AirMaestro WLAN Management Console User Guide
|
|
|
- Bruce Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AirMaestro WLAN Management Console User Guide Version 1.2 Important Note: This guide contains documentation for the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console and the AirMaestro WLAN Monitor Console. The WLAN Monitor Console supports only a subset of features offered by the full-featured WLAN Management Console. Throughout this guide, features that are not supported in the WLAN Monitor Console are noted.
2 Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console User Guide 2007 Bandspeed, Inc. All rights reserved. The information contained in this document, including design, text, and graphics, is the property of Bandspeed, Inc. Listen+Learn is a registered trademark of Bandspeed, Inc. Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi CERTIFIED, Wi-Fi Alliance, Wi-Fi logo, WMM, and WPA2 are trademarks of the Wi-Fi Alliance. Other trademarks are the property of the entities referenced herein. Bandspeed, Inc. Austin, TX ii
3 Table of Contents 1.0 Before You Get Started 1.1 Key Features of the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console 1.2 System Requirements 2.0 Installing the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console Software 2.1 Uninstalling the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console Software 3.0 Configuring the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point via the WLAN Management Console 3.1 Factory Default Settings 3.2 With a DHCP Server 3.3 Without a DHCP Server View or Change an Access Point's Configuration 4.0 Getting Familiar with the WLAN Management Console 4.1 User-Defined Clusters 4.2 Management Console Window Conventions 4.3 Overview of File, View, Tools, and Help Menus File Menu View Menu Tools Menu Help Menu 4.4 Voice and Data Services Toolbar 4.5 Tab Descriptions 4.6 Channels Legend (2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz) 4.7 Security Risk and Network Status Icons 5.0 Connecting New Access Points to the Wired Network 5.1 Establishing an IP Address for the Access Point 5.2 Configuring Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points Dynamic Transmit Power Control Bidding Process Discovery Process Powerize Process Access Points Running 5.3 Auto Configuration Process 5.4 Access Point Policy Restricting Channel Changes 6.0 Using the Access Point Details Dialog Box 6.1 Dual-band RF Spectrum Analyzer 7.0 Voice and Data Services 7.1 Default Service Group 7.2 Deploying Voice Services 7.3 Deploying Data Services iii
4 8.0 Using the Network Tab 8.1 Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point Icons 8.2 Interfering Access Points 8.3 Rogue Access Point Notification 8.4 Interferer Properties 8.5 Station Icons 8.6 Importing a Bitmap into the Network View 9.0 Using the Services Tab 10.0 Using the Access Points Tab 10.1 Enable/Disable Rogue Detection 10.2 Enable/Disable Rogue Mitigation 10.3 Connect to AP Web UI Interface 10.4 Setting WIF Options Set x Mode Set Monitoring Mode Stop WIF 11.0 Using the Stations Tab 12.0 Using the Status Tab 13.0 Rogue Access Point Detection, Notification, and Mitigation 13.1 Enable or Disable Rogue Access Point Detection 13.2 Enable or Disable Rogue Access Point Mitigation 13.3 Verifying Rogue Device Manager Settings 13.4 Default Settings Appendix A: Terminology and Definitions Index iv
5 1 Before You Get Started The Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG system was designed to ensure that deployment and ongoing management of your wireless network is simple and intuitive. In environments with an increasing amount of wireless interference and where performance of the wireless network is critical to your users, the AirMaestro solution makes it easy to deploy, manage, and utilize your wireless network. The Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point integrates dual-band wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi ) access (concurrent channels of IEEE b, g, and a), wireless security, and spectrum analysis into a complete wireless local area network (WLAN) management solution. Bandspeed Listen+Learn technology simplifies the installation and management of one or more AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points by automatically configuring the channel and transmit power settings for the access point(s). Listen+Learn monitors the radio frequency (RF) activity in the environment of both AirMaestro and non- AirMaestro access points. This data is used to select optimal channel and transmit power settings for the AirMaestro access points, resulting in increased performance of your network's data transfer throughput. Bandspeed s WLAN Management and WLAN Monitor Consoles aid in making centralized monitoring and management intuitive and simple. 1.1 Key Features of the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console Rogue access point detection, notification, and mitigation Wizard-driven tools that simplify WLAN service deployment and modification across the network Centralized remote network monitoring The ability to import your building's bitmap into the network view of the management console Centralized remote network management without the need for a dedicated wireless controller RF Dual-band Spectrum Analyzer tool to detect sources of RF interference and to allow corrective action 1.2 System Requirements Operating Systems supported: Windows, 2003, XP, or Vista PC CPU requirements: Intel/AMD x86 with at least 1 gigahertz (GHz) CPU Minimum memory: 512 megabytes (MB) of random access memory (RAM) or higher recommended (256 MB minimum supported; may limit performance) Minimum available disk space: 100 MB of available hard disk space. Miscellaneous: Super VGA (800 x 600) or higher-resolution video adapter; must support DirectX9, CD-ROM or DVD drive, a keyboard, and a Microsoft Mouse or compatible pointing device Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi CERTIFIED, Wi-Fi Alliance, Wi-Fi logo, WMM, and WPA2 are trademarks of the Wi-Fi Alliance. 1-1
6 2 Installing the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console Software The AirMaestro WLAN Management Console CD includes a copy of the Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console User Guide and the WLAN Management Console software. To install the software: 1. Insert the Installation CD into your computer s CD-ROM drive. The screen shown in Figure 2-1 appears. Figure 2-1: Software installation main screen. Note: If this screen does not automatically appear, you can manually launch it by browsing to your CD- ROM drive in Windows Explorer and double-clicking on Launch. 2-1
7 a. To manually launch the installation program, browse your CD-ROM drive, as shown in Figure 2-2. Figure 2-2: Browsing content on the CD. b. Double-click on Launch (AutoPlay Application), as shown in Figure 2-3, to open the main installation screen. Figure 2-3: Launch icon. 2-2
8 2. Click on the Install Software button, as shown previously in Figure 2-1, to begin the installation process. a. You can also click on the User Guide button to view the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console software documentation. A new screen appears, as shown in Figure 2-4. Click on the View User Guide button. Figure 2-4: Click View User Guide to view the documentation. 3. After clicking on the Install Software button, the InstallShield Wizard starts, as shown in Figure 2-5. Click on Next to continue. Figure 2-5: InstallShield Wizard screen. 2-3
9 4. Read the Bandspeed End User License Agreement, as shown in Figure 2-6, and accept the agreement. To print a copy for your records, click on Print. Click on Next to continue. Figure 2-6: Bandspeed End User License Agreement. 5. In the Choose Destination Location screen, shown in Figure 2-7, click on Next to install the AirMaestro Management Console Virtual Controller software in the default destination folder. You can also click on Browse to install the software in a different folder. Figure 2-7: Choose Destination Location screen. 2-4
10 6. The installation completes, and the AirMaestro Management Console Virtual Controller software is installed on your computer. The InstallShield Wizard Complete screen is shown in Figure 2-8. Figure 2-8: Final installation wizard screen. 7. Click on Exit, as shown in Figure 2-9. Figure 2-9: Exiting the installation software. 2-5
11 8. Depending on the software you purchased, the appropriate WLAN Console icon, shown in Figure 2-10, appears on your desktop. WLAN Management Console icon WLAN Monitor Console icon Figure 2-10: The AirMaestro WLAN icon appears on your desktop. 9. Select Start > All Programs > Bandspeed AirMaestro, as shown in Figure 2-11, to confirm that the AirMaestro software was installed. Figure 2-11: Verifying the software is installed. 2-6
12 2.1 Uninstalling the Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console Software To uninstall the Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console software, follow these steps: 1. Go to Windows Control Panel (Start > Control Panel) and double-click on Add or Remove Software, as shown in Figure Figure 2-12: Add or Remove Programs icon. 2-7
13 2. Click to select the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console entry, as shown in Figure Figure 2-13: The AirMaestro WLAN Management Console entry in the Add or Remove Programs applet. 3. Click on Remove to uninstall the Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console software. 2-8
14 3 Configuring the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point via the WLAN Management Console The following image illustrates elements found on a typical wireless network, and presumes the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console is running on the personal computer. Tip: For increased security, Bandspeed recommends you perform initial configuration tasks on an isolated Ethernet network before deploying access into your existing corporate network. Typical setup for configuring an AirMaestro WLAN over Ethernet. 3-1
15 3.1 Factory Default Settings The AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point is configured at the factory to obtain an Internet Protocol (IP) address automatically using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). It uses a default static IP address if it fails to acquire an IP address using DHCP. (See the Important Factory Defaults for the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point section in the Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point User Guide for more information.) 3.2 With a DHCP Server If your network uses a DHCP server for automatic IP address acquisition, no action is required. To determine which IP address the DHCP server assigned to the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point(s), run the WLAN Management Console application. The Network View screen shows access points represented by large, colored circles, as shown in Figure 3-1. A green triangle represents an authorized access point. Figure 3-1: The WLAN Management Console window, Network View screen. Note: Refer to Section 5, Connecting New Access Points to the Wired Network, for details about the Network View screen icons. 3-2
16 To view information about an access point, such as the Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) address and IP address assigned by the DHCP server, left-click on the access point icon (small green triangle). The Bandspeed 3100AG Access Point Details dialog box opens, as shown in Figure 3-2. Figure 3-2: Access Point Details dialog box. Note: You can also find the Ethernet MAC address on the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point enclosure. If your network utilizes a DHCP server to allocate IP addresses, skip to Section Without a DHCP Server Ensure that your PC is connected to the same Ethernet network as the access point. If your network does not use a DHCP server for automatic IP address acquisition, enter the factory default static IP address ( ) in your Web browser's address field, and press Enter. Tip: You can enter that IP address into a web browser on a computer on the same subnet to view the Access Point's system status or change its configuration View or Change an Access Point's Configuration This section provides instructions for entering an IP address into a Web browser to view an access point's status or change its configuration: 1. Connect one end of standard Ethernet cable to the notebook PC or desktop's local area network (LAN) connection. 2. Connect the other end into the LAN port on the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point. 3. Plug in the power supply into an AC outlet and the 12-volt DC volt connector into the access point power outlet. 3-3
17 4. In Microsoft Windows, right-click on the Local Area Network icon in the system tray (in the lower-right corner of the window, as shown in Figure 3-3), and then select Open Network Connections from the shortcut menu, as shown in Figure 3-4. The Network Connections window opens. Figure 3-3: Local Area Network icon. Figure 3-4: Selecting Open Network Connections. 5. Right-click on Local Area Connection, and then select Properties from the shortcut menu, as shown in Figure 3-5. The Local Area Connection Properties dialog box opens. Figure 3-5: Selecting the Properties menu item. 3-4
18 6. Scroll down and then click to highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), as shown in Figure 3-6, and then click on Properties. The Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box opens. Figure 3-6: Local Area Connection Properties dialog box. 7. Select Use the following IP address. 8. In the IP address field, enter x (where x is any number between 2 and 255). Note: The IP address of the Ethernet network interface card (NIC) or wireless NIC should be set to an address in the same subnet as the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point. For example, if the 3100AG is set to IP address , set the NIC to x, where x is a number between 2 and 255, so that the full IP address does not conflict with another device in the subnet. 3-5
19 9. In the Subnet mask field, enter , as shown in Figure 3-7. Figure 3-7: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box. 10. Leave the Default gateway and DNS server fields blank. 11. Click on OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box. 12. Click on OK to close the Local Area Connections Properties dialog box. 13. Close the Network Connections window. 3-6
20 4 Getting Familiar with the WLAN Management Console The Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console provides a means for monitoring the automatic configuration process and central management of the wireless network. After loading the WLAN Management Console software onto a PC and connecting the PC to the same network (using DHCP on the PC to obtain its IP address), you can monitor the auto-configuration process by opening the program. To start either of the WLAN Consoles, double-click on the appropriate AirMaestro WLAN icon, as shown in Figure 4-1. WLAN Management Console icon WLAN Monitor Console icon Figure 4-1: Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN icons. The AirMaestro WLAN Connection Manager window opens, as shown in Figure 4-2. Click on Connect to start the AirMaestro WLAN Management Console Local Default Cluster. Figure 4-2: Connection Manager window. 4-1
21 4.1 User-Defined Clusters Bandspeed recommends that you create a new cluster for your AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points. By default, 3100AG Access Points are assigned to the default cluster with the cluster name DefaultCluster. Every 3100AG Access Point is authorized for use on DefaultCluster. Moving your 3100AG access points into a user-defined cluster enhances network security and protects your network from unauthorized 3100AG access points being added to your network automatically. To put your AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points in a secure, user-defined cluster, rightclick on the Bandspeed Icon (green triangle, shown in Figure 4-3a), and select Connect to AP Web UI Interface, as shown in Figure 4-3b. Figure 4-3a: Bandspeed icon. Figure 4-3b: Select Connect to AP Web UI Interface. You are prompted to enter a user name and password, as shown in Figure 4-4. The default user name is admin; the default password is Bandspeed. Figure 4-4: Entering a user name and password. 4-2
22 This connects you to the access point's WWW interface (AP Web UI Interface). Navigate to the Basic Configuration >> Cluster screen, as shown in Figure 4-5. Figure 4-5: Basic Configuration >> Cluster screen. Enter a cluster name in the Enter New Cluster Name text box, and click on Create. For example, Figure 4-6 shows Austin TX store#1 entered. Figure 4-6: A newly entered cluster name. 4-3
23 The Current Cluster Information screen appears, as shown in Figure 4-7. Figure 4-7: The Current Cluster Information screen. Assign your newly created cluster an IP address. This IP address acts as a central IP address for all AirMaestro 3100AG Access Points in the cluster. The Cluster IP address needs to be routable via a router on the network, and it needs to be accessible from any PC on the LAN that will be monitoring or managing the cluster. It is recommended that this IP address not be in the scope of the DHCP server's address range. Enter the IP address in the Cluster IP Address field and click on Apply. Bandspeed recommends leaving Cluster SSL enabled; disabling it will make management of the cluster less secure. 4-4
24 You can easily add access points in DefaultCluster to the new, user-defined cluster. To add an access point to the cluster, place a check mark next to an access point, and click on Add, as shown in Figure 4-8. Figure 4-8: IP address ending in was added to the current cluster Additionally, you can remove access points from the cluster using the section of the screen shown in Figure 4-9. Just put a check mark next to each access point in the current cluster to be removed, and click on Remove. Removing access points from a user-defined cluster automatically places them into DefaultCluster. Figure 4-9: Removing an access point from a cluster. Now that a user-defined cluster has been created, you can assign a cluster password. This password will protect the cluster from unauthorized monitoring and management, as well as set a global password for all of the clustered access points. There are two ways to change or manage a cluster password: In the AP Web UI Interface In the WLAN Management Console 4-5
25 If you are currently in the AP Web UI Interface, go to the System >> Password section, as shown in Figure Figure 4-10: Changing a password in the AP Web UI Interface. In addition, you can change the cluster password from the WLAN Management Console Tools section. Select, Tools > Change Cluster Password, as shown in Figure Figure 4-11: Selecting Change Cluster Password. 4-6
26 The Change Password dialog box opens, as shown in Figure Enter the password, confirm the password, and then click on OK. Figure 4-12: The Change Password dialog box. To connect to your new user defined cluster, open the WLAN Monitor Console - Connection Manager shown in Figure 4-13, and click on Add Connection. Figure 4-13: Click on Add Connection in the Connection Manager window. 4-7
27 The Edit Connection Information dialog box opens, as shown in Figure Enter a name for the cluster; this does not have to be the same name as the cluster name assigned to the cluster during creation. This name serves as a convenient name that appears in the Connection Manager's cluster list. Figure 4-14: Edit Connection Information dialog box. Enter the cluster IP address you assigned to the cluster in a previous step. This IP address needs to be accessible from the PC that is connecting to it. The Region and Details fields are for additional information, which allow you to distinguish different clusters from each other and/or sort by a region; these fields are optional. When you are finished, click on OK. You are returned to the Connection Manager, as shown in Figure Figure 4-15: Connection Manager window with a new cluster connection. Select the new cluster from the list, and click on Connect. 4-8
28 A fully operational two-access point network looks similar to Figure Figure 4-16: A fully operational network. There are two AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points connected to this network, as indicated by the green triangles located in the middle of the larger circles. The surrounding small circles are the "interfering" access points that the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point can detect in the RF environment. The skull and crossbones icon represents a rogue access point, which is an unauthorized access point that is physically connected to your network. Rogue access points pose a serious security threat to your network. Note: For more details on the Network tab and icon definitions, refer to Section
29 4.2 Management Console Window Conventions The Management Console interface includes navigational elements, as shown in Figure WLAN Management Console WLAN Monitor Console Figure 4-17: The menu bar, toolbar, and tabs display across the top of the Console window. The navigational elements are described as follows: Menu bar: The menu bar appears along the top of the console window, displaying menu items such as File, View, Tools, and Help. Toolbar: The next row of icons is called the toolbar, which displays the New Voice Service, New Data Service, and Save buttons. Tabs: The last row of icons includes the Network, Services, Access points, Stations, and Status tabs. 4.3 Overview of File, View, Tools, and Help Menus This section describes the options provided under the File, View, Tools, and Help menus File Menu Select File from the menu bar. The drop-down menu appears, as shown in Figure Figure 4-18: The File menu. The File menu options are described as follows: Clear Screen: Removes all objects from the screen and redraws them. This is useful for clearing old state information. Open Background Bitmap: Allows you to load a bitmap image file, such as a floor plan, as the background for the Network View screen (accessed from the Network tab). If you have relatively few access points, you may turn on manual placement (see Section 8.4, Interferer Properties). 4-10
30 Clear Background Bitmap: Removes any image you currently have loaded as the Network View screen background. Open Network Map: Imports the access point position information stored in that file and moves the access point on the Network View screen to those positions. (If Auto-Arrange is turned OFF, see Figure 4-25.) Save Network Map: Saves the current access point position information in the current network map, if you manually position access points on the Network View screen. Save Network Map As: Saves to the file name of your choice. Return to Connection Manager: Closes the current session of the Management Console and returns you to the Connection Manager start screen. Exit: Exits the File menu View Menu Select View from the menu bar. The drop-down menu appears, as shown in Figure Figure 4-19: The View menu. The View menu options are described as follows: Show Toolbar: Toggles the toolbar display on/off. Show Channel Legend: Toggles the Channel Legend display on/off. Show Status Indicators: Toggles the Status Indicators display on/off. Show Interferers: Toggles the Interferers display on/off. Show Rogue Access Points: Toggles the Rogue Access Point display on/off. Show Station Associations: Toggles the Station Associations display on/off. Show AP Channel Circles: Toggles the Channel Circles display on/off. Turning off the display of interferers and rogue devices from the Network view limits your ability to monitor events that may pose a security threat to your network. 4-11
31 4.3.3 Tools Menu Select Tools from the menu bar. The drop-down menu appears, as shown in Figure WLAN Management Console WLAN Monitor Console Figure 4-20: The Tools menu. The Tools menu options are described as follows: Cluster Management: Is grayed out if the access points are operating in DefaultCluster. Cluster creation must be performed via the AP Web UI Interface or using command line interface (CLI) commands. Refer to the Section 4.1, User-Defined Clusters, in this user guide. A cluster is a unique, manageable entity to which a Cluster IP address is assigned. Centralized monitoring and management of the cluster can be achieved by connecting to the Cluster IP address via the Management Console. Whether you re connecting to a cluster from your LAN, over a virtual private network (VPN), or over the Internet, it is recommended that you assign a Cluster IP address. The Cluster IP address is user specified during the creation of a new cluster. The Cluster IP address must be static and outside of the scope of your network's DHCP server(s). The following are descriptions regarding how the PC with the Management Console software loaded connects to clusters in various network configurations: o Connecting to a cluster or Access Point from a LAN or VPN: When connecting to a cluster on the LAN or VPN, connect to its Cluster IP address. The PC with the Management Console software installed needs an IP address inside the same subnet as the Cluster IP address. If the PC and Cluster IP addresses are not in the same subnet, the Cluster IP address needs to be routable via a router on the network. Tip: If the IP addresses cannot be pinged, you cannot connect from the Management Console. If using a VPN, a VPN connection must be established from the PC with the Management Console software installed and a VPN server on the same physical network as the access points in the cluster. The PC with the Management Console installed needs an IP address in the same subnet as the Cluster IP address, or be routable. o Connecting to a cluster or access point from the Internet: When connecting to a cluster over the Internet, connect to its external Cluster IP address. The external Cluster IP address needs to be exposed to the Internet and be static (never changing). Contact 4-12
32 your IT administrator or your local broadband service provider for instructions on how to obtain an external, static IP address. The external Cluster IP address also needs to allow specific TCP traffic through the firewall; otherwise the firewall will reject all communication to the cluster. The TCP port required for forwarding is Consult your IT administrator or your firewall s documentation to determine how to open a port on the firewall. Bandspeed highly recommends enabling SSL communication when accessing a cluster from the Internet without a VPN connection. SSL encrypts the communication between the PC with the Management Console and the cluster, providing additional Internet security. Exposing any network device to the Internet may pose a security risk. 4-13
33 Rogue Device Manager: Opens the Rogue Device Manager dialog box, shown in Figure Figure 4-21: Rogue Device Manager dialog box. The dialog box sections and buttons are described as follows: o o o o o o o Interferers: Displays access points that are detected in the RF environment but have not been determined to be connected to the wired network. Status Information: Displays the status of Rogue Detection and the status of Rogue Mitigation (on/off). You can select the Audio Alert When Rogue Appears option to trigger an audio alert when a rogue access point appears in the network. Trusted APs: Displays access points that are connected to the wired network and authorized to be in your network. Rogue APs: Displays access points that are connected to your wired network but have not been authorized. Refresh button: Refreshes the screen to display new access points that have been added or moved to a different category. Close button: Closes the dialog box. Apply button: Saves the Trusted APs list to each access point on the network. 4-14
34 Radius Support: Options are Enable Radius Support, Disable Radius Support, and Configure Radius Support Settings, as shown in Figure Figure 4-22: Radius Support menu options. If a Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) server has been configured to be on your network, the Configure: RADIUS dialog box opens, as shown in Figure 4-23, allowing you to start, stop, and configure the AirMaestro interface to that RADIUS server. Figure 4-23: Configure: RADIUS dialog box. o o o o o Status: Displays the condition (stopped/started) of the AirMaestro interface to the client's RADIUS server. Server IP Address: Displays the RADIUS server s IP address. Port: Displays the RADIUS server s port number. Secret Key: Displays the key previously supplied when configuring the RADIUS server. Reauthentication Status: Allows you to enable or disable the periodic automatic reauthentication of the access point. 4-15
35 o o o o o o Reauthentication Timeout: Displays how often (in seconds) the device checks the port to reauthenticate the access point. Valid values are 1 through The default is Reauthentication Retries: Indicates the total amount of reauthentication requests sent. If a response is not received after the defined interval, the authentication process is restarted. Reauthentication Interval: Defines the amount of time (in seconds) that lapses before the access point resends a request to the authentication server. Key Cache Time (100-20,000 Sec.): Displays the number of seconds to preserve a record of a successful user authentication. Server Retry Timeout (1-200 Sec.): Displays the total number of seconds the access point waits for the RADIUS server to respond before timing out. Server Retries (1-10): Displays the number of attempts the access point makes to connect to the RADIUS server. Create Voice Service: Allows you to create a Voice Service. See Section 7.2 for more information. Create Data Service: Allows you to create a Data Service. See Section 7.3 for more information. Change Cluster Password: Allows you to change the password for all currently authorized access points within the cluster. Enter the new password in the Change Password dialog box, shown in Figure 4-24, confirm the new password, and click on OK. Figure 4-24: Change Password dialog box. Manual AP Authorization: Allows you to enter the password for access point authentication. If no new access points have been detected, a message displays to that effect. 4-16
36 Options: Opens the Options dialog box, shown in Figure Figure 4-25: Options dialog box. The Options dialog box offers the following options: Performance: The High Quality option produces a better image, especially on higher resolution monitors. Selecting Normal Quality improves speed and performance at the cost of slightly lower visual quality. Visualization: Options are Auto-Arrange Access Points and Auto-Scale Access Points. If the Auto-Arrange Access Points option is selected, the feature is enabled and the elements on the Network View screen are arranged automatically. If the option is not checked, the feature is disabled, allowing you to manually position the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point icons and network elements on the Network View screen. If the Auto-Scale option is not selected, you can use the slide bar to manually size the elements in the Network View screen. Lease Time: The number of seconds before a device is considered to be timed-out or inactive. Country and Indoor/Outdoor Usage: Clicking on Change opens the dialog box shown in Figure WLAN Management Console WLAN Monitor Console Figure 4-26: Country and Indoor/Outdoor Usage Info dialog box. These options include: o Country: Select the country in which the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point is used. 4-17
37 o Indoor/Outdoor: Select the environment in which the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point will be deployed. Your options are Indoors, Outdoors, or Indoors/Outdoors (a combination) Help Menu Select Help from the menu bar, as shown in Figure Figure 4-27: Help menu. The Help system window appears, as shown in Figure You can browse the Help topics (Contents tab), view an index of topics (Index tab), search for a specific topic (Search tab), or see a list of Favorites (Favorites tab). Figure 4-28: AirMaestro Help system. 4-18
38 4.4 Voice and Data Services Toolbar The buttons on the toolbar are shown in Figure Figure 4-29: Toolbar buttons. The buttons are described as follows: Voice Service Creation Wizard: Allows you to create a Voice Service Group that provides users with blanket Voice over WLAN (VoWLAN) coverage over a certain area. Voice Service Groups employ fast roaming, load balancing, and load limiting. Data Service Creation Wizard: Allows you to create a Data Service Group that provides users with blanket WLAN coverage over a certain area. Edit: Allows you to edit a voice or data service. Delete: Allows you to delete a voice or data service. 4.5 Tab Descriptions The Network, Services, Access points, Stations, and Status tabs are shown in Figure Figure 4-30: Tabs. The tabs are described as follows: Network: Displays a graphical representation of all network elements (see Section 8). Services: Displays details of the services currently supported in the network (see Section 9). Access points: Allows you to view specific details about each AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point in the network. This lists the services deployed on each wireless interface (WIF) for each access point, as well as displays the stations that are currently associated with that access point (see Section 10). Stations: Allows you to see which stations are currently associated with the network (see Section 11). Status: Displays a pie chart summarizing the current working status of the access points that are currently in the network (see Section 12). 4-19
39 4.6 Channels Legend (2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz) The Channels Legend on the left side of the screen, shown in Figure 4-31, displays a color for each channel in the 2.4 and 5.0 GHz bands. Each compliant access point, rogue, or interferer displays in the Management Console's main window (the Network View screen) in one of the colors from the legend. Figure 4-31: The Channels legend appears along the left side of the screen. The fill color of each circle represents the specific operating channel for each unique access point, including AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points, interferers, and rogue access points. Tip: You can turn off display of the legend from the View menu. 4-20
40 4.7 Security Risk and Network Status Icons In the upper-right portion of the Network View screen are two icons, Network Stats (Network Status) and Security Risk, as shown in Figure Figure 4-32: Network Stats and Security Risk icons. The icons are described as follows: Network Stats (Network Status): This icon is a pie chart displaying the percentage of your network that is operational. Red areas indicate how many access points (as a percentage) are currently non-operational. Green indicates functioning access points (again, as a percentage). A fully green chart indicates that all access points are up and running. Security Risk: This icon provides a quick view of the encryption and authentication settings on the services currently supported by the network. The Security Risk icon displays a red, yellow, or green shield. Red indicates that one or more services are operating without any security. Yellow indicates that one or more services are operating in Wired Equivalency Privacy (WEP) mode only, which is considered only moderately secure. A green shield indicates that all services are configured with a high level of security, using Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) or WPA2. Note: The default setting for the access point provides a Bandspeed service (SSID) in the 2.4 and 5.0 GHz bands. This service has no security setting, so the shield is initially red. Once the first service is deployed in the network through the Management Console, it replaces the default service. Tip: You can turn off the display of both icons from the View menu. 4-21
41 5 Connecting New Access Points to the Wired Network 5.1 Establishing an IP Address for the Access Point When an AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point is connected to the wired network (using factory default settings), it receives its IP address from the DHCP server, and then connects into the same Layer 2 network as other 3100AG devices on that network. As access points are added to the network, they appear automatically in the Network View screen of the Management Console, as shown in Figure 5-1. Figure 5-1: Network View screen displaying newly added access points. 5.2 Configuring Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points The following describes the process that occurs when AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points are being added to the network: Access Point Registration: After powering up, each AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point registers its participation in the cluster with the other AirMaestro access points through a self-discovery process. Once registered, each access point bids for the right to perform the automated and intelligent channel selection and transmit power setting. Access Point Bidding: Only one access point at a time wins the position to perform the autoconfiguration process. Once awarded, the access point starts the Discovery process. 5-1
42 Discovery Process: During the Discovery process, the access point scans every WLAN channel to detect other interfering access points within range. It scans all of the 2.4 GHz b/g channels using WIF-1. You can see this happen by watching the WLAN channel that WIF-1 is currently set to. Once WIF-1 completes the scan of the 2.4 GHz channels, WIF-3 starts scanning the 5.0 GHz a channels. Interference Database Development: Through both scans, the access point develops an interference database that includes specific information about each interfering access point. This information includes the SSID, MAC address, WLAN channel the interference was detected on, receive signal strength (RSS), and how many times packets were detected from the interfering access point. As an AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point detects interfering access points around the network, individual circular icons display on the Network View screen. Each circle is located next to the AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point that most strongly detects the interfering access point's signal and the circle takes on the color of the WLAN channel. The size of the circle is relative to the RSS from the interfering access point. Running/Bid_Denied: While one AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point is in the Discovery process, the other access point has either completed auto-configuration (status displays as RUNNING) or is waiting to go through auto-configuration (status displays as BID_DENIED). Optimal Channel Selection: After an access point completes the Discovery process, it runs an algorithm based on the information it accumulated in the interference database. This algorithm determines the optimal channel for that specific access point to select in the 2.4 GHz band on WIF-1. It performs the same calculation for channel selection for WIF-3 in the 5.0 GHz band. Powerize Mode: The AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point enters Powerize mode, where it communicates with other in-cluster 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points. These access points communicate through the air to negotiate back their transmit power settings. This allows them to minimize co-interference while maximizing coverage and performance. 5-2
43 5.2.1 Dynamic Transmit Power Control In the event an access point fails or is removed from the network, the other AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points detect the absence of the access point and increases their transmit power to newly negotiated power levels. Note: This provides some self-healing capability in the event of a failure of a single access point. Figure 5-2: Network View elements. In Figure 5-2, the triangle icon represents an AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access point. The filledin circle surrounding a triangle represents the channel setting and the power setting on the WIFs that are providing access. The color of the filled-in circle is the overlay of two filled-in circles, one for WIF-1 supporting access in the 2.4 GHz band (802.11b/g) and one for WIF-3 supporting access in the 5.0 GHz band (802.11a). The third, hollow circle that grows larger indicates that WIF-2 is scanning all WLAN channels as an integrated RF and security sensor. The text under each triangle displays access point information, including the last two bytes in the access point's IP address and the current status of the access point. 5-3
44 5.2.2 Bidding Process The Bidding process is shown in Figure 5-3. Because only one access point at a time wins the position to perform the auto-configuration process, one access point is denied the bid. Figure 5-3: The Bidding process when a second access point is added to the network. 5-4
45 5.2.3 Discovery Process The Discovery process is shown in Figure 5-4. Figure 5-4: The Discovery process. 5-5
46 5.2.4 Powerize Process The Powerize process is shown in Figure 5-5. Figure 5-5: The Powerize process. 5-6
47 5.2.5 Access Points Running Figure 5-6 shows that both in-network access points have completed the auto-configuration process and are running. Figure 5-6: Two in-network access points complete auto-configuration and are running. 5-7
48 5.3 Auto Configuration Process Access points sequentially perform the auto-configuration process until all in-network access points have completed it. After each access point completes the auto-configuration process, it communicates its interference database with the other in-network access points to determine if a better channel mapping should be adopted. If so, channel settings on each access point are adjusted accordingly. 5.4 Access Point Policy Restricting Channel Changes Each access point continues to scan the WLAN environment to maintain a current interference profile for the environment. If more optimal channels are identified, the access point automatically adopts the new channel setting as long as certain policies are met. Tip: A policy setting on the access point restricts channel changes if more than X stations are associated with the access point. By default, X is set to 3. You can change this setting via the access point's Web UI Interface or the CLI. 5-8
49 6 Using the Access Point Details Dialog Box You can view additional information specific to an access point by left-clicking on the access point triangle icon on the Network View screen, as shown in Figure 6-1. Figure 6-1: Clicking on the AirMaestro Access Point icon. The Access Point Details dialog box opens, as shown in Figure 6-2. Figure 6-2: Access Point Details dialog box. 6-1
50 This dialog box displays several fields, such as: MAC: The access point's MAC address IP: The access point's IP address The Access Point Details dialog box also includes three tabs: WIFs, Interferers, and Stations: WIFs tab: Shown previously in Figure 6-2, this displays the access point's MAC address, IP address, and information about the three AirMaestro wireless interfaces (WIF-1, WIF-2, and WIF- 3). Interferers tab: Shown in Figure 6-3, this displays the interferer database. This includes the SSID and MAC address of each interfering access point, as well as the channel the interference was detected on, which WIF detected it, the receive signal strength indicator (RSSI) of the interference on that channel, and how many times packets were detected from the interfering access point on that channel (Count). It also lists whether the interfering access point is a rogue access point, which is an unauthorized access point that has been connected to your wired network. If the access point is neither a trusted access point nor a rogue access point, it is identified as Unknown. Figure 6-3: Interferers tab. 6-2
51 Stations tab: Shown in Figure 6-4, this displays the stations associated with the access point. Figure 6-4: Stations tab. All of this occurs automatically, without user intervention. Once the network has intelligently and properly configured itself, you are ready to deploy services in the network. 6-3
52 6.1 Dual-band RF Spectrum Analyzer Click on the Spectrum button in the Access Point Details dialog box to open the Bandspeed AirMaestro RF Spectrum Analyzer, shown in Figure 6-5. This turns the Monitor WIF into a dual-band spectrum analyzer. Tip: As a shortcut, right-click on an access point triangle on the Network View screen, and then select Spectrum to open the analyzer. Figure 6-5: Bandspeed AirMaestro RF Spectrum Analyzer. When you close this window, the Monitor WIF converts back into Security Sensor mode. All of this occurs while the other two interfaces provide simultaneous access in both the 2.4 and 5.0 GHz bands. The Bandspeed AirMaestro Spectrum Analyzer display shows the RF energy in real time around that specific access point. The first line shows the 2.4 GHz frequency band, with b/g WLAN channels 1, 6, and 11 are overlaid in the display. The next three rows show the 5.0 GHz band, with a WLAN channels overlaid in the display. 6-4
53 To select the Peak Hold function, right-click anywhere on the AirMaestro Spectrum Analysis screen and select Enable Peak Hold, as shown in Figure 6-6. The banner line will indicate that Peak Hold is enabled. Figure 6-6: The Enable Peak Hold option. Cordless phones and microwave ovens are known to be disruptive to wireless networks. The Bandspeed AirMaestro RF Spectrum Analyzer provides a means to "see" a representation of radio signals as they occur, allowing cordless phones and microwave ovens that are in use and within range of a particular AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point to be detected. A typical "signature" for a cordless phone is a strong spike in signal strength on frequencies shared by an channel. Figure 6-7 shows the strong interference generated from an analog cordless phone functioning in the same frequency range as Channel 1 in the 2.4 GHz band. Figure 6-7: The AirMaestro Spectrum Analysis screen shows that a cordless phone was detected on the 2.4 GHz band. 6-5
54 A typical signature for a microwave oven is a broad pulsating signal, occupying one or more channels simultaneously. Figure 6-8 shows strong interference generated from a microwave oven that functions in the same frequency range as Channels 6 through 11 in the 2.4 GHz band. Figure 6-8: The Spectrum Analysis screen shows that a microwave oven was detected. Figure 6-9 shows an example of the AirMaestro Spectrum Analysis display when the microwave oven is turned off. Figure 6-9: The Spectrum Analyzer screen when the microwave oven is off. 6-6
55 7 WLAN Monitor Console Users The features in this section are not available to WLAN Monitor Console users. Voice and Data Services AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points can support up to 16 unique BSSIDs, or Bandspeed services. Each service can be uniquely tied to a virtual local area network (VLAN) for network isolation between services. This allows the administrator to set up multiple virtual network services that each has unique access to specific network resources. 7.1 Default Service Group The factory default for the AirMaestro Access Point includes a default Service Group called Bandspeed, with the security mode set to None, as shown in Figure 7-1. The first data or voice group that gets created replaces the default Service Group. Figure 7-1: The default Service Group. 7-1
56 7.2 Deploying Voice Services Voice Services are optimized to support voice traffic by providing load balancing and fast roaming between access points. Unique voice services may be offered only within a single WLAN frequency band, either the 2.4 or 5.0 GHz band. To establish a new Voice Service, click on the Create Voice Service icon on the toolbar (first from the left), as shown in Figure 7-2. Figure 7-2: Create Voice Service icon. The Voice Service Creation Wizard starts, as shown in Figure 7-3. Figure 7-3: The Voice Service Creation Wizard. This wizard allows you to create a Voice Service Group to provide users with blanket VoWLAN coverage over a certain area. Enter the name of the new Voice Service you want to create in the Name (SSID) text box. For example, you could enter Voice Services
57 Select the frequency band on which you would like to offer this service (2.4 or 5.0 GHz), as shown in Figure 7-4. Unlike Data Services a Voice Service can only be deployed across one frequency band. Figure 7-4: Selecting a frequency band. You can also select the specific channel you want this service supported on. Auto is the default setting and intelligently selects the optimal channel to avoid interference from other access points within range. You may also manually select another channel using the drop-down menu, as shown in Figure 7-5. Figure 7-5: Selecting a channel. Note: This could be important if you want to manually change the channel setting due to interference from a cordless phone or microwave oven. 7-3
58 Select the security mode you want supported on this service from the Security Mode drop-down list, as shown in Figure 7-6. For this example, WEP will be selected. Figure 7-6: Selecting the security mode. Based on the security mode you selected (in this case, WEP), the recommended authentication and encryption methods are automatically selected. You can change these using the Authentication dropdown menu, shown in Figure 7-7, if other selections are desired. Figure 7-7: Selecting the authentication method. You can uniquely assign each service to a VLAN by entering the VLAN ID and VLAN Priority settings on the right. If VLANs are not supported (for example, if you are using an unmanaged Ethernet switch), you can leave these fields set to 0. Click on Next. 7-4
59 The WEP Pre-Shared Key Configuration dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 7-8. Figure 7-8: WEP Pre-Shared Key Configuration dialog box. Enter the pre-shared keys for the service you are creating, and click on OK. The Voice Service Creation Wizard presents all of the available WIFs that are in the network and capable of supporting that service, as shown in Figure 7-9. Select which access point WIF(s) to include as part of the Voice Roaming Group. (Click on the icon to toggle selections on and off.) Then click on Finish. Figure 7-9: Available WIFs. 7-5
60 The WLAN Management Console asks you to confirm your settings, as shown in Figure Figure 7-10: Confirming your settings. By clicking on Yes, the newly defined service is deployed on all of the access points supporting interfaces for which you chose to provide that service. Service deployment may take a few seconds. A confirmation message appears, confirming you successfully created a Voice Service Group, as shown in Figure Click on OK. Figure 7-11: Voice Service created successfully. 7-6
61 A new Voice Service has been added (the default group has been updated to Voice Services 1). Your service is now active on the interfaces selected. In this case, Voice Services 1 was deployed as a 2.4 GHz (only) Voice Service. You can confirm that the service has been deployed by selecting the Services tab, as shown in Figure Figure 7-12: Confirmation that a new service is active. 7-7
62 7.3 Deploying Data Services To create a new Data Service, click on the Create Data Service toolbar icon (second from left), shown in Figure Figure 7-13: Create Data Service icon. The Data Service Creation Wizard starts, as shown in Figure Figure 7-14: Data Service Creation Wizard. 7-8
63 Enter the name of the new Data Service you want to create in the Name (SSID) text box, shown in Figure 7-15, and click on Next. Figure 7-15: Naming the new service. Note: Data Services will run with Auto Channel selection unless overridden on each access point's Web UI Interface. Select the security mode you want supported on this service, as shown in Figure WPA2 will be selected in this example. Figure 7-16: Selecting the security mode. Based on the security mode you selected (in this case, WPA2), the recommended authentication and encryption methods are automatically selected. You can change these using the drop-down menus shown in Figure 7-17 if other selections are desired. 7-9
64 Figure 7-17: Selecting the authentication method. You can uniquely assign each service to a VLAN by selecting the VLAN ID and VLAN Priority settings on the right. If VLANs are not supported (for example, if you are using an unmanaged Ethernet switch), you can leave these set to 0. Click on Next. The WPA/WPA2 Pre-shared Key Configuration dialog box appears, as shown in Figure Figure 7-18: WPA/WPA2 Pre-shared Key Configuration dialog box. Type the passphrase for the service you are creating, and click on OK. 7-10
65 The Data Service Creation Wizard presents all of the available WIFs that are in the network and capable of supporting that service. Select the access point WIFs you want to run the service on, as shown in Figure Figure 7-19: Selecting WIFs. Note: WIFs supporting data services can support different bands. Click on Finish. You'll be asked to confirm you want to deploy the new service, as shown in Figure Figure 7-20: Confirming service deployment. 7-11
66 Click on Yes, and the new service is loaded on all of the access points supporting interfaces for which you chose to provide that service. Once the service is deployed, which may take a few seconds, the confirmation message shown in Figure 7-21 appears. Click on OK. Figure 7-21: The service was successfully deployed. 7-12
67 Data Service 1 is now active on the selected interfaces, as shown in Figure In this case, Data Service 1 was deployed as a 5.0 GHz (only) data service. You could have deployed it as a dual-band service by selecting 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz interfaces during that part of the creation process. Figure 7-22: Data Service 1 shows an Active status. Note: The color is green to reflect a higher level of security. You can also deploy services on a subset of the in-network AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points by selecting only those interfaces during the process. One example is to deploy Guest Services on specific access points; for example, one by the lobby and one in a large meeting room. Through unique VLAN assignment, you can assign the Guest Service a VLAN that provides only Internet access, for example, and no access to the company's internal network resources. 7-13
68 8 Using the Network Tab 8.1 Bandspeed AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point Icons The Network tab displays AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point icons as triangles, as shown in Figure 8-1. A green triangle means the access point is up and running. A red triangle indicates an inactive access point. The last four digits of the IP address are displayed for identification purposes, as well as a text field indicating its current status. All three WIFs are also displayed along with their associated channel number. Figure 8-1: The Network tab (Network View screen). Surrounding the access point triangles are access point channel circles. An expanding ring is displayed to represent that the access point is scanning the radio channels. The color of the ring identifies the channel the WIF is monitoring. The ring changes color as the access point monitors successive channels in both the 2.4 and 5.0 GHz bands. 8-1
69 8.2 Interfering Access Points An interferer (for example, Ch 6 linksys shown in Figure 8-2) is color-coded according to the legend and displayed. Interferers are grouped with the access point that is receiving the interfering access point's signal the strongest. As a result, interferers occasionally "move" on the Network View screen from one access point to another as network conditions change. When the Management Console initially starts, there may considerable movement of the interferers while the program establishes an internal database of interference reports. Figure 8-2: Interferers group with AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Points. Note: The diameter of the interferer bubble indicates the relative RSS from the interferer (i.e., the larger the bubble, the greater the RSS). 8-2
70 8.3 Rogue Access Point Notification Interferers that are detected as rogue will be displayed with a skull and crossbones, as shown in Figure 8-3. You can reclassify rogue access points as Authorized devices from the Rogue Device Manager accessible from the Tools menu. Rogue access points are unauthorized access points that have been confirmed to be physically connected to your wired network. These devices may pose a serious security threat to your network, and Bandspeed recommends that Rogue Access Point Detection and Notification be enabled. Figure 8-3: A rogue access point appears with a skull-and-crossbones icon. Note: As shown in Figures 4-21 and 13-4, you can configure an audio alert to occur when a rogue access point appears on the network. 8-3
71 8.4 Interferer Properties Click on an interfering access point channel circle to open the Interferer Properties dialog box, as shown in Figure 8-4. Figure 8-4: Interferer Properties dialog box. The table in the Interferer Properties dialog box contains a list of all interference reports that have been made against the interferer currently being examined. Each line in the table represents one or more interference reports issued by an access point s WIF. For clarity, multiple reports are grouped if the access point, WIF, and channel match. In such cases, the RSSI strengths of the reports are averaged. Reports eventually time out and are discarded from these calculations. You can adjust the timeout value (lease time option) via Tools > Options (see Figure 4-25). The properties are described as follows: Reporter IP: Lists the access point which issued the interference report(s). Channel: Lists the channel on which the interference was detected. A single interferer can cause interference across several channels around its transmit frequency. For this reason, reports may be issued on several different channels for the same interferer. WIF: Lists the wireless interface that detected the interference. WIFs that are set to Monitor mode tend to pick up more interference and issue more reports because they scan more channels. WIFs that are not set to Monitor mode will only detect interference on its currently active channel. RSSI: Is the average receive signal strength indicator of all reports grouped for that line (grouped by matching access point, WIF, and channel). Count: The number of reports received. All reports eventually time out. Once the number of reports for a particular line reaches zero, that line is removed. Once the total number of reports for an interferer reaches zero, the interferer itself is removed. If manual placement is being used, you may click-and-drag on an interfering access point icon to any location on the screen. If manual placement is not being used, the interfering access point icon will be automatically positioned on the Network View screen. Once moved, as shown in Figure 8-5, interferers become free floating and will not move or free-associate. This is helpful if you want to manually place interfering access points on certain places on the monitor. You may press CTRL+N at any time to reset the screen to its default. 8-4
72 Figure 8-5: A rogue access point icon that has been moved away from an AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point. Note: Moving the access point away is a visual representation only and this action does not provide any rogue access point containment. 8-5
73 8.5 Station Icons Stations associated with an access point are displayed as a station icon, as shown in Figure 8-6. Figure 8-6: The icon for a station associated with an access point. Figure 8-7 shows a station icon along the perimeter of the channel bubble. The last two bytes of the station's MAC address are displayed for identification purposes. Figure 8-7: The station icon located on the channel bubble perimeter is associated with an access point. 8-6
74 8.6 Importing a Bitmap into the Network View The Bandspeed AirMaestro WLAN Management Console allows you to import a bitmap of your building layout for the background of the Network View. To do this, select File > Open Background Bitmap. Select the bitmap file you want to import, and click on Open. The bitmap imports into the background, as shown in Figure 8-8. Figure 8-8: A building layout serves as the background of the Network View screen. 8-7
75 9 WLAN Monitor Console Users The features in this section are not available to WLAN Monitor Console users. Using the Services Tab On the Services tab, you select a service by clicking on the service name. Once selected, you can use the toolbar buttons above the Services tab to edit, delete, or save the service. The Services tab displays details for each of the deployed services, as shown in Figure 9-1. The colors correspond to the security risk: Green: Indicates a lower security risk; WPA or WPA2 protocols are in use. Orange-yellow: Indicates a medium security risk; the WEP protocol is in use. Red: Indicates the highest risk, because no security protocols are in effect for that Service Group. Figure 9-1: The Services tab color-codes services. 9-1
76 To edit or delete a service, select it in the list, and then click on the appropriate toolbar button. The edit and delete buttons are shown in Figure 9-2. Edit button Delete button Figure 9-2: The Edit and Delete buttons on the toolbar. For example, Figure 9-3 shows the results of deleting a service. Figure 9-3: Deleting a service. 9-2
77 When you click on the Edit button, an edit wizard starts to guide you through the edit process, as shown in Figure 9-4. Figure 9-4: Data Service Creation Wizard. 9-3
78 10 WLAN Monitor Console Users The features in this section are not available to WLAN Monitor Console users. Using the Access Points Tab The Access points tab allows you to view specific details about each in-network AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point. This tab lists the services deployed on each interface for each access point, as well as the stations currently associated with that access point, as shown in Figure Figure 10-1: Access points tab. The Access Point screen shows the following: Access Point : o o o WIF-1 on WLAN Interface 1 is set to 2.4 GHz, is operating in the bg mode, and is active. There is one service associated with WIF-1 Voice Services 1 with a Service BSSID of 00:06:B8:00:15:50. WIF-2 is on WLAN Interface 2, is operating in RF Monitor mode, and is active. WIF-3 on WLAN Interface 3 is set to 5.0 GHz, is operating in the a mode, and is active. There are two services associated with WIF-3 Bandspeed Data and Data Service 1 with Service BSSIDs of 00:06:B8:00:15:80 and 00:06:B8:00:15:81, respectively. 10-1
79 Access Point : o WIF-1 on WLAN Interface 1 is set to 2.4 GHz, is operating in the bg mode, and is active. There is one service associated with WIF-1 Voice Services 1 with a Service BSSID of 00:06:B8:00:15:50. Note: Voice Service 1 shares the same BSSID number 00:06:B8:00:15:50 for both access points, allowing for seamless roaming. o o WIF-2 is on WLAN Interface 2, is operating in RF Monitor mode, and is active. WIF-3 on WLAN Interface 3 is set to 5.0 GHz, is operating in the a mode, and is active. There are two services associated with WIF-3 Bandspeed Data and Data Service 1 with Service BSSIDs of 00:06:B8:00:15:70 and 00:06:B8:00:15:71, respectively. Right-click on the access point's IP address in the interface to open a shortcut menu of options, as shown in Figure Figure 10-2: An access point's menu items. 10-2
80 10.1 Enable/Disable Rogue Detection Right-click on the access point's IP address in the interface and select Enable Rogue Detection, shown in Figure 10-3, or Disable Rogue Detection to enable/disable rogue detection. Section 13.1 covers these options in detail. Figure 10-3: Selecting Enable Rogue Detection. 10-3
81 10.2 Enable/Disable Rogue Mitigation Right-click on the access point's IP address in the interface and select Enable Rogue Mitigation, shown in Figure 10-4, or Disable Rogue Mitigation to enable/disable rogue mitigation. Section 13.2 covers these options in detail. Figure 10-4: Selecting Enable Rogue Mitigation. Enabling Rogue Mitigation will contain and effectively shut down the threat of rogue access points. Rogue Mitigation must be enabled on all access points for full network rogue access point mitigation. The 3100AG Access Points can only mitigate rogue access points that are within their wireless range. 10-4
82 10.3 Connect to AP Web UI Interface Right-click on the access point's IP address in the interface and select Connect to AP Web UI Interface, as shown in Figures 10-5a and 10-5b. WLAN Management Console WLAN Monitor Console Figure 10-5a: Selecting Connect to AP Web UI Interface. Right-click on the green access point (above), and select Connect to AP Web UI Interface (below). Figure 10-5b: Selecting Connect to AP Web UI Interface. You are prompted to enter a user name and password, as shown in Figure Figure 10-6: Entering a user name and password. This connects you to the access point's WWW interface (AP Web UI Interface). The default user name is admin; the default password is Bandspeed. 10-5
83 10.4 Setting WIF Options You can set the a,b,g mode, monitoring mode, or stop a WIF by right-clicking on a WIF and selecting one of the options shown in Figure Figure 10-7: WIF drop-down menu. 10-6
84 Set x Mode Right-click on a WIF and select Set x Mode, as shown in Figure 10-8, to set the WIF in a, b, or g mode. Figure 10-8: Selecting Set x Mode. 10-7
85 Set Monitoring Mode Right-click on a WIF and select Set Monitoring Mode, as shown in Figure 10-9, to set the WIF in RF Sensing Mode. This allows that WIF to function as a dual-band RF monitor as described in Section 6.1. Figure 10-9: Selecting Set Monitoring Mode. 10-8
86 Stop WIF Right-click on a WIF and select Stop WIF, as shown in Figure 10-10, to deactivate a WIF. Figure 10-10: Selecting Stop WIF. 10-9
87 11 WLAN Monitor Console Users The features in this section are not available to WLAN Monitor Console users. Using the Stations Tab The Stations tab allows you to see which stations are currently associated with the network, as shown in Figure This includes information such as the receive signal strength indicator from the station (RSSI). Figure 11-1: Stations tab. 11-1
88 12 Using the Status Tab The Status tab shows a pie chart, shown in Figure 12-1, summarizing the current working status of the access points that are currently in the network. The pie chart represents the percentage of access points that are up and running normally (green), up and partially running (yellow), or were in network and are now inactive (red). Figure 12-1: Pie chart shows access point status. 12-1
89 13 Rogue Access Point Detection, Notification, and Mitigation WLAN Monitor Console Users The features in this section are not available to WLAN Monitor Console users. In the default configuration mode, each access point provides simultaneous access in both Wi-Fi frequency bands (2.4 and 5.0 GHz) and also includes a simultaneous, non-disruptive, dual-band RF and security sensor. This third interface (WIF-2), when set to Monitor Mode (default), continually scans the RF environment and continually keeps the interference database up to date. This includes determining if any interferers have been determined to be rogue access points; any interferer that has connected to the internal wired AirMaestro network. Rogue detection is shown in Figure Figure 13-1: Rogue detection (IP address f4:21). Each time the WIF-2 scans a WLAN channel, it runs diagnostics on each interferer to determine if that interferer has been connected to the internal wired network. Tip: Access Points that are not authorized to be physically connected to your network can be detected by the WLAN Management Console and WLAN Monitor Console and an audio alert can be set to notify you (see Figures 4-21 and 13-4). 13-1
90 13.1 Enable or Disable Rogue Access Point Detection From the Access point tab, you can right-click on an access point IP address to display a list of access point-specific options, as shown in Figure To enable rogue access point detection, select Enable Rogue Detection. Likewise, you disable it by selecting Disable Rogue Detection. Figure 13-2: Enabling rogue detection. Repeat the process for every other access point IP addresses you want to enable/disable for rogue detection. Turning off rogue device detection from the network view limits your ability to detect events that may pose a security threat to your network. 13-2
91 13.2 Enable or Disable Rogue Access Point Mitigation Access points that are not authorized to be physically connected to your network (rogue access points) can be blocked from gaining access to your network by turning on the Mitigation feature in the WLAN Management Console. From the Access points tab, right-click on an access point IP address to display of a list of access pointspecific options, as shown in Figure To enable rogue access point mitigation, select Enable Rogue Mitigation. Likewise, you can disable it by selecting Disable Rogue Mitigation. Figure 13-3: Enabling rogue mitigation. Repeat the process for every other Access Point IP address you want to enable/disable for Rogue Mitigation. Enabling Rogue AP Mitigation will contain and effectively shut down the threat of rogue access points. Rogue Mitigation must be enabled on all access points for full network rogue access point mitigation. The access points can only mitigate rogue access points that are within their wireless range. Turning off rogue device mitigation from the Network View screen limits your ability to prevent events that may pose a security threat to your network. 13-3
92 13.3 Verifying Rogue Device Manager Settings To view rogue access point information, select the Tools drop-down menu, and then select Rogue Device Manager. The Rogue Device Manager dialog box opens, as shown in Figure Figure 13-4: Rogue Device Manager dialog box. The sections are described as follows: Interferers: Located in the upper-left part of the dialog box, it lists all interfering access points that are not connected to the wired network Trusted APs: Located on the right, it lists all access points that have been determined to be connected to the wired network. (Trusted access points are access points that have been authorized to be in the network.) Status Information: Displayed in the lower-left corner, it shows whether rogue detection and rogue mitigation is on or off. You can check the Audio Alert When Rogue Appears option to be notified when a rogue access point connects to the network. Rogue APs: Located in the lower-right part of the dialog box, it allows you to authorize a rogue access point to be in the network. Select the rogue access point in the Rogue APs list, click on the ^^ button to move the rogue access point to the Trusted APs list, and then click on Apply. Once a rogue access point has been authorized, the flashing notification on the Network View screen disappears (as shown in Figure 13-5) and stations will be allowed to associate with that access point. 13-4
93 Figure 13-5: The flashing notification in IP address f4:21 has disappeared. 13-5
94 Rogue access points are also listed in the Interferer database (in the Access Point Details dialog box) for each access point that has identified the rogue access point, as shown in Figure Figure 13-6: Rogue access points display in the Access Point Details dialog box. As long as a rogue access point remains unauthorized, it continues to be treated as a rogue access point and the alerts continue. You can use the Network View screen (click on the Network tab) to determine which AirMaestro 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point in the network is receiving the strongest signal from the rogue access point. The AirMaestro access point with the strongest signal is typically the one closest to the rogue access point. You can also view the Interferer database for the 3100AG Virtual Controller Access Point to determine how strong the received signal strength is from the rogue access point, which can also help determine distance from the reporting access point. 13-6
PMS 138 C Moto Black spine width spine width 100% 100%
 Series MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. 2009 Motorola, Inc. Table of
Series MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the US Patent & Trademark Office. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners. 2009 Motorola, Inc. Table of
Oct 2007 Version 1.01
 Oct 2007 Version 1.01 Table of Contents Introduction...4 System Requirement...4 Getting Started...4 Installing the Smart WLAN Manager...5 Discovering the Switch and AP...9 Understanding the Screen Layout...12
Oct 2007 Version 1.01 Table of Contents Introduction...4 System Requirement...4 Getting Started...4 Installing the Smart WLAN Manager...5 Discovering the Switch and AP...9 Understanding the Screen Layout...12
Version /20/2012. User Manual. AP Manager II Lite Business Class Networking
 Version 1.0 12/20/2012 User Manual AP Manager II Lite Business Class Networking Table of Contents Table of Contents Product Overview... 1 Minimum System Requirements... 2 Access Point Requirements... 2
Version 1.0 12/20/2012 User Manual AP Manager II Lite Business Class Networking Table of Contents Table of Contents Product Overview... 1 Minimum System Requirements... 2 Access Point Requirements... 2
DWS-4000 Series DWL-3600AP DWL-6600AP
 Unified Wired & Wireless Access System Configuration Guide Product Model: Release 1.0 DWS-4000 Series DWL-8600AP DWL-6600AP DWL-3600AP Page 1 Table of Contents 1. Scenario 1 - Basic L2 Edge Setup: 1 Unified
Unified Wired & Wireless Access System Configuration Guide Product Model: Release 1.0 DWS-4000 Series DWL-8600AP DWL-6600AP DWL-3600AP Page 1 Table of Contents 1. Scenario 1 - Basic L2 Edge Setup: 1 Unified
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
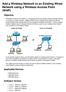 Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
Light Mesh AP. User s Guide. 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft
 Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
LevelOne. User Manual. WAP Mbps PoE Wireless AP V3.0.0
 LevelOne WAP-0005 108Mbps PoE Wireless AP User Manual V3.0.0 i TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 FIGURE 1: WIRELESS ACCESS POINT... 1 FEATURES OF YOUR WIRELESS ACCESS POINT... 1 Security Features...
LevelOne WAP-0005 108Mbps PoE Wireless AP User Manual V3.0.0 i TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 FIGURE 1: WIRELESS ACCESS POINT... 1 FEATURES OF YOUR WIRELESS ACCESS POINT... 1 Security Features...
Wireless N USB Adapter. User Guide
 Wireless N USB Adapter User Guide Part#: PL-18N Model: Hermes V. 0613 Contents Chapter 1 Getting Start...3 Chapter 2 Installation Guide...5 Installing the Drivers for Mac OS X...10 Uninstall the Drivers
Wireless N USB Adapter User Guide Part#: PL-18N Model: Hermes V. 0613 Contents Chapter 1 Getting Start...3 Chapter 2 Installation Guide...5 Installing the Drivers for Mac OS X...10 Uninstall the Drivers
802.11a g Dual Band Wireless Access Point. User s Manual
 802.11a+802.11g Dual Band Wireless Access Point User s Manual 0 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Feature Fully interoperable with IEEE 802.11b compliant products. High-Speed data transfer rate up to 11Mbps.
802.11a+802.11g Dual Band Wireless Access Point User s Manual 0 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Feature Fully interoperable with IEEE 802.11b compliant products. High-Speed data transfer rate up to 11Mbps.
Wireless-N USB Adapter User s Manual
 Wireless-N USB Adapter User s Manual Copyright 2007 EUSSO Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Table of Contents PREFACE... 3 WIRELESS LAN BASICS... 3 Warning... 3 INSTALLATION OVERVIEW... 4 INTRODUCTION...
Wireless-N USB Adapter User s Manual Copyright 2007 EUSSO Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Table of Contents PREFACE... 3 WIRELESS LAN BASICS... 3 Warning... 3 INSTALLATION OVERVIEW... 4 INTRODUCTION...
Wireless LAN USB Adaptor WL-2111 Quick Installation Guide V.1.0
 Wireless LAN USB Adaptor WL-2111 Quick Installation Guide V.1.0 Copyright Copyright 2001, All rights reserved. This manual and software described in it are copyrighted with all rights reserved. This manual
Wireless LAN USB Adaptor WL-2111 Quick Installation Guide V.1.0 Copyright Copyright 2001, All rights reserved. This manual and software described in it are copyrighted with all rights reserved. This manual
Copyright Statement. Disclaimer. Copyright 2016 IP-COM Networks Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
 Copyright Statement Copyright 2016 IP-COM Networks Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. IP-COM is the registered trademark of IP-COM Networks Co., Ltd. Other brand and product names mentioned herein are trademarks
Copyright Statement Copyright 2016 IP-COM Networks Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. IP-COM is the registered trademark of IP-COM Networks Co., Ltd. Other brand and product names mentioned herein are trademarks
Wireless USB Port Multi-Functional Printer Server. Model # AMPS240W. User s Manual. Ver. 1A
 Wireless USB 2.0 1-Port Multi-Functional Printer Server Model # AMPS240W User s Manual Ver. 1A Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 1.1 Package Contents... 3 1.2 System Requirements... 3 2 Multi-Functional
Wireless USB 2.0 1-Port Multi-Functional Printer Server Model # AMPS240W User s Manual Ver. 1A Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 1.1 Package Contents... 3 1.2 System Requirements... 3 2 Multi-Functional
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76xx Wi-Fi Access Points Master/Slave Architecture Guide
 Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76xx Wi-Fi Access Points Master/Slave Architecture Guide Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 4 DISCOVER AND PAIR GWN76XX ACCESS POINTS... 5 Discover GWN76xx... 5 Method 1: Discover
Grandstream Networks, Inc. GWN76xx Wi-Fi Access Points Master/Slave Architecture Guide Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 4 DISCOVER AND PAIR GWN76XX ACCESS POINTS... 5 Discover GWN76xx... 5 Method 1: Discover
Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID:
 69 Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID: WMM: Encryption: Select the SSID that the security settings will apply to. If Disabled, then the device will not be broadcasting the SSID. Therefore it will
69 Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID: WMM: Encryption: Select the SSID that the security settings will apply to. If Disabled, then the device will not be broadcasting the SSID. Therefore it will
EnGenius Quick Start Guide
 T he operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and the newer, faster 802.11g (2.4GHz, 54Mbpswireless standard. High output power and high sensitivity
T he operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and the newer, faster 802.11g (2.4GHz, 54Mbpswireless standard. High output power and high sensitivity
CUA-854 Wireless-G Long Range USB Adapter with Antenna. User s Guide
 CUA-854 Wireless-G Long Range USB Adapter with Antenna User s Guide Table of Contents Chapter 1. Introduction...5 1.1. About CUA-854...5 1.2. Key Features...5 1.3. Package Included...5 Chapter 2. Connect
CUA-854 Wireless-G Long Range USB Adapter with Antenna User s Guide Table of Contents Chapter 1. Introduction...5 1.1. About CUA-854...5 1.2. Key Features...5 1.3. Package Included...5 Chapter 2. Connect
Wireless-G Router User s Guide
 Wireless-G Router User s Guide 1 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction Installing Your Router System Requirements Installation Instructions Chapter 2: Preparing Your Network Preparing Your Network
Wireless-G Router User s Guide 1 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction Installing Your Router System Requirements Installation Instructions Chapter 2: Preparing Your Network Preparing Your Network
GHz g. Wireless A+G. User Guide. Notebook Adapter. Dual-Band. Dual-Band WPC55AG a. A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5 GHz 802.11a + GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Dual-Band Wireless A+G Notebook Adapter User Guide Model No. WPC55AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5 GHz 802.11a + GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Dual-Band Wireless A+G Notebook Adapter User Guide Model No. WPC55AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject
U S E R M A N U A L b/g PC CARD
 U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
Table of Contents. Page ii
 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Features... 1 Safety Instructions... 1 Package Contents... 2 Physical Details... 3 Chapter 2 Setup 5 Overview... 5 Using the Windows Wizard... 5 Chapter 3 Web-Based
Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction 1 Features... 1 Safety Instructions... 1 Package Contents... 2 Physical Details... 3 Chapter 2 Setup 5 Overview... 5 Using the Windows Wizard... 5 Chapter 3 Web-Based
WRE6606. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Dual-Band Wireless AC1300 Access Point. Default Login Details. Version 1.00 (ABDU.0) Edition 1, 10/2016
 WRE6606 Dual-Band Wireless AC1300 Access Point Version 1.00 (ABDU.0) Edition 1, 10/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details Web Address http://zyxelsetup http://dhcp-assigned IP www.zyxel.comhttp://192.168.1.2
WRE6606 Dual-Band Wireless AC1300 Access Point Version 1.00 (ABDU.0) Edition 1, 10/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details Web Address http://zyxelsetup http://dhcp-assigned IP www.zyxel.comhttp://192.168.1.2
Table of Contents. 1 Introduction. 2 Wireless Configurations. 3 Setting Up your LAN Administrator Station
 Table of Contents 1 Introduction About Avaya Wireless 1-1 About Avaya Wireless Tools 1-2 About Avaya Wireless Access Points 1-5 About This User s Guide 1-6 About Icons used in this Document 1-7 On-line
Table of Contents 1 Introduction About Avaya Wireless 1-1 About Avaya Wireless Tools 1-2 About Avaya Wireless Access Points 1-5 About This User s Guide 1-6 About Icons used in this Document 1-7 On-line
Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office
 Operating System Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office Microsoft Corporation Published: December 2004 Update: May 2005 Abstract Because small office/home
Operating System Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office Microsoft Corporation Published: December 2004 Update: May 2005 Abstract Because small office/home
802.11ac Wireless Access Point Model WAC104
 Point Model WAC104 User Manual October 2016 202-11698-01 350 E. Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You can visit www.netgear.com/support to register
Point Model WAC104 User Manual October 2016 202-11698-01 350 E. Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You can visit www.netgear.com/support to register
Wireless Presentation System User s Manual
 Téléchargé depuis www.lampe-videoprojecteur.info Wireless Presentation System User s Manual Version: 1.0 Date: 2008.1.11 User s Manual 1 Table of Contents 1. Overview... 3 2. First Setup of the Wireless
Téléchargé depuis www.lampe-videoprojecteur.info Wireless Presentation System User s Manual Version: 1.0 Date: 2008.1.11 User s Manual 1 Table of Contents 1. Overview... 3 2. First Setup of the Wireless
Wireless Access Point
 802.11g / 802.11b / WPA Wireless Access Point User's Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Features of your Wireless Access Point... 1 Package Contents... 4 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER
802.11g / 802.11b / WPA Wireless Access Point User's Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Features of your Wireless Access Point... 1 Package Contents... 4 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER
Quick Install & Troubleshooting Guide. WAP223NC Cloud Managed Wireless N Access Point
 Quick Install & Troubleshooting Guide WAP223NC Cloud Managed Wireless N Access Point Package Contents 1 x WAP223NC Indoor access point powered by CloudCommand 1 x wall and ceiling mounts 1 x 24V PoE power
Quick Install & Troubleshooting Guide WAP223NC Cloud Managed Wireless N Access Point Package Contents 1 x WAP223NC Indoor access point powered by CloudCommand 1 x wall and ceiling mounts 1 x 24V PoE power
Wireless Access Point
 802.11g / 802.11b / WPA Wireless Access Point User Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Features of your Wireless Access Point... 1 Package Contents... 4 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER 2
802.11g / 802.11b / WPA Wireless Access Point User Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Features of your Wireless Access Point... 1 Package Contents... 4 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER 2
WAP6405. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. 5GHz AC1750 Gigabit Wireless Bridge. Default Login Details. Version 1.00 Edition 1, 06/2016
 WAP6405 5GHz AC1750 Gigabit Wireless Bridge Version 1.00 Edition 1, 06/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 (AP Mode) http://192.168.1.5 (Repeater
WAP6405 5GHz AC1750 Gigabit Wireless Bridge Version 1.00 Edition 1, 06/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 (AP Mode) http://192.168.1.5 (Repeater
N150 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition. N300 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition
 N150 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D500 N300 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D1500 User Manual May 2018 202-11390-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support
N150 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D500 N300 WiFi DSL Modem Router Essentials Edition Model D1500 User Manual May 2018 202-11390-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support
NBG-416N. Wireless N-lite Home Router. Default Login Details. IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
 NBG-416N Wireless N-lite Home Router IMPORTANT! Default Login Details LAN IP https://192.168.1.1 Address User Name admin Password 1234 READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE. KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE. IMPORTANT!
NBG-416N Wireless N-lite Home Router IMPORTANT! Default Login Details LAN IP https://192.168.1.1 Address User Name admin Password 1234 READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE. KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE. IMPORTANT!
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Zonet Technology Inc. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright
Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Zonet Technology Inc. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright
Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration
 Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your WNR854T router. In planning your wireless network, you should consider the level of security required.
Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your WNR854T router. In planning your wireless network, you should consider the level of security required.
WRE6505 v2. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Wireless AC750 Range Extender. Default Login Details. Version 1.00 Edition 1, 10/2016
 WRE6505 v2 Wireless AC750 Range Extender Version 1.00 Edition 1, 10/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details Web Address http://zyxelsetup http://dhcp-assigned IP www.zyxel.comhttp://192.168.1.2
WRE6505 v2 Wireless AC750 Range Extender Version 1.00 Edition 1, 10/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details Web Address http://zyxelsetup http://dhcp-assigned IP www.zyxel.comhttp://192.168.1.2
USB Wireless Network Adapter User s Manual
 USB Wireless Network Adapter User s Manual Rev 0.9 Regulatory compliance FCC Warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15
USB Wireless Network Adapter User s Manual Rev 0.9 Regulatory compliance FCC Warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15
DCP585CW Windows Network Connection Repair Instructions
 Difficulty printing from your PC can occur for various reasons. The most common reason a networked Brother machine may stop printing, is because the connection between the computer and the Brother machine
Difficulty printing from your PC can occur for various reasons. The most common reason a networked Brother machine may stop printing, is because the connection between the computer and the Brother machine
IEEE g Wireless PC Card. User s Guide
 IEEE 802.11g Wireless PC Card User s Guide FCC Certifications Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
IEEE 802.11g Wireless PC Card User s Guide FCC Certifications Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
CWA-854HT 54 Mbps Wireless-G High Transmission Access Point User s Guide
 CWA-854HT 54 Mbps Wireless-G High Transmission Access Point User s Guide May 2006 Version 1.00 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 List of Figures... 4 List of Tables... 6 Chapter 1. Introduction...
CWA-854HT 54 Mbps Wireless-G High Transmission Access Point User s Guide May 2006 Version 1.00 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 List of Figures... 4 List of Tables... 6 Chapter 1. Introduction...
54Mbps Pocket Wireless Access Point (WL-330g)
 54Mbps Pocket Wireless Access Point (WL-330g) Copyright 2004 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved. Contents Conventions... 2 Welcome!... 3 Package contents... 3 System requirements... 3 Device installation...
54Mbps Pocket Wireless Access Point (WL-330g) Copyright 2004 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved. Contents Conventions... 2 Welcome!... 3 Package contents... 3 System requirements... 3 Device installation...
Quick Start Guide. System Release 1.0. Upgrade Notice Install Connectorized Radio Install Integrated Radio Power On Configure Units for Radio Link
 Quick Start Guide System Release 1.0 Upgrade Notice Install Connectorized Radio Install Integrated Radio Power On Configure Units for Radio Link SPECIAL SOFTWARE UPGRADE NOTICE Important! All users of
Quick Start Guide System Release 1.0 Upgrade Notice Install Connectorized Radio Install Integrated Radio Power On Configure Units for Radio Link SPECIAL SOFTWARE UPGRADE NOTICE Important! All users of
Figure 5-25: Setup Wizard s Safe Surfing Screen
 4. After the settings have been saved, the Safe Surfing screen will appear. Click the Norton Internet Security Suite button to install the special edition of Norton Internet Security on your computer,
4. After the settings have been saved, the Safe Surfing screen will appear. Click the Norton Internet Security Suite button to install the special edition of Norton Internet Security on your computer,
User Manual. WLAN USB Adapter for b/g/n
 User Manual WLAN USB Adapter for 802.11b/g/n Contents Chapter 1 Getting Start... 3 Minimum System Requirements...3 Optimize Wireless Performance...3 Installation...5 Uninstall...8 Chapter 2 Management
User Manual WLAN USB Adapter for 802.11b/g/n Contents Chapter 1 Getting Start... 3 Minimum System Requirements...3 Optimize Wireless Performance...3 Installation...5 Uninstall...8 Chapter 2 Management
AIRNET 54Mb b/g High Power USB Adapter. User s Manual
 AIRNET 54Mb 802.11b/g High Power USB Adapter User s Manual FCC Certifications Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
AIRNET 54Mb 802.11b/g High Power USB Adapter User s Manual FCC Certifications Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
airhaul Nexus sb3010
 u n w i r i n g o u r w o r l d TM airhaul Nexus sb3010 User Configuration Guide Version 1.3 Copyright smartbridges Pte Ltd. All Rights Reserved. About This Document This Software Configuration Guide is
u n w i r i n g o u r w o r l d TM airhaul Nexus sb3010 User Configuration Guide Version 1.3 Copyright smartbridges Pte Ltd. All Rights Reserved. About This Document This Software Configuration Guide is
HP Deskjet 6800 series
 HP Deskjet 6800 series Network Guide 網路指南 English English Edition 1 May 2004 Copyright 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Notice Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written
HP Deskjet 6800 series Network Guide 網路指南 English English Edition 1 May 2004 Copyright 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Notice Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without prior written
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Zonet Technology Inc. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright
Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Zonet Technology Inc. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright
Version /01/2013. User Manual. DAP-1665 Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access Point DAP-1665
 Version 1.0 10/01/2013 User Manual DAP-1665 Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access Point DAP-1665 Table of Contents Product Overview... 4 Package Contents... 4 System Requirements... 5 Introduction... 6 Features...
Version 1.0 10/01/2013 User Manual DAP-1665 Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access Point DAP-1665 Table of Contents Product Overview... 4 Package Contents... 4 System Requirements... 5 Introduction... 6 Features...
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band. Wireless A/G g a. User Guide. Game Adapter WIRELESS WGA54AG (EU/LA/UK) Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5GHz 2, 4GHz 802.11a 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless A/G Game Adapter User Guide Model No. WGA54AG (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5GHz 2, 4GHz 802.11a 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless A/G Game Adapter User Guide Model No. WGA54AG (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to
Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration
 Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration This chapter describes how to set up your NETGEAR Wireless-N Access Point WN802T v2 for wireless connectivity to your LAN. This basic configuration will enable
Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration This chapter describes how to set up your NETGEAR Wireless-N Access Point WN802T v2 for wireless connectivity to your LAN. This basic configuration will enable
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter with SRX 400. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54GX4. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SRX 400 User Guide Model No. WMP54GX4 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SRX 400 User Guide Model No. WMP54GX4 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
LevelOne User Manual WNC-0600USB N_One Wireless USB Adapter
 LevelOne User Manual WNC-0600USB N_One Wireless USB Adapter V2.0.0-0712 i Safety FCC WARNING This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
LevelOne User Manual WNC-0600USB N_One Wireless USB Adapter V2.0.0-0712 i Safety FCC WARNING This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
LocationFree Base Station LocationFree Player for PC
 2-681-469-11(1) LocationFree Base Station LocationFree Player for PC Operating Instructions LF-PK1 LF-B1 LFA-PC2 2006 Sony Corporation Contents What is the LocationFree Base Station?... 4 Identifying Parts
2-681-469-11(1) LocationFree Base Station LocationFree Player for PC Operating Instructions LF-PK1 LF-B1 LFA-PC2 2006 Sony Corporation Contents What is the LocationFree Base Station?... 4 Identifying Parts
7. Server Configuration Introduction Search for All Available MFP Server Status of MFP Server
 Copyright by Edimax Technology Co, LTD. all rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or computer
Copyright by Edimax Technology Co, LTD. all rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or computer
WAP3205 v2. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Wireless N300 Access Point. Default Login Details. Version 1.00 Edition 2, 12/2012
 WAP3205 v2 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.00 Edition 2, 12/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 Password 1234 www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL
WAP3205 v2 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.00 Edition 2, 12/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 Password 1234 www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL
User Guide. 450Mbps/300Mbps Wireless N Access Point TL-WA901ND/TL-WA801ND REV
 User Guide 450Mbps/300Mbps Wireless N Access Point TL-WA901ND/TL-WA801ND REV4.0.0 1910011930 Contents About This Guide...1 Chapter 1. Get to Know About Your Access Point.................... 2 1. 1. Product
User Guide 450Mbps/300Mbps Wireless N Access Point TL-WA901ND/TL-WA801ND REV4.0.0 1910011930 Contents About This Guide...1 Chapter 1. Get to Know About Your Access Point.................... 2 1. 1. Product
Configuration Guide for Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing
 Configuration Guide for Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing HUB INTERNET HOST CLIENTS Copyright 2002 Hughes Network Systems, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Hughes Electronics Corporation. All rights
Configuration Guide for Microsoft Internet Connection Sharing HUB INTERNET HOST CLIENTS Copyright 2002 Hughes Network Systems, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Hughes Electronics Corporation. All rights
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. USB Network Adapter. User Guide WIRELESS WUSB54G. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
CHAPTER 7 ADVANCED ADMINISTRATION PC
 ii Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Broadband ADSL Router Features... 1 Package Contents... 3 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION... 6 Requirements... 6 Procedure... 6 CHAPTER 3 SETUP...
ii Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Broadband ADSL Router Features... 1 Package Contents... 3 Physical Details... 4 CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION... 6 Requirements... 6 Procedure... 6 CHAPTER 3 SETUP...
802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter. User Manual
 802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter User Manual REGULATORY STATEMENTS FCC Certification The United States Federal Communication Commission (FCC) and the Canadian Department of Communications have established
802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter User Manual REGULATORY STATEMENTS FCC Certification The United States Federal Communication Commission (FCC) and the Canadian Department of Communications have established
WISNETWORKS. WisOS 11ac V /3/21. Software version WisOS 11ac
 WISNETWORKS User Manual V1.1 2016/3/21 Software version 1.0.0021 Table of contents 1. Setup& WMI... 3 1.1 Hardware Setup... 3 1.2 Web Management Interface... 3 2. Status... 4 2.1 Overview... 4 2.1.1 System...
WISNETWORKS User Manual V1.1 2016/3/21 Software version 1.0.0021 Table of contents 1. Setup& WMI... 3 1.1 Hardware Setup... 3 1.2 Web Management Interface... 3 2. Status... 4 2.1 Overview... 4 2.1.1 System...
Wireless LAN Access Point
 Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11b 11Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents... 2 1.2 Features... 2 1.3 Specifications... 2 1.4 Physical Description...
Wireless LAN Access Point IEEE 802.11b 11Mbps User s Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Package Contents... 2 1.2 Features... 2 1.3 Specifications... 2 1.4 Physical Description...
Figure 35: Active Directory Screen 6. Select the Group Policy tab, choose Default Domain Policy then click Edit.
 PC and Server Configuration Figure 35: Active Directory Screen 6. Select the Group Policy tab, choose Default Domain Policy then click Edit. Figure 36: Group Policy Tab 7. Select Computer Configuration
PC and Server Configuration Figure 35: Active Directory Screen 6. Select the Group Policy tab, choose Default Domain Policy then click Edit. Figure 36: Group Policy Tab 7. Select Computer Configuration
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. Access Point. User Guide WIRELESS. WAP54G ver Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G ver. 3.1 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G ver. 3.1 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
Wireless LAN Card. User s Manual. Contents. A i
 A i Contents Wireless LAN Card User s Manual The user guide is fit for both Long Range Wireless LAN Card WPC- 8110 and Wireless LAN Card WPC-2110 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 PACKAGE CONTENTS... 1
A i Contents Wireless LAN Card User s Manual The user guide is fit for both Long Range Wireless LAN Card WPC- 8110 and Wireless LAN Card WPC-2110 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 PACKAGE CONTENTS... 1
AWUS036NHR Long-Range Indoor IEEE n USB Adapter User Manual
 AWUS036NHR Long-Range Indoor IEEE 802.11n USB Adapter User Manual Alfa Network, Inc. Page 1 Table of Content Overview... 3 Unpacking information... 3 Introduction to the AWUS036NHR Indoor USB Adapter...
AWUS036NHR Long-Range Indoor IEEE 802.11n USB Adapter User Manual Alfa Network, Inc. Page 1 Table of Content Overview... 3 Unpacking information... 3 Introduction to the AWUS036NHR Indoor USB Adapter...
MODE COM WIRELESS NETWORK USB ADAPTER
 a p t e r U s e r U S B 2. 0 A d M a I E E E 8 n u 0 2. 1 1 b / a l MODE COM WIRELESS NETWORK USB ADAPTER g W i r e l e s s MC-105USB Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 1.1 Product Overview...4 1.2 Main
a p t e r U s e r U S B 2. 0 A d M a I E E E 8 n u 0 2. 1 1 b / a l MODE COM WIRELESS NETWORK USB ADAPTER g W i r e l e s s MC-105USB Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 1.1 Product Overview...4 1.2 Main
Configuring the network clients
 3 Configuring the network clients Accessing the wireless router Setting an IP address for wired or wireless clients To access the ASUS Wireless Router, you must have the correct TCP/IP settings on your
3 Configuring the network clients Accessing the wireless router Setting an IP address for wired or wireless clients To access the ASUS Wireless Router, you must have the correct TCP/IP settings on your
Access Connections 5.1 for Windows Vista: User Guide
 Access Connections 5.1 for Windows Vista: User Guide Access Connections 5.1 for Windows Vista: User Guide Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the general information in
Access Connections 5.1 for Windows Vista: User Guide Access Connections 5.1 for Windows Vista: User Guide Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the general information in
MSC-5100 Promotional Bundle Quickstart
 MSC-5100 Promotional Bundle Quickstart This Quickstart shows you how to install, configure, and use the MSC-5100 Promotional Bundle. For detailed configuration and operating information on the MSC-5100
MSC-5100 Promotional Bundle Quickstart This Quickstart shows you how to install, configure, and use the MSC-5100 Promotional Bundle. For detailed configuration and operating information on the MSC-5100
Installing driver over the network
 Installing driver over the network Command- line Definition Description Command- line Definition Description /a or /A /n or /N /nd or /ND Specifies
Installing driver over the network Command- line Definition Description Command- line Definition Description /a or /A /n or /N /nd or /ND Specifies
Content 1 OVERVIEW HARDWARE DESCRIPTION HARDWARE INSTALLATION PC CONFIGURATION GUIDE... 5 WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT GUIDE...
 Content 1 OVERVIEW...1 1.1FEATURES...1 1.2 PACKETCONTENTS...3 1.3 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 1.4 FACTORY DEFAULTS...4 1.5 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS...4 2 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION... 6 3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION...8 4
Content 1 OVERVIEW...1 1.1FEATURES...1 1.2 PACKETCONTENTS...3 1.3 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 1.4 FACTORY DEFAULTS...4 1.5 WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS...4 2 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION... 6 3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION...8 4
TEW-211BRP. Wireless AP Router. User s Manual
 TEW-211BRP Wireless AP Router User s Manual Version 1.4 - Jan 2002 CONTENTS Introduction...3 Hardware Installation...5 General Wireless AP Router System Connection...6 Wireless AP Router Default Settings
TEW-211BRP Wireless AP Router User s Manual Version 1.4 - Jan 2002 CONTENTS Introduction...3 Hardware Installation...5 General Wireless AP Router System Connection...6 Wireless AP Router Default Settings
Table of Contents. Chapter 1 Product Overview Features Package Contents LED Indicator and Panel Description...
 Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Monoprice. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright of the
Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Monoprice. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright of the
Hardware overview. Package contents V-M200, documentation, three antennas, and power supply.
 The HP V-M200 is a Wi-Fi Alliance authorized Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 802.11a/b/g and 802.11n product. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Logo is a certification mark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. In HP V-M200 802.11n Access Point Quickstart
The HP V-M200 is a Wi-Fi Alliance authorized Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 802.11a/b/g and 802.11n product. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Logo is a certification mark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. In HP V-M200 802.11n Access Point Quickstart
Notebook Adapter. Quick Installation Guide WPC300N (EU/LA) Package Contents
 Package Contents Wireless-N Notebook Adapter Setup Wizard CD-ROM User Guide (English only) on CD-ROM Quick Installation 24, GHz Wireless-N Notebook Adapter Wireless Model No. WPC300N (EU/LA) Quick Installation
Package Contents Wireless-N Notebook Adapter Setup Wizard CD-ROM User Guide (English only) on CD-ROM Quick Installation 24, GHz Wireless-N Notebook Adapter Wireless Model No. WPC300N (EU/LA) Quick Installation
WL5041 Router User Manual
 TECOM WL5041 Router User Manual TECOM CO., LTD. March 2003 2003 by TECOM CO., LTD. All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan Table of contents Package Contents--------------------------------------- 2 Installing
TECOM WL5041 Router User Manual TECOM CO., LTD. March 2003 2003 by TECOM CO., LTD. All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan Table of contents Package Contents--------------------------------------- 2 Installing
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. User Guide. Access Point WIRELESS. WAP54G v2. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G v2 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G v2 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2, g. Wireless-G. User Guide. Access Point WIRELESS WAP54G (EU/LA/UK) Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2,4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2,4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
WVL2 Wireless Vehicle Link 2 Installation and Setup Manual
 WVL2 Wireless Vehicle Link 2 Installation and Setup Manual Chapter 1: Introducing the Wireless Vehicle Link 2...1 WVL2 Components...2 Component Checklist...3 Product Specifications...4 System Requirements...5
WVL2 Wireless Vehicle Link 2 Installation and Setup Manual Chapter 1: Introducing the Wireless Vehicle Link 2...1 WVL2 Components...2 Component Checklist...3 Product Specifications...4 System Requirements...5
PePWave Mesh Connector User Manual
 PePWave Mesh Connector User Manual Document Rev. 1.0 Jun-07 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. Copyright 1999-2007 PePWave Ltd. All Rights Reserved. PePWave and
PePWave Mesh Connector User Manual Document Rev. 1.0 Jun-07 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. Copyright 1999-2007 PePWave Ltd. All Rights Reserved. PePWave and
APC-100. IEEE g Wireless USB Adapter. User s Guide v1.0
 APC-100 IEEE 802.11g Wireless USB Adapter User s Guide v1.0 FCC Certifications Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
APC-100 IEEE 802.11g Wireless USB Adapter User s Guide v1.0 FCC Certifications Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
Linksys EA-Series Routers
 Routers Table of Contents Table of Contents Product overview EA2700/EA3500 Back view Bottom view EA4500 Top view Back view Setting Up Your EA-Series Router Where to find more help How to set up your router
Routers Table of Contents Table of Contents Product overview EA2700/EA3500 Back view Bottom view EA4500 Top view Back view Setting Up Your EA-Series Router Where to find more help How to set up your router
LevelOne WBR User s Manual. 11g Wireless ADSL VPN Router. Ver
 LevelOne WBR-3407 11g Wireless ADSL VPN Router User s Manual Ver 1.00-0510 Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Wireless ADSL Router Features... 1 Package Contents... 5 Physical Details... 6 CHAPTER
LevelOne WBR-3407 11g Wireless ADSL VPN Router User s Manual Ver 1.00-0510 Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Wireless ADSL Router Features... 1 Package Contents... 5 Physical Details... 6 CHAPTER
XAVi Technologies Corporation Tel: Fax: F, No. 129, Hsing Te Road, Sanchung City, Taipei County 241, Taiwan
 XAVi Technologies Corporation Tel: +886-2-2995-7953 Fax: +886-2-29957954 9F, No. 129, Hsing Te Road, Sanchung City, Taipei County 241, Taiwan Copyright 2005, XAVi Technologies Corporation Information in
XAVi Technologies Corporation Tel: +886-2-2995-7953 Fax: +886-2-29957954 9F, No. 129, Hsing Te Road, Sanchung City, Taipei County 241, Taiwan Copyright 2005, XAVi Technologies Corporation Information in
3.1 Setting Up a Wireless Connection Using the WPS Button Manually Setting Up a Wireless Connection
 Contents 1 Product Overview... 1-1 1.1 Supported Features... 1-1 1.2 Ports and Buttons... 1-2 1.3 Indicators... 1-4 2 Hardware Installation... 2-1 2.1 Application Modes... 2-1 2.1.1 WiFi Router Mode...
Contents 1 Product Overview... 1-1 1.1 Supported Features... 1-1 1.2 Ports and Buttons... 1-2 1.3 Indicators... 1-4 2 Hardware Installation... 2-1 2.1 Application Modes... 2-1 2.1.1 WiFi Router Mode...
NM6000 User's guide v1.2
 USER S GUIDE NM6000 WLAN Clientt http://www.wiznet.co.kr Copyright 2004 WIZNET Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Table of Contents 1 INSTALLATION...3 1.1 POINTS TO REMEMBER BEFORE INSTALLATION...3 1.2 ACCESSING
USER S GUIDE NM6000 WLAN Clientt http://www.wiznet.co.kr Copyright 2004 WIZNET Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Table of Contents 1 INSTALLATION...3 1.1 POINTS TO REMEMBER BEFORE INSTALLATION...3 1.2 ACCESSING
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
AirCruiser G Wireless Router GN-BR01G
 AirCruiser G Wireless Router GN-BR01G User s Guide i Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 Overview...1 Features...1 Package Contents...2 AirCruiser G Wireless Router Rear Panel...2 AirCruiser G Wireless
AirCruiser G Wireless Router GN-BR01G User s Guide i Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 Overview...1 Features...1 Package Contents...2 AirCruiser G Wireless Router Rear Panel...2 AirCruiser G Wireless
11N Wireless USB Adapter User Guide
 -- 1 -- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
-- 1 -- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
NWD2705. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter. Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012
 NWD2705 Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL Communications Corporation IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE
NWD2705 Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL Communications Corporation IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE
User Guide. Omada Controller Software
 User Guide Omada Controller Software 1910012370 REV 2.6.0 March 2018 CONTENTS 1 Quick Start... 1 1.1 Determine the Network Topology...2 1.1.1 Management in the Same Subnet... 2 1.1.2 Management in Different
User Guide Omada Controller Software 1910012370 REV 2.6.0 March 2018 CONTENTS 1 Quick Start... 1 1.1 Determine the Network Topology...2 1.1.1 Management in the Same Subnet... 2 1.1.2 Management in Different
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit. Manual
 Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
User Guide. Pharos Control Software
 User Guide Pharos Control Software 1910012155 REV 2.0.1 April 2017 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd.
User Guide Pharos Control Software 1910012155 REV 2.0.1 April 2017 COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS Specifications are subject to change without notice. is a registered trademark of TP-Link Technologies Co., Ltd.
User Manual DIR-850L. Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Gigabit Router.
 User Manual DIR-850L Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Gigabit Router USER MANUAL: DIR-850L Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Gigabit Router SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Network Requirements Web-based Configuration Utility Requirements
User Manual DIR-850L Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Gigabit Router USER MANUAL: DIR-850L Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Gigabit Router SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS Network Requirements Web-based Configuration Utility Requirements
Windows Vista Installation Guide
 MFC-8870DW Windows Vista Installation Guide Before you can use the machine, you must set up the hardware and install the driver. Please read the Quick Setup Guide and this Windows Vista Installation Guide
MFC-8870DW Windows Vista Installation Guide Before you can use the machine, you must set up the hardware and install the driver. Please read the Quick Setup Guide and this Windows Vista Installation Guide
The MSM335 is a Wi-Fi Alliance authorized Wi-Fi CERTIFIED product. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Logo is a certification mark of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
 The MSM335 is a Wi-Fi Alliance authorized Wi-Fi CERTIFIED product. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Logo is a certification mark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. In MSM335 Access Point Quickstart This Quickstart shows you how
The MSM335 is a Wi-Fi Alliance authorized Wi-Fi CERTIFIED product. The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED Logo is a certification mark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. In MSM335 Access Point Quickstart This Quickstart shows you how
Outdoor Wireless USB Adapter User Guide
 Outdoor Wireless USB Adapter User Guide FCC STATEMENT This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
Outdoor Wireless USB Adapter User Guide FCC STATEMENT This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
WLAN a+b+g mini-pci Module
 WLAN a+b+g mini-pci Module User Manual Model: EM-500AG Version: 1.0 Feb 2003 Copyright Statement No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form
WLAN a+b+g mini-pci Module User Manual Model: EM-500AG Version: 1.0 Feb 2003 Copyright Statement No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form
Wireless a CPE User Manual
 NOTICE Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the user's authority to operate the equipment. Company has an on-going policy
NOTICE Changes or modifications to the equipment, which are not approved by the party responsible for compliance, could affect the user's authority to operate the equipment. Company has an on-going policy
