The Performance Analysis of Wireless Distribution System Using Point to Multipoint Network Topology
|
|
|
- Hugh Price
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Performance Analysis of Wireless Distribution System Using Point to Multipoint Network Topology Rizal Munadi 1,2*, Fardian 1,2, Zeri Falmiza 2, Ernita Dewi Meutia 1,2 and Roslidar 1,2 1 Wireless and Networking Research Group (Winner), Computer Network Laboratory, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Syiah Kuala University, Banda Aceh 23111, Indonesia 2 Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Syiah Kuala University, Banda Aceh 23111, Indonesia Abstract. Current information technology development continues to evolve along with the needs in obtaining data or information either audio, images or a combination of both which is growing rapidly. Therefore information technology must be able to provide services that could fulfill user expectations in terms of both quality and quantity. One of the prominent changes in information exchange field is the use of wireless technologies, including its network configurations. Besides having to function optimally, the performance of the wireless technology is also needed to be maintained. This research is about the technology performance of Wireless Distribution System (WDS) with point to multipoint network configuration using g access point. The research was conducted in two phases. The first phase was building a WDS network model using four access points that are connected to each other. The second one was examining WDS network performance on server side. Based on the results obtained seen throughput on each segment WDS tested in gradual decline and the sharpest occurred in the last segment. On the other side the value of jitter increased from WDS-1 to WDS-2 and WDS-3 in a normal number, as well as the value of packet loss which increased in a very good category. The results obtained indicate good quality and generally very appropriate WDS technology to expand wireless access. 1 Introduction The development of information device technology continues to increase along with the needs of users in communicating and using data communication applications. The growth of users who switch to communication with IP based services needs to be accompanied by good service quality. To maintain data transmission requirements, equipment integrated in the network must be designed according to the desired expectations. The need to give satisfaction in accessing the internet is what motivates the motivation of this research. * Corresponding author: rizal.munadi@unsyiah.ac.id The Authors, published by EDP Sciences. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (
2 Nowadays, computer network infrastructure technology shows remarkable development on wireless networks compared to wire networks. Various variants of wireless network technology with the standards are now starting to dominate with the n variant. Although the n variant offers a 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency band, it turns out that hardware manufacturers have even installed network cards on the latest computer products by adopting the most recent variant, ac. However, all installed hardware wireless network is intended to provide optimum results but with network configuration and unpredictable traffic conditions, can produce an impact value from the output that is beyond expectations. Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a coordination technology for wireless network (WLAN) networks to optimize the use of network resources and service area coverage. The use of WDS in network implementation can expand the coverage area and provide flexibility and mobility for users. Limitations of service coverage of a network by using only single Access Points have been solved. Although the problem of coverage is resolved, the use of WDS as a system also has drawbacks, namely a decrease in capacity. In terms of capacity, the increasing number of a node according to users, the traffic collision, the channel utilization rate, the total throughput is among the research focus in system performance. Network performance issues have provided challenges for researchers to conduct studies and provide solutions. The research conducted by Jeong [1], which proposed a new medium access scheme, showed that the results of throughput performance were better than the existing schemes. Sung, et al. have studied about signal quality and packet delivery and purposed an algorithm name Node Degree Algorithm for achieving throughput performance [2]. Another research which done by Tahar using multiple interfaces per participating Access Point (AP) in order to improve the end to end performance[3]. This paper is focused on network performance and describes an implementation of Wireless Distribution System point to multi point network in AP g. The purpose of the implementation is to figure out the performace of the network at the client site by evaluating the parameter of throughput, jitter, and packet loss of the WDS network that is connected to APs. The rest of this paper is organized as follows: section two explains the literature review; section three describes the research method; section four discusses the data analysis; and finally, the conclusion is summarized in section five. 2 Literature Review Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a wireless technology that uses air as a propagation medium to transmit data from the sender to the receiving device. In the operation of equipment, WLANs with standards use frequencies allocated for Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) purposes that get exemption from usage permits or are identified with unlicensed bands. Equipment that works and meets the designation of the ISM band is free to be used by anyone. In addition to the impact on this simplification of convenience for users and increasing popularity, on the other hand it provides opportunities and challenges for researchers to get better results. In its development, various types of standards try to provide high data transmission speeds in order to provide satisfying services for users. To connect between WLAN devices so that they can deliver information between interconnected entities, network topology needs to be planned. Theoretically, there are two topologies in a wireless network which are Ad-Hoc topology and infrastructure. Following is the short explanation of the topology: a. Ad-hoc mode 2
3 Ad-hoc mode is a simple mode of the WLAN network. Ad-hoc topology is similar to peer to peer network, where the network is built only by applying the component of wireless device. Ad hoc wireless networks, consisting of a collection of wireless nodes, all of which may be mobile, dynamically create a wireless network among themselves without using any such infrastructure or administrative support [4] The drawback of this mode is the computer is unable to communicate with the computer in the wired network. b. Infrastructure mode A more complex topology of the wireless network is the network topology with Basic Service Set (BSS) infrastructure mode. This configuration places the AP as a device that functions as data traffic in forwarding information in the network. As the agent, AP in addition to serving connected nodes also plays a role as a bridge with conventional networks that are physically connected via UTP cable. 2.1 Wireless distribution system Wireless Distribution System (WDS), which is also named as Wireless Repeater, is a system to develop a wireless network without using cable as the media of data transfer but applying the wireless path of each AP equipment. It is very contrast to conventional communication network, where the media of distribution system is cable (wired LAN). All of the base stations in WDS have to be configured using the same radio channel, the same encryption methode (without encryption, WEP, or WAP), and the same encryption keys. And the connection is a configuration using different Service Set Identifiers (SSID) on each user identity [5]. WDS allows the interconnection of each AP equipment in a wireless environment. By applying WDS, the connection in a wireless network can be expanded using some APs or base station without the requirement of backbone cable network. WDS can be applied in two features/modes connectivity between APs, which are: a. Wireless Bridging; where the communication between APs in the WDS network is limited and does not allow other wireless client or station (STA) to access the network. b. Wireless repeater; where AP can communicate with each other and to the wireless Station (STA). Zikri conducted a research using 2 APs for Wireless Distribution System (WDS) [6]. In this research, throughput, jitter, packet loss and Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) are used as evaluation parameters to measure the quality of the test network. The results obtained on the receiving-end from the test network throughput obtained showed that the average results decline of 51.3% from the maximum bandwidth. In the measurement of other parameters, indicating that the value of the jitter that occurs on average 1.95 ms and the number of packet loss of 0.1%. Another research evaluation showed that accessing a network with WDS system by a variation of client number might reduce the number of channel allocation that may be used by the client [7]. The calculation uses the same client that exists in the network with the WDS system. In the initial stages of testing with 1 client, it was known that the channel allocation in throughput degraded 40.3%. This percentage gradually decreased to 21. 2% on the test with clients, and increased again to 25.2% on the test with 12 clients. The last, the research conducted by using 3 APs with WDS technology [8]. As for the use of such research, WDS technology produces an average percentage decline in the value of the throughput generated by using one client on the AP-2 (WDS-1) is 31.27%, while the average percentage of the throughput on the AP-3 (WDS- 2) is 54.92%. Tests were performed using point-to-point network topology with the distance between the AP range of 20 meters conducted in open space. The results show a gradual decrease in throughput for each AP used. 3
4 2.2 Network performance Throughput Throughput is the real capability of a network in sending data. Throughput is always related to bandwidth even in some context it is also called bandwidth. The principal different is on their nature, while bandwidth is static of fixed, throughput, on the other hand, is dynamic. Globally speaking, through put is a measure of data traffic in a communication, with the unit of megabit per second (mbps). The higher the value, the better the network performance. Actual throughput will vary. Network conditions and environmental factors, including the volume of network traffic, building materials and construction, and network overhead, lower the actual data throughput rate Jitter Jitter is a delay variation due to time difference or interval of the arriving of receiving the packet. In data communication, packets delivered are varied and traffics that occur in the network are very dynamic in accordance with the volume of the data transaction. The amount of jitter that occurs is dependent on the number of collisions between packets that pass through in the network. The number of jilter in a reasonable tolerance is between 0 to 100 ms as shown in Table 1. As jitter indicates the package collision in the internet protocol, the heavier the traffic load, the bigger the possibility that collision will occur. This will have an impact on the value of the jitter will become larger. Category Excellent Good Poor Worst Table 1. Jitter criteria [9] Peak Jitter 0 ms 0-75 ms ms Packet loss The failure in the transmission of a data packet on its way to the destination is called packet loss. There are some factors that may cause the packet loss, including collision, congestion, error transmission of physical media, and the failure at the receiving side which may due to overflow on the buffer. Attempts to minimize the number of packet loss are a challenge that must be faced and very difficult to avoid. Therefore, if the smaller value of packet loss in a network the better the performance of the network. Performance categories of the packet loss are shown in Table 2. Table 2. Packet Loss Criteria Category Packet Loss Excellent 0 % Good 1-3 % Poor 4-15 % Worst % 4
5 3 Research Methodology In this research, four APs have been configured using point to multipoint topology approach to test their WDS performances. All APs placed in open space and examine their capabilities to deliver a message to the client under three scenarios as listed in Table 3. We propose throughput, jitter and packet loss as the parameters to measure their performances by using the jperf software. Fig. 1 shows the tested topology model in this research. Skenario Table 3. Testing scenarios AP-1 (main) AP-2 (WDS- 1) AP-3 (WDS- 3) AP-4 (WDS- 4) 1. Server Client Server - Client - 3. Server - - client AP (main) AP-1 (WDS-1) AP-2 (WDS-2) AP-3 (WDS-3) Fig. 1. The model of topology 4 Discussion This section discusses the result from the average value of throughput, jitter, and packet loss during the test. The average value from every result test will be compared with the result from throughput, jitter, and packet loss on WDS network that using point to multipoint topology. 4.1 Throughput This test uses one client for every AP-2 (WDS-1), AP-3 (WDS-2), AP-4 (WDS-3) and 1 server for AP-1. Port used for every client is 5001 (WD-S-1), 6001 (WDS-2), and 8001 (WDS-3). As shown in Fig. 2, throughput measurements are carried out involving 3 APs that work together as a WDS network. From the resulting test, it is found that the average throughput value of WDS-1 is Kbps, WDS-2 is Kbps, and WDS-3 is Kbps. In aggregate, there is a decrease in throughput when data traffic passes between APs gradually 5
6 Throughput Throughput (Kbps) WDS-1 WDS-2 WDS-3 Interval (sec) Fig. 2. Throughput average value 4.2 Jitter The results of Jitter's measurement are shown in Fig. 3. The result shows that WDS-1 is 2,215 ms for its average value and the highest value is 4,574 ms. On WDS-2, its average jitter value is 3,417 ms and the highest value is 3,966 ms. On WDS-3, its average value is 3,897 ms with the highest value is 5,660 ms. Unlike the results of throughput for each WDS stage, jitter measurement shows a gradual increase between each WDS. Jitter Jitter (ms) WDS-1 WDS-2 WDS-3 Interval (sec) Fig. 3. Jitter average value 4.3 Packet Loss The amount of packet loss on every WDS client is figured out in Fig. 4. The percentage of packet loss resulted from WDS-1 is 0,15%, WDS-2 is 0,18%, and WDS-3 0,35%. From this data, it can be seen that the amount of the packet losses is greater for every distance addition. 6
7 Packet Loss Packet Loss (%) WDS-1 WDS-2 WDS-3 Interval (sec) Fig. 4. The graphic of packet loss average value 4.4 Data Analysis Throughput Comparison Fig. 5 shows that the average value of WDS-1 is 6360,05 Kbps, WDS-2 is 6281,54 Kbps, and WDS-3 is 5535,04 Kbps. The percentage of decreasing value from WDS-1 to WDS-2 is 1,23%, from WDS-2 to WDS-3 is 11,88%, and from WDS-1 to WDS-3 is 12,97%. Throughput (Kbps) WDS-1, 1, WDS-2, 1, Throughput WDS-3, 1, WDS-1 WDS-2 WDS-3 Fig. 5. The comparison result of throughput average value Jitter Comparison Fig. 6 shows that the average value of jitter on WDS-1 is ms, WDS-2 is ms, and WDS-3 is ms. The percentage of jitter average value on the WDS-1 network is 1,20%, WDS-2 is 0,47%, and WDS-3 is 1,68%. The highest jitter value is found on WDS- 3, it is because there is packet queueing during data distribution process. All the jitter results are still categorized as good according to ITU-T G.8251, 2001 standard where the maximum value of allowed jitter is 75 ms. 7
8 Jitter (ms) WDS-1, 1, 2,215 Jitter WDS-2, 1, 3,417 WDS-3, 1, 3,897 WDS-1 WDS-2 WDS-3 Fig. 6. The comparison result of jitter average value Packet loss average value Fig. 7 shows the percentage of packet loss average values on WDS-1 is 0,15%, WDS-2 is 0,18%, and WDS-3 is 0,35%. The losses percentage occured during the test between WDS- 1 and WDS-2 is 0,03%, WDS-2 and WDS-3 is 0,17%, and WDS-1 and WDS-3 is 0,20%. But according to ITU TIPHON, 1998 standard, above losses are still categorizing good. The losses amount of data packet is influenced by throughput and jitter value on the network. The greater packet loss resulted from the low throughput value and the high jitter value. Packet Loss WDS-3, 1,.351% Packet Loss (%) WDS-1, 1,.147% WDS-2, 1,.184% WDS-1 WDS-2 WDS-3 Fig. 7. The comparison result of packet loss average value 5 Conclusion This research has shown the evaluation of throughput, jitter, and packet loss based on point to multi point topology and the WDS network. The results obtained indicate good quality and generally very appropriate WDS technology to expand wireless access. References 1. J. Jeong, W. Lim, and Y. Suh, "Throughput Enhancement for WDS-Based WLANs," 22 nd International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), Nassau, pp. 1-6 (2013). 8
9 2. Sung, T.-W. et al. An Algorithm for Improving Network Throughput of Wireless Distribution System. in 2016 Third International Conference on Computing Measurement Control and Sensor Network (CMCSN) R. Tahar, A. Belghith, and R. Braham, "Performance evaluation of IEEE multiinterface based wireless distribution system (MI-WDS)," 2009 IEEE/ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, Rabat, pp (2009). 4. J. Haas et al., Guest Editorial, IEEE JSAC, Special Issue on Wireless Networks, vol. 17, no. 8, (1999). 5. Sulistyo, W., Bayu, T. I., & Sathibi, A. (2012). Implementasi Dan Analisis Penggunaan Dd-Wrt Firmware Untuk Membangun Jaringan Wireless Distribution System Pada Jaringan Hotspot (Studi Kasus : FTI UKSW), 2012(Snati), K. Zikri, Analisis Performansi dan Kualitas Penerimaan Sinyal Pada Multi Access point Menggunakan Wireless Distribution System (WDS) Pada Jaringan WLAN IEEE g. Skripsi. Universitas Syiah Kuala, (2012). 7. Putra, D. L. A., and Subhan, A. Analisa Kinerja Implementasi Wireless Distribution System Pada Perangkat Access Point g Menggunakan OpenWRT. EEPIS Final Project (2011).. 8. R. Munadi, R. Wahyudi, Fardian, Ardiansyah, Analisis Kinerja Jaringan Wireless Distribution System Menggunakan Access Point g, Konferensi Nasional ke-7 Fortei (2013). 9. Sugeng, W., Istiyanto, J. E., Mustofa, K., & Ashari, A. The Impact of QoS Changes towards Network Performance. International Jurnal of Computer Networks and Communications Security, 3(2), Retrieved from (2015). 9
An Analysis of Quality of Service (QoS) In Live Video Streaming Using Evolved HSPA Network Media
 JAICT, Journal of Applied Information and Communication Technologies Vol.1, 1, 2016 An Analysis of Quality of Service (QoS) In Live Video Streaming Using Evolved HSPA Network Media AchmadZakaria Azhar
JAICT, Journal of Applied Information and Communication Technologies Vol.1, 1, 2016 An Analysis of Quality of Service (QoS) In Live Video Streaming Using Evolved HSPA Network Media AchmadZakaria Azhar
University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series. Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks
 University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks Rastin Pries and Klaus Heck Report No. 339 September 2004
University of Würzburg Institute of Computer Science Research Report Series Performance Comparison of Handover Mechanisms in Wireless LAN Networks Rastin Pries and Klaus Heck Report No. 339 September 2004
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Delivering Voice over IEEE WLAN Networks
 Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
Wireless LAN Access Point
 Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11b 11Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents... 2 1.2 Features... 2 1.3 Specifications... 2 1.4 Physical Description...
Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11b 11Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents... 2 1.2 Features... 2 1.3 Specifications... 2 1.4 Physical Description...
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK
 Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Introduction. High Speed LANs. Emergence of High-Speed LANs. Characteristics of High Speed LANS. Text ch. 6, High-Speed Networks and
 High Speed LANs 3BA33 David Lewis 2 nd Semester 2006-07 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 1 Characteristics of High Speed LANS 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 3 Introduction Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet Fibre Channel High-speed
High Speed LANs 3BA33 David Lewis 2 nd Semester 2006-07 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 1 Characteristics of High Speed LANS 3BA33 D.Lewis 2007 3 Introduction Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet Fibre Channel High-speed
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Guide to Networking Essentials Fifth Edition. Chapter 2 Network Design Essentials
 Guide to Networking Essentials Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Network Design Essentials Objectives Explain the basics of a network layout Describe the standard networking topologies Explain the variations on
Guide to Networking Essentials Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Network Design Essentials Objectives Explain the basics of a network layout Describe the standard networking topologies Explain the variations on
Node Density Performance Analysis on IEEE ah Standard for VoIP Service
 79 Node Density Performance Analysis on IEEE 802.11ah Standard for VoIP Service Triani Wulandari, Doan Perdana and Ridha Muldina Negara School of Electrical Engineering, Telkom University, Indonesia Abstract:
79 Node Density Performance Analysis on IEEE 802.11ah Standard for VoIP Service Triani Wulandari, Doan Perdana and Ridha Muldina Negara School of Electrical Engineering, Telkom University, Indonesia Abstract:
Wireless and WiFi. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Wireless and WiFi Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Wireless Networks 2/28 mobile phone subscribers now outnumber wired phone subscribers similar trend likely with Internet
Performance Analysis for Channel Utilization in Wireless LAN
 Performance Analysis for Channel Utilization in Wireless LAN Shweta Singh Naresh Chandra Arun Kumar Tripathi ABSTRACT Wireless network plays an important role in field of communication. Now a days people
Performance Analysis for Channel Utilization in Wireless LAN Shweta Singh Naresh Chandra Arun Kumar Tripathi ABSTRACT Wireless network plays an important role in field of communication. Now a days people
Wireless and Mobile Networks 7-2
 Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Wireless and Mobile Networks EECS3214 2018-03-26 7-1 Ch. 6: Wireless and Mobile Networks Background: # wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds # wired phone subscribers (5-to-1)! # wireless Internet-connected
Expanding the use of CTS-to-Self mechanism to improving broadcasting on IEEE networks
 Expanding the use of CTS-to-Self mechanism to improving broadcasting on IEEE 802.11 networks Christos Chousidis, Rajagopal Nilavalan School of Engineering and Design Brunel University London, UK {christos.chousidis,
Expanding the use of CTS-to-Self mechanism to improving broadcasting on IEEE 802.11 networks Christos Chousidis, Rajagopal Nilavalan School of Engineering and Design Brunel University London, UK {christos.chousidis,
ITM542 Spring 2004 Feasibility Study of a Wireless LAN network With-VoIP at IIT Rice campus Ninad Narkhede Masaaki Yana Saturday, 1 May 2004
 ITM542 Spring 2004 Feasibility Study of a Wireless LAN network With-VoIP at IIT Rice campus Ninad Narkhede Masaaki Yana Saturday, 1 May 2004 ABSTRACT Wireless technology has gained popularity in enterprises
ITM542 Spring 2004 Feasibility Study of a Wireless LAN network With-VoIP at IIT Rice campus Ninad Narkhede Masaaki Yana Saturday, 1 May 2004 ABSTRACT Wireless technology has gained popularity in enterprises
Wireless Router at Home
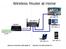 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users
 MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users Static Channel Allocation: Frequency Division Multiplexing
MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users Static Channel Allocation: Frequency Division Multiplexing
Measurements in the wireless
 Contents Measurements in the wireless Lecture slides for S-38.3183 6.4.2006 Mika Ilvesmäki Motivation Wireless environment spesifics Wireless trace collection Wireless measurement methods Mobility measurements
Contents Measurements in the wireless Lecture slides for S-38.3183 6.4.2006 Mika Ilvesmäki Motivation Wireless environment spesifics Wireless trace collection Wireless measurement methods Mobility measurements
Wireless Networks. CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: , Kurose and Ross
 Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Wireless Networks CSE 3461: Introduction to Computer Networking Reading: 6.1 6.3, Kurose and Ross 1 Wireless Networks Background: Number of wireless (mobile) phone subscribers now exceeds number of wired
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5
 Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Wireless and Mobile Networks Reading: Sections 2.8 and 4.2.5 Acknowledgments: Lecture slides are from Computer networks course thought by Jennifer Rexford at Princeton University. When slides are obtained
Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET
 Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET Holger Kuprian 1, Marek Meyer 2, Miguel Rios 3 1) Technische Universität Darmstadt, Multimedia Communications Lab Holger.Kuprian@KOM.tu-darmstadt.de
Evaluation of Information Dissemination Characteristics in a PTS VANET Holger Kuprian 1, Marek Meyer 2, Miguel Rios 3 1) Technische Universität Darmstadt, Multimedia Communications Lab Holger.Kuprian@KOM.tu-darmstadt.de
Delay Performance Evaluation of WIFI Release (IEEE a, b, g and n) Using OPNET for Data Types (Voice, , File Transfer, Video Convergence)
 Delay Performance Evaluation of WIFI Release (IEEE 802.11 a, b, g and n) Using OPNET for Data Types (Voice, email, File Transfer, Video Convergence) Amel Aboud Ali mohamed Alswelih 1 and Dr. Amin Babiker
Delay Performance Evaluation of WIFI Release (IEEE 802.11 a, b, g and n) Using OPNET for Data Types (Voice, email, File Transfer, Video Convergence) Amel Aboud Ali mohamed Alswelih 1 and Dr. Amin Babiker
Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering
 Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Technical Report MECSE-6-2006 Medium Access Control (MAC) Schemes for Quality of Service (QoS) provision of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Technical Report MECSE-6-2006 Medium Access Control (MAC) Schemes for Quality of Service (QoS) provision of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS
 BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
BROADBAND AND HIGH SPEED NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO DATA COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
Wireless LAN Tester Conformable to IEEE802.11ac
 Practical Field Information about Field Telecommunication Information Technologies about Telecommunication Technologies Wireless LAN Tester Conformable to IEEE802.11ac Abstract This article describes the
Practical Field Information about Field Telecommunication Information Technologies about Telecommunication Technologies Wireless LAN Tester Conformable to IEEE802.11ac Abstract This article describes the
Applications and Performance Analysis of Bridging with Layer-3 Forwarding on Wireless LANs
 Applications and Performance Analysis of Bridging with Layer-3 Forwarding on Wireless LANs James T. Yu and Chibiao Liu School of Computer Science, Telecommunications, and Information Systems DePaul University,
Applications and Performance Analysis of Bridging with Layer-3 Forwarding on Wireless LANs James T. Yu and Chibiao Liu School of Computer Science, Telecommunications, and Information Systems DePaul University,
Applications and Performance Analysis of Bridging with L3 Forwarding on Wireless LANs
 Applications and Performance Analysis of Bridging with L3 Forwarding on Wireless LANs Chibiao Liu and James Yu DePaul University School of CTI Chicago, IL {cliu1, jyu}@cs.depaul.edu Abstract This paper
Applications and Performance Analysis of Bridging with L3 Forwarding on Wireless LANs Chibiao Liu and James Yu DePaul University School of CTI Chicago, IL {cliu1, jyu}@cs.depaul.edu Abstract This paper
Performance Analysis of UGS and BE QoS classes in WiMAX
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 805-810 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Performance Analysis of UGS and
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 805-810 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Performance Analysis of UGS and
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
Monitoring the Network (CPE and WBS)
 Monitoring the Network (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. View the Device Information 2. View the Wireless Settings 3. View Wireless Signal Quality 4. View Radio Status 5. View the LAN Settings 6. View the WAN
Monitoring the Network (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. View the Device Information 2. View the Wireless Settings 3. View Wireless Signal Quality 4. View Radio Status 5. View the LAN Settings 6. View the WAN
Networking. Bin Li Assistant Professor Dept. of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University of Rhode Island
 Networking Bin Li Assistant Professor Dept. of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University of Rhode Island Why is Networking Needed? To enhance many devices Cars communicating to reduce
Networking Bin Li Assistant Professor Dept. of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University of Rhode Island Why is Networking Needed? To enhance many devices Cars communicating to reduce
On Admission of VoIP Calls Over Wireless Mesh Network
 On Admission of VoIP Calls Over Wireless Mesh Network Hung-yu Wei Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Taipei, Taiwan {hywei}@ntu.edu.tw Kyungtae Kim, Anand Kashyap and Samrat
On Admission of VoIP Calls Over Wireless Mesh Network Hung-yu Wei Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Taipei, Taiwan {hywei}@ntu.edu.tw Kyungtae Kim, Anand Kashyap and Samrat
Configure Wireless Distribution System (WDS) on the WAP131, WAP351, WAP150, or WAP361 Access Point
 Configure Wireless Distribution System (WDS) on the WAP131, WAP351, WAP150, or WAP361 Access Point Objective A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) lets you connect multiple access points together. WDS allows
Configure Wireless Distribution System (WDS) on the WAP131, WAP351, WAP150, or WAP361 Access Point Objective A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) lets you connect multiple access points together. WDS allows
NAVIGATING THE HOME WI- FI EXPERIENCE PART 2
 NAVIGATING THE HOME WI- FI EXPERIENCE PART 2 THE IMPORTANCE OF AIR TIME ALLOCATION IN WI- FI QUALITY OF SERVICE ELI BARUCH, SR. STAFF SOLUTIONS ARCHITECT TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 WIRELESS QUALITY
NAVIGATING THE HOME WI- FI EXPERIENCE PART 2 THE IMPORTANCE OF AIR TIME ALLOCATION IN WI- FI QUALITY OF SERVICE ELI BARUCH, SR. STAFF SOLUTIONS ARCHITECT TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... 3 WIRELESS QUALITY
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking
 CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
CSCD 433/533 Advanced Networking Lecture 6 Wireless LAN Components and Characteristics Winter 2017 Some Material in these slides from J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross All material copyright 1996-2007 1 Introduction
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Analysis of IEEE e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs
 Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
Goals. Fundamentals of Network Media. More topics. Topics. Multiple access communication. Multiple access solutions
 Fundamentals of Network Media Local Area Networks Ursula Holmström Goals Learn the basic concepts related to LAN technologies, for example use of shared media medium access control topologies Know the
Fundamentals of Network Media Local Area Networks Ursula Holmström Goals Learn the basic concepts related to LAN technologies, for example use of shared media medium access control topologies Know the
Wireless Network Security
 Wireless Network Security Wireless network overview Slide from 2 nd book 1 IT352 Network Security Najwa AlGhamdi IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802 committee for LAN standards IEEE 802.11 formed in 1990 s charter to
Wireless Network Security Wireless network overview Slide from 2 nd book 1 IT352 Network Security Najwa AlGhamdi IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802 committee for LAN standards IEEE 802.11 formed in 1990 s charter to
Simulative Investigation of Zigbee Network Coordinator Failure with Different QoS
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 11, November 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 11, November 2014,
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE standards
 HW Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11 standards WLAN Standard (IEEE 802.11) The IEEE 802.11 is a family of standards that governs the operations and functions of WLANs.
HW Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802.11 standards WLAN Standard (IEEE 802.11) The IEEE 802.11 is a family of standards that governs the operations and functions of WLANs.
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF WPA2 SECURITY PROTOCOL IN MODERN WIRELESS NETWORKS
 Impact of Internet on Business activities in Serbia and Worldwide Uticaj Interneta na poslovanje u Srbiji i svetu doi: 10.15308/SInteZa-2014-600-605 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF WPA2 SECURITY PROTOCOL IN
Impact of Internet on Business activities in Serbia and Worldwide Uticaj Interneta na poslovanje u Srbiji i svetu doi: 10.15308/SInteZa-2014-600-605 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF WPA2 SECURITY PROTOCOL IN
6.9 Summary. 11/20/2013 Wireless and Mobile Networks (SSL) 6-1. Characteristics of selected wireless link standards a, g point-to-point
 Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
Chapter 6 outline 6.1 Introduction Wireless 6.2 Wireless links, characteristics CDMA 6.3 IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs ( wi-fi ) 6.4 Cellular Internet Access architecture standards (e.g., GSM) Mobility 6.5
PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION
 PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION Phuc Khanh KIEU, Shinichi MIYAMOTO Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University 2-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka, 565-871 JAPAN
PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION Phuc Khanh KIEU, Shinichi MIYAMOTO Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University 2-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka, 565-871 JAPAN
Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Using Technology. Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager
 White Paper Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager Cable Broadband Communications Group, Texas Instruments Introduction Wireless home networking has emerged
White Paper Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager Cable Broadband Communications Group, Texas Instruments Introduction Wireless home networking has emerged
Chapter - 1 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter - 1 INTRODUCTION Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is based on IEEE 802.16 standard. This standard specifies the air interface of fixed Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) system
Chapter - 1 INTRODUCTION Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is based on IEEE 802.16 standard. This standard specifies the air interface of fixed Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) system
An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE WLANs
 An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE 802.11 WLANs Juki Wirawan Tantra, Chuan Heng Foh, and Bu Sung Lee Centre of Muldia and Network Technology School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological
An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE 802.11 WLANs Juki Wirawan Tantra, Chuan Heng Foh, and Bu Sung Lee Centre of Muldia and Network Technology School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological
SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER Quick Start Guide
 SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER Quick Start Guide About this guide This Quick Start Guide describes how to install and operate your SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER. Please read this manual before you install the
SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER Quick Start Guide About this guide This Quick Start Guide describes how to install and operate your SAGEM Wi-Fi 11g USB ADAPTER. Please read this manual before you install the
LAN Overview (part 2) Interconnecting LANs - Hubs
 LAN Overview (part 2) CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 November 2011 Interconnecting LANs - Hubs active central element of star layout each station connected to hub by two UTP lines hub acts as a repeater limited
LAN Overview (part 2) CSE 3213 Fall 2011 1 November 2011 Interconnecting LANs - Hubs active central element of star layout each station connected to hub by two UTP lines hub acts as a repeater limited
Chapter 7. Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration. Part I
 Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 7 Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 7-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Hubs, Bridges, and Switches (oh my) Hubs
 Hubs, Bridges, and Switches (oh my) Used for extending LANs in terms of geographical coverage, number of nodes, administration capabilities, etc. Differ in regards to: collision domain isolation layer
Hubs, Bridges, and Switches (oh my) Used for extending LANs in terms of geographical coverage, number of nodes, administration capabilities, etc. Differ in regards to: collision domain isolation layer
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking. Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology
 CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
IEEE 802 Standard Network s Comparison under Grid and Random Node Arrangement in 2.4 GHz ISM Band for Single and Multiple CBR Traffic
 3118 IEEE 802 Standard Network s Comparison under Grid and Random Node Arrangement in 2.4 GHz ISM Band for Single and Multiple CBR Traffic J.Jaslin deva gifty Department of ECE, Dr. Mahalingam College
3118 IEEE 802 Standard Network s Comparison under Grid and Random Node Arrangement in 2.4 GHz ISM Band for Single and Multiple CBR Traffic J.Jaslin deva gifty Department of ECE, Dr. Mahalingam College
Architecture. Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change
 802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
802.11 Architecture Copyright :I1996 IEEE. All rights reserved. This contains parts from an unapproved draft, subject to change What is unique about wireless? Difficult media - interference and noise -
Anil Saini Ph.D. Research Scholar Department of Comp. Sci. & Applns, India. Keywords AODV, CBR, DSDV, DSR, MANETs, PDF, Pause Time, Speed, Throughput.
 Volume 6, Issue 7, July 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Performance Analysis
Volume 6, Issue 7, July 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Performance Analysis
Alternate PHYs
 A whitepaper by Ayman Mukaddam 2018, LLC Page 1 of 12 Contents Modern 802.11 Amendments... 3 Traditional PHYs Review (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz PHYs)... 3 802.11ad Directional Multi-Gigabit - DMG PHY... 4 Frequency
A whitepaper by Ayman Mukaddam 2018, LLC Page 1 of 12 Contents Modern 802.11 Amendments... 3 Traditional PHYs Review (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz PHYs)... 3 802.11ad Directional Multi-Gigabit - DMG PHY... 4 Frequency
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE
 3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
EVALUATION OF EDCF MECHANISM FOR QoS IN IEEE WIRELESS NETWORKS
 MERL A MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORY http://www.merl.com EVALUATION OF EDCF MECHANISM FOR QoS IN IEEE802.11 WIRELESS NETWORKS Daqing Gu and Jinyun Zhang TR-2003-51 May 2003 Abstract In this paper,
MERL A MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORY http://www.merl.com EVALUATION OF EDCF MECHANISM FOR QoS IN IEEE802.11 WIRELESS NETWORKS Daqing Gu and Jinyun Zhang TR-2003-51 May 2003 Abstract In this paper,
EAP Wireless Access Point. 2.4 GHz b/g 54 Mbps
 EAP-3660 is a small form factor wireless product. It is stylish and looks like a smoke detector on the ceiling. EAP-3660 is a / Repeater / WDS that operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum
EAP-3660 is a small form factor wireless product. It is stylish and looks like a smoke detector on the ceiling. EAP-3660 is a / Repeater / WDS that operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
Module 1 Introduction Version 2, CSE IIT, Kharagpur Introduction In this module we shall highlight some of the basic aspects of computer networks in two lessons. In lesson 1.1 we shall start with the historical
54Mbps g Wireless LAN. CardBus PC Card. user manual
 54Mbps 802.11g Wireless LAN CardBus PC Card user manual TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 ABOUT WIRELESS LAN PC CARD -------------------------------------------------1 1-1 Features and Benefits---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
54Mbps 802.11g Wireless LAN CardBus PC Card user manual TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 ABOUT WIRELESS LAN PC CARD -------------------------------------------------1 1-1 Features and Benefits---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A Dynamic Channel Allocation Mechanism for IEEE Networks
 A Dynamic Channel Allocation Mechanism for IEEE 802.11 Networks Marcel William Rocha da Silva, José Ferreira de Rezende Abstract The great popularity of IEEE 802.11 along with channel scarcity may lead
A Dynamic Channel Allocation Mechanism for IEEE 802.11 Networks Marcel William Rocha da Silva, José Ferreira de Rezende Abstract The great popularity of IEEE 802.11 along with channel scarcity may lead
Optical networking technology
 1 Optical networking technology Technological advances in semiconductor products have essentially been the primary driver for the growth of networking that led to improvements and simplification in the
1 Optical networking technology Technological advances in semiconductor products have essentially been the primary driver for the growth of networking that led to improvements and simplification in the
CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK
 Introduction CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK 7.1 Conclusions... 154 7.2 Scope for Future Work... 157 7 1 Chapter 7 150 Department of Computer Science Conclusion and scope for future work In this
Introduction CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK 7.1 Conclusions... 154 7.2 Scope for Future Work... 157 7 1 Chapter 7 150 Department of Computer Science Conclusion and scope for future work In this
Wireless Communication
 Wireless Communication Hwajung Lee Key Reference: Prof. Jong-Moon Chung s Lecture Notes at Yonsei University Wireless Communications Bluetooth Wi-Fi Mobile Communications LTE LTE-Advanced WLAN WLAN (Wireless
Wireless Communication Hwajung Lee Key Reference: Prof. Jong-Moon Chung s Lecture Notes at Yonsei University Wireless Communications Bluetooth Wi-Fi Mobile Communications LTE LTE-Advanced WLAN WLAN (Wireless
QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET
 2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET Ashwini V. Biradar
2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET Ashwini V. Biradar
CS321: Computer Networks Introduction to Computer Networks and Internet
 CS321: Computer Networks Introduction to Computer Networks and Internet Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in What is Data Communication? Data communications
CS321: Computer Networks Introduction to Computer Networks and Internet Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in What is Data Communication? Data communications
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 ) 223 228 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, HIC 2016 An Improved Method of Avoiding RF Congestion
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 154 (2016 ) 223 228 12th International Conference on Hydroinformatics, HIC 2016 An Improved Method of Avoiding RF Congestion
CHAPTER 6 PILOT/SIGNATURE PATTERN BASED MODULATION TRACKING
 CHAPTER 6 PILOT/SIGNATURE PATTERN BASED MODULATION TRACKING 6.1 TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER Each modulated signal is preceded by a unique N bit pilot sequence (Manton, JH 2001). A switch in the transmitter
CHAPTER 6 PILOT/SIGNATURE PATTERN BASED MODULATION TRACKING 6.1 TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER Each modulated signal is preceded by a unique N bit pilot sequence (Manton, JH 2001). A switch in the transmitter
Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications
 Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications Jongho Bang Sirin Tekinay Nirwan Ansari New Jersey Center for Wireless Telecommunications Department of Electrical
Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications Jongho Bang Sirin Tekinay Nirwan Ansari New Jersey Center for Wireless Telecommunications Department of Electrical
Data Communications. Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs
 Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Data Communications Data Link Layer Protocols Wireless LANs Wireless Networks Several different types of communications networks are using unguided media. These networks are generally referred to as wireless
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
CHAPTER -1. Introduction to Computer Networks
 CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
CHAPTER -1 Introduction to Computer Networks PRELIMINARY DEFINITIONS computer network :: [Tanenbaum] a collection of autonomous computers interconnected by a single technology. communications network ::a
Configuring Advanced Radio Settings on the WAP371
 Article ID: 5069 Configuring Advanced Radio Settings on the WAP371 Objective Radio settings are used to configure the wireless radio antenna and its properties on the wireless access point (WAP) device
Article ID: 5069 Configuring Advanced Radio Settings on the WAP371 Objective Radio settings are used to configure the wireless radio antenna and its properties on the wireless access point (WAP) device
Chapter 4 NETWORK HARDWARE
 Chapter 4 NETWORK HARDWARE 1 Network Devices As Organizations grow, so do their networks Growth in number of users Geographical Growth Network Devices : Are products used to expand or connect networks.
Chapter 4 NETWORK HARDWARE 1 Network Devices As Organizations grow, so do their networks Growth in number of users Geographical Growth Network Devices : Are products used to expand or connect networks.
Chapter -6 IMPROVED CONGESTION CONTROL MECHANISM FOR REAL TIME DATA TRANSMISSION
 Chapter -6 IMPROVED CONGESTION CONTROL MECHANISM FOR REAL TIME DATA TRANSMISSION Chapter 6 IMPROVED CONGESTION CONTROL MECHANISM FOR REAL TIME DATA TRANSMISSION 6.1 Introduction Supporting Quality of Service
Chapter -6 IMPROVED CONGESTION CONTROL MECHANISM FOR REAL TIME DATA TRANSMISSION Chapter 6 IMPROVED CONGESTION CONTROL MECHANISM FOR REAL TIME DATA TRANSMISSION 6.1 Introduction Supporting Quality of Service
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide
 Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76XX Series Mesh Network Guide Table of Content SUPPORTED DEVICES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 5 MESH NETWORK ARCHITECTURE... 6 Terminology... 6 Mesh Network Architecture Models...
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer
 Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Last Lecture: Data Link Layer 1. Design goals and issues 2. (More on) Error Control and Detection 3. Multiple Access Control (MAC) 4. Ethernet, LAN Addresses and ARP 5. Hubs, Bridges, Switches 6. Wireless
Implementation of QoS of Different Multimedia Applications in WLAN
 Implementation of QoS of Different Multimedia Applications in WLAN Navdeep Singh Chauhan BHSBIET, Lehragaga Loveljeet Kaur SLIET,Longowal ABSTRACT In last deeecade wireless communication becomes a crucial
Implementation of QoS of Different Multimedia Applications in WLAN Navdeep Singh Chauhan BHSBIET, Lehragaga Loveljeet Kaur SLIET,Longowal ABSTRACT In last deeecade wireless communication becomes a crucial
Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE )
 Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11) -IEEE 802.11 Specifies a single Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer and 3 Physical Layer Specifications. Stations can operate in two configurations : Ad-hoc mode
Wireless Local Area Network (IEEE 802.11) -IEEE 802.11 Specifies a single Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer and 3 Physical Layer Specifications. Stations can operate in two configurations : Ad-hoc mode
Two-Tier WBAN/WLAN Healthcare Networks; Priority Considerations
 Two-Tier WBAN/WLAN Healthcare Networks; Priority Considerations Saeed Rashwand Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Jelena Mišić Department of Computer Science Ryerson University Abstract
Two-Tier WBAN/WLAN Healthcare Networks; Priority Considerations Saeed Rashwand Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Jelena Mišić Department of Computer Science Ryerson University Abstract
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536)
 Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
Princess Nora Bint Abdulrahman University College of computer and information sciences Networks department Networks Security (NET 536) Prepared by Dr. Samia Chelloug E-mail: samia_chelloug@yahoo.fr Content
New Signaling approach Improving the VoIP Quality of Service in Ad hoc Network
 New Signaling approach Improving the VoIP Quality of Service in Ad hoc Network Salma Rattal EEA&TI Laboratory Faculty of sciences and techniques Hassan 2nd University Mohammedia-Casablanca Morocco Abdelmajid
New Signaling approach Improving the VoIP Quality of Service in Ad hoc Network Salma Rattal EEA&TI Laboratory Faculty of sciences and techniques Hassan 2nd University Mohammedia-Casablanca Morocco Abdelmajid
CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW
 CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW P. 447 LAN (Local Area Network) A LAN consists of a shared transmission medium and a set of hardware and software for interfacing devices to the medium and regulating
CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW P. 447 LAN (Local Area Network) A LAN consists of a shared transmission medium and a set of hardware and software for interfacing devices to the medium and regulating
VOIP Network Pre-Requisites
 VOIP Network Pre-Requisites Executive Summary This document contains basic network requirements that are foundational for good voice quality when using Vogtec VoIP products/solutions over a data network.
VOIP Network Pre-Requisites Executive Summary This document contains basic network requirements that are foundational for good voice quality when using Vogtec VoIP products/solutions over a data network.
Quality of Service Mechanism for MANET using Linux Semra Gulder, Mathieu Déziel
 Quality of Service Mechanism for MANET using Linux Semra Gulder, Mathieu Déziel Semra.gulder@crc.ca, mathieu.deziel@crc.ca Abstract: This paper describes a QoS mechanism suitable for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
Quality of Service Mechanism for MANET using Linux Semra Gulder, Mathieu Déziel Semra.gulder@crc.ca, mathieu.deziel@crc.ca Abstract: This paper describes a QoS mechanism suitable for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
4G Technology in contrast with other G Technologies Raja Solanki,Vineeet Godara, Prashant Solanki, Dhronacharya Engineering College,Gurgaon,India
 Technology in contrast with other G Technologies Raja Solanki,Vineeet Godara, Prashant Solanki, Dhronacharya Engineering College,Gurgaon,India Abstract-Wireless services have the highest demand in internet
Technology in contrast with other G Technologies Raja Solanki,Vineeet Godara, Prashant Solanki, Dhronacharya Engineering College,Gurgaon,India Abstract-Wireless services have the highest demand in internet
Overview of IEEE Networks. Timo Smura
 Overview of IEEE 802.11 Networks Timo Smura 24.03.2004 Outline Introduction IEEE 802.11 standards Protocol model Network topologies 802.11 MAC layer 802.11 PHY layers Interoperability: Wi-Fi Alliance 3GPP
Overview of IEEE 802.11 Networks Timo Smura 24.03.2004 Outline Introduction IEEE 802.11 standards Protocol model Network topologies 802.11 MAC layer 802.11 PHY layers Interoperability: Wi-Fi Alliance 3GPP
Multiple Access in Cellular and Systems
 Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Data Communication. Chapter # 1: Introduction. By: William Stalling
 Data Communication Chapter # 1: By: Introduction William Stalling Data Communication The exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as cable wire. For data communications
Data Communication Chapter # 1: By: Introduction William Stalling Data Communication The exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission medium such as cable wire. For data communications
ANALYSIS OF THE POWER OF WIFI SIGNALS ON THE INFORMATICS ENGINEERING LABORATORY OF MUSAMUS UNIVERSITY USING INSIDDER
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 13, December 2018, pp. 266 272, Article ID: IJMET_09_13_029 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=13
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 9, Issue 13, December 2018, pp. 266 272, Article ID: IJMET_09_13_029 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=9&itype=13
EAP1200H a/b/g/n/ac Dual Radio Concurrent Ceiling Mount AP
 EAP1200H Key Features IEEE 802.11ac and IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n compliant Up to 300Mbps (2.4GHz) + 867Mbps (5GHz) wireless data transmission rate Gigabit Ethernet port with IEEE 802.3 at standard PoE support
EAP1200H Key Features IEEE 802.11ac and IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n compliant Up to 300Mbps (2.4GHz) + 867Mbps (5GHz) wireless data transmission rate Gigabit Ethernet port with IEEE 802.3 at standard PoE support
