A NOVICE APPROACH ON TRANSITION FROM IPV4-IPV6 USING TUNNELING AND PROTOCOLS OF TUNNELING
|
|
|
- Philip Jennings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A NOVICE APPROACH ON TRANSITION FROM IPV4-IPV6 USING TUNNELING AND PROTOCOLS OF TUNNELING Harjeet Singh Mehta 1, Dilip Kumar 2, Hemant Singhtth Rawat 3 1,2,3 Computer Science and Engineering Department, Tulas Institute of Engineering and Management College, Dehradun, (India) ABSTRACT In this era of Internet evolution, the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has become inevitable and fairly urgent. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has finally exhausted the IPv4 global address space, which leaves the community no choice but to push forward the IPv6 transition process. IPv4 and IPv6 networks both will exist during the transition period, while they were not compatible in nature with each other. Therefore it became necessary to maintain the availability, as well as to provide the inter-communication ability of IPv4 and IPv6. Years ago, a series of transition techniques were actually proposed. However because of some technical issues they failed to cover the solution space well. IPv6 mobility provides a mechanism for the host to roam around different links without losing any communication/connection and its IP address. This paper reconsiders the key difficulties in IPv4-IPv6 transition and introduces the principles of tunneling and the tunneling protocol. This paper looks into the characteristics and transition requirements of practical ISP networks, and proposes the usage and deployment strategy of the transition mechanisms in both backbone and edge networks. Keywords: Virtual Private Network (VPN), Packet buffer, Packet switching, Encapsulation, Sequenced Packet Protocol, frame-relay, interface, Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). I. INTRODUCTION In this we will be focusing more in IPv6. IPv4 is now completely exhausted. A similar issue would be if perhaps you want to connect to IPv6 internet, but your ISP is not ready to give you IPv6 address space. What happens is that we can end up with several sites running IPv6 islands, but those islands are connected via an IPv4 infrastructure. There are a few technologies that deal with how to connect IPv6 islands over an IPv4 network, and one of those technologies is IPv6 automatic 6to4 tunnels. We will be looking at that here. Complete transition from IPv4 to IPv6 s not still there because IPv6 is not backward compatible. This results in a situation where either site is on IPv6 or it is not. To overcome this, we have fewer technologies that can be used to ensure slow and smooth transition from IPv4 to IPv6 these are 1. Tunneling 2. Dual Stack Router 3. NAT Protocol Translation (NAT-PT) 405 P a g e
2 II. TUNNELING Tunneling is a protocol that allows the secure movement of the data from ine network to another. This involves allowing private network communication to be sent across a public network, such as the Internet, through a process called Encapsulation. This encapsulation process allows the data packets to appear as though there nature is public to a public network whereas they are actually private data packets, allowing them to pass through unnoticed. It is also called as PORT-FORWARDING. There are various protocols that allow tunneling to occur, including 2.1 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP): PPTP keeps proprietary data secure even when it is being communicated over public networks. Authorized users can access a private network called a virtual private network, which is provided by an Internet service provider. This is a private network in the virtual sense because it is actually being created in a tunneled environment. 2.1 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP): This type of tunneling protocol involves a combination of using PPTP and Layer 2 Forwarding. The scenario where different IP versions exist on intermediate path or transit networks, tunneling provides an enhanced solution where the data of the user can pass through a non-supported IP version. III. TUNNELING The above diagram depicts how two remote IPv4 networks can communicate via a Tunnel, where the intermediate network is on IPv6 and vice versa is also possible. Here we will be with a corporate network. Our network has three major sites connected over a Wide Area Network (WAN) in a hub and spoke topology. R5 is our HQ site and is the hub. R2 and R4 are spoke sites. R5 has frame relay Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs) directly to R2 and R4 whereas R2 and R4 donot talk directly with each other, only through the hub. Our corporate company is interested in IPv6 but wants to pilot it between the three major sites before committing to go fully IPv6 in the future. Unfortunately, Internet Service Provider (ISP) is still only running on IPv4 and so we have three IPv6 island networks connected through a IPv4 backbone. Let s checkout through a diagram 406 P a g e
3 IV. INITIAL CONFIGURATIONS Let s look at the initial configurations without any IPv6. We will be running Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) as our Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) over frame-relay. Each site will advertise its loopback address into OSPF. After we look at the frame-relay and OSPF configuration on each router we will verify OSPF adjacencies and make sure we can ping the other loopback addresses to ensure we have full IPv4 reachability between our routers. R2 interface Serial0/1/0 ip address encapsulation frame-relay ip ospf priority 0 frame-relay map ip frame-relay map ip frame-relay map ip broadcast no frame-relay inverse-arp frame-relay lmi-type cisco interface Loopback0 ip address router ospf P a g e
4 router-id log-adjacency-changes network area 0 network area 0 R2#sh ip ospf neigh Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/DR 00:01: Serial0/1/0 R2#ping so lo0 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 112/114/116 ms R2#ping so lo0 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/58/60 ms R4 interface Serial0/0 ip address encapsulation frame-relay ip ospf priority 0 frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip frame-relay map ip no frame-relay inverse-arp frame-relay lmi-type cisco interface Loopback0 ip address router ospf 1 router-id log-adjacency-changes network area 0 network area 0 R4#sh ip ospf neigh Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/DR 00:01: Serial0/0 R4#ping so lo0 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: 408 P a g e
5 Packet sent with a source address of Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 112/115/116 ms R4#ping so lo0 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/59/60 ms R5 interface Serial2/0 ip address encapsulation frame-relay ip ospf priority 255 serial restart-delay 0 frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip broadcast frame-relay map ip no frame-relay inverse-arp frame-relay lmi-type cisco interface Loopback0 ip address router ospf 1 router-id log-adjacency-changes network area 0 network area 0 neighbor neighbor R5#sh ip ospf neigh Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/DROTHER 00:01: Serial2/ FULL/DROTHER 00:01: Serial2/0 R5#ping so lo0 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/57/60 ms R5#ping so lo0 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of P a g e
6 Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 56/59/60 ms Basic IPv6 Configurations R2 ipv6 unicast-routing interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:2222:2222:2222::1/64 R4 ipv6 unicast-routing interface Ethernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 address FE80::4 link-local ipv6 address 2001:4444:4444:4444::1/64 R5 ipv6 unicast-routing interface Ethernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 address FE80::5 link-local ipv6 address 2001:5555:5555:5555::1/64 V. HOW IPV6 6TO4 TUNNELING WORK Here we will know how tunneling is actually going to work. We have three separate IPv6 islands now, yet we are connected via an IPv4 infrastructure. Essentially what a 6to4 tunnel does is it encapsulates IPv6 traffic into IPv4 packets. The IPv4 packet will have a source address of its loopback interface and a destination address of the destination router s loopback interface. The IPv4 packet on the outside will carry IP protocol 41 and on the inside will be our IPv6 packet with header and payload. Up until now, this sounds a lot like a simple ipv6ip tunnel, so what s the difference? In an ipv6ip tunnel you specify an IPv4 source and an IPv4 destination manually on the tunnel. It is strictly point-to-point. With IPv6 6to4 tunnels, you don t actually manually specify a tunnel destination, and the technology is multipoint. On each router we will only need a single 6to4 tunnel interface. The IPv6 prefix 2002::/16 is reserved specifically for the 6to4 tunneling technology. Your 6to4 tunnel interface will use an address from this range. Built into the address is an encoding scheme that takes your IPv4 address and encodes it into part of the IPv6 address. This works by encoding the IPv4 address into the IPv6 prefix so that your IPv6 prefix looks something like this: 2002:AABB:CCDD::/48. AABB:CCDD would be your IPv4 address. Once you have your /48 prefix you can utilize a /64 or whatever for your actual tunnel IPv6 address. When routers need to send packets to any address in the 2002::/16 range they will actually look at the 32 bits following 2002, convert them into an IPv4 address and thus figure out themselves the destination of the tunnel. 410 P a g e
7 VI. ENTITIES INVOLVED IN THIS TECHNOLOGY Mobile Node: The device that needs IPv6 mobility. Home Link: This link is configured with the home subnet prefix and this is where the Mobile IPv6 device gets its Home Address. Home Address: This is the address which the Mobile Node acquires from the Home Link. This is the permanent address of the Mobile Node. If the Mobile Node remains in the same Home Link, the communication among various entities take place as usual. Home Agent: This is a router that acts as a registrar for Mobile Nodes. Foreign Link: Any other Link that is not Mobile Node s Home Link. Care-of Address: When a Mobile Node gets attached to a Foreign Link, it acquires a new IP address of that Foreign Link subnet. Home Agent maintains the information of both Home Address and Care-of Address. Multiple Care-of addresses can be assigned to a Mobile Node, but at any instance, only one Care-of Address could get bind with the Home Address. Correspondent Node: Any IPv6 enabled device that intends to have communication with Mobile Node. VII. MOBILITY OPERATION When Mobile Node stays in its Home Link, all communications take place on its Home Address as depicted in the figure below: VIII. MOBILE NODE CONNECTED TO THE HOME LINK When a Mobile Node leaves its Home Link and is connected to some Foreign Link, the Mobility feature of IPv6 comes into play. After getting connected to a Foreign Link, the Mobile Node acquires an IPv6 address from the Foreign Link. This address is called Care-of Address. The Mobile Node sends a binding request to its Home Agent with the new Care-of Address. The Home Agent binds the Mobile Node s Home Address with the Careof Address, establishing a Tunnel between both. Whenever a Correspondent Node wanted to establish a connection with the Mobile Node, the Home Agent intercepts the packet and forwards to Mobile Node s Care-of Address over the Tunnel which has already been established. 411 P a g e
8 Mobile Node Connected To Foreign Link IX. PROPOSED WORK Through tunneling the transition from IPv4-IPv6 the transition takes place through certain protocols pf tunneling which ultimately is increasing the time-complexity. It would be better if the transition occurs without tunneling which reduces the complexity of time. X. CONCLUSION This document discusses ways to provide a seamless Internet experience to user accessing IPv4 internet services though completely new IPv6-ip. We have discussed over the difference between the IPv6 and IPv6-ip. We have seen the need of transition from IPv4 to IPv6. We should also keep in mind the security for this we have discussed certain protocols of tunneling. It also describes how established content providers and content enablers can transparently provide existing or new services to IPv6 Internet users by deploying Network Address Translation IPv6 to IPv4 (NAT64) technology with little or no change in their existing network infrastructure, thus maintaining business continuity. XI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We thank Dr. Pramod Kumar Jain (Director, Tulas Institute Dehradun). We would also like to thanks Mrs. Mitali Chugh (HOD of CSE Department, Tulas Institute) for her assistance and comments that greatly improved our manuscript. We would also like to show our gratitude to Mrs. Shuchi Jain (Assistant Professor CSE Department, Tulas Institute) for sharing their pearls of wisdom with us during the course of this research. Although any errors are our own and should not tarnish the reputations of these esteemed persons. REFERENCES [1]. [2]. [3] P a g e
9 [4]. [5]. [6] P a g e
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Network System Security
 Network System Security Unit 32 Internet Protocol v6 (IPv6) Internet Protocol v6(ipv6) Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest revision of the Internet Protocol (IP) and the first version of the
Network System Security Unit 32 Internet Protocol v6 (IPv6) Internet Protocol v6(ipv6) Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest revision of the Internet Protocol (IP) and the first version of the
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Unit 5 - IPv4/ IPv6 Transition Mechanism(8hr) BCT IV/ II Elective - Networking with IPv6
 5.1 Tunneling 5.1.1 Automatic Tunneling 5.1.2 Configured Tunneling 5.2 Dual Stack 5.3 Translation 5.4 Migration Strategies for Telcos and ISPs Introduction - Transition - the process or a period of changing
5.1 Tunneling 5.1.1 Automatic Tunneling 5.1.2 Configured Tunneling 5.2 Dual Stack 5.3 Translation 5.4 Migration Strategies for Telcos and ISPs Introduction - Transition - the process or a period of changing
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Service Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Service Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...5 1.1 Overview...5 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel...6 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel...6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Service Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...5 1.1 Overview...5 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel...6 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel...6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
Initial motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated. Additional motivation:
 IPv6 Initial motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated. Additional motivation: header format helps speed processing/forwarding header changes to facilitate QoS IPv6 datagram format:
IPv6 Initial motivation: 32-bit address space soon to be completely allocated. Additional motivation: header format helps speed processing/forwarding header changes to facilitate QoS IPv6 datagram format:
LAB 5: DMVPN BGP. LAB 5: Diagram. Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M.
 LAB 5: DMVPN BGP LAB 5: Diagram Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M. LAB 5: Configure BGP over DMVPN Configuration Step 1: Enable loopback and physical interfaces
LAB 5: DMVPN BGP LAB 5: Diagram Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M. LAB 5: Configure BGP over DMVPN Configuration Step 1: Enable loopback and physical interfaces
Cisco IOS LISP Application Note Series: Access Control Lists
 Cisco IOS LISP Application Note Series: Access Control Lists Version 1.1 (28 April 2011) Background The LISP Application Note Series provides targeted information that focuses on the integration and configuration
Cisco IOS LISP Application Note Series: Access Control Lists Version 1.1 (28 April 2011) Background The LISP Application Note Series provides targeted information that focuses on the integration and configuration
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
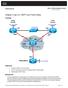 Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Lab 2-4a EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Router Used As Frame Switch
 Lab 2-4a EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Router Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth-percent command onfigure EIGRP
Lab 2-4a EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Router Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth-percent command onfigure EIGRP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing Cisco 300-101 Dumps Available Here at: /cisco-exam/300-101-dumps.html Enrolling now you will get access to 190 questions in a unique set of 300-101 dumps Question 1 Automatic
Implementing Cisco IP Routing Cisco 300-101 Dumps Available Here at: /cisco-exam/300-101-dumps.html Enrolling now you will get access to 190 questions in a unique set of 300-101 dumps Question 1 Automatic
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Lab 2-4b EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Adtran Used As Frame Switch
 Lab 2-4b EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Adtran Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth percentage onfigure EIGRP over
Lab 2-4b EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Adtran Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth percentage onfigure EIGRP over
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Security Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Security Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...4 1.1 Overview... 4 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel... 5 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel... 6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Security Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...4 1.1 Overview... 4 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel... 5 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel... 6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites
 Case Study 1 Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: Asynchronous
Case Study 1 Configure ISDN Connectivity between Remote Sites Cisco Networking Academy Program CCNP 2: Remote Access v3.1 Objectives In this case study, the following concepts are covered: Asynchronous
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II I2 R2 4 N1. DOiT-200v6 Lab 16 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario. For CCIE Candidates
 Revision 7.0 (10/26/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 16 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II 4 I2 R2 3 3 R5 I5 3 3 R6 R1 4 N1 4 4 2 2 1 4 I3 R3 3 1 R4 3 N2 N1 I4 1 R7 DOiT-200v6
Revision 7.0 (10/26/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 16 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II 4 I2 R2 3 3 R5 I5 3 3 R6 R1 4 N1 4 4 2 2 1 4 I3 R3 3 1 R4 3 N2 N1 I4 1 R7 DOiT-200v6
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example
 Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Introduction to Segment Routing
 Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 10 Case Study
 Objectives: Use OSPF single area to illustrate basic Link State components and operation. Migrate from EIGRP to OSPF single area. Intro: Trevni Inc. decided to upgrade their routing protocol from EIGRP
Objectives: Use OSPF single area to illustrate basic Link State components and operation. Migrate from EIGRP to OSPF single area. Intro: Trevni Inc. decided to upgrade their routing protocol from EIGRP
Configuration and Management of Networks
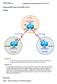 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
EEC-684/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-684/584 Computer Networks Lecture 14 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 Review of last lecture Internetworking
EEC-684/584 Computer Networks Lecture 14 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 Review of last lecture Internetworking
v5.0 Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Physical or Logical
 CCIE Foundation v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Physical or Logical R&S Foundation by Narbik Kocharians CCIE R&S Foundation v5.0 Page 1 of 90 LAB 2
CCIE Foundation v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Physical or Logical R&S Foundation by Narbik Kocharians CCIE R&S Foundation v5.0 Page 1 of 90 LAB 2
Internet Protocol, Version 6
 Outline Protocol, Version 6 () Introduction to Header Format Addressing Model ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Transition from to vs. Taken from:chun-chuan Yang Basics: TCP/ Protocol Suite Protocol (IP) Features:
Outline Protocol, Version 6 () Introduction to Header Format Addressing Model ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Transition from to vs. Taken from:chun-chuan Yang Basics: TCP/ Protocol Suite Protocol (IP) Features:
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 7: Introduction to IPv6 Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 IPv6 Features The ability to scale networks for future demands requires a limitless supply of
Planning for Information Network Lecture 7: Introduction to IPv6 Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 IPv6 Features The ability to scale networks for future demands requires a limitless supply of
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Manually Configured IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnels
 This feature provides support for manually configured IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels. A manually configured tunnel is equivalent to a permanent link between two IPv6 domains over an IPv4 backbone. Finding Feature
This feature provides support for manually configured IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels. A manually configured tunnel is equivalent to a permanent link between two IPv6 domains over an IPv4 backbone. Finding Feature
CSEP 561 Internetworking. David Wetherall
 CSEP 561 Internetworking David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Internetworking t Focus: Joining multiple, different networks into one larger network Forwarding models Application Heterogeneity Transport
CSEP 561 Internetworking David Wetherall djw@cs.washington.edu Internetworking t Focus: Joining multiple, different networks into one larger network Forwarding models Application Heterogeneity Transport
Implementing Tunneling for IPv6
 Implementing Tunneling for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 This module describes how to configure overlay tunneling techniques used by the Cisco IOS software to support the transition from IPv4-only networks
Implementing Tunneling for IPv6 Last Updated: July 31, 2012 This module describes how to configure overlay tunneling techniques used by the Cisco IOS software to support the transition from IPv4-only networks
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2
 Cisco 200-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 R1# show running-config description ***Loopback*** ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 Question: 374 description **Connected to R1-LAN**
Cisco 200-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 R1# show running-config description ***Loopback*** ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 Question: 374 description **Connected to R1-LAN**
IPv6 Feature Facts
 12.1.2 IPv6 Feature Facts The current IP addressing standard, version 4, will eventually run out of unique addresses, so a new system is being developed. It is named IP version 6 or IPv6. You should know
12.1.2 IPv6 Feature Facts The current IP addressing standard, version 4, will eventually run out of unique addresses, so a new system is being developed. It is named IP version 6 or IPv6. You should know
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN
 Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Cisco Exam CCNA Version: 4.1 [ Total Questions: 215 ]
![Cisco Exam CCNA Version: 4.1 [ Total Questions: 215 ] Cisco Exam CCNA Version: 4.1 [ Total Questions: 215 ]](/thumbs/76/73554916.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 640-801 CCNA Version: 4.1 [ Total Questions: 215 ] Question No : 1 Which router command can be used to verify the type of cable connected to interface serial 0/0? A. show interfaces serial
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 640-801 CCNA Version: 4.1 [ Total Questions: 215 ] Question No : 1 Which router command can be used to verify the type of cable connected to interface serial 0/0? A. show interfaces serial
The Interconnection Structure of. The Internet. EECC694 - Shaaban
 The Internet Evolved from the ARPANET (the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), a project funded by The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) in 1969. ARPANET's purpose was to provide the U.S. Defense
The Internet Evolved from the ARPANET (the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), a project funded by The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) in 1969. ARPANET's purpose was to provide the U.S. Defense
Chapter 7: IP Addressing CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0
 Chapter 7: IP Addressing CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 CCNET v6 13 Chapter 7 - Sections & Objectives 7.1 IPv4 Network Addresses Convert between binary and decimal numbering
Chapter 7: IP Addressing CCENT Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 CCNET v6 13 Chapter 7 - Sections & Objectives 7.1 IPv4 Network Addresses Convert between binary and decimal numbering
IPv6 Rapid Deployment: Provide IPv6 Access to Customers over an IPv4-Only Network
 White Paper IPv6 Rapid Deployment: Provide IPv6 Access to Customers over an IPv4-Only Network What You Will Learn IPv6 Rapid Deployment (6rd) (RFC 5969) 6rd is a stateless tunneling mechanism which allows
White Paper IPv6 Rapid Deployment: Provide IPv6 Access to Customers over an IPv4-Only Network What You Will Learn IPv6 Rapid Deployment (6rd) (RFC 5969) 6rd is a stateless tunneling mechanism which allows
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, Jan. 2013, pp
 MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 15 20 15 MPLS and NGN Networks: The Future Aspects for Railways Communication System Alok Pandey E,
MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 3, No. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 15 20 15 MPLS and NGN Networks: The Future Aspects for Railways Communication System Alok Pandey E,
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Easy Virtual Network Simplifying Layer 3 Network Virtualization
 Easy Virtual Network Simplifying Layer 3 Network Virtualization This paper introduces the new Layer 3 network virtualization solution Easy Virtual Network (EVN). It discusses the need for enterprise network
Easy Virtual Network Simplifying Layer 3 Network Virtualization This paper introduces the new Layer 3 network virtualization solution Easy Virtual Network (EVN). It discusses the need for enterprise network
MIGRATION OF INTERNET PROTOCOL V4 TO INTERNET PROTOCOL V6 USING DUAL-STACK TECHNIQUE
 MIGRATION OF INTERNET PROTOCOL V4 TO INTERNET PROTOCOL V6 USING DUAL-STACK TECHNIQUE 1 SHEETAL BORSE, 2 MRUDUL DIXIT 1,2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Cummins College of Engineering
MIGRATION OF INTERNET PROTOCOL V4 TO INTERNET PROTOCOL V6 USING DUAL-STACK TECHNIQUE 1 SHEETAL BORSE, 2 MRUDUL DIXIT 1,2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Cummins College of Engineering
OSPF, MTU and LSA Packing Tech Note
 OSPF, MTU and LSA Packing Tech Note Document ID: 116119 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Jul 29, 2013 Contents Introduction OSPF Packet Size MTU in DBD Packet OSPF Behavior and Packing
OSPF, MTU and LSA Packing Tech Note Document ID: 116119 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Jul 29, 2013 Contents Introduction OSPF Packet Size MTU in DBD Packet OSPF Behavior and Packing
Performance Comparison of Internet Protocol v4 with Internet Protocol v6
 Performance Comparison of Internet Protocol v4 with Internet Protocol v6 Mrs. Sheetal Mali Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Parvatibai Genba Sopanrao Moze College of Engineering Wagholi,
Performance Comparison of Internet Protocol v4 with Internet Protocol v6 Mrs. Sheetal Mali Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Parvatibai Genba Sopanrao Moze College of Engineering Wagholi,
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configuration DN Bit Verify Troubleshoot Related Cisco Support Community Discussions Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configuration DN Bit Verify Troubleshoot Related Cisco Support Community Discussions Introduction
CONCEPTION ON TRANSITION METHODS: DEPLOYING NETWORKS FROM IPV4 TO IPV6
 CONCEPTION ON TRANSITION METHODS: DEPLOYING NETWORKS FROM IPV4 TO IPV6 1 MS. CHAITA JANI, 2 PROF.MEGHA MEHTA 1 M.E.[C.E] Student, Department Of Computer Engineering, Noble Group Of Institutions, Junagadh,Gujarat
CONCEPTION ON TRANSITION METHODS: DEPLOYING NETWORKS FROM IPV4 TO IPV6 1 MS. CHAITA JANI, 2 PROF.MEGHA MEHTA 1 M.E.[C.E] Student, Department Of Computer Engineering, Noble Group Of Institutions, Junagadh,Gujarat
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
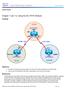 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Modification to Ipv6 Neighbor Discovery and Mobile Node Operation
 RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 6 (October 2012), PP 39-49 www.researchinventy.com Modification to Ipv6 Neighbor Discovery and Mobile Node
RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 6 (October 2012), PP 39-49 www.researchinventy.com Modification to Ipv6 Neighbor Discovery and Mobile Node
Adapted from the Synchronization example in g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html
 Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Lab 3.2 Configuring a Basic GRE Tunnel
 Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Lecture 3. The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
This tutorial will help you in understanding IPv6 and its associated terminologies along with appropriate references and examples.
 About the Tutorial Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest revision of the Internet Protocol (IP) and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. IPv6 was developed by the Internet
About the Tutorial Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the latest revision of the Internet Protocol (IP) and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. IPv6 was developed by the Internet
On Distributed Communications, Rand Report RM-3420-PR, Paul Baran, August 1964
 The requirements for a future all-digital-data distributed network which provides common user service for a wide range of users having different requirements is considered. The use of a standard format
The requirements for a future all-digital-data distributed network which provides common user service for a wide range of users having different requirements is considered. The use of a standard format
Introduction to MPLS APNIC
 Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
IP Routing & Bridging
 CHAPTER 2 TCP/IP Routing: Ethernet Dialog Box To access this dialog box (Figure 2-1), select Ethernet/TCP/IP Routing from the Device View. Figure 2-1 TCP/IP Routing: Ethernet Configuration Dialog Box If
CHAPTER 2 TCP/IP Routing: Ethernet Dialog Box To access this dialog box (Figure 2-1), select Ethernet/TCP/IP Routing from the Device View. Figure 2-1 TCP/IP Routing: Ethernet Configuration Dialog Box If
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
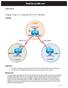 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
Radware ADC. IPV6 RFCs and Compliance
 Radware ADC IPV6 s and Compliance Knowledgebase Team February 2016 Scope: This document lists most of the s that relevant to IPv6. Legend: Yes supported N/A not applicable No Currently not supported Relevance:
Radware ADC IPV6 s and Compliance Knowledgebase Team February 2016 Scope: This document lists most of the s that relevant to IPv6. Legend: Yes supported N/A not applicable No Currently not supported Relevance:
Introduction Mobility Support Handover Management Conclutions. Mobility in IPv6. Thomas Liske. Dresden University of Technology
 2005 / High Speed Networks II Outline Introduction Mobility Support Overview of IPv6 Mobility Support Handover Management Mobility Support What means Mobility Support? allow transparent routing of IPv6
2005 / High Speed Networks II Outline Introduction Mobility Support Overview of IPv6 Mobility Support Handover Management Mobility Support What means Mobility Support? allow transparent routing of IPv6
MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses
 MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN Inter-AS with Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses feature allows
MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN Inter-AS with Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses feature allows
MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs: Inter-AS and CSC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15SY
 MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs: Inter-AS and CSC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15SY First Published: October 15, 2012 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs: Inter-AS and CSC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15SY First Published: October 15, 2012 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates
 DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
OSI Data Link & Network Layer
 OSI Data Link & Network Layer Erkki Kukk 1 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Compare OSI and TCP/IP model 2 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Explain protocol data units (PDU) and encapsulation 3 Addressing
OSI Data Link & Network Layer Erkki Kukk 1 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Compare OSI and TCP/IP model 2 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Explain protocol data units (PDU) and encapsulation 3 Addressing
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 1 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
OSI Data Link & Network Layer
 OSI Data Link & Network Layer Erkki Kukk 1 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Compare OSI and TCP/IP model 2 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Explain protocol data units (PDU) and encapsulation 3 Addressing
OSI Data Link & Network Layer Erkki Kukk 1 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Compare OSI and TCP/IP model 2 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Explain protocol data units (PDU) and encapsulation 3 Addressing
3 ROUTER SETUP WITH FRAME RELAY CONFIGURATION OF FRAME RELAY ROUTER
 3 ROUTER SETUP WITH FRAME RELAY R2 s0 Network 192.168.1.0 s1 DCE * Frame Relay Network * s0 192.168.1.0 s0 DCE R1 Hardware Requirement: 1 Router with t 2 Serials 2 Router with 1 Serial 2 DTE/DCE Serial
3 ROUTER SETUP WITH FRAME RELAY R2 s0 Network 192.168.1.0 s1 DCE * Frame Relay Network * s0 192.168.1.0 s0 DCE R1 Hardware Requirement: 1 Router with t 2 Serials 2 Router with 1 Serial 2 DTE/DCE Serial
OSI Data Link & Network Layer
 OSI Data Link & Network Layer Erkki Kukk 1 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Compare OSI and TCP/IP model 2 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Explain protocol data units (PDU) and encapsulation 3 Addressing
OSI Data Link & Network Layer Erkki Kukk 1 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Compare OSI and TCP/IP model 2 Layers with TCP/IP and OSI Model Explain protocol data units (PDU) and encapsulation 3 Addressing
L2VPN Interworking. Finding Feature Information
 Interworking is a transforming function that is required to interconnect two heterogeneous attachment circuits (ACs). Several types of interworking functions exist. The function that is used would depend
Interworking is a transforming function that is required to interconnect two heterogeneous attachment circuits (ACs). Several types of interworking functions exist. The function that is used would depend
Configuring MPLS L2VPN
 Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 MPLS L2VPN overview 1 About MPLS L2VPN 1 Comparison with traditional VPN 2 Comparison with MPLS L3VPN 2 Basic concepts 2 MPLS L2VPN implementation 3 MPLS L2VPN configuration
Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 MPLS L2VPN overview 1 About MPLS L2VPN 1 Comparison with traditional VPN 2 Comparison with MPLS L3VPN 2 Basic concepts 2 MPLS L2VPN implementation 3 MPLS L2VPN configuration
Configuring MPLS L2VPN
 Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 MPLS L2VPN overview 1 Basic concepts of MPLS L2VPN 2 Implementation of MPLS L2VPN 2 MPLS L2VPN configuration task list 4 Configuring MPLS L2VPN 5 Configuring CCC MPLS
Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 MPLS L2VPN overview 1 Basic concepts of MPLS L2VPN 2 Implementation of MPLS L2VPN 2 MPLS L2VPN configuration task list 4 Configuring MPLS L2VPN 5 Configuring CCC MPLS
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS
 Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS Philip Smith philip@nsrc.org SAFNOG 2 7 th -8 th April 2015 Mbabane Last updated 27 March 2014 1 Presentation slides p Available at: n http://bgp4all.com/ftp/seminars/safnog2-
Migrating from OSPF to IS-IS Philip Smith philip@nsrc.org SAFNOG 2 7 th -8 th April 2015 Mbabane Last updated 27 March 2014 1 Presentation slides p Available at: n http://bgp4all.com/ftp/seminars/safnog2-
Configuring MPLS L2VPN
 Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 Overview 1 Comparison with traditional VPN 1 Comparison with MPLS L3VPN 2 Basic concepts 2 MPLS L2VPN implementation 3 MPLS L2VPN configuration task list 4 Configuring
Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 Overview 1 Comparison with traditional VPN 1 Comparison with MPLS L3VPN 2 Basic concepts 2 MPLS L2VPN implementation 3 MPLS L2VPN configuration task list 4 Configuring
EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the "IP[v6] Unnumbered" Command Configuration Example
![EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the IP[v6] Unnumbered Command Configuration Example EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the IP[v6] Unnumbered Command Configuration Example](/thumbs/92/108645128.jpg) EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the "IP[v6] Unnumbered" Command Configuration Example Document ID: 116346 Contributed by Michal Garcarz and Olivier Pelerin, Cisco TAC Engineers. Sep 18, 2013
EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the "IP[v6] Unnumbered" Command Configuration Example Document ID: 116346 Contributed by Michal Garcarz and Olivier Pelerin, Cisco TAC Engineers. Sep 18, 2013
LAB8: OSPF IPv4. OSPF: Virtual Link. Disclaimer
 Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 AB8: OSPF IPv4 Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458
 DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
GLOSSARY. See ACL. access control list.
 GLOSSARY A access control list ACL API Application Programming Interface area AS ASN ATM autonomous system autonomous system number See ACL. access control list. application programming interface. APIs
GLOSSARY A access control list ACL API Application Programming Interface area AS ASN ATM autonomous system autonomous system number See ACL. access control list. application programming interface. APIs
DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II. Version 2: with two 3550 and two 3560 Catalyst switches SAMPLE LAB ANSWER KEY FOR CCIE CANDIDATES
 Revision 7.0 (4/18/2007) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO-SAMPLE Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II Version 2: with two 3550 and two 3560 Catalyst switches SAMPLE LAB ANSWER
Revision 7.0 (4/18/2007) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO-SAMPLE Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II Version 2: with two 3550 and two 3560 Catalyst switches SAMPLE LAB ANSWER
DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II. DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario. For CCIE Candidates
 Revision 7.0 (10/20/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 3 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario For CCIE Candidates Revision
Revision 7.0 (10/20/2005) DOiT-200v6-SCENARIO 3 Page 1 NETMASTERCLASS ROUTING AND SWITCHING CCIE TRACK DOiT-200v6 VOLUME II DOiT-200v6 Lab 3 Multi-Topic CCIE-Level Scenario For CCIE Candidates Revision
CCNA Questions/Answers IPv6. Select the valid IPv6 address from given ones. (Choose two) A. FE63::0043::11:21 B :2:11.1 C.
 Select the valid IPv6 address from given ones. (Choose two) A. FE63::0043::11:21 B. 191.2.1.2:2:11.1 C. 2001::98 D. 2002:c0a8:101::42 E. :2001:: F. 2002.cb0a:3cdd:1::1 Answer: C, D. 2013 1 Which method
Select the valid IPv6 address from given ones. (Choose two) A. FE63::0043::11:21 B. 191.2.1.2:2:11.1 C. 2001::98 D. 2002:c0a8:101::42 E. :2001:: F. 2002.cb0a:3cdd:1::1 Answer: C, D. 2013 1 Which method
IPv6 Protocols and Networks Hadassah College Spring 2018 Wireless Dr. Martin Land
 IPv6 1 IPv4 & IPv6 Header Comparison IPv4 Header IPv6 Header Ver IHL Type of Service Total Length Ver Traffic Class Flow Label Identification Flags Fragment Offset Payload Length Next Header Hop Limit
IPv6 1 IPv4 & IPv6 Header Comparison IPv4 Header IPv6 Header Ver IHL Type of Service Total Length Ver Traffic Class Flow Label Identification Flags Fragment Offset Payload Length Next Header Hop Limit
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
CS475 Networks Lecture 8 Chapter 3 Internetworking. Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
 Assignments Reading for Lecture 9: Section 3.3 3.2 Basic Internetworking (IP) Bridges and LAN switches from last section have limited ability CS475 Networks Lecture 8 Chapter 3 Internetworking is a logical
Assignments Reading for Lecture 9: Section 3.3 3.2 Basic Internetworking (IP) Bridges and LAN switches from last section have limited ability CS475 Networks Lecture 8 Chapter 3 Internetworking is a logical
Question: 1 Which three parameters must match to establish OSPF neighbor adjacency? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 217 Questions Question: 1 Which three parameters must match to establish OSPF neighbor adjacency? (Choose three.) A. the process ID B. the hello interval C. the subnet mask D. authentication E.
Volume: 217 Questions Question: 1 Which three parameters must match to establish OSPF neighbor adjacency? (Choose three.) A. the process ID B. the hello interval C. the subnet mask D. authentication E.
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Cisco 360 CCIE R&S Advanced Workshop 2 Assessment Lab 1
 CIERSASSESS-5-AK Cisco 360 CCIE R&S Advanced Workshop 2 Assessment Lab 1 The Cisco 360 CCIE Routing and Switching (R&S) Advanced Workshop 2 is a five-day course for CCIE candidates who are ready to attempt
CIERSASSESS-5-AK Cisco 360 CCIE R&S Advanced Workshop 2 Assessment Lab 1 The Cisco 360 CCIE Routing and Switching (R&S) Advanced Workshop 2 is a five-day course for CCIE candidates who are ready to attempt
Configuring IS IS over IPv6
 Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
 A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or
A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay
 Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Vanguard Managed Solutions
 Vanguard Managed Solutions Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Notice 2003 Vanguard Managed Solutions, LLC 575 West Street Mansfield, Massachusetts 02048
Vanguard Managed Solutions Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Notice 2003 Vanguard Managed Solutions, LLC 575 West Street Mansfield, Massachusetts 02048
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
 TCP/IP Protocol Suite Computer Networks Lecture 5 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 TCP/IP Network protocols used in the Internet also used in today's intranets TCP layer 4 protocol Together with UDP IP - layer 3 protocol
TCP/IP Protocol Suite Computer Networks Lecture 5 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 TCP/IP Network protocols used in the Internet also used in today's intranets TCP layer 4 protocol Together with UDP IP - layer 3 protocol
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
 ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
