Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith AfNOG 2003, Kampala, Uganda
|
|
|
- Harold Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith Kampala, Uganda AfNOG2003 1
2 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/afnog2003-bgp- Troubleshooting.pdf 2
3 Assumptions Presentation assumes working knowledge of BGP Beginner and Intermediate experience of protocol Knowledge of Cisco CLI Hopefully you can translate concepts into your own router CLI If in any doubt, please ask! 3
4 Fundamentals of Troubleshooting Before we begin/troubleshooting is about: Not panicking Creating a checklist Working to that checklist Starting at the bottom and working up This presentation will have references throughout to checklists They are the best way to work to a solution They are what many NOC staff follow when diagnosing and solving network problems 4
5 Agenda Peer Establishment Missing Routes Internet Reachability Problems 5
6 Peer Establishment Routers establish a TCP session Port 179 Permit in ACLs IP connectivity (route from IGP) OPEN messages are exchanged Peering addresses must match the TCP session Local AS configuration parameters 6
7 Common Problems Sessions are not established No IP reachability Incorrect configuration Peers are flapping Layer 2 problems 7
8 Peer Establishment Diagram? R1 ibgp R2 ebgp AS 1 R2#sh run begin ^router bgp R3 AS 2? router bgp 1 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor remote-as 2 8
9 Peer Establishment Symptoms R2#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier , local AS number 1 BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State never Active never Idle Both peers are having problems State may change between Active, Idle and Connect 9
10 Peer Establishment Is the Local AS configured correctly? Is the remote-as assigned correctly? Verify with your diagram or other documentation! Local AS R2# router bgp 1 neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor remote-as 2 ibgp Peer ebgp Peer 10
11 Peer Establishment ibgp Assume that IP connectivity has been checked Check TCP to find out what connections we are accepting R2#show tcp brief all TCB Local Address Foreign Address (state) 005F2934 * * LISTEN 0063F3D4 * * LISTEN We Are Listening for TCP Connections for Port 179 for the Configured Peering Addresses Only! R2#debug ip tcp transactions TCP special event debugging is on R2# TCP: sending RST, seq 0, ack TCP: sent RST to :26385 from :179 Remote Is Trying to Open the Session from Address 11
12 Peer Establishment ibgp What about Us? R2#debug ip bgp BGP debugging is on R2# BGP: open active, local address BGP: open failed: Connection refused by remote host We Are Trying to Open the Session from Address R2#sh ip route Routing entry for /32 Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0 (connected) * directly connected, via Serial1 Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1 R2#show ip interface brief include Serial1 Serial YES manual up up 12
13 Peer Establishment ibgp Source address is the outgoing interface towards the destination but peering in this case is using loopback interfaces! Force both routers to source from the correct interface Use update-source to specify the loopback when loopback peering R2# router bgp 1 neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor update-source Loopback0 neighbor remote-as 2 neighbor update-source Loopback0 13
14 Peer Establishment Diagram R1 ibgp AS 1 R2 ebgp R3 AS 2? R1 is established now The ebgp session is still having trouble! 14
15 Peer Establishment ebgp Trying to load-balance over multiple links to the ebgp peer Verify IP connectivity Check the routing table Use ping/trace to verify two way reachability R2#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/4/8 ms Routing towards destination correct, but 15
16 Peer Establishment ebgp R2#ping ip Target IP address: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) Use extended pings to test loopback to loopback connectivity R3 does not have a route to our loopback,
17 Peer Establishment ebgp Assume R3 added a route to Still having problems R2#sh ip bgp neigh BGP neighbor is , remote AS 2, external link BGP version 4, remote router ID BGP state = Idle Last read 00:00:04, hold time is 180, keepalive interval is 60 seconds Received 0 messages, 0 notifications, 0 in queue Sent 0 messages, 0 notifications, 0 in queue Route refresh request: received 0, sent 0 Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 30 seconds For address family: IPv4 Unicast BGP table version 1, neighbor version 0 Index 2, Offset 0, Mask 0x4 0 accepted prefixes consume 0 bytes Prefix advertised 0, suppressed 0, withdrawn 0 Connections established 0; dropped 0 Last reset never External BGP neighbor not directly connected. No active TCP connection 17
18 Peer Establishment ebgp R2# router bgp 1 neighbor remote-as 2 neighbor ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor update-source Loopback0 ebgp peers are normally directly connected By default, TTL is set to 1 for ebgp peers If not directly connected, specify ebgp-multihop At this point, the session should come up 18
19 Peer Establishment ebgp R2#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier , local AS number 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd never Active Still having trouble! Connectivity issues have already been checked and corrected 19
20 Peer Establishment ebgp R2#debug ip bgp events 14:06:37: BGP: open active, local address :06:37: BGP: went from Active to OpenSent 14:06:37: BGP: sending OPEN, version 4 14:06:37: BGP: received NOTIFICATION 2/2 (peer in wrong AS) 2 bytes :06:37: BGP: remote close, state CLOSEWAIT 14:06:37: BGP: service reset requests 14:06:37: BGP: went from OpenSent to Idle 14:06:37: BGP: closing If an error is detected, a notification is sent and the session is closed R3 is configured incorrectly Has neighbor remote-as 10 Should have neighbor remote-as 1 After R3 makes this correction the session should come up 20
21 ebgp summary Remember to allow TCP/179 through filters Common ebgp implementation error access-list 100 permit tcp host eq 179 host access-list 100 permit tcp host host eq 179 Need to be careful with ebgp-multihop Peer between loopback interfaces Needed to loadshare Remember update-source loopback 0 TTL must be at least 2 for ebgp-multihop between directly connected neighbours Use TTL value carefully 21
22 Peer Establishment Passwords Using passwords on ibgp and ebgp sessions Link won t come up Been through all the previous troubleshooting steps R2#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier , local AS number 1 Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd never Active 22
23 Peer Establishment Passwords R2# router bgp 1 neighbor remote-as 2 neighbor ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor update-source Loopback0 neighbor password F1C221C Configuration on R2 looks fine! Check the log messages enable log-neighbor-changes %TCP-6-BADAUTH: No MD5 digest from :179 to :11272 %TCP-6-BADAUTH: No MD5 digest from :179 to :11272 %TCP-6-BADAUTH: No MD5 digest from :179 to :
24 Peer Establishment Passwords R3# router bgp 2 neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor ebgp-multihop 2 neighbor update-source Loopback0 Check configuration on R3 Password is missing from the ebgp configuration Fix the R3 configuration Peering should now come up! But it does not 24
25 Peer Establishment Passwords Let s look at the log messages again for any clues R2# %TCP-6-BADAUTH: Invalid MD5 digest from :11024 to :179 %TCP-6-BADAUTH: Invalid MD5 digest from :11024 to :179 %TCP-6-BADAUTH: Invalid MD5 digest from :11024 to :179 We are getting invalid MD5 digest messages password mismatch! 25
26 Peer Establishment Passwords We must have typo ed the password on one of the peering routers Fix the password best to re-enter password on both routers ebgp session now comes up %TCP-6-BADAUTH: Invalid MD5 digest from :11027 to :179 %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor Up 26
27 Flapping Peer Diagram AS 1 R1 ebgp AS 2 R2 Layer 2 ATM or FR Cloud Symptoms the ebgp session flaps ebgp peering establishes, then drops, re-establishes, then drops, 27
28 Flapping Peer Enable bgp log-neighbor-changes so you get a log message when a peer flaps R1 and R2 are peering over ATM cloud R2# %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor Down BGP Notification sent %BGP-3-NOTIFICATION: sent to neighbor /0 (hold time expired) 0 bytes R2#show ip bgp neighbor include Last reset Last reset 00:01:02, due to BGP Notification sent, hold time expired We are not receiving keepalives from the other side! 28
29 Flapping Peer Let s take a look at our peer! R1#show ip bgp sum BGP router identifier , local AS number 1 BGP table version is 10167, main routing table version network entries and paths using bytes of memory 1 BGP path attribute entries using 60 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP activity 10166/300 prefixes, 10166/0 paths, scan interval 15 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd :02:15 0 R1#show ip bgp summary begin Neighbor Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd :03:04 0 Hellos are stuck in OutQ behind update packets! Notice that the MsgSent counter has not moved 29
30 Flapping Peer R1#ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 16/21/24 m R1#ping ip Target IP address: Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: 1500 Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 1500-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) Normal pings work but a ping of 1500 fails? 30
31 Flapping Peer Diagram AS 1 R1 ebgp AS 2 R2 Small Packets Layer 2 ATM or FR Cloud Large Packets Small packets are ok Large packets are lost in the cloud BGP session flaps 31
32 Flapping Peer Things to check MTU values Traffic shaping Rate-limiting parameters Looks like a Layer 2 problem At this point we have verified that BGP is not at fault Next step is to troubleshoot layer 2 32
33 Flapping Peer Diagram AS 1 R1 ebgp AS 2 R2 Small Packets Layer 2 ATM or FR Cloud Large Packets Large packets are ok now BGP session is stable! 33
34 Troubleshooting Tips Extended ping/traceroute allow you to verify Loopback to loopback IP connectivity TTL issues show ip bgp summary Displays the state of all peers show ip bgp neighbor Gives a lot of information regarding the peer 34
35 Troubleshooting Tips debug ip bgp Should give you a good hint as to why a peer will not establish debug ip bgp events Displays state transitions for peers show ip bgp neighbor include Last reset Will show you the last reset reason for all peers 35
36 Agenda Peer Establishment Missing Routes Internet Reachability Problems 36
37 Quick Review Once the session has been established, UPDATEs are exchanged All the locally known routes Only the bestpath is advertised Incremental UPDATE messages are exchanged afterwards 37
38 Quick Review Bestpath received from ebgp peer Advertise to all peers Bestpath received from ibgp peer Advertise only to ebgp peers A full ibgp mesh must exist 38
39 Missing Routes Agenda Route Origination UPDATE Exchange Filtering ibgp mesh problems 39
40 Route Origination Example I Network statement R1# show run include network mask BGP is not originating the route??? R1# show ip bgp include R1# Do we have the exact route? R1# show ip route % Network not in table 40
41 Route Origination Example I Nail down routes you want to originate ip route Null0 254 Check the RIB R1# show ip route /22 is subnetted, 1 subnets S [1/0] via Null 0 BGP originates the route!! R1# show ip bgp include *> /
42 Route Origination Example II Trying to originate an aggregate route aggregate-address summary-only The RIB has a component but BGP does not create the aggregate??? R1# show ip route longer /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C [1/0] is directly connected, Loopback 0 R1# show ip bgp i R1# 42
43 Route Origination Example II Remember, to have a BGP aggregate you need a BGP component, not a RIB (Routing Information Base, a.k.a. the routing table) component R1# show ip bgp longer R1# Once BGP has a component route we originate the aggregate network mask R1# show ip bgp longer *> / i s> / i s means this component is suppressed due to the summary-only argument 43
44 Troubleshooting Tips BGP Network statement rules Always need an exact route (RIB) aggregate-address looks in the BGP table, not the RIB show ip route x.x.x.x y.y.y.y longer Great for finding RIB component routes show ip bgp x.x.x.x y.y.y.y longer Great for finding BGP component routes 44
45 Missing Routes Route Origination UPDATE Exchange Filtering ibgp mesh problems 45
46 Missing Routes Example I Two RR clusters R1 is a RR for R3 R2 is a RR for R4 R4 is advertising /8 R2 has the route but R1 and R3 do not? R1 R3 R2 R4 46
47 Missing Routes Example I First, did R2 advertise the route to R1? R2# show ip bgp neighbors advertised-routes BGP table version is 2, local router ID is Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i I Did R1 receive it? R1# show ip bgp neighbors routes Total number of prefixes 0 47
48 Missing Routes Example I Time to debug!! access-list 100 permit ip host host R1# debug ip bgp update 100 Tell R2 to resend his UPDATEs R2# clear ip bgp out R1 shows us something interesting *Mar 1 21:50:12.410: BGP(0): rcv UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop , origin i, localpref 100, metric 0, originator , clusterlist , path, community, extended community *Mar 1 21:50:12.410: BGP(0): rcv UPDATE about /8 -- DENIED due to: ORIGINATOR is us; Cannot accept an update with our Router-ID as the ORIGINATOR_ID. Another means of loop detection in BGP 48
49 Missing Routes Example I R1 and R4 have the same Router-ID R1# show ip bgp summary include identifier. BGP router identifier , local AS number 100. R4# show ip bgp summary include identifier. BGP router identifier , local AS number 100. Can be a problem in multicast networks; for RP (Rendezvous Point) purposes the same address may be assigned to multiple routers Specify a unique Router-ID R1#show run include router-id bgp router-id R4#show run include router-id bgp router-id
50 Missing Routes Example II One RR cluster R1 and R2 are RRs R3 and R4 are RRCs R4 is advertising /8 R2 has it R1 and R3 do not R1 R3 R2 R4 R1#show run include cluster bgp cluster-id 10 R2#show run include cluster bgp cluster-id 10 50
51 Missing Routes Example II Same steps as last time! Did R2 advertise it to R1? R2# show ip bgp neighbors advertised-routes BGP table version is 2, local router ID is Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i i Did R1 receive it? R1# show ip bgp neighbor routes Total number of prefixes 0 51
52 Missing Routes Example II Time to debug!! access-list 100 permit ip host host R1# debug ip bgp update 100 Tell R2 to resend his UPDATEs R2# clear ip bgp out R1 shows us something interesting *Mar 3 14:28:57.208: BGP(0): rcv UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop , origin i, localpref 100, metric 0, originator , clusterlist , path, community, extended community *Mar 3 14:28:57.208: BGP(0): rcv UPDATE about /8 -- DENIED due to: reflected from the same cluster; Remember, all RRCs must peer with all RRs in a cluster; allows R4 to send the update directly to R1 52
53 Troubleshooting Tips show ip bgp neighbor x.x.x.x advertised-routes Lets you see a list of NLRI that you sent a peer Note: The attribute values shown are taken from the BGP table; attribute modifications by outbound route-maps will not be shown show ip bgp neighbor x.x.x.x routes Displays routes x.x.x.x sent to us that made it through our inbound filters show ip bgp neighbor x.x.x.x received-routes Can only use if soft-reconfig inbound is configured Displays all routes received from a peer, even those that were denied 53
54 Troubleshooting Tips More on usefulness of soft-reconfiguration Ideal for troubleshooting problems with inbound filters and attributes show ip bgp neighbor x.x.x.x routes alpha#sh ip bgp neigh routes Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i i *>i / i show ip bgp neighbor x.x.x.x received-routes alpha#sh ip bgp neigh received-routes Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i i * i i * i / i 54
55 Troubleshooting Tips clear ip bgp x.x.x.x in Ask x.x.x.x to resend his UPDATEs to us clear ip bgp x.x.x.x out Tells BGP to resend UPDATEs to x.x.x.x debug ip bgp update Always use an ACL to limit output Great for troubleshooting Automatic Denies debug ip bgp x.x.x.x update Allows you to debug updates to/from a specific peer Handy if multiple peers are sending you the same prefix 55
56 Missing Routes Route Origination UPDATE Exchange Filtering ibgp mesh problems 56
57 Update Filtering Type of filters Prefix filters AS_PATH filters Community filters Route-maps Applied incoming and/or outgoing 57
58 Missing Routes Update Filters Determine which filters are applied to the BGP session show ip bgp neighbors x.x.x.x show run include neighbor x.x.x.x Examine the route and pick out the relevant attributes show ip bgp x.x.x.x Compare the attributes against the filters 58
59 Missing Routes Update Filters /8??? R /8 R2 Missing /8 in R1 ( ) Not received from R2 ( ) R1#show ip bgp neigh routes Total number of prefixes 0 59
60 Missing Routes Update Filters R2 originates the route Does not advertise it to R1 R2#show ip bgp neigh advertised-routes Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path R2#show ip bgp BGP routing table entry for /8, version 1660 Paths: (1 available, best #1) Not advertised to any peer Local from ( ) Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best 60
61 Missing Routes Update Filters Time to check filters! ^ matches the beginning of a line $ matches the end of a line ^$ means match any empty AS_PATH Filter looks correct R2#show run include neighbor neighbor remote-as 3 neighbor filter-list 1 out R2#sh ip as-path 1 AS path access list 1 permit ^$ 61
62 Missing Routes Update Filters R2#show ip bgp filter-list 1 R2#show ip bgp regexp ^$ BGP table version is 1661, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> i Nothing matches the filter-list??? Re-typing the regexp gives the expected output 62
63 Missing Routes Update Filters Copy and paste the entire regexp line from the configuration R2#show ip bgp regexp ^$ Nothing matches again! Let s use the up arrow key to see where the cursor stops R2#show ip bgp regexp ^$ End of Line Is at the Cursor There is a trailing white space at the end It is considered part of the regular expression 63
64 Missing Routes Update Filters Force R2 to resend the update after the filter-list correction Then check R1 to see if it has the route R2#clear ip bgp out R1#show ip bgp % Network not in table R1 still does not have the route Time to check R1 s inbound policy for R2 64
65 Missing Routes Update Filters R1#show run include neighbor neighbor remote-as 12 neighbor route-map POLICY in R1#show route-map POLICY route-map POLICY, permit, sequence 10 Match clauses: ip address (access-lists): as-path (as-path filter): 1 Set clauses: Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes R1#show access-list 100 Extended IP access list 100 permit ip host host R1#show access-list 101 Extended IP access list 101 permit ip host R1#show ip as-path 1 AS path access list 1 permit ^12$ 65
66 Missing Routes Update Filters /8??? R /8 R2 Confused? Let s run some debugs R1#show access-list 99 Standard IP access list 99 permit R1#debug ip bgp update 99 BGP updates debugging is on for access list 99 for neighbor R1# 4d00h: BGP(0): rcvd UPDATE w/ attr: nexthop , origin i, metric 0, path 12 4d00h: BGP(0): rcvd /8 -- DENIED due to: route-map; 66
67 Missing Routes Update Filters R1#sh run include neighbor neighbor remote-as 12 neighbor route-map POLICY in R1#sh route-map POLICY route-map POLICY, permit, sequence 10 Match clauses: ip address (access-lists): as-path (as-path filter): 1 Set clauses: Policy routing matches: 0 packets, 0 bytes R1#sh access-list 100 Extended IP access list 100 permit ip host host R1#sh access-list 101 Extended IP access list 101 permit ip host R1#sh ip as-path 1 AS path access list 1 permit ^12$ 67
68 Missing Routes Update Filters Wrong mask! Needs to be /8 and the ACL allows a /16 only! Extended IP access list 100 Should be permit ip host host Extended IP access list 100 permit ip host host Use prefix-list instead, more difficult to make a mistake ip prefix-list my_filter permit /8 What about ACL 101? Multiple matches on the same line are ORed Multiple matches on different lines are ANDed ACL 101 does not matter because ACL 100 matches which satisfies the OR condition 68
69 Missing Routes Community Problems /8??? R /8 R2 Missing /8 in R1 ( ) Not received from R2 ( ) R1#show ip bgp neigh routes Total number of prefixes 0 69
70 Missing Routes Community Problems R2 originates the route R2#show ip bgp BGP routing table entry for /8, version 1660 Paths: (1 available, best #1) Not advertised to any peer Local from ( ) Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best But the community is not set Would be displayed in the sh ip bgp output 70
71 Missing Routes Community Problems Fix the configuration so community is set R2#show run begin bgp router bgp 2 network route-map set-community... route-map set-community permit 10 set community 2:2 1:50 R2#show ip bgp BGP routing table entry for /8, version 1660 Paths: (1 available, best #1) Not advertised to any peer Local from ( ) Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best Community 2:2 1:50 71
72 Missing Routes Community Problems R2 now advertises prefix with community to R1 But R1 still doesn t see the prefix R1 insists there is nothing wrong with their configuration R1#show ip bgp neigh routes Total number of prefixes 0 Configuration verified on R2 No filters blocking announcement on R2 So what s wrong? 72
73 Missing Routes Community Problems Check R2 configuration again! R2#show run begin bgp router bgp 2 network route-map set-community neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor prefix-list my-agg out neighbor prefix-list their-agg in! ip prefix-list my-agg permit /8 ip prefix-list their-agg permit /8! route-map set-community permit 10 set community 2:2 1:50 Looks okay filters okay, route-map okay But forgotten neighbor send-community Cisco IOS does NOT send communities by default 73
74 Missing Routes Community Problems R2 now advertises prefix with community to R1 But R1 still doesn t see the prefix Nothing wrong on R2 now, so turn attention to R1 R1#show run begin bgp router bgp 1 neighbor remote-as 2 neighbor route-map R2-in in neighbor route-map R1-out out! ip community-list 1 permit 1:150! route-map R2-in permit 10 match community 1 set local-preference
75 Missing Routes Community Problems Community match on R1 expects 1:150 to be set on prefix But R2 is sending 1:50 Typo or miscommunication between operations? R2 is also using the route-map to filter If the prefix does not have community 1:150 set, it is dropped there is no next step in the route-map Watch the route-map rules in Cisco IOS they are basically: if <match> then <set> and exit route-map else if <match> then <set> and exit route-map else if <match> then <set> etc Blank route-map line means match everything, set nothing 75
76 Missing Routes Community Problems Fix configuration on R2 to set community 1:150 on announcements to R1 Fix configuration on R1 to also permit prefixes not matching the route-map troubleshooting is easier with prefix-filters doing the filtering R1#show run begin ^route-map route-map R2-in permit 10 match community 1 set local-preference 150 route-map R2-in permit 20 R1#show ip bgp neigh routes Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * i Total number of prefixes 1 76
77 Missing Routes Community Problems Watch route-maps Route-map rules often catch out operators when they are used for filtering Absence of an appropriate match means the prefix will be discarded Don t forget to configure send-community Include it in your default template for ibgp It should be ibgp default in a Service Provider Network Remember that it is required to send communities for ebgp too 77
78 Missing Routes General Problems Stick to simple policy rules: Prefix-lists Filter-lists Route-maps fi filter prefix announcements fi filter on AS-paths fi apply policies By applying policies I mean setting attributes on groups of prefixes, rather than simply filtering 78
79 Missing Routes Route Origination UPDATE Exchange Filtering ibgp mesh problems 79
80 Missing Routes ibgp Symptom: customer complains about patchy Internet access Can access some, but not all, sites connected to backbone Can access some, but not all, of the Internet 80
81 Missing Routes ibgp R R1 ibgp R2 AS 1 ebgp ebgp R3 R B AS /24 A AS 2 Customer connected to R1 can see AS3, but not AS2 Also complains about not being able to see sites connected to R5 No complaints from other customers 81
82 Missing Routes ibgp Diagnosis: This is the classic ibgp mesh problem The full mesh isn t complete how do we know this? Customer is connected to R1 Can t see AS2 R3 is somehow not passing routing information about AS2 to R1 Can t see R5 R5 is somehow not passing routing information about sites connected to R5 But can see rest of the Internet his prefix is being announced to some places, so not an ibgp origination problem 82
83 Missing Routes ibgp R3#sh ip bgp sum begin ^Neigh Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd d10h Active d16h d16h d16h d16h 100 R3# BGP summary shows that the peering with router R1 is down Up/Down is 3 days 10 hours, yet active Which means it was last up 3 days and 10 hours ago So something has broken between R1 and R3 83
84 Missing Routes ibgp Now check configuration on R1 R1#sh conf b bgp router bgp 1 neighbor ibgp-ipv4-peers peer-group neighbor ibgp-ipv4-peers remote-as 1 neighbor ibgp-ipv4-peers update-source Loopback0 neighbor ibgp-ipv4-peers send-community neighbor ibgp-ipv4-peers prefix-list ibgp-prefixes out neighbor peer-group ibgp-ipv4-peers neighbor peer-group ibgp-ipv4-peers neighbor peer-group ibgp-ipv4-peers Where is the peering with R3? Restore the missing line, and the ibgp with R3 comes back up 84
85 Missing Routes ibgp R3#sh ip bgp sum begin ^Neigh Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd :00: d16h d16h d16h d16h 100 R3# BGP summary shows that no prefixes are being heard from R5 This could be due to inbound filters on R3 on the ibgp with R5 But there were no filters in the configuration on R3 This must be due to outbound filters on R5 on the ibgp with R3 85
86 Missing Routes ibgp Now check configuration on R5 R5#sh conf b neighbor neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor update-source loopback0 neighbor prefix-list ebgp-filters out neighbor remote-as 1 neighbor update-source loopback0 neighbor prefix-list ibgp-filters out! ip prefix-list ebgp-filters permit /8 ip prefix-list ibgp-filters permit /8 Error in prefix-list in R3 ibgp peering ebgp-filters has been used instead of ibgp-filters Typo another advantage of using peer-groups! 86
87 Missing Routes ibgp Fix the prefix-list on R5 Check the ibgp again on R3 Peering with R1 is up Peering with R5 has prefixes Confirm that all is okay with customer R3#sh ip bgp sum begin ^Neigh Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd :01: d16h d16h d16h d16h 100 R3# 87
88 Troubleshooting Tips Watch the ibgp full mesh Use peer-groups both for efficiency and to avoid making policy errors within the ibgp mesh Use route reflectors to avoid accidentally missing ibgp peers, especially as the mesh grows in size 88
89 Troubleshooting Tips show ip as-path-access-list Displays the filter show ip bgp filter-list Displays BGP paths that match the filter show ip bgp regexp Displays BGP paths that match the as-path regular expression; handy for troubleshooting filter-list issues 89
90 Troubleshooting Tips show ip community-list Displays the filter show ip bgp community-list Displays BGP paths that match the filter show ip prefix-list Displays the filter Prefix-lists are generally easier to use than ACLs show ip bgp prefix-list Displays BGP paths that match the filter 90
91 Troubleshooting Tips show route-map Displays the filter show ip bgp route-map Displays BGP paths that match the filter show access-list Displays the filter debug ip bgp update ACL After going through the config, debug! Don t forget the ACL 91
92 Agenda Peer Establishment Missing Routes Internet Reachability Problems 92
93 Internet Reachability Problems BGP Attribute Confusion To Control Traffic in fi Send MEDs and AS-PATH prepends on outbound announcements To Control Traffic out fi Attach local-preference to inbound announcements Troubleshooting of multihoming and transit is often hampered because the relationship between routing information flow and traffic flow is forgotten 93
94 Internet Reachability Problems BGP Path Selection Process Each vendor has tweaked the path selection process Know it, learn it, for your router equipment saves time later MED confusion Default MED on Cisco IOS is ZERO it may not be this on your router, or your peer s router 94
95 Internet Reachability Problems Community confusion set community does just that it overwrites any other community set on the prefix Use additive keyword to add community to existing list Use Internet format for community (AS:xx) not the 32- bit IETF format Cisco IOS never sends community by default Other implementations may send community by default for ibgp and/or ebgp Never assume that your neighbouring AS will honour your no-export community ask first! 95
96 Internet Reachability Problems AS-PATH prepends 20 prepends won t lessen the priority of your path any more than 10 prepends will check it out at a Looking Glass The Internet is on average only 5 ASes deep, maximum AS prepend most ISPs have to use is around this too Know you BGP path selection algorithm Some ISPs use bgp maxas-path 15 to drop prefixes with ridiculously long AS-paths 96
97 Internet Reachability Problems Private ASes should not ever appear in the Internet Cisco IOS remove-private-as command does not remove every instance of a private AS e.g. won t remove private AS appearing in the middle of a path surrounded by public ASNs Apparent non-removal of private-asns may not be a bug, but a configuration error somewhere else 97
98 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example I AS /24 R1 AS 3 R3 R2 AS 2 Symptom: AS1 announces /24 to AS2 but AS3 cannot see the network 98
99 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example I Checklist: AS1 announces, but does AS2 see it? We are checking ebgp filters on R1 and R2. Remember that R2 access will require cooperation and assistance from your peer Does AS2 see it over entire network? We are checking ibgp across AS2 s network (unneeded step in this case, but usually the next consideration). Quite often ibgp is misconfigured, lack of full mesh, problems with RRs, etc. 99
100 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example I Checklist: Does AS2 send it to AS3? We are checking ebgp configuration on R2. There may be a configuration error with as-path filters, or prefix-lists, or communities such that only local prefixes get out Does AS3 see all of AS2 s originated prefixes? We are checking ebgp configuration on R3. Maybe AS3 does not know to expect prefixes from AS1 in the peering with AS2, or maybe it has similar errors in as-path or prefix or community filters 100
101 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example I Troubleshooting connectivity beyond immediate peers is much harder Relies on your peer to assist you they have the relationship with their BGP peers, not you Quite often connectivity problems are due to the private business relationship between the two neighbouring ASNs 101
102 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II AS R1 AS 3 R3 The Internet Symptom: AS1 announces /24 to its upstreams but AS3 cannot see the network 102
103 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II Checklist: AS1 announces, but do its upstreams see it? We are checking ebgp filters on R1 and upstreams. Remember that upstreams will need to be able to help you with this Is the prefix visible anywhere on the Internet? We are checking if the upstreams are announcing the network to anywhere on the Internet. See next slides on how to do this. 103
104 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II Help is at hand the Looking Glass Many networks around the globe run Looking Glasses These let you see the BGP table and often run simple ping or traceroutes from their sites for IPv4 for IPv6 Many still use the original: nitrous.digex.net Next slides have some examples of a typical looking glass in action 104
105 105
106 106
107 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II Hmmm. Looking Glass can see /14 This includes /24 So the problem must be with AS3, or AS3 s upstream A traceroute confirms the connectivity 107
108 108
109 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II Help is at hand RouteViews The RouteViews router has BGP feeds from around 60 peers explains the project Gives access to a real router, and allows any provider to find out how their prefixes are seen in various parts of the Internet Complements the Looking Glass facilities Anyway, back to our problem 109
110 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II Checklist: Does AS3 s upstream send it to AS3? We are checking ebgp configuration on AS3 s upstream. There may be a configuration error with as-path filters, or prefix-lists, or communities such that only local prefixes get out. This needs AS3 s assistance. Does AS3 see any of AS1 s originated prefixes? We are checking ebgp configuration on R3. Maybe AS3 does not know to expect the prefix from AS1 in the peering with its upstream, or maybe it has some errors in as-path or prefix or community filters 110
111 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example II Troubleshooting across the Internet is harder But tools are available Looking Glasses, offering traceroute, ping and BGP status are available all over the globe Most connectivity problems seem to be found at the edge of the network, rarely in the transit core Problems with the transit core are usually intermittent and short term in nature 111
112 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III The Internet AS 2 AS 3 R2 R3 R1 AS 1 Symptom: AS1 is trying to loadshare between its upstreams, but has trouble getting traffic through the AS2 link 112
113 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III Checklist: What does trouble mean? Is outbound traffic loadsharing okay? Can usually fix this with selectively rejecting prefixes, and using local preference Generally easy to fix, local problem, simple application of policy Is inbound traffic loadsharing okay? Errummm, bigger problem if not Need to do some troubleshooting if configuration with communities, AS-PATH prepends, MEDs and selective leaking of subprefixes don t seem to help 113
114 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III Checklist: AS1 announces, but does AS2 see it? We are checking ebgp filters on R1 and R2. Remember that R2 access will require cooperation and assistance from your peer Does AS2 see it over entire network? We are checking ibgp across AS2 s network. Quite often ibgp is misconfigured, lack of full mesh, problems with RRs, etc. 114
115 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III Checklist: Does AS2 send it to its upstream? We are checking ebgp configuration on R2. There may be a configuration error with as-path filters, or prefix-lists, or communities such that only local prefixes get out Does the Internet see all of AS2 s originated prefixes? We are checking ebgp configuration on other Internet routers. This means using looking glasses. And trying to find one as close to AS2 as possible. 115
116 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III Checklist: Repeat all of the above for AS3 Stopping here and resorting to a huge prepend towards AS3 won t solve the problem There are many common problems listed on next slide And tools to help decipher the problem 116
117 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III No inbound traffic from AS2 AS2 is not seeing AS1 s prefix, or is blocking it in inbound filters A trickle of inbound traffic Switch on NetFlow (if the router has it) and check the origin of the traffic If it is just from AS2 s network blocks, then is AS2 announcing the prefix to its upstreams? If they claim they are, ask them to ask their upstream for a show ip bgp output or use a Looking Glass to check 117
118 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example III A light flow of traffic from AS2, but 50% less than from AS3 Looking Glass comes to the rescue LG will let you see what AS2, or AS2 s upstreams are announcing AS1 may choose this as primary path, but AS2 relationship with their upstream may decide otherwise NetFlow comes to the rescue Allows AS1 to see what the origins are, and with the LG, helps AS1 to find where the prefix filtering culprit might be 118
119 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example IV The Internet AS 2 AS 3 R2 R3 R1 AS 1 Symptom: AS1 is loadsharing between its upstreams, but the traffic load swings randomly between AS2 and AS3 119
120 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example IV Checklist: Assume AS1 has done everything in this tutorial so far All the configurations look fine, the Looking Glass outputs look fine, life is wonderful Apart from those annoying traffic swings every hour or so L2 problem? Route Flap Damping? Since BGP is configured fine, and the net has been stable for so long, can only be an L2 problem, or Route Flap Damping side-effect 120
121 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example IV L2 upstream somewhere has poor connectivity between themselves and the rest of the Internet Only real solution is to impress upon upstream that this isn t good enough, and get them to fix it Or change upstreams 121
122 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example IV Route Flap Damping Many ISPs implement route flap damping Many ISPs simply use the vendor defaults Vendor defaults are generally far too severe There is even now some real concern that the more lenient RIPE-229 values are too severe Again Looking Glasses come to the operator s assistance 122
123 123
124 Troubleshooting Connectivity Example IV Most Looking Glasses allow the operators to check the flap or damped status of their announcements Many oscillating connectivity issues are usually caused by L2 problems Route flap damping will cause connectivity to persist via alternative paths even though primary paths have been restored Quite often, the exponential back off of the flap damping timer will give rise to bizarre routing Common symptom is that bizarre routing will often clear away by itself 124
125 Troubleshooting Summary Most troubleshooting is about: Experience Recognising the common problems Not panicking Logical approach Check configuration first Check locally first before blaming the peer Troubleshoot layer 1, then layer 2, then layer 3, etc 125
126 Troubleshooting Summary Most troubleshooting is about: Using the available tools The debugging tools on the router hardware Internet Looking Glasses Colleagues and their knowledge Public mailing lists where appropriate 126
127 Agenda Peer Establishment Missing Routes Internet Reachability Problems 127
128 Troubleshooting BGP The End! AfNOG
Troubleshooting BGP. Philip Smith NANOG February 2007 Toronto, Ontario Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith 4-7 February 2007 Toronto, Ontario 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com /pfs/seminars/nanog39-bgp-troubleshooting.pdf And on the NANOG
Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith 4-7 February 2007 Toronto, Ontario 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com /pfs/seminars/nanog39-bgp-troubleshooting.pdf And on the NANOG
Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith NANOG 29, Chicago, October 2003
 Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith NANOG 29, Chicago, October 2003 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/-bgp- Troubleshooting.pdf 2 Assumptions Presentation
Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith NANOG 29, Chicago, October 2003 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/-bgp- Troubleshooting.pdf 2 Assumptions Presentation
Module 6 Implementing BGP
 Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting BGP Phil Smith Presentation_ID 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. 2 BGP in Large Scale Networks Scalable Stable Simple 3 Avoid the Problem in the
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting BGP Phil Smith Presentation_ID 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. 2 BGP in Large Scale Networks Scalable Stable Simple 3 Avoid the Problem in the
Introduction to BGP. ISP Workshops. Last updated 30 October 2013
 Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) What Is BGP?
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP `2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job `2005,
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP `2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job `2005,
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
Introduction to BGP. ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
Configuration and Management of Networks 2012
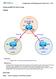 Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
BGP on IOS: Getting Started
 BGP on IOS: Getting Started ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 IOS Good Practices p ISPs should start off with the following BGP commands as a basic template: router bgp 64511 bgp deterministic-med
BGP on IOS: Getting Started ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 IOS Good Practices p ISPs should start off with the following BGP commands as a basic template: router bgp 64511 bgp deterministic-med
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
TROUBLESHOOTING AND ADVANCED BGP
 TROUBLESHOOTING AND ADVANCED BGP SESSION 1 Assumptions BGP operational experience Basic configuration Show commands Clear commands Understand the attributes Understand the decision algorithm 2 Printed
TROUBLESHOOTING AND ADVANCED BGP SESSION 1 Assumptions BGP operational experience Basic configuration Show commands Clear commands Understand the attributes Understand the decision algorithm 2 Printed
MD5 Authentication Between BGP Peers Configuration Example
 MD5 Authentication Between BGP Peers Configuration Example Document ID: 112188 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
MD5 Authentication Between BGP Peers Configuration Example Document ID: 112188 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram
Border Gateway Protocol - BGP
 BGP Fundamentals Border Gateway Protocol - BGP Runs over TCP (port 179) TCP connection required before BGP session Need to be reachable! Path vector routing protocol Best path selection based on path attributes
BGP Fundamentals Border Gateway Protocol - BGP Runs over TCP (port 179) TCP connection required before BGP session Need to be reachable! Path vector routing protocol Best path selection based on path attributes
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Configuring a BGP Route Server
 BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP for Internet Service Providers
 BGP for Internet Service Providers Philip Smith Seoul KIOW 2002 1 BGP current status RFC1771 is quite old, and no longer reflects current operational practice nor vendor implementations
BGP for Internet Service Providers Philip Smith Seoul KIOW 2002 1 BGP current status RFC1771 is quite old, and no longer reflects current operational practice nor vendor implementations
BGP Enhancements for IPv6. ISP Training Workshops
 BGP Enhancements for IPv6 ISP Training Workshops Adding IPv6 to BGP RFC4760 Defines Multi-protocol Extensions for BGP4 Enables BGP to carry routing information of protocols other than IPv4 e.g. MPLS, IPv6,
BGP Enhancements for IPv6 ISP Training Workshops Adding IPv6 to BGP RFC4760 Defines Multi-protocol Extensions for BGP4 Enables BGP to carry routing information of protocols other than IPv4 e.g. MPLS, IPv6,
CertifyMe. CertifyMe
 CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Introduction. Keith Barker, CCIE #6783. YouTube - Keith6783.
 Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics. 30 September :00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Revision: 2.0
 APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
Monitoring BGP. Configuring the Router
 You have to be extra careful if the prefix you want to announce over BGP is already present in the global routing table. This happens in the situation where your ISP announced your address block but you
You have to be extra careful if the prefix you want to announce over BGP is already present in the global routing table. This happens in the situation where your ISP announced your address block but you
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing. Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
CCIE R&Sv5 Mock Lab 1 Mohamed Jaziri 3xCCIE P a g e 1
 CCIE R&Sv5 Mock Lab 1 Mohamed Jaziri 3xCCIE P a g e 1 Ticket 3 - BGP Traffic Engineering R18 of the Large Office 1 must be able to reach 4 BGP networks located behind R100 in the Internet SP (AS 10000).
CCIE R&Sv5 Mock Lab 1 Mohamed Jaziri 3xCCIE P a g e 1 Ticket 3 - BGP Traffic Engineering R18 of the Large Office 1 must be able to reach 4 BGP networks located behind R100 in the Internet SP (AS 10000).
BGP Route Reflector Commands
 This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
BGP Attributes and Path Selection
 BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP Table Version. Contents. Introduction. Network Diagram. Best Path
 BGP Table Version Document ID: 116511 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Sep 30, 2013 Contents Introduction Network Diagram Best Path Types of Table Versions Initial Table Version Number
BGP Table Version Document ID: 116511 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Sep 30, 2013 Contents Introduction Network Diagram Best Path Types of Table Versions Initial Table Version Number
Configuring a Basic BGP Network
 Configuring a Basic BGP Network This module describes the basic tasks to configure a basic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network. BGP is an interdomain routing protocol that is designed to provide loop-free
Configuring a Basic BGP Network This module describes the basic tasks to configure a basic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network. BGP is an interdomain routing protocol that is designed to provide loop-free
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Scaling Techniques
 BGP Scaling Techniques ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated
BGP Scaling Techniques ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Rev External BGP
 Rev. 00.. External BGP c c n a c o o k b o o k. c o m C O N C E P T S AS (Autonomous System) A network under a single administrative control, like a single company or a single ISP. ASN (AS Number) used
Rev. 00.. External BGP c c n a c o o k b o o k. c o m C O N C E P T S AS (Autonomous System) A network under a single administrative control, like a single company or a single ISP. ASN (AS Number) used
BGP Scaling Techniques
 BGP Scaling Techniques 1 BGP Scaling Techniques Original BGP specification and implementation was fine for the Internet of the early 1990s But didn t scale Issues as the Internet grew included: Scaling
BGP Scaling Techniques 1 BGP Scaling Techniques Original BGP specification and implementation was fine for the Internet of the early 1990s But didn t scale Issues as the Internet grew included: Scaling
Configuring BGP. Cisco s BGP Implementation
 Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
LACNIC XIII. Using BGP for Traffic Engineering in an ISP
 LACNIC XIII Using BGP for Traffic Engineering in an ISP Program Using BGP Attributes Implementing IBGP Implementing EBGP Emphasis in Stability, Scalability and Configuration Examples BGP Review Why use
LACNIC XIII Using BGP for Traffic Engineering in an ISP Program Using BGP Attributes Implementing IBGP Implementing EBGP Emphasis in Stability, Scalability and Configuration Examples BGP Review Why use
Configuring basic MBGP
 Contents Configuring MBGP 1 MBGP overview 1 Protocols and standards 1 MBGP configuration task list 1 Configuring basic MBGP 2 Controlling route advertisement and reception 2 Configuration prerequisites
Contents Configuring MBGP 1 MBGP overview 1 Protocols and standards 1 MBGP configuration task list 1 Configuring basic MBGP 2 Controlling route advertisement and reception 2 Configuration prerequisites
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) structure of the Internet Tier 1 ISP Tier 1 ISP Google
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) structure of the Internet Tier 1 ISP Tier 1 ISP Google
Troubleshooting High CPU Caused by the BGP Scanner or BGP Router Process
 Troubleshooting High CPU Caused by the BGP Scanner or BGP Router Process Document ID: 107615 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Understanding BGP Processes
Troubleshooting High CPU Caused by the BGP Scanner or BGP Router Process Document ID: 107615 Contents Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Understanding BGP Processes
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
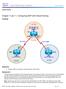 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
2015/07/23 23:32 1/8 More ibgp and Basic ebgp
 2015/07/23 23:32 1/8 More ibgp and Basic ebgp More ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Connect your ISP to a Transit provider and the Internet Exchange Point using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
2015/07/23 23:32 1/8 More ibgp and Basic ebgp More ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Connect your ISP to a Transit provider and the Internet Exchange Point using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
Protecting an EBGP peer when memory usage reaches level 2 threshold 66 Configuring a large-scale BGP network 67 Configuring BGP community 67
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Techniques for ISP. Terutaka Komorizono
 BGP Techniques for ISP Terutaka Komorizono Introduction Presentation has many configuration examples Using Cisco IOS CLI Aimed at Service Providers Techniques can be used by many enterprises
BGP Techniques for ISP Terutaka Komorizono Introduction Presentation has many configuration examples Using Cisco IOS CLI Aimed at Service Providers Techniques can be used by many enterprises
BGP route filtering and advanced features
 2015/07/23 23:33 1/13 BGP route filtering and advanced features BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings
2015/07/23 23:33 1/13 BGP route filtering and advanced features BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings
BGP Dynamic Neighbors
 BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
Configuring BGP community 43 Configuring a BGP route reflector 44 Configuring a BGP confederation 44 Configuring BGP GR 45 Enabling Guard route
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Configuring Advanced BGP
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure advanced features of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on the Cisco NX-OS switch. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About Advanced
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure advanced features of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) on the Cisco NX-OS switch. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About Advanced
Table of Contents 1 MBGP Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 MBGP Configuration 1-1 MBGP Over 1-1 Protocols and Standards 1-2 MBGP Configuration Task List 1-2 Configuring MBGP Basic Functions 1-2 Prerequisites 1-2 Configuration Procedure 1-3
Table of Contents 1 MBGP Configuration 1-1 MBGP Over 1-1 Protocols and Standards 1-2 MBGP Configuration Task List 1-2 Configuring MBGP Basic Functions 1-2 Prerequisites 1-2 Configuration Procedure 1-3
Multihoming Complex Cases & Caveats
 Multihoming Complex Cases & Caveats ISP Workshops Last updated 6 October 2011 Complex Cases & Caveats p Complex Cases n Multiple Transits n Multi-exit backbone n Disconnected Backbone n IDC Multihoming
Multihoming Complex Cases & Caveats ISP Workshops Last updated 6 October 2011 Complex Cases & Caveats p Complex Cases n Multiple Transits n Multi-exit backbone n Disconnected Backbone n IDC Multihoming
Operation Manual BGP. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 BGP/MBGP Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to BGP... 1-1 1.1.2 BGP Message Types... 1-2 1.1.3 BGP Routing Mechanism... 1-2 1.1.4 MBGP... 1-3 1.1.5 BGP Peer
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 BGP/MBGP Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to BGP... 1-1 1.1.2 BGP Message Types... 1-2 1.1.3 BGP Routing Mechanism... 1-2 1.1.4 MBGP... 1-3 1.1.5 BGP Peer
BGP Support for 4-byte ASN
 The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
BGP Protocol & Configuration. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008
 BGP Protocol & Configuration Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Case Study 1, Exercise 1: Single upstream Part 6: BGP Protocol Basics Part 7: BGP Protocol - more
BGP Protocol & Configuration Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Case Study 1, Exercise 1: Single upstream Part 6: BGP Protocol Basics Part 7: BGP Protocol - more
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands
 Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Q&As. CCIP Configuring BGP on Cisco Routers (BGP) Pass Cisco Exam with 100% Guarantee
 642-661 Q&As CCIP Configuring BGP on Cisco Routers (BGP) Pass Cisco 642-661 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee 100% Money Back
642-661 Q&As CCIP Configuring BGP on Cisco Routers (BGP) Pass Cisco 642-661 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee 100% Money Back
BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments
 BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments Note: Refer to this sheet for your IP assignments throughout the BGP lab exercises. Anatomy of a BGP Configuration ip bgp-community new-format router bgp 3582
BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments Note: Refer to this sheet for your IP assignments throughout the BGP lab exercises. Anatomy of a BGP Configuration ip bgp-community new-format router bgp 3582
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
BGP Multi-homing Design and Troubleshooting. Manigandan Ganesan
 BGP Multi-homing Design and Troubleshooting Manigandan Ganesan Thank You for Joining Us Today The Live Ask the Expert Event Will Begin at 10:00 am Pacific Time 2 Thank You for Joining Us Today Before We
BGP Multi-homing Design and Troubleshooting Manigandan Ganesan Thank You for Joining Us Today The Live Ask the Expert Event Will Begin at 10:00 am Pacific Time 2 Thank You for Joining Us Today Before We
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Contents. BGP commands 1
 Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
Multiprotocol BGP (MBGP)
 Multiprotocol BGP (MBGP) Module 5 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Copyright 1998-2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Module5.ppt 1 Module Objectives Understand that MBGP is NOT a replacement for PIM Understand the basic
Multiprotocol BGP (MBGP) Module 5 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Copyright 1998-2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. Module5.ppt 1 Module Objectives Understand that MBGP is NOT a replacement for PIM Understand the basic
BGP. Autonomous system (AS) BGP version 4
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam March 11, 2008 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers, Customers and Peers External
BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam March 11, 2008 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers, Customers and Peers External
BGP Nonstop Routing was made a default feature.
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that allows you to create loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems. An autonomous system is a set of routers under a
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that allows you to create loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems. An autonomous system is a set of routers under a
BGP. Autonomous system (AS) BGP version 4
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.5, 2011/03/06 13:35:28) Monday, March 7, 2011 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers,
BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.5, 2011/03/06 13:35:28) Monday, March 7, 2011 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers,
BGP. Autonomous system (AS) BGP version 4
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.3, 2010/03/10 20:05:02) Monday, March 8, 2010 General ideas behind BGP Background
BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.3, 2010/03/10 20:05:02) Monday, March 8, 2010 General ideas behind BGP Background
Configuring Internal BGP Features
 This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
Configuration prerequisites 45 Configuring BGP community 45 Configuring a BGP route reflector 46 Configuring a BGP confederation 46 Configuring BGP
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands
 Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands NOTE: This chapter describes commands in the BGP configuration level, which is present on HP devices that support IPv4 only. For information about BGP commands and configuration
Chapter 17 BGP4 Commands NOTE: This chapter describes commands in the BGP configuration level, which is present on HP devices that support IPv4 only. For information about BGP commands and configuration
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
Module 8 Multihoming Strategies Lab
 Module 8 Multihoming Strategies Lab Objective: Introduction to routing policy, the manipulation of BGP attributes to control traffic flow in a multihomed network. Prerequisite: Module 6 and 7 Topology
Module 8 Multihoming Strategies Lab Objective: Introduction to routing policy, the manipulation of BGP attributes to control traffic flow in a multihomed network. Prerequisite: Module 6 and 7 Topology
IP NAT Troubleshooting. Solutions. Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527
 IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
IP NAT Troubleshooting Solutions Luke Bibby, CCIE #45527 Quick Overview of Scenario Solutions Scenario #1 R2 s E0/0 should be NAT inside not NAT outside ACL 100 is configured incorrectly NAT policy missing
BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
BGP-4 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Primer
 BGP-4 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Primer Diarmuid Ó Briain Last updated: 18 April 2017 2 Routing primer 2017 by C²S Consulting Policies made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial
BGP-4 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Primer Diarmuid Ó Briain Last updated: 18 April 2017 2 Routing primer 2017 by C²S Consulting Policies made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial
Multihoming with BGP and NAT
 Eliminating ISP as a single point of failure www.noction.com Table of Contents Introduction 1. R-NAT Configuration 1.1 NAT Configuration 5. ISPs Routers Configuration 3 15 7 7 5.1 ISP-A Configuration 5.2
Eliminating ISP as a single point of failure www.noction.com Table of Contents Introduction 1. R-NAT Configuration 1.1 NAT Configuration 5. ISPs Routers Configuration 3 15 7 7 5.1 ISP-A Configuration 5.2
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
BGP Tutorial. APRICOT 2004, Kuala Lumpur February Philip Smith APRICOT , Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 BGP Tutorial Philip Smith , Kuala Lumpur February 2004 1 APRICOT BGP Tutorials Two Tutorials Part 1 Introduction Part 2 Multihoming Morning Afternoon 2 BGP Tutorial Part 1 Introduction Philip
BGP Tutorial Philip Smith , Kuala Lumpur February 2004 1 APRICOT BGP Tutorials Two Tutorials Part 1 Introduction Part 2 Multihoming Morning Afternoon 2 BGP Tutorial Part 1 Introduction Philip
BGP. Autonomous system (AS) BGP version 4. Definition (AS Autonomous System)
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.9, 2012/03/14 10:21:22) Monday, March 12, 2012 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers,
BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 1.9, 2012/03/14 10:21:22) Monday, March 12, 2012 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers,
Lecture 07c Routing Border Gateway Protocol
 BSc in Telecommunications Engineering TEL3214 Computer Communication Networks Lecture 07c Routing Border Gateway Protocol Eng Diarmuid O'Briain, CEng, CISSP 7c-2 TEL3214 - Computer Communication Networks
BSc in Telecommunications Engineering TEL3214 Computer Communication Networks Lecture 07c Routing Border Gateway Protocol Eng Diarmuid O'Briain, CEng, CISSP 7c-2 TEL3214 - Computer Communication Networks
Configuring BGP on Cisco Routers Volume 1
 Volume 1 I. Course Introduction A. Overview/Learner Skills and Knowledge B. Course Flow C. Additional References 1. Cisco Glossary of Terms D. Your Training Curriculum II. BGP Overview III. Introducing
Volume 1 I. Course Introduction A. Overview/Learner Skills and Knowledge B. Course Flow C. Additional References 1. Cisco Glossary of Terms D. Your Training Curriculum II. BGP Overview III. Introducing
BGP. Autonomous system (AS) BGP version 4. Definition (AS Autonomous System)
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol A short introduction Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 18.3, 2018/12/03 13:53:22) Tuesday, December 4, 2018 General ideas behind BGP Background
BGP Border Gateway Protocol A short introduction Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 18.3, 2018/12/03 13:53:22) Tuesday, December 4, 2018 General ideas behind BGP Background
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature
 IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4
 Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4 This chapter provides details on how to configure Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP4) on HP products using the CLI and the Web management interface. BGP4 is supported on
Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4 This chapter provides details on how to configure Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP4) on HP products using the CLI and the Web management interface. BGP4 is supported on
BGP can also be used for carrying routing information for IPv6 prefix over IPv6 networks.
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Border Gateway Protocol (). About, page 1 Guidelines for, page
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Border Gateway Protocol (). About, page 1 Guidelines for, page
BGP. Border Gateway Protocol A short introduction. Karst Koymans. Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam. (version 18.3, 2018/12/03 13:53:22)
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol A short introduction Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 18.3, 2018/12/03 13:53:22) Tuesday, December 4, 2018 Karst Koymans (UvA) BGP Tuesday,
BGP Border Gateway Protocol A short introduction Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 18.3, 2018/12/03 13:53:22) Tuesday, December 4, 2018 Karst Koymans (UvA) BGP Tuesday,
This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics:
 Appendix C BGP Supplement This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics: BGP Route Summarization Redistribution with IGPs Communities Route
Appendix C BGP Supplement This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics: BGP Route Summarization Redistribution with IGPs Communities Route
Service Provider Multihoming
 Service Provider Multihoming ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last
Service Provider Multihoming ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last
BGP. Autonomous system (AS) BGP version 4. Definition (AS Autonomous System)
 BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 310, 2014/03/11 10:50:06) Monday, March 10, 2014 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers,
BGP Border Gateway Protocol (an introduction) Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 310, 2014/03/11 10:50:06) Monday, March 10, 2014 General ideas behind BGP Background Providers,
Table of Contents. BGP Configuration 1
 Table of Contents BGP Configuration 1 BGP Overview 1 Formats of BGP Messages 2 BGP Path Attributes 5 BGP Route Selection 9 ibgp and IGP Synchronization 11 Settlements for Problems in Large Scale BGP Networks
Table of Contents BGP Configuration 1 BGP Overview 1 Formats of BGP Messages 2 BGP Path Attributes 5 BGP Route Selection 9 ibgp and IGP Synchronization 11 Settlements for Problems in Large Scale BGP Networks
Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
BGP Part-1.
 BGP Part-1 www.ine.com Comparison between IGPs & BGP» Similarities and differences between BGP and IGPs (OSPF and EIGRP): BGP needs to form neighborship like IGPs. BGP needs to advertise prefixes, just
BGP Part-1 www.ine.com Comparison between IGPs & BGP» Similarities and differences between BGP and IGPs (OSPF and EIGRP): BGP needs to form neighborship like IGPs. BGP needs to advertise prefixes, just
Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
BGP Multihoming Techniques
 BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith , Oakland 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Presentation Slides Available on NANOG Web site www.nanog.org/mtg-0110/smith.html Available
BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith , Oakland 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Presentation Slides Available on NANOG Web site www.nanog.org/mtg-0110/smith.html Available
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Advanced Multihoming. BGP Traffic Engineering
 Advanced Multihoming BGP Traffic Engineering 1 Service Provider Multihoming Previous examples dealt with loadsharing inbound traffic Of primary concern at Internet edge What about outbound traffic? Transit
Advanced Multihoming BGP Traffic Engineering 1 Service Provider Multihoming Previous examples dealt with loadsharing inbound traffic Of primary concern at Internet edge What about outbound traffic? Transit
