CCIE Foundation. WorkBooks.com. Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP. 3550/3560 Switching. Answers
|
|
|
- Bartholomew O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of 55
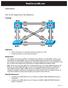
2 Router to Switch connection SW 1 F0/1 F0/2 R3 F0/3 F0/4 F0/5 F0/6 R1 F0/0 F0/1 R2 F0/0 F0/1 R3 F0/0 F0/1 R4 F0/0 F0/1 R5 F0/0 F0/1 R6 F0/0 F0/1 SW 2 F0/1 F0/2 F0/3 F0/4 F0/5 F0/6 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 2 of 55
3 Switch to Switch Connection SW 1 F0/20 F0/19 SW 2 F0/22 F0/21 F0/21 F0/22 F0/19 SW 3 F0/20 SW 4 SW 1 F0/7 F0/8 SW 4 SW 2 F0/7 F0/8 SW 3 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 3 of 55
4 Lab /3560 Switching Task 1 The first Catalyst switch should be configured with a hostname of SW 1 and the second Catalyst should have a hostname of SW 2. On the first Switch Switch(config)#Hostname SW 1 On the Second Switch Switch(config)#Hostname SW 2 Task 2 Configure SW 1 to be in VTP domain called CCIE, this configuration should be propagated to SW 2 via VTP messages. Maintaining a consistent list of VLANs in a huge network where there are many interconnected switches can be an administrative nightmare, in order to reduce this administrative overhead switches that share a common VLAN information can be organized into logical groups called VTP domains. These domain do not create a layer two boundary, they only create different management domains. Switches in a given VTP domain exchange VTP updates to synchronize VLAN information. In order for two or more switches to exchange VTP updates, the two switches must have a trunk established between them, this is because VTP messages can ONLY cross trunk links. Note the two switches are connected with 2 cross over ethernet cables, if these switches are 3550s, the two ports would negotiate an ISL trunk, but if the two switches are 3560s, they would NOT negotiate a trunk, because by default the ports on 3560 switches are in auto mode, whereas, the ports on 3550 switches are in desirable mode. To see this on the switches: CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 4 of 55
5 On 3550 switches: 3550#Show interface status Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type Fa0/1 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100BaseTX Fa0/2 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100BaseTX Fa0/3 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100BaseTX Fa0/4 notconnect 1 auto auto 10/100BaseTX (The rest of the output is omitted) On 3560 switches: 3560#Show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2102 bytes! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport mode dynamic desirable! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport mode dynamic desirable! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport mode dynamic desirable (The rest of the output is omitted) To create the trunk, we should first check to see if the trunk was automatically negotiated, if the switches are 3560s, they will NOT negotiate a trunk, as follows: 3560#Show int trunk SW 1# Note the trunk is not negotiated. If the switches are 3550s, you should see that the trunk is automatically negotiated using Cisco proprietary trunking protocol called ISL, as follows: 3550#Show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/20 desirable n isl trunking 1 Fa0/21 desirable n isl trunking 1 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 5 of 55
6 Note the status is n isl, which means negotiated ISL. To configure the ports as trunk: On Both switches: (config)#int range f0/19 20 (config if range)#switchport trunk encapsulation isl (config if range)#switchport mode trunk These commands will be explained in later steps. To verify the configuration: On Both switches: #Show int trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/19 on isl trunking 1 Fa0/20 on isl trunking 1 (The rest of the output is omitted) Now that the trunk is established between the two switches, you can go on with VTP configuration as follows: By default the 3550/3560 switches are member of a domain called NULL, in this mode the switches will not propagate VLAN information from one switch to another. Enter the following to change the VTP domain name to CCIE. SW 1(config)#VTP domain CCIE Note once the above command is entered, you should see the following message telling you that the domain name was changed from the default name of NULL to CCIE. Changing VTP domain name from NULL to CCIE This task could also be accomplished by entering the VLAN database as follows: SW 1#Vlan database SW 1(vlan)#Vtp domain CCIE CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 6 of 55
7 SW 1(vlan)#Exit When a command is entered in the Vlan database, you must perform the exit or the apply command for the changes to take effect. Note the display below reveals that VTP propagated the VTP domain information to the second switch: On SW 2: SW 2#Sh vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 5 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x57 0xCD 0x40 0x65 0x63 0x59 0x47 0xBD Configuration last modified by at :00:00 Local updater ID is (no valid interface found) Task 3 This VTP domain should be password protected using Cisco as the password. VTP password can be changed in three ways: Privilege mode: Switch#vtp password Cisco Vlan Database: Vlan database Vtp password Cisco Exit Global config mode: Switch(config)#vtp password Cisco In this task it is configured in Global config mode as follows: CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 7 of 55
8 On both switches (config)#vtp password Cisco You should get the following message: Setting device VLAN database password to Cisco Note, if a domain name is not assigned to the switches and the default name (NULL) is used, a password can not be assigned. This VTP password command can be entered in global configuration mode, privilege configuration mode or in the VLAN database mode. The password command must be configured statically on both switches because this change will NOT get propagated via VTP messages. To verify the configuration: On any of the switches: #Show VTP password VTP Password: Cisco This verifies the password, remember Spaces will not show Task 4 SW 2 should NOT have the ability to create, delete or rename VLAN or VLAN information. On SW 2 SW 2(config)#Vtp mode client This configuration can be performed in the vlan database or global config mode. The above command was entered in the global config mode. If this command must be configured in the vlan database, you must first enter the vtp database command in the privilege mode, then, enter vtp client and lastly the exit command must be used for the changes to take effect. Once the command is entered you should get the following message: Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode. CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 8 of 55
9 The switches can operate in three different VTP modes and they are as follows: Server mode: Creates, modifies and deletes VLANs Sends and forwards VTP advertisements Synchronizes VLAN information Saves VLAN information in vlan.dat in the flash memory Client mode: CAN NOT create, modify or delete VLAN information Forwards the VTP advertisements Synchronizes VLAN information CAN NOT save the configuration in the NVRAM Transparent mode: Creates, deletes and modifies VLANs locally Forwards the VTP advertisements Does NOT process VTP messages Saves VLAN information in NVRAM and NOT the VLAN database Task 5 Create and configure the following VLAN assignments: Router Interface VLAN number CAT Switches Port R1 F0/0 12 SW1 F0/1 R2 F0/0 12 SW1 F0/2 R3 F0/0 34 SW1 F0/3 R4 F0/0 34 SW1 F0/4 R5 F0/0 56 SW1 F0/5 R6 F0/0 56 SW1 F0/6 R1 F0/1 111 SW2 F0/1 30 SW 1(config)#interface range f0/1 2 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 9 of 55
10 SW 1(config if)#switch mode access SW 1(config if)#switch access vlan 12 SW 1(config)#interface range f0/3 4 SW 1(config if)#switch mode access SW 1(config if)#switch access vlan 34 SW 1(config)#interface range F0/5 6 SW 1(config if)#switch mode access SW 1(config if)#switch access vlan 56 SW 1(config)Vlan 30 SW 1(config)exit Note the Vlan information will be propagated to the other switch (SW 2), because both switches are in the same VTP domain, password and they have a trunk connecting them to each other. On SW 2 SW 2#Show vlan brie VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12 Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16 Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/23, Fa0/24 Gi0/1, Gi0/2 12 VLAN0012 active 34 VLAN0034 active 56 VLAN0056 active 30 VLAN0030 active (The rest of the output is omitted) SW 2#Show VTP Status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 4 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 8 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 10 of 55
11 VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x97 0x9D 0xF1 0xF9 0xFE 0x21 0xCC 0x1D Configuration last modified by at :06:11 Local updater ID is (no valid interface found) SW 1#Show VTP Status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 4 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 8 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x97 0x9D 0xF1 0xF9 0xFE 0x21 0xCC 0x1D Configuration last modified by at :06:11 Local updater ID is (no valid interface found) Note, VTP version is 2, Configuration revision is 4, number of existing VLANs is 8 on both switches, (because they are synchronized), and the reason the VLAN information was propagated is because the VTP domain name and the password is identical on both switches and the switches are trunked. SW 1 should be used to create VLAN 111, this is because SW 2 is in VTP client mode. You should see the following error message if SW 2 is used to create VLAN 111. SW 2(config)#vlan 111 VTP VLAN configuration not allowed when device is in CLIENT mode. SW 1(config)#vlan 111 SW 1(config vlan)#exit To verify the configuration: On SW 2 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 11 of 55
12 SW 2#Show vlan brief VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12 Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16 Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/21, Fa0/22 Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2 12 VLAN0012 active 34 VLAN0034 active 56 VLAN0056 active 111 VLAN0111 active 30 VLAN0030 active Task 6 Ensure that SW1 s Loopback0 ( /8) interface is used as the preferred source for the VTP IP updater address. Note in the last Task when the show vtp status command was entered on SW 1, the last line of the output displayed the fact that (no valid interface found). SW 1 can be configured such that the IP address of any of it s interfaces in this case Loopback0 is used as the source of all VTP messages, as follows: SW 1(config)# Interface Loopback 0 SW 1(config if)# Ip address SW 1(config if)# Exit SW 1(config)# Vtp interface Loopback0 Note the above command is not needed, as long as SW 1 has an IP address configured the source of all VTP updates will use that specific IP address as the source IP address of all VTP messages, if your switch is configured with multiple IP addresses, and you must use a specific IP address as the source of the updates, then, the above command can be used to specify the IP address of a given interface as the source of all VTP updates. SW 1#Show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 4 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 12 of 55
13 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 8 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x97 0x9D 0xF1 0xF9 0xFE 0x21 0xCC 0x1D Configuration last modified by at :06:11 Local updater ID is on interface Lo0 (preferred interface) Preferred interface name is lo0 On SW 2 SW 2#Show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 4 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 8 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x97 0x9D 0xF1 0xF9 0xFE 0x21 0xCC 0x1D Configuration last modified by at :22:29 Create a VLAN (VLAN 80) on SW 1 so you can see that the change was made by an IP address of on SW 2. This VLAN should be deleted before proceeding to the next task. SW 1(config)#Vlan 80 Sw 1(config)#exit On SW 2 SW 2#Show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 5 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 13 of 55
14 Number of existing VLANs : 9 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x02 0x05 0x92 0x34 0xF0 0xC0 0x35 0x9D Configuration last modified by at :34:33 SW 1(config)#No vlan 80 Task 7 Configure the switches such that flooded traffic is restricted to the trunk links that the traffic must use to reach the destination device. This task calls for VTP pruning and the following Show command reveals the current status of VTP pruning: On SW 2 SW 2#Show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 5 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 8 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled Pruning is disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x97 0x9D 0xF1 0xF9 0xFE 0x21 0xCC 0x1D Configuration last modified by at :12:48 Local updater ID is o interface Lo0 (First layer3 interface found) Note the above show command reveals that VTP Pruning is disabled CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 14 of 55
15 SW 1#Vtp pruning This command can be configured in privilege mode, Global config mode, and/or in the Vlan database. Once this feature is enabled, it will get propagated to the other switches within the VTP domain. To verify the configuration on both switches: On SW 2 SW 2#Show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 6 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 8 VTP Operating Mode : Server VTP Domain Name : CCIE VTP Pruning Mode : Enabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0x97 0x9D 0xF1 0xF9 0xFE 0x21 0xCC 0x1D Configuration last modified by at :12:48 Note VTP messages propagate the change through the entire VTP domain. Its possible to have a switch within the enterprise that does not have local port membership in a given VLAN/s. VTP pruning increases the available bandwidth on the trunk links by restricting flooded traffic to those trunk links that the traffic must use to access the give host. Remember that VLAN 1 is always ineligible for pruning and traffic from VLAN 1 can not be pruned. Remember that this can ONLY be configured on the switches that are in VTP server mode. Task 8 Ensure that SW 1 is the root bridge for the VLANs 12 and SW 2 is the root bridge for VLAN 56. Do NOT use the priority command to accomplish this task. There are three commands that can be used to display the BID for a given switch: Show version Show spanning tree bridge Show interface Vlan 1 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 15 of 55
16 SW 1#Show version SW 1#Show ver Cisco IOS Software, C3560 Software (C3560 ADVIPSERVICESK9 M), Version 12.2(25)SEE2, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Copyright (c) by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 28 Jul 06 12:34 by yenanh Image text base: 0x , data base: 0x012237D0 (The output of this show command is modified) 512K bytes of flash simulated non volatile configuration memory. Base ethernet MAC Address : 00:19:06:7F:89:00 Motherboard assembly number : Power supply part number : Motherboard serial number : CAT10297MHE Power supply serial number : AZS V Model revision number : D0 The rest of the output is omitted The base MAC The following command reveals the base MAC address of the switch, the combination of priority and the base MAC address is the BID for a given switch. SW 1#Show spanning tree bridge Hello Max Fwd Vlan Bridge ID Time Age Dly Protocol VLAN (32768, 1) f ieee VLAN (32768, 12) f ieee VLAN (32768, 34) f ieee VLAN (32768, 56) f ieee VLAN (32768, 30) f ieee Note the priority starts with 32768, each VLAN that is created adds it s VLAN number to the default priority value (If the base priority and the VLAN number is added within the parenthesis, the sum will be the priority for that given VLAN, which is displayed to the left of the parenthesis), VLAN 12 adds 12 to the default priority value, therefore, the priority is and VLAN 34 adds 34 to the default priority value, therefore, the priority is Note that the MAC is the base MAC address and it remains the same, in this case ( f.8900). Note your MAC address maybe different. CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 16 of 55
17 SW 1#Show int Vlan 1 Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is EtherSVI, address is f.8940 (bia f.8940) MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit, DLY 10 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 The output of the above command will reveal the bia or the MAC address of VLAN 1 interface which is also the base MAC address of the switch To find out the BID and the root bridge for a given VLAN, enter the following Show command: SW 1#Show spanning tree vlan 12 SW 1#Show spanning tree vlan 12 VLAN0012 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee The MAC address of the root bridge Root ID Priority Address 0018.b This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority (priority sys id ext 12) Address 0018.b Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 The Mac address of the local switch Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/19 Desg FWD P2p Fa0/20 Desg FWD P2p Note even though the above show commands reveals that SW 1 is the root bridge for VLAN 12 we should statically configure this switch so in the future a topology change will not change the root bridge for this VLAN. Enter the following commands to configure SW 1 to be the root bridge for VLANs 12: SW 1(config)#Spanning tree vlan 12 root primary The above command configures SW 1 to be the root for VLAN 12; the root keyword is a CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 17 of 55
18 macro that reduces the BID of the switch for a given VLAN by a value of 8192 (The lower value is the preferred value). SW 1#Show spanning tree vlan 12 VLAN0012 Note = Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority Address 0018.b This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority (priority sys id ext 12) Address 0018.b Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/19 Desg FWD P2p Fa0/20 Desg FWD P2p On SW 2 SW 2(config)##Spanning tree vlan 56 root primary To verify the configuration: On SW 2 SW 2#Sh spanning tree vlan 56 VLAN0056 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority Address 001a.2f0a.2000 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority (priority sys id ext 56) Address 001a.2f0a.2000 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 15 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 18 of 55
19 Fa0/19 Desg FWD P2p Fa0/20 Desg FWD P2p Task 9 Configure SW 1 to be the root bridge for VLAN 34 and SW 2 to be the root bridge for VLAN 111; you should use the priority command to accomplish this task. When it comes to priority and values, Cisco plays two games, basketball and golf, what I mean by that is that sometimes the lower number has more preference and sometimes the higher number. When it comes to spanning tree, the lower number has more preference. SW 1(config)#spanning tree vlan 34 priority 0 Note the priority of this VLAN is set to zero, which is the lowest number within the range. To verify the configuration On Sw 1 SW 1#Show spanning tree vlan 34 VLAN0034 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 34 Address 001a.2f0a.2000 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 34 (priority 0 sys id ext 34) Address 001a.2f0a.2000 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 300 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/19 Desg FWD P2p Fa0/20 Desg FWD P2p On Sw 2 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 19 of 55
20 SW 2(config)#spanning tree vlan 111 priority 0 To verify the configuration: On Sw 2 SW 2#Show spanning tree vlan 111 VLAN0111 Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee Root ID Priority 111 Address 001a.2f0a.2000 This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 111 (priority 0 sys id ext 111) Address 001a.2f0a.2000 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 15 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type Fa0/19 Desg FWD P2p Fa0/20 Desg FWD P2p Task 10 Configure SW 1 such that the ports that the routers are connected to bypass listening and learning state. If any of these ports receive BPDU packets, they should transition into errdisable state. Use minimum number of commands to accomplish this task. This configuration should only be applied to the ports that the routers R1 R6 are connected to. Spanning tree PortFast causes an interface that is configured as a layer 2 access port to transition from blocking to forwarding state immediately by bypassing the listening and learning states. PortFast should be configured on interfaces that have a single host connected. If PortFast is enabled on a port connecting to another switch, a Spanning tree loop may result. If BPDU guard is configured, and an interface configured as PortFast receives BPDUs, the port will transition into err disable mode blocking all traffic. CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 20 of 55
21 SW 1(config)#Spanning tree portfast bpduguard default SW 1(config)#Interface range F0/1 6 SW 1(config if)#spanning tree portfast This command could also be configured globally, by using the Spanning tree portfast default command; this command enables PortFast on all non trunking ports. Once the portfast command is entered you should see the following warning message: %Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc... to this Interface when portfast is enabled, can cause temporary bridging loops. Use with CAUTION %Portfast will be configured in 6 interfaces due to the range command but will only have effect when the interfaces are in a non trunking mode. The spanning tree portfast bpduguard default command in global config mode will shut the port down in err disable mode if any portfast enabled port receives BPDU packets. Task 11 Ensure that ports F0/19 of both switches are trunking. These ports should NOT use any DTP for establishing the trunk Ensure that VLAN 111 does not get tagged as the traffic for this VLAN traverses this trunk link. Ensure that traffic for VLAN 30 does NOT traverse this trunk link. A trunk by default carries traffic for all VLANs; in order to differentiate traffic from different VLANs a trunking protocol is used. Basically the sending switch marks each frame with a VLAN ID before sending the traffic through the trunk link so the receiving switch can distinguish the destination VLAN of the frames. For security or other reasons it s a good practice to configure the trunk links such that they ONLY carry traffic for intended VLANs, in this task the traffic for VLAN 30 should NOT traverse this trunk link. A trunk can be established between the following devices: Between two Switches A switch and a router A switch and a NIC that has the capability of establishing a trunk CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 21 of 55
22 In CCIE lab exam, I highly recommend reading each section entirely before configuring the tasks within that section. In this case if this entire section was read before, this task and task 19 would have been configured already. The last item of this task requires us to configure DOT1Q trunking. Remember that when a switch configured with DOT1Q receives an untagged frame, it will assign it to the native VLAN. In DOT1Q the native VLAN traffic is NOT tagged, the native VLAN is VLAN 1 by default. Because of this fact, you must ensure that native VLAN is identical on both ends of the trunk. If VLANs are not identical on both ends of a trunk, the traffic from different VLANs will merge, in order to prevent this from occurring, the trunk link will go down if the VLANs are not identical on both ends of a trunk. On Both Switches (config)#interface F0/19 (config if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q (config if)#switchport mode trunk The Switchport trunk encapsulation command can have the following parameters: Dot1q Specifies dot1q encapsulation on the trunk link. ISL Specifies dot1q encapsulation on the trunk link. Negotiate Specifies that the local interface should negotiate with the neighboring interface (The interface to which it is connected to) to become either dot1q or ISL, depending on the configuration of the neighboring interface. The Switchport mode trunk command puts the interface into permanent trunking mode. To verify the configuration: On both Switches SW 1#Show int trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/19 on 802.1q trunking 1 Fa0/20 on isl trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 22 of 55
23 Fa0/ Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/19 1,12,30, 34,56, 111 Fa0/20 1,12,30, 34,56, 111 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/19 1,12,30, 34,56 Fa0/20 12,34 To configure the second bullet item: To see the default setting: On Both Switches: SW 2#Show int f0/19 switchport Name: Fa0/19 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled (The rest of the output is omitted) Note the negotiation of trunking is ON To change this setting: On Both Switches: (config)#int f0/19 (config if)#switchport nonegotiate To verify the configuration: On Both Switches: #Show int f0/19 switchport CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 23 of 55
24 Name: Fa0/19 Note the trunking negotiation is OFF Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Operational Trunking Encapsulation: dot1q Negotiation of Trunking: Off Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) (The rest of the output is omitted) To configure the third bullet item: SW 1(config if)#switchport trunk native vlan 111 Note once this command is entered you should see the following console message: %CDP 4 NATIVE_VLAN_MISMATCH: Native VLAN mismatch discovered on FastEthernet0/19 (111), with SW 2 FastEthernet0/19 On Sw 2 SW 1(config if)#switchport trunk native vlan 111 To configure the forth item: To see the default behavior: SW 1#Show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/19 on 802.1q trunking 111 Fa0/20 on isl trunking 1 Note by default all VLAN are allowed to Port Vlans allowed on trunk to traverse the trunk Fa0/ Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/19 1,12,30,34,56,111 Fa0/20 1,12,30,34,56,111 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/19 1 Fa0/20 1 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 24 of 55
25 To configure this item: On Both Switches: (config if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan except 30 Note the following reveals all options: (config if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan? WORD VLAN IDs of the allowed VLANs when this port is in trunking mode add add VLANs to the current list all all VLANs except all VLANs except the following none no VLANs remove remove VLANs from the current list You can use some of these options to accomplish this task. To verify the configuration: On Both Switches: #Show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/19 on 802.1q trunking 111 Fa0/20 on isl trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Note VLAN 30 is NOT allowed to traverse Fa0/ , the trunk Fa0/ Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/19 1,12,34,56,111 Fa0/20 1,12,30,34,56,111 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/19 1 Fa0/20 1 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 25 of 55
26 Task 12 You received a request from the IT department to monitor and analyze all the packets sent and received by the host connected to port F0/14 on SW 1, you have connected the packet analyzer to port F0/15 on the same switch, configure the switch to accommodate this request. SW 1(config)#monitor session 1 source interface F0/14 both The above command identifies the source interface, which is the interface that needs to be monitored in both directions. SW 1(config)#monitor session 1 destination interface F0/15 This command identifies the destination port, this is the port to which the packet analyzer is connected to. Note the following: There can only be two monitor sessions configured on a given switch Their direction to monitor can be configured as Rx, Tx, or Both, Rx is for received traffic, Tx is for Transmitted traffic, and both is in both direction. VLANs can ONLY be configured in Rx direction. To verify the configuration, enter the Show monitor session 1 command. To verify the configuration: SW 1#Show monitor session 1 Session 1 Type : Local Session Source Ports : Both :Fa0/14 Destination Ports : Fa0/15 Encapsulation : Native Ingress : Disabled CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 26 of 55
27 Task 13 You received another request from your IT department to keep track of all the MAC addresses that are learned by SW 2 port F0/18. The switch must use the NMS located at /24, configure the switch to handle this request. You should use an IP address of /8 with traps called PRIVATE to accomplish this task. On SW 2 SW 2(config)#Snmp server host trap PRIVATE %IP_SNMP 3 SOCKET: can't open UDP socket Unable to open socket on port 161 Note since this switch is not configured with an IP address, it will fail to configure the Snmp server. Therefore, an IP address should be configured before entering the snmp server command as follows: SW 2(config)#Int lo0 SW 2(config if)#ip addr SW 2(config)#snmp server host traps PRIVATE To setup the Snmp Server s IP address and the traps PRIVATE SW 2(config)#snmp server enable traps mac notification Configures the switch to send mac address traps to the NMS SW 2(config)#mac address table notification To enable MAC address notification SW 2(config)#Inter f0/18 SW 2(config if)#snmp trap mac notification added The above command enables the SNMP trap on interface F0/18 and configures the switch to send MAC notification traps whenever a MAC address is learned (added). If the switch must be configured to report the MAC addresses that are learnt and expired, then snmp trap mac notification removed command must also be configured under the interface. To verify the configuration: SW 2#Show mac address table notification interface f0/18 MAC Notification Feature is Enabled on the switch Interface MAC Added Trap MAC Removed Trap FastEthernet0/18 Enabled Disabled CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 27 of 55
28 Note if the snmp trap mac notification removed command was also entered for F0/19 interface, under the MAC removed Trap column you would also see as Enabled. SW 2#Show mac address table notification MAC Notification Feature is Enabled on the switch Interval between Notification Traps : 1 secs Number of MAC Addresses Added : 0 Number of MAC Addresses Removed : 0 Number of Notifications sent to NMS : 0 Maximum Number of entries configured in History Table : 1 Current History Table Length : 0 MAC Notification Traps are Enabled History Table contents Task 14 Configure SW 2 using the following policy: The ports that routers R1 R6 are connected should be configured such that they only allow one MAC address to be detected, if any other MAC address besides the pertaining router s MAC address is detected on any of these ports, the appropriate switch should drop the traffic for the newly learned MAC addresses, the switch should not send an SNMP trap or syslog message. You should use a regular and a smart port macro to accomplish this task. On SW 2 SW 2(config)#Define interface range ROUTER PORTS F0/1 6 The above command defines a range of ports on the switch and names them ROUTER PORTS SW 2(config)#Macro name PORT SECUR Enter macro commands one per line. End with the character '@'. switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security maximum 1 switchport port security violation SW 2(config)# The above configuration configures a smartport macro. A smartport macro is started by the CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 28 of 55
29 Macro name global config command and then followed by an arbitrary name that is assigned to the macro. Once that command is entered, a message is displayed in the command line. This message tells us to use sign in order to end and exit from this macro. Lines 3 to 6 contain the actual commands that the macro will execute. A smartport macro can be applied to an interface, interface range, or a regular macro. Lastly the Smartport Macro is applied to the regular macro, as follows: SW 2(config)#Interface range macro ROUTER PORTS SW 2(config if range)#macro apply PORT SECUR To verify the configuration, a Show run command is entered, most of the output from this show command is omitted and only the pertaining parts are shown: SW 2#Show run Building configuration...! macro name Port Secur switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security mac address sticky switchport port security maximum 1 switchport port security violation interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security violation protect macro description ROUTER SECUR! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security violation protect macro description ROUTER SECUR! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security violation protect macro description ROUTER SECUR! CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 29 of 55
30 interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security violation protect macro description ROUTER SECUR! interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security violation protect macro description ROUTER SECUR! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport mode access switchport port security switchport port security violation protect macro description ROUTER SECUR! define interface range Router Ports FastEthernet0/1 6! end Task 15 On SW 2 port F0/14 configure the amount of bandwidth utilization for broadcast traffic to 50%. On SW 2 SW 2(config)#Interface F0/14 SW 2(config if)#storm control broadcast level Storm control can be used for Broadcast, Unicast and Multicast traffic, this command specifies traffic suppression level for a given type of traffic for a particular interface. The level can be from 0 to 100 and an optional fraction of a level can also be configured from A threshold value of 100 percent means that no limit is placed for the specified type of traffic; a value of 0.0 means that the particular type of traffic is blocked all together. On 3550 switches when the rate of Multicast traffic exceeds a predefined threshold, all incoming traffic (Broadcast, Multicast and Unicast) is dropped until the level of Multicast traffic is dropped below the threshold level. When the interface is in blocking mode, only the Spanning tree packets are forwarded. When Broadcast or Unicast thresholds are exceeded, traffic is blocked for only the type of traffic that exceeded the threshold. CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 30 of 55
31 To verify the configuration: SW 2#Show storm control f0/14 broadcast Interface Filter State Upper Lower Current Fa0/14 Forwarding 50.00% 50.00% 0.00% Task 16 SW 2 s ports F0/15 and F0/16 are connected to company s web and e mail server. These ports should be configured in VLAN 88. Ensure that these ports can t communicate with each other. You should NOT use private VLANs to accomplish this task. SW 1(config)#Vlan 88 To see the default setting: On SW 2 SW 2(config)#Interface range F0/15 16 SW 2(config if range)#switchport mode access SW 2(config if range)#switch access vlan 88 SW 2#Show inter f0/15 switch Name: Fa0/15 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: static access Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Negotiation of Trunking: Off Access Mode VLAN: 88 (Inactive) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private vlan host association: none Administrative private vlan mapping: none Administrative private vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 31 of 55
32 Administrative private vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL Protected: false Note the port is not in protected mode Unknown unicast blocked: disabled Unknown multicast blocked: disabled Appliance trust: none SW 2# On SW 2 Interface range F0/15 16 Switchport protected To verify the configuration: On SW 2 SW 2#Show inter f0/15 switch Name: Fa0/15 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: static access Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Negotiation of Trunking: Off Access Mode VLAN: 88 (Inactive) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private vlan host association: none Administrative private vlan mapping: none Administrative private vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 32 of 55
33 Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL Protected: true The port is now in protected mode Unknown unicast blocked: disabled Note unknown unicast or multicast Unknown multicast blocked: disabled traffic is not blocked Appliance trust: none SW 2# Typically port blocking is implemented when protected ports are configured. By default the switch will flood packets with unknown destination MAC addresses to all ports but the port that the packet/s was received. If unknown unicast or multicast traffic is forwarded to a protected port, there could be security issues. In order to prevent this behavior, unknown broadcast or unicast packets should be blocked, as follows: SW 2(config)#Interface range F0/15 16 SW 2(config if range)#switchport block unicast SW 2(config if range)#switchport block multicast To verify the configuration: SW 2#Show inter f0/15 switch Name: Fa0/15 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: static access Operational Mode: down Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Negotiation of Trunking: Off Access Mode VLAN: 88 (Inactive) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none Administrative private vlan host association: none Administrative private vlan mapping: none Administrative private vlan trunk native VLAN: none Administrative private vlan trunk Native VLAN tagging: enabled Administrative private vlan trunk encapsulation: dot1q Administrative private vlan trunk normal VLANs: none Administrative private vlan trunk private VLANs: none Operational private vlan: none Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Pruning VLANs Enabled: Capture Mode Disabled Capture VLANs Allowed: ALL CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 33 of 55
34 Protected: true Unknown unicast blocked: enabled Unknown multicast blocked: enabled Appliance trust: none SW 2# The ports are now blocking unknown unicast and multicast Note in the CCIE lab you should ONLY implement what is asked from you, if you are in doubt, always ask the proctor for clarification Task 17 Mac addresses learnt dynamically by these two switches should not stay in the MAC address table if they are inactive for longer than 10 minutes. By default the MAC addresses that are inactive will expire within 300 seconds, this task is asking for a 10 minutes threshold, 10 minutes equates to 600 seconds, the following command will accomplish this task: Before configuring this task, the default settings should be displayed as follows: and SW 2 #Sh mac address table aging time Vlan Aging Time To change the default settings: On Both Switches: (config)#mac address table aging time 600 To verify the configuration: On Both Switches: CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 34 of 55
35 #Sh mac address table aging time Vlan Aging Time Note this setting can also be changed for a given VLAN using the following command: (config)#mac address table aging time 600 vlan? <1 4094> VLAN id Task 18 For management purposes, assign an IP address of /24 to SW 1, with a default gateway of /24. SW 1(config)#Inter Vlan 1 SW 1(config if)#ip address SW 1(config if)#no shut SW 1(config if)#exit SW 1(config)#Ip default gateway To verify the configuration: SW 1#sh run int vlan 1 interface Vlan1 ip address end SW 1#Sh ip route Default gateway is CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 35 of 55
36 Host Gateway Last Use Total Uses Interface ICMP redirect cache is empty Task 19 Configure the F0/20 port of these two switches to trunk. You should use a Cisco proprietary solution for this trunk. This task was configured in Task 2 Task 20 Configure Multi instance of Spanning Tree on the switches using the follows policy: There should be two instances of STP, instance 1 and 2 Instance 1 should handle VLANs 12 and 34 Instance 2 should handle VLAN 56 and 111 All future VLANs should use instance 0 Instance 1 should use F0/19 Instance 2 should use F0/20 SW 1 should be the root bridge for the first instance SW 2 should be the root bridge for the second instance The name of this configuration should be CCIE The revision number should be 1 On Both Switches The default mode for spanning tree is PVST, the following Show command verifies this information: SW 1#Show spanning tree summary Switch is in pvst mode Root bridge for: none Extended system ID is enabled (The rest of the output is omitted) On Both Switches (config)#spanning tree mode mst This command changes the mode of the switch to MST. CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 36 of 55
37 (config)#spanning tree mst configuration (config mst)#revision 1 (config mst)#name CCIE (config mst)#instance 1 vlan 12,34 (config mst)#instance 2 vlan 56,111 The first command allows us to enter in the MST configuration mode. The second command specifies the configuration revision number; the range for this number is The third command specifies the name for this configuration, in this case CCIE. The forth and fifth commands map the requested VLANs to the specified instances, MST supports 16 instances, by default all the future VLANs will be assigned to instance 0, instance 0 is the catch all instance. To verify this configuration: On both Switches Show spanning tree mst configuration Name [CCIE] Revision 1 Instance Vlans mapped ,13 33,35 55, , , ,111 Note instance 0 handles the rest of the vlans that are not assigned to a given instance; instance 0 is the catch all instance. To Verify the configuration before configuring the next portion of the task: Show spanning tree bridge Hello Max Fwd MST Instance Bridge ID Time Age Dly Protocol MST (32768, 0) f mstp MST (32768, 1) f mstp MST (32768, 2) f mstp CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 37 of 55
38 Note this command displays the BID for your switch, and instead of assigning a BID to each VLAN, there is a BID for each instance. SW 1#Show spanning tree root Root Hello Max Fwd MST Instance Root ID Cost Time Age Dly Root Port MST f MST f MST f The above command displays the BID of the root bridge for different instances. Note in this case SW 1 is the root for all instances. SW 1(config)#Spanning tree mst 1 priority 0 SW 1(config)#Spanning tree mst 2 priority 4096 On SW 2 SW 2(config)#Spanning tree mst 1 priority 4096 SW 2(config)#Spanning tree mst 2 priority 0 The above commands will change the switch priority and make it more likely that SW 1 will be chosen as the root switch for instance 1 and SW 2 will be chosen as the root bridge for instance 2. This number must be in increments of Remember the lower value has higher preference. To verify the configuration: SW 1#Show spanning root Root Hello Max Fwd MST Instance Root ID Cost Time Age Dly Root Port MST f MST f MST a.2f0a Fa0/19 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 38 of 55
39 Note the local switch (SW 1) is the root bridge for instance 0 and 1, whereas, SW 2 is the root for instances 2. On SW 2 SW 2#Show spanning root Root Hello Max Fwd MST Instance Root ID Cost Time Age Dly Root Port MST f Fa0/19 MST f Fa0/19 MST a.2f0a Note SW 2 is the root bridge for instance 2, whereas, SW 1 is the root for instance 0 and 1. To configure the last portion of this task, port priority feature is used as follows: On Both Switches (config)#int F0/19 (config if)#spanning tree mst 1 port priority 0 (config if)# Spanning tree mst 2 port priority 128 High priority (config)#int F0/20 (config if)#spanning tree mst 1 port priority 128 (config if)#spanning tree mst 2 port priority 0 In this task Port priority is used when selecting an interface to put into the forwarding state for a given instance; a lower value has a higher priority. In this case port F0/21 will be used by all the VLANs that are assigned to instance 1, because it has a higher priority (Lower value), and the second instance will use port F0/22 because it has been configured with a higher priority (Lower value). To verify the configuration: SW 1#Show spanning tree int f0/19 Mst Instance Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 39 of 55
40 MST0 Desg FWD P2p MST1 Desg FWD P2p MST2 Altn BLK P2p SW 1#Sh spanning tree int f0/20 Mst Instance Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type MST0 Desg FWD P2p MST1 Desg FWD P2p MST2 Root FWD P2p On SW 2 SW 2#Show spanning tree int f0/19 Mst Instance Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type MST0 Root FWD P2p MST1 Root FWD P2p MST2 Desg FWD P2p SW 2#Sh spanning tree int f0/20 Mst Instance Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type MST0 Altn BLK P2p MST1 Altn BLK P2p MST2 Desg FWD P2p Note mst instance 1 is blocked on port F0/20 but forwarded on F0/19 and mst instance 2 is blocked on interface F0/19 and forwarded on F0/20. Task 21 There is another protocol analyzer connected to F0/18 on SW 2. You received a request to monitor and analyze all packets for port F0/16 on SW 1. Configure the switches to accommodate this request. CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 40 of 55
41 SW 1(config)#Vlan 90 SW 1(config vlan)#remote span SW 1(config vlan)#exit The creation of this VLAN can only be done in the global configuration mode, because this is the only mode that allows us to set the VLAN as remote span. Ensure that this VLAN is propagated to SW 2. Note in this case we had to create the VLAN on SW 1, because if you remember SW 2 was in VTP client mode. To verify the configuration: : SW 1#Sh vlan brie VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10 Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14 Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18 Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/23, Fa0/24 Gi0/1, Gi0/2 12 VLAN0012 active Fa0/1, Fa0/2 30 VLAN0030 active 34 VLAN0034 active Fa0/3, Fa0/4 56 VLAN0056 active Fa0/5, Fa0/6 90 VLAN0090 active Ensure that this VLAN is propagated to SW 2 On SW 2 SW 2#Sh vlan brie VLAN Name Status Ports 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12 Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16 Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20 Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2 CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 41 of 55
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
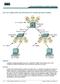 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
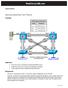 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
CCNP Bootcamp. Introduction
 0101010101010101101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010 010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101 1010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101010101010101010110101010101010101
0101010101010101101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010 010101010101010110101010101010101010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101 1010101010101011010101010101010110101010101010101101010101010101010101010101010110101010101010101
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
RealCiscoLAB.com. Multiple Spanning Tree. Topology. Objective. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH. Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST).
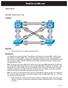 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Multiple Spanning Tree Topology Objective Background Observe the behavior of multiple spanning tree (MST). Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer
: Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks
 Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Chapter 2: Layer 2 Technologies
 Chapter 2: Layer 2 Technologies Troubleshooting Switch Administration Troubleshooting the switch can be tricky because there may or may not be an involvement of switch in network performance degradation.
Chapter 2: Layer 2 Technologies Troubleshooting Switch Administration Troubleshooting the switch can be tricky because there may or may not be an involvement of switch in network performance degradation.
Lab Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior
 Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Lab 3.10.7 Port Level Tuning to Control STP Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to use PortFast, UplinkFast, BPDU guard, root guard, and UDLD to control STP behavior on a port. Scenario Note:
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created,
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
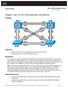 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
VLANs and Trunking C H A P T E R. 6-1: VLAN Configuration. Section 6-1
 C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
PracticeDump. Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam
 PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure port-based traffic control features on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure port-based traffic control features on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter,
Authorized CCNP. Student. LabManual SWITCH.
 Authorized CCNP SWITCH Student LabManual Web:www.networkershome.com Email:info@networkershome.com www.networkershome.com Authorized CCNPSWITCHWORKBOOK Module:01to20 CopyrightsNetworkersHome2007-2015 Website:htp:/www.networkershome.com;info@networkershome.com
Authorized CCNP SWITCH Student LabManual Web:www.networkershome.com Email:info@networkershome.com www.networkershome.com Authorized CCNPSWITCHWORKBOOK Module:01to20 CopyrightsNetworkersHome2007-2015 Website:htp:/www.networkershome.com;info@networkershome.com
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series ISR
 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 Overview of Port-Based Traffic Control, page 1 Finding Feature Information, page 2 Information About Storm Control, page 2 How to Configure Storm Control, page 4 Information About Protected Ports, page
Overview of Port-Based Traffic Control, page 1 Finding Feature Information, page 2 Information About Storm Control, page 2 How to Configure Storm Control, page 4 Information About Protected Ports, page
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring Smart Port Macros
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes how to configure and apply smart port macros. Release 12.2(33)SXH and later releases support smart port macros. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes how to configure and apply smart port macros. Release 12.2(33)SXH and later releases support smart port macros. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0
 Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
Advanced Troubleshooting CCIE Routing & Switching v5.0 www.micronicstraining.com Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP Switching-I Questions & Answers CCIE R&S by Narbik Kocharians Advanced
examcollection.premium.exam.157q. Exam code: Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version 15.0
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
Understanding and Configuring VTP
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Agenda» What Problem is Solved by STP?» Understanding STP Root Bridge Election» BPDU Details and Pathcost» Understanding STP Root and Designated Port Election» Understanding and
Spanning-Tree Protocol Agenda» What Problem is Solved by STP?» Understanding STP Root Bridge Election» BPDU Details and Pathcost» Understanding STP Root and Designated Port Election» Understanding and
Table of Contents. co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern
 outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
Lab Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype
 Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
Lab 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
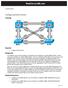 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0
 Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview Explain the origins and functions of VLAN trunking Describe how trunking enables the implementation of VLANs in a large network
Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview Explain the origins and functions of VLAN trunking Describe how trunking enables the implementation of VLANs in a large network
Configuring VTP. Understanding How VTP Version 1 and Version 2 Work CHAPTER
 10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 6500 series switches For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this
10 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Catalyst 6500 series switches For complete syntax and usage information for the commands that are used in this
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CCNP Switch Questions/Answers Labs
 Acme is small export company that has an existing enterprise network comprised of 5 switches; CORE, DSW1, DSW2, ASW1 and ASW2. The topology diagram indicates their desired pre-vlan spanning tree mapping.
Acme is small export company that has an existing enterprise network comprised of 5 switches; CORE, DSW1, DSW2, ASW1 and ASW2. The topology diagram indicates their desired pre-vlan spanning tree mapping.
Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Transparent Bridging Implementing Spanning Tree Protocol A switch has the same characteristics as a transparent bridge., Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior
 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.
![2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords. 2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown. This command has no arguments or keywords.](/thumbs/72/66270180.jpg) 2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface.
2V] Chapter 2 Catalyst 3560 Switch Cisco IOS Commands shutdown shutdown Use the shutdown interface configuration command to disable an interface. Use the no form of this command to restart a disabled interface.
Configuring Private VLANs
 36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Application Guide. VLANs for improved Q-SYS performance
 Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Configuring VTP. Understanding How VTP Works CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
CHAPTER 13 This chapter describes how to configure the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) on the Cisco 7600 series routers. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security
 ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 Overview of Port-Based Traffic Control, page 2 Finding Feature Information, page 2 Information About Storm Control, page 2 How to Configure Storm Control, page 4 Finding Feature Information, page 9 Information
Overview of Port-Based Traffic Control, page 2 Finding Feature Information, page 2 Information About Storm Control, page 2 How to Configure Storm Control, page 4 Finding Feature Information, page 9 Information
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
3. What could you use if you wanted to reduce unnecessary broadcast, multicast, and flooded unicast packets?
 Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
2.2 Cisco IOS Commands for the Catalyst 4500 Series Switches snmp ifindex clear. This command has no arguments or keywords.
 Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
Chapter 2 2.2 snmp ifindex clear snmp ifindex clear To clear any previously configured snmp ifindex commands that were entered for a specific interface, use the snmp ifindex clear command. snmp ifindex
Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008
 Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008 VLAN is a logically separate IP subnetwork. This allows multiple networks to exist on a switch and provide
Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008 VLAN is a logically separate IP subnetwork. This allows multiple networks to exist on a switch and provide
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement Multiple Spanning Tree Leverage VTP version 3 with MST Background Cisco s Per VLAN Spanning Tree
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 4 Lab 4-2 Multiple Spanning Tree INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement Multiple Spanning Tree Leverage VTP version 3 with MST Background Cisco s Per VLAN Spanning Tree
1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.)
 CCNA 2 Chapter 3 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.) The size of the collision domain is reduced. The number of required switches in
CCNA 2 Chapter 3 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.) The size of the collision domain is reduced. The number of required switches in
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Configuring VLAN Trunks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior
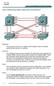 Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Scenario Four switches have just been
Lab 3-2 Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Objective The purpose of this lab is to observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Scenario Four switches have just been
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Exam Answers
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트
 PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a
Question 5.1. Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain.
 Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
