South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
|
|
|
- Tamsin Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga Miguel Baptista Simon Muyal
2 Laboratory Exercise: Multiprotocol BGP configuration Objectives In this laboratory exercise you will complete the following tasks: Establish IPv6 unicast BGP sessions; Check the exchanged routing information and perform application-level tests towards addresses received from the BGP sessions; Filter routes announced and received through peerings. 2/16
3 Visual Objective The following figure shows the configuration of the current laboratory Router #1 Router #2 AS 100 AS200 AS300 Router #3 Multiprotocol BGP Router #4 AS400 AS500 AS600 Router #5 Router #6 Figure 1 - Multiprotocol BGP 3/16
4 Setup/Scenario There will be 4 students per router. The distribution will be the same as in the previous exercise. All routers will run an ebgp process and each one will belong to a different AS, peering with two or three neighbours, according to the topology. 2001:DB8:CAFE:A::/64 LAB Address Space 2001:DB8:CAFE::/ /16 Router #1 Router #2 ::1 2001:DB8:CAFE:12::/64 ::1 ::2 ::2 2001:DB8:CAFE:B::/64 ::1 ::2 2001:DB8:CAFE:13::/64 Router #3 2001:DB8:CAFE:23::/64 ::3 ::3 ::3 ::3 2001:DB8:CAFE:C::/ :DB8:CAFE:34::/ :DB8:CAFE:D::/64 ::4 ::4 2001:DB8:CAFE:45::/64 ::4 Router #4 ::4 2001:DB8:CAFE:46::/ :DB8:CAFE:E::/64 Router #5 Router #6 ::6 ::5 2001:DB8:CAFE:56::/64 ::5 ::5 ::6 ::6 2001:DB8:CAFE:F::/64 Figure 2 Scenario Topology Preparing the LAB If your router is not yet configured, load the configuration from the flash memory: RouterX# copy flash:initv6-config running-config RouterX# wr 4/16
5 Router 1: Bellow you ll find one table per router with the different addresses for each of the router s interface: Interface IPv6 Address FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:12::1 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:13::1 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:A::1 /64 Router 2: Table 1: Addresses for each interface on router 1 Interface IPv6 Address FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:12::2 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:23::2 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:B::2 /64 Router 3: Table 2: Addresses for each interface on router 2 Interface IPv6 Address FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:13::3 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:23::3 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:34::3 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:C::3 /64 Router 4: Table 3: Addresses for each interface on router 3 Interface IPv6 Address FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:34::4 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:45::4 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:46::4 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:D::4 /64 Router 5: Table 4: Addresses for each interface on router 4 5/16
6 Interface IPv6 Address FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:45::5 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:56::5 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:E::5 /64 Table 5: Addresses for each interface on router 5 Router 6: Interface IPv6 Address FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:46::6 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:56::6 /64 FastEthernet :DB8:CAFE:F::6 /64 Table 6: Addresses for each interface on router 6 6/16
7 Task 1: Enabling the MBGP Complete the following steps for creating a MBGP process on your router. Step 1: Testing connectivity Connect to your router. Use the IPv6 auto configuration and plug your PC to a FastEthernet port on the router and telnet to it. The first step you must do is to see if your router has IPv6 routing active. The global ipv6 unicast-routing command should appear in the configuration. Try to ping another router that is not directly connected you yours. Step 2: Configuring the BGP process and router ID Configure the ebgp main process on your router. Remember that in the case of MBGP you will have to create an IPv6 address family and configure a BGP router ID. (Tip: router bgp <as_number> address-fammily ) Also note, that if you don t have any IPv4 addresses on your router, you must configure a router ID, or your BGP process will not start and you ll get an error message %BGP-4-NORTRID: BGP could not pick a router-id. Please configure manually.. (Tip: bgp router-id ) For your AS number, you should use the following peering table: Group AS Number Router ID Peer With AS , 200 and , 500 and Step 3: Peering with the neighbours Table 7 Peering configuration 7/16
8 Use Table 7 to check your peer routers. (Tip: neighbour X:X:X:X::X/<0-128> ) You should use the addresses directly connected to your interface. If it was ibgp you could use the loopback addresses as they would be known by you IGP. Step 4: Advertise your route Now advertise your routes to your peers. (Tip: network ) The network you should use is listed in the following table: Group Advertised Network :DB8:CAFE:1::/ :DB8:CAFE:2::/ :DB8:CAFE:3::/ :DB8:CAFE:4::/ :DB8:CAFE:5::/ :DB8:CAFE:6::/64 Table 8 Advertised Routes Step 5: Check BGP Summary See the status of your BGP process and how many routes you are receiving. (Tip: show bgp ipv6 unicast ) Note: In case you are having trouble, look at your synchronization and autosummary configuration. Step 6: Check advertised routes Look at the route you are advertising to your peer. Are they correct? (Tip: show bgp ipv6 unicast ) Step 7: Check received routes 8/16
9 Verify the routes you are receiving from your peers. Are they correct? Is the AS Path for each route correct? Elaborate a query using the regexp expression, to find routes from a neighbour not directly connected to you. Step 8: Test Application level Create a Loopback interface and configure an IPv6 address on it, according to the following table. Router 1 Advertised Network :DB8:CAFE:1::1/ :DB8:CAFE:2::1/ :DB8:CAFE:3::1/ :DB8:CAFE:4::1/ :DB8:CAFE:5::1/ :DB8:CAFE:6::1/128 Table 9 IPv6 address for loopback interface Try to ping one of these addresses. Did you succeed? Why? Step 9: Reset a BGP neighbour 9/16
10 Add another route to announce to your peer according to the following table: Group Advertised Network :DB8:CAFE:11::/ :DB8:CAFE:12::/ :DB8:CAFE:13::/ :DB8:CAFE:14::/ :DB8:CAFE:15::/ :DB8:CAFE:16::/64 Table 10 - Advertised Routes See if you are advertising the route. Now reset the BGP process. How long does it take to have the peers exchanging routes again? Perform a soft reset to the BGP process. What is the difference? Step 10: ibgp configuration With the same topology, now there will be only two Autonomous Systems. So, only router 3 and 4 will run ebgp, all others will be running only ibgp. In this case the distribution of routers to AS will be according to the following table: Group/Router Advertised Network 1, 2, 3 AS 100 4, 5, 6 AS 400 Table 11 Configuration fot two AS Which modifications do you have to do in your router s configuration? Now place all routers in the same AS. Can you ping all routers? Summary After completing these exercises, you should be able to: 10/16
11 Configure the BGP Process Debug and analyse information from the process Reset the process 11/16
12 Appendix Step 1: Testing connectivity From your PC ping the other routers or any PC from a computer not directly connected to your router. Step 2: Configuring the BGP process and router ID Configure the ebgp main process and router ID. Router3# configure terminal Router3(config)# router bgp 300 Router3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast Router3(config-router-af)# bgp router-id Step 3: Peering with the neighbours Router3(config)# router bgp 300 Router3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:13::1 remote-as 100 Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:13::1 activate Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::4 remote-as 400 Router1(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::4 activate Step 4: Advertise your routes Router3(config)# router bgp 300 Router3(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast Router3(config-router-af)# network 2001:690::/32 Step 5: Check BGP Summary Router1# show bgp ipv6 unicast summary BGP router identifier , local AS number 300 ( ) Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down Ste/PfRd 2001:DB8:CAFE:13:: :00: :DB8:CAFE:34:: :23: /16
13 Step 6: Check advertised routes Router3#show bgp ipv6 unicast nei 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::4 advertised-routes (...) Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/ :DB8:CAFE:13:: i *> 2001:DB8:CAFE:3::/64 :: i *> 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::/ :DB8:CAFE:34:: i Total number of prefixes 3 You might be having trouble and find out that your route is not being announced. If this happens, try: Router1(config-router)# no synchronization Router1(config-router)# no auto-summary Remember that you can only advertise routes that you are able to announce. So if the network you are advertising is not being used, you must force it to be up. For example, to force the route on router 3, do: Router3#(config)# ipv6 route 2001:DB8:CAFE:3::/64 Null0 Step 7: Check received routes Router4# show bgp ipv6 unicast nei 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::4 routes BGP table version is 4, local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/ :DB8:CAFE:34:: i *> 2001:DB8:CAFE:3::/ :DB8:CAFE:34:: i Total number of prefixes 2 Here you can see the routes received, the AS-Path (in bold), and check the origin of the routes. You can also filter using regular expressions. 13/16
14 Eg: filter the ones from AS 300 appears: Router4# show bgp ipv6 unicast regexp 300 (...) Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::/ :DB8:CAFE:34:: i Step 8: Test Application level Try to ping to one of the addresses. If you can t reach it, try debugging one IPv6 packet on the destination. Can you see why you are not reaching? Now, try an extended IPv6 ping using the loopback address as your origin IPv6 address. Can you ping now? Eg: Router4# ping ipv6 Target IPv6 address: 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::1 Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands? [no]: y Source address or interface: 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1 UDP protocol? [no]: Verbose? [no]: Precedence [0]: DSCP [0]: Include hop by hop option? [no]: Include destination option? [no]: Sweep range of sizes? [no]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 2001:DB8:CAFE:1::1!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/4 ms Step 9: Reset a BGP neighbour Router4# clear bgp ipv6 unicast 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::3 Router4# clear bgp ipv6 unicast 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::3 soft Step 10: ibgp configuration With ibgp you should not calculate the next-hop. So all ibgp neighbours must be configured with next-hop-self option. 14/16
15 Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:13::1 next-hop-self Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::4 next-hop-self Now try putting all routers in AS300. See if in your router you see al the routes? Do you know why? Your transit routers must reflect the addresses that they are receiving. They must be reflector routers. Eg: Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:13::1 route-reflectorclient Router3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:34::4 route-reflectorclient Some useful commands Router1(config)# alias exec bgp6 show bgp ipv6 unicast summary Debug commands debug bgp ipv6 updates debug bgp ipv6 neighbour 2001:DB8:CAFE:<Y>::1 updates in debug bgp ipv6 neighbour 2001:DB8:CAFE:<Y>::1 updates out How to Filter Announcements When receiving nothing from your peer, first you have to create the prefix list and then, apply this filter to the neighbor you wish. Eg: Router1# config term Router1(config)# ipv6 prefix-list NOTHING seq 5 deny ::/0 le 128 Router1(config)# router bgp 300 Router1(config-router)# address-family ipv6 unicast Router1(config-router-af)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:<X>::1 prefix-list NOTHING in If you have time, create a prefix-list to guarantee that you are only announcing your network 2001:DB8:CAFE:<router_number>::/64 to your neighbors. Router1(config)# ipv6 prefix-list <router_number>announce seq 5 accept 2001:DB8:CAFE:<VLAN>::/64 Router1(config)# ipv6 prefix-list < router_number >ANNOUNCE seq 10 deny ::/0 le 128 Router1(config)# router bgp <AS> 15/16
16 Router1(config-router)# neighbor 2001:DB8:CAFE:<X>::1 prefix-list <router_number > ANNOUNCE out Router1(config-router)# exit Router1(config)# exit Router1# exit 16/16
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) RIP for IPv6 Configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) RIP for IPv6 Configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06) Router Configuration #2 (continued)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Router Configuration #2 (continued) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt)
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Router Configuration #2 (continued) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt)
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands
 Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Configuration and Management of Networks 2012
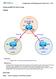 Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
NIS Workshop - Ashgabad April Routing hands-on: Local Lab
 NIS Workshop - Ashgabad 25-27 April 2007 Routing hands-on: Local Lab Piers O'Hanlon Peter Kirstein Janos Mohacsi Nikolay Pakulin
NIS Workshop - Ashgabad 25-27 April 2007 Routing hands-on: Local Lab Piers O'Hanlon Peter Kirstein Janos Mohacsi Nikolay Pakulin
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
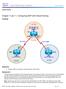 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
BGP Support for 4-byte ASN
 The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing. Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations OSPF EIGRP RIP Troubleshoot Introduction This document describes how to redistribute Internal Border
Configuring a BGP Route Server
 BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
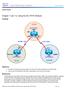 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments
 BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments Note: Refer to this sheet for your IP assignments throughout the BGP lab exercises. Anatomy of a BGP Configuration ip bgp-community new-format router bgp 3582
BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments Note: Refer to this sheet for your IP assignments throughout the BGP lab exercises. Anatomy of a BGP Configuration ip bgp-community new-format router bgp 3582
H3C BGP Configuration Examples
 H3C BGP Configuration Examples Copyright 2017 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
H3C BGP Configuration Examples Copyright 2017 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07
 Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 IPv6 Router s Configuration #2 Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Piers O'Hanlon (p.ohanlon@cs.ucl.ac.uk)
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 IPv6 Router s Configuration #2 Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Piers O'Hanlon (p.ohanlon@cs.ucl.ac.uk)
BGP on IOS: Getting Started
 BGP on IOS: Getting Started ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 IOS Good Practices p ISPs should start off with the following BGP commands as a basic template: router bgp 64511 bgp deterministic-med
BGP on IOS: Getting Started ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 IOS Good Practices p ISPs should start off with the following BGP commands as a basic template: router bgp 64511 bgp deterministic-med
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics. 30 September :00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Revision: 2.0
 APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
BGP Enhancements for IPv6. ISP Training Workshops
 BGP Enhancements for IPv6 ISP Training Workshops Adding IPv6 to BGP RFC4760 Defines Multi-protocol Extensions for BGP4 Enables BGP to carry routing information of protocols other than IPv4 e.g. MPLS, IPv6,
BGP Enhancements for IPv6 ISP Training Workshops Adding IPv6 to BGP RFC4760 Defines Multi-protocol Extensions for BGP4 Enables BGP to carry routing information of protocols other than IPv4 e.g. MPLS, IPv6,
Introduction to BGP. ISP Workshops. Last updated 30 October 2013
 Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
address-family ipv4 vrf vrf-name - Selects a per-vrf instance of a routing protocol.
 LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup LAB 2: Running OSPF between PE and CE Routers LAB 3: Running BGP between PE and CE Routers LAB 4: Overlapping VPNs LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup Introduction: Introduction
LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup LAB 2: Running OSPF between PE and CE Routers LAB 3: Running BGP between PE and CE Routers LAB 4: Overlapping VPNs LAB 1: Initial MPLS VPN Setup Introduction: Introduction
Adapted from the Synchronization example in g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html
 Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
Step 2. Manual configuration of global unicast and link-local addresses
 Lab: ICMPv6 and ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz DHCPv6 Lab. Part 1: Setup Step 1. Basics a. Log into NetLab: ccnp.bayict.cabrillo.edu
Lab: ICMPv6 and ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz DHCPv6 Lab. Part 1: Setup Step 1. Basics a. Log into NetLab: ccnp.bayict.cabrillo.edu
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting BGP Phil Smith Presentation_ID 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. 2 BGP in Large Scale Networks Scalable Stable Simple 3 Avoid the Problem in the
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting BGP Phil Smith Presentation_ID 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. 2 BGP in Large Scale Networks Scalable Stable Simple 3 Avoid the Problem in the
Configuring a Basic BGP Network
 Configuring a Basic BGP Network This module describes the basic tasks to configure a basic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network. BGP is an interdomain routing protocol that is designed to provide loop-free
Configuring a Basic BGP Network This module describes the basic tasks to configure a basic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network. BGP is an interdomain routing protocol that is designed to provide loop-free
MultiVRF Deployment Example
 MultiVRF Deployment Example BGP Session Per VRF Loopback13 192.168.1.13/32 AVPN VLAN10/VE10/RED VRF/172.16.16.2/30 VLAN11/VE11/GREEN VRF/172.16.16.6/30 VLAN13/VE13/Manage VRF/172.16.16.10/30 (2) Customer
MultiVRF Deployment Example BGP Session Per VRF Loopback13 192.168.1.13/32 AVPN VLAN10/VE10/RED VRF/172.16.16.2/30 VLAN11/VE11/GREEN VRF/172.16.16.6/30 VLAN13/VE13/Manage VRF/172.16.16.10/30 (2) Customer
Module 6 Implementing BGP
 Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Configuration and Management of Networks
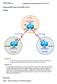 Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
Configuring BGP using the AS_PATH attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter
IPv6 Module 1c ibgp. Prerequisites: IPv6 Module 1a (OSPF) or IPv6 Module 1b (ISIS).
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1c ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with chosen IGP and one BGP AS number running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1c ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with chosen IGP and one BGP AS number running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites:
The information in this document is based on Cisco IOS Software Release 15.4 version.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Test case 1 Test case 2 Test case 3 Troubleshoot Introduction
Layer3 VPN with RIP protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
2016/09/07 08:37 1/5 Internal BGP Lab. Set up Internal BGP (ibgp) within the each Group autonomous system to carry routing information within the AS.
 2016/09/07 08:37 1/5 Internal BGP Lab Internal BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Set up Internal BGP (ibgp) within the each Group autonomous system to carry routing information within
2016/09/07 08:37 1/5 Internal BGP Lab Internal BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Set up Internal BGP (ibgp) within the each Group autonomous system to carry routing information within
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
2015/07/23 23:31 1/7 ibgp
 2015/07/23 23:31 1/7 ibgp ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with IGP and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites:
2015/07/23 23:31 1/7 ibgp ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with IGP and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites:
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 Stateless and Stateful Auto-configuration using Router Advertisements
 Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 Stateless and Stateful Auto-configuration using Router Advertisements Miguel Baptista(miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Piers O'Hanlon
Central America Workshop - Guatemala City Guatemala 30 January - 1 February 07 Stateless and Stateful Auto-configuration using Router Advertisements Miguel Baptista(miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Piers O'Hanlon
BGP Best External. Finding Feature Information
 The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp
 IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
BGP Dynamic Neighbors
 BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
LAB 5: DMVPN BGP. LAB 5: Diagram. Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M.
 LAB 5: DMVPN BGP LAB 5: Diagram Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M. LAB 5: Configure BGP over DMVPN Configuration Step 1: Enable loopback and physical interfaces
LAB 5: DMVPN BGP LAB 5: Diagram Note: This Lab was developed on Cisco IOS Version15.2(4) M1 ADVENTERPRISEK9-M. LAB 5: Configure BGP over DMVPN Configuration Step 1: Enable loopback and physical interfaces
Configure the IPv6 BGP Local Preference Feature
 Configure the IPv6 BGP Local Preference Feature Document ID: 113035 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configure the IPv6 BGP Local Preference Feature Document ID: 113035 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configurations
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP `2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job `2005,
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP `2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job `2005,
Step 1: IP Configuration: On R1: On R2: On R3: R1(config)#int s1/2 R1(config-if)#ip addr R1(config-if)#no shu
 Step 1: IP Configuration: n R1: R1(config)#int s1/2 R1(config-if)#ip addr 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shu R1(config-if)#int lo0 R1(config-if)#ip addr 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 R1(config-if)#int lo1
Step 1: IP Configuration: n R1: R1(config)#int s1/2 R1(config-if)#ip addr 12.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shu R1(config-if)#int lo0 R1(config-if)#ip addr 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 R1(config-if)#int lo1
Introduction to BGP. ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 1 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 1 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith AfNOG 2003, Kampala, Uganda
 Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith , Kampala, Uganda AfNOG2003 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/afnog2003-bgp- Troubleshooting.pdf 2 Assumptions Presentation
Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith , Kampala, Uganda AfNOG2003 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/afnog2003-bgp- Troubleshooting.pdf 2 Assumptions Presentation
Table of Contents 1 MBGP Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 MBGP Configuration 1-1 MBGP Over 1-1 Protocols and Standards 1-2 MBGP Configuration Task List 1-2 Configuring MBGP Basic Functions 1-2 Prerequisites 1-2 Configuration Procedure 1-3
Table of Contents 1 MBGP Configuration 1-1 MBGP Over 1-1 Protocols and Standards 1-2 MBGP Configuration Task List 1-2 Configuring MBGP Basic Functions 1-2 Prerequisites 1-2 Configuration Procedure 1-3
BGP Attributes and Path Selection
 BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
Configuring basic MBGP
 Contents Configuring MBGP 1 MBGP overview 1 Protocols and standards 1 MBGP configuration task list 1 Configuring basic MBGP 2 Controlling route advertisement and reception 2 Configuration prerequisites
Contents Configuring MBGP 1 MBGP overview 1 Protocols and standards 1 MBGP configuration task list 1 Configuring basic MBGP 2 Controlling route advertisement and reception 2 Configuration prerequisites
BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing
 2016/09/08 10:01 1/6 BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Apply the concepts of BGP policy learned in class to achieve the
2016/09/08 10:01 1/6 BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Apply the concepts of BGP policy learned in class to achieve the
Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
BGP Next Hop Unchanged
 BGP Next Hop Unchanged Last Updated: September 8, 2011 In an external BGP (ebgp) session, by default, the router changes the next hop attribute of a BGP route (to its own address) when the router sends
BGP Next Hop Unchanged Last Updated: September 8, 2011 In an external BGP (ebgp) session, by default, the router changes the next hop attribute of a BGP route (to its own address) when the router sends
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
BGP-4 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Primer
 BGP-4 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Primer Diarmuid Ó Briain Last updated: 18 April 2017 2 Routing primer 2017 by C²S Consulting Policies made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial
BGP-4 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Primer Diarmuid Ó Briain Last updated: 18 April 2017 2 Routing primer 2017 by C²S Consulting Policies made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial
BGP Cost Community. Prerequisites for the BGP Cost Community Feature
 The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Contents. BGP commands 1
 Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 Topology
CCIE R&Sv5 Mock Lab 1 Mohamed Jaziri 3xCCIE P a g e 1
 CCIE R&Sv5 Mock Lab 1 Mohamed Jaziri 3xCCIE P a g e 1 Ticket 3 - BGP Traffic Engineering R18 of the Large Office 1 must be able to reach 4 BGP networks located behind R100 in the Internet SP (AS 10000).
CCIE R&Sv5 Mock Lab 1 Mohamed Jaziri 3xCCIE P a g e 1 Ticket 3 - BGP Traffic Engineering R18 of the Large Office 1 must be able to reach 4 BGP networks located behind R100 in the Internet SP (AS 10000).
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network
 Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Configuring IS IS over IPv6
 Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support
 Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
DE-CIX Academy: BGP - Multihoming
 Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
Lecture 07c Routing Border Gateway Protocol
 BSc in Telecommunications Engineering TEL3214 Computer Communication Networks Lecture 07c Routing Border Gateway Protocol Eng Diarmuid O'Briain, CEng, CISSP 7c-2 TEL3214 - Computer Communication Networks
BSc in Telecommunications Engineering TEL3214 Computer Communication Networks Lecture 07c Routing Border Gateway Protocol Eng Diarmuid O'Briain, CEng, CISSP 7c-2 TEL3214 - Computer Communication Networks
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS
 CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
Lab Guide 2 - BGP Configuration
 IXP Workshop Lab Lab Guide 2 - BGP Configuration Objective: The focus of this lab is to connect 8 customers with IXP. Customers are connected with AS17821 as transit and received customer prefixes, also
IXP Workshop Lab Lab Guide 2 - BGP Configuration Objective: The focus of this lab is to connect 8 customers with IXP. Customers are connected with AS17821 as transit and received customer prefixes, also
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
AS 100 AS 300. Lab -1 Private Communities - II .1 S1/2. Task 1. On R1: / / /24. Configure the above topology.
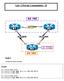 Lab -1 Private Communities - II AS 100.1 R1 S1/2 12.1.1.0/24 S1/1.2 R2 S1/3 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 23.1.1.0/24 S1/1.3 R3 S1/2 Lo0 6.6.6.0/24 Lo1 7.7.7.0/24 AS 300 Task 1 Configure the above topology. On R1:
Lab -1 Private Communities - II AS 100.1 R1 S1/2 12.1.1.0/24 S1/1.2 R2 S1/3 S1/3 13.1.1.0/24 23.1.1.0/24 S1/1.3 R3 S1/2 Lo0 6.6.6.0/24 Lo1 7.7.7.0/24 AS 300 Task 1 Configure the above topology. On R1:
Page1. Cisco IOS Software, Linux Software (I86BI_LINUX-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)M1, DEVELOPMENT TEST SOFTWARE
 BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
BGP Route Reflector Commands
 This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
Lab 2 BGP route filtering and advanced features
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Lab 2 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network concepts of Lab 1, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Lab 2 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network concepts of Lab 1, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour
Troubleshooting BGP. Philip Smith NANOG February 2007 Toronto, Ontario Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith 4-7 February 2007 Toronto, Ontario 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com /pfs/seminars/nanog39-bgp-troubleshooting.pdf And on the NANOG
Troubleshooting BGP Philip Smith 4-7 February 2007 Toronto, Ontario 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com /pfs/seminars/nanog39-bgp-troubleshooting.pdf And on the NANOG
Module 1 Device and Infrastructure Security Lab
 Module 1 Device and structure Security Lab Objective: All the routers are pre-configured with basic (No security) interface, OSPF and BGP configuration according to the following topology diagram. Create
Module 1 Device and structure Security Lab Objective: All the routers are pre-configured with basic (No security) interface, OSPF and BGP configuration according to the following topology diagram. Create
BGP Attributes and Policy Control. BGP Attributes. BGP Attributes. Agenda. What Is an Attribute? AS-Path. ISP/IXP Workshops.
 genda GP ttributes and Policy ontrol ISP/IXP Workshops GP ttributes GP Path Selection pplying Policy ISP/IXP Workshops 2000, isco Systems, Inc. 1 2 GP ttributes GP ttributes What is an attribute? S path
genda GP ttributes and Policy ontrol ISP/IXP Workshops GP ttributes GP Path Selection pplying Policy ISP/IXP Workshops 2000, isco Systems, Inc. 1 2 GP ttributes GP ttributes What is an attribute? S path
Configuring Internal BGP Features
 This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
IPv6 Module 7 BGP Route Filtering and Advanced Features
 IPv6 Module 7 BGP Route Filtering and Advanced Features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour filtering and more
IPv6 Module 7 BGP Route Filtering and Advanced Features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 6, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate neighbour filtering and more
Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 (IS-IS)
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites: Module 1 (IS-IS)
This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics:
 Appendix C BGP Supplement This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics: BGP Route Summarization Redistribution with IGPs Communities Route
Appendix C BGP Supplement This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics: BGP Route Summarization Redistribution with IGPs Communities Route
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with.
 Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Static Routing 2.
Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Static Routing 2.
Module 1b IS-IS. Prerequisites: The setup section of Module 1. The following will be the common topology used for the first series of labs.
 Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
Module 1b IS-IS Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one IS-IS Area. Ensure that all routers, interfaces, cables and connections are working properly. Prerequisites: The setup section
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008
 Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008 Background Why? How? Problems encountered? What next? 7 PoP sites 29 Connected Sites Including Kent Schools Network 5 HE s KM Core BT wavestream circuits (DWDM) 2.5Gbps
Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008 Background Why? How? Problems encountered? What next? 7 PoP sites 29 Connected Sites Including Kent Schools Network 5 HE s KM Core BT wavestream circuits (DWDM) 2.5Gbps
