Chapter 2: Layer 2 Technologies
|
|
|
- Paula Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2: Layer 2 Technologies Troubleshooting Switch Administration Troubleshooting the switch can be tricky because there may or may not be an involvement of switch in network performance degradation. If slower speed of network is reported, there may be heavy traffic on the network or switch may be involved in it dropping the packets. If we consider the basic troubleshooting of a switch there may be two errors: Port Error Duplex Error Port Error In order to troubleshoot, the switch starts with layer 1. Check the cabling and connectivity first. By observing the statistics of port, number of packets sent and received, as well as dropped, can be measured which helps to troubleshoot the issue. Dropping of packet may be due to congestion in the network or Bad Cabling. Auto MDIX (Medium Dependant Interface Crossover) enables the switch to auto detect the cable type. Straight through and Crossover both cables can be used for like and unlike devices if Auto-MDIX feature is enabled on switch. Duplex Error If a switch connected to a device configured with half duplex, then switch is configured with full duplex on an interface. The interface will face duplex mismatch and packet are dropped due to collusion. Cisco Switch can be configured as auto negotiation for both speed and Duplex settings to negotiate with respect to the device it is connected with. SDM Template SDM is Switching Database Manager. It is used to manage the switching information of Layer 2 up to Layer 3. For this, Ternary Content Addressable Memory or TCAM is used. Basic purpose of TCAM is forwarding Lookups. As far as SDM Templates are concerned, there are four templates: Routing Template Routing Template is used for allocation of resources to the routing process. This feature is used for the routers placed in the centre of the network so IPv4 Unicast routing has preferred to allocate more resources. VLAN Template The VLAN template is used to disable routing and it supports the maximum number of unicast MAC addresses. Default Template Default template gives balanced resources to all functions. Access Template The access template allocates maximum system resources for Access control lists (ACLs) to support a large number of ACLs. IPSpecialist.net 26
2 Figure 9. Approximate Number of Resources Allowed by Each Template for Desktop or Aggregator Switches SDM Configuration: Switch(config)# sdm prefer default Switch(config)# end Switch# reload Mind Map IPSpecialist.net 27
3 MAC Address Table Switch supports multiple MAC addresses on all ports so we can connect individual workstation as well as multiple devices through switch or router as well. By the feature of Dynamic Addressing, switch updates the source address received from the incoming packets and binds it to the interface from which it is received. As the devices are added or removed, they are updated dynamically. By default, aging time of MAC address is 300 seconds. Switch is configured to learn dynamically the MAC addresses by default. MAC address and VLAN In a Private VLAN, learning of addresses depends upon the type of MAC address, dynamically-learned MAC addresses in a Private VLAN are replicated in associated VLAN Static MAC address should be configured statically on private as well as associated VLAN. Changing MAC address table Aging time Switch# Switch(config)#mac address-table aging-time? <0-0> Enter 0 to disable aging < > Aging time in seconds Switch(config)#mac address-table aging-time 10 Switch(config)#end Switch# Switch#show mac address-table aging-time Global Aging Time: 10 VLAN Aging Time IPSpecialist.net 28
4 Removing MAC address Entries Switch#clear mac address-table dynamic // Removes all dynamically learned entries Switch#clear mac address-table dynamic address {mac address} // Removes specific dynamically learn address Switch#clear mac address-table dynamic interface {interface type} {interface number} // Removes dynamically learned address from an interface Switch#clear mac address-table dynamic VLAN {VLAN number} // Removes dynamically learn addresses of VLAN Display MAC Address table Entries IPSpecialist.net 29
5 Mind Map Error Disabled Recovery When a situation of error is detected on the port, the status of that port is automatically changed to down. In other words, when the IOS of Switch detects the error encountered on any port, it brings the port into error-disabled mode. In errordisabled mode, the port is shut down and no traffic is passed in or out from the port. The Port LED turns Orange when the port is in error-disabled mode. When a switch is configured globally with error-disabled recovery feature, then there is no need to shut down the error-disabled port and then re enable it. Recovery feature automatically enable the error-disabled port. If the recovery is not configured, manually shut down the port and then re-enable it. Enable Error-Disabled Recovery Switch(config)#errdisable detect cause security-violation shutdown VLAN Switch(config)#errdisable recovery cause security-violation IPSpecialist.net 30
6 IPSpecialist.net 31
7 Troubleshooting Layer 2 Protocols Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) Cisco Discovery Protocol is a layer 2 protocol for all cisco devices and for all network management applications to discover the cisco devices at the neighbour. This CDP protocol is enabled by default. To enable: Switch(config)# cdp run Switch(config)# end To disable: Switch(config)#no cdp run Switch(config)# end Monitoring and Maintaining CDP clear cdp counters clear cdp table show cdp show cdp traffic // Clear the CDP Counters // Clear CDP Tables // Show Global Informaiton // Show CDP traffic show cdp neighbors [ interface-id ] [ detail ] // Information about neighbour, device type, holdtime etc show cdp interface [ interface-id ] // Show CDP info related to interface show cdp entry entry-name [ protocol version ] // Information about specific Neighbour IPSpecialist.net 32
8 Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) As the Cisco devices are allowed to share information at layer 2 using CDP protocol, IEEE developed a protocol 802.1AB for the support of Non Cisco devices, which also run over layer 2. Configuring LLDP Switch>en Switch#config t Switch(config)#lldp run Switch(config)#int eth 0/0 Switch(config-if)#lldp transmit Switch(config-if)#lldp receive Switch(config-if)#ex //Enable LLDP Globally // Send LLDP Packets // Receive LLDP Packets Characteristics of LLDP Hold time Time in seconds, device hold the LLDP packets before discarding ranging from 0 to seconds with default value of 120 seconds Command: Switch(config)#lldp holdtime 150 Reinit Time delay in second to initial LLDP on an interface ranging from 2 to 5 secs. 2 seconds is default Command: Switch(config)#lldp reinit 5 Timer Time in second to send LLDP updates. Range of the timer is from 5 seconds to seconds, default value is 30 seconds. Command: Switch(config)#lldp timer 120 IPSpecialist.net 33
9 Unidirectional Link Detection Protocol (UDLD) UDLD is Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) protocol that is used for monitoring physical configuration of the devices connected by fiber optics or Ethernet cables. It is also used to detect unidirectional links existence. Devices must support this protocol in order to identify and disable the unidirectional links successfully. UDLD is disabled by default. ATM ports do not support this feature. For UDLD detection, it is necessary that port at both ends is capable of UDLD feature as well as the same mode is configured on the both ends. UDLD- Enable Mode (default) UDLD- Aggressive Mode Configure UDLD Enable mode: Switch(config)#udld enable Switch(config)#int eth 0/0 Switch(config-if)#udld port // Enable UDLD enable mode globally // Enable UDLD enable mode on interface Configure UDLD aggressive mode: Switch(config)#udld aggressive Switch(config)#int eth 0/0 Switch(config-if)#udld port aggressive // Enable UDLD Aggressive mode globally // Enable UDLD Aggressive mode on interface IPSpecialist.net 34
10 Troubleshooting VLANs For troubleshooting VLANs, keep in mind that all the ports of switch are assigned to VLAN 1 by default. If there are VLANs created in a switched network, make sure that interfaces are correctly assigned with their respective VLANs. While creating or modifying a VLAN, make sure that VLAN ID you are using is not reserved. Access Ports: By default Switch, ports are assigned to Dynamic Auto. These switch ports can be changed to Access and Trunk ports as well. Commands Switch(config)#int fa 0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode? access dynamic trunk Set trunking mode to ACCESS unconditionally Set trunking mode to dynamically negotiate access or trunk mode Set trunking mode to TRUNK unconditionally Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#ex Verification: Switch#show int fa 0/1 switchport IPSpecialist.net 35
11 Trunk Ports: Switch(config)#int fa 0/2 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)#ex Verification: Switch#show int fa 0/2 switchport IPSpecialist.net 36
12 For troubleshooting the interfaces assigned to VLANs, issue the command Show VLAN in privilege EXEC mode. IPSpecialist.net 37
13 For troubleshooting the interfaces assigned to a specific VLAN, issue the command Show VLAN id {VLAN id} in privilege EXEC mode. Command Switch#show VLAN id 1 IPSpecialist.net 38
14 Default Settings of Switch port Default configuration of a switch port is set to dynamic auto. It should be set according to requirement. Command Switch#show int fa 0/3 switchport For troubleshooting IP parameters of VLAN, issue the command show ip int VLAN 1 IPSpecialist.net 39
15 Command Switch# show ip int VLAN 1 IPSpecialist.net 40
16 VLAN Database Mode VLANs can be configured by either running configuration mode or by using VLAN database mode. VLAN in running configuration mode stores its VLAN configuration in running configuration and removed if not copied in start-up configuration. In database configuration mode, VLAN parameters are saved in VLAN.dat file rather than saved in running or start-up configuration. As we know, user-configurable VLAN ID ranging from 1 to Database Mode support VLAN ID ranging from 1 to Database Mode does not support extended ID rang from 1006 to Make sure that VLAN database mode is an older method for configuring VLANs and it is deprecated, but kept for backward compatibility. Configuration: Normal VLAN Configuration Switch#config t Switch(config)#VLAN 10 Switch(config-VLAN)#ex VLAN Database Configuration Switch#VLAN database % Warning: It is recommended to configure VLAN from config mode, as VLAN database mode is being deprecated. Please consult user documentation for configuring VTP/VLAN in config mode. Switch(VLAN)#VLAN? <1-1005> ISL VLAN index Switch(VLAN)#VLAN 10 VLAN 10 modified: Switch(VLAN)#ex APPLY completed. Exiting... Verification: Switch#show VLAN 10 IPSpecialist.net 41
17 Voice VLAN As far as Voice VLANs are concerned, remember the basic characteristics of Voice VLAN. As Voice VLAN enables access port to forward the traffic of IP voice from an IP Phone. This IP Voice traffic is send with precedence of Layer 3 and Layer 2 CoS (Class of Service). The default vlaues of Both Layer 3 Precedence and Layer 2 CoS is set to 5. Quality of Service support is IEEE 802.1p CoS based. Voice VLAN feature is disabled by default. Configuration: Switch(config)#int fa 0/2 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#mls qos trust cos // Classify incoming traffic packets by using the packet CoS value. Switch(config-if)#switchport voice VLAN 1 Switch(config-if)#switchport priority extend cos? <0-7> Priority for devices on appliance Switch(config-if)#switchport priority extend cos 7 Switch(config-if)#ex Switch(config)#ex IPSpecialist.net 42
18 Verification IPSpecialist.net 43
19 Troubleshooting Trunking VTP Version 1 VTP version 1 supports the normal-range of VLANs Only (1 to 1005). In VTP versions 1 and 2, the switch must be configured in VTP transparent mode when private VLANs is created and configured, Do not change the VTP mode from transparent mode to client mode or server mode. In VTP versions 1 and 2, in VTP client mode, VLAN configurations are not saved in NVRAM. Default operation uses VTPv1 VTP Version 2 VTP version 2 only supports normal-range VLANs (1 to 1005). In a VTP network, you must decide which version of VTP to use. By default, VTP operates in version 1. VTP version 2 supported features that are not in version 1: Token Ring support Unrecognized Type Version-Dependent Transparent Mode Consistency Checks VTP Version 3 VTP version 3 supports the entire VLAN range (VLANs 1 to 4094). Extended range VLANs (VLANs 1006 to 4094) are supported only in VTP version 3. You cannot convert from VTP version 3 to VTP version 2 if extended VLANs are configured in the domain. Cisco IOS Release 12.2(52)SE and later support VTP version 3. VTP version 3 supports these features that are not supported in version 1 or version 2: Enhanced authentication Support for extended range VLAN Private VLAN support. Support for any database in a domain. VTP primary server and VTP secondary servers. The option to turn VTP on or off on a per-trunk (per-port) basis. VTP Pruning VTP pruning ranges only to VLANs 1 to 1005, and VLANs 1002 to 1005 are reserved and cannot be modified. VTP pruning increases network bandwidth availability by restricting or blocking the flooded traffic over the trunk links that the traffic must use to reach the destination devices. Without VTP pruning, a switch floods unknown unicast, broadcast, and multicast traffic across all trunks within a VTP domain even though receiving switches might discard them. VTP pruning is disabled by default. VTP pruning blocks unneeded flooded traffic to VLANs on trunk ports that are included in the pruning-eligible list. Only VLANs included in the pruning-eligible list can be pruned. By default, VLANs 2 through 1001 is pruning eligible switch trunk ports. If the VLANs are configured as pruning-ineligible, the flooding continues. VTP pruning is supported in all VTP versions. IPSpecialist.net 44
20 802.1Q Encapsulation Dot 1Q Trunking DOt1Q is actually the IEEE standard 802.1Q that is used for trunking encapsulation. In a switched network, Dot1Q encapsulation on a trunk port allows the tagged frames of multiple VLANs to be transported. Supporting Modes of Trunk Dynamic Auto Dynamic Desirable Trunk No negotiate Dot 1Q Tunnelling 802.1Q is also used for tunneling by service providers to provide clients with layer 2 VPN connectivity. Customers can continue to use their own VLAN ID configurations while the Internet service provider maintains those tagging. The Service Provider configures their customer-facing interface as 802.1Q tunnel. As the frame arrives as the Service Provider s port, it encapsulates it with another VLAN tag (the VLAN assigned to the customer). It is also called QinQ. Manual Pruning By default, VLANs ranging from are added in pruning list. IPSpecialist.net 45
21 SW1(config)#interface Ethernet 0/0 SW1(config-if)#switchport trunk pruning VLAN remove 20,25,30,35 SW1(config-if)#end To verify Manual Pruning, issue the command show int eth 0/0 switchport IPSpecialist.net 46
22 Troubleshooting Ether Channel When we use Ether Channel Feature to create a virtual link consist of Multiple Physical links, there are many things to keep them in mind to prevent error in configuration. For example Port configuration mismatching or Ether Channel parameters mismatching. Port Configuration Error All the ports participating in the Ether Channel link must be configured with the same parameters. Same Speed, Same Duplex settings, Trunk mode, allowed VLANs as well as Native VLANs. Ether Channel Configuration Error Ports Participating in Ether channel should be configured with same protocols, same mode of those protocols. Modes of Ether Channel PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol) LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) On (Manual) Compatibility of PAgP Compatibility of LACP Compatibility of Manual Setting IPSpecialist.net 47
23 Note: These features are not compatible with each other Lab 2-1 : Layer 2 Ether Channel Configuration: SW1(config)#interface range Ethernet 0/0-1 SW1(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on SW1(config-if-range)#exit SW1(config)#exit SW2(config)#interface range gigabitethernet 0/0-1 SW2(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on SW2(config-if-range)#exit SW2(config)#exit Verification IPSpecialist.net 48
24 IPSpecialist.net 49
25 Lab 2-2 : Layer 3 Ether Channel Configuration: Router 1 Router(config)#int port-channel 1 *Mar 1 00:00:43.367: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel1, changed state to down.0.1 Router(config-if)#ip add Router(config-if)#no sh Router(config-if)#ex Router(config)#int range fa 0/0-1 Router(config-if)#channel-group 1 %Interface MTU set to channel-group MTU Router(config-if)#no sh FastEthernet0/0 added as member-1 to port-channel1 *Mar 1 00:01:42.399: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:01:43.399: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:01:45.367: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel1, changed state to up %Interface MTU set to channel-group MTU FastEthernet0/1 added as member-2 to port-channel1 *Mar 1 00:02:14.411: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:02:15.411: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router(config-if)#ex Router(config)#ip cef IPSpecialist.net 50
26 Router 2 Router(config)#int port-channel 1 *Mar 1 00:01:31.659: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel1, changed state to down Router(config-if)#ip add Router(config-if)#no sh Router(config-if)#ex Router(config)#int range fa 0/0-1 Router(config-if)#channel-group 1 %Interface MTU set to channel-group MTU Router(config-if)#no sh FastEthernet0/0 added as member-1 to port-channel1 *Mar 1 00:02:14.847: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:02:15.847: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:02:17.859: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Port-channel1, changed state to up FastEthernet0/1 added as member-2 to port-channel1 *Mar 1 00:02:34.483: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:02:35.483: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up Router(config-if)#ex Router(config)#ip cef Verification: Router# show ip int brief Router# show int port-channel 1 IPSpecialist.net 51
27 IPSpecialist.net 52
28 Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol Troubleshooting Spanning Tree with Default configuration Spanning Tree Protocol is enabled by default in cisco Layer 2 device to prevent loops. Switch with lowest value of Priority wins the election process. With default configurations on the device, all devices will have same priority hence, the lowest MAC address will win the election. To verify the Root Bridge, issue the command show spanning-tree. Lab 2-3 : Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol MAC : DD.5992 MAC : 000A.41BE.B79A Switch 3 Switch 4 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/1 Fa0/2 Fa0/2 Fa 0/3 Fa0/2 Fa0/2 Fa 0/1 Fa 0/1 Switch 2 Switch 1 MAC : 000B.BEE8.C653 MAC : 000C.CF01.567D Switch 1 Switch1#show spanning-tree VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority Address DD.5992 Cost 38 Port 2(FastEthernet0/2) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Priority of Root Bridge Indicates MAC address of Root Bridge Cost to Root Bridge Bridge ID Priority (priority sys-id-ext 1) Priority of Switch 1 Address 000C.CF01.567D Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Switch 1 MAC address IPSpecialist.net 53
29 Fa0/2 Root FWD P2p This Port is Root Port Fa0/1 Altn BLK P2p This Port is blocked Port Switch1# Switch 3 Switch3#show spanning-tree VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority Address DD.5992 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Root Bridge Bridge ID Priority (priority sys-id-ext 1) Address DD.5992 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/1 Desg FWD P2p All Ports are Designated Fa0/2 Desg FWD P2p Switch3# Switch3# Case Study: A Junior Network Administrator is trying to add a new switch in the network for his personal Practice. As he connects the interface, it goes down automatically. He tries to issue no shutdown command but it s not working. Keep in mind that no other switch is allowed to be connected in the Company Network. IPSpecialist.net 54
30 Troubleshooting: Switch 3 Switch3#show run Building configuration...! spanning-tree mode pvst! interface Ethernet0/0 spanning-tree bpduguard enable! interface Ethernet0/1! interface Ethernet0/2! interface Ethernet0/3! (BPDU Guard Is Enabled) Switch3#show spanning-tree interface Ethernet 0/0 no spanning tree info available for Ethernet0/0 (Interface Is not involved in STP) Action: Explanation: In order to add the switch3 in the company network, issue the commands: IPSpecialist.net 55
31 Switch3(config)#int eth 0/3 Switch3(config-if)#spanning-tree bpduguard disable Switch3(config-if)#ex Reload all switches. Lab 2-4 :PVST+ Network Administrator reports an issue that load of all the traffic of All VLANs are on Switch A. He has configured PVST+ but Bridge is Switch A for All the VLANs. MAC Address 000A.F3C0.C586 MAC Address 00D0.586D.ABBE Switch A Switch B Switch C MAC Address 00D0.FFE1.A173 Troubleshooting //Issue the command on any switch SwitchA#show spanning-tree detail VLAN0001 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 1, 00D0.586D.ABBE Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 00D0.586D.ABBE Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding IPSpecialist.net 56
32 Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 00D0.586D.ABBE Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default VLAN0010 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 10, 00D0.586D.ABBE Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority Root port is 1 (FastEthernet0/1), cost of root path is 19 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0010 is root forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address 00E0.B0D2.B601 Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0010 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address 00E0.B0D2.B601 Designated bridge has priority 32778, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default VLAN0020 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 20, 00D0.586D.ABBE Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority Root port is 1 (FastEthernet0/1), cost of root path is 19 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0020 is root forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address 00E0.B0D2.B601 Designated bridge has priority 32788, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default IPSpecialist.net 57
33 Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0020 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address 00E0.B0D2.B601 Designated bridge has priority 32788, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default VLAN0030 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 30, 00D0.586D.ABBE Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority Root port is 1 (FastEthernet0/1), cost of root path is 19 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0030 is root forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address 00E0.B0D2.B601 Designated bridge has priority 32798, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0030 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address 00E0.B0D2.B601 Designated bridge has priority 32798, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Switch# //After examination of the results, it is found that Priorities are not set, by taking default calculations; Switch with Lowest MAC wins the Election for every VLAN. Hence Load is on Bridge Switch Solution: Switch A: SwitchA(config)#spanning-tree VLAN 10 priority 0 SwitchA(config)#ex Switch B: SwitchB(config)#spanning-tree VLAN 20 priority 0 SwitchB(config)#ex Switch C: // Making Switch A Bridge for VLAN 10. // Making Switch B Bridge for VLAN 20. IPSpecialist.net 58
34 SwitchC(config)#spanning-tree VLAN 30 priority 0 SwitchC(config)#ex // Making Switch C Bridge for VLAN 30. Switch#show spanning-tree detail VLAN0001 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 1, 00D0.FFE1.A173 Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 2 (FastEthernet0/2) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 00D0.FFE1.A173 Designated port id is 128.2, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 00D0.FFE1.A173 Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default VLAN0010 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 10, 00D0.FFE1.A173 Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority 10 Root port is 2 (FastEthernet0/2), cost of root path is 19 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 2 (FastEthernet0/2) of VLAN0010 is root forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address FB Designated bridge has priority 10, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default IPSpecialist.net 59
35 Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0010 is alternate blocking Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address FB Designated bridge has priority 10, address 000A.F3C0.C586 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default VLAN0020 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 20, 00D0.FFE1.A173 Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority 20 Root port is 3 (FastEthernet0/3), cost of root path is 19 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 2 (FastEthernet0/2) of VLAN0020 is alternate blocking Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address FB Designated bridge has priority 20, address 00D0.586D.ABBE Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0020 is root forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 128, address FB Designated bridge has priority 20, address 00D0.586D.ABBE Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default VLAN0030 is executing the ieee compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 0, sysid 30, 00D0.FFE1.A173 Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority 30 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 2 (FastEthernet0/2) of VLAN0030 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated bridge has priority 30, address 00D0.FFE1.A173 Designated port id is 128.2, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default IPSpecialist.net 60
36 Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3) of VLAN0030 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated bridge has priority 30, address 00D0.FFE1.A173 Designated port id is 128.3, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Switch# Case Study: Ethernet 0/0 Switch A MAC ADDRESS AABB.CC Ethernet 0/1 Switch B MAC ADDRESS AABB.CC An Issue is reported that two switches are not participating in Spanning tree Election. No information are exchanging between them. Troubleshooting Switch1#Show spanning-tree Switch2#Show spanning-tree IPSpecialist.net 61
37 Switch#show spanning-tree interface eth 0/0 detail Port 1 (Ethernet0/0) of VLAN0001 is broken (Root Inconsistent) Port path cost 100, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 32769, address aabb.cc Designated bridge has priority 32769, address aabb.cc Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0 Timers: message age 1, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is shared by default Root guard is enabled on the port BPDU: sent 34, received 294 Switch#show spanning-tree interface eth 0/1 detail Port 2 (Ethernet0/1) of VLAN0001 is broken (Root Inconsistent) Port path cost 100, Port priority 128, Port Identifier Designated root has priority 32769, address aabb.cc Designated bridge has priority 32769, address aabb.cc Designated port id is 128.2, designated path cost 0 Timers: message age 2, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is shared by default Root guard is enabled on the port BPDU: sent 34, received 318 Solution: Switch 2 Switch(config)#int eth 0/0 Switch(config-if)#no spanning-tree guard root *May 6 09:38:32.139: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_CONFIG_CHANGE: Root guard disabled on port Ethernet0/0. *May 6 09:38:32.139: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_UNBLOCK: Root guard unblocking port Ethernet0/0 on VLAN0001. IPSpecialist.net 62
38 Switch(config)#int eth 0/1 Switch(config-if)#no spanning-tree guard root *May 6 09:39:01.415: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_CONFIG_CHANGE: Root guard disabled on port Ethernet0/1. *May 6 09:39:01.415: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_UNBLOCK: Root guard unblocking port Ethernet0/1 on VLAN0001. Verification: Switch1#show spanning-tree // Switch1 with lower MAC addressm becoe root bridge IPSpecialist.net 63
39 Lab 2-5 :Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) Issue is reported that no communication is taking place between the switched using MST. Trunk is configured along with encapsulation. Ethernet 0/0 Switch A MAC ADDRESS AABB.CC Ethernet 0/1 Switch B MAC ADDRESS AABB.CC Configuration: Switch 1: S1(config)#VLAN 10 S1(config-VLAN)#ex S1(config)#VLAN 20 S1(config-VLAN)#ex S1(config)#VLAN 30 S1(config-VLAN)#ex S1(config)#VLAN 40 S1(config-VLAN)#ex S1(config)# S1(config)#int range Ethernet 0/0,Ethernet 0/1 S1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q // First change the encapsulation from Auto to dot1q S1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk //Change the Port from Access to Trunk S1(config-if-range)#ex S1(config)# S1(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration S1(config-mst)#instance 1030 VLAN 10,30 //Remember Instance Number, Assign Correct VLANs // Remember Priority (33,798) will be the sum of Default Priority (32768) andn Instance Number(1030) S1(config-mst)#name IPS //Requires the same Configuration on all switches S1(config-mst)#revision 1 //Requires the same Configuration on all switches S1(config-mst)#exit S1(config)#spanning-tree mst 0 priority 0 //Priority for MST 0 will be 0+0 = 0 (Highest) S1(config)#spanning-tree mst 1030 priority //Priority for MST 1030 will be ( ,768) = 33,798 S1(config)#spanning-tree mode mst // Must Enable MST IPSpecialist.net 64
40 Switch 2: S2(config)#VLAN 10 S2(config-VLAN)#ex S2(config)#VLAN 20 S2(config-VLAN)#ex S2(config)#VLAN 30 S2(config-VLAN)#ex S2(config)#VLAN 40 S2(config-VLAN)#ex S2(config)# //Make sure all VLANs are the same as in switch 1 S2(config)#int range Ethernet 0/0,Ethernet 0/1 S2(config-if-range)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q // First change the encapsulation from Auto to dot1q S2(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk //Change the Port from Access to Trunk S2(config-if-range)#ex S2(config)# S2(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration S2(config-mst)#instance 1030 VLAN 10,30 //Verify Instance Number from Switch 1, Assign same VLANs S2(config-mst)#name IPS //Requires the same Configuration on all switches S2(config-mst)#revision 1 //Requires the same Configuration on all switches S2(config-mst)#exit S2(config)#spanning-tree mst 0 priority //Priority for MST 0 will be = S2(config)#spanning-tree mst 1030 priority 0 //Priority for MST 1030 will be = 1030 S2(config)#spanning-tree mode mst //Enable MST Troubleshooting S1#show spanning-tree mst IPSpecialist.net 65
41 Output shows that MST0 is mapped with 1-9, 11-29, VLANs. Priority is 0 and Root shows that this is the Root Bridge. Timer is set to the default values. As we use Ethernet 0/0 and Ethernet 0/1 Interface as Trunk, Both are in Designated Forwarding state. The Output also shows the details of MST1030 that VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 are mapped on it. Root Bridge is the MAC address AABB.CC with Priority MAC Addres of this switch is AABB.CC and the Priority of this switch is for MST Interface Ethernet 0/0 is the Root port in forwarding state whereas Ethernet 0/1 is in Alternate Blocking Port status. S2#show spanning-tree mst IPSpecialist.net 66
42 Output shows that MST0 is mapped with 1-9, 11-29, VLANs. Priority the 0 and Root MAC address shows that the Root Bridge is the Switch having MAC AABB.CC MAC address of this Switch is AABB.CC and the priority is Timers are set to the default values. As we use Ethernet 0/0 is the Root port in forwarding state and Ethernet 0/1 Interface Alternate port in blocking state. The Output also shows the details of MST1030 that VLAN 10 and VLAN 30 are mapped on it. Root Bridge is the MAC address AABB.CC with Priority 1030 which this switch. MAC Address of this switch is AABB.CC and the Priority of this switch is 1030 for MST Interface Ethernet 0/0 is the Designated port in forwarding state similarly Ethernet 0/1 is also Designated Port in forwarding state as it is the Root bridge fro MST S1#show spanning-tree mst configuration IPSpecialist.net 67
43 MST configuration should be the same in all the switches participating in Election. S2#show spanning-tree mst configuration MST configuration should be the same in all the switches participating in Election. Compare the Results of Both Switches S1#show spanning-tree mst interface Ethernet 0/0 From the output, we can see the status of the Interface Ethernet 0/0, which is the trunk port between Switch 1 and Switch 2. This Interface is not enabled with any Port guard Feature, any bpdu filter or any bpdu guard. Instance 0 is in designated Port Role IPSpecialist.net 68
44 and Status is forwarding. Instance 1030 is in Root port role and in forwarding State. Similarly, compare the Output of Switch 2. It should be the opposite and vice versa. S2#show spanning-tree mst interface Ethernet 0/0 From the output, we can see the status of the Interface Ethernet 0/0 which is the trunk port between Switch 1 and Switch 2. This Interface is not enabled with any Port guard Feature, any bpdu filter or any bpdu guard. Instance 0 is in Root Port Role and Status is Forwarding. Instance 1030 is in Designated port role and in forwarding State. Where as from previous output of Switch 1 For instance 0 is Designated Port. That s all we need from MST. S1#show spanning-tree IPSpecialist.net 69
45 The command Show spanning-tree also shows the Output of MST ports so we can also just use Show Spanning-tree command. S2#show spanning-tree IPSpecialist.net 70
46 IPSpecialist.net 71
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCNP TSHOOT. Quick Reference Sheet Exam
 CCNP TSHOOT Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-135 Chapter 1. Network Principles Troubleshooting Steps Problem Identification Collection of Information Examination and Action Plan Verification Basic Troubleshooting
CCNP TSHOOT Quick Reference Sheet Exam 300-135 Chapter 1. Network Principles Troubleshooting Steps Problem Identification Collection of Information Examination and Action Plan Verification Basic Troubleshooting
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
CCIE Foundation. WorkBooks.com. Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP. 3550/3560 Switching. Answers
 CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
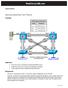 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Lab 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
examcollection.premium.exam.157q. Exam code: Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version 15.0
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 9.0. Cisco Questions & Answers
 300-115 Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Questions & Answers Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Exam Topic 1, Layer
300-115 Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Questions & Answers Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 9.0 Cisco 300-115 Exam Topic 1, Layer
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Lab Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
RealCiscoLAB.com. Multiple Spanning Tree. Topology. Objective. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH. Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST).
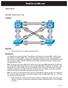 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
Configuring Private VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for Private VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for Private VLANs, on page 1 Information About Private VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure Private VLANs, on
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for Private VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for Private VLANs, on page 1 Information About Private VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure Private VLANs, on
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security,
CHAPTER 8 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the same security,
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
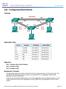 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 9 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the
9 CHAPTER Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Virtual private networks (VPNs) provide enterprise-scale connectivity on a shared infrastructure, often Ethernet-based, with the
PracticeDump. Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam
 PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway. Ports Assignment Network
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
Configuring Optional STP Features
 CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
CHAPTER 29 This chapter describes how to configure optional STP features. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master List, at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series ISR
 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min
 300-115 cisco Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Sections 1. Layer 2 Technologies 2. Infrastructure Security 3. Infrastructure Services 4. Mix QUESTIONS Exam A QUESTION 1 What is the
300-115 cisco Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Sections 1. Layer 2 Technologies 2. Infrastructure Security 3. Infrastructure Services 4. Mix QUESTIONS Exam A QUESTION 1 What is the
Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands
 CHAPTER Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands New Commands call-home (global configuration) call-home request call-home send call-home send alert-group call-home test clear energywise neighbors clear errdisable
CHAPTER Catalyst 4500 Series IOS Commands New Commands call-home (global configuration) call-home request call-home send call-home send alert-group call-home test clear energywise neighbors clear errdisable
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version: 10.0
 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 10.0 Topic 1, Layer 2 Technologies Cisco 300-115 Exam QUESTION NO: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco
Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version: 10.0 Topic 1, Layer 2 Technologies Cisco 300-115 Exam QUESTION NO: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter defines the types of Catalyst 2975 interfaces and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch stack. Understanding
CHAPTER 12 This chapter defines the types of Catalyst 2975 interfaces and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch stack. Understanding
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
examcollection.premium.exam.191q
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.191q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 10.0 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 10.0 Sections 1. Layer 2 Technologies
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.191q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 10.0 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 10.0 Sections 1. Layer 2 Technologies
Configuring Private VLANs
 36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
VLANs and Trunking C H A P T E R. 6-1: VLAN Configuration. Section 6-1
 C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2
 Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Copyright 2014 CertificationKits LLC. All Rights Reserved. 2 Spanning Tree Protocol is a bridge protocol that enables a learning bridge to dynamically work around loops in a network topology by creating
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Catalyst 3750 switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch
CHAPTER 11 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Catalyst 3750 switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement Multiple Spanning Tree Leverage VTP version 3 with MST Background Cisco s Per VLAN Spanning Tree
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement Multiple Spanning Tree Leverage VTP version 3 with MST Background Cisco s Per VLAN Spanning Tree
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
Configuring Control-Plane Security
 CHAPTER 32 This chapter describes the control-plane security feature in the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. In any network, Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches exchange control packets with other switches
CHAPTER 32 This chapter describes the control-plane security feature in the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. In any network, Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches exchange control packets with other switches
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Describing the STP. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Describing the STP 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 IEEE Documents IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
CCENT Study Guide. Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing
 CCENT Study Guide Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.4 Configure, verify, and troubleshoot
CCENT Study Guide Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.4 Configure, verify, and troubleshoot
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min.
 300-115 cisco Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13
300-115 cisco Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13
::::::::Notes::::::::: (802.1q Tunneling/QinQ Tunneling)(Used for Metro-Ethernet Networks/Layer 2 VPN)
 ::::::::Notes::::::::: (802.1q Tunneling/QinQ Tunneling)(Used for Metro-Ethernet Networks/Layer 2 VPN) 1.Layer 2 VPN over switched ethernet network (similar to lightweight version of MPLS L2VPN)(Any transport
::::::::Notes::::::::: (802.1q Tunneling/QinQ Tunneling)(Used for Metro-Ethernet Networks/Layer 2 VPN) 1.Layer 2 VPN over switched ethernet network (similar to lightweight version of MPLS L2VPN)(Any transport
Exam Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH)
 Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Exam 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Multiple Choice Questions (2018-05-08 Updated) (300-115) Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Exam 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Multiple Choice Questions (2018-05-08 Updated) (300-115) Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Storm Control over EVC
 This chapter describes and procedures to configure., page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Configuring, page 2 Examples, page 3 Verification, page 5 Storm control prevents traffic on a LAN from being disrupted
This chapter describes and procedures to configure., page 1 Restrictions for, page 1 Configuring, page 2 Examples, page 3 Verification, page 5 Storm control prevents traffic on a LAN from being disrupted
CCNP Bootcamp. Introduction
 0101010101010101101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010 010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101 1010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101010101010101010110101010101010101
0101010101010101101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010 010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101 1010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101010101010101010110101010101010101
Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior
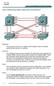 Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Scenario Four switches have just been
Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Scenario Four switches have just been
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
Configuring VLAN Trunks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
 CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
Braindumps questions. Cisco Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
 Braindumps.300-115.156 questions Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.5 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks A questions are all in the dump file and
Braindumps.300-115.156 questions Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.5 Cisco 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks A questions are all in the dump file and
BraindumpsIT. BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf!
 BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Actualtests Galvin 158q. Exam code: Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
 Actualtests 300-115 Galvin 158q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 16.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Actualtests 300-115 Galvin 158q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 16.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Download: PT-Topology-STP2.pkt
 IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
IEEE Documents Describing the STP IEEE 802.1D IEEE 802.1Q IEEE 802.1w IEEE 802.1s - Media Access Control (MAC) bridges - Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks - Rapid Reconfiguration (Supp. to 802.1D) -
Nexus 7000 Peer Switch Configuration (Hybrid Setup)
 Nexus 7000 Peer Switch Configuration (Hybrid Setup) Document ID: 116140 Contributed by Andy Gossett and Rajesh Gatti, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 09, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Nexus 7000 Peer Switch Configuration (Hybrid Setup) Document ID: 116140 Contributed by Andy Gossett and Rajesh Gatti, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 09, 2013 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure port-based traffic control features on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure port-based traffic control features on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
