Authorized CCNP. Student. LabManual SWITCH.
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Authorized CCNP SWITCH Student LabManual Web:
2 Authorized CCNPSWITCHWORKBOOK Module:01to20 CopyrightsNetworkersHome Page2of40
3 Lab 1- VTP, Trunking, VLANs and Inter- VLAN Routing R5 F 0/0 (.5) /24 VLAN 10 F 0/0.1 (.1) R1 F 0/0.2 (.1) /24 VLAN 20 F0/0.1 (.3) R /24 VLAN 30 F0/0.2 (.3) F 0/0 (.4) VLAN 30 (.15) R /24 VLAN 40 VLAN 40 (.15) F 0/0 (.2) R2 Task 1 Configure the Switches with Hostnames of and SW2 respectively. Hostname SW2 Hostname SW2 Page 3 of 40
4 Task 2 Configure both switches to be in a VTP Domain CISCO. should be configured as a Server and SW2 as a Client. VTP domain CISCO VTP mode Server SW2 VTP domain CISCO VTP mode client Task 3 The CISCO VTP Domain should be password protected using NETMET as the Password. VTP password NETMET SW2 VTP password NETMET Task 4 Configure Trunking between and SW2 on all ports that connect the switches to each other. Use an Industry standard encapsulation mechanism. Interface Range F0/XX Fast0/YY Switchport Trunk Encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk SW2 Interface Range F0/XX Fast0/YY Switchport Trunk Encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk Task 5 Create VLAN s based on the Diagram. Assign the appropriate ports to the appropriate VLAN s based on the Logical Diagram. Use an industry standard encapsulation wherever required. VLAN 10 VLAN 20 VLAN 30 VLAN 40 interface F0/1, F0/3 Switchport Trunk Encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk interface F0/2 Switchport access vlan 40 Page 4 of 40
5 Switchport mode access Interface F0/4 Switchport access vlan 30 Switchport mode access Interface F0/5 Switchport access vlan 10 Switchport mode access Task 6 Configure the Routers and with the Appropriate IP addresses based on the Logical Diagram. R1 Interface F 0/0 No shut Interface F 0/0.1 Encapsulation dot1q 10 IP Address Interface F0/0.2 Encapsulation dot1q 20 IP Address R3 Interface F 0/0 No shut Interface F 0/0.1 Encapsulation dot1q 20 IP Address Interface F0/0.2 Encapsulation dot1q 30 IP Address R5 R2 Interface F 0/0 IP Address No shut R4 Interface F 0/0 IP Address No shut Interface F 0/0 IP Address No shut IP Routing Interface VLAN 30 IP Address Page 5 of 40
6 Interface VLAN 40 IP Address Task 7 Configure a Loopback 0 interface on each Rotuer with an IP Address of X.X.X.X/8 (where X is the Router # - R1=1, R2=2.). Loopback 0 on as /8. Run RIP v2 on all the routers and such that all networks are reachable from all devices. R1 Interface Loopback 0 IP Address Router RIP Version 2 No auto-summary Network Network Network R3 Interface Loopback 0 IP Address Router RIP Version 2 No auto-summary Network Network Network R5 Interface Loopback 0 IP Address Router RIP Version 2 No auto-summary Network Network R2 Interface Loopback 0 IP Address Router RIP Version 2 No auto-summary Network Network R4 Interface Loopback 0 IP Address Router RIP Version 2 No auto-summary Network Network Interface Loopback 0 IP Address Router RIP Version 2 No auto-summary Network Network Network Page 6 of 40
7 Lab 2 Configuring Etherchannels Task 1 Configure the Trunk Ports connecting and SW2 to be part of an Etherchannel. The Etherchannel should use an Industry standard protocol. Inteface F0/XX, F0/YY Channel-group 1 mode active SW2 Inteface F0/XX, F0/YY Channel-group 1 mode active Task 2 Configure the Load Balancing mechanism method to be done based on a combination of the Source and Destination IP. Port-channel load-balance src-dst-ip SW2 Port-channel load-balance src-dst-ip Task 3 Verify the Etherchannel status. Show etherchannel 1 port-channel Port-channels in the group: Port-channel: Po1 (Primary Aggregator) Age of the Port-channel = 00d:00h:01m:09s Logical slot/port = 1/0 Number of ports = 0 HotStandBy port = null Port state = Port-channel Ag-Not-Inuse Protocol = LACP Page 7 of 40
8 Explanation: An EtherChannel consists of individual Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet links bundled into a single logical link. If a link within an EtherChannel fails, traffic previously carried over that failed link changes to the remaining links within the EtherChannel. A trap is sent for a failure, identifying the switch, the EtherChannel, and the failed link. Inbound broadcast and multicast packets on one link in an EtherChannel are blocked from returning on any other link of the EtherChannel. NOTE: All interfaces in each Etherchannel must be the same speed and duplex, same trunking encapsulation or the same access vlan ID, also the STP cost for each port must be the same and none of the Etherchannel ports can be involved in SPAN, RSPAN configuration or neither 802.1X. Understanding Port-Channel Interfaces You create an EtherChannel for Layer 2 interfaces differently from Layer 3 interfaces. Both configurations involve logical interfaces. With Layer 3 interfaces, you manually create the logical interface by using the interface port-channel global configuration command. With Layer 2 interfaces, the logical interface is dynamically created. With both Layer 3 and 2 interfaces, you manually assign an interface to the EtherChannel by using the channel-group interface configuration command. This command binds the physical and logical ports together An Etherchannel cannot be configured in both the PAgP and LACP modes. Page 8 of 40
9 Lab 3 Configuring MSTP Task 1 Disable the Etherchannel configured in the previous lab on and SW2 to test MSTP. Inteface F0/XX, F0/YY No Channel-group 1 mode active SW2 Inteface F0/XX, F0/YY No Channel-group 1 mode active Task 2 Configure Multi-instance of Spanning Tree on the switches as follows: There should be two instances of STP, instance 1 and 2 Instance 1 should handle VLANs 10 and 20 Instance 2 should handle VLAN 30 and 40 should be the root bridge for the first instance SW2 should be the root bridge for the second instance MST configuration should use the following: o Name : CISCO o Revision : 1 Instance 1 should use the lower Trunk Interface as the Primary forwarding port Instance 2 should use the lower Trunk Interface as the Primary forwarding port Spanning-tree mode mst Spanning-tree mst configuration Revision 1 Name CISCO Instance 1 vlan 10,20 Instance 2 vlan 30,40 Spanning-tree mst 1 priority 0 Spanning-tree mst 2 priority 4096 Int F0/XX Spanning-tree mst 1 port-priority 0 SW2 Spanning-tree mode mst Spanning-tree mst configuration Revision 1 Name CISCO Instance 1 vlan 10,20 Instance 2 vlan 30,40 Spanning-tree mst 1 priority 4096 Spanning-tree mst 2 priority 0 Int F0/YY Spanning-tree mst 1 port-priority 0 Page 9 of 40
10 Lab 4 Configuring SPAN/RSPAN Task 1 There is a protocol analyzer connected to SW2 port F0/18. You received a request to monitor and analyze all packets for port F0/16 on, configure the switches to accommodate this request. Vlan 90 Remote-span Monitor session 1 source interface F0/16 Monitor session 1 destination remote vlan 90 SW2 Monitor session 1 source vlan 90 Monitor session 1 destination interface F 0/18 Page 10 of 40
11 Lab 5 Configuring VLAN ACLs (VACL) Task 1 You have been requested to implement the following policy on : Deny IGMP in VLAN 10 Deny TFTP in VLAN 20 Deny ICMP and TFTP in VLAN 30 There is a MAC address trying to attack VLAN 40. Block this MAC address from accessing any device in VLAN 40. Access-list 101 permit igmp any any Access-list 102 permit udp any any eq 69 Access-list 103 permit igmp any any Access-list 103 permit udp any any eq 69 Mac access-list extended MAC-ACL Permit host any Vlan access-map VLAN10 10 Match ip addr 101 Action drop Vlan access-map VLAN Vlan access-map VLAN20 10 Match ip addr 102 Action drop Vlan access-map VLAN Vlan access-map VLAN30 10 Match ip addr 103 Action drop Vlan access-map VLAN Vlan access-map VLAN40 10 Match mac address MAC-ACL Page 11 of 40
12 Action drop Vlan access-map VLAN Vlan filter VLAN10 vlan-list 10 Vlan filter VLAN20 vlan-list 20 Vlan filter VLAN30 vlan-list 30 Vlan filter VLAN40 vlan-list 40 Page 12 of 40
13 Lab 6 Configuring Port Security Task 1 Configure VLAN 50 on. Configure Ports F 0/3 and F0/4 on SW2 in VLAN 50. Configure SW2 such that only R3 F 0/1 and R4 F 0/1 can connect to ports F 0/3 and F0/4 on SW2 respectively. If another port tries to connect to these ports, the ports should be error disabled. VLAN 50 SW2 Interface F 0/3 Switchport mode access Switchport access vlan 50 Switchport port-security Switchport port-security mac xxxx.xxxx.xxxx Interface F 0/4 Switchport mode access Switchport access vlan 50 Switchport port-security Switchport port-security mac xxxx.xxxx.xxxx Task 2 Configure F 0/5 F 0/8 in VLAN 50 on SW2. Enable Port Security for these ports such that only 1 MAC address can be connected to them. You would like to learn the MAC address dynamically. SW2 Int range F 0/5 F 0/8 Switchport mode access Switchport access vlan 50 Switchport port-security Switchport port-security mac-address sticky Task 3 Configure F 0/15 also in VLAN 50 on SW2. Enable Port security for these ports such that 5 MAC addresses can be connected to this port. The first 2 MAC addresses that are allowed to connect are AB12 and AB13. The remaining 3 can be learned dynamically. Page 13 of 40
14 SW2 Int F 0/15 Switchport mode access Switchport access vlan 50 Switchport port-security Switchport port-security max 5 Switcport port-security mac-address AB12 Switcport port-security mac-address AB13 Switcport port-security mac-address sticky Page 14 of 40
15 Lab 7 Regular and Smart Macros Task 1 Configure switchports on that connect to R2, R4 and R5 as Regular Macro with a name of RP. Define interface-range RP F0/2, F 0/4, F0/5 The above command defines a range of ports on the switch and names them Router-Ports, in some documentation this is referred to as a regular macro Task 2 Configure the RP Ports with Port Security. should learn the MAC addresses dynamically. Use a Smart Macro to accomplish this task. Macro name Port-Secure switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security mac-address Interface range macro RP Macro apply Port-Secure The above configuration configures a smartport macro. A smartport macro is started by the Macro name command and then followed by an arbitrary name that is assigned to the macro. Once that command is entered, a message is displayed in the next command line. This message tells us to use sign in order to end this macro. To run the Macro, use the Macro Apply command under the interface. Page 15 of 40
16 Task 1 The PCs that are connected or will be connected to ports F0/17 18 should get authenticated before they are allowed access to the network. These PC s belong to VLAN 40. This authentication should use a RADIUS server located at using cisco as the key. Aaa new-model aaa authentication dot1x default group radius Dot1x system-auth-control Interface range F 0/17 18 Switch mode access Swithcport access vlan 40 Dot1x port-control auto Task 2 If the PC does not support Dot1X authentication, it should be put into VLAN 60. If the user fails authentication, it should be put into VLAN 61. Lab 8 Configuring Dot1X Authentication VLAN 60 VLAN 61 Interface range F 0/17 18 Dot1x guest-vlan 60 Dot1x auth-fail vlan 61 Page 16 of 40
17 Lab 9 Configuring Storm Control Task 1 Configure SW2 port F0/14 such that broadcast and multicast traffic do not use more than 50% of the Interface bandwidth. SW2 Interface F0/14 Storm-control broadcast level Storm-control multicast level Page 17 of 40
18 Lab 10 Configuring QinQ Tunneling Interface IP Address Configuration SW3 (Customer Switch) SInterfSWace IP Address Subnet Mask Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Int SVI Int SVI SW4 (Customer Switch) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Int SVI Int SVI Task 1 Only Keep 1 Trunk link up between the switches. Also, make sure only the following links are up: SW3 SW2 SW2 SW4 Page 18 of 40
19 Interface range F0/X Y Shutdown Description All trunk ports on Interface range F 0/A, F 0/B No shutdown Description One Trunk each towards SW2 and SW3 SW2 Interface range F0/X Y Shutdown Description All trunk ports on SW2 Interface range F 0/A, F 0/B No shutdown Description One Trunk each towards and SW4 SW3 Interface range F0/X Y Shutdown Description All trunk ports on SW3 Interface F 0/A No shutdown Description One Trunk link towards SW4 Interface range F0/X Y Shutdown Description All trunk ports on SW4 Interface F 0/A No shutdown Description One Trunk link towards SW2 Page 19 of 40
20 Task 2 Configure Q-in-Q tunneling on and SW2 in such a way that allows customer VLANs to cross the trunk linkds without alteration in the Customer switches. Also, allow VLAN overlapping between other Service Provider Customers. Change the MTU size to accommodate Q-in-Q tunneling. Assign the Customer to a VLAN 120. System mtu 1504 *** requires a reload*** VLAN 120 Interface F0/A Description Trunk ports connecting towards SW3-Customer Switch Switchport access vlan 120 Switchport mode dot1q-tunnel Interface F0/B Description Trunk port towards the other Service Provider Switch(s) Switchport trunk encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk SW2 System mtu 1504 *** requires a reload*** VLAN 120 Interface F0/A Description Trunk ports connecting towards SW4-Customer Switch Switchport access vlan 120 Switchport mode dot1q-tunnel Interface F0/B Description Trunk port towards the other Service Provider Switch(s) Switchport trunk encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk Page 20 of 40
21 Task 3 Configure the Customer Side Switches with Dot1Q trunking encapsulation. SW3 Interface F0/B Description Trunk port towards the Service Provider Cloud Switchport trunk encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk SW4 Interface F0/B Description Trunk port towards the Service Provider Cloud Switchport trunk encap dot1q Switchport mode trunk Task 4 Configure QinQ and Layer Protocol Forwarding (metro) in such a way that allows switches to forward CDP and VTP customer's frames transparently. Configure switches and SW2 ports facing SW3 and SW4 respectively. Interface F0/A Description Trunk ports connecting towards SW3-Customer Switch L2protocol-tunnel cdp L2protocol-tunnel vtp SW2 Interface F0/A Description Trunk ports connecting towards SW4-Customer Switch L2protocol-tunnel cdp L2protocol-tunnel vtp Page 21 of 40
22 Lab 11 Configuring Private VLANs R /24 VLAN 10 VLAN 10 Primary F 0/0 (.1) /24 F 0/0 (.2) F0/0 (.3) F 0/0 (.4) F 0/0 (.5) R2 R3 R4 R5 VLAN 20 Community VLAN 30 Isolated Interface IP Address Configuration R1 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ R2 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ R3 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ Page 22 of 40
23 R4 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ R5 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ Task 1 Configure VTP Transparent mode in and create the following configuration: Vlan 10 as Private-Vlan Primary Vlan 20 as Private-Vlan Community Vlan 30 as Private-Vlan Isolated Vtp mode transparent Vlan 10 Private-vlan primary Vlan 20 Private-vlan community Vlan 30 Private-vlan isolated Vlan 10 Private-vlan association add 20, 30 Task 2 Configure such that the following is accomplished keeping the VLAN designations from Task1: R1 should be able to communicate to all other devices. R2 and R3 should be able to communicate to each other and R1 but should not have access to R4 or R5. R4 and R5 should only be able to communicate to R1. They should not be able to communicate to each other or R2 or R3. Page 23 of 40
24 Interface F0/1 Switchport mode private-vlan promiscuous Switchport private-vlan mapping 10 add 20, 30 Interface range F0/2 3 Switchport mode private-vlan host Switchport private-vlan host-assoc Interface range F0/4 5 Switchport mode private-vlan host Switchport private-vlan host-assoc Page 24 of 40
25 Explanation: Private VLANs provide Layer 2 isolation between ports within the same private VLAN. There are three types of private VLAN ports: Promiscuous A promiscuous port can communicate with all interfaces, including the community and isolated ports within a private VLAN. Isolated An isolated port has complete Layer 2 separation from other ports within the same private VLAN except for the promiscuous port. Private VLANs block all traffic to isolated ports except traffic from promiscuous ports. Traffic received from an isolated port is forwarded only to promiscuous ports. Community Community ports communicate among themselves and with their promiscuous ports. These interfaces are isolated at Layer 2 from all other interfaces in other communities or isolated ports within their private VLAN. NOTE: Because trunks can support the VLANs carrying traffic between isolated, community, and promiscuous ports, isolated and community port traffic might enter or leave the switch through a trunk interface. Private VLAN ports are associated with a set of supporting VLANs that are used to create the private VLAN structure. A private VLAN uses VLANs three ways: Primary VLAN Carries traffic from promiscuous ports to isolated, community, and other promiscuous ports. Isolated VLAN Carries traffic from isolated ports to promiscuous ports. Community VLAN Carries traffic between community ports and to promiscuous ports. You can configure multiple community VLANs in a private VLAN. NOTE: Isolated and community VLANs are both called secondary VLANs. A promiscuous port can serve only one primary VLAN and can serve as many isolated or community VLANs as desired Page 25 of 40
26 Lab 12 Tuning STP Startup Times Task 1 Create a VLAN 50 on. Assign ports F 0/6 F 0/8 to VLAN 50. VLAN 50 Interface range F 0/6 8 Switchport access vlan 50 Switchport mode access Task 2 Users in Vlan 50 are complaining about the time it usually takes for an interface to come up after they have plugged in the network cable. Configure the TOTAL link startup delay until the port becomes forwarding to 16 seconds. Configure to accomplish this without jumping any state. Spanning-tree vlan 50 forward-time 8 Output of command: show spanning-tree vlan 50 brief VLAN50 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 8192 Address cc08.01f8.000c Cost 32 Port 50 (FastEthernet0/6) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 8 sec Bridge ID Priority Address cc06.0a4c.000c Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 8 sec Aging Time 0 Interface Designated Page 26 of 40
27 Explanation: Forwarding delay is the time spent by a port in the learning and listening states. By default it has a value of 15 seconds so a normal port without portfast enable on it usually takes 50 seconds to start forwarding packets because it goes through learning (15 seconds) plus listening (15 seconds) and maximum age time (which is 20 seconds by default) when changing the forwarding delay to 8 the time the port for the first time a desktop is plugged into a port in a switch it would take (if it s using the default value) so it would takes 36 seconds instead of 50 seconds in that case. Page 27 of 40
28 Lab 13 Configuring Port-Fast Task 1 Configure the port range from F0/1 6 on in a way that, the link will come up as soon as someone plug in a network cable into some of these ports bypassing STP learning/listening states. Interface range F0/1-6 Spanning-tree portfast Output of command: show spanning-tree interface F0/1 portfast VLAN10 enabled. Explanation: After a port on the switch has linked and joined the bridge group, STP runs on that port. A port that runs STP can be in one of five states: blocking listening learning forwarding disabled STP dictates that the port starts out blocking, and then immediately moves through the listening and learning phases. By default, the port spends approximately 15 seconds listening and 15 seconds learning. During the listening state, the switch tries to determine where the port fits in the spanning tree topology. The switch especially wants to know whether this port is part of a physical loop. If the port is part of a loop, the port can be chosen to go into blocking mode. Page 28 of 40
29 The blocking state means that the port does not send or receive user data in order to eliminate loops. If the port is not part of a loop, the port proceeds to the learning state, in which the port learns which MAC addresses live off this port. This entire STP initialization process takes about 30 seconds. If you connect a workstation or a server with a single NIC card or an IP phone to a switch port, the connection cannot create a physical loop. These connections are considered leaf nodes. There is no reason to make the workstation wait 30 seconds while the switch checks for loops if the workstation cannot cause a loop. Cisco added the PortFast or fast-start feature. With this feature, the STP for this port assumes that the port is not part of a loop and immediately moves to the forwarding state and does not go through the blocking, listening, or learning states. This command does not turn STP off. This command makes STP skip a few initial steps (unnecessary steps, in this circumstance) on the selected port. NOTE: Never use the PortFast feature on switch ports that connect to other switches, hubs, or routers. These connections can cause physical loops, and spanning tree must go through the full initialization procedure in these situations. A spanning tree loop can bring your network down. If you turn on PortFast for a port that is part of a physical loop, there can be a window of time when packets are continuously forwarded (and can even multiply) in such a way that the network cannot recover. At the global level, you enable BPDU guard on Port Fast-enabled NNIs by using the spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default global configuration command. Spanning tree shuts down NNIs that are in a Port Fast-operational state if any BPDU is received on those NNIs. In a valid configuration, Port Fast-enabled NNIs do not receive BPDUs. Receiving a BPDU on a Port Fastenabled NNI signals an invalid configuration, such as the connection of an unauthorized device,and the BPDU guard feature puts the interface in the error-disabled state. At the interface level, you enable BPDU guard on any NNI by using the spanning-tree bpduguard enable interface configuration command without also enabling the Port Fast feature. When the NNI receives a BPDU, it is put in the error-disabled state. Page 29 of 40
30 Lab 14 - Configuring BPDU Guard Task 1 The IT departament just found out that someone in the lobby area just plugged in a switch into port F0/6 on. Configure a command globally on that if someone connects a hub or a switch to any of the access ports, the port will be disabled. Also make sure that after 4 minutes the disabled port comes up automatically Spanning-tree portfast bpduguard Errdisable recovery cause bpduguard Errdisable recovery interval 240 Output of command: show errdisable recovery ErrDisable Reason Timer Status udld Disabled bpduguard Enabled rootguard Disabled pagp-flap Disabled dtp-flap Disabled link-flap Disabled Timer interval: 240 seconds Interfaces that will be enabled at the next timeout: show spanning-tree summary Root bridge for: VLAN1, VLAN10, VLAN13, VLAN16, VLAN19, VLAN20, VLAN30 PortFast BPDU Guard is enabled UplinkFast is disabled BackboneFast is disabled Page 30 of 40
31 Explanation: Port Fast-enabled ports do not receive BPDUs. Receiving a BPDU on a Port Fast-enabled port signals an invalid configuration, such as the connection of an unauthorized device, and the BPDU guard feature puts the port in the error-disabled state. The BPDU guard feature provides a secure response to invalid configurations because you must manually put the port back in service. Use the BPDU guard feature in a service-provider network to prevent an access port from participating in the spanning tree. Use the spanning-tree portfast default global configuration command to globally enable the Port Fast feature on all nontrunking ports. Configure Port Fast only on ports that connect to end stations; otherwise, an accidental topology loop could cause a data packet loop and disrupt switch and network operation. A Port Fast-enabled port moves directly to the spanning-tree forwarding state when linkup occurs without waiting for the standard forwarddelay time. You can also configure bpduguard under an interface using the command spanning-tree bpduguard. Page 31 of 40
32 Lab 15 Configuring BPDU Filter Task 1 Configure SW2 port F0/15 such that this port won t send or receive any BDPU packets. SW2 Interface F0/15 Spanning-tree bpdufilter enable Explanation: BPDU Filtering The BPDU filtering feature can be globally enabled on the switch or can be enabled per interface, but the feature operates with some differences. At the global level, you can enable BPDU filtering on Port Fast-enabled interfaces by using the spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default global configuration command. This command prevents interfaces that are in a Port Fast-operational state from sending or receiving BPDUs. The interfaces still send a few BPDUs at link-up before the switch begins to filter outbound BPDUs. You should globally enable BPDU filtering on a switch so that hosts connected to these interfaces do not receive BPDUs. If a BPDU is received on a Port Fast-enabled interface, the interface loses its Port Fastoperational status, and BPDU filtering is disabled. At the interface level, you can enable BPDU filtering on any interface by using the spanning-tree bpdufilter enable interface configuration command without also enabling the Port Fast feature. This command prevents the interface from sending or receiving BPDUs. Task 2 Configure such that any port configured with portfast should be limited from sending or receiving BPDU. Don t use any interface level command to accomplish this. Spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default Page 32 of 40
33 Output of command: SW show spanning-tree summary Switch is in pvst mode Root bridge for: none EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled Extended system ID is enabled Portfast Default is disabled PortFast BPDU Guard Default is disabled Portfast BPDU Filter Default is enabled Loopguard Default is disabled UplinkFast is disabled BackboneFast is disabled Configured Pathcost method used is short Page 33 of 40
34 Lab 16 Configuring UplinkFast Task 1 On configure a feature to improve the uplinks and make sure that if a root port has failed, the switch will choose a new root port and put it directly to FORWARDING state. Spanning-tree uplinkfast Output of command: show spanning-tree uplinkfast UplinkFast is enabled Station update rate set to 150 packets/sec. UplinkFast statistics Number of transitions via uplinkfast (all VLANs) : 0 Number of proxy multicast addresses transmitted (all VLANs) : 0 Name Interface List.. Explanation: UplinkFast provides fast convergence after a spanning-tree topology change and achieves load balancing between redundant links using uplink groups. An uplink group is a set of ports (per VLAN), only one of which is forwarding at any given time. Specifically, an uplink group consists of the root port (which is forwarding) and a set of blocked ports, except for self-looping ports. The uplink group provides an alternate path in case the currently forwarding link fails. UplinkFast is most useful in wiring-closet switches. This feature may not be useful for other types of applications. NOTE: In other words UplinkFast is used to designate a Backup Root Port in case of direct failure of a link. Page 34 of 40
35 Lab 17 Configuring Backbone Fast Task 1 Configure and make sure that if an inferior BPDU is received on a root port or blocked port this inferior BPDUs is ignored on those ports. Spanning-tree backbonefast Output of command: show spanning-tree summary Switch is in pvst mode Root bridge for: none EtherChannel misconfig guard is enabled Extended system ID is enabled Portfast Default is disabled PortFast BPDU Guard Default is disabled Portfast BPDU Filter Default is enabled Loopguard Default is disabled UplinkFast is enabled BackboneFast is enabled Configured Pathcost method used is short Number of transitions via uplinkfast (all VLANs) : 0 Number of proxy multicast addresses transmitted (all VLANs) : 0 BackboneFast statistics Number of transition via backbonefast (all VLANs) : 0 Number of inferior BPDUs received (all VLANs) : 0 Number of RLQ request PDUs received (all VLANs) : 0 Number of RLQ response PDUs received (all VLANs) : 0 Number of RLQ request PDUs sent (all VLANs) : 0 Number of RLQ response PDUs sent (all VLANs) : 0 Page 35 of 40
36 Explanation: BackboneFast is initiated when a root port or blocked port on a switch eceives inferior BPDUs from its designated bridge. An inferior BPDU identifies one switch as both the root bridge and the designated bridge. When a switch receives an inferior BPDU, it indicates that a link to which the switch is not directly connected (an indirect link) has failed (that is, the designated bridge has lost its connection to the root bridge). Under normal spanning-tree rules, the switch ignores inferior BPDUs for the configured maximum aging time, as specified by the agingtime variable. The switch tries to determine if it has an alternate path to the root bridge. If the inferior BPDU arrives on a blocked port, the root port and other blocked ports on the switch become alternate paths to the root bridge. (Self-looped ports are not considered alternate paths to the root bridge.)if the inferior BPDU arrives on the root port, all blocked ports become alternate paths to the rootbridge. If the inferior BPDU arrives on the root port and there are no blocked ports, the switch assumes that it has lost connectivity to the root bridge, causes the maximum aging time on the root to expire, and becomes the root switch according to normal spanning-tree rules. If the switch has alternate paths to the root bridge, it uses these alternate paths to transmit a new kind of PDU called the Root Link Query PDU. The switch sends the Root Link Query PDU out all alternate paths to the root bridge. If the switch determines that it still has an alternate path to the root, it causes the maximum aging time on the ports on which it received the inferior BPDU to expire. If all the alternate paths to the root bridge indicate that the switch has lost connectivity to the root bridge, the switch causes the maximum aging times on the ports on which it received an inferior BPDU to expire. If one or more alternate paths can still connect to the root bridge, the switch makes all ports on which it received an inferior BPDU its designated ports and moves them out of the blocking state (if they were in blocking state), through the listening and learning states, and into the forwarding state. Page 36 of 40
37 Lab 18 Configuring Root Guard Task 1 Configure the ports that connect to SW2 in such a way that if for some reason the spanning-tree causes one of those ports to be selected as root port, the port transition to a root-inconsistent (blocked) state. Interface range F0/X Y Description Connection towards SW2 Spanning-tree guard root Explanation: The Layer 2 network of a service provider (SP) can include many connections to switches that are not owned by the SP. In such a topology, the spanning tree can reconfigure itself and select a customer switch as the root switch, You can avoid this situation by enabling root guard on SP switch interfaces that connect to switches in your customer's network. If spanning-tree calculations cause an interface in the customer network to be selected as the root port, root guard then places the interface in the rootinconsistent (blocked) state to prevent the customer's switch from becoming the root switch or being in the path to the root. If a switch outside the SP network becomes the root switch, the interface is blocked (rootinconsistent state), and spanning tree selects a new root switch. The customer's switch does not become the root switch and is not in the path to the root. If the switch is operating in multiple spanning-tree (MST) mode, root guard forces the interface to be a designated port. If a boundary port is blocked in an internal spanning-tree (IST) instance because of root guard, the interface also is blocked in all MST instances. A boundary port is an interface that connects to a LAN, the designated switch of which is either an 802.1D switch or a switch with a different MST region configuration. Root guard enabled on an interface applies to all the VLANs to which the interface belongs. VLANs can be grouped and mapped to an MST instance. You can enable this feature by using the spanning-tree guard root interface configuration command. Page 37 of 40
38 Lab 19 DHCP Snooping & DAI Task 1 Configure DHCP Snooping on Switch1. It should be enabled for VLAN 50. It should maintain a MAC-IP database based on the Addresses assigned to DHCP Clients from DHCP Servers. IP DHCP snooping IP DHCP snooping vlan 50 Task 2 The DHCP server resides on the F 0/16 on. Assign this port to VLAN 50. Interface F 0/16 Switchport mode access Switchport access vlan 50 Task 3 Make sure the switch only allows DHCP replies from port F 0/16 on. SW2 Interface F 0/16 Ip dhcp snooping trust Task 4 Configure such that it intercepts all packets received on untrusted ports. It should verify valid IP-MAC mappings against the DHCP Snooping Database. If it does not match, it should drop the packets. It should be enabled on VLAN 50. Ip arp inspection vlan 50 Interface F 0/16 Ip arp inspection trust Page 38 of 40
39 Lab 20 Configuring HSRP R1 F 0/0 (.1) /24 VLAN 11 F 0/1 (.3) F 0/1 (.4) R3 R4 F 0/1 (.3) F 0/1 (.4) /24 VLAN 20 F0/0(.2) R2 Interface IP Address Configuration R1 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ R2 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ Loopback R3 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ F 0/ Loopback R4 Interface IP Address Subnet Mask F 0/ F 0/ Loopback Page 39 of 40
40 Task 1 Configure EIGRP in AS 100 on R2, R3 and R4. Advertise the Loopback 0 and the physical links in EIGRP 100. R2 Router EIGRP 100 No auto-summary Network Network R4 R3 Router EIGRP 100 No auto-summary Network Network Network Router EIGRP 100 No auto-summary Network Network Network Task 2 Configure HSRP between R3 and R4 on VLAN 11. Use.34 as the Virtual HSRP address. R3 should be the preferred Router. Have R1 point to the virtual HSRP address as the Default Gateway. R3 Interface F 0/1 Standby 1 ip Standby 1 priority 105 Standby 1 preempt R1 R3 Interface F 0/1 Standby 1 ip IP route Testing: Type Show standby on R3 and R4. Which router is the Active HSRP Router? Which router is the Standby HSRP Router? Why? Page 40 of 40
Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
 CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
CHAPTER 20 This chapter describes how to configure optional spanning-tree features on the Catalyst 3750-E or 3560-E switch. You can configure all of these features when your switch is running the per-vlan
Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands
 CHAPTER Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands New Commands dot1x guest-vlan supplicant ip dhcp snooping information option allow-untrusted port-security mac-address port-security mac-address sticky port-security
CHAPTER Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands New Commands dot1x guest-vlan supplicant ip dhcp snooping information option allow-untrusted port-security mac-address port-security mac-address sticky port-security
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Catalyst 6500 Series Switch
STP Optional Characteristic Configuration
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring STP Optional Characteristic... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Introduction... 1 1.1.1 Port Fast... 1 1.1.2 BPDU Guard... 2 1.1.3 BPDU Filter...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Configuring STP Optional Characteristic... 1 1.1 STP Optional Characteristic Introduction... 1 1.1.1 Port Fast... 1 1.1.2 BPDU Guard... 2 1.1.3 BPDU Filter...
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands
 CHAPTER Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands New Commands call-home (global configuration) call-home request call-home send call-home send alert-group call-home test clear energywise neighbors clear errdisable
CHAPTER Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands New Commands call-home (global configuration) call-home request call-home send call-home send alert-group call-home test clear energywise neighbors clear errdisable
Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 9.0. Cisco Questions & Answers
 300-115 Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Questions & Answers Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Exam Topic 1, Layer
300-115 Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Questions & Answers Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Exam Topic 1, Layer
Describing the STP. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.
![2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords. 2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.](/thumbs/72/66270180.jpg) 2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface.
2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface.
Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt
 IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
Describing the STP. IEEE Documents. Download this file. Enhancements to STP. Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt STP
 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) - Multiple Spanning Tree
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Symbols. Numerics INDEX
 INDEX Symbols $ matches the end of a string 7 ( ) in commands 10 * matches 0 or more sequences of a pattern 7 + matches 1 or more sequences of a pattern 7. matches any single character 7? command 1? matches
INDEX Symbols $ matches the end of a string 7 ( ) in commands 10 * matches 0 or more sequences of a pattern 7 + matches 1 or more sequences of a pattern 7. matches any single character 7? command 1? matches
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
2.2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Catalyst 4500 Series Switches snmp ifindex clear. This command has no arguments or keywords.
 Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
examcollection.premium.exam.157q. Exam code: Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version 15.0
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial
 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
Cisco. Exam Questions SWITCH Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version:Demo
 Cisco Exam Questions 300-115 SWITCH Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version:Demo 1. Which type of information does the DHCP snooping binding database contain? A. untrusted hosts with leased IP
Cisco Exam Questions 300-115 SWITCH Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version:Demo 1. Which type of information does the DHCP snooping binding database contain? A. untrusted hosts with leased IP
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Vendor: Cisco. Exam Code: Exam Name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version: Demo
 Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 642-813 Exam Name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 Which two RSTP port roles include the port as part of the active topology? (Choose two) A. Root
Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 642-813 Exam Name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 Which two RSTP port roles include the port as part of the active topology? (Choose two) A. Root
ActualTest v by-VA
 ActualTest-642-813-v2012-10-29-by-VA Number: 154 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 140 min File Version: 2.7 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) I rearranged the last
ActualTest-642-813-v2012-10-29-by-VA Number: 154 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 140 min File Version: 2.7 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) I rearranged the last
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
0] Chapter 2 Cisco ME 3400E Ethernet Access Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.
![0] Chapter 2 Cisco ME 3400E Ethernet Access Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords. 0] Chapter 2 Cisco ME 3400E Ethernet Access Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.](/thumbs/71/66077699.jpg) 0] Chapter 2 shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface. shutdown no shutdown Syntax Description
0] Chapter 2 shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface. shutdown no shutdown Syntax Description
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
3. What could you use if you wanted to reduce unnecessary broadcast, multicast, and flooded unicast packets?
 Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
Lab Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
BraindumpsIT. BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf!
 BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
CCNP SWITCH (22 Hours)
 CCNP SWITCH 642-813 (22 Hours) Chapter-1 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1.1 IIN & SONA 1.2 Campus Network 1.3 Enterprise Model 1.4 Nonhierarchical Network Devices Layer-2 Switching, Layer-3 Routing Multilayer
CCNP SWITCH 642-813 (22 Hours) Chapter-1 Enterprise Campus Network Design 1.1 IIN & SONA 1.2 Campus Network 1.3 Enterprise Model 1.4 Nonhierarchical Network Devices Layer-2 Switching, Layer-3 Routing Multilayer
Cisco Exam Bundle
 Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 22.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Exam Name: Cisco implementing cisco switched networks
Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 22.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Exam Name: Cisco implementing cisco switched networks
Configuring STP Extensions
 Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
PracticeDump. Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam
 PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
: Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks
 Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Integrated Switch Technology
 CHAPTER 2 This section discusses the following topics: Cisco Intelligent Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the IBM BladeCenter Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the HP BladeSystem Cisco Intelligent
CHAPTER 2 This section discusses the following topics: Cisco Intelligent Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the IBM BladeCenter Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Switch Module for the HP BladeSystem Cisco Intelligent
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series ISR
 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Configuring STP Extensions
 This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
Configuring Private VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for Private VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for Private VLANs, on page 1 Information About Private VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure Private VLANs, on
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for Private VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for Private VLANs, on page 1 Information About Private VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure Private VLANs, on
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
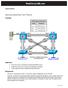 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Commands
 Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Commands A Commands action apply attach auto-sync B Commands boot config C Commands cd channel-group channel-protocol class-map clear catalyst6000 traffic-meter clear counters
Catalyst 6500 Series Cisco IOS Commands A Commands action apply attach auto-sync B Commands boot config C Commands cd channel-group channel-protocol class-map clear catalyst6000 traffic-meter clear counters
Cisco Exam Bundle
 Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 22.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Exam Name: Cisco implementing cisco switched networks
Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 22.3 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Exam Name: Cisco implementing cisco switched networks
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
Cisco Networking Academy CCNP
 Semester 3 v5 -Chapter 8 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Minimizing Service Loss and Data Theft in a Campus Network Switch security concerns Network security coverage often focuses on edge-routing devices
Semester 3 v5 -Chapter 8 Cisco Networking Academy CCNP Minimizing Service Loss and Data Theft in a Campus Network Switch security concerns Network security coverage often focuses on edge-routing devices
Cisco CCNP Exam
 Cisco CCNP 642-813 Exam Number: 160 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1301 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco CCNP 642-813 Exam EnsurePass.com Vendor:Cisco Exam Code:642-813 Contact us:
Cisco CCNP 642-813 Exam Number: 160 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1301 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Cisco CCNP 642-813 Exam EnsurePass.com Vendor:Cisco Exam Code:642-813 Contact us:
FSOS. Ethernet Configuration Guide
 FSOS Ethernet Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring Interface... 1 1.1 Overview...1 1.2 Configuring Interface State...1 1.2.1 Configurations...1 1.2.2 Validation...1 1.3 Configuring Interface Speed...
FSOS Ethernet Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring Interface... 1 1.1 Overview...1 1.2 Configuring Interface State...1 1.2.1 Configurations...1 1.2.2 Validation...1 1.3 Configuring Interface Speed...
Pass-Through Technology
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture,
CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture,
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security,
CHAPTER 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security,
examcollection.premium.exam.68q. Exam code: Exam name: Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT) Version 15.
 300-135.examcollection.premium.exam.68q Number: 300-135 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 / Exam code: 300-135 Exam name: Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT)
300-135.examcollection.premium.exam.68q Number: 300-135 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 / Exam code: 300-135 Exam name: Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT)
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
Campus Networking Workshop. Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs
 Campus Networking Workshop Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs Switching Loop When there is more than one path between two switches What are the potential problems? Switching Loop If there is more
Campus Networking Workshop Layer 2 engineering Spanning Tree and VLANs Switching Loop When there is more than one path between two switches What are the potential problems? Switching Loop If there is more
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 9 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the
9 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2
 Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security
 ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
Cisco Exam Bundle
 Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 26.2 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Sections 1. Layer 2, VTP, VLAN design 2. Security 3. Layer 3, ip routing 4.
Cisco 642-813 Exam Bundle Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 790 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 26.2 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Sections 1. Layer 2, VTP, VLAN design 2. Security 3. Layer 3, ip routing 4.
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Configuring STP Extensions Using Cisco NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) extensions on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About
This chapter describes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) extensions on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About
examcollection.premium.exam.191q
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.191q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 10.0 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 10.0 Sections 1. Layer 2 Technologies
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.191q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 10.0 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 10.0 Sections 1. Layer 2 Technologies
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards
 Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards First Published: May 17, 2005 Last Updated: July 28, 2010 This document provides configuration tasks for the 4-port Cisco HWIC-4ESW and the 9-port
Cisco HWIC-4ESW and HWIC-D-9ESW EtherSwitch Interface Cards First Published: May 17, 2005 Last Updated: July 28, 2010 This document provides configuration tasks for the 4-port Cisco HWIC-4ESW and the 9-port
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
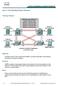 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Configuring Private VLANs
 36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Massimiliano Sbaraglia
 Massimiliano Sbaraglia Printer Layer 2 access connections to End-Point Layer 2 connections trunk or layer 3 p2p to pair distribution switch PC CSA PVST+ or MST (Spanning Tree Protocol) VLANs LapTop VoIP
Massimiliano Sbaraglia Printer Layer 2 access connections to End-Point Layer 2 connections trunk or layer 3 p2p to pair distribution switch PC CSA PVST+ or MST (Spanning Tree Protocol) VLANs LapTop VoIP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing ( )
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (300-101) Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE 300-101) is a 120-minute qualifying exam with 50 60 questions for the Cisco CCNP and CCDP certifications. The ROUTE 300-101
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (300-101) Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE 300-101) is a 120-minute qualifying exam with 50 60 questions for the Cisco CCNP and CCDP certifications. The ROUTE 300-101
Actualtests Q
 Actualtests.300-135 55Q Number: 300-135 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 5.4 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 300-135 Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT) Passed today
Actualtests.300-135 55Q Number: 300-135 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 5.4 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 300-135 Troubleshooting and Maintaining Cisco IP Networks (TSHOOT) Passed today
CCNP Switch. Quick Reference Sheet Exam
 CCNP Switch Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-115 Chapter 1 : Layer 2 Technologies Administering the Switch System Clock The heart of the time service is the system clock. This clock operates from the moment
CCNP Switch Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-115 Chapter 1 : Layer 2 Technologies Administering the Switch System Clock The heart of the time service is the system clock. This clock operates from the moment
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on the IEEE 802.1s standard.
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
SPOTO CCIE LAB RS V5.0 H3 CFG Solution. SPOTO CCIE CLUB offers all Cisco track written and lab dumps.spoto CCIE
 SPOTO CCIE LAB RS V5.0 H3 CFG Solution SPOTO CCIE CLUB offers all Cisco track written and lab dumps.spoto CCIE CLUB had already helped more than 700 CCIE candidates obtain the magical CCIE number since
SPOTO CCIE LAB RS V5.0 H3 CFG Solution SPOTO CCIE CLUB offers all Cisco track written and lab dumps.spoto CCIE CLUB had already helped more than 700 CCIE candidates obtain the magical CCIE number since
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
/ ) / ) ) ( \ / ) ) ) ( ( ) ( ) / \ \ \ \ ) ) \ ) \ ) _ ) _ \_ ( /
 / ) / ) ) ( \ / ) ) ) ( ( ) ( ) / \ \ \ \ ) ) \ ) \ ) _ ) _ \_ ( / / ) / \ ( \( ) ( / \( ) ) / ) ( ( ) ) ( ( \ \ / ( ) ) \ \ ) ) \ \ ) ) ( / _ _ \ / _ \_ _ _ _ \ / _ ) / Version 4.2 (Includes Troubleshooting)
/ ) / ) ) ( \ / ) ) ) ( ( ) ( ) / \ \ \ \ ) ) \ ) \ ) _ ) _ \_ ( / / ) / \ ( \( ) ( / \( ) ) / ) ( ( ) ) ( ( \ \ / ( ) ) \ \ ) ) \ \ ) ) ( / _ _ \ / _ \_ _ _ _ \ / _ ) / Version 4.2 (Includes Troubleshooting)
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring Private VLANs Using NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on Cisco NX-OS devices. Private VLANs provide additional protection at the Layer 2 level. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature
This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on Cisco NX-OS devices. Private VLANs provide additional protection at the Layer 2 level. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature
actualtests.cisco.ccnp switch by.passforu
 actualtests.cisco.ccnp.642-813.switch.2012.07.02.by.passforu Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ www.passforu.com obtain your it certifications
actualtests.cisco.ccnp.642-813.switch.2012.07.02.by.passforu Number: 642-813 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ www.passforu.com obtain your it certifications
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
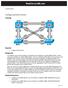 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN)
 Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) Table of Contents Module 1 Defining VLANs Implementing Best Practices for VLAN Topologies Describing Issues in a Poorly Designed Network Grouping Business
Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks (BCMSN) Table of Contents Module 1 Defining VLANs Implementing Best Practices for VLAN Topologies Describing Issues in a Poorly Designed Network Grouping Business
Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version: 10.0
 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 10.0 Topic 1, Layer 2 Technologies Cisco 300-115 Exam QUESTION NO: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco
Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 10.0 Topic 1, Layer 2 Technologies Cisco 300-115 Exam QUESTION NO: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco
CCNP Switch Questions/Answers Securing Campus Infrastructure
 What statement is true about a local SPAN configuration? A. A port can act as the destination port for all SPAN sessions configured on the switch. B. A port can be configured to act as a source and destination
What statement is true about a local SPAN configuration? A. A port can act as the destination port for all SPAN sessions configured on the switch. B. A port can be configured to act as a source and destination
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
Configuring Flex Links
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
