is placed away from an access point. For many networking technologies the effective range is limited and thus the home network may be limited by the distance that devices are positioned away from each other. Wireless technologies can suffer from interference from other home appliances or from the walls between devices being too thick for an effective signal to penetrate. If Phoneline technologies are used for a home network together with an ADSL internet connection, there is some evidence to show that there may be some interference issues between the Phoneline technology and the ADSL signal. Data rates The data transfer rates for the networking technologies described differ considerably. If a high number of devices in the home needed to share a network connection at the same time for activities such as streaming video to each device, then the data rate of a network may be an issue. Alternatively, if a number of devices in the home were being networked together to share a 512Kbps ADSL broadband connection, then the issue of data rates may be diminished as many of the networking technologies described above send data at a substantially higher data rate than 512Kbps. Available expertise Some of the networking technologies described above generally need a higher degree of technical expertise to install and maintain than other technologies. For example, an Ethernet network generally demands a higher degree of technical expertise to install and maintain than a Powerline network. Costs Implementation costs for the networks described vary considerably. Attention should be paid to what equipment is already available in the home. Questions worth considering include: How much new wiring will be needed if a wired network is chosen? Are there enough convenient power points for a Powerline network? And to plug in devices to the mains supply? Are there enough telephone points working from the same telephone number if a Phoneline network is being considered? Does any of the equipment already have a NIC such as a WLAN card, or will cards need to be purchased separately? Is the equipment widely available in the UK or will some of it need to be bought abroad? If equipment is bought from abroad is it compatible with UK equipment. Is the standard associated with the network equipment under consideration the latest version? If not it could be that the data rates, for example, are inferior to the latest version. If Phoneline or Powerline technologies are chosen, is the respective wiring in the home in good condition? Becta page 8 of 10
9 Line of sight Before line-of-sight technologies such as direct infrared are chosen for a home network, careful consideration should be given to whether a clear line of sight will always be available. Interoperability Many of the technologies mentioned in this document are interoperable, although it is worth considering if further technical expertise or equipment is needed to achieve this. In some cases, standards within technologies are not interoperable. For example, b network equipment is currently not interoperable with a wireless network equipment. Some suppliers are starting to design and supply home network gateways. These will allow computers, televisions, PDAs and other devices to gain access to the internet via one access point attached to the gateway. Whilst this will not solve all networking interoperability issues, it does mean that all devices attached to the gateway should be enabled to gain internet access simultaneously. Standards relating to home networking Ethernet [ Phoneline [ b/a/g [ Powerline [ Infrared [ Bluetooth [ Home RF (standard no longer available) Further sources of information Becta Wireless Local Area Networks technical paper [ [ Young People and ICT 2002 [ Reviews Phoneline [ Becta page 9 of 10
10 Powerline [ Smart displays [ Wireless networking [ Technical Ethernet [ Phoneline [ [ Powerline [ Smart displays [ [ Infrared [ Bluetooth (RTF document) [ HomeRF [ [ Network implementation [ sing/productdoc/en/hnw_requirements.asp] Becta page 10 of 10
Home and Wireless Networks 7
 Contents Contents= 1 2 3 Home and Wireless Networks 7 What is a Home Network? 8 Wired Ethernet 10 Phoneline Network 11 Powerline Network 12 Wireless Home Networking 13 How Networks Operate 14 Peer Group
Contents Contents= 1 2 3 Home and Wireless Networks 7 What is a Home Network? 8 Wired Ethernet 10 Phoneline Network 11 Powerline Network 12 Wireless Home Networking 13 How Networks Operate 14 Peer Group
Digital Entertainment. Networking Made Easy
 Digital Entertainment 2003 by TiVo Inc. Reproduction in whole or in part without written permission is prohibited. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. TiVo, TiVo Central, and TiVolution are registered
Digital Entertainment 2003 by TiVo Inc. Reproduction in whole or in part without written permission is prohibited. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. TiVo, TiVo Central, and TiVolution are registered
It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
 1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
1 Communications It is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers. Numerous applications depend on communication systems: E-mail Instant messaging (IM) Internet
HomePNA Overview. Home network standards. Examples. HomePNA Overview. HomePNA. Reference:
 Home network standards HomePNA HomeRF HomePlug HAVi Reference: www.homepna.com/ www.homepna.org/ electronics.howstuffworks.com/phone-network.htm Automated Network Technology & Applications: Home Network
Home network standards HomePNA HomeRF HomePlug HAVi Reference: www.homepna.com/ www.homepna.org/ electronics.howstuffworks.com/phone-network.htm Automated Network Technology & Applications: Home Network
dlan Highspeed Starter Kit Ethernet/ Ethernet
 2 Highspeed HomePlug Ethernet adapters for 85Mbps PC networking & Internet access extension over your existing household power circuit dlan* Highspeed Starter Kit for 85Mbps PC networking & Internet access
2 Highspeed HomePlug Ethernet adapters for 85Mbps PC networking & Internet access extension over your existing household power circuit dlan* Highspeed Starter Kit for 85Mbps PC networking & Internet access
Discovering Computers Chapter 9 Communications and Networks
 Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Discovering Computers 2009 Chapter 9 Communications and Networks Chapter 9 Objectives Discuss the components required for successful communications Identify various sending and receiving devices Describe
Introduction. State of the Market
 Introduction State of the Market The Digital Age of Consumer Electronics 1001010100010100100000000 1010001010001010101001011 Digital technology brings 0101111010001001010100101 Higher accuracy 1100010111110101011111000
Introduction State of the Market The Digital Age of Consumer Electronics 1001010100010100100000000 1010001010001010101001011 Digital technology brings 0101111010001001010100101 Higher accuracy 1100010111110101011111000
Wireless Home Networking Chapter 1 Outline
 Wireless Home Networking Chapter 1 Outline Wireless Home Networking: The By Charles Severance and Richard Wiggins O Reilly, 2003 Chapter 1: Wireless Networking in Your Home Is Wireless Home Networking
Wireless Home Networking Chapter 1 Outline Wireless Home Networking: The By Charles Severance and Richard Wiggins O Reilly, 2003 Chapter 1: Wireless Networking in Your Home Is Wireless Home Networking
The Connected Home Raymond Lee Dy Director, Technology Direction
 The Connected Home Raymond Lee Dy Director, Technology Direction 26 November 2002 Outline Overall Trends Home Networking Technologies Digital Home Platforms End-to-End Technology Singapore Landscape Conclusion
The Connected Home Raymond Lee Dy Director, Technology Direction 26 November 2002 Outline Overall Trends Home Networking Technologies Digital Home Platforms End-to-End Technology Singapore Landscape Conclusion
Virtual private networks
 Technical papers Virtual private networks Virtual private networks Virtual private networks (VPNs) offer low-cost, secure, dynamic access to private networks. Such access would otherwise only be possible
Technical papers Virtual private networks Virtual private networks Virtual private networks (VPNs) offer low-cost, secure, dynamic access to private networks. Such access would otherwise only be possible
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks
 Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Wireless Personal Area Networks & Wide Area Networks Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline In the lecture we will: Look at PAN s in more detail Look at example networks
Communications and Networks
 Information Technology Skills (DUT 122) CHAPTER 6: Communications and Networks Miss Wan Nor Ashiqin Wan Ali School of Human Development and Technocommunication Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose of
Information Technology Skills (DUT 122) CHAPTER 6: Communications and Networks Miss Wan Nor Ashiqin Wan Ali School of Human Development and Technocommunication Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose of
Networking. Prof. Abdul Hameed
 Networking Prof. Abdul Hameed http://informationtechnology.pk http://informationtechnology.pk 0 Chapter Topics Networking Fundamentals Network Architectures and Components Connecting to the Internet Installing
Networking Prof. Abdul Hameed http://informationtechnology.pk http://informationtechnology.pk 0 Chapter Topics Networking Fundamentals Network Architectures and Components Connecting to the Internet Installing
Computer Overview. A computer item you can physically see or touch. A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate.
 Hardware Computer Overview A computer item you can physically see or touch. Software A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate. Information Technology (IT) The broad subject related
Hardware Computer Overview A computer item you can physically see or touch. Software A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate. Information Technology (IT) The broad subject related
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
November, Exploring Home Networking
 November, 2000 Exploring Home Networking EXPLORING HOME NETWORKING PAGE 1 Executive Summary Just as television has revolutionized entertainment and news during the last fifty years, today the Internet
November, 2000 Exploring Home Networking EXPLORING HOME NETWORKING PAGE 1 Executive Summary Just as television has revolutionized entertainment and news during the last fifty years, today the Internet
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
VISUAL SUMMARY COMMUNICATION CHANNELS COMMUNICATIONS. Communications and Networks
 Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Communications and Networks COMMUNICATIONS COMMUNICATION CHANNELS Communications is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
Rev.Confirming Pages VISUAL SUMMARY Communications and Networks COMMUNICATIONS COMMUNICATION CHANNELS Communications is the process of sharing data, programs, and information between two or more computers.
Introduction to. Computer Networking. Issued by. National Centre for Technology in Education (NCTE)
 Introduction to Computer Networking Issued by National Centre for Technology in Education (NCTE) 1 1.0 Introduction This document includes information under the following main headings: Introduction to
Introduction to Computer Networking Issued by National Centre for Technology in Education (NCTE) 1 1.0 Introduction This document includes information under the following main headings: Introduction to
Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks 9.1 Uses of a network Networks are used in many situations. We can see networks in places like offices, airports and factories. In fact we use networks in many situations
Chapter 9 Introduction to Networks 9.1 Uses of a network Networks are used in many situations. We can see networks in places like offices, airports and factories. In fact we use networks in many situations
Understanding Routers, Switches, and Network Hardware
 Understanding Routers, Switches, and Network Hardware Rather than start off with a glossary of networking terms and in the process slam you with a technical terms with no easy point of reference let s
Understanding Routers, Switches, and Network Hardware Rather than start off with a glossary of networking terms and in the process slam you with a technical terms with no easy point of reference let s
Home Networking. A home network generally conforms to one of the following configurations
 Home Networking A home network generally conforms to one of the following configurations A stand-alone computer connected to the Internet. A peer-to-peer network containing two or more computers with no
Home Networking A home network generally conforms to one of the following configurations A stand-alone computer connected to the Internet. A peer-to-peer network containing two or more computers with no
CSC Introduction to Computers and Their Applications
 CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 6 An Introduction to Networks Communication Systems Networks can be classified in many ways; as a network user, you ll want to keep in
CSC 170 - Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture 6 An Introduction to Networks Communication Systems Networks can be classified in many ways; as a network user, you ll want to keep in
The Features and Uses of Computer Networking. Unit 11 Task 1
 The Features and Uses of Computer Networking Unit 11 Task 1 Features Office Network Peer to peer A peer to peer network is mostly used in homes or small businesses. The network consists of two or more
The Features and Uses of Computer Networking Unit 11 Task 1 Features Office Network Peer to peer A peer to peer network is mostly used in homes or small businesses. The network consists of two or more
Technology in Action 12/11/2014. Networking Fundamentals. Chapter Topics. Networking Fundamentals (cont.) Networking Fundamentals (cont.
 Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Technology in Action Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices Eleventh Edition Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright
Technology in Action Alan Evans Kendall Martin Mary Anne Poatsy Technology in Action Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices Eleventh Edition Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright
Networks. Computer Technology
 Networks Computer Technology Network Two or more computers and other devices (printers or scanners) that are connected, for the purpose of sharing data and programs Advantages of Networks Communication
Networks Computer Technology Network Two or more computers and other devices (printers or scanners) that are connected, for the purpose of sharing data and programs Advantages of Networks Communication
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
Objectives Overview. Chapter 9 Networks and Communications. Discovering Computers Instructor: Imran Khalil MSc-IT 1 st semester Fall 2016
 Chapter 9 Networks and Communications Instructor: Imran Khalil MSc-IT 1 st semester Fall 2016 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose
Chapter 9 Networks and Communications Instructor: Imran Khalil MSc-IT 1 st semester Fall 2016 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Objectives Overview Discuss the purpose
Getting to Know Your Network. Internet Speeds and Services
 Internet Speeds and Services The Internet is an integral part of our Extension Offices. Its uses are seemingly endless from updating travel, to loading 4-H registration forms on the county website, and
Internet Speeds and Services The Internet is an integral part of our Extension Offices. Its uses are seemingly endless from updating travel, to loading 4-H registration forms on the county website, and
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs
 Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 12. Network Organization and Architecture
 Chapter 12 Network Organization and Architecture Chapter 12 Objectives Learn the basic physical components of networks. Become familiar with routing protocols. 2 Computer networks are often classified
Chapter 12 Network Organization and Architecture Chapter 12 Objectives Learn the basic physical components of networks. Become familiar with routing protocols. 2 Computer networks are often classified
ICT Theory Revision Presentation - Networks and the effects of using them 4.1 Networks. Chapter 4: Networks and the effects of using them
 Understand how a router works and its purpose Understand the use of other common network devices, including: network interface cards, hubs, bridges, switches, modems Understand the use of WiFi and Bluetooth
Understand how a router works and its purpose Understand the use of other common network devices, including: network interface cards, hubs, bridges, switches, modems Understand the use of WiFi and Bluetooth
Computer Networks. Cables Radio signals (wireless/wifi) Telephone lines Satellite links (Long distance)
 COMPUTER NETWORKS Computer Networks A network is two or more computers connected together to allow them to share information and resources. Network connections are created by Cables Radio signals (wireless/wifi)
COMPUTER NETWORKS Computer Networks A network is two or more computers connected together to allow them to share information and resources. Network connections are created by Cables Radio signals (wireless/wifi)
Unit title: Mobile Technology: Device Connectivity (SCQF level 5) Outcome 1
 1 Outcome 1 A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current Wi-Fi methods. A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current GSM mobile telephony methods. A
1 Outcome 1 A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current Wi-Fi methods. A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current GSM mobile telephony methods. A
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
How to get the Internet to every room of your home
 How to get the Internet to every room of your home Can t get your wireless signal all over your house? Wireless too slow? Then read on! Wireless networking is all well and good if you are close to your
How to get the Internet to every room of your home Can t get your wireless signal all over your house? Wireless too slow? Then read on! Wireless networking is all well and good if you are close to your
COMPUTER SKILLS COMP101
 COMPUTER SKILLS COMP101 Chapter 4 Introduction to Computer Networks Definitions and Terminologies Computer Network A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources
COMPUTER SKILLS COMP101 Chapter 4 Introduction to Computer Networks Definitions and Terminologies Computer Network A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources
Ethernet Powerline Adaptor. User Manual
 Ethernet Powerline Adaptor User Manual Copyright The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, stored, transcribed in an information retrieval system, translated into
Ethernet Powerline Adaptor User Manual Copyright The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, stored, transcribed in an information retrieval system, translated into
Chapter 15: Advanced Networks
 Chapter 15: Advanced Networks IT Essentials: PC Hardware and Software v4.1 1 Chapter 15 Objectives 15.1 Identify potential safety hazards and implement proper safety procedures related to networks 15.2
Chapter 15: Advanced Networks IT Essentials: PC Hardware and Software v4.1 1 Chapter 15 Objectives 15.1 Identify potential safety hazards and implement proper safety procedures related to networks 15.2
A Guide to Routers. Connectivity Type. ADSL (Telephone Type)
 A Guide to Routers Besides enabling wireless internet connections, routers also keep sensitive data private by safeguarding networks. Wireless routers are increasingly common, even in public spaces. This
A Guide to Routers Besides enabling wireless internet connections, routers also keep sensitive data private by safeguarding networks. Wireless routers are increasingly common, even in public spaces. This
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18. The Internet. What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback
 ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
ECS 15; Lectures 17 and 18 The Internet What is the internet, and how does it work? TA feedback Python -- Run your code!! Term paper: Start a paragraph with the point of the paragraph, not in modern times
Introduction to HomePlug 1.0 & AV
 Introduction to HomePlug 1.0 & AV Networking-over-mains uses the existing mains power wiring in your home to carry Ethernet signals. The technology for carrying signals through the mains has been around,
Introduction to HomePlug 1.0 & AV Networking-over-mains uses the existing mains power wiring in your home to carry Ethernet signals. The technology for carrying signals through the mains has been around,
Simply powerful. Wireless freedom for everyday people.
 Simply powerful. Wireless freedom for everyday people. LINKSYS HOME NETWORKING SOLUTIONS Wireless freedom for every home Choose the wireless networking product to suit your needs Introducing Cisco s wireless
Simply powerful. Wireless freedom for everyday people. LINKSYS HOME NETWORKING SOLUTIONS Wireless freedom for every home Choose the wireless networking product to suit your needs Introducing Cisco s wireless
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 1 Introduction to Wireless Communications Jorge Olenewa jolenewa@georgebrown.ca Office: E425 ext. 6809 Objectives Explain how the major wireless technologies
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 1 Introduction to Wireless Communications Jorge Olenewa jolenewa@georgebrown.ca Office: E425 ext. 6809 Objectives Explain how the major wireless technologies
Chapter 8 Networking and Digital Communication
 Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e George Beekman Michael J. Quinn Networking and Digital Communication 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 1 A computer network is any system of two or more computers that are
Tomorrow s Technology and You 8/e George Beekman Michael J. Quinn Networking and Digital Communication 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 1 A computer network is any system of two or more computers that are
Chapter 8 Communications and Networks
 Chapter 8 Communications and Networks Today Group work Review the 6 parts of the IT model Communications and networks Discussion Think about it Imagine a traveling business person. This person s company
Chapter 8 Communications and Networks Today Group work Review the 6 parts of the IT model Communications and networks Discussion Think about it Imagine a traveling business person. This person s company
Getting the most out of your WiFi at home
 Getting the most out of your WiFi at home A Guide by Ripplecom Enjoying your WiFi service To ensure our customers enjoy the best possible performance from their newly installed service, we ve put together
Getting the most out of your WiFi at home A Guide by Ripplecom Enjoying your WiFi service To ensure our customers enjoy the best possible performance from their newly installed service, we ve put together
Getting the most from your WiFi modem
 Getting the most from your WiFi modem A Brief Guide to optimising the WiFi experience in your home or business premises Post- Install Tips In order to enable customers to get the best performance from
Getting the most from your WiFi modem A Brief Guide to optimising the WiFi experience in your home or business premises Post- Install Tips In order to enable customers to get the best performance from
CAO 152C. Intermediate Windows Week 5
 CAO 152C Intermediate Windows Week 5 From Thursday 2 Homework: users how d you do? Any left-over questions? Set File and Folder Sharing To share a file or folder means to make it accessible by users other
CAO 152C Intermediate Windows Week 5 From Thursday 2 Homework: users how d you do? Any left-over questions? Set File and Folder Sharing To share a file or folder means to make it accessible by users other
Learning Objectives. Introduction. Advantages of WLAN. Information Technology. Mobile Computing. Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.
 Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
Information Technology Mobile Computing Module: Wireless Local Area Network: IEEE 802.11 Learning Objectives Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network Advantages of WLAN Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11 standards
16/06/56. Communications and Networks. Communications and Networks. Communications and Networks
 Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
Discuss connectivity, the wireless revolution, and communication systems. Describe physical and wireless communications channels. Discuss connection devices and services, including dial-up, DSL, cable,
(Network Programming) Basic Networking Hardware
 EEE 448 Computer Networks with (Network Programming) Basic Networking Hardware Lecture #2 Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Çukurova University Agenda What is a network device? Network Media
EEE 448 Computer Networks with (Network Programming) Basic Networking Hardware Lecture #2 Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Çukurova University Agenda What is a network device? Network Media
Twelfth Edition. Chapter 8: Wired and Wireless Communication. Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1
 Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 8: Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012
Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 8: Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Wired and Wireless Communication Copyright 2012
Networks. Unit 5 Terminology Study Assignment Review Computer Technology. S3 Obj 2 1-3
 Networks Unit 5 Terminology Study Assignment Review Computer Technology S3 Obj 2 1-3 Network A computer network, or simply a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware components interconnected
Networks Unit 5 Terminology Study Assignment Review Computer Technology S3 Obj 2 1-3 Network A computer network, or simply a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware components interconnected
MOTHER TERESA SR. SEC. CO-ED SCHOOL. CLASS VIII (Comp Sc.) CHAPTER-1 : ABOUT NETWORKING
 Q1. Multiple Choice Questions MOTHER TERESA SR. SEC. CO-ED SCHOOL 1) WLAN stands for : CLASS VIII (Comp Sc.) 2017-18 CHAPTER-1 : ABOUT NETWORKING a) Wide Local Area Network b) World Local Area Network
Q1. Multiple Choice Questions MOTHER TERESA SR. SEC. CO-ED SCHOOL 1) WLAN stands for : CLASS VIII (Comp Sc.) 2017-18 CHAPTER-1 : ABOUT NETWORKING a) Wide Local Area Network b) World Local Area Network
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications. Communication and Networks. What will we learn?
 Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
Lecture #25: Networks and Communications Communication and Networks What will we learn? How a communications system works What a network is What networks used for What network operating systems do What
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies. Networks
 ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
ITP 140 Mobile Applications Technologies Networks A First Look Under the Hood 2 3 Communication Channels Mediums for transporting data from one system to another Physical Twisted Pair (CAT-3, CAT-5/6)
Home Networking. Kaikham Onedamdy Rachel Krajc Kareem Sumner
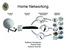 Home Networking Kaikham Onedamdy Rachel Krajc Kareem Sumner Agenda Introduction Home Networking Trends Methodology Design Goals Assumptions Needs Analysis Geographic Scope Network Users Proposed Solution
Home Networking Kaikham Onedamdy Rachel Krajc Kareem Sumner Agenda Introduction Home Networking Trends Methodology Design Goals Assumptions Needs Analysis Geographic Scope Network Users Proposed Solution
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
The ULTIMATE GUIDE. to Buying Networking Equipment
 The ULTIMATE GUIDE to Buying Networking Equipment 1 Networks allow people to share information, resources and devices. Built with a combination of computer hardware and software,networks vary in their
The ULTIMATE GUIDE to Buying Networking Equipment 1 Networks allow people to share information, resources and devices. Built with a combination of computer hardware and software,networks vary in their
Installation Guide for Models 1000 and 1000W
 Installation Guide for Models 1000 and 1000W Notice to Users 2002 2Wire, Inc. All rights reserved. This manual in whole or in part, may not be reproduced, translated, or reduced to any machine-readable
Installation Guide for Models 1000 and 1000W Notice to Users 2002 2Wire, Inc. All rights reserved. This manual in whole or in part, may not be reproduced, translated, or reduced to any machine-readable
Home Networks. Principles, Applications and Desirability
 Home Networks Principles, Applications and Desirability Index 1. Introduction 2. Why the demand? 3. Technologies 4. Cat5e UTP structured wiring 5. Modular concept 6. Typical applications 7. Technical information
Home Networks Principles, Applications and Desirability Index 1. Introduction 2. Why the demand? 3. Technologies 4. Cat5e UTP structured wiring 5. Modular concept 6. Typical applications 7. Technical information
Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT
 Network Basics Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT E-mail :Agha.m@mcit.gov.af Cell:0700148122 After this lesson,you will be able to : Define
Network Basics Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT E-mail :Agha.m@mcit.gov.af Cell:0700148122 After this lesson,you will be able to : Define
Not long ago, home local area networks were proof of their owner s geekhood. They were very
 03 54473X Ch01.qxd 12/24/03 8:35 AM Page 3 Chapter 1 What Is a LAN? Not long ago, home local area networks were proof of their owner s geekhood. They were very expensive, cantankerous, difficult to set
03 54473X Ch01.qxd 12/24/03 8:35 AM Page 3 Chapter 1 What Is a LAN? Not long ago, home local area networks were proof of their owner s geekhood. They were very expensive, cantankerous, difficult to set
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks. Computer Concepts 2013
 Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
Computer networks 2013
 Chapter 4 EXERCISE 1 1 Describe what is meant by each of the following: a Router b Bridge c Proxy server Answers: see the Glossary. 2 Many small businesses have computer networks. a List three advantages
Chapter 4 EXERCISE 1 1 Describe what is meant by each of the following: a Router b Bridge c Proxy server Answers: see the Glossary. 2 Many small businesses have computer networks. a List three advantages
COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS
 COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS Data Communications Data communications describes a process in which one computer transfers data, instructions, and information to another computer. The basic model for data
COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKS Data Communications Data communications describes a process in which one computer transfers data, instructions, and information to another computer. The basic model for data
Get the most from your Broadband
 Get the most from your Broadband June 2016 Fleur Telecom How to Get the Most from your Broadband 1. The Technical Bit: Router Basics Your router is the glue that holds your home network together. It connects
Get the most from your Broadband June 2016 Fleur Telecom How to Get the Most from your Broadband 1. The Technical Bit: Router Basics Your router is the glue that holds your home network together. It connects
How to successfully set up your service.
 CenturyLink Business VoIP How to successfully set up your service. Onboarding process for Business VoIP This guide will review the steps needed to get you up and running. Welcome to CenturyLink Business
CenturyLink Business VoIP How to successfully set up your service. Onboarding process for Business VoIP This guide will review the steps needed to get you up and running. Welcome to CenturyLink Business
CONTENTS IN DETAIL INTRODUCTION
 CONTENTS IN DETAIL ACKNOWLEDGMENTS xiii INTRODUCTION xv 1 HOW A NETWORK WILL IMPROVE YOUR LIFE 1 What s a Network?... 2 Sneakernet... 3 Data Networks and What You Can Do with Them... 4 File Sharing...
CONTENTS IN DETAIL ACKNOWLEDGMENTS xiii INTRODUCTION xv 1 HOW A NETWORK WILL IMPROVE YOUR LIFE 1 What s a Network?... 2 Sneakernet... 3 Data Networks and What You Can Do with Them... 4 File Sharing...
Module 11. OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards
 Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
Module 11 OSI Model, Network Devices, and Network Standards Objectives 1. Networking A.Differentiate between layers of the OSI model B.2.9 Compare network devices C.Compare network standards D.2.7 Compare
AV2000 TL-PA9020P KIT. 2-port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit. Highlights
 AV2000 2-port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit Highlights HomePlug AV2 Provides ultra-fast powerline transfer speeds of up to 1 2X2 MIMO with Beamforming Establishes multiple simultaneous connections
AV2000 2-port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit Highlights HomePlug AV2 Provides ultra-fast powerline transfer speeds of up to 1 2X2 MIMO with Beamforming Establishes multiple simultaneous connections
Lesson 1: Network Communications
 Lesson 1: Network Communications This lesson introduces the basic building blocks of network communications and some of the structures used to construct data networks. There are many different kinds of
Lesson 1: Network Communications This lesson introduces the basic building blocks of network communications and some of the structures used to construct data networks. There are many different kinds of
end systems, access networks, links circuit switching, packet switching, network structure
 Introduction Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and
Introduction Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 What is the Internet? 1.2 Network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 Network core circuit switching, packet switching, network structure 1.4 Delay, loss and
Objectives. Learn how computers are connected. Become familiar with different types of transmission media
 Objectives Learn how computers are connected Become familiar with different types of transmission media Learn the differences between guided and unguided media Learn how protocols enable networking 2 Objectives
Objectives Learn how computers are connected Become familiar with different types of transmission media Learn the differences between guided and unguided media Learn how protocols enable networking 2 Objectives
Technology in Action. Chapter Topics. Participation Question. Participation Question 8/17/11. Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices
 Technology in Action Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices 1 2 Chapter Topics Networking fundamentals Network architecture Network components Peer-to-peer networks Ethernet networks Power-line
Technology in Action Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices 1 2 Chapter Topics Networking fundamentals Network architecture Network components Peer-to-peer networks Ethernet networks Power-line
Powerline Communication
 Networking & Communication Powerline Communication Powerline to Ethernet Converter PL-101E USB to Powerline Network Adapter - PL-101U USER S MANUAL 1 Copyright Copyright (C) 2002 PLANET Technology Corp.
Networking & Communication Powerline Communication Powerline to Ethernet Converter PL-101E USB to Powerline Network Adapter - PL-101U USER S MANUAL 1 Copyright Copyright (C) 2002 PLANET Technology Corp.
Celestix Networks, Inc. 702 Brown Road. Fremont, California Ph Fx Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network
 Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network white paper Introduction A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a flexible data communications system that can use either infrared or radio frequency (RF) technology
Introduction to Wireless Local Area Network white paper Introduction A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a flexible data communications system that can use either infrared or radio frequency (RF) technology
Video, Data, and Voice: Delivering the Home Network Experience
 Video, Data, and Voice: Delivering the Home Network Experience Tuesday, October 25 1:30 3:00 p.m. Venetian Ballroom I Technology Forum at TELECOM 05 Video, Data and Voice: Delivering the Home Networking
Video, Data, and Voice: Delivering the Home Network Experience Tuesday, October 25 1:30 3:00 p.m. Venetian Ballroom I Technology Forum at TELECOM 05 Video, Data and Voice: Delivering the Home Networking
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, 8th Edition. Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling
 A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling Objectives Learn about network types and topologies Learn about the hardware used to build local networks Learn
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling Objectives Learn about network types and topologies Learn about the hardware used to build local networks Learn
CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Engineering CEN 538 Wireless LAN & MAN Networks Dr. Ridha OUNI rouni@ksu.edu.sa LMS web site References Text book
WLAN TRENDS. Dong Wang. Prof. Dr. Eduard Heindl 05/27/2009. E-Business Technologies
 WLAN TRENDS Dong Wang 232495 Prof. Dr. Eduard Heindl E-Business Technologies 05/27/2009 1 Declaration I, Dong Wang, hereby declare that this paper is my own work and all the related work cites are shown
WLAN TRENDS Dong Wang 232495 Prof. Dr. Eduard Heindl E-Business Technologies 05/27/2009 1 Declaration I, Dong Wang, hereby declare that this paper is my own work and all the related work cites are shown
Systems and Principles Unit Syllabus
 Systems and Principles Unit Syllabus Level 2 Networking Principles 7540-002 www.cityandguilds.com October 2010 Version 2.0 About City & Guilds City & Guilds is the UK s leading provider of vocational qualifications,
Systems and Principles Unit Syllabus Level 2 Networking Principles 7540-002 www.cityandguilds.com October 2010 Version 2.0 About City & Guilds City & Guilds is the UK s leading provider of vocational qualifications,
A network is two or more computers, or other electronic devices, connected together so that they can exchange data.
 Computer Networks What is a Network? A network is two or more computers, or other electronic devices, connected together so that they can exchange data. For example; a network allows computers to share
Computer Networks What is a Network? A network is two or more computers, or other electronic devices, connected together so that they can exchange data. For example; a network allows computers to share
Introduction to Networks and the Internet
 Introduction to Networks and the Internet CMPE 80N Announcements First quiz on Friday, 01.16. Covers material up to and including 01.14. Closed books, notes, etc. Winter 2004 Lecture 5 1 2 Data Transmission
Introduction to Networks and the Internet CMPE 80N Announcements First quiz on Friday, 01.16. Covers material up to and including 01.14. Closed books, notes, etc. Winter 2004 Lecture 5 1 2 Data Transmission
TL-PA8030P KIT. 3-Port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit. Highlights AV1200
 AV1200 3-Port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit Highlights AV1200 HomePlug AV2 standard compliant, high-speed data transfer rates of up to 1200Mbps, supports all your online needs MIMO Technology
AV1200 3-Port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit Highlights AV1200 HomePlug AV2 standard compliant, high-speed data transfer rates of up to 1200Mbps, supports all your online needs MIMO Technology
Can I Add A Second Wireless Router To My Home Network
 Can I Add A Second Wireless Router To My Home Network How do I connect another router to my existing Linksys router? Improve the performance of the network without removing your older router, Connect The
Can I Add A Second Wireless Router To My Home Network How do I connect another router to my existing Linksys router? Improve the performance of the network without removing your older router, Connect The
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band. Wireless A/G g a. User Guide. Game Adapter WIRELESS WGA54AG (EU/LA/UK) Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5GHz 2, 4GHz 802.11a 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless A/G Game Adapter User Guide Model No. WGA54AG (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5GHz 2, 4GHz 802.11a 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless A/G Game Adapter User Guide Model No. WGA54AG (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to
ITRAINONLINE MMTK BASIC WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE AND TOPOLOGIES HANDOUT
 ITRAINONLINE MMTK BASIC WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE AND TOPOLOGIES HANDOUT Developed by: Sebastian Buettrich, wire.less.dk Alberto Escudero Pascual, IT +46 Table of Contents 1. About this document...1 1.1
ITRAINONLINE MMTK BASIC WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE AND TOPOLOGIES HANDOUT Developed by: Sebastian Buettrich, wire.less.dk Alberto Escudero Pascual, IT +46 Table of Contents 1. About this document...1 1.1
Feature. What exactly is WLAN? More reading:
 The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
WHITEPAPER. Connectivity - An Overview of Connectivity Technologies
 WHITEPAPER Connectivity - An Overview of Connectivity Technologies Connectivity - An Overview of Connectivity Technologies Introduction The definition of connectivity differs depending on the viewpoint
WHITEPAPER Connectivity - An Overview of Connectivity Technologies Connectivity - An Overview of Connectivity Technologies Introduction The definition of connectivity differs depending on the viewpoint
Internet User Guide. For the ZTE H298N routers. LAN4 LAN3 LAN2 LAN1 WAN Phone USB2 WAN WLAN WLAN
 Internet User Guide For the ZTE H298N routers Power WAN LAN1 Internet LAN3 LAN2 LAN4 WLAN WPS Phone USB1 Reset WPS USB2 LAN4 LAN3 LAN2 LAN1 WAN Phone On/Off Power WLAN Internet seethelight.co.uk User Guide,
Internet User Guide For the ZTE H298N routers Power WAN LAN1 Internet LAN3 LAN2 LAN4 WLAN WPS Phone USB1 Reset WPS USB2 LAN4 LAN3 LAN2 LAN1 WAN Phone On/Off Power WLAN Internet seethelight.co.uk User Guide,
Typical Network Uses
 Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Computer Networks Introduction The next Great Revolution - Computer Networks- computers connected together for exchanging information Our information-oriented society - applications in education, commerce,
Msystems Ltd. AV1200 TL-PA8030P KIT. 3-Port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit. Highlights
 AV1200 3-Port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit Highlights AV1200 HomePlug AV2 standard compliant, high-speed data transfer rates of up to 1200Mbps, supports all your online needs MIMO Technology
AV1200 3-Port Gigabit Passthrough Powerline Starter Kit Highlights AV1200 HomePlug AV2 standard compliant, high-speed data transfer rates of up to 1200Mbps, supports all your online needs MIMO Technology
Your guide to getting the most out of the internet
 Your guide to getting the most out of the internet kcomhome.com/lightstream Contents Page > What KCOM s responsible for... 4 > What you re responsible for... 5 > Getting the best from your router... 6
Your guide to getting the most out of the internet kcomhome.com/lightstream Contents Page > What KCOM s responsible for... 4 > What you re responsible for... 5 > Getting the best from your router... 6
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005
 Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Introduction to Information Technology Turban, Rainer and Potter John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Copyright 2005 Network and Telecommunications Basics Chapter Outline The telecommunications system Network services
Welcome. Equipment Set Up Guide
 Welcome Equipment Set Up Guide 1. What s included in your install 2. How to set up and get connected SSID is simply the technical term for your Wireless Network. When you set up a wireless home network,
Welcome Equipment Set Up Guide 1. What s included in your install 2. How to set up and get connected SSID is simply the technical term for your Wireless Network. When you set up a wireless home network,
Networks. Unit 5 Terminology Study Assignment Review Computer Technology. S3 Obj 2
 Networks Unit 5 Terminology Study Assignment Review Computer Technology S3 Obj 2 Network A computer network, or simply a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware components interconnected
Networks Unit 5 Terminology Study Assignment Review Computer Technology S3 Obj 2 Network A computer network, or simply a network, is a collection of computers and other hardware components interconnected
Wireless. Networkin. cpue. Indianapolis, 800 East 96th Street, Indiana 46240
 Wireless Networkin cpue 800 East 96th Street, Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 iv Table of Contents Introduction 1 How This Book Is Organized 3 Conventions Used in This Book 4 Windows or Mac? 4 Web Page Addresses
Wireless Networkin cpue 800 East 96th Street, Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 iv Table of Contents Introduction 1 How This Book Is Organized 3 Conventions Used in This Book 4 Windows or Mac? 4 Web Page Addresses
