Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6
|
|
|
- Sabina Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity between all IPv4 subnets. Then you create a manual IPv6 tunnel and run EIGRP for IPv6 over it. Note: This lab uses Cisco 1841 routers with Cisco IOS Release 12.4(24)T1 and the Advanced IP Services image c1841-advipservicesk9-mz t1.bin. You can use other routers (such as a 2801 or 2811) and Cisco IOS Software versions if they have comparable capabilities and features. Depending on the router All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 6
2 model and Cisco IOS Software version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in this lab. Required Resources 3 routers (Cisco 1841 with Cisco IOS Release 12.4(24)T1 Advanced IP Services or comparable) Serial and console cables Step 1: Prepare the routers for the lab. Cable the network as shown in the topology diagram. Erase the startup configuration, and reload each router to clear the previous configurations. Configure the hostnames as shown. Step 2: Configure loopbacks and physical interfaces. Configure the loopback interfaces with IPv4 addresses and IPv6 addresses, where appropriate. Also configure the serial interfaces with the IPv4 addresses shown in the diagram. Set the clock rates on the appropriate interfaces, and issue the no shutdown command on all serial connections. Verify that you have local subnet connectivity with ping. R1(config)# interface loopback0 R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0::1:1/112 R1(config-if)# interface serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# clockrate R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config)# interface loopback0 R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# interface serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# interface serial0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip address R2(config-if)# clockrate R2(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R2(config-if)# no shutdown R3(config)# interface loopback0 R3(config-if)# ip address R3(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0::3:1/112 R3(config-if)# interface serial0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip address R3(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R3(config-if)# no shutdown Step 3: Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Configure EIGRP for AS 1 for the major networks and on all three routers. Make sure that you disable auto-summarization. You should have full IPv4 connectivity after this. R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# no auto-summary R1(config-router)# network R1(config-router)# network All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 6
3 R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# no auto-summary R2(config-router)# network R2(config-router)# network R3(config)# router eigrp 1 R3(config-router)# no auto-summary R3(config-router)# network R3(config-router)# network Step 4: Configure a manual IPv6 tunnel. A tunnel is a logical interface that acts as a logical connection between two endpoints. It is similar to a loopback interface in that there is no corresponding physical interface, but it is different in that there is more than one router involved. An IPv6 manual tunnel is a type of tunnel that has hard-coded source and destination addresses, with an IPv6 address on the tunnel itself. a. Use the interface tunnel number command to create a manual tunnel. For simplicity, use tunnel number 0 on both routers. Configure the tunnel mode for a manual tunnel with the tunnel mode ipv6ip command. Then configure an IPv6 address with the ipv6 address address/mask command. Finally, assign source and destination addresses for the tunnel using the tunnel source address and tunnel destination address commands. You can also specify the source by interface. R1(config)# interface tunnel0 R1(config-if)# tunnel mode ipv6ip R1(config-if)# tunnel source serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# tunnel destination R1(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0::13:1/112 R3(config)# interface tunnel0 R3(config-if)# tunnel mode ipv6ip R3(config-if)# tunnel source serial0/0/1 R3(config-if)# tunnel destination R3(config-if)# ipv6 address FEC0::13:3/112 b. Verify that you can ping across the tunnel from one side to the other using the tunnel address of the opposite router. R1# ping FEC0::13:3 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FEC0::13:3, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/66/68 ms R3# ping FEC0::13:1 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FEC0::13:1, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/66/68 ms Note: Although not done in this lab, you can configure the tunnel interfaces using only the ipv6 enable command, instead of unicast IPv6 addresses. This command configures the tunnel interfaces for IPv6 operation and assigns automatically generated link-local addresses to them. This allows the tunnel to transport IPv6 packets and an IGP can be run over it. The individual endpoints of the tunnel are not globally addressable, but the tunnel does not require global unicast addresses. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 3 of 6
4 Step 5: Configure EIGRP for IPv6 over a tunnel. a. Enable IPv6 routing with the ipv6 unicast-routing command on R1 and R3. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 on those routers to run over the tunnel and advertise the loopback interfaces into IPv6-EIGRP AS 100. R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R1(config)# interface loopback0 R1(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 100 R1(config-if)# interface tunnel0 R1(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 100 R3(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R3(config)# interface loopback0 R3(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 100 R3(config-if)# interface tunnel0 R3(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 100 b. Verify the configuration using the show ipv6 eigrp neighbor command. R1# show ipv6 eigrp neighbor IPv6-EIGRP neighbors for process 100 % EIGRP 100 is in SHUTDOWN c. IPv6 EIGRP routing is shut down by default. To enable IPv6-EIGRP for process 100, use the following commands on R1 and R3. R1(config-if)# ipv6 router eigrp 100 R1(config-rtr)# no shutdown *Apr 19 17:27:08.639: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IPv6-EIGRP(0) 100: Neighbor FE80::AC10: 1703 (Tunnel0) is up: new adjacency d. Verify the configuration using the show ipv6 eigrp neighbors command. R1# show ipv6 eigrp neighbors IPv6-EIGRP neighbors for process 100 H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num 0 Link-local address: Tu :01: FE80::AC10:1703 Note: The link-local neighbor address is the IPv6 equivalent (AC10:1703) of the R3 serial interface IPv4 address ( ). e. Ping the R3 Lo0 IPv6 address from R1, and ping the R1 Lo0 IPv6 address from R3. R1# ping FEC0::3:1 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FEC0::3:1, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/64/68 ms R3# ping FEC0::1:1 Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to FEC0::1:1, timeout is 2 seconds: Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/66/68 ms All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 6
5 f. Use the following Tcl script on R1 and R3 to verify connectivity for R1 and R3. R1# tclsh foreach address { FEC0::1:1 FEC0::3:1 FEC0::13:1 FEC0::13:3 } { ping $address } Were all pings successful? g. Run the Tcl script on R2. Were all IP addresses reachable? Explain. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 6
6 Router Interface Summary Table Router Model Ethernet Interface # Fast Ethernet 0 (FA0) 1800 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (FA0/0) 2600 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (FA0/0) 2800 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (FA0/0) Router Interface Summary Ethernet Interface #2 Fast Ethernet 1 (FA1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial Interface #1 Serial 0 (S0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial Interface #2 Serial 1 (S1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. Rather than list all combinations of configurations for each router class, this table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router might contain one. For example, for an ISDN BRI interface, the string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 6 of 6
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Lab 3.2 Configuring a Basic GRE Tunnel
 Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Lab 3.2 onfiguring a Basic GRE Tunnel Learning Objectives onfigure a GRE tunnel onfigure EIGRP on a router onfigure and test routing over the tunnel interfaces Topology iagram Scenario This lab is designed
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Instructor Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
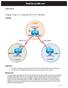 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS
 Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, OSPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization
 NPv6 RUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-3, SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization Topology bjectives Background onfigure multi-area SPF on a r. Verify multi-area behavior. reate an SPF virtual link. Summarize an area.
NPv6 RUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-3, SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization Topology bjectives Background onfigure multi-area SPF on a r. Verify multi-area behavior. reate an SPF virtual link. Summarize an area.
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
Chapter 2 Lab 2-5, EIGRP Authentication and Timers Topology Objectives Background Review a basic configuration of EIGRP. Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters. Configure EIGRP hello interval
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing. Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
Chapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch Topology Objectives Review a basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface. onfigure EIGRP over Frame
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 2 Lab 2-4, EIGRP Frame Relay Hub-and-Spoke: Router Used as a Frame Relay Switch Topology Objectives Review a basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface. onfigure EIGRP over Frame
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers
 Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
Lab 2-5 EIGRP Authentication and Timers Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP Configure and verify EIGRP authentication parameters Configure EIGRP hello interval and hold time Verify
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Lab 2-4a EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Router Used As Frame Switch
 Lab 2-4a EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Router Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth-percent command onfigure EIGRP
Lab 2-4a EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Router Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth-percent command onfigure EIGRP
Chapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances
 hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
hapter 4 Lab 4-3, Manipulating Administrative Distances Topology bjectives Background onfigure RIP on a router. onfigure SPF on a router. Manipulate administrative distances. ompare routing protocol behavior.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF
 hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
hapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between RIP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review configuration and verification of RIP and OSPF. onfigure passive interfaces in both RIP and OSPF. Filter routing updates
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Lab 2-4b EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Adtran Used As Frame Switch
 Lab 2-4b EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Adtran Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth percentage onfigure EIGRP over
Lab 2-4b EIGRP Frame Relay Hub and Spoke: Adtran Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP on a serial interface onfigure the bandwidth percentage onfigure EIGRP over
Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features Topology
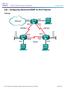 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
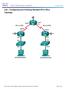 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control Using PBR. Topology. Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Configuration and Management of Networks 2012
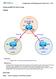 Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Configuration and Management of Networks
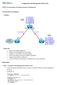 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv2
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
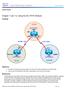 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
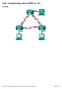 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
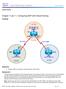 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Lab 4.9 QoS Pre-classify
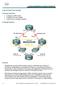 Lab 4.9 QoS Pre-classify Learning Objectives Configure a GRE tunnel Configure QoS pre-classify Verify QoS pre-classify operation Topology Diagram Scenario Weighted fair queuing (WFQ) allows routers to
Lab 4.9 QoS Pre-classify Learning Objectives Configure a GRE tunnel Configure QoS pre-classify Verify QoS pre-classify operation Topology Diagram Scenario Weighted fair queuing (WFQ) allows routers to
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
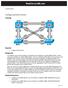 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
Configuration and Management of Networks
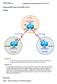 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
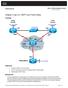 Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay Topology Objectives Background Configure OSPF over Frame Relay. Use non-broadcast and point-to-multipoint OSPF network types. Modify default OSPF timers. You are
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the "IP[v6] Unnumbered" Command Configuration Example
![EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the IP[v6] Unnumbered Command Configuration Example EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the IP[v6] Unnumbered Command Configuration Example](/thumbs/92/108645128.jpg) EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the "IP[v6] Unnumbered" Command Configuration Example Document ID: 116346 Contributed by Michal Garcarz and Olivier Pelerin, Cisco TAC Engineers. Sep 18, 2013
EIGRP on SVTI, DVTI, and IKEv2 FlexVPN with the "IP[v6] Unnumbered" Command Configuration Example Document ID: 116346 Contributed by Michal Garcarz and Olivier Pelerin, Cisco TAC Engineers. Sep 18, 2013
Lab 4-3a Configuring IS-IS over Frame Relay: Router Used As Frame Switch
 Lab 4-3a Configuring IS-IS over Frame Relay: Router Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Configure and verify Frame Relay point-to-point subinterfaces Configure and verify the operation of Integrated
Lab 4-3a Configuring IS-IS over Frame Relay: Router Used As Frame Switch Learning Objectives Configure and verify Frame Relay point-to-point subinterfaces Configure and verify the operation of Integrated
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv3 Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme
 Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G00 NA G01 NA Lo0 Lo1 NA NA S1 VLAN 1
Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G00 NA G01 NA Lo0 Lo1 NA NA S1 VLAN 1
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP
 Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing Topology
 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1.1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1.1 192.168.1.1
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example
 Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Implement Static Routes for IPv6 Configuration Example Document ID: 113361 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Related Information
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Lab : OSPF Troubleshooting Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 16 Addressing Table Assessment Objectives Device
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 16 Addressing Table Assessment Objectives Device
Lab - Configuring IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Configuring IS IS over IPv6
 Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
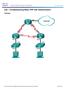 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0
 Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay
 Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab Configuring HSRP and GLBP Topology
 Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub / / /24
 Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub Lo0 1.1.0.1/24 1.1.1.1/24 Lo1 200.1.1.1/24 200.2.2.2/24 F0/0.1.2 F0/0 R1 1.1.2.1/24 Lo2.1 S1/2 CE 1.1.3.1/24 Lo3 12.1.1.0 /24.2 S1/1 2.2.3.2/24 Lo3 R2 2.2.2.2/24 Lo2 Lo0 2.2.0.2/24 2.2.1.2/24
Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub Lo0 1.1.0.1/24 1.1.1.1/24 Lo1 200.1.1.1/24 200.2.2.2/24 F0/0.1.2 F0/0 R1 1.1.2.1/24 Lo2.1 S1/2 CE 1.1.3.1/24 Lo3 12.1.1.0 /24.2 S1/1 2.2.3.2/24 Lo3 R2 2.2.2.2/24 Lo2 Lo0 2.2.0.2/24 2.2.1.2/24
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Chapter 2: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 : Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
: Configuring the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol CCNP ROUTE: Implementing IP Routing ROUTE v6 1 Objectives Describe the basic operation of EIGRP. Plan and implement EIGRP routing. Configure
Lab Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS
 Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Lab 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
 Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Skills Assessment (OSPF) Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment (OSPF) Student Training Exam Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 17 Addressing Table Assessment Objectives Device
Skills Assessment (OSPF) Student Training Exam Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 17 Addressing Table Assessment Objectives Device
Lab Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
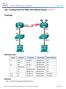 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
