(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Chowdhury (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2004
|
|
|
- Kristopher Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
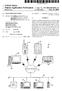
1 US 2004O266450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1 Chowdhury (43) Pub. Date: (54) MAINTAINING ACOMMUNICATIONS Publication Classification SESSION WITH A MOBILE STATION (51) Int. Cl."... H04Q 7/00 (75) Inventor: Kuntal Chowdhury, Plano, TX (US) (52) U.S. Cl /452.2; 370/329 Correspondence Address: TROPPRUNER & HU, PC (57) ABSTRACT 8554 KATY FREEWAY SUTE 100 HOUSTON, TX (US) A mobile communications network includes various entities, Such as a mobile Station, a radio network, and a packet data (73) Assignee: Nortel Networks Limited, St. Laurent node. In one implementation, the mobile Station is enabled (CA) for an always-on Service. In response to detecting that the mobile Station is an always-on mobile Station, the packet (21) Appl. No.: 10/606,998 data node denies requests from the radio network to tear down a packet data Session of the mobile Station unless Some (22) Filed: Jun. 26, 2003 predetermined criterion has been met. s Kai 116 DORMANT OUT OF RADIO COWERAGE ACCESS-REQUEST ACCESSACCEPT INACTIVITYTIMEREXPRES PAGE 1138 LCP-ECHO TIMEOUT 140 TEARDOWN REOUEST RESPONSE (ACK)
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 2 37/100W
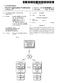
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 2 US 2004/ A PACKETDAIA SOSETUP 102 AB/A10 SETUP 104 PACKETDATASERVICEINSTANCE SETUP 108 4CCESS-REQUESLZ ACCESS ACCEPT (ALWAYS-ON INDICATOR) PACKETDATASERVICEINSTANCE SETUPSUCCESS 110 DATA TRANSFER/PACKETDA zin at H) C DORMANT C INACTIVITYTIMEREXPRES 18 OUT OF RADIO COVERAGE 122 LCP-ECHO 132 DECREMENT RETRIES COUNTER 140 TEARDOWN REQUEST 142 f44 RESPONSE (ACK) 146 FIG. 2
4 MANTAINING A COMMUNICATIONS SESSION WITH A MOBILE STATION TECHNICAL FIELD This invention relates to maintaining a communi cations Session with a mobile Station. BACKGROUND A mobile communications network is typically made up of a plurality of cells. Each cell includes a radio base Station, with each base Station connected to a mobile Switching center or a packet Service node that manages communications Sessions between mobile Stations and ter minals coupled to a public Switched telephone network (PSTN) or a packet-based data network. Communications between mobile Stations and base Stations are performed over wireless links Traditional wireless protocols provide for circuit Switched communications. Such protocols include time division multiple access (TDMA) protocols and code-divi Sion multiple access (CDMA) protocols. In a circuit Switched network, a channel portion between two endpoints (e.g., two mobile Stations) is occupied for the duration of the connection between the endpoints However, with the wide availability of the Internet and intranets, packet-switched communications (e.g., web browsing, electronic mail, and So forth) have become more common. Generally, a circuit-switched connection is an inefficient technique for communicating packet data. AS a result, third generation (3G) and beyond wireless technolo gies are being developed and implemented to provide higher bandwidth and more efficient packet-switched communica tions (of data as well as voice and other forms of real-time data) over wireless networks One example of a packet-switched wireless tech nology is defined by the CDMA 2000 family of standards, developed by the Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2). A CDMA2000 wireless communications network is capable of Supporting both circuit-switched Services and packet-switched services. For TDMA, packet-switched wireless communications protocols have also been devel oped, such as the Enhanced General Packet Radio Service (EGPRS) protocolas defined by the 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project) UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommu nications System) Release 1999 Standard, and others In packet-switched communications, packets that are Sent across a data network are routed based on a Source network address and a destination network address con tained in each packet. In one example, packets Sent over a packet-based data network are defined by the Internet Pro tocol (IP) Once a packet data session is established between a mobile Station and another end device, communications of packet data can occur between the mobile Station and the other end device. Typically, in response to a teardown request, the packet data session is terminated. CDMA2000 provides an always-on feature that is intended to maintain a Subscriber's packet data Session on a data network So that the mobile network does not initiate release of the Subscriber's packet data Session unless the mobile network determines that the Subscriber is no longer reachable. However, an efficient messaging mechanism has not been provided to handle the release of an always-on mobile Station. SUMMARY In general, an efficient mechanism is provided to maintain a packet data Session of a mobile Station. For example, according to one embodiment, a method for use in a mobile communications network includes receiving a request to terminate a communications Session with the mobile Station. In response to receiving the request to terminate, an indicator is checked to determine whether the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station. In response to determining that the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station, the method generates a message to deny the request to terminate the communications Session Other or alternative features will become apparent from the following description, from the drawings, and from the claims. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0010 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an example arrange ment of a mobile or wireless communications network that is coupled to a packet data network and a public Switched telephone network (PTSN) FIG. 2 is a message flow diagram of a procedure for determining whether a communications Session for an always-on mobile Station is to be released, in accordance with one embodiment of the invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION In the following description, numerous details are Set forth to provide an understanding of the present inven tion. However, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without these details and that numerous variations or modifications from the described embodiments may be possible FIG. 1 illustrates an example arrangement that includes a mobile or wireless communications network 10, which has a mobile Station 12, a radio network 14, and a packet data serving node (PDSN) 16. The example mobile communications network 10 of FIG. 1 is according to a code-division multiple access (CDMA) 2000 protocol, defined by the CDMA2000 family of standards, as promul gated by the Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2). A CDMA 2000 wireless network is capable of Supporting both circuit-switched Services and packet Switched services. TIA/EIA/IS-835 is a standard that defines requirements for Support of wireless packet data networking capability in a CDMA2000 network. One version of TIA/ EIA/IS-835 is IS-835-B Although described in the context of a CDMA 2000 network, other embodiments of the invention can be implemented in other types of mobile communications net works, such as other CDMA-based networks including 1xEV-DO, 1xEV-DV, and so forth. Alternatively, such other types of mobile communications networks can also include time-division multiple access (TDMA) networks, such as networks that conform to the Enhanced General Packet Radio Service (EGPRS) protocol, as defined by the 3GPP UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication System)
5 Standards. The wireless protocols listed above are provided as examples only, and are not to be considered limiting, as other types of protocols in a wireless network can be used in other embodiments. Furthermore, even though described in the context of a wireless network that Supports packet Switched communications, the invention is also not to be limited in that regard. Other embodiments of the invention can be implemented in circuit-switched communications networks The mobile station 12 is capable of communicating over a wireless link with the radio network 14, which includes a base Station controller 18 and a packet control function (PCF) 20. The BSC 18 communicates over the wireless link with the mobile station 12. For circuit-switched communications, the BSC 18 communicates control and data information to the mobile Switching center (MSC) 22, which is in turn coupled to a public Switched telephone network (PSTN) 24, or to other MSCs. For packet-switched communications, the BSC 18 communicates control and data information through the PCF 20 to the PDSN 16. The PCF 20 manages the relay of packets between the BSC 18 and the PDSN 16. The PDSN establishes, maintains, and terminates link layer (e.g., PPP) and network layer sessions (e.g., Simple IP and Mobile IP) to mobile stations, and routes mobile Station-originated or mobile Station-termi nated packet data traffic. The PDSN 16 is coupled to a packet data network 26, Such as a local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), or a public network Such as the Internet. The packet data network 26 is coupled to various nodes, Such as an end Station 28, which can be a computer, a network telephone, or the like As used here, the term radio network refers to any entity or collection of entities (in any one of a CDMA, TDMA, or other type of mobile network) that controls radio communication with mobile Stations within a predefined coverage area, Such as a cell, cell Sector, or group of cells or cell sectors. More generally, a wireless network refers to any entity or collection of entities that controls wireless communication with mobile Stations in a predefined cover age area. In addition, the term "packet data node refers to an entity or collection of entities in the mobile network that provides the interface between the mobile network and a packet data network. One example of a packet data node is the PDSN Examples of packet-switched communications include web browsing, electronic mail, text chat Sessions, file transfers, interactive game Sessions, voice-over-ip (inter net protocol) sessions, and So forth. In one embodiment, packet-switched communications utilize a connectionless internetwork layer defined by IP. One version of IP is IPv4, described in RFC 791, entitled Internet Protocol, dated September 1981; and another version of IP is IPv6, described in RFC 2460, entitled Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6) Specification, dated December In packet Switched communications, packets or other units of data carry routing information (in the form of network addresses) that are used to route the packets or data units over one or more paths to a destination endpoint According to some embodiments of the invention, the mobile station 12 is an always-on mobile station. One implementation of an always-on feature is defined by IS-835-B, entitled CDMA2000 Wireless IP Network Stan dard, dated September An always-on service refers to a Service in which a communications Session involving a mobile Station, Such as mobile Station 12, is maintained even though there has been Some period of inactivity. An always on mobile station refers to a mobile station that has subscribed to or is enabled for the always-on feature. Although a version of CDMA2000 provides for always-on Service, it is contemplated that other wireless network pro tocols can also provide for Such Service According to some embodiments of the invention, the PDSN 16 determines whether a particular mobile station is an always-on mobile Station. For Such mobile Stations, the PDSN 16 keeps track of the activity of the mobile station 12. When inactivity is detected, such as by use of an inactivity timer, the PDSN 16 sends an echo message to the mobile station to determine whether the mobile station is still connected to the communications Session. AS used here, being connected to a communications Session refers to a mobile Station or other entity being capable of transmitting or receiving data in the communications Session, which can be a packet communications Session between the mobile Station and another device. As an example, the packet communications session may be a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) communications session. PPP is described by RFC 1661, entitled The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). dated July An inactivity timer 30 in the PDSN detects for inactivity for each communications Session involving the mobile station 12. The initial value of the inactivity timer 30 is programmed or Set by a Service provider, with example values being in the range between about five minutes to five hours. Note that there are multiple inactivity timers 30 for corresponding communications Sessions involving multiple mobile stations. When the inactivity timer 30 expires, the PDSN 16 sends an echo request message to the mobile station 12. If the mobile station 12 is still connected to the communications Session, then the mobile Station 12 is able to provide a reply to the echo message. However, if the mobile Station does not respond to the echo message, then the PDSN 16 decrements (or increments), as appropriate, a "retries' counter 32, which is a counter that tracks the number of times the PDSN 16 has attempted to seek a reply from the mobile station 12 with the echo message. For the ensuing discussion, it is assumed that the retries counter 32 Starts with a non-zero value (e.g., 2 to 10) programmed or set by a service provider, with the retries counter 32 being decremented each time the PDSN 16 is unable to receive an echo reply message from the mobile Station. Prior to the retries counter 332 reaching the value Zero, the PDSN 16 does not allow the communications Session of the mobile station 12 to be terminated. However, once the retries counter 32 has decremented to the value Zero, that is an indication that the mobile Station 12 may be unreachable, So that the PDSN 16 allows the teardown of the communica tions Session. Alternatively, the retries counter 32 starts with a Zero value and is incremented with each attempt until the retries counter 32 reaches a predetermined value In accordance with some embodiments of the invention, an efficient mechanism is provided for controlling whether or not to teardown a communications Session involving the mobile station 12 due to inactivity. This mechanism involves the PDSN 16 either acknowledging or not acknowledging a request from the BSC 18 to tear down
6 a communications Session. An acknowledge (or ACK) indi cation allows the BSC 18 to perform the teardown, whereas a no-acknowledge (or NACK) is an indication to the BSC 18 that teardown should not be performed. A benefit provided by some embodiments of the invention is that BSC 18 does not need to keep track of whether the mobile station 12 is an always-on mobile Station. Rather, the intelligence is pro vided by the PDSN 16, with the PDSN 16 providing the appropriate response to a request from the BSC 18 to terminate a communications Session to control whether the BSC 18 is allowed to perform the session teardown FIG. 1 further shows layers within the mobile station 12, radio network 14, and PDSN 16 to enable communication among the respective nodes of the mobile communications network 10. The various layers conform to the CDMA2000 standard The mobile station 12 includes an airlink layer 50 (which enables radio frequency communications over the air link between the mobile station 12 and the radio network 14), a medium access control (MAC) layer 52, a link access control (LAC) layer 54, a PPP layer 56, and an IP layer 58. Additionally, layer(s) 60 are also logically provided above the IP layer 58. Examples of the functions of such other layers 60 include layers that provide for mobile IP, and so forth The radio network 14 also includes various layers, which can be implemented in the BSC 18 and/or PCF 20. The air interface (the interface to the mobile station 12) includes an airlink layer 62, a MAC layer 64, and an LAC layer 66. The interface to the PDSN 16 includes an R-P (radio network-pdsn) layer 68, and a physical layer 70. Similarly, the PDSN 16 includes a physical layer 72, an R-P layer 74, a PPP layer 76, an IPlayer 78, and other layers 80. The PPP layer 76 in the PDSN 16 interacts with the PPP layer 56 in the mobile station 12 to establish a PPP session In addition to the various layers, the PDSN 16 also includes a link Status determination module 82, which is responsible for determining whether a particular Session involving the mobile station 12 is to be torn down or not. The link status determination module 82, the inactivity timer 30, and the retries counter 32 can be implemented in the PPP player 76 or at some other layer in the PDSN 16 (e.g., an application layer). The Software modules making up the link status determination module 82, the inactivity timer 30, and the retries counter 32 are executable on a processor 84, which is coupled to storage 86 (e.g., memory, a mass storage device, and So forth). Instead of being implemented in Software, the link Status determination module 82, the inac tivity timer 30, and the retries counter 32 can be imple mented in hardware FIG. 2 shows a message flow diagram of a proce dure to determine whether teardown of a packet data Session involving an always-on mobile Station is to be allowed, in accordance with one embodiment. Initially, messaging is exchanged (at 102) between the mobile station 12 and the radio network 14 to Set up a packet data Session, referred to as a packet data Service option Setup. This Setup procedure enables the mobile Station 12 to be connected to a commu nications Session that also involves an endpoint on the packet data network 26 or another mobile Station. In response to the packet data Service option Setup, the radio network 14 performs an A8/A10 setup (at 104) with the PDSN 16. An A8 interface is provided between the BSC 18 and PCF 20 to carry user traffic, and an A9 interface is provided between the same entities to carry Signaling. Simi larly, an A10 interface is provided between the PCF 20 and the PDSN 16 for carrying user traffic, and an A11 interface is defined between these entities to carry signaling. A8/A10 setup refers to the setup of the A8 and A10 connections between the respective entities (BSC 18, PCF 20, and PDSN 16) Once the A8/A10 connections are established, a packet data Service instance Setup is performed (at 106) to exchange various messaging between the mobile Station 12 and PDSN 16. This includes exchanges of messaging to perform link layer procedures to Start the establishment of a PPP Session. Messages are also exchanged to negotiate compression and other items for the PPP session. Also, messages are exchanged between the mobile Station 12 and PDSN 16 for mobile IP registration. Mobile IP enables a mobile Station to change its point of attachment between different networks (such as a home network and foreign network). Mobile IP is defined by the Mobile Internet Protocol, as described in RFC 3344, entitled IP Mobility Support for IPv4, dated August A version of mobile IP also exists for IPv In the link layer procedures (at 106), the PDSN 26 sends a Link Control Protocol (LCP) Configure-Request message for a new PPP session to the mobile station 12. LCP, which is part of PPP, is used for establishing, config uring, and testing a data-link connection. If configuration options contained in the Configure-Request message are recognizable by the mobile station 12, the mobile station 12 returns a Configure-Ack message Further, for authentication purposes, the PDSN sends (at 108) an Access-Request message to an AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) server 17 (FIG. 1). The AAA server 17 is an entity that is defined to enable mobility of nodes between different wireless net works. The AAA server 17 also provides authentication and authorization Services for network nodes. AAA is described in RFC 2977, entitled Mobile IP Authentication, Authori zation, and Accounting Requirements, dated October The CDMA 2000 requirements for AAA are described in RFC 3141, entitled CDMA2000 Wireless Data Require ments for AAA, dated June ) Note that although reference is made to mobile IP, other embodiments of the invention can be applied to communications Sessions that employ simple IP (where mobility of a mobile station between different networks is not Supported). 0031) The Access-Request message sent (at 108) by the PDSN 16 to the AAA server 17 contains the network address identifier (NAI) of the mobile station 12 and information used for authentication purposes. If the AAA server 17 recognizes the mobile Station 12, it sends an Access-Accept message (at 110) back to the PDSN 16. The Access-Accept message contains an always-on indicator to indicate that the mobile Station 12 is associated with the always-on feature. Other information contained in the Access-Accept message may include the IP address of the DNS (domain name System) server, configuration information, and So forth Various information in the Access-Accept message are stored by the PDSN 16 in the storage 86 (FIG. 1). Among the information Stored is an always-on indicator 87 (FIG. 1) to indicate that a given mobile station is an always-on mobile station. The PDSN 16 next sends (at 112) messaging back to the mobile Station 12 to indicate that the
7 packet data Service instance Setup has been Successful. Next, packet data transfer is performed between the mobile Station 12 and another end station (at 114) At some point, the mobile station 12 goes dormant (at 116). For example, if a user is browsing the web on the mobile Station 12, and the user has paused for whatever reason, no further data is exchanged between the mobile Station 12 and the other end Station during this period of inactivity. Also, there is the possibility that the mobile Station 12 goes out of radio coverage of the mobile com munications network (at 118). This may occur due to obstructions causing gaps in the coverage area of the mobile communications network. Alternatively, a user may be on the edge of the mobile communications network, and the resultant weak signaling may cause the mobile Station to go in and out of radio coverage. 0034). In the PDSN 16, the PPP inactivity timer 30 starts running when it detects inactivity in the communications session between the mobile station 12 and the other end station. Upon expiration (at 120) of the inactivity timer 30, the PDSN 16 sends (at 122) an LCP-Echo Request message to the radio network 14. The LCP-Echo Request message is intended to elicit an LCP-Echo-Reply/Reject message (a response message) from the mobile station. Note that instead of the LCP-Echo Request message, other types of echo messages can be employed. More generally, an "echo' message refers to any message that is Sent from a first node to a Second node for the purpose of eliciting a response from the Second node for indicating that the Second node remains connected to the communications Session. 0035) In response to the LCP-Echo Request message, the base station controller 18 in the radio network 14 pages (at 124) the mobile station 12. The example of FIG.2 assumes that the mobile Station is currently out of radio coverage, So that the mobile Station 12 does not receive this page from the radio network 14. As a result, no response is received from the mobile station for some time-out period. The wireless session between the mobile station 12 and the radio network 14 has effectively been terminated (since the mobile station became dormant), thus requiring the radio network 14 to page the mobile Station 12 to reestablish the wireless Ses Sion. Note that the wireless Session can be terminated without terminating the PPP or other packet data session involving the mobile station ) When the radio network 14 detects (at 125) no response from the mobile station by the end of the time-out period, the radio network 14 sends (at 126) an A9/A11 Registration-Request message with a parameter Lifetime Set equal to zero. This effectively is an R-P teardown request for tearing down the communications Session In response to receiving this request to terminate the communications session, the PDSN 16 determines (at 128) whether the retries counter 32 has a count that is greater than Zero. If so, the PDSN 16 sends an A9/A11 Registration Reply message back to the radio network 14. Normally, the PDSN 16, in response to the teardown request, sends back an A9/A11 Registration-Reply message (with the Lifetime parameter Set to Zero and an accept indicator Set to acknowl edge the teardown request). Note that the Registration-Reply message is an A11 message sent from the PDSN 16 to the PCF20. In response to the A11 Registration Reply message, the PCF20 sends an A9-release-A8 complete message to the BSC 18. Similarly, to initiate the Registration-Request mes sage with Lifetime=0, the BSC 18 send an A9-release-A8 message with a Cause value Set to normal call release' to instruct the PCF 20 to release the associated dedicated resource and the associated A10 connection However, in accordance with some embodiments of the invention, if the retries counter count Value is greater than Zero, the PDSN 16 does not accept the teardown request, but instead sends back an A11 Registration-Reply message (at 130) with a NACK (or no-acknowledge) indi cator. The no-acknowledge indicator is effectively an indi cation that the teardown request is denied So that the radio network 14 is not allowed to teardown the communications Session. In response to this, the radio network 14 does nothing to teardown the communications Session In conjunction with sending the NACK indicator in the A11 Registration-Reply message, the PDSN 16 also decrements (at 132) the retries counter 32. Assume that this decrement causes the retries counter 32 to be decremented to Zero. The PDSN 16 sends another LCP-Echo message (at 136) to the radio network 14. Since the mobile station is still out of radio coverage, the radio network 14 pages (at 138) the mobile station 12. If no response is received from the mobile station 12, and after a preset time-out period (at 140), the radio network 14 sends (at 142) an A11 Registration Request message with the parameter Lifetime Set equal to Zero to perform an R-P teardown request. At this time, the PDSN 16 determines (at 144) that the retries counter has a Zero value. Therefore, the PDSN enables the R-P teardown procedure by Sending an A11 Registration-Reply message with Lifetime=0 and an accept indicator (at 146) to the radio network 14. After Subsequent exchanges of messaging, the R-P connection is terminated, along with the PPP session Instructions of the various Software routines or modules discussed herein (Such as the link status determi nation module 82, the inactivity timer 30, and the retries counter 32) are loaded for execution on corresponding control units or processors. The control units or processors include microprocessors, microcontrollers, processor mod ules or Subsystems (including one or more microprocessors or microcontrollers), or other control or computing devices. AS used here, a controller refers to hardware, Software, or a combination thereof. A controller can refer to a single component or to plural components (whether Software or hardware). 0041) Data and instructions (of the various software routines or modules) are stored in one or more machine readable Storage media. The Storage media include different forms of memory including Semiconductor memory devices Such as dynamic or Static random access memories (DRAMs or SRAMS), erasable and programmable read-only memo ries (EPROMs), electrically erasable and programmable read-only memories (EEPROMs) and flash memories; mag netic disks Such as fixed, floppy and removable disks; other magnetic media including tape; and optical media Such as compact disks (CDs) or digital video disks (DVDs) The instructions of the software routines or mod ules are loaded or transported to a System in one of many different ways. For example, code Segments including instructions stored on floppy disks, CD or DVD media, a hard disk, or transported through a network interface card, modem, or other interface device are loaded into the System and executed as corresponding Software routines or mod ules. In the loading or transport process, data Signals that are embodied in carrier waves (transmitted over telephone lines, network lines, wireless links, cables, and the like) commu nicate the code Segments, including instructions, to the
8 System. Such carrier waves are in the form of electrical, optical, acoustical, electromagnetic, or other types of Sig nals While the invention has been disclosed with respect to a limited number of embodiments, those skilled in the art will appreciate numerous modifications and varia tions therefrom. It is intended that the appended claims cover Such modifications and variations as fall within the true Spirit and Scope of the invention. What is claimed is: 1. A method for use in a mobile communications network, comprising: receiving a request from a wireless network to terminate a communications Session with a mobile Station; in response to receiving the request to terminate, checking an indicator to determine whether the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station; and in response to determining that the communications Ses Sion is to be maintained for the mobile Station, gener ating a message to deny the request to terminate the communications Session. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein receiving the message from the wireless network comprises receiving the message from a base Station controller. 3. The method of claim 2, wherein receiving the message comprises receiving the message by a packet data Serving node (PDSN). 4. The method of claim 3, further comprising Sending the message to deny the request from the PDSN to the wireless network. 5. The method of claim 1, further comprising determining whether the mobile Station is an always-on mobile Station. 6. The method of claim 5, further comprising determining whether the mobile Station is a code-division multiple access (CDMA) always-on mobile station. 7. The method of claim 1, wherein generating the message to deny the request comprises generating a NACK message. 8. The method of claim 7, wherein receiving the request to terminate comprises receiving an A11 Registration Request with a Lifetime parameter Set to Zero. 9. The method of claim 8, wherein generating the NACK message comprises generating an A11 Registration-Reply message with a no-acknowledge indicator. 10. The method of claim 1, further comprising counting a number of attempts made to reach the mobile Station, wherein determining that the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station is in response to detecting that less than a predetermined number of attempts have been made. 11. The method of claim 10, further comprising sending an echo message to the mobile Station in each attempt to reach the mobile Station. 12. The method of claim 10, further comprising: Starting an inactivity timer; and in response to expiration of the inactivity timer, Sending an echo message to a mobile Station. 13. An article comprising at least one Storage medium containing instructions that when executed cause a System to: receive a request to terminate a communications Session with a mobile station; in response to receiving the request to terminate, checking an indicator to determine whether the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station; and in response to determining that the communications Ses Sion is to be maintained for the mobile Station, gener ating a message to deny the request to terminate the communications Session. 14. The article of claim 13, wherein receiving the message comprises receiving the message from a wireless network. 15. The article of claim 14, wherein the system comprises a packet data serving node (PDSN). 16. The article of claim 14, wherein the instructions when executed cause the System to determine whether the mobile Station is an always-on mobile Station. 17. The article of claim 16, wherein the instructions when executed cause the System to exchange messaging with an Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting Server to determine whether the mobile station is an always-on mobile Station. 18. The article of claim 12, wherein generating the message to deny the request comprises generating a NACK message. 19. The article of claim 18, wherein receiving the request to terminate comprises receiving an A11 Registration Request with a Lifetime parameter Set to Zero. 20. The article of claim 12, wherein the instructions when executed cause the System to count a number of attempts made to reach the mobile Station, wherein determining that the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station is in response to detecting that less than a predetermined number of attempts have been made. 21. The article of claim 20, wherein the instructions when executed cause the System to Send an echo message to the mobile Station in each attempt to reach the mobile Station. 22. A System comprising: an interface to receive, from a wireless network, a request to terminate a communications Session with a mobile Station; and a controller to check an indicator to determine whether the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station, and in response to determining that the communications Session is to be maintained for the mobile Station, generate a message to deny the request to terminate the communications Session. 23. The system of claim 22, wherein the controller is adapted to determine whether the mobile Station is an always-on mobile Station. 24. The System of claim 22, comprising a packet data node. 25. The system of claim 22, comprising a CDMA packet data Serving node. 26. The System of claim 22, wherein the message is an A11 Registration-Reply message with a no-acknowledge indication.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
4. DHCPINFORM --- relay instruction
 (19) United States US 2004O162892A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0162892 A1 HSu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2004 (54) PROVISIONING SERVER INFORMATION IN (76) (21) (22) A MOBILE
(19) United States US 2004O162892A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0162892 A1 HSu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2004 (54) PROVISIONING SERVER INFORMATION IN (76) (21) (22) A MOBILE
1xEV-DO Inter-Operability Specification (IOS) for CDMA 2000 Access Network Interfaces
 June, 00 SP--000 (TIA/EIA/IS-) xev-do IOS Ballot Version GPP A.S000 Ballot Version Date: June, 00 xev-do Inter-Operability Specification (IOS) for CDMA 000 Access Network Interfaces Release 0 (Ballot Version)
June, 00 SP--000 (TIA/EIA/IS-) xev-do IOS Ballot Version GPP A.S000 Ballot Version Date: June, 00 xev-do Inter-Operability Specification (IOS) for CDMA 000 Access Network Interfaces Release 0 (Ballot Version)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,526,272 B1
 USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Oliver et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 2005O289047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0289047 A1 Oliver et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) VIRTUAL MARKETPLACE FOR WIRELESS (22) Filed: Jun.
US 2005O289047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0289047 A1 Oliver et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) VIRTUAL MARKETPLACE FOR WIRELESS (22) Filed: Jun.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
Data Service Options for Spread Spectrum Systems:
 GPP C.S00-0-A Version.0 May, 00 Data Service Options for Spread Spectrum Systems: Service Options and GPP 00 GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
GPP C.S00-0-A Version.0 May, 00 Data Service Options for Spread Spectrum Systems: Service Options and GPP 00 GPP and its Organizational Partners claim copyright in this document and individual Organizational
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B1
 US007844295B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,844.295 B1 Ngan (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2010 (54) USING AWIRELESS INTERCOM TO 2004/0009.751 A1 1/2004 Michaelis et al.... 455,434 TALK-AROUNDA
US007844295B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,844.295 B1 Ngan (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2010 (54) USING AWIRELESS INTERCOM TO 2004/0009.751 A1 1/2004 Michaelis et al.... 455,434 TALK-AROUNDA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015037.0644A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0370644 A1 Graefe et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOVERING PAGES OF A DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 11/1451
US 2015037.0644A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0370644 A1 Graefe et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) RECOVERING PAGES OF A DATABASE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 11/1451
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0064.075 A1 Chatterjee US 20170064.075A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) CONTINUOUS CALL RECORDING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0064.075 A1 Chatterjee US 20170064.075A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) CONTINUOUS CALL RECORDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0009.525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009525A1 Evslin (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS PHONE WITH INTERFACE TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005.0009.525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009525A1 Evslin (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS PHONE WITH INTERFACE TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK
 SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004OO32936A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0032936A1 Horel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004 (54) TRANSACTION PROCESSING (76) Inventors: Gerald Horel,
(19) United States US 2004OO32936A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0032936A1 Horel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004 (54) TRANSACTION PROCESSING (76) Inventors: Gerald Horel,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
Query Request. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Listening Module. Expiration Module. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010463 A1 Christenson et al. US 2011 0010463A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) PROPOGATION OF DNS SERVER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010463 A1 Christenson et al. US 2011 0010463A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) PROPOGATION OF DNS SERVER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0059573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0059573 A1 Gong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2013 (54) MULTIPLE PARTY COMMUNICATIONS FOR Publication Classification
US 2013 0059573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0059573 A1 Gong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2013 (54) MULTIPLE PARTY COMMUNICATIONS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0049861A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0049861 A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY
(19) United States US 2010.0049861A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0049861 A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
/ID I INTERFACE STORAGE DEVICE. caddy. (21) Appl. No.: 10/918,304
 US 20060036786A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2006/0036786 A1 Kreiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOGICAL REMAPPING OF STORAGE DEVICES (76) Inventors: Barrett
US 20060036786A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2006/0036786 A1 Kreiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOGICAL REMAPPING OF STORAGE DEVICES (76) Inventors: Barrett
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
US 2016035.0099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/035.0099 A1 Suparna et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) APPLICATION DEPLOYMENT TO VIRTUAL Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013
 (19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(19) United States US 201302011 12A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0201112 A1 Large et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) LOW-LATENCY TOUCH-INPUT DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O1815O1A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0181501 A1 Nova et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR MACHINE TO MACHINE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2002O1815O1A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0181501 A1 Nova et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR MACHINE TO MACHINE COMMUNICATION
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 US 20100050092A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0050092 A1 Williams et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) CONTENT SHARING AND INSTANT (21) Appl. No.:
US 20100050092A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0050092 A1 Williams et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) CONTENT SHARING AND INSTANT (21) Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,269,252 B1
 USOO62692B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hutchings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 31, 2001 (54) PROGRAMMABLE BRIDGING APPARATUS 5,564,076 10/1996 Auvray... 455/76 TO CONNECT MULTIPLE NETWORKS
USOO62692B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hutchings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 31, 2001 (54) PROGRAMMABLE BRIDGING APPARATUS 5,564,076 10/1996 Auvray... 455/76 TO CONNECT MULTIPLE NETWORKS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,856,601 B1. Bell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005
 USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
401 () f f. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. Reddy et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.
 (19) United States US 2004O147254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0147254A1 Reddy et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOCATION BASED METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR WIRELESS MOBILE UNIT COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O147254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0147254A1 Reddy et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOCATION BASED METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR WIRELESS MOBILE UNIT COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O232386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0232386 A1 Dong (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR ALLOWING A UICC TO MANAGE THE POPCONTEXT PARAMETHERS (76)
(19) United States US 2010O232386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0232386 A1 Dong (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR ALLOWING A UICC TO MANAGE THE POPCONTEXT PARAMETHERS (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 2014.0004952A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0004952 A1 Kern (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXCHANGINGVIRTUAL REWARDS FOR (52) U.S. Cl. COMPUTING RESOURCES USPC...
US 2014.0004952A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0004952 A1 Kern (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXCHANGINGVIRTUAL REWARDS FOR (52) U.S. Cl. COMPUTING RESOURCES USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) United States Patent
 US007617236B2 (12) United States Patent Gaurav et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 10, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING RESULTS OF A DYNAMIC SEARCH (75) Inventors: Vishal Gaurav,
US007617236B2 (12) United States Patent Gaurav et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 10, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAYING RESULTS OF A DYNAMIC SEARCH (75) Inventors: Vishal Gaurav,
(12) United States Patent
 US007058076B1 (12) United States Patent Jiang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) INTERNET PROTOCOL (IP)-BASED WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE NETWORK (75) Inventor: Hong Jiang, Westfield,
US007058076B1 (12) United States Patent Jiang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 6, 2006 (54) INTERNET PROTOCOL (IP)-BASED WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE NETWORK (75) Inventor: Hong Jiang, Westfield,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
I lllll llllllll II llllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Requena et al. I lllll llllllll II llllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US 20020181495Al (10) Pub. No.:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Requena et al. I lllll llllllll II llllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US 20020181495Al (10) Pub. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0152175A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0152175 A1 Hromoko et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILITY (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(19) United States US 2013 0152175A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0152175 A1 Hromoko et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) MULTI-INTERFACE MOBILITY (52) U.S. Cl. USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al.
 United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al. USOO540602A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 1995 54). METHOD FOR KEY MANAGEMENT OF POINT TO-POINT COMMUNICATIONS 75 Inventors: Louis D. Finkelstein,
United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al. USOO540602A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 1995 54). METHOD FOR KEY MANAGEMENT OF POINT TO-POINT COMMUNICATIONS 75 Inventors: Louis D. Finkelstein,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0162029 A1 Allen et al. US 2002O162029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 31, 2002 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0162029 A1 Allen et al. US 2002O162029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 31, 2002 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,377,725 B1
 USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
