Outline. Overview Label Encapsulations Label Distribution Protocols Constraint Based Routing with CR-LDP Summary
|
|
|
- Laura Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MPLS
2 Outline Overview Label Encapsulations Label Distribution Protocols Constraint Based Routing with CR-LDP Summary
3 What Is MPLS? A switched fowarding technique based on IP Delivers explicit, switched forwarding to IP-based internetworks IETF Goals Higher performance Routing table efficiency Frame/Cell integration DiffServ "New" Goals Traffic engineering DiffServ
4 Goals of Multiprotocol Label Switching MPLS extends traditional IP in the following areas: Simplified Forwarding Based on labels instead of longest prefix-match Efficient Explicit Routing Route is specified once by source at path setup time Traffic Engineering Split traffic load over multiple parallel or alternate routes QoS Routing Select routes based upon QoS requirements Non-trivial Mappings of IP Datagrams onto Paths Performed only at network edges/borders
5 BEST OF BOTH WORLDS PACKET Forwarding HYBRID CIRCUIT SWITCHING IP MPLS +IP ATM MPLS + IP form a middle ground that combines the best of IP and the best of circuit switching technologies. ATM and Frame Relay cannot easily come to the middle so IP has!!
6 MPLS Terminology The Easy Stuff Label Label Switch Router Label Switch Path Label Information Base Forwarding Equivalence Class The Harder Stuff Label Distribution Protocol Constraint-Based LDP (CR-LDP) RSVP for Traffic Engineering (RSVP-TE)
7 Label Encapsulation L2 Label ATM FR Ethernet PPP VPI VCI DLCI Shim Label Shim Label. IP PAYLOAD MPLS Encapsulation is specified over various media types. Top labels may use existing format, lower label(s) use a new shim label format.
8 Label Structure MPLS "shim" headers Layer 2 Header... IP Packet Label Exp. S TTL 4 Octets Label: 20-bit value, (0-16 reserved) Exp.: 3-bits Experimental (former ToS) S: 1-bit Bottom of stack TTL: 8-bits Time To Live
9 Label Substitution Have a friend go to B ahead of you using one of the previous two techniques. At every road they reserve a lane just for you. At ever intersection they post a big sign that says for a given lane which way to turn and what new lane to take. LANE#1 LANE#1 TURN RIGHT USE LANE#2 LANE#2
10 ROUTE AT EDGE, SWITCH IN CORE IP IP #L1 IP #L2 IP #L3 IP IP Forwarding LABEL SWITCHING IP Forwarding
11 Label Edge Routers Label Edge Router (LER) 47.3 IP A tunnel (LSP) endpoint Ingress Egress Push and Pop LER 1 10 MB 40 MB LER IP
12 Label Switch Router Label Switch Router (LSR) A tunnel transit point active LSR LSR IP IP LSR LSR
13 Label Switch Path The path followed by packets that have the same label! IP Source Network IP Destination Network The Internet
14 Label Information Base (LIB) The LSR routing table where a label ID is associated with an outbound port IP Source Network IP Destination Network Label (In) Label (Out) O/P Port Ser_1 Ser_2 The Internet
15 Forwarding Equivalence Classes LER LSR LSR LER LSP IP1 IP1 #L1 IP1 #L2 IP1 #L3 IP1 IP2 IP2 #L1 IP2 #L2 IP2 #L3 IP2 Packets are destined for different address prefixes, but can be mapped to common path FEC = A subset of packets that are all treated the same way by a router The concept of FECs provides for a great deal of flexibility and scalability In conventional routing, a packet is assigned to a FEC at each hop (i.e. L3 look-up), in MPLS it is only done once at the network ingress.
16 MPLS Routing Protocols OSPF BGP ISIS By jove! These look familiar!
17 Routing Protocols Required for topology determination Existing Routing Protocols Can Be Used With MPLS But they do not support ER/TE
18 MPLS: Partitioning Routing and Forwarding Routing OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, RIP Forwarding MPLS Forwarding Table Based on: Classful Addr. Prefix? Classless Addr. Prefix? Multicast Addr.? Port No.? ToS Field? Based on: Exact Match on Fixed Length Label Current network has multiple forwarding paradigms - class-ful longest prefix match (Class A,B,C boundaries) - classless longest prefix match (variable boundaries) - multicast (exact match on source and destination) - type-of-service (longest prefix. match on addr. + exact match on ToS) As new routing methods change, new route look-up algorithms are required - introduction of CIDR Next generation routers will be based on hardware for route look-up - changes will require new hardware with new algorithm MPLS has a consistent algorithm for all types of forwarding; partitions routing/fwding - minimizes impact of the introduction of new forwarding methods MPLS introduces flexibility through consistent forwarding paradigm
19 Routing & Label Distribution Label Assignment Control-Driven Topology-Driven Request-Driven Traffic Driven
20 Label Distribution Options Manual LIB Entries Analogous To Static Routes Will Not Scale May Be Used In Early Interoperability Tests and Trade Show Demos Label Distribution Protocols "A set of procedures by which one Label Switched Router (LSR) informs another of the label/fec bindings it has made"
21 Scenario C.3 IP Source Network 1.1 Router1 2.1 LSR LSR3 3.2 A.1 Router2 B.2 C.1 IP Destination Network LSR1 LSR4 LSR6 A.2 LSR5 B.1 MPLS Domain
22 Now Let's Fill The LIBs Routing Table or LIB Inbound Label Outbound Label Dest. Net Next Hop I/F ID Router 1 None None C Ser_1 LSR 1 None 12* C.0 N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR 5 8 None** C.0 B.2 Ser_4 Router 2 C.0 C.0 C.0 Direct Eth_4 * Label appended ** Label stripped N/A = This field not parsed
23 Now Let's Fill The LIBs Routing Table or LIB Inbound Label Outbound Label Dest. Net Next Hop I/F ID Router 1 None None C Ser_1 LSR 1 None 12* C.0 N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR 5 8 None** C.0 B.2 Ser_4 Router 2 C.0 C.0 C.0 Direct Eth_4 * Label appended ** Label stripped N/A = This field not parsed
24 Now Let's Fill The LIBs Routing Table or LIB Inbound Label Outbound Label Dest. Net Next Hop I/F ID Router 1 None None C Ser_1 LSR 1 None 12* C.0 N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR 5 8 None** C.0 B.2 Ser_4 Router 2 C.0 C.0 C.0 Direct Eth_4 * Label appended ** Label stripped N/A = This field not parsed
25 Now Let's Fill The LIBs Routing Table or LIB Inbound Label Outbound Label Dest. Net Next Hop I/F ID Router 1 None None C Ser_1 LSR 1 None 12* C.0 N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR 5 8 None** C.0 B.2 Ser_4 Router 2 C.0 C.0 C.0 Direct Eth_4 * Label appended ** Label stripped N/A = This field not parsed
26 Now Let's Fill The LIBs Routing Table or LIB Inbound Label Outbound Label Dest. Net Next Hop I/F ID Router 1 None None C Ser_1 LSR 1 None 12* C.0 N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR 5 8 None** C.0 B.2 Ser_4 Router 2 C.0 C.0 C.0 Direct Eth_4 * Label appended ** Label stripped N/A = This field not parsed
27 Now Let's Fill The LIBs Routing Table or LIB Inbound Label Outbound Label Dest. Net Next Hop I/F ID Router 1 None None C Ser_1 LSR 1 None 12* C.0 N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR N/A N/A Ser_2 LSR 5 8 None** C.0 B.2 Ser_4 Router 2 C.0 C.0 C.0 Direct Eth_4 * Label appended ** Label stripped N/A = This field not parsed
28 Label Distribution Protocols LDP Why have one when two can be even more confusing? RSVP Label Distribution Protocol "A set of procedures by which one Label Switched Router (LSR) informs another of the label/fec bindings it has made" draft-ietf-mpls-arch-05.txt
29 Label Distribution Protocols LDP, RSVP Maps unicast IP destinations into labels RSVP-TE, CR-LDP Used for Traffic Engineering and Resource Reservation PIM BGP For multicast group-to-label mapping For "extra" external label mapping
30 Upstream vs Downstream LSR1 Downstream Router Upstream LSR6 Router Request LSR2 LSR3 LSR1 LSR4 LSR6 LSR5 MPLS Domain
31 Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) Label distribution ensures that adjacent routers have a common view of FEC <-> label bindings Routing Table: Addr-prefix Next Hop /8 LSR2 Routing Table: Addr-prefix Next Hop /8 LSR3 LSR1 LSR2 LSR3 IP Packet Label Information Base: Label-In FEC Label-Out XX /8 17 For /8 use label 17 Label Information Base: Label-In FEC Label-Out /8 XX Step 3: LSR inserts label value into forwarding base Step 2: LSR communicates binding to adjacent LSR Step 1: LSR creates binding between FEC and label value Common understanding of which FEC the label is referring to! Label distribution can either piggyback on top of an existing routing protocol, or a dedicated label distribution protocol (LDP) can be created.
32 Label Distribution - Methods Label Distribution can take place using one of two possible methods Downstream Unsolicited Label Distribution Downstream-on-Demand Label Distribution LSR1 LSR2 LSR1 LSR2 Label-FEC Binding LSR2 and LSR1 are said to have an LDP adjacency (LSR2 being the downstream LSR) LSR2 discovers a next hop for a particular FEC LSR2 generates a label for the FEC and communicates the binding to LSR1 LSR1 inserts the binding into its forwarding tables If LSR2 is the next hop for the FEC, LSR1 can use that label knowing that its meaning is understood Request for Binding Label-FEC Binding LSR1 recognizes LSR2 as its next-hop for an FEC A request is made to LSR2 for a binding between the FEC and a label If LSR2 recognizes the FEC and has a next hop for it, it creates a binding and replies to LSR1 Both LSRs then have a common understanding Both methods are supported, even in the same network at the same time For any single adjacency, LDP negotiation must agree on a common method
33 Downstream On Demand ordered Ingress requests label from egress Ingress LSR 1 Label Request LSR 6 Egress Upstream Label Assign Downstream Data Flow
34 Distribution Control: Ordered v. Independent MPLS path forms as associations are made between FEC next-hops and incoming and outgoing labels Incoming Label Next Hop (for FEC) Outgoing Label Definition Independent LSP Control Each LSR makes independent decision on when to generate labels and communicate them to upstream peers Communicate label-fec binding to peers once next-hop has been recognized LSP is formed as incoming and outgoing labels are spliced together Ordered LSP Control Label-FEC binding is communicated to peers if: - LSR is the egress LSR to particular FEC - label binding has been received from downstream LSR LSP formation flows from egress to ingress Comparison Labels can be exchanged with less delay Does not depend on availability of egress node Granularity may not be consistent across the nodes at the start May require separate loop detection/mitigation method Requires more delay before packets can be forwarded along the LSP Depends on availability of egress node Mechanism for consistent granularity and freedom from loops Used for explicit routing and multicast Both methods are supported in the standard and can be fully interoperable
35 INDEPENDENT MODE #216 D #14 #99 #963 #311 #311 #311 #963 D #612 D #5 D #14 D D #99 D #311 D #462
36 Label Retention Methods An LSR may receive label bindings from multiple LSRs LSR1 Binding for LSR5 LSR2 LSR5 Some bindings may come from LSRs that are not the valid next-hop for that FEC Binding for LSR5 Binding for LSR5 LSR4 LSR3 Liberal Label Retention Label Bindings for LSR5 LSR4 s Label LSR3 s Label LSR2 s Label LSR1 Valid Next Hop LSR2 LSR3 LSR4 LSR maintains bindings received from LSRs other than the valid next hop If the next-hop changes, it may begin using these bindings immediately May allow more rapid adaptation to routing changes Requires an LSR to maintain many more labels Conservative Label Retention Label Bindings for LSR5 LSR4 s Label LSR3 s Label LSR2 s Label LSR1 Valid Next Hop LSR2 LSR only maintains bindings received from valid next hop If the next-hop changes, binding must be requested from new next hop Restricts adaptation to changes in routing Fewer labels must be maintained by LSR LSR3 LSR4 Label Retention method trades off between label capacity and speed of adaptation to routing changes
37 LIBERAL RETENTION MODE #216 D D #422 These labels are kept in case they are needed after a failure. #963 D #622 D #612 D #5 D #14 D D #99 D #311 D #462
38 CONSERVATIVE RETENTION MODE #216 D D #422 These labels are released the moment they are received. #612 D #5 D #963 D #14 D D #99 #622 D D #311 D #462
39 IP FOLLOWS A TREE TO DESTINATION Dest=a.b.c.d Dest=a.b.c.d Dest=a.b.c.d - IP will over-utilize best paths and under-utilize less good paths.
40 HOP-BY-HOP(A.K.A Vanilla) LDP #216 #612 #5 #14 #99 #963 #311 #462 - Ultra fast, simple forwarding a.k.a switching - Follows same route as normal IP datapath - So like IP, LDP will over-utilize best paths and under-utilize less good paths.
41 IP FORWARDING USED BY HOP-BY-HOP CONTROL 47.3 IP Dest Out Dest Out IP IP Dest Out IP
42 MPLS Label Distribution Intf Label Dest Intf Label In In Out Out Intf Label Dest Intf In In Out Request: 47.1 Intf Dest Intf Label In Out Out Mapping:
43 Label Switched Path (LSP) Intf Label Dest Intf Label In In Out Out Intf Label Dest Intf In In Out Intf Dest Intf Label In Out Out IP IP
44 Traffic Engineering B C Demand A D Traffic engineering is the process of mapping traffic demand onto a network Network Topology Purpose of traffic engineering: Maximize utilization of links and nodes throughout the network Engineer links to achieve required delay, grade-of-service Spread the network traffic across network links, minimize impact of single failure Ensure available spare link capacity for re-routing traffic on failure Meet policy requirements imposed by the network operator Traffic engineering key to optimizing cost/performance
45 Traffic Engineering Using Explicit Routing Based On ATM PNNI Experience Explicit Routing allows Traffic Flows to be mapped onto specific paths LDP CR-LDP Label Distribution ER / TE RSVP RSVP-TE
46 CR-LDP CR = Constraint based Routing eg: USE: (links with sufficient resources AND (links of type somecolor ) AND (links that have delay less than 200 ms) & & =
47 Hop-by-Hop vs. Explicit Routing Hop-by-Hop Routing Explicit Routing Distributes routing of control traffic Builds a set of trees either fragment by fragment like a random fill, or backwards, or forwards in organized manner. Reroute on failure impacted by convergence time of routing protocol Existing routing protocols are destination prefix based Difficult to perform traffic engineering, QoS-based routing Source routing of control traffic Builds a path from source to dest Requires manual provisioning, or automated creation mechanisms. LSPs can be ranked so some reroute very quickly and/or backup paths may be pre-provisioned for rapid restoration Operator has routing flexibility (policybased, QoS-based, Adapts well to traffic engineering Explicit routing shows great promise for traffic engineering
48 EXPLICITLY ROUTED OR ER-LSP Route= {A,B,C} #216 B #14 #972 A #14 #972 C #462 - ER-LSP follows route that source chooses. In other words, the control message to establish the LSP (label request) is source routed.
49 Explicit Routing - MPLS vs. IP Source Routing Connectionless nature of IP implies that routing is based on information in each packet header. Source routing is possible, but path must be contained in each IP header. Lengthy paths increase size of IP header, make it variable size, increase overhead. Some gigabit routers require slow path option-based routing of IP packets. Source routing has not been widely adopted in IP and is seen as impractical. Some network operators may filter source routed packets for security reasons. MPLS enables the use of source routing by its connection-oriented capabilities. - paths can be explicitly set up through the network - the label can now represent the explicitly routed path Loose and strict source routing can be supported.
50 EXPLICITLY ROUTED LSP ER-LSP Intf In Dest Intf Out Label Out IP Intf Label Dest Intf Label In In Out Out Intf Label Dest Intf In In Out IP
51 ER LSP - advantages Operator has routing flexibility (policy-based, QoSbased) Can use routes other than shortest path Can compute routes based on constraints in exactly the same manner as ATM based on distributed topology database. (traffic engineering)
52 ER LSP - discord! Two signaling options proposed in the standards: CR-LDP, RSVP extensions: CR-LDP = LDP + Explicit Route RSVP ext = Traditional RSVP + Explicit Route + Scalability Extension ITU has decided on LDP/CR-LDP for public networks. Survival of the fittest not such a bad thing although RSVP has lots of work in scalability to do.
53 Constraint-based LSP Setup using LDP Uses LDP Messages (request, map, notify) Shares TCP/IP connection with LDP Can coexist with vanilla LDP and inter-work with it, or can exist as an entity on its own Introduces additional data to the vanilla LDP messages to signal ER, and other Constraints
54 ER-LSP Setup using CR-LDP 6. When LER A receives label mapping, the ER established. LER A 1. Label Request message. It contains ER path < B,C,D> 2. Request message processed and next node determined. Path list modified to <C,D> 5. LSR C receives label to use for sending data to 4. Label mapping LER D. Label table message updated originates. LSR B LSR C LER D 3. Request message terminates. Ingress ER Label Switched Path Egress
55 LDP/CR-LDP INTERWORKING #216 INSERT ER{A,B,C} #99 #14 A #311 B C #612 #462 #5 LDP CR-LDP - It is possible to take a vanilla LDP label request let it flow vanilla to the edge of the core, insert an ER hop list at the core boundary at which point it is CR-LDP to the far side of the core.
56 Basic LDP Message additions LSPID: A unique tunnel identifier within an MPLS network. ER: An explicit route, normally a list of IPV4 addresses to follow (source route) the label request message. Resource Class (Color): to constrain the route to only links of this Color. Basically a 32 bit mask used for constraint based computations. Traffic Parameters: similar to ATM call setup, which specify treatment and reserve resources.
57 CR-LDP Traffic Parameters Flags control negotiability of parameters U F Flags Traf. Param. TLV Frequency Reserved Peak Data Rate (PDR) Peak Burst Size (PBS) Length Committed Data Rate (CDR) Committed Burst Size (CBS) Excess Burst Size (EBS) Weight 32 bit fields are short IEEE floating point numbers Any parameter may be used or not used by selecting appropriate values Frequency constrains the variable delay that may be introduced Weight of the CRLSP in the relative share Peak rate (PDR+PBS) maximum rate at which traffic should be sent to the CRLSP Committed rate (CDR+CBS) the rate that the MPLS domain commits to be available to the CRLSP Excess Burst Size (EBS) to measure the extent by which the traffic sent on a CRLSP exceeds the committed rate
58 CRLSP characteristics The approach is like diff-serv s separation of PHB from Edge The parameters describe the path behavior of the CRLSP, i.e. the CRLSP s characteristics Dropping behavior is not signaled Dropping may be controlled by DS packet markings CRLSP characteristics may be combined with edge functions (which are undefined in CRLDP) to create services Edge functions can perform packet marking Example services are in an appendix
59 Peak rate The maximum rate at which traffic should be sent to the CRLSP Defined by a token bucket with parameters Peak data rate (PDR) Peak burst size (PBS) Useful for resource allocation If a network uses the peak rate for resource allocation then its edge function should regulate the peak rate May be unused by setting PDR or PBS or both to positive infinity
60 Committed rate The rate that the MPLS domain commits to be available to the CRLSP Defined by a token bucket with parameters Committed data rate (CDR) Committed burst size (CBS) Committed rate is the bandwidth that should be reserved for the CRLSP CDR = 0 makes sense; CDR = + less so CBS describes the burstiness with which traffic may be sent to the CRLSP
61 Excess burst size Measure the extent by which the traffic sent on a CRLSP exceeds the committed rate Defined as an additional limit on the committed rate s token bucket Can be useful for resource reservation If a network uses the excess burst size for resource allocation then its edge function should regulate the parameter and perhaps mark or drop packets EBS = 0 and EBS = + both make sense
62 Frequency Specifies how frequently the committed rate should be given to CRLSP Defined in terms of granularity of allocation of rate Constrains the variable delay that the network may introduce Constrains the amount of buffering that a LSR may use Values: Very frequently: no more than one packet may be buffered Frequently: only a few packets may be buffered Unspecified: any amount of buffering is acceptable
63 Weight Specifies the CRLSP s weight in the relative share algorithm Implied but not stated: CRLSPs with a larger weight get a bigger relative share of the excess bandwidth Values: 0 the weight is not specified weights; larger numbers are larger weights The definition of relative share is network specific
64 Negotiation flags Res F6 F5 F4 F3 F2 F1 Weight Negotiation Flag EBS Negotiation Flag CBS Negotiation Flag CDR Negotiation Flag PBS Negotiation Flag PDR Negotiation Flag If a parameter is flagged as negotiable then LSRs may replace the parameter value with a smaller value in the label request message. LSRs discover the negotiated values in the label mapping message. Label request - possible downward negotiation Label mapping - no negotiation
65 CR-LDP PREEMPTION A CR-LSP carries an LSP priority. This priority can be used to allow new LSPs to bump existing LSPs of lower priority in order to steal their resources. This is especially useful during times of failure and allows you to rank the LSPs such that the most important obtain resources before less important LSPs. These are called the setuppriority and a holdingpriority and 8 levels are provided.
66 CR-LDP PREEMPTION When an LSP is established its setuppriority is compared with the holdingpriority of existing LSPs, any with lower holdingpriority may be bumped to obtain their resources. This process may continue in a domino fashion until the lowest holdingpriority LSPs either clear or are on the worst routes.
67 PREEMPTION A.K.A. BUMPING Route= {A,B,C} #216 A B #14 #972 C #462
68 ER-LSP setup using RSVP 5. When LER A receives Resv, the ER established. 1. Path message. It contains ER path < B,C,D> 2. New path state. Path message sent to next node 4. New reservation state. Resv message propagated upstream 3. Resv message originates. Contain the label to use and the required traffic/qos para. Per-hop Path and Resv refresh unless suppressed LER A LSR B LSR C LER D Per-hop Path and Resv refresh unless suppressed Per-hop Path and Resv refresh unless suppressed
69 THE BASIC DIFFERENCE: RSVP REFRESHES CONTINUALLY!! RSVP LDP/CR-LDP NODE A NODE B NODE A NODE B TIME PATH RESV PATH RESV PATH RESV PATH RESV PATH RESV FOREVER!! REQUEST MAPPING THAT S ALL!!
70 Summary of Motivations for MPLS Simplified forwarding based on exact match of fixed length label - initial drive for MPLS was based on existence of cheap, fast ATM switches Separation of routing and forwarding in IP networks - facilitates evolution of routing techniques by fixing the forwarding method - new routing functionality can be deployed without changing the forwarding techniques of every router in the Internet Facilitates the integration of ATM and IP - allows carriers to leverage their large investment of ATM equipment - eliminates the adjacency problem of VC-mesh over ATM Enables the use of explicit routing/source routing in IP networks - can be easily used for such things as traffic management, QoS routing Promotes the partitioning of functionality within the network - move granular processing of packets to edge; restrict core to packet forwarding - assists in maintaining scalability of IP protocols in large networks Improved routing scalability through stacking of labels - removes the need for full routing tables from interior routers in transit domain; only routes to border routers are required Applicability to both cell and packet link-layers - can be deployed on both cell (eg. ATM) and packet (eg. FR, Ethernet) media - common management and techniques simplifies engineering
71 PROBABLY THE ONLY OPTION FOR ROUTING AT LIGHT SPEEDS Optical Label Switch l Routing Control l 1 l 2 l n Fabric l 1 l 2 l n l 1 l 2 l n l 1 l 2 l 1 l 2 l n When we get to true frequency to frequency switching there is no way to route and LDP will be required to setup OSPF routes. CR-LDP will be required to engineer. l is just another label to distribute. No new protocols required.
72 Where Would We Deploy MPLS? In The Core of the Internet Alternative to S-PVC mesh over ATM Enables DiffServ implementation In Metropolitan Networks Mechanism for VPN deployment In Large Enterprises Not totally clear about value/complexity trade-off
73 Summary MPLS is an exciting promising emerging technology. Basic functionality (Encapsulation and basic Label Distribution) has been defined by the IETF. Traffic engineering based on MPLS/CR- LDP is just round the corner. MPLS/LDP/CR-LDP have been recommended by the ITU for IP transport on ATM in public networks. Convergence is one step closer...
NANOG. MPLS Tutorial and Operational Experiences. Bilel Jamoussi, October, 1999
 MPLS Tutorial and Operational Experiences Peter Ashwood-Smith, Bilel Jamoussi, October, 1999 Tutorial Outline Overview Label Encapsulations Label Distribution Protocols MPLS & ATM Constraint Based Routing
MPLS Tutorial and Operational Experiences Peter Ashwood-Smith, Bilel Jamoussi, October, 1999 Tutorial Outline Overview Label Encapsulations Label Distribution Protocols MPLS & ATM Constraint Based Routing
MultiProtocol Label Switching - MPLS ( RFC 3031 )
 Outline MultiProtocol Label Switching - MPLS ( RFC 3031 ) 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? 2. What MPLS is used for? 3. Label Distribution Protocols 1 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? MPLS is
Outline MultiProtocol Label Switching - MPLS ( RFC 3031 ) 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? 2. What MPLS is used for? 3. Label Distribution Protocols 1 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? MPLS is
MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching)
 Fixed Internetworking Protocols and Networks MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) Rune Hylsberg Jacobsen Aarhus School of Engineering rhj@iha.dk 1 2011 ITIFN Circuit switching Dedicated communication
Fixed Internetworking Protocols and Networks MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) Rune Hylsberg Jacobsen Aarhus School of Engineering rhj@iha.dk 1 2011 ITIFN Circuit switching Dedicated communication
Internet Routing - MPLS. By Richard Harris
 Internet Routing - MPLS By Richard Harris MPLS Presentation Outline Introduction Problems of Internet size Methods for overcoming potential problems What is MPLS? Overview MPLS terminology MPLS Architecture
Internet Routing - MPLS By Richard Harris MPLS Presentation Outline Introduction Problems of Internet size Methods for overcoming potential problems What is MPLS? Overview MPLS terminology MPLS Architecture
A Comparison Of MPLS Traffic Engineering Initiatives. Robert Pulley & Peter Christensen
 A Comparison Of MPLS Traffic Engineering Initiatives Robert Pulley & Peter Christensen Need for MPLS Problems in today's network QoS and CoS requirements Need for Resource Reservation Why not RSVP MPLS
A Comparison Of MPLS Traffic Engineering Initiatives Robert Pulley & Peter Christensen Need for MPLS Problems in today's network QoS and CoS requirements Need for Resource Reservation Why not RSVP MPLS
Telematics Chapter 7: MPLS
 Telematics Chapter 7: MPLS User watching video clip Beispielbild Application Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Server with video clips Application Layer Presentation Layer Session
Telematics Chapter 7: MPLS User watching video clip Beispielbild Application Layer Presentation Layer Session Layer Transport Layer Server with video clips Application Layer Presentation Layer Session
Overview. Hop-by-hop or source routing to establish labels Uses label native to the media Multi level label substitution transport.
 Tutorial line Tutorial Overview Encapsulations istribution Protocols & Constraint Based Routing with CR-LP Summary Substitution what is it? One of the many ways of getting from A to B: BROACAST: Go everywhere,
Tutorial line Tutorial Overview Encapsulations istribution Protocols & Constraint Based Routing with CR-LP Summary Substitution what is it? One of the many ways of getting from A to B: BROACAST: Go everywhere,
Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia. Guy Leduc. Chapter 2 MPLS networks. Chapter 2: MPLS
 Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia Guy Leduc Chapter 2 MPLS networks Chapter based on Section 5.5 of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
Computer Network Architectures and Multimedia Guy Leduc Chapter 2 MPLS networks Chapter based on Section 5.5 of Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley,
Multi Protocol Label Switching (an introduction) Karst Koymans. Thursday, March 12, 2015
 .. MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 4.3, 2015/03/09 13:07:57) Thursday, March 12, 2015 Karst Koymans (UvA) MPLS
.. MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 4.3, 2015/03/09 13:07:57) Thursday, March 12, 2015 Karst Koymans (UvA) MPLS
سوي يچينگ و مسيريابي در شبكه
 سوي يچينگ و مسيريابي در شبكه دكتر فرهاد فغاني استاديار دانشكده مهندسي برق قسمت ششم : Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) 1 One of the many ways of getting from A to B: BROADCAST: Go everywhere, stop
سوي يچينگ و مسيريابي در شبكه دكتر فرهاد فغاني استاديار دانشكده مهندسي برق قسمت ششم : Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) 1 One of the many ways of getting from A to B: BROADCAST: Go everywhere, stop
MPLS MULTI PROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING OVERVIEW OF MPLS, A TECHNOLOGY THAT COMBINES LAYER 3 ROUTING WITH LAYER 2 SWITCHING FOR OPTIMIZED NETWORK USAGE
 MPLS Multiprotocol MPLS Label Switching MULTI PROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING OVERVIEW OF MPLS, A TECHNOLOGY THAT COMBINES LAYER 3 ROUTING WITH LAYER 2 SWITCHING FOR OPTIMIZED NETWORK USAGE Peter R. Egli 1/21
MPLS Multiprotocol MPLS Label Switching MULTI PROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING OVERVIEW OF MPLS, A TECHNOLOGY THAT COMBINES LAYER 3 ROUTING WITH LAYER 2 SWITCHING FOR OPTIMIZED NETWORK USAGE Peter R. Egli 1/21
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF
 LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 05 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND LABEL DISTRIBUTION PROTOCOL (LDP) 1 by Xantaro IP Routing In IP networks, each router makes an independent
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 05 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND LABEL DISTRIBUTION PROTOCOL (LDP) 1 by Xantaro IP Routing In IP networks, each router makes an independent
Advanced Telecommunications
 ternet Routing - MPLS By Richard Harris MPLS Presentation line troduction Problems of ternet size Methods for overcoming potential problems What is MPLS? Overview MPLS terminology MPLS Architecture The
ternet Routing - MPLS By Richard Harris MPLS Presentation line troduction Problems of ternet size Methods for overcoming potential problems What is MPLS? Overview MPLS terminology MPLS Architecture The
2D1490 p MPLS, RSVP, etc. Olof Hagsand KTHNOC/NADA
 2D1490 p4 2007 MPLS, RSVP, etc Olof Hagsand KTHNOC/NADA Literature Handouts: MPLS-Enabled applications (Minei, Lucek). Parts of Section 1. JunOS Cookbook: Chapter 14 Background MPLS - Multiprotocol Label
2D1490 p4 2007 MPLS, RSVP, etc Olof Hagsand KTHNOC/NADA Literature Handouts: MPLS-Enabled applications (Minei, Lucek). Parts of Section 1. JunOS Cookbook: Chapter 14 Background MPLS - Multiprotocol Label
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino)
 MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 From MPLS Forum Documents MPLS is the enabling technology
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 From MPLS Forum Documents MPLS is the enabling technology
Ahmed Benallegue RMDCN workshop on the migration to IP/VPN 1/54
 MPLS Technology Overview Ahmed Benallegue A.Benallegue@ecmwf.int RMDCN workshop on the migration to IP/VPN 1/54 Plan 1. MPLS basics 2. The MPLS approach 3. Label distribution RSVP-TE 4. Traffic Engineering
MPLS Technology Overview Ahmed Benallegue A.Benallegue@ecmwf.int RMDCN workshop on the migration to IP/VPN 1/54 Plan 1. MPLS basics 2. The MPLS approach 3. Label distribution RSVP-TE 4. Traffic Engineering
Migration Strategies for IP Service Growth: Cell-switched MPLS or IP-routed MPLS
 White Paper Migration Strategies for IP Service Growth: Cell-switched MPLS or IP-routed MPLS Chuck Semeria Marketing Engineer Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408
White Paper Migration Strategies for IP Service Growth: Cell-switched MPLS or IP-routed MPLS Chuck Semeria Marketing Engineer Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94089 USA 408
Multi-Protocol Label Switching
 Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Otto Spaniol Multi-Protocol Label Switching Seminar: Datenkommunikation und Verteilte Systeme SS 2003
Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen Lehrstuhl für Informatik IV Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Otto Spaniol Multi-Protocol Label Switching Seminar: Datenkommunikation und Verteilte Systeme SS 2003
MPLS Intro. Cosmin Dumitru March 14, University of Amsterdam System and Network Engineering Research Group ...
 MPLS Intro Cosmin Dumitru c.dumitru@uva.nl University of Amsterdam System and Network Engineering Research Group March 14, 2011 Disclaimer Information presented in these slides may be slightly biased towards
MPLS Intro Cosmin Dumitru c.dumitru@uva.nl University of Amsterdam System and Network Engineering Research Group March 14, 2011 Disclaimer Information presented in these slides may be slightly biased towards
Table of Contents Chapter 1 MPLS Basics Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 MPLS Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Basic Concepts of MPLS... 1-2 1.1.2 Architecture of MPLS... 1-5 1.1.3 MPLS and Routing Protocols... 1-7 1.1.4 Applications of MPLS...
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 MPLS Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Basic Concepts of MPLS... 1-2 1.1.2 Architecture of MPLS... 1-5 1.1.3 MPLS and Routing Protocols... 1-7 1.1.4 Applications of MPLS...
Trafffic Engineering 2015/16 1
 Traffic Engineering 2015/2016 Traffic Engineering: from ATM to MPLS fernando.silva@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico Trafffic Engineering 2015/16 1 Outline Traffic Engineering revisited Traffic
Traffic Engineering 2015/2016 Traffic Engineering: from ATM to MPLS fernando.silva@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico Trafffic Engineering 2015/16 1 Outline Traffic Engineering revisited Traffic
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Technology Basics Integrates label-based forwarding paradigm with network layer routing label forwarding + label swapping similar to ATM/FR switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Technology Basics Integrates label-based forwarding paradigm with network layer routing label forwarding + label swapping similar to ATM/FR switching
MPLS/Tag Switching. Background. Chapter Goals CHAPTER
 28 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the advantages of MPLS. Learn the components of an MPLS system. Compare and contrast MPLS and hop-by-hop routing. Describe the two methods of label distribution. Explain
28 CHAPTER Chapter Goals Understand the advantages of MPLS. Learn the components of an MPLS system. Compare and contrast MPLS and hop-by-hop routing. Describe the two methods of label distribution. Explain
MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone TEST. 26 April 2016 AN. Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC PBB-TE VPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS GMPLS SR RSVP-TE OSPF-TE PCEP
 Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
Multi Protocol Label Switching
 MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network Management and QoS Provisioning - 1 MPLS: introduction
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Network Management and QoS Provisioning - 1 MPLS: introduction
Operation Manual MPLS. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 MPLS Architecture... 1-1 1.1 MPLS Overview... 1-1 1.2 MPLS Basic Concepts... 1-1 1.2.1 FEC... 1-1 1.2.2 Label... 1-1 1.2.3 LDP... 1-3 1.3 MPLS Architecture...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 MPLS Architecture... 1-1 1.1 MPLS Overview... 1-1 1.2 MPLS Basic Concepts... 1-1 1.2.1 FEC... 1-1 1.2.2 Label... 1-1 1.2.3 LDP... 1-3 1.3 MPLS Architecture...
COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching
 COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching Switching in IP Networks with MPLS http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs9332 1 Lecture Overview This lecture introduces the concept of switching, which allows faster processing
COMP9332 Network Routing & Switching Switching in IP Networks with MPLS http://www.cse.unsw.edu.au/~cs9332 1 Lecture Overview This lecture introduces the concept of switching, which allows faster processing
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching
 MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Computer Networks Design and Management - 1 MPLS: introduction
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Andrea Bianco Telecommunication Network Group firstname.lastname@polito.it http://www.telematica.polito.it/ Computer Networks Design and Management - 1 MPLS: introduction
Introduction to MPLS APNIC
 Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching Multiprotocol, it supports ANY network layer protocol, i.e. IPv4, IPv6,
Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision:
![Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision: Introduction to MPLS. What is MPLS? 1/23/17. APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. [201609] Revision:](/thumbs/79/79964001.jpg) Introduction to MPLS APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, 2017. NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 1 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching
Introduction to MPLS APNIC Technical Workshop January 23 to 25, 2017. NZNOG2017, Tauranga, New Zealand. Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] What is MPLS? 2 1 Definition of MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching
Tag Switching. Background. Tag-Switching Architecture. Forwarding Component CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 Tag Switching Background Rapid changes in the type (and quantity) of traffic handled by the Internet and the explosion in the number of Internet users is putting an unprecedented strain on the
CHAPTER 23 Tag Switching Background Rapid changes in the type (and quantity) of traffic handled by the Internet and the explosion in the number of Internet users is putting an unprecedented strain on the
HP MSR Router Series. MPLS Configuration Guide(V5) Part number: Software version: CMW520-R2513 Document version: 6PW
 HP MSR Router Series MPLS Configuration Guide(V5) Part number: 5998-8188 Software version: CMW520-R2513 Document version: 6PW106-20150808 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development
HP MSR Router Series MPLS Configuration Guide(V5) Part number: 5998-8188 Software version: CMW520-R2513 Document version: 6PW106-20150808 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development
MPLS опорни мрежи MPLS core networks
 MPLS опорни мрежи MPLS core networks Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov http://niau.org Objectives Identify the drawbacks of traditional IP routing Describe basic MPLS concepts and LSR types. MPLS Labels
MPLS опорни мрежи MPLS core networks Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov http://niau.org Objectives Identify the drawbacks of traditional IP routing Describe basic MPLS concepts and LSR types. MPLS Labels
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers Feature History Release 11.1CT 12.1(3)T 12.1(5)T 12.0(14)ST 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S Modification The document introduced MPLS and was titled Tag Switching
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department for Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department for Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Chair for
Outline. Circuit Switching. Circuit Switching : Introduction to Telecommunication Networks Lectures 13: Virtual Things
 8-5: Introduction to Telecommunication Networks Lectures : Virtual Things Peter Steenkiste Spring 05 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/nets-ece Outline Circuit switching refresher Virtual Circuits - general Why virtual
8-5: Introduction to Telecommunication Networks Lectures : Virtual Things Peter Steenkiste Spring 05 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/nets-ece Outline Circuit switching refresher Virtual Circuits - general Why virtual
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Technology in Brief Inserts underlying label-based forwarding layer under traditional network layer routing label forwarding + label swapping similar
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Technology in Brief Inserts underlying label-based forwarding layer under traditional network layer routing label forwarding + label swapping similar
HP A-MSR Router Series MPLS. Configuration Guide. Abstract
 HP A-MSR Router Series MPLS Configuration Guide Abstract This document describes the software features for the HP A Series products and guides you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration
HP A-MSR Router Series MPLS Configuration Guide Abstract This document describes the software features for the HP A Series products and guides you through the software configuration procedures. These configuration
Table of Contents. Cisco MPLS FAQ For Beginners
 Table of Contents MPLS FAQ For Beginners...1 Document ID: 4649...1 Questions...1 Introduction...1 Q. What is Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)?...1 Q. What is a label? What is the structure of the
Table of Contents MPLS FAQ For Beginners...1 Document ID: 4649...1 Questions...1 Introduction...1 Q. What is Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)?...1 Q. What is a label? What is the structure of the
6 MPLS Model User Guide
 6 MPLS Model User Guide Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a multi-layer switching technology that uses labels to determine how packets are forwarded through a network. The first part of this document
6 MPLS Model User Guide Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a multi-layer switching technology that uses labels to determine how packets are forwarded through a network. The first part of this document
MPLS. David Byers. IDA/ADIT/IISLAB David Byers
 MPLS David Byers davby@ida.liu.se IDA/ADIT/IISLAB 1 Why MPLS More efficient backbone routing Support for end-to-end QoS Improved link utilization Rapid recovery from failures Improved route control MPLS
MPLS David Byers davby@ida.liu.se IDA/ADIT/IISLAB 1 Why MPLS More efficient backbone routing Support for end-to-end QoS Improved link utilization Rapid recovery from failures Improved route control MPLS
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series
 HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-4676a Software version: Release 23xx Document version: 6W101-20150320 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
HP 5920 & 5900 Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-4676a Software version: Release 23xx Document version: 6W101-20150320 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard
AToM (Any Transport over MPLS)
 I N D E X A AAL5 over MPLS operation, 459 460 configuration, 462 463 flowchart configuration, 461 PE router, 461 provider router, 461 verification, 463 465 AAL5 to VLAN Interworking, 515 517 AC (Attachment
I N D E X A AAL5 over MPLS operation, 459 460 configuration, 462 463 flowchart configuration, 461 PE router, 461 provider router, 461 verification, 463 465 AAL5 to VLAN Interworking, 515 517 AC (Attachment
MPLS. 9 March 2018 AN
 MPLS 9 March 2018 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP MP-BGP H-VPLS OSPF-TE LIB MPLS is not alone LSP ISIS-TE EVPN GMPLS MPLS-TE T-MPLS LFIB LABEL LDP TAG Used in many (most?) provider networks to
MPLS 9 March 2018 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP MP-BGP H-VPLS OSPF-TE LIB MPLS is not alone LSP ISIS-TE EVPN GMPLS MPLS-TE T-MPLS LFIB LABEL LDP TAG Used in many (most?) provider networks to
HP MSR Router Series. MPLS Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: Software version: CMW710-R0106 Document version: 6PW
 HP MSR Router Series MPLS Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: 5998-5680 Software version: CMW710-R0106 Document version: 6PW100-20140607 Legal and notice information Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development
HP MSR Router Series MPLS Configuration Guide(V7) Part number: 5998-5680 Software version: CMW710-R0106 Document version: 6PW100-20140607 Legal and notice information Copyright 2014 Hewlett-Packard Development
MPLS etc.. 9 May 2017 AN
 MPLS etc.. 9 May 2017 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP MPLS is not alone LSP TAG H-VPLS GMPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS RSVP-TE SR OSPF-TE T-MPLS PCEP Multi-Protocol
MPLS etc.. 9 May 2017 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP MPLS is not alone LSP TAG H-VPLS GMPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS RSVP-TE SR OSPF-TE T-MPLS PCEP Multi-Protocol
CS High Speed Networks. Dr.G.A.Sathish Kumar Professor EC
 CS2060 - High Speed Networks Dr.G.A.Sathish Kumar Professor EC UNIT V PROTOCOLS FOR QOS SUPPORT UNIT V PROTOCOLS FOR QOS SUPPORT RSVP Goals & Characteristics RSVP operations, Protocol Mechanisms Multi
CS2060 - High Speed Networks Dr.G.A.Sathish Kumar Professor EC UNIT V PROTOCOLS FOR QOS SUPPORT UNIT V PROTOCOLS FOR QOS SUPPORT RSVP Goals & Characteristics RSVP operations, Protocol Mechanisms Multi
HP Routing Switch Series
 HP 12500 Routing Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3414 Software version: 12500-CMW710-R7128 Document version: 6W710-20121130 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard
HP 12500 Routing Switch Series MPLS Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3414 Software version: 12500-CMW710-R7128 Document version: 6W710-20121130 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012 Hewlett-Packard
Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN
 Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent. Exam Code: 4A Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Multiprotocol Label Switching. Version: Demo
 Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-103 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Multiprotocol Label Switching Version: Demo QUESTION 1 You wish to advertise LDP labels for all local networks; which is the most effective
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-103 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Multiprotocol Label Switching Version: Demo QUESTION 1 You wish to advertise LDP labels for all local networks; which is the most effective
Lecture 8. Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 8 Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets Network
Lecture 8 Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets Network
ENTERPRISE MPLS. Kireeti Kompella
 ENTERPRISE MPLS Kireeti Kompella AGENDA The New VLAN Protocol Suite Signaling Labels Hierarchy Signaling Advanced Topics Layer 2 or Layer 3? Resilience and End-to-end Service Restoration Multicast ECMP
ENTERPRISE MPLS Kireeti Kompella AGENDA The New VLAN Protocol Suite Signaling Labels Hierarchy Signaling Advanced Topics Layer 2 or Layer 3? Resilience and End-to-end Service Restoration Multicast ECMP
Service Providers Networks & Switching (MPLS) 20/11/2009. Local Team
 Service Providers Networks & Benefits of Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) 20/11/2009 Local Team Service Provider Networks & Carrier Networks A telephone company (or telco) provides telecommunication
Service Providers Networks & Benefits of Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) 20/11/2009 Local Team Service Provider Networks & Carrier Networks A telephone company (or telco) provides telecommunication
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino)
 MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 MPLS - 2 Copyright notice This set of transparencies,
MPLS Multi-protocol label switching Mario Baldi Politecnico di Torino (Technical University of Torino) http://staff.polito.it/mario.baldi MPLS - 1 MPLS - 2 Copyright notice This set of transparencies,
Quality of Service Monitoring and Delivery Part 01. ICT Technical Update Module
 Quality of Service Monitoring and Delivery Part 01 ICT Technical Update Module Presentation Outline Introduction to IP-QoS IntServ Architecture DiffServ Architecture Post Graduate Certificate in Professional
Quality of Service Monitoring and Delivery Part 01 ICT Technical Update Module Presentation Outline Introduction to IP-QoS IntServ Architecture DiffServ Architecture Post Graduate Certificate in Professional
Lecture 3. The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1
 Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Lecture 3 The Network Layer (cont d) Network Layer 1-1 Agenda The Network Layer (cont d) What is inside a router? Internet Protocol (IP) IPv4 fragmentation and addressing IP Address Classes and Subnets
Presentation Outline. Evolution of QoS Architectures. Quality of Service Monitoring and Delivery Part 01. ICT Technical Update Module
 Quality of Service Monitoring and Delivery Part 01 ICT Technical Update Module Presentation Outline Introduction to IP-QoS IntServ Architecture DiffServ Architecture Post Graduate Certificate in Professional
Quality of Service Monitoring and Delivery Part 01 ICT Technical Update Module Presentation Outline Introduction to IP-QoS IntServ Architecture DiffServ Architecture Post Graduate Certificate in Professional
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 2 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
Quality of Service in the Internet. QoS Parameters. Keeping the QoS. Leaky Bucket Algorithm
 Quality of Service in the Internet Problem today: IP is packet switched, therefore no guarantees on a transmission is given (throughput, transmission delay, ): the Internet transmits data Best Effort But:
Quality of Service in the Internet Problem today: IP is packet switched, therefore no guarantees on a transmission is given (throughput, transmission delay, ): the Internet transmits data Best Effort But:
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Technology in Brief Inserts underlying label-based forwarding layer under traditional network layer routing label forwarding + label swapping similar
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Petr Grygárek rek 1 Technology in Brief Inserts underlying label-based forwarding layer under traditional network layer routing label forwarding + label swapping similar
A Segment Routing (SR) Tutorial. R. Bonica NANOG70 June 6, 2017
 A Segment Routing (SR) Tutorial R. Bonica NANOG70 June 6, 2017 AKA: SPRING IETF Standardization Source Packet Routing In Networking (SPRING) WG ISIS, OSPF, IDR and MPLS WGs What is SR? A tunneling technology
A Segment Routing (SR) Tutorial R. Bonica NANOG70 June 6, 2017 AKA: SPRING IETF Standardization Source Packet Routing In Networking (SPRING) WG ISIS, OSPF, IDR and MPLS WGs What is SR? A tunneling technology
MPLS Networks: Design and Routing Functions
 MPLS Networks: Design and Routing Functions Course Description This course provides an understanding of how MPLS works its advantages and limitations and how it can be deployed to provide effective services
MPLS Networks: Design and Routing Functions Course Description This course provides an understanding of how MPLS works its advantages and limitations and how it can be deployed to provide effective services
Quality of Service II
 Quality of Service II Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline Common QoS Approaches Best Effort Integrated Services Differentiated Services Integrated Services Integrated
Quality of Service II Patrick J. Stockreisser p.j.stockreisser@cs.cardiff.ac.uk Lecture Outline Common QoS Approaches Best Effort Integrated Services Differentiated Services Integrated Services Integrated
Multiprotocol Label Switching Overview
 This chapter describes the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) distribution protocol. MPLS is a high-performance packet forwarding technology that integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities
This chapter describes the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) distribution protocol. MPLS is a high-performance packet forwarding technology that integrates the performance and traffic management capabilities
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) on Cisco Routers This document describes commands for configuring and monitoring Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) functionality on Cisco routers and switches. This
Computer Networks. Wenzhong Li. Nanjing University
 Computer Networks Wenzhong Li Nanjing University 1 Chapter 4. Internetworking The Internet Protocol IP Address ARP and DHCP ICMP IPv6 Mobile IP Internet Routing BGP and OSPF IP Multicasting Multiprotocol
Computer Networks Wenzhong Li Nanjing University 1 Chapter 4. Internetworking The Internet Protocol IP Address ARP and DHCP ICMP IPv6 Mobile IP Internet Routing BGP and OSPF IP Multicasting Multiprotocol
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2017 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching MPLS introduction
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2017 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching MPLS introduction
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS)
 36 CHAPTER Prerequisites for MPLS, page 36-1 Restrictions for MPLS, page 36-1 Information About MPLS, page 36-2 Default Settings for MPLS, page 36-7 How to Configure MPLS Features, page 36-7 Configuration
36 CHAPTER Prerequisites for MPLS, page 36-1 Restrictions for MPLS, page 36-1 Information About MPLS, page 36-2 Default Settings for MPLS, page 36-7 How to Configure MPLS Features, page 36-7 Configuration
Lecture 13. Quality of Service II CM0256
 Lecture 13 Quality of Service II CM0256 Types of QoS Best Effort Services Integrated Services -- resource reservation network resources are assigned according to the application QoS request and subject
Lecture 13 Quality of Service II CM0256 Types of QoS Best Effort Services Integrated Services -- resource reservation network resources are assigned according to the application QoS request and subject
MPLS, THE BASICS CSE 6067, UIU. Multiprotocol Label Switching
 MPLS, THE BASICS CSE 6067, UIU Multiprotocol Label Switching Basic Concepts of MPLS 2 Contents Drawbacks of Traditional IP Forwarding Basic MPLS Concepts MPLS versus IP over ATM Traffic Engineering with
MPLS, THE BASICS CSE 6067, UIU Multiprotocol Label Switching Basic Concepts of MPLS 2 Contents Drawbacks of Traditional IP Forwarding Basic MPLS Concepts MPLS versus IP over ATM Traffic Engineering with
MPLS VPN. 5 ian 2010
 MPLS VPN 5 ian 2010 What this lecture is about: IP CEF MPLS architecture What is MPLS? MPLS labels Packet forwarding in MPLS MPLS VPNs 3 IP CEF & MPLS Overview How does a router forward packets? Process
MPLS VPN 5 ian 2010 What this lecture is about: IP CEF MPLS architecture What is MPLS? MPLS labels Packet forwarding in MPLS MPLS VPNs 3 IP CEF & MPLS Overview How does a router forward packets? Process
Concepts and Operation of MPLS VPNs. Francisco Bolanos
 Concepts and Operation of MPLS VPNs Francisco Bolanos fbolanos@cisco.com 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda MPLS Concepts Label Structure Label assignment and distribution RD, RT and
Concepts and Operation of MPLS VPNs Francisco Bolanos fbolanos@cisco.com 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda MPLS Concepts Label Structure Label assignment and distribution RD, RT and
MPLS & Frame Relay Alliance. MPLS PVC User to Network Interface. Implementation Agreement MPLS & FR 2.0.1
 MPLS & Frame Relay Alliance MPLS PVC User to Network Interface Implementation Agreement MPLS & FR 2.0.1 MPLS & Frame Relay Alliance Technical Committee May 2003 Note: The user s attention is called to
MPLS & Frame Relay Alliance MPLS PVC User to Network Interface Implementation Agreement MPLS & FR 2.0.1 MPLS & Frame Relay Alliance Technical Committee May 2003 Note: The user s attention is called to
MPLS Core Networks Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov
 Label Assignment and Distribution Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov Contents Label Assignment and Distribution Typical Label Distribution in Packet-mode MPLS Convergence in Packet-mode MPLS MPLS Label
Label Assignment and Distribution Николай Милованов/Nikolay Milovanov Contents Label Assignment and Distribution Typical Label Distribution in Packet-mode MPLS Convergence in Packet-mode MPLS MPLS Label
Configuration Guide - MPLS
 Release: Document Revision: 5.3 01.01 www.nortel.com NN46240-506 324560-A Rev01 Release: 5.3 Publication: NN46240-506 Document Revision: 01.01 Document status: Standard Document release date: 30 March
Release: Document Revision: 5.3 01.01 www.nortel.com NN46240-506 324560-A Rev01 Release: 5.3 Publication: NN46240-506 Document Revision: 01.01 Document status: Standard Document release date: 30 March
Cisco Training - HD Telepresence MPLS: Implementing Cisco MPLS V3.0. Upcoming Dates. Course Description. Course Outline
 Cisco Training - HD Telepresence MPLS: Implementing Cisco MPLS V3.0 From the technology basics to advanced VPN configuration. $3,995.00 5 Days Upcoming Dates Dec 10 - Dec 14 Mar 25 - Mar 29 Course Description
Cisco Training - HD Telepresence MPLS: Implementing Cisco MPLS V3.0 From the technology basics to advanced VPN configuration. $3,995.00 5 Days Upcoming Dates Dec 10 - Dec 14 Mar 25 - Mar 29 Course Description
Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Label Distribution Protocol 2
Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Label Distribution Protocol 2
MPLS MPLS. Basically: 9 March 2018 AN. Multi-Protocol Label Switching. A bit of history. Multi-Protocol Label Switching.
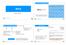 Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP MP-BGP H-VPLS OSPF-TE LIB MPLS MPLS is not alone LSP ISIS-TE EVPN GMPLS MPLS-TE 9 March 2018 AN T-MPLS LFIB LABEL LDP TAG Used in many (most?) provider networks to
Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP MP-BGP H-VPLS OSPF-TE LIB MPLS MPLS is not alone LSP ISIS-TE EVPN GMPLS MPLS-TE 9 March 2018 AN T-MPLS LFIB LABEL LDP TAG Used in many (most?) provider networks to
Testking.4A0-103,249.QA 4A Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching
 Testking.4A0-103,249.QA Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-103 Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching 1. These are the most accurate
Testking.4A0-103,249.QA Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-103 Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching 1. These are the most accurate
MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING: REIVEW KAISER ALI BHAT
 GSJ: Volume 5, Issue 12, December 2017 176 GSJ: Volume 5, Issue 12, December 2017, Online: ISSN 2320-9186 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING: REIVEW KAISER ALI BHAT kaiserali21@gmail.com M.Tech Cyber Security
GSJ: Volume 5, Issue 12, December 2017 176 GSJ: Volume 5, Issue 12, December 2017, Online: ISSN 2320-9186 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING: REIVEW KAISER ALI BHAT kaiserali21@gmail.com M.Tech Cyber Security
MPLS. Multi-Protocol Label Switching
 MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Agenda Review ATM IP over WAN Problems (Traditional Approach) MPLS Principles Label Distribution Methods MPLS Details (Cisco) RFCs 2012, D.I. Lindner MPLS v4.6 2 ATM
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Agenda Review ATM IP over WAN Problems (Traditional Approach) MPLS Principles Label Distribution Methods MPLS Details (Cisco) RFCs 2012, D.I. Lindner MPLS v4.6 2 ATM
MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV
 MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps service providers monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly
MPLS LSP Ping Traceroute for LDP TE and LSP Ping for VCCV The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps service providers monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly
Practice exam questions for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam
 Practice exam questions for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam The following questions will test your knowledge and prepare you for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam. Compare your responses with the Answer
Practice exam questions for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam The following questions will test your knowledge and prepare you for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam. Compare your responses with the Answer
Configuring Quality of Service for MPLS Traffic
 CHAPTER 20 Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) combines the performance and capabilities of Layer 2 (data link layer) switching with the proven scalability of Layer 3 (network layer) routing. MPLS enables
CHAPTER 20 Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) combines the performance and capabilities of Layer 2 (data link layer) switching with the proven scalability of Layer 3 (network layer) routing. MPLS enables
Introduction to Segment Routing
 Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Segment Routing (SR) is a flexible, scalable way of doing source routing. Overview of Segment Routing, page 1 How Segment Routing Works, page 2 Examples for Segment Routing, page 3 Benefits of Segment
Virtual Link Layer : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Institute of Computer Technology - Vienna University of Technology. L85 - Multiprotocol Label Switching
 MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Agenda Review Datagram- versus Virtual Call Service IP over WAN Problems (Traditional Approach) MPLS Principles Label Distribution Methods MPLS Details (Cisco) RFC s
MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching Agenda Review Datagram- versus Virtual Call Service IP over WAN Problems (Traditional Approach) MPLS Principles Label Distribution Methods MPLS Details (Cisco) RFC s
Virtual Link Layer : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
Virtual Link Layer 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Administrivia 3 Lectures left HW #2
IP Datagram Service MPLS. Virtual Call Call Request (CR) Agenda
 Datenkommunikation 384.8 - SS 29 Datenkommunikation 384.8 - SS 29 IP Datagram Service IP Host R IP Router R2 Destination Net Hop A R B R4 C.. R3.. R3 A2 B A2 B MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching User
Datenkommunikation 384.8 - SS 29 Datenkommunikation 384.8 - SS 29 IP Datagram Service IP Host R IP Router R2 Destination Net Hop A R B R4 C.. R3.. R3 A2 B A2 B MPLS Multi-Protocol Label Switching User
Configuring MPLS L2VPN
 Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 MPLS L2VPN overview 1 Basic concepts of MPLS L2VPN 2 Implementation of MPLS L2VPN 2 MPLS L2VPN configuration task list 4 Configuring MPLS L2VPN 5 Configuring CCC MPLS
Contents Configuring MPLS L2VPN 1 MPLS L2VPN overview 1 Basic concepts of MPLS L2VPN 2 Implementation of MPLS L2VPN 2 MPLS L2VPN configuration task list 4 Configuring MPLS L2VPN 5 Configuring CCC MPLS
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering
 9/27/16 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) Cisco Public Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter- Domain Traffic Engineering
9/27/16 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) Cisco Public Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter- Domain Traffic Engineering
MPLS AToM Overview. Documentation Specifics. Feature Overview
 MPLS AToM Overview This document provides an introduction to MPLS AToM and includes the following sections: Documentation Specifics, page 14 Feature Overview, page 14 Benefits, page 26 What To Do Next,
MPLS AToM Overview This document provides an introduction to MPLS AToM and includes the following sections: Documentation Specifics, page 14 Feature Overview, page 14 Benefits, page 26 What To Do Next,
This chapter covers the following topics: Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) AToM operations
 This chapter covers the following topics: Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) AToM operations C H A P T E R 6 Understanding Any Transport over MPLS To provide Layer 2 VPN services over an IP/Multiprotocol
This chapter covers the following topics: Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) AToM operations C H A P T E R 6 Understanding Any Transport over MPLS To provide Layer 2 VPN services over an IP/Multiprotocol
MPLS TRAFFIC ENGINEERING: A CHOICE OF SIGNALING PROTOCOLS
 MPLS TRAFFIC ENGINEERING: A CHOICE OF SIGNALING PROTOCOLS Analysis of the similarities and differences between the two primary MPLS label distribution protocols: RSVP and CR-LDP January 17, 2000 Paul Brittain,
MPLS TRAFFIC ENGINEERING: A CHOICE OF SIGNALING PROTOCOLS Analysis of the similarities and differences between the two primary MPLS label distribution protocols: RSVP and CR-LDP January 17, 2000 Paul Brittain,
Copyright (C) The Internet Society (2002). All Rights Reserved.
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 3270 Category: Standards Track F. Le Faucheur, Editor L. Wu B. Davie Cisco Systems S. Davari PMC-Sierra Inc. P. Vaananen Nokia R. Krishnan Axiowave Networks
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 3270 Category: Standards Track F. Le Faucheur, Editor L. Wu B. Davie Cisco Systems S. Davari PMC-Sierra Inc. P. Vaananen Nokia R. Krishnan Axiowave Networks
Label Switching. The idea. Add a small label (sometimes called a tag ) on the front of a packet and route the packet based on the label. cs670.
 Label Switching The idea Add a small label (sometimes called a tag ) on the front of a packet and route the packet based on the label label How it works IP IP payload When the packet reaches a router,
Label Switching The idea Add a small label (sometimes called a tag ) on the front of a packet and route the packet based on the label label How it works IP IP payload When the packet reaches a router,
Chapter 4. Advanced Internetworking. 4.3 MPLS 4.4 Mobile IP
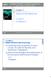 Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, 5e Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. Davie Advanced Internetworking 4.3 MPLS 4.4 Mobile IP Copyright 2, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved 4.3 MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label
Computer Networks: A Systems Approach, 5e Larry L. Peterson and Bruce S. Davie Advanced Internetworking 4.3 MPLS 4.4 Mobile IP Copyright 2, Elsevier Inc. All rights Reserved 4.3 MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label
MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV
 MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV First Published: January 26, 2004 Last Updated: February 27, 2009 The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps
MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV First Published: January 26, 2004 Last Updated: February 27, 2009 The MPLS LSP Ping/Traceroute for LDP/TE, and LSP Ping for VCCV feature helps
Implementing MPLS Label Distribution Protocol
 The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-based solution driven by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that was devised to convert the Internet and IP backbones from best-effort networks
The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a standards-based solution driven by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that was devised to convert the Internet and IP backbones from best-effort networks
Multiprotocol Label Switching
 Multiprotocol Label Switching Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a mechanism in highperformance telecommunications networks which directs and carries data from one network node to the next with the
Multiprotocol Label Switching Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a mechanism in highperformance telecommunications networks which directs and carries data from one network node to the next with the
