8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look
|
|
|
- Nora Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 243 The anchoring of the media in TrGW also has an implicit topology-hiding effect. Without anchoring, the SDP answer provided to the other network would contain the transport address of, for example, a media-plane entity in the operator s network, such as A-SBG or IM-MGW. By media anchoring in TrGW, the SDP answer will contain the transport address of the TrGW. During S session establishment, it is preferable to negotiate equal codec(s) between users, so as to prevent the necessity for media transcoding at TrGW (or another entity). Alternatively, IBCF allows the user plane to be established end to end, without traversing the TrGW. In such an example, the user plane may theoretically not traverse the operator s network at all. That would be the case when the destination subscriber is currently IMS roaming, i.e. registered through a P-CSCF in an IMS network other than the Home IMS network (see Figure 8.13 ). Another group of interworking is formed by calls arriving from the circuit-switched (CS) network, such as the Public Switched Telephony Network (PSTN) or Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) see Figure Operators often restrict interconnection with the IMS network to PSTN or PLMN. Often, the PSTN or PLMN to which the IMS network interconnects is the PSTN or PLMN of FIGURE 8.13 Transparent end-to-end routing of media. FIGURE 8.14 Network architecture related to ingress routing from a CS network. CH008.indd 243 6/30/ :17:13 PM
2 244 CHAPTER 8 Introduction to the IMS Network the same operator. Even when the operators use both a PSTN and a PLMN, interworking with IMS may be confined to PSTN. In that manner, the operator has fewer interworking agreements to arrange. When a call from the operator s IMS network needs to be routed to a network from another operator, existing PSTN interconnect agreements are then used. Interworking between the IMS and CS networks is done through the media gateway control function (MGCF) and multimedia media gateway (IM-MGW). MGCF caters for protocol conversion between the control-plane protocol used in the CS network, typically ISUP, and the control-plane protocol used in the IMS network, S. Instead of ISUP, the CS network may use BICC or S-I. ISUP and S are different paradigms, as far as protocol messages are concerned. ISUP and S also use different state models. ISUP messages need to be mapped to corresponding S request or response messages and vice versa. Not all capability that is defined on ISUP can be mapped to S, and vice versa. Figure 8.15 shows a typical message sequence for a call arriving from a CS domain. 3GPP TS specifies the exact mapping between ISUP messages (and parameters) and S messages (including headers, parameters, SDP). Within the IMS network, there is no FIGURE 8.15 Message sequence for ingress routing from a CS domain. CH008.indd 244 6/30/ :17:13 PM
3 8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 245 ringback tone generated in the user plane; the S terminal establishing a call is responsible for its own ringtone generation to the calling party. When MGCF receives 180 Ringing from the remote party, it instructs the IM-MGW to generate local ringback tone into the CS network. When MGCF receives ISUP IAM, it creates a S INVITE and sends the INVITE to a S server. MGCFs may have the capability to configure S profi les. MGCF parses the received ISUP IAM through number analysis (e.g. A-number analysis and B-number analysis), resulting in the selection of a S profile. The S profile includes a set of parameters that are used for the S signaling from MGCF into the IMS network, such as: S server address; default will be I-CSCF, for terminating S session handling Transport protocol (UDP, TCP) URI format (tel: URI versus sip: URI) for R-URI and for certain S headers. When ISUP in the CS network is being transported over the SS7 network, the ISUP signaling must first be converted to ISUP over. ISUP over is done in accordance with 3GPP TS Refer to Figure ISUP ISUP ISUP S S S MTP3 MTP2 L1 SS7 MTP3 MTP2 L1 M3UA SCTP M3UA SCTP TCP/ UDP/ SCTP TCP/ UDP/ SCTP SS7 signaling function Signaling gateway function Media gateway control function S signaling function FIGURE 8.16 ISUP SS7-based signaling adaptation to ISUP -based signaling. Source: 3GPP TS v8.13.0, fi gure GPP TM and TRs are the property of ARIB, ATIS, CCSA, ETSI, TTA and TTC who jointly own the copyright in them. They are subject to further modifications and are therefore provided to you as is for information purposes only. Further use is strictly prohibited. The conversion between ISUP over SS7 and ISUP over is done in a signaling gateway (SGw). SGw represents a functional entity. Practically, the SGw is often integrated in MGCF. Besides conversion between ISUP and S, there is also conversion between TDM-based media and RTP-based media. It is a common goal that there is no transcoding required for the media. For example, the call in the CS domain may be established with a circuit for 64 kb/s PCM A-law encoding (G.711). The same coding may be used in the packet-switched network. Whereas the media in a CS network is transported through a TDM channel, in E1 CH008.indd 245
4 246 CHAPTER 8 Introduction to the IMS Network links (or STM links) the same media is transported in an IMS network through RTP encapsulation. The RTP media stream will have an RTCP channel associated with it. For the CS IMS interworking case, the media is always traversing the IMS network (via IM-MGW). For the IMS IMS interworking case, on the other hand, IBCF may decide not to anchor the media in a TrGW. The reason media anchoring is necessary in media gateway CS IMS interworking is because both control plane and user plane use different protocols in the respective networks. MGCF may be deployed as a stand-alone node, in which case it is referred to as a media gateway controller (MGC). Alternatively, MGCF may be integrated in mobile softswitch (MSS) or in telephony softswitch (TSS) see Figure Also, the IM-MGW may be integrated in circuit-switched mobile MGW (CS-MGW), as used in the mobile network. These integrations of functional entities allow for optimized network deployment, with fewer nodes and fewer interfaces. The MSS that includes MGCF may be a visited MSC, i.e. MSC with connection to radio access network (RAN). The interface between MSS with integrated MGCF and combined CS-MGW IM-MGW is a combination of the Mc reference point (between the MSC server and CS-MGW) and Mn reference point (between MGCF and IM-MGW). Even when integrated, MGCF and IM-MGW remain separate functional entities. However, when functional entities are integrated, signaling between these entities does not have to comply with standardized reference points. There may be multiple MGCFs in the IMS network, as well as multiple IM-MGWs. These functional entities do not contain user data. Interworking between CS networks may therefore run through one of a multitude of MGCFs, e.g. nearest MGCF, with other MGCFs as a fallback option. The MGCF will, when handling a call, select an IM-MGW. One IM-MGW is controlled by one MGCF. One MGCF may control one or more IM-MGWs. An IM-MGW may be split into logical MGWs, whereby each logical MGW is controlled by one MGCF. Egress routing, from an IMS network to other networks, is explained with reference to Figure Only control-plane entities are shown. ViG is short for video gateway. When S-CSCF handles originating S session establishment, one of the steps to be taken by S-CSCF is to determine the destination serving network. The destination serving network FIGURE 8.17 Integration of IMS border gateway in PLMN nodes. CH008.indd 246
5 8.4 IMS Network Architecture A Closer Look 247 FIGURE 8.18 Egress routing through BGCF (break-out). is derived from the R-URI. If a call is established to a phone number, then the S-CSCF may attempt to obtain a S URI associated with the phone number. The S URI would then be used for egress routing. Obtaining the S URI from the phone number is done through ENUM query (see section 8.7 for more details on ENUM). If, however, the ENUM query by the S-CSCF does not render a S URI, then the S-CSCF will initiate break-out. The rationale of the break-out is that the S-CSCF is a S server and can route only on S URIs, not on phone numbers. The break-out implies that the call will be routed to another network that is capable of routing on phone numbers. An example of such a network is PSTN or PLMN. This other network may be the network that is determined to be the serving network for the destination subscriber. Alternatively, the network to which the break-out occurs is not determined to be the serving network for the destination subscriber, but will act as an intermediate network, routing the call further to the appropriate serving network. For break-out, the S-CSCF forwards the S INVITE (or other request message) to a break-out gateway control function (BGCF). The BGCF is a S proxy that forwards the request further, to a break-out gateway. The BGCF may be deployed on a designated host or may be integrated into S-CSCF. BGCF will select the (most) appropriate break-out gateway for this request, which may be based on one or more of the following criteria: Originating party (calling party) Destination party (called party) Destination network Number portability information Note Indication of destination network or number portability of this call may have been received by S-CSCF from ENUM and included as a parameter in the R-URI. Media session type SDP offer (call type; e.g. voice or voice video) Preferred long-distance carrier. CH008.indd 247
6 248 CHAPTER 8 Introduction to the IMS Network Note Preferred long-distance carrier could form part of the calling subscriber subscription profi le or may be provided by an application server. The selection of break-out gateway by the BGCF may be based on internal configuration or may be done with the aid of an external database query. The exact behavior of the BGCF, with respect to selecting break-out gateway, is vendor specific. A common use of the BGCF is the selection of an MGCF, for routing the call into the CS domain, such as PLMN. Within the CS domain, the call would then be routed further to the appropriate destination, based on techniques like B-number analysis, number portability, and intelligent networks. Routing the break-out call through an MGCF implies that the media of this call will be anchored in an IM-MGW, controlled by the MGCF. Break-out gateway selection based on call type may be done to apply distinctive routing for voice calls and video calls. Whereas voice calls may be routed to a voice-only MGCF, video calls would be routed to a video-capable MGCF, also referred to as video gateway (ViG). For specific interworking cases, the BGCF may select an IBCF for break-out. This method may be applied when the BGCF has determined that a S-based network-tonetwork interworking agreement exists with the destination network. In this case, the destination subscriber may be an IMS subscriber, but the operators have not shared ENUM information. This case is illustrated in Figure The break-out from BGCF to IBCF is subject to certain conditions, such as: 1. Request URI is a S URI. 2. The domain name part of the R-URI points to the network serving the called party; this would not have to be the case when the R-URI is a phone number with an enterprisespecific domain name. FIGURE 8.19 Break-out to other IMS network. CH008.indd 248
7 8.5 Registration 249 The default action by the IBCF in the receiving IMS network is to forward the INVITE request (or other S request) to I-CSCF for further processing, including HSS query and forwarding to S-CSCF. There may be multiple IBCFs in an IMS network, as well as multiple TrGWs. Neither of these maintains a subscriber state between sessions. Per break-out/break-in case, one of a group of IBCFs may be selected, typically through DNS-based load sharing. DNS-based load sharing implies that DNS returns multiple host names in response to an SRV query. The DNS client uses one of these hosts for routing. The multiple host names received from DNS may have a priority or a weight factor associated with them. 8.5 REGISTRATION In this section, we describe the registration process in detail. The goal of registration was briefly mentioned in Chapter 6, namely to create and maintain binding in a S registrar. Such binding allows the establishment of communication sessions to the subscriber using a public user identity. The binding is used to forward the communication sessions to the subscriber s current address. Before looking into the registration procedure, we consider the subscriber data structure in HSS. An IMS subscriber is provisioned in HSS with one or more of each of the following two identification items: IMS public user identity (IMPU). IMPU is used to identify an IMS subscriber over the public communication network, e.g. to establish a communication session with that subscriber. It is also used as identification of the originator of a communication session. The IMPU conforms to the structure of Universal Resource Identifier (URI). Examples include: sip:john.smith@abc-company.se tel: sip: @my-company.nl sip: @ims.mnc004.mcc204.3gppnetwork.org IMS private user identity (IMPI). IMPI is used together with the IMPU to identify the service profile of the subscriber and to determine what authentication should be used for the registration. IMPI has the format of Network Access Identifier (NAI) as defined in IETF RFC 4282 (it has the form of a URI, excluding the schema). Examples of IMPI include: john.smith@abc-company.se @my-company.nl @ims.mnc004.mcc204.3gppnetwork.org The IMPU sip: @ims.mnc004.mcc204.3gppnetwork.org and the IMPI @ims.mnc004.mcc204.3gppnetwork.org are temporary IMPU and IMPI respectively. Temporary IMPU and temporary IMPI may be used when IMS registration CH008.indd 249
8 250 CHAPTER 8 Introduction to the IMS Network takes place from a mobile phone (GPRS, UMTS) that is not equipped with an IMS subscriber identification module (ISIM). 3GPP TS describes how temporary IMPU and temporary IMPI are constructed, based on the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI). IMPU and IMPI form part of the subscriber profile in HSS (see Figure 8.20 ). In the example in Figure 8.20, IMPU #2 is associated with both IMPI #1 and IMPI #2. IMPUs within one implicit registration set (IRS) may have the same service profile or may have different service profiles. The concept of IRS is explained in a later section. When an IMS subscriber registers, in other words creates binding in S-CSCF, the IMS subscriber provides his/her IMPU (or one of his/her IMPUs) to the IMS network and optionally IMPI. By providing IMPU to the IMS network during registration, the subscriber indicates which IMPU or group of IMPUs should be registered. Let s first look at the registration process, step by step. We will first consider the initial registration. An explanation is given with reference to Figure Registration includes, among others, the following two procedures: Authorization. The HSS determines whether the subscriber trying to register is a subscriber to this network. Authentication. Authentication is performed jointly by the HSS and S-CSCF. It is verified that the person or application attempting to register is entitled to use this subscription (has the right credentials). A step-by-step description of the registration process follows. FIGURE 8.20 Relation between IMPU and IMPI in HSS subscriber profi le (example). CH008.indd 250
9 8.5 Registration 251 FIGURE 8.21 IMS registration message sequence. Step 1. S REGISTER from UE to P-CSCF Before the terminal can initiate registration, it has to obtain connectivity. The connectivity may be obtained through corporate LAN, residential WLAN, 3G mobile access, etc. The connectivity should allow for communication over (public) infrastructure, so the IMS terminal (user equipment, UE) can communicate with the public IMS network. IMS registration would now be initiated by sending a registration request towards the IMS network. However, the subscriber should first acquire the following information: Home IMS realm: this is the domain name of the IMS network that this subscriber belongs to for example, ims-operator.se IMPU: as described IMPI: as described P-CSCF address: this is the address ( address or domain name) of the P-CSCF through which the registration should be done. The user of the IMS terminal may configure these information elements. Alternatively, the IMPU, IMPI, and Home IMS realm may be stored on ISIM. The CH008.indd 251 6/30/ :17:15 PM
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (
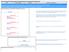 This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side bearer termination. When
This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side bearer termination. When
This sequence diagram was generated with EventStudio System Designer (http://www.eventhelix.com/eventstudio).
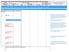 10-Jan-13 16:23 (Page 1) This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side
10-Jan-13 16:23 (Page 1) This call flow covers the handling of a CS network originated call with ISUP. In the diagram the MGCF requests seizure of the IM CN subsystem side termination and CS network side
3GPP TS V8.1.0 ( )
 TS 29.164 V8.1.0 (2009-05) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the CS Domain with BICC or ISUP as
TS 29.164 V8.1.0 (2009-05) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the CS Domain with BICC or ISUP as
3GPP TS V7.2.0 ( )
 TS 23.167 V7.2.0 (2006-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
TS 23.167 V7.2.0 (2006-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
Sh Gy. Ro Gx. Cx Ici. Mr Mj
 Sh Ro Cx Ici SIP UT IMS Sv LTE Mr Mj Mi Mg ISC Mw LTE / VoLTE IMS Protocols Interfaces LTE Protocol Stack IMS Protocol Stack LTE (4G) IMS PSTN / LTE Ex : S1, S5, SGi LTE Control Plane Ex : S1, S10, S11,
Sh Ro Cx Ici SIP UT IMS Sv LTE Mr Mj Mi Mg ISC Mw LTE / VoLTE IMS Protocols Interfaces LTE Protocol Stack IMS Protocol Stack LTE (4G) IMS PSTN / LTE Ex : S1, S5, SGi LTE Control Plane Ex : S1, S10, S11,
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 29.163 V7.24.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network
TS 29.163 V7.24.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.167 V7.11.0 (2008-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
TS 23.167 V7.11.0 (2008-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
 Pilsung AB Taegyun A Fathur AB Afif A Hari A Gary A Dhika AB April AB Mulya AB Yusuf AB Anin A Rizka B Dion AB Siska AB Mirel AB Hani AB Airita AB List of countries by number of Internet users 100,00%
Pilsung AB Taegyun A Fathur AB Afif A Hari A Gary A Dhika AB April AB Mulya AB Yusuf AB Anin A Rizka B Dion AB Siska AB Mirel AB Hani AB Airita AB List of countries by number of Internet users 100,00%
3GPP TS V7.3.0 ( )
 TS 23.167 V7.3.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
TS 23.167 V7.3.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (Release
3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status
 3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status 2 nd SDO Emergency Services Coordination Workshop (ESW07) Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA April 10-12, 2007 Stephen Edge, Qualcomm,
3GPP support for IP based Emergency Calls - April 2007 Status 2 nd SDO Emergency Services Coordination Workshop (ESW07) Library of Congress, Washington, DC, USA April 10-12, 2007 Stephen Edge, Qualcomm,
IP Multimedia Subsystem Application Servers
 IP Multimedia Subsystem Application Servers Second part of the project Presented by: Masood Khosroshahy B E G I N N I N G 1 June 2006 Project supervisor: Prof. Elie Najm IMS Application Servers HSS IMS
IP Multimedia Subsystem Application Servers Second part of the project Presented by: Masood Khosroshahy B E G I N N I N G 1 June 2006 Project supervisor: Prof. Elie Najm IMS Application Servers HSS IMS
3GPP TS V7.4.0 ( )
 Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IM CN subsystem and IP networks () GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IM CN subsystem and IP networks () GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
 The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Miguel A. Garcia Martin Nokia Siemens Networks Application and Services in Internet Helsinki University of Technology October 24, 2007 1 Nokia Siemens Networks IMS / Miguel
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Miguel A. Garcia Martin Nokia Siemens Networks Application and Services in Internet Helsinki University of Technology October 24, 2007 1 Nokia Siemens Networks IMS / Miguel
MED: Voice over IP systems
 Course aim: Online course specification MED: Voice over IP systems This course describes the functional components and operation of telephony systems based on the Internet Protocol (IP) with emphasis on
Course aim: Online course specification MED: Voice over IP systems This course describes the functional components and operation of telephony systems based on the Internet Protocol (IP) with emphasis on
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 29.162 V10.3.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IM CN subsystem and IP networks
TS 29.162 V10.3.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IM CN subsystem and IP networks
3GPP TS V8.7.0 ( )
 TS 23.237 V8.7.0 (2010-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage
TS 23.237 V8.7.0 (2010-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Service Continuity; Stage
IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS) and Its Applications
 KNOM Conference April 26 ~ 27 2007 IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS) and Its Applications 2007. 4. 26 Jun-Won Lee 1 Contents IMS Overview IMS Architecture Contents IMS Applications IMS Enablers & Clients 2
KNOM Conference April 26 ~ 27 2007 IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS) and Its Applications 2007. 4. 26 Jun-Won Lee 1 Contents IMS Overview IMS Architecture Contents IMS Applications IMS Enablers & Clients 2
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 24.341 V12.6.0 (2014-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage 3 (Release 12) The
TS 24.341 V12.6.0 (2014-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage 3 (Release 12) The
3G TS V2.0.0 ( )
 Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - Stage 2 (3G TS 23.228 version 2.0.0) The present document
Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia (IM) Subsystem - Stage 2 (3G TS 23.228 version 2.0.0) The present document
ETSI TR V1.1.1 ( )
 TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Technical Report Methods for Testing and Specification (MTS) IMS Integration Testing Infrastructure Testing Methodology 2 TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Reference DTR/MTS-00099
TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Technical Report Methods for Testing and Specification (MTS) IMS Integration Testing Infrastructure Testing Methodology 2 TR 102 422 V1.1.1 (2005-04) Reference DTR/MTS-00099
3GPP TR V7.0.0 ( )
 TR 29.802 V7.0.0 (2007-06) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; (G)MSC-S (G)MSC-S Nc Interface based on the SIP-I protocol; (Release
TR 29.802 V7.0.0 (2007-06) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; (G)MSC-S (G)MSC-S Nc Interface based on the SIP-I protocol; (Release
ETSI TS V1.1.1 ( )
 TS 183 028 V1.1.1 (2006-04) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet Converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Common basic communication procedures; Protocol specification
TS 183 028 V1.1.1 (2006-04) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet Converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Common basic communication procedures; Protocol specification
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 24.525 V12.1.0 (2014-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Business trunking; Architecture and functional description
TS 24.525 V12.1.0 (2014-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Business trunking; Architecture and functional description
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.228 V12.9.0 (2015-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 (Release 12) The
TS 23.228 V12.9.0 (2015-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 (Release 12) The
ARIB STD-T V10.7.0
 ARIB STD-T63-23.228 V10.7.0 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 (Release 10) Refer to Industrial Property
ARIB STD-T63-23.228 V10.7.0 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 (Release 10) Refer to Industrial Property
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.292 V10.3.0 (2011-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) centralized services; Stage
TS 23.292 V10.3.0 (2011-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) centralized services; Stage
4.2 IMS Service Creation
 4.2 IMS Service Creation 63 IMS service layer application servers IMS basic telephony Simulation servers Subscriber data HSS -AS #1 -AS #2 MMTel application servers Cx IP access network Gm P-CSCF Mw S-CSCF
4.2 IMS Service Creation 63 IMS service layer application servers IMS basic telephony Simulation servers Subscriber data HSS -AS #1 -AS #2 MMTel application servers Cx IP access network Gm P-CSCF Mw S-CSCF
ETSI TS V ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 129 163 V7.20.0 (2010-10) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between the IP Multimedia
TS 129 163 V7.20.0 (2010-10) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between the IP Multimedia
3GPP TS V6.4.0 ( )
 TS 22.234 V6.4.0 (2006-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Requirements on system to Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
TS 22.234 V6.4.0 (2006-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Requirements on system to Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Key technologies in IMS YUAN ZHANG. China telecom Beijing Research Institute
 Key technologies in IMS YUAN ZHANG China telecom Beijing Research Institute Course Objectives: To learn the key technologies in IMS, including the service model, the numbering mechanisms, the network architecture,
Key technologies in IMS YUAN ZHANG China telecom Beijing Research Institute Course Objectives: To learn the key technologies in IMS, including the service model, the numbering mechanisms, the network architecture,
IP Multimedia Subsystem and its protocols: a step to convergence
 IP Multimedia Subsystem and its protocols: a step to convergence Ewa Gałczyńska, Wojciech Zabierowski, Andrzej Napieralski Abstract- Today s world has been changing drastically over few past years in aspect
IP Multimedia Subsystem and its protocols: a step to convergence Ewa Gałczyńska, Wojciech Zabierowski, Andrzej Napieralski Abstract- Today s world has been changing drastically over few past years in aspect
3GPP TS V9.2.0 ( )
 TS 29.163 V9.2.0 (2010-06) Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network
TS 29.163 V9.2.0 (2010-06) Technical Specification 3 rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Interworking between the IP Multimedia (IM) Core Network
Overview and Status of NGN Standardization Activities. Naotaka Morita Vice Chairman of SG13, ITU-T NTT Service Integration Laboratories
 Overview and Status of NGN Standardization Activities Naotaka Morita Vice Chairman of SG13, ITU-T NTT Service Integration Laboratories Contents 1. Outline of NGN 2. Key Technologies of NGN 3. Summary and
Overview and Status of NGN Standardization Activities Naotaka Morita Vice Chairman of SG13, ITU-T NTT Service Integration Laboratories Contents 1. Outline of NGN 2. Key Technologies of NGN 3. Summary and
3GPP TS V6.0.1 ( )
 TS 23.228 V6.0.1 (2003-01) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 (Release 6) The
TS 23.228 V6.0.1 (2003-01) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 (Release 6) The
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 24.229 V5.25.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on Session Initiation
TS 24.229 V5.25.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; IP Multimedia Call Control Protocol based on Session Initiation
IMS signalling for multiparty services based on network level multicast
 IMS signalling for multiparty services based on network level multicast Ivan Vidal, Ignacio Soto, Francisco Valera, Jaime Garcia, Arturo Azcorra UniversityCarlosIIIofMadrid Av.Universidad,30 E-28911, Madrid,
IMS signalling for multiparty services based on network level multicast Ivan Vidal, Ignacio Soto, Francisco Valera, Jaime Garcia, Arturo Azcorra UniversityCarlosIIIofMadrid Av.Universidad,30 E-28911, Madrid,
3GPP TR V ( )
 TR 23.849 V11.0.0 (2012-03) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Study on Stage 2 aspects of Optimised Service Charging and Allocation
TR 23.849 V11.0.0 (2012-03) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Study on Stage 2 aspects of Optimised Service Charging and Allocation
IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem)/ SDP (Service Delivery Platform) 네트워크 / 응용서비스구조및적용
 2008 KNOM Conference IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem)/ SDP (Service Delivery Platform) 네트워크 / 응용서비스구조및적용 한국기술교육대학교 (KUT) 이재오 Contents Related Standards Bodies IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) Network Architecture
2008 KNOM Conference IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem)/ SDP (Service Delivery Platform) 네트워크 / 응용서비스구조및적용 한국기술교육대학교 (KUT) 이재오 Contents Related Standards Bodies IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) Network Architecture
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain
 GPP X.S00-00-0 Version.0 Version Date: July 00 0 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia (IMS) session handling; IP Multimedia (IM) Call Model; Stage 0 COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational
GPP X.S00-00-0 Version.0 Version Date: July 00 0 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia (IMS) session handling; IP Multimedia (IM) Call Model; Stage 0 COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational
Timmins Training Consulting
 VoLTE Core Network Course Outline Short Description VoLTE stands for voice over Long-Term Evolution. It is a combination of LTE and IMS technology which enables processing of digital packet voice service
VoLTE Core Network Course Outline Short Description VoLTE stands for voice over Long-Term Evolution. It is a combination of LTE and IMS technology which enables processing of digital packet voice service
3GPP TS V8.1.0 ( )
 TS 29.205 V8.1.0 (2009-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Application of Q.1900 series to bearer independent Circuit
TS 29.205 V8.1.0 (2009-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Application of Q.1900 series to bearer independent Circuit
3GPP TS V4.3.0 ( )
 TS 29.205 V4.3.0 (2006-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Application of Q.1900 series to bearer-independent Circuit Switched (CS)
TS 29.205 V4.3.0 (2006-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Application of Q.1900 series to bearer-independent Circuit Switched (CS)
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain
 GPP X.S00-00-A v.0 Version.0 Date: November 00 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Stage 0 0 COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document
GPP X.S00-00-A v.0 Version.0 Date: November 00 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Stage 0 0 COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document
3GPP TS V7.0.0 ( )
 TS 23.417 V7.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Telecommunications and Internet
TS 23.417 V7.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Telecommunications and Internet
NG40 IMS Emulator. Key features: IMS Registration VoLTE Basic SRVCC (one-way HO of single active speech session from 4G PS to 3G CS)
 NG40 IMS Emulator IMS Emulation for LTE has been added to the ng4t portfolio. The NG40 IMS Emulator is an extension to the NG40 eutran and to the NG40 EPC Emulator. The NG40 eutran Emulator simulates the
NG40 IMS Emulator IMS Emulation for LTE has been added to the ng4t portfolio. The NG40 IMS Emulator is an extension to the NG40 eutran and to the NG40 EPC Emulator. The NG40 eutran Emulator simulates the
3GPP TR V ( )
 3GPP TR 29.949 V12.0.0 (2014-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Study on technical aspects on roaming end-to-end scenarios
3GPP TR 29.949 V12.0.0 (2014-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Study on technical aspects on roaming end-to-end scenarios
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain
 GPP X.S00-00-B Version.0 Date: December 00 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Stage COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and
GPP X.S00-00-B Version.0 Date: December 00 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Stage COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and
ETSI TS V8.2.0 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 129 235 V8.2.0 (2009-04) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between SIP-I based circuit-switched
TS 129 235 V8.2.0 (2009-04) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between SIP-I based circuit-switched
Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence
 Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence Prepared for: WOCC 2007 Fuchun Joseph Lin Chief Scientist fjlin@research.telcordia.com Telcordia Technologies, Inc. April 28, 2007
Status of IMS-Based Next Generation Networks for Fixed Mobile Convergence Prepared for: WOCC 2007 Fuchun Joseph Lin Chief Scientist fjlin@research.telcordia.com Telcordia Technologies, Inc. April 28, 2007
ETSI TS V ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 129 163 V10.1.1 (2011-04) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between the IP Multimedia
TS 129 163 V10.1.1 (2011-04) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between the IP Multimedia
3GPP TR V8.0.1 ( )
 TR 23.892 V8.0.1 (2008-03) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) centralized services (Release 8)
TR 23.892 V8.0.1 (2008-03) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) centralized services (Release 8)
ETSI TS V2.0.4 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 182 006 V2.0.4 (2008-05) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 description
TS 182 006 V2.0.4 (2008-05) Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Stage 2 description
VoIP Core Technologies. Aarti Iyengar Apricot 2004
 VoIP Core Technologies Aarti Iyengar Apricot 2004 Copyright 2004 Table Of Contents What is Internet Telephony or Voice over IP? VoIP Network Paradigms Key VoIP Protocols Call Control and Signaling protocols
VoIP Core Technologies Aarti Iyengar Apricot 2004 Copyright 2004 Table Of Contents What is Internet Telephony or Voice over IP? VoIP Network Paradigms Key VoIP Protocols Call Control and Signaling protocols
3GPP TS V7.2.0 ( )
 TS 24.341 V7.2.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage 3 (Release 7) GLOBAL
TS 24.341 V7.2.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Support of SMS over IP networks; Stage 3 (Release 7) GLOBAL
ETSI TS V7.4.0 ( )
 TS 124 279 V7.4.0 (2007-03) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Combining Circuit Switched (CS) and IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) services; Stage 3 (3GPP TS 24.279
TS 124 279 V7.4.0 (2007-03) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Combining Circuit Switched (CS) and IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) services; Stage 3 (3GPP TS 24.279
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain
 GPP X.S00-00-0 Version.0 Date: December 00 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem - Charging Architecture 0 0 COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright
GPP X.S00-00-0 Version.0 Date: December 00 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem - Charging Architecture 0 0 COPYRIGHT NOTICE GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Charging Architecture
 3 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Charging Architecture 4 5 6 7 8 3 Contents 3Foreword...ii 4 Scope... 5 References... 63 Definitions, abbreviations and symbols... 7 8 9 3.
3 All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain IP Multimedia Subsystem Charging Architecture 4 5 6 7 8 3 Contents 3Foreword...ii 4 Scope... 5 References... 63 Definitions, abbreviations and symbols... 7 8 9 3.
3GPP TS V8.0.0 ( )
 TS 23.517 V8.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Protocols for Advanced Networking
TS 23.517 V8.0.0 (2007-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Protocols for Advanced Networking
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 23.204 V12.4.0 (2013-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
TS 23.204 V12.4.0 (2013-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
ETSI TS V7.5.0 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 123 206 V7.5.0 (2008-01) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Voice Call Continuity (VCC) between Circuit
TS 123 206 V7.5.0 (2008-01) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Voice Call Continuity (VCC) between Circuit
3GPP TS V8.3.0 ( )
 TS 29.527 V8.3.0 (2009-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols
TS 29.527 V8.3.0 (2009-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols
JJ Common interconnection interface between IMS operator's networks (English Edition)
 JJ-90.30 Common interconnection interface between IMS operator's networks (English Edition) Version 4.1 June 5, 2017 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE Introduction This document provides the TTC
JJ-90.30 Common interconnection interface between IMS operator's networks (English Edition) Version 4.1 June 5, 2017 THE TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY COMMITTEE Introduction This document provides the TTC
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 129 164 V14.0.0 (2017-04) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Interworking between the 3GPP CS domain
TS 129 164 V14.0.0 (2017-04) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Interworking between the 3GPP CS domain
Introduction to 3G 1
 Introduction to 3G 1 References [1] Carrier Grade Voice over IP, D. Collins, McGraw-Hill, Second Edition, 2003. [2] 3GPP TS 23.228 [3] 3GPP TS 24.228 [4] 3GPP TS 23.102 2 Outline Mobile Technology Evolution
Introduction to 3G 1 References [1] Carrier Grade Voice over IP, D. Collins, McGraw-Hill, Second Edition, 2003. [2] 3GPP TS 23.228 [3] 3GPP TS 24.228 [4] 3GPP TS 23.102 2 Outline Mobile Technology Evolution
ARIB STD-T V IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS); Stage 2 (Release 6)
 ARIB STD-T63-23.228 V6.5.0 IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS); Stage 2 (Release 6) Refer to "Industrial Property Rights (IPR)" in the preface of ARIB STD-T63 for Related Industrial Property Rights. Refer to
ARIB STD-T63-23.228 V6.5.0 IP Multimedia Subsystem(IMS); Stage 2 (Release 6) Refer to "Industrial Property Rights (IPR)" in the preface of ARIB STD-T63 for Related Industrial Property Rights. Refer to
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 129 235 V14.0.0 (2017-04) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between SIP-I based
TS 129 235 V14.0.0 (2017-04) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Interworking between SIP-I based
3GPP TS V8.0.0 ( )
 TS 29.527 V8.0.0 (2008-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols
TS 29.527 V8.0.0 (2008-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols
3GPP TR V7.0.0 ( )
 TR 24.930 V7.0.0 (2006-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Signalling flows for the session setup in the IP Multimedia core
TR 24.930 V7.0.0 (2006-12) Technical Report 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Signalling flows for the session setup in the IP Multimedia core
Chapter 3: IP Multimedia Subsystems and Application-Level Signaling
 Chapter 3: IP Multimedia Subsystems and Application-Level Signaling Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao Zhang IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. January 2004 Outline 3.1
Chapter 3: IP Multimedia Subsystems and Application-Level Signaling Jyh-Cheng Chen and Tao Zhang IP-Based Next-Generation Wireless Networks Published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. January 2004 Outline 3.1
ETSI TC INT ACTIVITIES IN THE FIELD OF IMS STANDARDIZATION AND TESTING. Giulio Maggiore ETSI TC INT Chairman Martin Brand ETSI TC INT Vice Chairman
 ETSI TC INT ACTIVITIES IN THE FIELD OF IMS STANDARDIZATION AND TESTING Giulio Maggiore ETSI TC INT Chairman Martin Brand ETSI TC INT Vice Chairman Outline of presentation Core Network Testing 3GPP specs
ETSI TC INT ACTIVITIES IN THE FIELD OF IMS STANDARDIZATION AND TESTING Giulio Maggiore ETSI TC INT Chairman Martin Brand ETSI TC INT Vice Chairman Outline of presentation Core Network Testing 3GPP specs
VoIP Basics. 2005, NETSETRA Corporation Ltd. All rights reserved.
 VoIP Basics Phone Network Typical SS7 Network Architecture What is VoIP? (or IP Telephony) Voice over IP (VoIP) is the transmission of digitized telephone calls over a packet switched data network (like
VoIP Basics Phone Network Typical SS7 Network Architecture What is VoIP? (or IP Telephony) Voice over IP (VoIP) is the transmission of digitized telephone calls over a packet switched data network (like
3GPP TS V ( )
 TS 29.165 V10.10.0 (2012-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Inter-IMS Network to Network Interface (NNI) (Release
TS 29.165 V10.10.0 (2012-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Inter-IMS Network to Network Interface (NNI) (Release
End-to-end IP Service Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 -
 End-to-end IP Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
End-to-end IP Quality and Mobility - Lecture #6 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
Request for Comments: 4083 Category: Informational May 2005
 Network Working Group M. Garcia-Martin Request for Comments: 4083 Nokia Category: Informational May 2005 Input 3rd-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Release 5 Requirements on the Session Initiation
Network Working Group M. Garcia-Martin Request for Comments: 4083 Nokia Category: Informational May 2005 Input 3rd-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Release 5 Requirements on the Session Initiation
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 124 523 V12.2.0 (2015-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Core and enterprise Next Generation Network (NGN) interaction scenarios; Architecture and functional
TS 124 523 V12.2.0 (2015-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Core and enterprise Next Generation Network (NGN) interaction scenarios; Architecture and functional
Multi-Service Access and Next Generation Voice Service
 Hands-On Multi-Service Access and Next Generation Voice Service Course Description The next generation of telecommunications networks is being deployed using VoIP technology and soft switching replacing
Hands-On Multi-Service Access and Next Generation Voice Service Course Description The next generation of telecommunications networks is being deployed using VoIP technology and soft switching replacing
3GPP TS V9.2.0 ( )
 TS 24.259 V9.2.0 (2010-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Personal Network Management (PNM); Stage 3 (Release 9) The
TS 24.259 V9.2.0 (2010-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Personal Network Management (PNM); Stage 3 (Release 9) The
IP Multimedia Subsystem Part 5 Marek Średniawa
 IP Multimedia Subsystem Part 5 Marek Średniawa mareks@tele.pw.edu.pl Institute of Telecommunications Project is co-financed by European Union within the European Social Fund 1 Identification in IMS Identities
IP Multimedia Subsystem Part 5 Marek Średniawa mareks@tele.pw.edu.pl Institute of Telecommunications Project is co-financed by European Union within the European Social Fund 1 Identification in IMS Identities
All-IP Core Network Multimedia Domain
 1 2 3 3GPP2 X.S0013-000-0 Version 1.0 Version Date: December, 2003 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 All-IP Core Multimedia Domain Overview 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 COPYRIGHT NOTICE 3GPP2 and its Organizational Partners
1 2 3 3GPP2 X.S0013-000-0 Version 1.0 Version Date: December, 2003 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 All-IP Core Multimedia Domain Overview 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 COPYRIGHT NOTICE 3GPP2 and its Organizational Partners
Technical White Paper for NAT Traversal
 V300R002 Technical White Paper for NAT Traversal Issue 01 Date 2016-01-15 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. 2016. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
V300R002 Technical White Paper for NAT Traversal Issue 01 Date 2016-01-15 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. 2016. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
3GPP TS V7.1.0 ( )
 TS 29.427 V7.1.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols
TS 29.427 V7.1.0 (2011-09) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 13 年 5 月 27 日星期 一
 Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a data
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS 2. Third Party Voice over IP 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem 4. Circuit Switched Fallback 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a data
ISC Reference Architecture Functional Planes
 ISC Reference Architecture Functional Planes v1.0, Jan 2002 Management Plane Service/Application Plane Application/Feature Servers (SCP, Service Logic), Server IN/AIN Open APIs (Parlay, Jain, CAMEL, SIP,
ISC Reference Architecture Functional Planes v1.0, Jan 2002 Management Plane Service/Application Plane Application/Feature Servers (SCP, Service Logic), Server IN/AIN Open APIs (Parlay, Jain, CAMEL, SIP,
V. Mancuso, I. Tinnirello
 UMTS Core Network GSM/GPRS Network Architecture Radio access network BSS GSM/GPRS core network MS BTS BSC MSC VLR GMSC HLR PSTN, ISDN BTS PCU SGSN AuC EIR IP Backbone GGSN database Internet 3GPP Rel. 99
UMTS Core Network GSM/GPRS Network Architecture Radio access network BSS GSM/GPRS core network MS BTS BSC MSC VLR GMSC HLR PSTN, ISDN BTS PCU SGSN AuC EIR IP Backbone GGSN database Internet 3GPP Rel. 99
ETSI TR V1.1.1 ( )
 Technical Report Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Organization of user data 2 Reference DTR/TISPAN-02027-NGN-R1 Keywords architecture,
Technical Report Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); Organization of user data 2 Reference DTR/TISPAN-02027-NGN-R1 Keywords architecture,
IMS Client Framework for All IP-Based Communication Networks
 IMS Client Framework for All IP-Based Communication Networks D. Jayaram, S. Vijay Anand, Vamshi Raghav, Prashanth Kumar, K. Riyaz & K. Kishan Larsen & Toubro InfoTech Limited Research and Development Group,
IMS Client Framework for All IP-Based Communication Networks D. Jayaram, S. Vijay Anand, Vamshi Raghav, Prashanth Kumar, K. Riyaz & K. Kishan Larsen & Toubro InfoTech Limited Research and Development Group,
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 123 228 V15.2.0 (2018-07) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS);
TS 123 228 V15.2.0 (2018-07) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS);
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 123 226 V11.0.0 (2012-09) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Global text telephony (GTT); Stage 2
TS 123 226 V11.0.0 (2012-09) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Global text telephony (GTT); Stage 2
ETSI TS V9.0.0 ( ) Technical Specification
 TS 129 231 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Application of SIP-I Protocols to Circuit Switched
TS 129 231 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Application of SIP-I Protocols to Circuit Switched
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 123 228 V14.6.0 (2018-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS);
TS 123 228 V14.6.0 (2018-01) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS);
Interconnection & Roaming IMS Signalling Profile (Release 2.0) May 2013
 INTERNATIONAL INTERCONNECTION FORUM FOR SERVICES OVER IP (www.i3forum.org) (i3 FORUM) Source: Workstream Technical Aspects i3 forum keyword: IMS, Signalling Interconnection & Roaming IMS Signalling Profile
INTERNATIONAL INTERCONNECTION FORUM FOR SERVICES OVER IP (www.i3forum.org) (i3 FORUM) Source: Workstream Technical Aspects i3 forum keyword: IMS, Signalling Interconnection & Roaming IMS Signalling Profile
TIM Specification for Gm Interface between an User Equipment and the Fixed IMS Network: MultiMedia Telephony Supplementary Services
 TIM Specification for Gm Interface between an User Equipment and the Fixed IMS Network: MultiMedia Telephony Supplementary Services Rev. 1.1 06/11/2018 1 INDICE DEGLI ARGOMENTI 1. SCOPE... 3 2. APPLICABILITY...
TIM Specification for Gm Interface between an User Equipment and the Fixed IMS Network: MultiMedia Telephony Supplementary Services Rev. 1.1 06/11/2018 1 INDICE DEGLI ARGOMENTI 1. SCOPE... 3 2. APPLICABILITY...
Transporting Voice by Using IP
 Transporting Voice by Using IP National Chi Nan University Quincy Wu Email: solomon@ipv6.club.tw 1 Outline Introduction Voice over IP RTP & SIP Conclusion 2 Digital Circuit Technology Developed by telephone
Transporting Voice by Using IP National Chi Nan University Quincy Wu Email: solomon@ipv6.club.tw 1 Outline Introduction Voice over IP RTP & SIP Conclusion 2 Digital Circuit Technology Developed by telephone
The Interworking of IP Telephony with Legacy Networks
 The Interworking of IP Telephony with Legacy Networks Yang Qiu Valmio 0/ 0080 Helsinki Yang.Qiu@nokia.com Abstract This document describes the Interworking of IP Telephony networks with legacy networks.
The Interworking of IP Telephony with Legacy Networks Yang Qiu Valmio 0/ 0080 Helsinki Yang.Qiu@nokia.com Abstract This document describes the Interworking of IP Telephony networks with legacy networks.
Spirent Landslide VoLTE
 /IMS Node and SIP UE Emulation Voice over LTE () is the combination of IMS-based voice, messaging and video services over the 4G mobile network. To ensure a successful transition, mobile carriers and equipment
/IMS Node and SIP UE Emulation Voice over LTE () is the combination of IMS-based voice, messaging and video services over the 4G mobile network. To ensure a successful transition, mobile carriers and equipment
3GPP TS V7.6.0 ( )
 TS 23.204 V7.6.0 (2009-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
TS 23.204 V7.6.0 (2009-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Support of Short Message Service (SMS) over generic Internet
3GPP TS V8.0.0 ( )
 TS 23.221 V8.0.0 (2008-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Architectural requirements () The present document has
TS 23.221 V8.0.0 (2008-03) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects; Architectural requirements () The present document has
Emergency Services and Priority Signaling
 ITU-T / ATIS Workshop Next Generation Technology and Standardization Emergency Services and Priority Signaling Martin Dolly AT&T (With credit to Percy Tarapore (AT&T) for Priority contributions) ITU-T
ITU-T / ATIS Workshop Next Generation Technology and Standardization Emergency Services and Priority Signaling Martin Dolly AT&T (With credit to Percy Tarapore (AT&T) for Priority contributions) ITU-T
ETSI TS V1.2.1 ( )
 Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); PSTN/ISDN simulation services; Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) and
Technical Specification Telecommunications and Internet converged Services and Protocols for Advanced Networking (TISPAN); PSTN/ISDN simulation services; Terminating Identification Presentation (TIP) and
ETSI TS V7.4.0 ( )
 TS 123 167 V7.4.0 (2007-03) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (3GPP TS 23.167 version 7.4.0 Release 7) 1 TS 123
TS 123 167 V7.4.0 (2007-03) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) emergency sessions (3GPP TS 23.167 version 7.4.0 Release 7) 1 TS 123
