Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial
|
|
|
- Russell Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
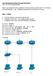
1 5/24/2015 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS GENI: geni Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Overview: This is a simple OpenFlow tutorial that will guide you through the writing of simple OpenFlow controllers to showcase some of the OpenFlow capabilities. We are going to write three different controllers: 1. Write a controller that will duplicate all the traffic of the OpenFlow switch out a specific port 2. TCP Port Forward controller. Divert all traffic destined to host A on TCP port X to TCP port Y 3. Proxy Controller. Write a controller that will divert all traffic destined to host A, TCP port X to host B, TCP port Y In this tutorial we have a choice of using an OpenFlow Software Switch, Open vswitch (OVS), or using an OpenFlow Capable Hardware Switch. The general topology is as pictured below. In general, the controller just needs to have a public IP address, so that it can exchange messages with the OpenFlow switch. The controller for the switch can run anywhere in the Internet. For this tutorial we are going to use a POX based controller, which is just one example of many controller frameworks. Prerequisites: Tools: A GENI account, if you don't have one sign up! Familiarity with how to reserve GENI resources with any of the GENI Tools (GENI Experimenter Portal, Omni, Flack). If you don't know you can take any of the tutorials: Reserving resources using Flack tutorial Reserving resources using Omni tutorial Familiarity with logging in to GENI compute resources. Basic understanding of OpenFlow. If you are doing this tutorial at home, flip through the tutorial's slides Familiarity with the Unix Command line Familiarity with the python programming language. We are going to use the POX controller, which is just one example of many controller frameworks, and POX is written in python. Open vswitch. OVS will be be installed. Installation was completed as described here. POX controller. POX controller is installed as part of the resource reservation. Where to get help: If you need help with GENI, geni users@googlegroups.com If you have questions about OpenFlow, OVS, Pox you can subscribe to openflow discuss or 1/2
2 5/24/2015 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS GENI: geni Resources: any of the other mailing lists listed. Learn more about OpenFlow POX wiki Learn more about OVS Tutorial Instructions Part I: Design/Setup Step 1: Reserve Resources OpenFlow using Open vswitch (OVS): Reserve topology in one rack [Recommended] OpenFlow using a Hardware Switch: Reserve topology in one rack using the HW OF switch Step 2: Configure and Initialize Services Part II: Execute Step 3: Execute Experiment Part III: Finish Step 4: Teardown Experiment Attachments IntroToOpenFlow_ pptx (2.6 MB) added by sedwards@bbn.com 16 months ago. "Intro To Openflow slides" 2/2
3 5/24/2015 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS/DesignSetup GENI: geni Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial (OVS) Step 1. Obtain resources [wiki:geniexperimenter/tutorials/openflowovs Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Step 1. Obtain resources This tutorial can use Step 2. Configure and Initialize compute resources from any 2a. Configure the Software Switch (OVS Window) 2c. Point your switch to a controller InstaGENI rack. For a list of standalone vs secure mode available InstaGENI racks Prev: Introduction see the GENI Production Next: Execute Resources page. If doing this outside a tutorial, use Utah DDC InstaGENI. The experiment will need: 1 Xen VM with a public IP to run an OpenFlow controller 1 Xen VM to be the OpenFlow switch 3 Xen VMs as hosts In this tutorial we are going to use Open vswitch (OVS) as an OpenFlow switch connected to three hosts. OVS is a software switch running on a compute resource. The other three hosts can only communicate through the OVS switch. If you are attending a Tutorial, the resources might have been reserved for you, check with your instructor and skip this step. You can use any reservation tool you want to reserve this topology. We will need two slices for this tutorial: A slice with a single VM that runs your OpenFlow controller A slice with your compute resources including a VM with OVS installed. To reserve resources use your favorite resource reservation tool (Omni, Portal, jfed): 1. In your slice that will run the OpenFlow controller: Reserve a VM running the controller using the request RSpec controller.rspec. This RSpec is available in the Portal and is called XEN VM POX Ctrl 2. In the slice that will run your hosts: Reserve the topology using the request rspec 1/4
4 5/24/2015 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS/DesignSetup GENI: geni support/openflowovs/openflowovs allxen.rspec.xml. This RSpec is available in the Portal and is called OpenFlow OVS all XEN Step 2. Configure and Initialize Although OVS is installed and initialized on the host that is meant to act as a software switch, it has not been configured yet. There are two main things that need to be configured: (1) configure your software switch with the interfaces as ports and (2) point the switch to an OpenFlow controller. In order to configure the OVS switch, we first login to the host that will be used as an OpenFlow switch. Depending on which tool and OS you are using there is a slightly different process for logging in. If you don't know how to SSH to your reserved hosts learn how to login. 2a. Configure the Software Switch (OVS Window) Now that you are logged in, we need first to configure OVS. To save time in this tutorial, we have already started OVS and we have added an Ethernet bridge that will act as our software switch. Try the following to show the configured bridge: sudo ovs-vsctl list-br You should see only one bridge br0. Now we need to add the interfaces to this bridge that will act as the ports of the software switch. 1. List all the interfaces of the node ifconfig Write down the interface names that correspond to the connections to your hosts. This information will be needed for one of the exercises. The correspondence is: Interface with IP '' '' to host1 ethx Interface with IP '' '' to host2 ethy Interface with IP '' '' to host3 ethz Be careful not to bring down eth0. This is the control interface, if you bring that interface down you won't be able to login to your host. For all interfaces other than eth0 and l0, remove the IP from the interfaces (your interface names may vary): sudo ifconfig ethx 0 sudo ifconfig ethy 0 sudo ifconfig ethz 0 Add all the data interfaces to your switch (bridge):be careful not to add interface eth0. This is the control interface. The other three interfaces are your data interfaces. (Use the same interfaces as you used in the previous step.) sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 ethx sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 ethy sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 ethz 2/4
5 5/24/2015 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS/DesignSetup GENI: geni Congratulations! You have configured your software switch. To verify the three ports configured run: sudo ovs-vsctl list-ports br0 2c. Point your switch to a controller In the controller window, find the control interface IP of your controller, use ifconfig and note down the IP address of eth0. An OpenFlow switch will not forward any packet unless instructed by a controller. Basically the forwarding table is empty, until an external controller inserts forwarding rules. The OpenFlow controller communicates with the switch over the control network and it can be anywhere in the Internet as long as it is reachable by the OVS host. In order to point our software OpenFlow switch to the controller, in the ovs window, run: sudo ovs-vsctl set-controller br0 tcp:<controller_ip>:6633 standalone vs secure mode The OpenFlow controller is responsible for setting up all flows on the switch, which means that when the controller is not running there should be no packet switching at all. Depending on the setup of your network, such a behavior might not be desired. It might be best that when the controller is down, the switch should default back to being a learning layer 2 switch. In other circumstances however this might be undesirable. In OVS this is a tunable parameter, called failsafe-mode which can be set to the following parameters: standalone [default]: in this case OVS will take responsibility for forwarding the packets if the controller fails secure: in this case only the controller is responsible for forwarding packets, and if the controller is down all packets are dropped. In OVS when the parameter is not set it falls back to the standalone mode. For the purpose of this tutorial we will set the fail-safe-mode to secure, since we want to be the ones controlling the forwarding. Run: sudo ovs-vsctl set-fail-mode br0 secure You can verify your OVS settings by issuing the following: 3/4
6 Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Step 3. Execute Experiment Now that the switch is up and running we are ready to start working on the controller. For this tutorial we are going to use the POX controller. The software is already installed in the controller host for running POX and can also be found here. Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Step 3. Execute Experiment 3a. Login to your hosts 3b. Use a Learning Switch Controller Soft vs Hard Timeouts Useful Tips for writing your controller 3c. Debugging your Controller i. Print messages ii. Check the status in the switch iii. Use Wireshark to see the OpenFlow messages 3d. Run a traffic duplication controller 3d. Run a port forward Controller 3e. Run a Server Proxy Controller 4. Moving to a Hardware Switch [wiki:geniexperimenter/tutorials/openflowovs/designsetup Prev: Design and [wiki:geniexperimenter/tutorials/openflowovs/hw/designsetup Prev: Design Next: Finish 3a. Login to your hosts To start our experiment we need to ssh all of our hosts. To get ready for the tutorial you will need to have the following windows open: one window with ssh into the controller four windows with ssh into OVS one window with ssh into host1 two windows with ssh into host2 one window with ssh into host3 Depending on which tool and OS you are using there is a slightly different process for logging in. If you don't know how to SSH to your reserved hosts learn how to login. Once you have logged in follow the rest of the instructions. 3b. Use a Learning Switch Controller In this example we are going to run a very simple learning switch controller to forward traffic between host1 and host2. 1. First start a ping from host1 to host2, which should timeout, since there is no controller running. ping host2 -c We have installed the POX controller under /tmp/pox on the controller host. POX comes with a set of example modules that you can use out of the box. One of the modules is a learning switch. Start the learning switch controller which is already available by running the following two commands: 1/7
7 "l2" below uses the letter `l` as in level and is not the number one. And you should wait for the '''INFO... connected''' line to ensure that the switch and the controller are communicating. cd /tmp/pox./pox.py --verbose forwarding.l2_learning The output should look like this: POX (betta) / Copyright James McCauley, et al. DEBUG:core:POX (betta) going up... DEBUG:core:Running on CPython (2.7.3/Apr :39:59) DEBUG:core:Platform is Linux generic-x86_64-with-Ubuntu precise INFO:core:POX (betta) is up. DEBUG:openflow.of_01:Listening on :6633 INFO:openflow.of_01:[9e-38-3e-8d ] connected DEBUG:forwarding.l2_learning:Connection [9e-38-3e-8d ] In the event that you need to move the port of your controller, this is the command sudo./pox.py --verbose openflow.of_01 --port=443 forwarding.l2_learning Do not forget to tell the ovs switch that the controller will be listening on this new port, i.e change 6633 to 443 in Step 2c. 3. In the terminal of host1, ping host2: [experimenter@host1 ~]$ ping host2 PING host2-lan1 ( ) 56(84) bytes of data. From host1-lan0 ( ) icmp_seq=2 Destination Host Unreachable From host1-lan0 ( ) icmp_seq=3 Destination Host Unreachable From host1-lan0 ( ) icmp_seq=4 Destination Host Unreachable 64 bytes from host2-lan1 ( ): icmp_req=5 ttl=64 time=23.9 ms 64 bytes from host2-lan1 ( ): icmp_req=6 ttl=64 time=0.717 ms 64 bytes from host2-lan1 ( ): icmp_req=7 ttl=64 time=0.654 ms 64 bytes from host2-lan1 ( ): icmp_req=8 ttl=64 time=0.723 ms 64 bytes from host2-lan1 ( ): icmp_req=9 ttl=64 time=0.596 ms Now the ping should work. 4. If you are using OVS, go back to your OVS host and take a look at the print outs. You should see that your controller installed flows based on the mac addresses of your packets. There is no way to get this information from the OpenFlow capable hardware switch. 5. If you are using OVS, to see the flow table entries on your OVS switch: sudo ovs-ofctl dump-flows br0 You should see at least two table entries: One for ICMP Echo (icmp_type=8) messages from host1 to host2 and one for ICMP Echo Reply (icmp_type=0) messages from host2 to host1. You may also see flow entries for arp packets. 6. To see messages go between your switch and your controller, open a new ssh window to your controller node and run tcpdump on the eth0 interface and on the tcp port that your 2/7
8 controller is listening on usually (You can also run tcpdump on the OVS control interface if you desire. However, when using the hardware switch, you can only do the tcpdump on your controller host.) sudo tcpdump -i eth0 tcp port 6633 You will see (1) periodic keepalive messages being exchanged by the switch and the controller, (2) messages from the switch to the controller (e.g. when there is a table miss) and an ICMP Echo message in, and (3) messages from the controller to the switch (e.g. to install new flow entries). 7. Kill your POX controller by pressing Ctrl-C: DEBUG:forwarding.l2_learning:installing flow for 02:c7:e8:a7:40:65.1 -> 0 INFO:core:Going down... INFO:openflow.of_01:[3a-51-a1-ab-c3-43 1] disconnected INFO:core:Down. 8. Notice what happens to your ping on host1. 9. If you are using OVS, check the flow table entries on your switch: sudo ovs-ofctl dump-flows br0 Since you set your switch to "secure" mode, i.e. don't forward packets if the controller fails, you will not see flow table entries. If you see flow table entries, try again after 10 seconds to give the entries time to expire. Soft vs Hard Timeouts All rules on the switch have two different timeouts: Soft Timeout: This determines for how long the flow will remain in the forwarding table of the switch if there are no packets received that match the specific flow. As long as packets from that flow are received the flow remains on the flow table. Hard Timeout: This determines the total time that a flow will remain at the forwarding table, independent of whether packets that match the flow are received; i.e. the flow will be removed after the hard timeout expires. Can you tell now why there were packets flowing even after you killed your controller? Useful Tips for writing your controller In order to make this first experience of writing a controller easier, we wrote some helpful functions that will abstract some of the particularities of POX away. These functions are located in /tmp/pox/ext/utils.py, so while you write your controller consult this file for details. Functions that are implemented include: packetisip : Test if the packet is IP packetisarp : Test if the packet is ARP packetisrequestarp : Test if this is an ARP Request packet packetisreplyarp : Test if this is an ARP Reply packet packetarpdstip : Test what is the destination IP in an ARP packet packetarpsrcip : Test what is the sources IP in an ARP packet packetistcp : Test if a packet is TCP packetdstip : Test the destination IP of a packet packetsrcip : Test the source IP of a packet 3/7
9 packetdsttcpport : Test the destination TCP port of a packet packetsrctcpport : Test the source TCP port of a packet createofaction : Create one OpenFlow action getfullmatch : get the full match out of a packet createflowmod : create a flow mod createarprequest : Create an Arp Request for a different destination IP createarpreply : Create an Arp Reply for a different source IP 3c. Debugging your Controller While you are developing your controller, some useful debugging tools are: i. Print messages Run your controller in verbose mode (add verbose) and add print messages at various places to see what your controller is seeing. ii. Check the status in the switch If you are using an OVS switch, you can dump information from your switch. For example, to dump the flows: sudo ovs-ofctl dump-flows br0 Two other useful commands show you the status of your switch: sudo ovs-vsctl show sudo ovs-ofctl show br0 iii. Use Wireshark to see the OpenFlow messages Many times it is useful to see the OpenFlow messages being exchanged between your controller and the switch. This will tell you whether the messages that are created by your controller are correct and will allow you to see the details of any errors you might be seeing from the switch. If you are using OVS then you can use wireshark on both ends of the connection, in hardware switches you have to rely only on the controller view. The controller host and OVS has wireshark installed, including the openflow dissector. For more information on wireshark you can take a look at the wireshark wiki. Here we have a simple case of how to use the OpenFlow dissector for wireshark. If you are on a Linux friendly machine (this includes MACs) open a terminal and ssh to your controller machine using the Y command line argument, i.e. ssh -Y <username>@<controller> Assuming that the public IP address on the controller is eth0, run wireshark by typing: sudo wireshark -i eth0& When the wireshark window pops up, you might still have to choose eth0 for a live capture. And you will want to use a filter to cut down on the chatter in the wireshark window. One such filter might be just seeing what shows up on port To do that type tcp.port eq 6633 in the filter window, assuming that 6633 is the port that the controller is listening on. And once you have lines, you can choose one of the lines and choose "Decode as..." and choose the OFP protocol. 4/7
10 3d. Run a traffic duplication controller In the above example we ran a very simple learning switch controller. The power of OpenFlow comes from the fact that you can decide to forward the packet anyway you want based on the supported OpenFlow actions. A very simple but powerful modification you can do, is to duplicate all the traffic of the switch out a specific port. This is very useful for application and network analysis. You can imagine that at the port where you duplicate traffic you connect a device that does analysis. For this tutorial we are going to verify the duplication by doing tcpdump on two ports on the OVS switch. 1. Use the interfaces that are connected to host2 and host3. Software Switch (OVS): If you have not noted them down you can use the manifest and the MAC address of the interfaces (ovs:if1 and ovs:if2) to figure this out. But you should have noted down the interfaces in Section 2 when you were configuring the software switch. Run tcpdump on these interfaces; one in each of the two ovs terminals you opened. This will allow you to see all traffic going out the interfaces. Hardware Switch: Refer to this Section to figure out ports: UsefulTips. If you are using a hardware switch, you may not see the traffic on host3, but if you observe your controller output, you will notice that flows are being installed for forwarding to host2 and host3. To see that duplication is happening, on the ovs host, run: sudo tcpdump -i <data_interface_name> [data_interface to host2] sudo tcpdump -i <data_interface_name> [data_interface to host3] You should see traffic from host1 to host2 showing up in the tcpdump window for host3. As a comparison, you will notice that no traffic shows up in that window when the controller is running the learning switch. 2. In the controller host directory /tmp/pox/ext you should see two files: i. myduplicatetraffic.py : This is the file that has instructions about how to complete the missing information. Go ahead and try to implement your first controller. ii. DuplicateTraffic.py : This has the actual solution. You can just run this if you don't want to bother with writing a controller. 3. Run your newly written controller on the <data_interface_name> that corresponds to OVS:if2 (which is connected to host3): cd /tmp/pox./pox.py --verbose myduplicatetraffic --duplicate_port=? For example, if OVS:if2 corresponds to "eth1", enter./pox.py --verbose myduplicatetraffic --duplicate_port=eth1 4. To test it go to the terminal of host1 and try to ping host2: ping If your controller is working, your packets will register in both terminals running tcpdump. 5. Stop the POX controller: DEBUG:myDuplicateTraffic:Got a packet : [02:f1:ae:bb:e3:a8>02:c7:e8:a7:40 DEBUG:SimpleL2Learning:installing flow for 02:f1:ae:bb:e3:a8.2 -> 02:c7:e 5/7
11 INFO:core:Going down... INFO:openflow.of_01:[3a-51-a1-ab-c3-43 1] disconnected INFO:core:Down. 3d. Run a port forward Controller Now let's do a slightly more complicated controller. OpenFlow gives you the power to overwrite fields of your packets at the switch, for example the TCP source or destination port and do port forwarding. You can have clients trying to contact a server at port 5000, and the OpenFlow switch can redirect your traffic to a service listening on port Under the /tmp/pox/ext directory there are two files PortForwarding.py and myportforwarding.py that are similar like the previous exercise. Both of these controller are configured by a configuration file at ext/port_forward.config. Use myportforwarding.py to write your own port forwarding controller. 2. To test your controller we are going to use netcat. Go to the two terminals of host2. In one terminal run: nc -l 5000 and in the other terminal run nc -l Now, start the simple layer 2 forwarding controller. We are doing this to see what happens with a simple controller. cd /tmp/pox./pox.py --verbose forwarding.l2_learning 4. Go to the terminal of host1 and connect to host2 at port 5000: nc Type something and you should see it at the the terminal of host2 at port Now, stop the simple layer 2 forwarding controller: DEBUG:forwarding.l2_learning:installing flow for 02:d4:15:ed:07:4e.3 -> 0 INFO:core:Going down... INFO:openflow.of_01:[ b-d7-16-4b 1] disconnected INFO:core:Down. 7. And start your port forwarding controller:./pox.py --verbose myportforwarding 8. Repeat the netcat scenario described above. Now, your text should appear on the other terminal of host2 which is listening to port Stop your port forwarding controller: DEBUG:myPortForwarding:Got a packet : [02:aa:a3:e8:6c:db>33:33:ff:e8:6c:d INFO:core:Going down... INFO:openflow.of_01:[ b-d7-16-4b 1] disconnected 6/7
12 INFO:core:Down. 3e. Run a Server Proxy Controller As our last exercise, instead of diverting the traffic to a different server running on the same host, we will divert the traffic to a server running on a different host and on a different port. 1. Under the /tmp/pox/ext/ directory there are two files Proxy.py and myproxy.py that are similar like the previous exercise. Both of these controllers are configured by the configuration file proxy.config. Use myproxy.py to write your own proxy controller. 2. On the terminal of host3 run a netcat server: nc -l On your controller host, open the /tmp/pox/ext/myproxy.py file, and edit it to implement a controller that will divert traffic destined for host2 to host3. Before you start implementing think about what are the side effects of diverting traffic to a different host. Is it enough to just change the IP address? Is it enough to just modify the TCP packets? If you want to see the solution, it's available in file /tmp/pox/ext/proxy.py file. 4. To test your proxy controller run: cd /tmp/pox./pox.py --verbose myproxy 5. Go back to the terminal of host1 and try to connect netcat to host2 port 5000 nc If your controller works correctly, you should see your text showing up on the terminal of host3. 4. Moving to a Hardware Switch To try your controller with a GENI Hardware OpenFlow switch: Delete resources in your slice with the compute resources. Do not delete resources in your slice with the controller. Follow the instructions at OpenFlow Design and Setup for Hardware Switch If you do not want to do the Hardware OpenFlow portion of the tutorial, proceed to Finish Prev: Design and Setup for OVS Prev: Design and Setup for Hardware Switch Next: Finish 7/7
13 5/24/2015 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS/Finish GENI: geni Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Step 4. Teardown Experiment After you are done with this experiment release your resources. In the GENI Portal select the slice click on the "Delete Resources" button: If you have used other tools to run this experiment than release resources as described in the Prerequisites for Tutorials on reservation tools pages. Now you can start designing and running your own experiments! Prev: Execute Introduction 1/1
Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial
 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS-Floodlight GENI: geni Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Overview: This is a simple OpenFlow tutorial that will guide you how to use the Floodlight Controller in conjunction
GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/OpenFlowOVS-Floodlight GENI: geni Intro to OpenFlow Tutorial Overview: This is a simple OpenFlow tutorial that will guide you how to use the Floodlight Controller in conjunction
OpenFlow Firewall and NAT Devices
 OpenFlow Firewall and NAT Devices OpenFlow Firewall and NAT Devices Step by step Instructions Overview: This is a very simple tutorial with two topologies demonstrating an OpenFlow Firewall and an OpenFlow
OpenFlow Firewall and NAT Devices OpenFlow Firewall and NAT Devices Step by step Instructions Overview: This is a very simple tutorial with two topologies demonstrating an OpenFlow Firewall and an OpenFlow
How to Work with Fast-Failover OpenFlow Groups
 How to Work with Fast-Failover OpenFlow Groups Background Redundant links are frequently used in network topology design in order to reduce the risk of end-to-end connectivity failure due to a single link
How to Work with Fast-Failover OpenFlow Groups Background Redundant links are frequently used in network topology design in order to reduce the risk of end-to-end connectivity failure due to a single link
Lab Zero: A First Experiment Using GENI and Jacks Tool
 Lab Zero: A First Experiment Using GENI and Jacks Tool These instructions are at: http://tinyurl.com/geni labzero Overview This is a first, simple experiment on GENI useful for familiarizing new experimenters
Lab Zero: A First Experiment Using GENI and Jacks Tool These instructions are at: http://tinyurl.com/geni labzero Overview This is a first, simple experiment on GENI useful for familiarizing new experimenters
Lab Zero: A First Experiment Using GENI and Jacks Tool
 GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/jacks/GettingStarted_PartI/Procedure GENI: geni 2/27/16, 14:35 Lab Zero: A First Experiment Using GENI and Jacks Tool These instructions are at: http://tinyurl.com/geni-labzero
GENIExperimenter/Tutorials/jacks/GettingStarted_PartI/Procedure GENI: geni 2/27/16, 14:35 Lab Zero: A First Experiment Using GENI and Jacks Tool These instructions are at: http://tinyurl.com/geni-labzero
 Are you ready for the tutorial? 1. Grab a worksheet and instructions 3. Connect to the network Connect to Texas A&M s wireless network 2. Did you do the pre-work? A. Do you have an account? B. Have you
Are you ready for the tutorial? 1. Grab a worksheet and instructions 3. Connect to the network Connect to Texas A&M s wireless network 2. Did you do the pre-work? A. Do you have an account? B. Have you
Network softwarization Lab session 2: OS Virtualization Networking
 Network softwarization Lab session 2: OS Virtualization Networking Nicolas Herbaut David Bourasseau Daniel Negru December 16, 2015 1 Introduction 1.1 Discovering docker 1.1.1 Installation Please launch
Network softwarization Lab session 2: OS Virtualization Networking Nicolas Herbaut David Bourasseau Daniel Negru December 16, 2015 1 Introduction 1.1 Discovering docker 1.1.1 Installation Please launch
Lab I: Using tcpdump and Wireshark
 Objectives To get the student familiar with basic network protocol analyzer, tools and equipment used in later labs, including tcpdump and Wireshark. Lab Readings Go to http://www.tcpdump.org/tcpdump_man.html
Objectives To get the student familiar with basic network protocol analyzer, tools and equipment used in later labs, including tcpdump and Wireshark. Lab Readings Go to http://www.tcpdump.org/tcpdump_man.html
ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Assignment 9: Introduction to OpenFlow
 Spring Term 2015 ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Assignment 9: Introduction to OpenFlow Assigned on: 7 May 2015 Due by: 20 May 2015, 23:59 1 Introduction The goal of this assignment is to give an introduction
Spring Term 2015 ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Assignment 9: Introduction to OpenFlow Assigned on: 7 May 2015 Due by: 20 May 2015, 23:59 1 Introduction The goal of this assignment is to give an introduction
ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Assignment 9: Introduction to OpenFlow
 Spring Term 2014 ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Assignment 9: Introduction to OpenFlow Assigned on: 8 May 2014 Due by: 21 May 2014, 23:59 1 Introduction The goal of this assignment is to give an introduction
Spring Term 2014 ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Assignment 9: Introduction to OpenFlow Assigned on: 8 May 2014 Due by: 21 May 2014, 23:59 1 Introduction The goal of this assignment is to give an introduction
Outline. SDN Overview Mininet and Ryu Overview Mininet VM Setup Ryu Setup OpenFlow Protocol and Open vswitch Reference
 1 Mininet and Ryu 2 Outline SDN Overview Mininet and Ryu Overview Mininet VM Setup Ryu Setup OpenFlow Protocol and Open vswitch Reference 3 SDN Overview Decoupling of control and data planes Directly Programmable
1 Mininet and Ryu 2 Outline SDN Overview Mininet and Ryu Overview Mininet VM Setup Ryu Setup OpenFlow Protocol and Open vswitch Reference 3 SDN Overview Decoupling of control and data planes Directly Programmable
Mininet/Openflow. Objectives. Network Topology. You will need a Number
 Mininet/Openflow Objectives In this lab, you will start by learning the basics of running Mininet in a virtual machine. Mininet facilitates creating and manipulating Software Defined Networking components.
Mininet/Openflow Objectives In this lab, you will start by learning the basics of running Mininet in a virtual machine. Mininet facilitates creating and manipulating Software Defined Networking components.
Exercises: Basics of Network Layer Experiential Learning Workshop
 Exercises: Basics of Network Layer Experiential Learning Workshop 1 General Guidelines 1. Make a team of two or three unless stated otherwise. 2. For each exercise, use wireshark capture to verify contents
Exercises: Basics of Network Layer Experiential Learning Workshop 1 General Guidelines 1. Make a team of two or three unless stated otherwise. 2. For each exercise, use wireshark capture to verify contents
Packet Capturing with TCPDUMP command in Linux
 Packet Capturing with TCPDUMP command in Linux In this tutorial we will be looking into a very well known tool in Linux system administrators tool box. Some times during troubleshooting this tool proves
Packet Capturing with TCPDUMP command in Linux In this tutorial we will be looking into a very well known tool in Linux system administrators tool box. Some times during troubleshooting this tool proves
Assignment 5: Software Defined Networking CS640 Spring 2015
 Assignment 5: Software Defined Networking CS640 Spring 2015 Due: Thursday, May 7 at 11pm Overview For this project you will implement two control application for a software defined network (SDN). A layer
Assignment 5: Software Defined Networking CS640 Spring 2015 Due: Thursday, May 7 at 11pm Overview For this project you will implement two control application for a software defined network (SDN). A layer
netkit lab IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (NDP)
 netkit lab IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (NDP) Version 1.0 Author(s) E-mail Web Description S. Doro based on work ARP by G. Di Battista, M. Patrignani, M. Pizzonia, F. Ricci, M. Rimondini sandro.doro@gmail.com
netkit lab IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (NDP) Version 1.0 Author(s) E-mail Web Description S. Doro based on work ARP by G. Di Battista, M. Patrignani, M. Pizzonia, F. Ricci, M. Rimondini sandro.doro@gmail.com
Title: Running RINA on GENI
 Title: Running RINA on GENI Overview: Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a new network architecture based on the fundamental principle that networking is Inter- Process Communication (IPC).
Title: Running RINA on GENI Overview: Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) is a new network architecture based on the fundamental principle that networking is Inter- Process Communication (IPC).
Introduction to Omni Tutorial
 Introduction to Omni Tutorial Overview: This tutorial will guide you through your first [http://trac.gpolab.bbn.com/gcf/wiki/omni Omni] experiment. [http://trac.gpolab.bbn.com/gcf/wiki/omni Omni] is a
Introduction to Omni Tutorial Overview: This tutorial will guide you through your first [http://trac.gpolab.bbn.com/gcf/wiki/omni Omni] experiment. [http://trac.gpolab.bbn.com/gcf/wiki/omni Omni] is a
Lab 1: Introduction to Linux Networking
 CMPE 150: Introduction to Computer Networks Fall 2011 http://courses.soe.ucsc.edu/courses/cmpe150/fall11/01/ Lab 1: Introduction to Linux Networking Materials: Please bring a USB drive to each lab section.
CMPE 150: Introduction to Computer Networks Fall 2011 http://courses.soe.ucsc.edu/courses/cmpe150/fall11/01/ Lab 1: Introduction to Linux Networking Materials: Please bring a USB drive to each lab section.
Exercises: Basics of Networking II Experiential Learning Workshop
 Exercises: Basics of Networking II Experiential Learning Workshop 1 General Guidelines 1. Make a team of two or three unless stated otherwise. 2. For each exercise, use wireshark capture to verify contents
Exercises: Basics of Networking II Experiential Learning Workshop 1 General Guidelines 1. Make a team of two or three unless stated otherwise. 2. For each exercise, use wireshark capture to verify contents
Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa Network and Computer Security. Lab guide: Traffic analysis and TCP/IP Vulnerabilities
 Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa Network and Computer Security Lab guide: Traffic analysis and TCP/IP Vulnerabilities Revised on 2016-10-18 Alpha version: This is an early version and
Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa Network and Computer Security Lab guide: Traffic analysis and TCP/IP Vulnerabilities Revised on 2016-10-18 Alpha version: This is an early version and
COMPUTER NETWORKS. CPSC 441, Winter 2016 Prof. Mea Wang Department of Computer Science University of Calgary
 COMPUTER NETWORKS CPSC 441, Winter 2016 Prof. Mea Wang Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Introduction: Wireshark and tshark Running tshark Running Wireshark Exercise: Analyze HTTP traffic
COMPUTER NETWORKS CPSC 441, Winter 2016 Prof. Mea Wang Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Introduction: Wireshark and tshark Running tshark Running Wireshark Exercise: Analyze HTTP traffic
Lab Assignment 4 for ECE671 Posted: 11/15/16 Due: 11/29/16. Network Address Translation (NAT) on GENI
 ECE671: Lab Assignment 4 1 Lab Assignment 4 for ECE671 Posted: 11/15/16 Due: 11/29/16 Network Address Translation (NAT) on GENI This assignment builds on assignment 3 and has the goal to introduce you
ECE671: Lab Assignment 4 1 Lab Assignment 4 for ECE671 Posted: 11/15/16 Due: 11/29/16 Network Address Translation (NAT) on GENI This assignment builds on assignment 3 and has the goal to introduce you
OpenFlow Tutorial. March, Version: 1.
 March, 2015 Version: 1 www.pica8.com Pica8, Inc. 1032 Elwell Court, Suite 105 Palo Alto, CA. 94303 +1 (650) 614-5838 sales@pica8.com support@pica8.com Copyright 2015 Pica8 Inc. Pica8 is a registered trademark
March, 2015 Version: 1 www.pica8.com Pica8, Inc. 1032 Elwell Court, Suite 105 Palo Alto, CA. 94303 +1 (650) 614-5838 sales@pica8.com support@pica8.com Copyright 2015 Pica8 Inc. Pica8 is a registered trademark
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
OpenFlow Configuration Lab
 APNIC SDN Workshop Lab OpenFlow Configuration Lab Objective: As part of this hands-on module, you will be installing the Mininet network emulator on your PC. You will then configure a standalone OpenFlow
APNIC SDN Workshop Lab OpenFlow Configuration Lab Objective: As part of this hands-on module, you will be installing the Mininet network emulator on your PC. You will then configure a standalone OpenFlow
Homework 3 CSC/ECE , Fall, 2016
 Homework 3 CSC/ECE 573-001, Fall, 2016 Every question requires response in one or more of the following ways. If the question, in part or whole, requires textual response, include your response to it in
Homework 3 CSC/ECE 573-001, Fall, 2016 Every question requires response in one or more of the following ways. If the question, in part or whole, requires textual response, include your response to it in
TOWARDS REMOTE ACCESS TO VIRTUALIZED TELECOM RESEARCH INFRASTRACTURS
 TOWARDS REMOTE ACCESS TO VIRTUALIZED TELECOM RESEARCH INFRASTRACTURS By ABREHA, HAFTAY GEBRESLASIE Supervisor PROF. FABRIZIO GRANELLI University of Trento MOTIVATION SDN-NFV reinvents telecom network&
TOWARDS REMOTE ACCESS TO VIRTUALIZED TELECOM RESEARCH INFRASTRACTURS By ABREHA, HAFTAY GEBRESLASIE Supervisor PROF. FABRIZIO GRANELLI University of Trento MOTIVATION SDN-NFV reinvents telecom network&
Mininet & OpenFlow 24/11/2016
 Mininet & OpenFlow 24/11/2016 Firt steps: configure VM PREREQUISITE: download and install the mininet VM from http://mininet.org/download/ THEN: Change network settings by enabling «bridge» Start the mininet
Mininet & OpenFlow 24/11/2016 Firt steps: configure VM PREREQUISITE: download and install the mininet VM from http://mininet.org/download/ THEN: Change network settings by enabling «bridge» Start the mininet
Module 2 OpenFlow Configuration Lab
 APNIC SDN Workshop Lab Module 2 OpenFlow Configuration Lab Objective: As part of this hands-on module, you will be installing the Mininet network emulator on your PC. You will then configure a standalone
APNIC SDN Workshop Lab Module 2 OpenFlow Configuration Lab Objective: As part of this hands-on module, you will be installing the Mininet network emulator on your PC. You will then configure a standalone
Fundamentals of Computer Networking AE6382
 Computer networks are an integral part of the modern computing infrastructure The local network (LAN) is usually Ethernet LAN s are inter-connected with other LAN s in a hierarchical fashion eventually
Computer networks are an integral part of the modern computing infrastructure The local network (LAN) is usually Ethernet LAN s are inter-connected with other LAN s in a hierarchical fashion eventually
To see how ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) works. ARP is an essential glue protocol that is used to join Ethernet and IP.
 Lab Exercise ARP Objective To see how ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) works. ARP is an essential glue protocol that is used to join Ethernet and IP. Requirements Wireshark: This lab uses the Wireshark
Lab Exercise ARP Objective To see how ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) works. ARP is an essential glue protocol that is used to join Ethernet and IP. Requirements Wireshark: This lab uses the Wireshark
Project 4: SDNs Due: 11:59 PM, Dec 12, 2018
 CS168 Computer Networks Fonseca Project 4: SDNs Due: 11:59 PM, Dec 12, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Overview 2 2.1 Architecture......................................... 3 3 Shortest-path Switching
CS168 Computer Networks Fonseca Project 4: SDNs Due: 11:59 PM, Dec 12, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Overview 2 2.1 Architecture......................................... 3 3 Shortest-path Switching
Making GENI Experiments Repeatable and Replicable
 Making GENI Experiments Repeatable and Replicable Vic Thomas GENI Project Office Sponsored by the National Science Foundation MAKING EXPERIMENTS REPEATABLE www.geni.net 2 Experiment Repeatability Experiment
Making GENI Experiments Repeatable and Replicable Vic Thomas GENI Project Office Sponsored by the National Science Foundation MAKING EXPERIMENTS REPEATABLE www.geni.net 2 Experiment Repeatability Experiment
Using ping, tracert, and system debugging
 Contents Using ping, tracert, and system debugging 1 Ping 1 Using a ping command to test network connectivity 1 Ping example 1 Tracert 3 Prerequisites 4 Using a tracert command to identify failed or all
Contents Using ping, tracert, and system debugging 1 Ping 1 Using a ping command to test network connectivity 1 Ping example 1 Tracert 3 Prerequisites 4 Using a tracert command to identify failed or all
Network Test and Monitoring Tools
 ajgillette.com Technical Note Network Test and Monitoring Tools Author: A.J.Gillette Date: December 6, 2012 Revision: 1.3 Table of Contents Network Test and Monitoring Tools...1 Introduction...3 Link Characterization...4
ajgillette.com Technical Note Network Test and Monitoring Tools Author: A.J.Gillette Date: December 6, 2012 Revision: 1.3 Table of Contents Network Test and Monitoring Tools...1 Introduction...3 Link Characterization...4
SIMPLE ROUTER PROJECT 2. - Balachander Padmanabha - TA CSE 123 (FALL 2017) - OH (Wed 9-11am B240A)
 SIMPLE ROUTER PROJECT 2 - Balachander Padmanabha - TA CSE 123 (FALL 2017) - OH (Wed 9-11am B240A) MININET It is a network emulation orchestration system which runs a collection of end-hosts, switches,
SIMPLE ROUTER PROJECT 2 - Balachander Padmanabha - TA CSE 123 (FALL 2017) - OH (Wed 9-11am B240A) MININET It is a network emulation orchestration system which runs a collection of end-hosts, switches,
521262S Computer Networks 2 (fall 2007) Laboratory exercise #4: Multimedia, QoS and testing
 521262S Computer Networks 2 (fall 2007) Laboratory exercise #4: Multimedia, QoS and testing Name Student ID Signature In this exercise we will take a little look at the multimedia and Quality of Service
521262S Computer Networks 2 (fall 2007) Laboratory exercise #4: Multimedia, QoS and testing Name Student ID Signature In this exercise we will take a little look at the multimedia and Quality of Service
GIMI/LabWiki Tutorial
 GIMI/LabWiki Tutorial Mike Zink, Divyashri Bhat, Cong Wang, Thierry Rakotoarivelo March 22 nd 2014, UC Davis, CA Experiment Design Perform basic measurements on GENI testbeds ü GENI slice (network & compute
GIMI/LabWiki Tutorial Mike Zink, Divyashri Bhat, Cong Wang, Thierry Rakotoarivelo March 22 nd 2014, UC Davis, CA Experiment Design Perform basic measurements on GENI testbeds ü GENI slice (network & compute
Lab Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Static routing lab KTH/CSC. Juniper version. Group Nr. Name 1. Name 2. Name 3. Name 4. Date. Grade. Instructor s Signature
 KTH/CSC Static routing lab Juniper version Group Nr Name 1 Name 2 Name 3 Name 4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparation questions...3 3 Host configuration...4 4 Static
KTH/CSC Static routing lab Juniper version Group Nr Name 1 Name 2 Name 3 Name 4 Date Grade Instructor s Signature Table of Contents 1 Goals...3 2 Preparation questions...3 3 Host configuration...4 4 Static
I Commands. iping, page 2 iping6, page 4 itraceroute, page 5 itraceroute6 vrf, page 6. itraceroute vrf encap vxlan, page 12
 iping, page 2 iping6, page 4 itraceroute, page 5 itraceroute6 vrf, page 6 itraceroute6 vrf encap vlan, page 7 itraceroute6 vrf encap vxlan dst-mac, page 8 itraceroute vrf, page 9 itraceroute vrf encap
iping, page 2 iping6, page 4 itraceroute, page 5 itraceroute6 vrf, page 6 itraceroute6 vrf encap vlan, page 7 itraceroute6 vrf encap vxlan dst-mac, page 8 itraceroute vrf, page 9 itraceroute vrf encap
COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 4
 Name 1: Name 2: Group number: COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 4 IPV6 December 14, 2009 Abstract In this TP you will revisit some of the basic networking tools that were introduced in TP1, only this
Name 1: Name 2: Group number: COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 4 IPV6 December 14, 2009 Abstract In this TP you will revisit some of the basic networking tools that were introduced in TP1, only this
Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included in the quiz.
 Lab: Introducing Global Unicast Addresses CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included
Lab: Introducing Global Unicast Addresses CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included
Contents. Note: pay attention to where you are. Note: Plaintext version. Note: pay attention to where you are... 1 Note: Plaintext version...
 Contents Note: pay attention to where you are........................................... 1 Note: Plaintext version................................................... 1 Hello World of the Bash shell 2 Accessing
Contents Note: pay attention to where you are........................................... 1 Note: Plaintext version................................................... 1 Hello World of the Bash shell 2 Accessing
PVS Deployment in the Cloud. Last Updated: June 17, 2016
 PVS Deployment in the Cloud Last Updated: June 17, 2016 Contents Amazon Web Services Introduction 3 Software Requirements 4 Set up a NAT Gateway 5 Install PVS on the NAT Gateway 11 Example Deployment 12
PVS Deployment in the Cloud Last Updated: June 17, 2016 Contents Amazon Web Services Introduction 3 Software Requirements 4 Set up a NAT Gateway 5 Install PVS on the NAT Gateway 11 Example Deployment 12
Lab Using Wireshark to Examine Ethernet Frames
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine the Header Fields in an Ethernet II Frame Part 2: Use Wireshark to Capture and Analyze Ethernet Frames Background / Scenario When upper layer protocols communicate with
The trace is here: https://kevincurran.org/com320/labs/wireshark/trace-dhcp.pcap
 Lab Exercise DHCP Objective To see how DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) works. The trace is here: https://kevincurran.org/com320/labs/wireshark/trace-dhcp.pcap Network Setup Recall that DHCP
Lab Exercise DHCP Objective To see how DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) works. The trace is here: https://kevincurran.org/com320/labs/wireshark/trace-dhcp.pcap Network Setup Recall that DHCP
Comodo Dome Data Protection Software Version 3.8
 Comodo Dome Data Protection Software Version 3.8 Installation Guide Guide Version 3.8.102417 Comodo Security Solutions 1255 Broad Street Clifton, NJ 07013 Table of Contents 1.About Dome Data Protection...
Comodo Dome Data Protection Software Version 3.8 Installation Guide Guide Version 3.8.102417 Comodo Security Solutions 1255 Broad Street Clifton, NJ 07013 Table of Contents 1.About Dome Data Protection...
Mininet & OpenFlow 19/05/2017
 Mininet & OpenFlow 19/05/2017 Setup 1: Mininet-based Single Switch sudo mn --topo single,3 --switch ovsk --controller remote c0 Controller port6633 virtual switch loopback (127.0.0.1:6633) s1 OpenFlow
Mininet & OpenFlow 19/05/2017 Setup 1: Mininet-based Single Switch sudo mn --topo single,3 --switch ovsk --controller remote c0 Controller port6633 virtual switch loopback (127.0.0.1:6633) s1 OpenFlow
ICS 351: Networking Protocols
 ICS 351: Networking Protocols IP packet forwarding application layer: DNS, HTTP transport layer: TCP and UDP network layer: IP, ICMP, ARP data-link layer: Ethernet, WiFi 1 Networking concepts each protocol
ICS 351: Networking Protocols IP packet forwarding application layer: DNS, HTTP transport layer: TCP and UDP network layer: IP, ICMP, ARP data-link layer: Ethernet, WiFi 1 Networking concepts each protocol
The flow of transferring the machining programs of the server PC and starting an automatic operation is as below.
 CONTENTS 1 OUTLINE... 1 2 OVERALL FLOW... 1 3 NETWORK CONNECTION... 1 4 SETTING EXAMPLE... 1 5 SET SERVER PC... 2 5.1 Windows 7... 2 5.1.1 Install IIS... 2 5.1.2 Set IIS... 4 5.1.3 Set firewall... 9 5.1.4
CONTENTS 1 OUTLINE... 1 2 OVERALL FLOW... 1 3 NETWORK CONNECTION... 1 4 SETTING EXAMPLE... 1 5 SET SERVER PC... 2 5.1 Windows 7... 2 5.1.1 Install IIS... 2 5.1.2 Set IIS... 4 5.1.3 Set firewall... 9 5.1.4
Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45
 Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45 2016 Preparations In order to succeed with the lab, you must have understood some important parts of the course. Therefore, before you come to the lab
Material for the Networking lab in EITF25 & EITF45 2016 Preparations In order to succeed with the lab, you must have understood some important parts of the course. Therefore, before you come to the lab
Computer Networks A Simple Network Analyzer Decoding Ethernet and IP headers
 Computer Networks A Simple Network Analyzer Decoding Ethernet and IP headers Objectives The main objective of this assignment is to gain an understanding of network activities and network packet formats
Computer Networks A Simple Network Analyzer Decoding Ethernet and IP headers Objectives The main objective of this assignment is to gain an understanding of network activities and network packet formats
Spring 2017 Gabriel Kuri
 Lab 2 ECE 431L Spring 2017 Gabriel Kuri This lab is made up of two parts. Part 1 will consist of familiarizing yourself with the Raspberry Pi (RPi). It includes running Unix/Linux commands to become somewhat
Lab 2 ECE 431L Spring 2017 Gabriel Kuri This lab is made up of two parts. Part 1 will consist of familiarizing yourself with the Raspberry Pi (RPi). It includes running Unix/Linux commands to become somewhat
5. Write a capture filter for question 4.
 Pre-Lab 2: Single Segment IP Networks 1. Review Linux man pages for arp at www.linuxmanpages.com (in both Sections 7 and 8), the ARP RFC (RFC 826) at www.ietf.org, and Section 3.4 of the IBM Red Book.
Pre-Lab 2: Single Segment IP Networks 1. Review Linux man pages for arp at www.linuxmanpages.com (in both Sections 7 and 8), the ARP RFC (RFC 826) at www.ietf.org, and Section 3.4 of the IBM Red Book.
Configuration and Management of Networks
 Final Laboratory Configuration and Management of Networks The final Lab consists in configuring a series of case study routing topologies to configure without instructions. Each scenario has a small description
Final Laboratory Configuration and Management of Networks The final Lab consists in configuring a series of case study routing topologies to configure without instructions. Each scenario has a small description
Lab #9: Basic Linux Networking
 CTEC1767 Data Communications & Networking 2017 Lab #9: Basic Linux Networking Understanding Linux networks starts with understanding Linux network commands and the information they provide. We will use
CTEC1767 Data Communications & Networking 2017 Lab #9: Basic Linux Networking Understanding Linux networks starts with understanding Linux network commands and the information they provide. We will use
Configuration and Management of Networks 2014 / 2015
 ! Departamento de Engenharia Electrotécnica Configuration and Management of Networks 2014 / 2015 Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Electrotécnica e de Computadores 4º ano 8º semestre Final Lab part II:
! Departamento de Engenharia Electrotécnica Configuration and Management of Networks 2014 / 2015 Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Electrotécnica e de Computadores 4º ano 8º semestre Final Lab part II:
Assignment 2 TCP/IP Vulnerabilities
 LEIC/MEIC - IST Alameda LEIC/MEIC/MERC IST Taguspark DEASegInf Network and Computer Security 2012/2013 Assignment 2 TCP/IP Vulnerabilities Goals Gather information about the machines in the network. Explore
LEIC/MEIC - IST Alameda LEIC/MEIC/MERC IST Taguspark DEASegInf Network and Computer Security 2012/2013 Assignment 2 TCP/IP Vulnerabilities Goals Gather information about the machines in the network. Explore
BSc Year 2 Data Communications Lab - Using Wireshark to View Network Traffic. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 BSc Year 2 Data Communications Lab - Using Wireshark to View Network Traffic Topology Objectives Part 1: (Optional) Download and Install Wireshark Part 2: Capture and Analyze Local ICMP Data in Wireshark
BSc Year 2 Data Communications Lab - Using Wireshark to View Network Traffic Topology Objectives Part 1: (Optional) Download and Install Wireshark Part 2: Capture and Analyze Local ICMP Data in Wireshark
COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 1 BASIC CONFIGURATION AND TOOLS FOR EVERYBODY:
 Name 1: Name 2: Group number: COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 1 BASIC CONFIGURATION AND TOOLS FOR EVERYBODY: PING(6), DIG, TRACEROUTE(6), NETSTAT September 24, 2012 Abstract In this TP you will
Name 1: Name 2: Group number: COMPUTER NETWORKING LAB EXERCISES (TP) 1 BASIC CONFIGURATION AND TOOLS FOR EVERYBODY: PING(6), DIG, TRACEROUTE(6), NETSTAT September 24, 2012 Abstract In this TP you will
Lab 8: Introduction to Pen Testing (HPING)
 Lab 8: Introduction to Pen Testing (HPING) Aim: To provide a foundation in understanding of email with a focus on hping to provide security assessments and in understanding the trails of evidence produced.
Lab 8: Introduction to Pen Testing (HPING) Aim: To provide a foundation in understanding of email with a focus on hping to provide security assessments and in understanding the trails of evidence produced.
Tailflow An OpenFlow Controller Framework. Torbjörn Törnkvist 22 March 2013
 Tailflow An OpenFlow Controller Framework Torbjörn Törnkvist 22 March 2013 Tail-f Systems Founded 2005 HQ in Stockholm Sweden, with US sales Software Products: ConfD On-device Management Agent NCS Network
Tailflow An OpenFlow Controller Framework Torbjörn Törnkvist 22 March 2013 Tail-f Systems Founded 2005 HQ in Stockholm Sweden, with US sales Software Products: ConfD On-device Management Agent NCS Network
521262S Computer Networks 2 (fall 2007) Laboratory exercise #2: Internetworking
 521262S Computer Networks 2 (fall 2007) Laboratory exercise #2: Internetworking Name Student ID Signature In this exercise we will connect our LANs made in first exercise with routers and build an internet.
521262S Computer Networks 2 (fall 2007) Laboratory exercise #2: Internetworking Name Student ID Signature In this exercise we will connect our LANs made in first exercise with routers and build an internet.
Mininet Tutorial. Leonardo Richter Bays Gustavo Mio7o Marcelo Caggiani Luizelli Luciano Paschoal Gaspary
 Mininet Tutorial Leonardo Richter Bays Gustavo Mio7o Marcelo Caggiani Luizelli Luciano Paschoal Gaspary Outline Introduc?on Installing Mininet SeAng Up First Steps in Mininet Ini?aliza?on Main commands
Mininet Tutorial Leonardo Richter Bays Gustavo Mio7o Marcelo Caggiani Luizelli Luciano Paschoal Gaspary Outline Introduc?on Installing Mininet SeAng Up First Steps in Mininet Ini?aliza?on Main commands
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 Ping 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Configuring Ping 1-1 Ping Configuration Example 1-2 Tracert 1-4 Introduction 1-4
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 Ping 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Configuring Ping 1-1 Ping Configuration Example 1-2 Tracert 1-4 Introduction 1-4
FINAL EXAM - SLOT 2 TCP/IP NETWORKING Duration: 90 min. With Solutions
 First name: Family name: FINAL EXAM - SLOT 2 TCP/IP NETWORKING Duration: 90 min. With Solutions Jean-Yves Le Boudec, Patrick Thiran 2011 January 15 INSTRUCTIONS 1. The exam is in two time slots. Slot 1
First name: Family name: FINAL EXAM - SLOT 2 TCP/IP NETWORKING Duration: 90 min. With Solutions Jean-Yves Le Boudec, Patrick Thiran 2011 January 15 INSTRUCTIONS 1. The exam is in two time slots. Slot 1
Practical Exercises in Computer Networks
 Practical Exercises in Computer Networks IP forwarding between directly connected stations, ARP and ICMP (WIP) 2015, José María Foces Morán. All rights reserved. Internet is composed of a large number
Practical Exercises in Computer Networks IP forwarding between directly connected stations, ARP and ICMP (WIP) 2015, José María Foces Morán. All rights reserved. Internet is composed of a large number
ICS 451: Today's plan
 ICS 451: Today's plan ICMP ping traceroute ARP DHCP summary of IP processing ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol, 2 functions: error reporting (never sent in response to ICMP error packets) network
ICS 451: Today's plan ICMP ping traceroute ARP DHCP summary of IP processing ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol, 2 functions: error reporting (never sent in response to ICMP error packets) network
Guide to your Plug Computer
 This document lives here: http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/fa11/project3/guide-to-plug.pdf Guide to your Plug Computer UC Berkeley, EE 122, Fall 2011 Version 1 This document is a step-by-step guide
This document lives here: http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/fa11/project3/guide-to-plug.pdf Guide to your Plug Computer UC Berkeley, EE 122, Fall 2011 Version 1 This document is a step-by-step guide
Duke University CompSci 356 Midterm Spring 2016
 Duke University CompSci 356 Midterm Spring 2016 Name (Print):, (Family name) (Given name) Student ID Number: Date of Exam: Feb 25, 2016 Time Period: 11:45am-1pm Number of Exam Pages: 15 (including this
Duke University CompSci 356 Midterm Spring 2016 Name (Print):, (Family name) (Given name) Student ID Number: Date of Exam: Feb 25, 2016 Time Period: 11:45am-1pm Number of Exam Pages: 15 (including this
Computer Security II Lab Network Security
 Computer Security II Lab Network Security Setup Boot lab machine into Windows. In Windows Explorer, navigate to \\evs2\compga02\ and download the three Virtual Machines clientvm1819.zip, servervm1819.zip
Computer Security II Lab Network Security Setup Boot lab machine into Windows. In Windows Explorer, navigate to \\evs2\compga02\ and download the three Virtual Machines clientvm1819.zip, servervm1819.zip
Lab 3: Simple Firewall using OpenFlow
 Lab 3: Simple Firewall using OpenFlow This lab builds on the knowledge acquired through Lab 1 where you were first introduced to the Mininet environment. It will also help you prepare for the class project.
Lab 3: Simple Firewall using OpenFlow This lab builds on the knowledge acquired through Lab 1 where you were first introduced to the Mininet environment. It will also help you prepare for the class project.
Secure Communications Over a Network
 Secure Communications Over a Network Course: MITS:5400G Proffessor: Dr. Xiaodong Lin By: Geoff Vaughan 100309160 March 20th 2012 Abstract The purpose of this experiment is to transmit an encrypted message
Secure Communications Over a Network Course: MITS:5400G Proffessor: Dr. Xiaodong Lin By: Geoff Vaughan 100309160 March 20th 2012 Abstract The purpose of this experiment is to transmit an encrypted message
Assignment 5. 2 Assignment: Emulate a Data Center and Manage it via a Cloud Network Controller
 University of Crete Computer Science Department Lecturer: Prof. Dr. X. Dimitropoulos TAs: Dimitrios Gkounis, George Nomikos Manos Lakiotakis, George Vardakis HY436 - Software Defined Networks Tasks of
University of Crete Computer Science Department Lecturer: Prof. Dr. X. Dimitropoulos TAs: Dimitrios Gkounis, George Nomikos Manos Lakiotakis, George Vardakis HY436 - Software Defined Networks Tasks of
Fundamentals of Linux Platform Security
 Fundamentals of Linux Platform Security Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2012 Hands-On Network Security Module 1 Reconnaissance Tools Roadmap Review of generally
Fundamentals of Linux Platform Security Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2012 Hands-On Network Security Module 1 Reconnaissance Tools Roadmap Review of generally
Fundamentals of Linux Platform Security. Hands-On Network Security. Roadmap. Security Training Course. Module 1 Reconnaissance Tools
 Fundamentals of Linux Platform Security Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2012 Hands-On Network Security Module 1 Reconnaissance Tools Roadmap Review of generally
Fundamentals of Linux Platform Security Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2012 Hands-On Network Security Module 1 Reconnaissance Tools Roadmap Review of generally
ovs dpctl(8) Open vswitch Manual ovs dpctl(8)
 NAME ovs dpctl administer Open vswitch datapaths SYNOPSIS ovs dpctl [options] command [switch] [args...] DESCRIPTION The ovs dpctl program can create, modify, and delete Open vswitch datapaths. A single
NAME ovs dpctl administer Open vswitch datapaths SYNOPSIS ovs dpctl [options] command [switch] [args...] DESCRIPTION The ovs dpctl program can create, modify, and delete Open vswitch datapaths. A single
15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2017 Homework 3
 15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2017 Homework 3 Assigned: Feb 15, 2018 Due: Mar 19, 2018 Lead TA: M.Ahmed Shah 1. Chapter 3: Exercise 41, page 294 2. Chapter 3: Exercise 43, page
15-441: Computer Networks Spring 2017 Homework 3 Assigned: Feb 15, 2018 Due: Mar 19, 2018 Lead TA: M.Ahmed Shah 1. Chapter 3: Exercise 41, page 294 2. Chapter 3: Exercise 43, page
SECURITY+ LAB SERIES. Lab 3: Protocols and Default Network Ports Connecting to a Remote System
 SECURITY+ LAB SERIES Lab 3: Protocols and Default Network Ports Connecting to a Remote System Document Version: 2015-09-24 otherwise noted, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported
SECURITY+ LAB SERIES Lab 3: Protocols and Default Network Ports Connecting to a Remote System Document Version: 2015-09-24 otherwise noted, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported
HOW-TO-GUIDE: demonstrating Fabric Attach using OpenVSwitch
 HOW-TO-GUIDE: demonstrating Fabric Attach using OpenVSwitch 1 Target audience System Engineers interested to understand the Fabric Attach (FA) technology and/or for demo proposes. Why does it make sense
HOW-TO-GUIDE: demonstrating Fabric Attach using OpenVSwitch 1 Target audience System Engineers interested to understand the Fabric Attach (FA) technology and/or for demo proposes. Why does it make sense
Internet Layers. Physical Layer. Application. Application. Transport. Transport. Network. Network. Network. Network. Link. Link. Link.
 Internet Layers Application Application Transport Transport Network Network Network Network Link Link Link Link Ethernet Fiber Optics Physical Layer Wi-Fi ARP requests and responses IP: 192.168.1.1 MAC:
Internet Layers Application Application Transport Transport Network Network Network Network Link Link Link Link Ethernet Fiber Optics Physical Layer Wi-Fi ARP requests and responses IP: 192.168.1.1 MAC:
Lab - TCP Traffic Generator
 ECE4110 Fall Semester, 2010 Lab - TCP Traffic Generator Assigned: Sep 10, 2010 Due: Sep 20, 2010 Group Number: Member Names: Lab Goals 1. Finish a TCP sockets programs to transmit and receive TCP data.
ECE4110 Fall Semester, 2010 Lab - TCP Traffic Generator Assigned: Sep 10, 2010 Due: Sep 20, 2010 Group Number: Member Names: Lab Goals 1. Finish a TCP sockets programs to transmit and receive TCP data.
Experiment 2: Wireshark as a Network Protocol Analyzer
 Experiment 2: Wireshark as a Network Protocol Analyzer Learning Objectives: To become familiarized with the Wireshark application environment To perform basic PDU capture using Wireshark To perform basic
Experiment 2: Wireshark as a Network Protocol Analyzer Learning Objectives: To become familiarized with the Wireshark application environment To perform basic PDU capture using Wireshark To perform basic
ovs dpctl(8) Open vswitch Manual ovs dpctl(8)
 NAME ovs dpctl administer Open vswitch datapaths SYNOPSIS ovs dpctl [options] command [switch] [args...] DESCRIPTION The ovs dpctl program can create, modify, and delete Open vswitch datapaths. A single
NAME ovs dpctl administer Open vswitch datapaths SYNOPSIS ovs dpctl [options] command [switch] [args...] DESCRIPTION The ovs dpctl program can create, modify, and delete Open vswitch datapaths. A single
Layer 4: UDP, TCP, and others. based on Chapter 9 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers
 Layer 4: UDP, TCP, and others based on Chapter 9 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers Concepts application set transport set High-level, "Application Set" protocols deal only with how handled
Layer 4: UDP, TCP, and others based on Chapter 9 of CompTIA Network+ Exam Guide, 4th ed., Mike Meyers Concepts application set transport set High-level, "Application Set" protocols deal only with how handled
Week Date Teaching Attended 5 Feb 2013 Lab 7: Snort IDS Rule Development
 Weekly Tasks Week 5 Rich Macfarlane 2013 Week Date Teaching Attended 5 Feb 2013 Lab 7: Snort IDS Rule Development Aim: The aim of these labs are to further investigate the Snort, network IDS, and methods
Weekly Tasks Week 5 Rich Macfarlane 2013 Week Date Teaching Attended 5 Feb 2013 Lab 7: Snort IDS Rule Development Aim: The aim of these labs are to further investigate the Snort, network IDS, and methods
Lab Assignment 4 ECE374 Spring Posted: 03/22/18 Due: 03/29/18. In this lab, we ll take a quick look at the ICMP and IP protocols.
 Lab Assignment 4 ECE374 Spring 2018 Posted: 03/22/18 Due: 03/29/18 In this lab, we ll take a quick look at the ICMP and IP protocols. Whenever possible you should hand in Wireshark screenshots that you
Lab Assignment 4 ECE374 Spring 2018 Posted: 03/22/18 Due: 03/29/18 In this lab, we ll take a quick look at the ICMP and IP protocols. Whenever possible you should hand in Wireshark screenshots that you
State of the Internet The Need for a New Network Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Network Data Plane SDN Data Plane Technology: OpenFlow
 State of the Internet The Need for a New Network Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Network Data Plane SDN Data Plane Technology: OpenFlow SDN Tutorial 2 SDN Tutorial 3 Proposed in the late 1970s Open Systems
State of the Internet The Need for a New Network Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Network Data Plane SDN Data Plane Technology: OpenFlow SDN Tutorial 2 SDN Tutorial 3 Proposed in the late 1970s Open Systems
GENI Tutorial with tmix Derek O'Neill UNC Chapel Hill
 GENI Tutorial with tmix Derek O'Neill UNC Chapel Hill The purpose of this tutorial is to give an introduction on how to set up and run a simple experiment using the tmix TCP traffic generator on a GENI
GENI Tutorial with tmix Derek O'Neill UNC Chapel Hill The purpose of this tutorial is to give an introduction on how to set up and run a simple experiment using the tmix TCP traffic generator on a GENI
Table of Contents. Cisco NAT Order of Operation
 Table of Contents NAT Order of Operation...1 Document ID: 6209...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 NAT Overview...1 NAT Configuration and Output...2
Table of Contents NAT Order of Operation...1 Document ID: 6209...1 Introduction...1 Prerequisites...1 Requirements...1 Components Used...1 Conventions...1 NAT Overview...1 NAT Configuration and Output...2
Computer Networks Security: intro. CS Computer Systems Security
 Computer Networks Security: intro CS 166 - Computer Systems Security A very easy network 3/14/16 Computer Networks: Intro 2 Two philosophers example Translator Language Translator Engineer Communication
Computer Networks Security: intro CS 166 - Computer Systems Security A very easy network 3/14/16 Computer Networks: Intro 2 Two philosophers example Translator Language Translator Engineer Communication
Lecture 8. Reminder: Homework 3, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 20 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 8 1
 Lecture 8 Reminder: Homework 3, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 20 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 8 1 Outline Chapter 3 - Internetworking 3.1 Switching and Bridging 3.2
Lecture 8 Reminder: Homework 3, Programming Project 2 due on Thursday. Questions? Tuesday, September 20 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 8 1 Outline Chapter 3 - Internetworking 3.1 Switching and Bridging 3.2
IP Addressing, monitoring and packet analyzing
 IP Addressing, monitoring and packet analyzing CS-335a Fall 2012 Computer Science Department Manolis Surligas surligas@csd.uoc.gr 1 TCP/IP stack 2 TCP/IP stack At sending: Each layer adds information to
IP Addressing, monitoring and packet analyzing CS-335a Fall 2012 Computer Science Department Manolis Surligas surligas@csd.uoc.gr 1 TCP/IP stack 2 TCP/IP stack At sending: Each layer adds information to
Network Security Laboratory 23 rd May STATEFUL FIREWALL LAB
 Network Security Laboratory 23 rd May 2016. STATEFUL FIREWALL LAB 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION I. What is Stateful Firewall II. Difference between Stateful and Stateless III. Example of Stateful firewall IV.
Network Security Laboratory 23 rd May 2016. STATEFUL FIREWALL LAB 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION I. What is Stateful Firewall II. Difference between Stateful and Stateless III. Example of Stateful firewall IV.
CS475 Networks Lecture 8 Chapter 3 Internetworking. Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
 Assignments Reading for Lecture 9: Section 3.3 3.2 Basic Internetworking (IP) Bridges and LAN switches from last section have limited ability CS475 Networks Lecture 8 Chapter 3 Internetworking is a logical
Assignments Reading for Lecture 9: Section 3.3 3.2 Basic Internetworking (IP) Bridges and LAN switches from last section have limited ability CS475 Networks Lecture 8 Chapter 3 Internetworking is a logical
Creating a Virtual Network with Virt-manager
 Creating a Virtual Network with Virt-manager Our goal today will be to create three virtual machines on our host machine, network them together using virtual bridges, and pass some very simple traffic
Creating a Virtual Network with Virt-manager Our goal today will be to create three virtual machines on our host machine, network them together using virtual bridges, and pass some very simple traffic
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING
 Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
LAN Setup Reflection
 LAN Setup Reflection After the LAN setup, ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external? o Are you able to log into other
LAN Setup Reflection After the LAN setup, ask yourself some questions: o Does your VM have the correct IP? o Are you able to ping some locations, internal and external? o Are you able to log into other
