MT90826 Quad Digital Switch
|
|
|
- Caren Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
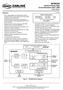
1 MT9826 Quad Digital Switch Features 4,96 4,96 channel non-blocking switching at 892 or 6384 Mbps Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Accepts 32 ST-BUS streams of 248 Mbps, 496 Mbps, 892 Mbps or 6384 Mbps Split Rate mode provides a rate conversion option to convert data from one rate to another rate Automatic frame offset delay measurement for ST-BUS input streams Per-stream input delay programming Per-stream output advancement programming Per-channel high impedance output control Bit Error Monitoring on selected ST-BUS input and output channels Per-channel message mode Connection memory block programming IEEE-49 (JTAG) Test Port 33 V local I/O with 5 V tolerant inputs and TTL compatible outputs Ordering Information MT9826AL 6 Pin MQFP Trays MT9826AG 6 Ball PBGA Trays MT9826AV 44 Ball LBGA Trays MT9826AL 6 Pin MQFP* Trays MT9826AG2 6 Ball PBGA** Trays *Pb Free Matte Tin **Pb Free Tin/Silver/Copper -4 C to +85 C Applications Medium switching platforms CTI application Voice/data multiplexer Digital cross connects WAN access system Wireless base stations January 26 V DD V SS TMS TDI TDO TCK TRST RESET ODE Test Port STi/FEi STi/FEi STi3/FEi3 Serial to Parallel Converter Multiple Buffer Data Memory Internal Registers Output MUX Connection Memory Parallel to Serial Converter STo STo STo3 Timing Unit Microprocessor Interface PLLV DD PLLV SS CLK Fi DS CS R/W A3-A DTA D5-D Figure - Functional Block Diagram Zarlink Semiconductor Inc Zarlink, ZL and the Zarlink Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Zarlink Semiconductor Inc Copyright 23-26, Zarlink Semiconductor Inc All Rights Reserved
2 MT9826 Description The MT9826 Quad Digital Switch has a non-blocking switch capacity of 4,96 x 4,96 channels at a serial bit rate of 892 Mbps or 6384 Mbps, 2,48 x 2,48 channels at 496 Mbps and 24 x 24 channels at 248 Mbps The device has many features that are programmable on a per stream or per channel basis, including message mode, input offset delay and high impedance output control The per stream input and output delay control is particularly useful for managing large multi-chip switches with a distributed backplane Operating in Split Rate mode allows rate conversion for switching between two groups of bit rate streams 2 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
3 MT9826 Table of Contents Device Overview 2 2 Functional Description 4 2 Data and Connection Memory 4 22 Connection and Message Modes 4 23 Clock Timing Requirements 5 3 Switching Configurations 5 3 Serial Input Frame Alignment Evaluation 6 32 Input Frame Offset Selection 6 33 Output Advance Offset Selection 6 34 Memory Block Programming 7 35 Bit Error Rate Monitoring 7 4 Delay Through the MT Variable Delay Mode (TM=, TM=) 8 42 Constant Delay Mode (TM=, TM=) 8 5 Microprocessor Interface 8 6 Memory Mapping 29 7 Connection Memory Control 29 8 DTA Data Transfer Acknowledgment Pin 29 9 Initialization of the MT JTAG Support 3 Test Access Port (TAP) 3 2 Instruction Register 3 3 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
4 MT9826 List of Figures Figure - Functional Block Diagram Figure 2-6-Pin MQFP Pin Connections 7 Figure 3-6 Ball PBGA Pin Connections 8 Figure 4-44 Ball LBGA Pin Connections 9 Figure 5 - Example for Frame Alignment Measurement 22 Figure 6 - Examples for Input Offset Delay Timing 26 Figure 7 - Examples for Frame Output Offset Timing 28 Figure 8 - ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 6384 Mbps 37 Figure 9 - ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 892 Mbps when CLK = 6384 MHz 38 Figure - ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 496 Mbps when CLK = 6384 MHz 38 Figure - ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 496 Mbps when CLK = 892 MHz 38 Figure 2 - ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 248 Mbps when CLK = 6384 MHz 39 Figure 3 - -BUS Timing for Stream rate of 248 Mbps when CLK = 892 MHz 39 Figure 4 - Serial Output and External Control 39 Figure 5 - Output Driver Enable (ODE) 4 Figure 6 - Motorola Non-Multiplexed Bus Timing 42 4 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
5 MT9826 List of Tables Table - Stream Usage under Various Operation Modes 3 Table 2 - Output High Impedance Control 3 Table 3 - Address Map for Registers (A3 = ) 3 Table 4 - Address Map for Memory Locations (A3 = ) 7 Table 5 - Control Register Bits 9 Table 6 - Serial Data Rate Selections and External Clock Rates 2 Table 7 - Frame Alignment (FAR) Register Bits 2 Table 8 - Frame Delay Offset Register (DOS) Bits 23 Table 9 - Frame delay Bits (FD9, FD2-) and Input Offset Bits (IFn3-) 25 Table - Frame Output Offset (FOR) Register Bits 27 Table - Output Offset Bits (FD9, FD2-) 27 Table 2 - Bit Error Input Selection (BISR) Register Bits 28 Table 3 - Bit Error Count (BECR) Register Bits 28 Table 4 - Connection Memory Bits 34 Table 5 - SAB and CAB Bits Programming for Various Interface Mode 34 5 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
6 MT9826 Changes Summary The following table captures the changes from the April 25 issue Page Item Change 26 Figure 6 Examples for Input Offset Delay Timing 3 Section 9 Initialization of the MT AC Electrical Characteristics - Serial Streams for ST-BUS 37 Figure 8 ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 6384 Mbps 38 Figure 9 ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 892 Mbps when CLK = 6384 MHz 38 Figure ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 496 Mbps when CLK = 6384 MHz 39 Figure 2 ST-BUS Timing for Stream rate of 248 Mbps when CLK = 6384 MHz Clarified the mid-point sampling of the 6 Mbps input data Added the 6 µs waiting time needed for the APLL module to be stabilized before starting the next microprocessor port access cycle Clarified the 6, 8, 4 and 2 Mbps Input Data Sampling timing Clarified the input data sampling position at 6 Mbps data rate Added the input data sampling position at 8 Mbps data rate Added the input data sampling position at 4 Mbps data rate Added the input data sampling position at 2 Mbps data rate 6 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
7 MT9826 STo2 STo2 VSS STi23/FEi23 STi22/FEi22 STi2/FEi2 STi2/FEi2 VSS STo9 STo8 STo7 STo6 VSS STi9/FEi9 STi8/FEi8 STi7/FEi7 STi6/FEi6 VSS STo5 STo4 STo3 STo2 VSS STi3/FEi3 STi2/FEi2 VSS STo STo STo9 STo8 VSS STi/FEi STi/FEi STo22 STo23 VSS STi24/FEi24 STi25/FEi25 STI26/FEi26 STi27/FEi27 VSS STo24 STo25 STo26 STo27 VSS STi28/FEi28 STi29/FEi29 STi3/FEi3 STi3/FEi3 VSS STo28 STo29 STo3 STo3 VSS D D D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 VSS D8 STi9/FEi9 STi8/FEi8 VSS STo7 STo6 STo5 STo4 VSS STi7/FEi7 STi6/FEi6 STi5/FEi5 STi4/FEi4 VSS STo3 STo2 STo STo VSS STi3/FEi3 STi2/FEi2 STi/FEi STi/FEi ODE VSS CLK PLL PLLGND Fi IC3 VSS IC2 RESET IC D9 D D D2 D3 DTA VSS A2 A3 A4 A8 A9 A A A2 A3 TMS TDI TDO TCK TRST STi5/FEi5 STi4/FEi Pin MQFP 28 mm x 28 mm Pin Pitch 65 mm D4 D5 CS R/W DS A A VSS A5 A6 A7 VSS Figure 2-6-Pin MQFP Pin Connections 7 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
8 MT A STi26 STi24 STo2 STi22 STi2 STi8 STi6 STo5 STo3 STo STo8 STi STi9 B STi27 STi25 STo2 STi23 STi2 STi9 STi7 STo4 STo2 STo STo9 STi STi8 C STo26 STo25 STo23 STo9 STo8 STo7 STo6 STi5 STi4 STi3 STi2 STo7 STo5 D STo27 STo24 STo22 GND GND STo3 STo6 STo4 E STi3 STi28 GND GND GND GND GND STo2 STi7 STi6 F STi3 STi29 GND GND STo STi5 STi4 G STo28 STo29 D GND TOP VIEW GND STo STi3 STi2 H STo3 STo3 D2 GND GND GND STi STi J D D3 D4 GND GND GND GND GND ODE K D5 D6 D7 GND PLL PLLGND Fi CLK L D8 D9 A9 A A2 A3 IC IC2 IC3 M D D D2 DTA CS A A3 A7 A8 A TDI TRST RESET N D3 D4 D5 R/W DS A A2 A4 A5 A6 TMS TDO TCK - A corner is identified by metallized markings 23mm x 23mm Ball Pitch 5mm Figure 3-6 Ball PBGA Pin Connections 8 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
9 MT9826 PINOUT DIAGRAM: (as viewed through top of package) A corner identified by metallized marking, mould indent, ink dot or right-angled corner A STo23 STo2 STi2 STi2 STi7 STi6 STo4 STo3 STo STo9 STi STi9 B STo22 STo2 STi23 STi22 STi9 STi8 STo5 STo2 STo STo8 STI STi8 C STi26 STi25 STo24 STo9 STo8 STo7 STo6 STi4 STi3 STi2 STo7 STo5 D STi27 STi24 STo25 GND STi5 GND STo2 STo6 STo4 E STi29 STi28 STo27 STo26 GND GND GND GND STo3 STi7 STi6 F STi3 STi3 STo28 GND GND GND GND STo STi4 STi5 G STo3 STo3 STo29 GND GND GND GND PLL STo STi3 STi2 H D D2 D GND GND GND GND PLLGND ODE STi STi J D3 D7 D4 GND DS FOi CLK K D5 D5 D D3 CS A2 A5 A8 A9 RESET IC IC3 L D6 D8 D9 R/W A3 A A4 A A2 TCK TDO IC2 M D D2 D4 DTA A A3 A6 A7 A TMS TDI TRST Figure 4-44 Ball LBGA Pin Connections 9 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
10 MT9826 Pin Description Pin # MQFP Pin # PBGA Pin # LBGA Name Description 2,22,33,54, 66,77,9,, 2,25,36, 47,57,2,32,45, 53,6,65,7, 76,84,89,95,,6,, 7,24,3, 35,4,46, 56 D5,D6,D7,D8,D9, E4,E,F4, F,G4,G, H4,J4,J,K5, K6,K7 D4,D,E5,E6, E7,E8,E9,F5, F9,G5,G9,H5, H9,H,J5,J6, J7,J8,J9,K4 D5,D6,D7,E9, F4,F9,G4,H4, J6,J7,J8 D4,D9,E5,E6, E7,E8,F5,F6, F7,F8,G5,G6, G7,G8,H5,H6, H7,H8,J4 V DD V ss +33 Volt Power Supply Ground 34 N M TMS Test Mode Select (33 V Input with Internal pull-up) JTAG signal that controls the state transitions of the TAP controller This pin is pulled high by an internal pull-up when not driven 35 M M TDI Test Serial Data In (33 V Input with Internal pull-up) JTAG serial test instructions and data are shifted in on this pin This pin is pulled high by an internal pull-up when not driven 36 N2 L TDO Test Serial Data Out (33 V Output) JTAG serial data is output on this pin on the falling edge of TCK This pin is held in high impedance state when JTAG scan is not enabled 37 N3 L TCK Test Clock (5 V Tolerant Input) Provides the clock to the JTAG test logic 38 M2 M2 TRST Test Reset (33 V Input with internal pull-up) Asynchronously initializes the JTAG TAP controller by putting it in the Test-Logic-Reset state This pin is pulled by an internal pull-up when not driven This pin should be pulsed low on power-up, or held low, to ensure that the device is in the normal functional mode 42 L K IC Internal Connection (33 V Input with internal pull-down) Connect to V SS for normal operation 43 M3 K RESET Device Reset (5 V Tolerant Input) This input (active LOW) puts the device in its reset state which clears the device internal counters and registers Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
11 MT9826 Pin Description (continued) Pin # MQFP Pin # PBGA Pin # LBGA Name Description 44 L2 L2 IC2 Internal Connection 2 (33 V Input with internal pull-down) Connect to V SS for normal operation 46 L3 K2 IC3 Internal Connection 3 (33 V Input with internal pull-down) Connect to V SS for normal operation 47 K2 J Fi Master Frame Pulse (5 V Tolerant Input) This input accepts a 22 ns or 6 ns wide negative frame pulse The CPLL bit in the control register determines the usage of the frame pulse width See Table 6 for details 5 K H9 PLLGND Phase Lock Loop Ground 5 K9 G9 PLL Phase Lock Loop Power Supply 33 V 52 K3 J2 CLK Master Clock (5 V Tolerant Input) Serial clock for shifting data in/out on the serial streams This pin accepts a clock frequency of 892 MHz or 6384 MHz The CPLL bit in the control register determines the usage of the clock frequency See Table 6 for details 55 J3 H ODE Output Drive Enable (5 V Tolerant Input) This is the output-enable control pin for the STo to STo3 serial outputs See Table 2 for details ,79 82, ,9 22, H3 H2 G3 G2 F3,F2,E3,E2 B3,A3 A2,B2 C,C,C9,C8 A7,B7,A6,B6 A5,B5,A4,B4 A2,B2,A,B E2,F2,E,F G,F,E,D D3,C3,D2,C2 A,B,A,B B9,A9,B8,A8 C7,C6,C5,C4 A3,B3 D3,C3 D2,C2,C,D G,G2,H,H2 H H2 G2 G F,F2,E2,E B2,A2 B,A C,C9,C8,D8 A6,A5,B6,B5, A4,A3,B4,B3 D2,C2,C,D E2,E,F,F2 G,F,D,E D2,C2,D,C B,A,B9,A9 B8,A8,A7,B7 C7,C6,C5,C4 A2,B2 B,A C3,D3,E4,E3 F3,G3,G,G2 STi/FEi, STi/FEi STi2/FEi2 STi3/FEi3 STi4-7/FEi4-7 STi8-9/FEi8-9 STi-/FEi- STi2-5/FEi2-5 STi6-9/FEi6-9 STi2-23/FEi2-23 STi24-27/FEi24-27 STi28-3/FEi28-3 STo - 3 STo4-7 STo8 - STo2-5 STo6-9 STo2, STo2 STo22, STo23 STo24-27 STo28-3 Serial Input Streams to 3 and Frame Evaluation Inputs to 3 (5 V Tolerant Inputs) Serial data input streams These streams may have data rates of 248, 496, 892 or 6384 Mbps, depending upon the value programmed at bits DR - DR2 in the control register In the frame evaluation mode, they are used as the frame evaluation inputs ST-BUS Output to 3 (Three-state Outputs) Serial data output streams These streams may have data rates of 248, 496, 892, or 6384 Mbps, depending upon the value programmed at bits DR - DR2 in the control register Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
12 MT9826 Pin Description (continued) Pin # MQFP Pin # PBGA Pin # LBGA Name Description , ,9 G3,J,H3,J2,J3,K, K2,K3 L L2,M,M2,M3,N, N2,N3 Device Overview H3,H,H2,J,J3,K L,J2 L2 L3,M,K3,M2,K4 M3,K2 D - 5, D6, D7 D8 D9-3 D4, D5 Data Bus to 5 (5 V Tolerant I/O) These pins form the 6-bit data bus of the microprocessor port M4 M4 DTA Data Transfer Acknowledgment (Three-state Output) This output pulses low from tristate to indicate that a databus transfer is complete A pullup resistor is required to hold a HIGH level when the pin is tristated 5 N5 J5 DS Data Strobe (5 V Tolerant Input) This active low input works in conjunction with CS to enable the read and write operations 4 N4 L4 R/W Read/Write (5 V Tolerant Input) This input controls the direction of the data bus lines (D-D5) during a microprocessor access 3 M5 K5 CS Chip Select (5 V Tolerant Input) Active low input used by a microprocessor to activate the microprocessor port ,2,39,4,4,48, 49,8,8,2, 2,59,6 M6,N6,N7,M7,N8 N9,N,M8,M9,L7 L8,M,L9,L E3,F3,H,J, J2,K8,K, L3,L4,L5,L6 M5,L6,K6,M6,L7, K7,M7,M8,K8,K9, L8,M9,L9,L5 A - A4 A5 - A3 Address to 3 (5 V Tolerant Input) These lines provide the A - A3 address lines when accessing the internal registers or memories J9,J No Connect These pins have to be left unconnected The MT9826 Quad Digital Switch is capable of switching up to 4,96 4,96 channels The MT9826 is designed to switch 64 Kbps PCM or N x 64 Kbps data The device maintains frame integrity in data applications and minimum throughput delay for voice applications on a per channel basis The serial input streams of the MT9826 can have a bit rate of 248, 496, 892 or 6384 Mbps and are arranged in 25 µs wide frames, which contain 32, 64,28 or 256 channels, respectively The data rates on input and output streams match All inputs and outputs may be programmed to 248, 496 or 892 Mbps STi-5 and STo-5 may be set to 6384 Mbps Combinations of two bit rates, N and 2N are provided See Table By using Zarlink s message mode capability, the microprocessor can access input and output timeslots on a per channel basis This feature is useful for transferring control and status information for external circuits or other ST- BUS devices To correct for backplane delays, the MT9826 has a frame offset calibration function which allows users to measure the frame delay on any of the input streams, This information can then be used to program the input offset dealy for each individual stream Refer to Table 7, 8, and 9 and Figure 6 In addition, the MT9826 allow users to advance 2 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
13 MT9826 the output data position up to 45ns to compensate for the output delay caused by excessive output loading conditions See Figure 7 Examples for Frame Output Offset Timing Serial Interface Mode Input Stream Input Data Rate Output Stream Output Data Rate 8 Mbps STi-3 8 Mbps STo-3 8 Mbps 6 Mbps STi-5 6 Mbps STo-5 6 Mbps 4 Mbps and 8 Mbps STi-5 4 Mbps STo-5 4 Mbps STi5-3 8 Mbps STo6-3 8 Mbps 6 Mbps and 8 Mbps STi- 6 Mbps STo- 6 Mbps STi2-9 8 Mbps STo2-9 8 Mbps 4 Mbps STi-3 4 Mbps STo-3 4 Mbps 2 Mbps and 4 Mbps STi-5 2 Mbps STo-5 2 Mbps STi6-3 4 Mbps STo6-3 4 Mbps 2 Mbps STi-3 2 Mbps STo-3 2 Mbps Table - Stream Usage under Various Operation Modes ODE pin OSB bit in Control register OE bit in Connection Memory ST-BUS Output Driver X High-Z X X Per Channel High-Z Enable Enable Enable Table 2 - Output High Impedance Control The microport interface is compatible with Motorola non-multiplexed buses Connection memory locations may be directly written to or read from; data memory locations may be directly read from A DTA signal is provided to hold the bus until the asynchronous microport operation is queued into the device A3 A2 A A A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A A Location Control Register, CR Frame Alignment Register, FAR Input Offset Selection Register, DOS Input Offset Selection Register, DOS Input Offset Selection Register 2, DOS2 Input Offset Selection Register 3, DOS3 Input Offset Selection Register 4, DOS4 Table 3 - Address Map for Registers (A3 = ) 3 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
14 MT9826 A3 A2 A A A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A A Location Input Offset Selection Register 5, DOS5 Input Offset Selection Register 6, DOS6 Input Offset Selection Register 7, DOS7 Frame Output Offset Register, FOR Frame Output Offset Register, FOR Frame Output Offset Register, FOR2 Frame Output Offset Register, FOR3 Unused Unused Unused Bit Error Input Selection Register, BISR Bit Error Count Register, BECR 2 Functional Description A functional Block Diagram of the MT9826 is shown in Figure 2 Data and Connection Memory For all data rates, the received serial data is converted to parallel format by internal serial-to-parallel converters and stored sequentially in the data memory Depending upon the selected operation programmed in the control register, the usable data memory may be as large as 4,96 bytes The sequential addressing of the data memory is performed by an internal counter, which is reset by the input 8 khz frame pulse (Fi) to mark the frame boundaries of the incoming serial data streams Data to be output on the serial streams may come from either the data memory or connection memory Locations in the connection memory are associated with particular ST-BUS output channels When a channel is due to be transmitted on an ST-BUS output, the data for this channel can be switched either from an ST-BUS input in connection mode, or from the lower half of the connection memory in message mode Data destined for a particular channel on a serial output stream is read from the data memory or connection memory during the previous channel timeslot This allows enough time for memory access and parallel-to-serial conversion 22 Connection and Message Modes Table 3 - Address Map for Registers (A3 = ) (continued) In the connection mode, the addresses of the input source data for all output channels are stored in the connection memory The connection memory is mapped in such a way that each location corresponds to an output channel on the output streams For details on the use of the source address data (CAB and SAB bits), see Table 4 Once the source address bits are programmed by the microprocessor, the contents of the data memory at the selected address are transferred to the parallel-to-serial converters and then onto an ST-BUS output stream By having several output channels connected to the same input source channel, data can be broadcast from one input channel to several output channels In message mode, the microprocessor writes data to the connection memory locations corresponding to the output stream and channel number The lower half (8 least significant bits) of the connection memory content is 4 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
15 MT9826 transferred directly to the parallel-to-serial converter This data will be output on the ST-BUS streams in every frame until the data is changed by the microprocessor The three most significant bits of the connection memory controls the following for an output channel: message or connection mode, constant or variable delay mode, enables/tristate the ST-BUS output drivers and bit error test pattern enable If an output channel is set to a high-impedance state by setting the OE bit to zero in the connection memory, the ST-BUS output will be in a high impedance state for the duration of that channel In addition to the perchannel control, all channels on the ST-BUS outputs can be placed in a high impedance state by pulling the ODE input pin low and programming the output stand by (OSB) bit in the control register to low This action overrides the individual per-channel programming by the connection memory bits See Table 2 for detail The connection memory data can be accessed via the microprocessor interface through the D to D5 pins The addressing of the device internal registers, data and connection memories is performed through the address input pins and the Memory Select (MS) bit of the control register 23 Clock Timing Requirements The master clock (CLK) frequency must be either at 892 MHz or 6384 MHz for serial data rate of 248, 496, 892 and 6384 Mbps; see Table 6 for the selections of the master clock frequency 3 Switching Configurations The MT9826 maximum non-blocking switching configurations is determined by the data rates selected for the serial inputs and outputs The switching configuration is selected by three DR bits in the control register See Table 5 and Table 6 8 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR=) When the 8 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 32-input/32-output data streams each having Kbps channels This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of 4,96 x 4,96 channels Table summarizes the switching configurations and the relationship between different serial data rates and the master clock frequencies 6 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR =) When the 6 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 6-input/6-output data streams each having Kbps channels This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of 4,96 x 4,96 channels 4 Mbps and 8 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR=) When the 4 Mbps and 8 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 32-input/32-output data streams STi-5/STo-5 have a data rate of 4 Mbps and STi6-3/STo6-3 have a data rate of 8 Mbps This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of 3,72 x 3,72 channels The MT9826 is capable of rate conversion, allowing 4 Mbps input to be converted to 8 Mbps output and vice versa 6 Mbps and 8 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR=) When the 6 Mbps and 8 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 2-input/2-output data streams STi-/STo- have a data rate of 6 Mbps and STi2-9/STo2-9 have a data rate of 8 Mbps This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of 4,96 x 4,96 channels The MT9826 is capable of rate conversion, allowing 6 Mbps input to be converted to 8 Mbps output and vice versa 4 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR=) When the 4 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 32-input/32-output data streams each having Kbps channels This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of 2,48 x 2,48 channels 5 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
16 MT Mbps and 4 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR=) When the 2 Mbps and 4 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 32-input/32-output data streams STi-5/STo-5 have a data rate of 2 Mbps and STi6-3/STo6-3 have a data rate of 4 Mbps This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of,536 x,536 channels The MT9826 is capable of rate conversion, allowing 2 Mbps input to be converted to 4 Mbps output and vice versa 2 Mbps mode (DR2=, DR=, DR =) When the 2 Mbps mode is selected, the device is configured with 32-input/32-output data streams each having Kbps channels This mode allows a maximum non-blocking capacity of,24 x,24 channels 3 Serial Input Frame Alignment Evaluation The MT9826 provides the frame evaluation inputs, FEi to FEi3, to determine different data input delays with respect to the frame pulse Fi By using the frame evaluation input select bits (FE to FE4) of the frame alignment register (FAR), users can select one of the thirty-two frame evaluation inputs for the frame alignment measurement The internal master clock, which has a fixed relationship with the CLK and Fi depending upon the mode of operation, is used as the reference timing signal to determine the input frame delays See Figure 5 for the signal alignments between the internal and the external master clocks A measurement cycle is started by setting the start frame evaluation (SFE) bit low for at least one frame Then the evaluation starts when the SFE bit in the control register is changed from low to high Two frames later, the complete frame evaluation (CFE) bit of the frame alignment register changes from low to high to signal that a valid offset measurement is ready to be read from bits to 9 of the FAR register The SFE bit must be set to zero before a new measurement cycle started The falling edge of the frame measurement signal (FEi) is evaluated against the falling edge of the frame pulse (Fi) See Table 7 for the description of the frame alignment register 32 Input Frame Offset Selection Input frame offset selection allows the channel alignment of individual input streams, which operate at 496 Mbps, 892 Mbps or 6384 Mbps, to be shifted against the input frame pulse (Fi) The input offset selection is not available for streams operated at 248 Mbps This feature is useful in compensating for variable path delays caused by serial backplanes of variable lengths, which may be implemented in large centralized and distributed switching systems Each input stream has its own delay offset value programmed by the input delay offset registers Each delay offset register can control 4 input streams There are eight delay offset registers (DOS to DOS7) to control 32 input streams Possible adjustment can range up to +45 internal master clock periods forward with resolution of 5 internal master clock period See Table 8 and Table 9 for frame input delay offset programming 33 Output Advance Offset Selection The MT9826 allows users to advance individual output streams up to 45 ns with a resolution of 5 ns when the device is in 8 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 4 and 8 Mbps or 6 and 8 Mbps mode The output delay adjustment is useful in compensating for variable output delays caused by various output loading conditions The frame output offset registers (FOR & FOR3) control the output offset delays for each output streams via the programming of the OFn bits See Table and Table for the frame output offset programming 6 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
17 MT Zarlink Semiconductor Inc 34 Memory Block Programming The MT9826 provides users with the capability of initializing the entire connection memory block in two frames Bits 3 to 5 of every connection memory location will be programmed with the pattern stored in bits 3 to 5 of the control register The block programming mode is enabled by setting the memory block program (MBP) bit of the control register high When the block programming enable (BPE) bit of the control register is set to high, the block programming data will be loaded into the bits 3 to 5 of every connection memory location The other connection memory bits (bit to 2) are loaded with zeros When the memory block programming is complete, the device resets the BPE bit to zero 35 Bit Error Rate Monitoring The MT9826 allows users to perform bit error rate monitoring by sending a pseudo random pattern to a selected ST-BUS output channel and receiving the pattern from a selected ST-BUS input channel The pseudo random pattern is internally generated by the device with the polynomial of Users can select the pseudo random pattern to be presented on a ST-BUS channel by programming the TM and TM bits in the connection memory When TM and TM bits are high, the pseudo random pattern is output to the selected ST-BUS output channel The pseudo random pattern is then received by a ST-BUS input channel which is selected using the BSA and BCA bits in the bit error rate input selection register (BISR) An internal bit error counter keeps track of the error counts which is then stored in the bit error count register (BECR) The bit error test is enabled and disabled by the SBER bit in the control register Setting the bit from zero to one initiates the bit error test and enables the internal bit error counter When the bit is programmed from one to zero, A3 Stream Address (ST-3) Channel Address (Ch-255) A2 A A A9 A8 Stream Location A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A A Channel Location Stream Stream Stream 2 Stream 3 Stream 4 Stream 5 Stream 6 Stream 7 Stream 8 Stream 22 Stream 23 Stream 24 Stream 25 Stream 26 Stream 27 Stream 28 Stream 29 Stream 3 Stream 3 Ch Ch Ch 3 Ch 3 (Note 2) Ch 32 Ch 33 Ch 62 Ch 63 (Note 3) Ch 64 Ch 65 Ch 26 Ch 27 (Note 4) Ch 28 Ch 29 Ch 254 Ch 255 (Note 5) Bit A3 must be high for access to data and connection memory positions Bit A3 must be low for access to registers 2 Channels to 3 are used when serial stream is at 2Mbps 3 Channels to 63 are used when serial stream is at 4Mbps 4 Channels to 27 are used when serial stream is at 8Mbps 5 Channels to 255 are used when serial stream is at 6Mbps Table 4 - Address Map for Memory Locations (A3 = )
18 MT9826 the device stops the bit error rate test and the internal bit error counter and transfers the error counts to the bit error count register In the control register, a zero to one transition of the CBER bit resets the bit error count register and the internal bit error counter The MT9826 does not recognize an input of all s as an error If all s are being fed into the input stream and channel, the BERT on chip BECR does not increment This test is performed by sending defined data through the message mode to ensure there is proper connectivity, and then running the BER test normally 4 Delay Through the MT9826 The switching of information from the input serial streams to the output serial streams results in a throughput delay The device can be programmed to perform timeslot interchange functions with different throughput delay capabilities on the per-channel basis For voice application, select variable throughput delay to ensure minimum delay between input and output data In wideband data applications, select constant throughput delay to maintain the frame integrity of the information through the switch The delay through the device varies according to the type of throughput delay selected by the TM bits in the connection memory 4 Variable Delay Mode (TM=, TM=) The delay in this mode is dependent only on the combination of source and destination channels and is independent of input and output streams The delay through the switch can vary from 3 channels to frame + 3 channels The Variable delay is only available for odd number output streams but not for the even number output streams Avoid programming the TM and TM bits to zero in the connection memory when the destination output streams are STo, 2, 4,, 28 and 3 42 Constant Delay Mode (TM=, TM=) In this mode, frame integrity is maintained in all switching configurations by making use of a multiple data memory buffer The delay through the switch is always two frames The constant delay mode is available for all output streams 5 Microprocessor Interface The MT9826 provides a parallel microprocessor interface for non-multiplexed bus structures This interface is compatible with Motorola non-multiplexed buses The required microprocessor signals are the 6-bit data bus (D- D5), 4-bit address bus (A-A3) and 4 control lines (CS, DS, R/W and DTA) See Figure 6 for Motorola nonmultiplexed microport timing The MT9826 microport provides access to the internal registers, connection and data memories All locations provide read/write access except for the data memory and BECR registers which are read only For data memory read operations, two consecutive microprocessor cycles are required The read address (A-A3) should remain the same for the two consecutive read cycles The data memory content from the first read cycle should be ignored 8 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
19 MT9826 Read/Write Address: H, Reset Value: H BPD2 BPD BPD CPLL CBER SBER SFE BPE MBP MS OSB DR2 DR DR Bit Name Description 5-3 BPD2- Block Programming Data These bits carry the value to be loaded into the connection memory block whenever the memory block programming feature is activated After the MBP bit is set to and the BPE bit is set to, the contents of the bits BPD2- are loaded into bit 5 to bit 3 of the connection memory Bit 2 to bit of the connection memory are set to 2 Unused Must be zero for normal operation CPLL PLL Input Frequency Select When zero or one, the CLK input is 6384 MHz and the Fi input is 6 ns wide When one, the CLK input is 892 MHz and the Fi input is 22 ns wide See Table 6 for the usage of the clock frequency CBER Clear Bit Error Rate Register A zero to one transition in this bit resets the internal bit error counter and the bit error count register to zero 9 SBER Start Bit Error Rate Test A zero to one transition in this bit starts the bit error rate test The bit error test result is kept in the bit error count register A one to zero transition stops the bit error rate test and the internal bit error counter 8 SFE Start Frame Evaluation A zero to one transition in this bit starts the frame evaluation procedure When the CFE bit in the frame alignement (FAR) register changes from zero to one, the evaluation procedure stops To start another frame evaluation cycle, set this bit to zero 7 Unused Must be zero for normal operation 6 BPE Begin Block programming Enable A zero to one transition of this bit enables the memory block programming function The BPE and BPD2- bits have to be defined in the same write operation Once the BPE bit is set high, the device requires two frames to complete the block programming After the programming function has finished, the BPE bit returns to zero to indicate the operation is completed When the BPE =, the BPE or MBP can be set to to abort the programming operation When BPE =, the other bits in the control register must not be changed for two frames to ensure proper operation 5 MBP Memory Block Program When, the connection memory block programming feature is ready to program Bit3 to Bit5 of the connection memory When, feature is disabled Table 5 - Control Register Bits 9 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
20 MT9826 Read/Write Address: H, Reset Value: H BPD2 BPD BPD CPLL CBER SBER SFE BPE MBP MS OSB DR2 DR DR Bit Name Description 4 MS Memory Select When, connection memory is selected for read or write operations When, the data memory is selected for read operations and connection memory is selected for write operations (No microprocessor write operation is allowed for the data memory) For data memory read operations, two consecutive microprocessor cycles are required The read address should remain the same for the two consecutive read cycles The data memory content from the first read cycle should be ignored The correct data memory content will be presented to the data bus on the second read cycle 3 OSB Output Stand By This bit controls the device output drivers OSB bit ODE pin OE bit STo - 3 Enable Enable Enable X High impedance state X X Per-channel high impedance 2 - DR2- Data Rate Select Input/Output data rate selection See next table (Table 6) for detailed programming Table 5 - Control Register Bits (continued) DR2 DR DR Serial Interface Mode 8 Mbps 6 Mbps CLK (CPLL=) CLK (CPLL=) 4 and 8 Mbps 6384 MHz 6384 MHz 6 and 8 Mbps 4 Mbps 6384 MHz 892 MHz 2 and 4 Mbps 2 Mbps 6384 MHz 892 MHz Table 6 - Serial Data Rate Selections and External Clock Rates 2 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
21 MT9826 Read/Write Address: H, Reset Value: H FE4 FE3 FE2 FE FE CFE FD9 FD8 FD7 FD6 FD5 FD4 FD3 FD2 FD FD Bit Name Description 5 - FE4- Frame Evaluation Input Select The binary value expressed in these bits refers to the frame evaluation inputs, FEi to FEi3 CFE Complete Frame Evaluation When CFE =, the frame evaluation is completed and FD9 to FD bits contains a valid frame alignment offset This bit is reset to zero, when SFE bit in the control register is changed from to 9 FD9 Frame Delay Bit 9 The falling edge of FEi input is sampled during the internal master clock high phase (FD9 = ) or during the low phase (FD9 = ) This bit allows the measurement resolution to /2 internal master clock cycle See Figure 5 for clock signal alignment Internal Master Clock C8i C6i C32i Operation Mode 2 Mbps 4 Mbps, 2&4 Mbps 8 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 4&8 Mbps, 6&8 Mbps 8 - FD8- Frame Delay Bits The binary value expressed in these bits refers to the measured input offset value These bits are reset to zero when the SFE bit of the control register changes from to (FD8 = MSB, FD = LSB) Table 7 - Frame Alignment (FAR) Register Bits 2 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
22 MT9826 Frame Boundary Fi CLK (6384 MHz) Internal master clock at 32 MHz Offset Value FEi Input For 8 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 4&8 Mbps and 6&8 Mbps modes (FD[8:] = 6 H, frame offset of six C32i clock cycles) (FD9 =, sample at internal C32i low phase) Fi CLK (6384 MHz) Internal master clock at 6 MHz Offset Value FEi Input For 4 Mbps and 2&4 Mbps modes (FD[8:] = 3 H, frame offset of three C6i clock cycles) (FD9 =, sample at internal C6i low phase) Fi CLK (6384 MHz) Internal master clock at 8 MHz Offset Value FEi Input For 2 Mbps mode (FD[8:] = 2 H, frame offset of two C8i clock cycles) (FD9 =, sample at internal C8i high phase) Figure 5 - Example for Frame Alignment Measurement 22 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
23 MT9826 Read/Write Address: 2 H for DOS register, 3 H for DOS register, 4 H for DOS2 register, 5 H for DOS3 register, 6 H for DOS4 register, 7 H for DOS5 register, 8 H for DOS6 register, 9 H for DOS7 register, Reset value: H for all DOS registers IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 IF3 IF2 IF IF IF3 IF2 IF IF DOS register IF73 IF72 IF7 IF7 IF63 IF62 IF6 IF6 IF53 IF52 IF5 IF5 IF43 IF42 IF4 IF4 DOS register IF3 IF2 IF IF IF3 IF2 IF IF IF93 IF92 IF9 IF9 IF83 IF82 IF8 IF8 DOS2 register IF53 IF52 IF5 IF5 IF43 IF42 IF4 IF4 IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 DOS3 register IF93 IF92 IF9 IF9 IF83 IF82 IF8 IF8 IF73 IF72 IF7 IF7 IF63 IF62 IF6 IF6 DOS4 register IF233 IF232 IF23 IF23 IF223 IF222 IF22 IF22 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 DOS5 register IF273 IF272 IF27 IF27 IF263 IF262 IF26 IF26 IF253 IF252 IF25 IF25 IF243 IF242 IF24 IF24 DOS6 register IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF293 IF292 IF29 IF29 IF283 IF282 IF28 IF28 DOS7 register Name (Note ) IFn3- Description Input Offset Bits 3,2, & These four bits define how long the serial interface receiver takes to recognize and store bit from the STi pin: ie, to start a new frame The input frame offset can be selected to +225 external clock periods (or 45 internal clock cycles) from the point where the external frame pulse input signal is applied to the Fi inputs of the device See Table 9 When the STi pin has a stream rate of 248 Mbps, the input offset cannot be adjusted and the input offset bits have to be set to zero Table 8 - Frame Delay Offset Register (DOS) Bits 23 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
24 MT9826 Read/Write Address: 2 H for DOS register, 3 H for DOS register, 4 H for DOS2 register, 5 H for DOS3 register, 6 H for DOS4 register, 7 H for DOS5 register, 8 H for DOS6 register, 9 H for DOS7 register, Reset value: H for all DOS registers IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 IF3 IF2 IF IF IF3 IF2 IF IF DOS register IF73 IF72 IF7 IF7 IF63 IF62 IF6 IF6 IF53 IF52 IF5 IF5 IF43 IF42 IF4 IF4 DOS register IF3 IF2 IF IF IF3 IF2 IF IF IF93 IF92 IF9 IF9 IF83 IF82 IF8 IF8 DOS2 register IF53 IF52 IF5 IF5 IF43 IF42 IF4 IF4 IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 DOS3 register IF93 IF92 IF9 IF9 IF83 IF82 IF8 IF8 IF73 IF72 IF7 IF7 IF63 IF62 IF6 IF6 DOS4 register IF233 IF232 IF23 IF23 IF223 IF222 IF22 IF22 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 IF23 IF22 IF2 IF2 DOS5 register IF273 IF272 IF27 IF27 IF263 IF262 IF26 IF26 IF253 IF252 IF25 IF25 IF243 IF242 IF24 IF24 DOS6 register IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF33 IF32 IF3 IF3 IF293 IF292 IF29 IF29 IF283 IF282 IF28 IF28 DOS7 register Name (Note ) Description Note : n denotes a STi stream number from to 3 Table 8 - Frame Delay Offset Register (DOS) Bits (continued) 24 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
25 MT9826 Input Stream Offset No internal master clock shift (Default) Measurement Result from Frame Delay Bits Corresponding Input Offset Bits FD9 FD2 FD FD IFn3 IFn2 IFn IFn + 5 internal master clock shift + internal master clock shift + 5 internal master clock shift + 2 internal master clock shift + 25 internal master clock shift + 3 internal master clock shift + 35 internal master clock shift + 4 internal master clock shift + 45 internal master clock shift Table 9 - Frame delay Bits (FD9, FD2-) and Input Offset Bits (IFn3-) 25 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
26 MT9826 Fi CLK (6384 MHz) Internal master clock at 32 MHz 8Mbps STi Stream Bit 7 IFn= 8Mbps STi Stream Bit 7 IFn= denotes the 3/4 point of the 8M bps bit cell Fi CLK (6384 MHz) Internal master clock at 32 MHz 6Mbps STi Stream Bit 7 IFn= 6Mbps STi Stream Bit 7 IFn= denotes the /2 point of the 6M bps bit cell Figure 6 - Examples for Input Offset Delay Timing 26 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
27 MT9826 Read/Write Address: Reset value: A H for FOR register, B H for FOR register, C H for FOR2 register, D H for FOR3 register, H for all FOR registers OF7 OF7 OF6 OF6 OF5 OF5 OF4 OF4 OF3 OF3 OF2 OF2 OF OF OF OF FOR register OF5 OF5 OF4 OF4 OF3 OF3 OF2 OF2 OF OF OF OF OF9 OF9 OF8 OF8 FOR register OF23 OF23 OF22 OF22 OF2 OF2 OF2 OF2 OF9 OF9 OF8 OF8 O7 OF7 OF6 OF6 FOR2 register OF3 OF3 OF3 OF3 OF29 OF29 OF28 OF28 OF27 OF27 OF26 OF26 OF25 OF25 OF24 OF24 FOR3 register Name (Note ) OFn, OFn (n = to 3) Description Output Offset Bits - These two bits define how soon the serial interface transmitter output the bit from the STo pin The output stream offset can be selected to -45 ns from the point where the external frame pulse input signal is applied to the Fi inputs of the device See Table and Figure 6 Table - Frame Output Offset (FOR) Register Bits Corresponding Output Offset Bits OFn OFn Output Stream Offset for 8 Mbps, 6 Mbps, 4&8 Mbps and 6&8 Mbps modes (Not available for 2 Mbps, 4 Mbps and 2&4 Mbps modes) ns -5 ns -3 ns -45 ns Table - Output Offset Bits (FD9, FD2-) 27 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
28 MT9826 Fi CLK (6384MHz) STo Stream Bit 7 offset=, (ns) STo Stream Bit 7 offset=, (-5ns) denotes the starting point of the bit cell Figure 7 - Examples for Frame Output Offset Timing Read/Write Address: Reset value: H for BISR register, H BSA4 BSA3 BSA2 BSA BSA BCA7 BCA6 BCA5 BCA4 BCA3 BCA2 BCA BCA Bit Name Description 2-8 BSA4 - BSA BER Input Stream Address Bits The number expressed in binary notation on these bits refers to the input data stream which receives the pseudo random pattern 7 - BCA7 - BCA BER Input Channel Address Bits The number expressed in binary notation on these bits refers to the input channel which receives the pseudo random pattern Table 2 - Bit Error Input Selection (BISR) Register Bits Read Address: 2 H for BECR register, BER5 BER4 BER3 BER2 BER BER BER9 BER8 BER7 BER6 BER5 BER4 BER3 BER2 BER BER Bit Name Description 5 - BER5 - BER Bit Error Rate Count Bits The number expressed in binary notation on these bits refers to the bit error counts The register content can be cleared by programming the CBER bit in the control register from zero to one Table 3 - Bit Error Count (BECR) Register Bits The correct data memory content will be presented to the data bus (D-D5) on the second read cycle 28 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
29 MT Memory Mapping The address bus on the microprocessor interface selects the internal registers and memories of the MT9826 If the A3 address input is low, then the registers are addressed by A2 to A according to Table 3 If the A3 is high, the remaining address input lines are used to select location in the data or connection memory depending upon MS bit in the control register For data memory reads, the serial inputs are selected For connection memory writes, the serial outputs are selected The destination stream address bits and channel address bits are defined by A2 to A8 and A7 to A respectively See Table 4 for the memory address mapping The control register controls all the major functions of the device It selects the internal memory locations that specify the input and output channels selected for switching and should be programmed immediately after system power-up to establish the desired switching configuration as explained in the Switching Configurations sections The data in the control register consists of the block programming (BPD-2), the DPLL control (CPLL), the clear BER test (CBER), the start BER test (SBER), the start frame evaluation (SFE), the block programming enable (BPE), the memory block programming bit (MBP), the memory select bits (MS), the output stand by bit (OSB) and the data rate selection (DR-2) bits See Table 5 for the description of the control register bits 7 Connection Memory Control The connection memory controls the switching configuration of the device Locations of the connection memory are associated with particular STo output streams The TM and TM bits of each connection memory location allows the selection of Variable throughput delay, Constant throughput delay, Message or Bit error test mode for all STo channels When the variable or constant throughput delay mode is selected, (TM=/, TM=), the contents of the stream address bit (SAB) and the channel address bit (CAB) of the connection memory defines the source information (stream and channel) of the timeslot that will be switched to the STo streams When the message mode is selected, (TM=, TM=), only the lower half byte (8 least significant bits) of the connection memory is transferred to the associated STo output channel When the bit error test mode is selected, (TM=, TM=), the pseudo random pattern will be output on the associated STo output channel See Table 4 for the description of the connection memory bits 8 DTA Data Transfer Acknowledgment Pin The DTA pin is driven LOW by internal logic, to indicate to the CPU that a data bus transfer is complete When the read or write cycle ends, this pin changes to the high-impedance state 29 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
30 MT Initialization of the MT9826 During power up, the TRST pin should be pulsed low, or held low continuously, to ensure that the MT9826 is in the normal functional mode A 5 K pull-down resistor can be connected to the TRST pin so that the device will not enter the JTAG test mode during power up An external RC network with a time constant of five times the power supply rise time should be connected to the RESET pin to ensure that the device is properly reset after power up After power up, the contents of the connection memory can be in any state The ODE pin should be held low after power up to keep all serial outputs in a high impedance state until the microprocessor has initialized the switching matrix This procedure prevents two serial outputs from driving the same stream simultaneously Wait for 6 µs for the APLL module to be stabilized before starting the microprocessor initialization routine During the microprocessor initialization routine, the microprocessor should program the desired active paths through the switch Users can also consider using the memory block programming feature to quickly initialize the OE, TM and TM bits in the connection memory When this process is complete, the microprocessor controlling the matrices can either bring the ODE pin high or enable the OSB bit in control register to relinquish the high impedance state control JTAG Support The MT9826 JTAG interface conforms to the Boundary-Scan standard IEEE49 This standard specifies a design-for-testability technique called Boundary-Scan test (BST) The operation of the boundary-scan circuitry is controlled by an external test access port (TAP) Controller Test Access Port (TAP) The Test Access Port (TAP) provides access to the many test functions of the MT9826 It consists of three input pins and one output pin The following pins are from the TAP Test Clock Input (TCK) TCK provides the clock for the test logic The TCK does not interfere with any on-chip clock and thus remain independent The TCK permits shifting of test data into or out of the Boundary-Scan register cells concurrently with the operation of the device and without interfering with the on-chip logic Test Mode Select Input (TMS) The logic signals received at the TMS input are interpreted by the TAP Controller to control the test operations The TMS signals are sampled at the rising edge of the TCK pulse This pin is internally pulled to Vdd when it is not driven from an external source Test Data Input (TDI) Serial input data applied to this port is fed either into the instruction register or into a test data register, depending on the sequence previously applied to the TMS input Both registers are described in a subsequent section The received input data is sampled at the rising edge of TCK pulses This pin is internally pulled to Vdd when it is not driven from an external source Test Data Output (TDO) Depending on the sequence previously applied to the TMS input, the contents of either the instruction register or data register are serially shifted out towards the TDO The data out of the TDO is clocked on the falling edge of the TCK pulses When no data is shifted through the boundary scan cells, the TDO driver is set to a high impedance state Test Reset (TRST) Resets the JTAG scan structure This pin is internally pulled to 3 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
31 MT Instruction Register In accordance with the IEEE 49 standard, the MT9826 uses public instructions The JTAG Interface contains a three-bit instruction register Instructions are serially loaded into the instruction register from the TDI when the TAP Controller is in its shifted-ir state Subsequently, the instructions are decoded to achieve two basic functions: to select the test data register that may operate while the instruction is current, and to define the serial test data register path, which is used to shift data between TDI and TDO during data register scanning Test Data Register As specified in IEEE 49, the MT9826 JTAG Interface contains three test data registers: The Boundary-Scan register The Boundary-Scan register consists of a series of Boundary-Scan cells arranged to form a scan path around the boundary of the MT9826 core logic The Bypass Register The Bypass register is a single stage shift register that provides a one-bit path from TDI to its TDO The Device Identification Register The device identification register is a 32-bit register with the register contain of: MSB LSB The LSB bit in the device identification register is the first bit clock out The MT9826 scan register contains 65 bits 3 Zarlink Semiconductor Inc
MT V Rate Conversion Digital Switch
 MT63 3 V Rate Conversion Digital Switch Features 2,4 52 and 52 x 52 switching among backplane and local streams Rate conversion between 2.4, 4.6 and.2 Mb/s Optional sub-rate switch configuration for 2.4
MT63 3 V Rate Conversion Digital Switch Features 2,4 52 and 52 x 52 switching among backplane and local streams Rate conversion between 2.4, 4.6 and.2 Mb/s Optional sub-rate switch configuration for 2.4
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT90820 Large Digital Switch
 CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT982 Large Digital Switch Features 2,48 2,48 channel non-blocking switching at 892 Mb/s Per-channel variable or cotant throughput delay Automatic identification of ST-BUS/GCI interfaces
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT982 Large Digital Switch Features 2,48 2,48 channel non-blocking switching at 892 Mb/s Per-channel variable or cotant throughput delay Automatic identification of ST-BUS/GCI interfaces
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 2,048 x 2,048
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 2,048 x 2,048 IDT72V90823 FEATURES: 2,048 x 2,048 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 2,048 x 2,048 IDT72V90823 FEATURES: 2,048 x 2,048 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic
V SS (GND) RESET. Backplane Data Memories (8,192 channels) Local Connection Memory (4,096 locations) Backplane Connection Memory (8,192 locations)
 12 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 48 Inputs and 48 Outputs Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional
12 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 48 Inputs and 48 Outputs Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional
Data Memory. Connection Memory. Output Timing. Microprocessor Interface and Control Registers D31-0 BERR R/W DTA D16B A18-0 SIZ1-0 WAIT
 Features ZL50073 32 K Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Rate Conversion per Group of 4 Streams (8, 16, 32 or 64 Mbps), and 128 Inputs and 128 Outputs January 2006 32,768 channel x 32,768
Features ZL50073 32 K Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Rate Conversion per Group of 4 Streams (8, 16, 32 or 64 Mbps), and 128 Inputs and 128 Outputs January 2006 32,768 channel x 32,768
V SS (GND) Backplane Data Memories (8,192 channels) Backplane Connection Memory (8,192 locations) Local Connection Memory (8,192 locations)
 16 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 64 Inputs and 64 Outputs Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional
16 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 64 Inputs and 64 Outputs Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional
FEATURES: DESCRIPTION: FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH WITH RATE MATCHING 16,384 X 16,384 CHANNELS IDT72V73263
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH WITH RATE MATCHING 16,384 16,384 CHANNELS IDT72V73263 FEATURES: Up to 64 serial input and output streams Maximum 16,384 x 16,384 channel non-blocking switching
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH WITH RATE MATCHING 16,384 16,384 CHANNELS IDT72V73263 FEATURES: Up to 64 serial input and output streams Maximum 16,384 x 16,384 channel non-blocking switching
MT90869 Flexible 16 K Digital Switch (F16kDX)
 Flexible 16 K Digital Switch (F16kDX) Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching
Flexible 16 K Digital Switch (F16kDX) Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching
MT90870 Flexible 12 k Digital Switch (F12kDX)
 Flexible 12 k Digital Switch (F12kDX) Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching
Flexible 12 k Digital Switch (F12kDX) Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching
DESCRIPTION: FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM. 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 8,192 x 8,192 JUNE Internal Registers
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 8,192 x 8,192 IDT72V73250 FEATURES: 8K x 8K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 16 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 8,192 x 8,192 IDT72V73250 FEATURES: 8K x 8K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 16 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 16,384 X 16,384 GND RESET TX0 RX0. Data Memory MUX. Connection Memory. Internal Registers
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 16,384 X 16,384 IDT72V73260 FEATURES: 16K x 16K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 32 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 16,384 X 16,384 IDT72V73260 FEATURES: 16K x 16K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 32 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 52 x 52 IDT72V70200 FEATURES: 52 x 52 channel non-blocking switching at 2.048 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 52 x 52 IDT72V70200 FEATURES: 52 x 52 channel non-blocking switching at 2.048 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512 IDT72V70800 FEATURES: 512 x 512 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512 IDT72V70800 FEATURES: 512 x 512 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT89L80 Digital Switch
 CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT89L8 Digital Switch Features 3.3 volt supply 5 V lerant inputs and TTL compatible outputs. 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Accepts serial streams at 2.48 Mb/s Per-channel
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT89L8 Digital Switch Features 3.3 volt supply 5 V lerant inputs and TTL compatible outputs. 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Accepts serial streams at 2.48 Mb/s Per-channel
Boundary Scan Implementation
 OpenCORES s Boundary Scan Implementation Abstract This document describes Boundary Scan Implementation (software and hardware solution. It is fully IEEE 1149.1 compliant. Date : August 6, 2000 Version:
OpenCORES s Boundary Scan Implementation Abstract This document describes Boundary Scan Implementation (software and hardware solution. It is fully IEEE 1149.1 compliant. Date : August 6, 2000 Version:
SECTION 11 JTAG PORT
 nc. SECTION JTAG PORT MOTOROLA DSP5662 User s Manual - nc.. INTRODUCTION....................................-3.2 JTAG PINS........................................-5.3 TAP CONTROLLER.................................-6.4
nc. SECTION JTAG PORT MOTOROLA DSP5662 User s Manual - nc.. INTRODUCTION....................................-3.2 JTAG PINS........................................-5.3 TAP CONTROLLER.................................-6.4
IDT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 256 x 256 EATURES: UNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
 TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 256 x 256 IDT728985 EATURES: 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Automatic signal identification (ST-BUS, GCI) 8 RX inputs 32 channels at 64 Kbit/s per serial line
TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 256 x 256 IDT728985 EATURES: 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Automatic signal identification (ST-BUS, GCI) 8 RX inputs 32 channels at 64 Kbit/s per serial line
1.8V MULTI-QUEUE FLOW-CONTROL DEVICES (128 QUEUES) 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION 1,179,648 bits 2,359,296 bits 4,718,592 bits Q127 Q126 Q125
 1.8V MULTI-QUEUE FLOW-CONTROL DEVICES (128 QUEUES) 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION 1,179,648 bits 2,359,296 bits 4,718,592 bits ADVANCE INFORMATION IDT72P51749 IDT72P51759 IDT72P51769 FEATURES Choose from among
1.8V MULTI-QUEUE FLOW-CONTROL DEVICES (128 QUEUES) 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION 1,179,648 bits 2,359,296 bits 4,718,592 bits ADVANCE INFORMATION IDT72P51749 IDT72P51759 IDT72P51769 FEATURES Choose from among
IDT72V VOLT Time SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 1,024 x 1,024 DATASHEET
 3.3 VOLT Time SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 1,024 x 1,024 IDT72V70810 DATASHEET FEATURES: 1,024 x 1,024 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay
3.3 VOLT Time SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 1,024 x 1,024 IDT72V70810 DATASHEET FEATURES: 1,024 x 1,024 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay
Flexible MVIP Interface Circuit
 CMOS MT90810 Flexible MVIP Interface Circuit Features MVIP and ST-BUS compliant MVIP Enhanced Switching with 384x384 channel capacity (256 MVIP channels; 128 local channels) On-chip PLL for MVIP master/slave
CMOS MT90810 Flexible MVIP Interface Circuit Features MVIP and ST-BUS compliant MVIP Enhanced Switching with 384x384 channel capacity (256 MVIP channels; 128 local channels) On-chip PLL for MVIP master/slave
SECTION 2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
 SECTION 2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION Figure 2-1 displays the block diagram of the MCF5206 along with the signal interface. This section describes the MCF5206 input and output signals. The descriptions
SECTION 2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION Figure 2-1 displays the block diagram of the MCF5206 along with the signal interface. This section describes the MCF5206 input and output signals. The descriptions
CPE/EE 421/521 Fall 2004 Chapter 4 The CPU Hardware Model. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. The CPU Hardware Model - Overview
 CPE/EE 421/521 Fall 2004 Chapter 4 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH Fall 2004 1 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model - Overview 68000 interface Timing diagram Minimal configuration using the
CPE/EE 421/521 Fall 2004 Chapter 4 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH Fall 2004 1 The 68000 CPU Hardware Model - Overview 68000 interface Timing diagram Minimal configuration using the
1 Megabit Serial Flash EEPROM SST45LF010
 EEPROM FEATURES: Single.0-.V Read and Write Operations Serial Interface Architecture SPI Compatible: Mode 0 and Mode Byte Serial Read with Single Command Superior Reliability Endurance: 00,000 Cycles (typical)
EEPROM FEATURES: Single.0-.V Read and Write Operations Serial Interface Architecture SPI Compatible: Mode 0 and Mode Byte Serial Read with Single Command Superior Reliability Endurance: 00,000 Cycles (typical)
Aeroflex Colorado Springs Application Note
 Synchronous SRAM (SSRAM) JTAG Operation Table : Cross Reference of Applicable Products Product Name: Manufacturer Part Number SMD # Device Type Internal PIC #. Overview 64Mbit Synchronous SRAM UT8SP2M32
Synchronous SRAM (SSRAM) JTAG Operation Table : Cross Reference of Applicable Products Product Name: Manufacturer Part Number SMD # Device Type Internal PIC #. Overview 64Mbit Synchronous SRAM UT8SP2M32
Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 General Description The DS75 digital thermometer and thermostat provides 9, 10, 11, or 12-bit digital temperature readings over a -55 C to +125 C range with ±2 C accuracy over a -25 C to +100 C range.
General Description The DS75 digital thermometer and thermostat provides 9, 10, 11, or 12-bit digital temperature readings over a -55 C to +125 C range with ±2 C accuracy over a -25 C to +100 C range.
72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM
 72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 2132 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 1066 MHz Read latency
72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 2132 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 1066 MHz Read latency
IEEE JTAG Boundary Scan Standard
 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan Standard Bed-of-nails tester Motivation System view of boundary scan hardware Elementary scan cell Test Access Port (TAP) controller Boundary scan instructions Example *Joint
IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan Standard Bed-of-nails tester Motivation System view of boundary scan hardware Elementary scan cell Test Access Port (TAP) controller Boundary scan instructions Example *Joint
SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE (JTAG) Port
 Enhanced SCAN bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111 extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1 test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a multidrop
Enhanced SCAN bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111 extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1 test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a multidrop
ZL30132 OC-192/STM-64 SONET/SDH/10GbE Network Interface Synchronizer
 OC-192/STM-64 SONET/SDH/10bE Network Interface Synchronizer Features Synchronizes to standard telecom or Ethernet backplane clocks and provides jitter filtered output clocks for SONET/SDH, DH and Ethernet
OC-192/STM-64 SONET/SDH/10bE Network Interface Synchronizer Features Synchronizes to standard telecom or Ethernet backplane clocks and provides jitter filtered output clocks for SONET/SDH, DH and Ethernet
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS
 MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 8085 8085 Microprocessor - Architecture and its operation, Concept of instruction execution and timing diagrams, fundamentals of
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER BASED SYSTEMS UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO 8085 8085 Microprocessor - Architecture and its operation, Concept of instruction execution and timing diagrams, fundamentals of
Chapter 7 Debugging Support
 Chapter 7 Debugging Support The DSP563 modules and features for debugging applications during system development are as follows: JTAG Test Access Port (TAP): Provides the TAP and Boundary Scan functionality
Chapter 7 Debugging Support The DSP563 modules and features for debugging applications during system development are as follows: JTAG Test Access Port (TAP): Provides the TAP and Boundary Scan functionality
SCANSTA111. SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE (JTAG) Port. Literature Number: SNLS060J
 SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port Literature Number: SNLS060J Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111
SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port Literature Number: SNLS060J Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111
AT45DQ321. Features. 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory with Dual-I/O and Quad-I/O Support
 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory with Dual-I/O and Quad-I/O Support Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory with Dual-I/O and Quad-I/O Support Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
Boundary Scan. Sungho Kang. Yonsei University
 Boundary Scan Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outiline Introduction TAP Controller Instruction Register Test Data Registers Instructions Hardware Test Innovations PCB Test Conclusion 2 Boundary Scan Improve
Boundary Scan Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outiline Introduction TAP Controller Instruction Register Test Data Registers Instructions Hardware Test Innovations PCB Test Conclusion 2 Boundary Scan Improve
Configuring APEX 20K, FLEX 10K & FLEX 6000 Devices
 Configuring APEX 20K, FLEX 10K & FLEX 6000 Devices December 1999, ver. 1.02 Application Note 116 Introduction APEX TM 20K, FLEX 10K, and FLEX 6000 devices can be configured using one of six configuration
Configuring APEX 20K, FLEX 10K & FLEX 6000 Devices December 1999, ver. 1.02 Application Note 116 Introduction APEX TM 20K, FLEX 10K, and FLEX 6000 devices can be configured using one of six configuration
72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM
 72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 1334 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 667 MHz Read latency
72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 1334 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 667 MHz Read latency
MT8952B. ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY HDLC Protocol Controller. Features. Description. Applications
 ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY HDLC Protocol Controller Features Formats data as per X.25 (CCITT) level-2 standards Go-Ahead sequence generation and detection Single byte address recognition Microprocessor port
ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY HDLC Protocol Controller Features Formats data as per X.25 (CCITT) level-2 standards Go-Ahead sequence generation and detection Single byte address recognition Microprocessor port
DS1676 Total Elapsed Time Recorder, Erasable
 www.dalsemi.com Preliminary DS1676 Total Elapsed Time Recorder, Erasable FEATURES Records the total time that the Event Input has been active and the number of events that have occurred. Volatile Elapsed
www.dalsemi.com Preliminary DS1676 Total Elapsed Time Recorder, Erasable FEATURES Records the total time that the Event Input has been active and the number of events that have occurred. Volatile Elapsed
1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor
 1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor Control Unit Generates signals within up to carry out the instruction, which has been decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the
1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor Control Unit Generates signals within up to carry out the instruction, which has been decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the
DS75 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature Measurements Require No External Components Measures Temperatures from -55 C to +125 C (-67 F to +257 F) 2 C Accuracy Over a -25 C to +100 C Range Thermometer Resolution
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature Measurements Require No External Components Measures Temperatures from -55 C to +125 C (-67 F to +257 F) 2 C Accuracy Over a -25 C to +100 C Range Thermometer Resolution
4-Megabit 2.7-volt Only Serial DataFlash AT45DB041. Features. Description. Pin Configurations
 Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Interface Architecture Page Program Operation Single Cycle Reprogram (Erase and Program) 2048 Pages (264 Bytes/Page) Main Memory Two 264-Byte SRAM Data Buffers
Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Interface Architecture Page Program Operation Single Cycle Reprogram (Erase and Program) 2048 Pages (264 Bytes/Page) Main Memory Two 264-Byte SRAM Data Buffers
Preliminary Data Sheet, DS 1, Nov SWITI Switching IC. Version 1.3. Wired Communications. Never stop thinking.
 Preliminary Data Sheet, DS 1, Nov. 2001 SWITI Switching IC PEF 20451 PEF 20471 PEF 24471 Version 1.3 HTSI HTSI-L HTSI-XL Wired Communications Never stop thinking. Edition 2001-11-16 Published by Infineon
Preliminary Data Sheet, DS 1, Nov. 2001 SWITI Switching IC PEF 20451 PEF 20471 PEF 24471 Version 1.3 HTSI HTSI-L HTSI-XL Wired Communications Never stop thinking. Edition 2001-11-16 Published by Infineon
Chapter 8 Summary: The 8086 Microprocessor and its Memory and Input/Output Interface
 Chapter 8 Summary: The 8086 Microprocessor and its Memory and Input/Output Interface Figure 1-5 Intel Corporation s 8086 Microprocessor. The 8086, announced in 1978, was the first 16-bit microprocessor
Chapter 8 Summary: The 8086 Microprocessor and its Memory and Input/Output Interface Figure 1-5 Intel Corporation s 8086 Microprocessor. The 8086, announced in 1978, was the first 16-bit microprocessor
1.3inch OLED User Manual
 1.3inch OLED User Manual 1. Key Parameters Table 1: Key Parameters Driver Chip SH1106 Interface 3-wire SPI 4-wire SPI I2C Resolution 128*64 Display Size 1.3 inch Dimension 29mm*33mm Colors Yellow, Blue
1.3inch OLED User Manual 1. Key Parameters Table 1: Key Parameters Driver Chip SH1106 Interface 3-wire SPI 4-wire SPI I2C Resolution 128*64 Display Size 1.3 inch Dimension 29mm*33mm Colors Yellow, Blue
18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM
 18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM 18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM Features Functional Description Supports bus operation up to 250 MHz Available speed grades are 250, 200, and 167 MHz Registered
18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM 18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM Features Functional Description Supports bus operation up to 250 MHz Available speed grades are 250, 200, and 167 MHz Registered
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 16,384-BIT EPROM WITH I/O! 2048 Words x 8 Bits! Single + 5V Power Supply
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 16,384-BIT EPROM WITH I/O! 2048 Words x 8 Bits! Single + 5V Power Supply
DS1626/DS1726 High-Precision 3-Wire Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 www.maxim-ic.com DESCRIPTION The DS1626 and DS1726 digital thermometers/thermostats provide temperature measurements and stand-alone thermostat capability over a -55 C to +125 C range. The DS1626 offers
www.maxim-ic.com DESCRIPTION The DS1626 and DS1726 digital thermometers/thermostats provide temperature measurements and stand-alone thermostat capability over a -55 C to +125 C range. The DS1626 offers
Control Unit: The control unit provides the necessary timing and control Microprocessor resembles a CPU exactly.
 Unit I 8085 and 8086 PROCESSOR Introduction to microprocessor A microprocessor is a clock-driven semiconductor device consisting of electronic logic circuits manufactured by using either a large-scale
Unit I 8085 and 8086 PROCESSOR Introduction to microprocessor A microprocessor is a clock-driven semiconductor device consisting of electronic logic circuits manufactured by using either a large-scale
Address connections Data connections Selection connections
 Interface (cont..) We have four common types of memory: Read only memory ( ROM ) Flash memory ( EEPROM ) Static Random access memory ( SARAM ) Dynamic Random access memory ( DRAM ). Pin connections common
Interface (cont..) We have four common types of memory: Read only memory ( ROM ) Flash memory ( EEPROM ) Static Random access memory ( SARAM ) Dynamic Random access memory ( DRAM ). Pin connections common
DS1821 Programmable Digital Thermostat and Thermometer
 ma www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Requires no external components Unique 1-Wire interface requires only one port pin for communication Operates over a -55 C to +125 C (-67 F to +257 F) temperature range Functions
ma www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Requires no external components Unique 1-Wire interface requires only one port pin for communication Operates over a -55 C to +125 C (-67 F to +257 F) temperature range Functions
Implementing LVDS in Cyclone Devices
 Implementing LVDS in Cyclone Devices March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 254 Introduction Preliminary Information From high-speed backplane applications to high-end switch boxes, LVDS is the technology
Implementing LVDS in Cyclone Devices March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 254 Introduction Preliminary Information From high-speed backplane applications to high-end switch boxes, LVDS is the technology
SSD1322. Product Preview. 480 x 128, Dot Matrix High Power OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1322 Product Preview 480 x 128, Dot Matrix High Power OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a product under
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1322 Product Preview 480 x 128, Dot Matrix High Power OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a product under
13. Configuring Stratix & Stratix GX Devices
 13. Configuring Stratix & Stratix GX Devices S52013-2.0 Introduction You can configure Stratix TM and Stratix GX devices using one of several configuration schemes. All configuration schemes use either
13. Configuring Stratix & Stratix GX Devices S52013-2.0 Introduction You can configure Stratix TM and Stratix GX devices using one of several configuration schemes. All configuration schemes use either
December 2000 MSDS Speech SPSU020
 User s Guide December 2000 MSDS Speech SPSU020 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product or service
User s Guide December 2000 MSDS Speech SPSU020 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product or service
16COM/80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 6COM/80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It is capable of displaying or 2 lines with
6COM/80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It is capable of displaying or 2 lines with
VC Look-Up Table. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory. Figure 1 - MT90528 Block Diagram
 28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
DS 1682 Total Elapsed Time Recorder with Alarm
 DS 1682 Total Elapsed Time Recorder with Alarm www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Records the total time that the Event Input has been active and the number of events that have occurred. Volatile Elapsed Time Counter
DS 1682 Total Elapsed Time Recorder with Alarm www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Records the total time that the Event Input has been active and the number of events that have occurred. Volatile Elapsed Time Counter
AT25PE40. 4-Mbit DataFlash-L Page Erase Serial Flash Memory ADVANCE DATASHEET. Features
 4-Mbit DataFlash-L Page Erase Serial Flash Memory Features ADVANCE DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS operation
4-Mbit DataFlash-L Page Erase Serial Flash Memory Features ADVANCE DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS operation
PI7C7300D 3-PORT PCI-to-PCI BRIDGE Revision 1.01
 3-PORT PCI-to-PCI BRIDGE Revision 1.01 3545 North 1 ST Street, San Jose, CA 95134 Telephone: 1-877-PERICOM (1-877-737-4266) FAX: 408-435-1100 Internet: http://www.pericom.com LIFE SUPPORT POLICY Pericom
3-PORT PCI-to-PCI BRIDGE Revision 1.01 3545 North 1 ST Street, San Jose, CA 95134 Telephone: 1-877-PERICOM (1-877-737-4266) FAX: 408-435-1100 Internet: http://www.pericom.com LIFE SUPPORT POLICY Pericom
AT45DB021E. 2-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 64-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory PRELIMINARY DATASHEET. Features
 AT45DB021E 2-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 64-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features PRELIMINARY DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
AT45DB021E 2-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 64-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features PRELIMINARY DATASHEET Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
IP-THERMISTOR. 6 CHANNELS TEMPERATURE 8-CHANNEL VOLTAGE Industry Pack module HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL. Revision 1.0 JANUARY, 2008
 IP-THERMISTOR 6 CHANNELS TEMPERATURE 8-CHANNEL VOLTAGE Industry Pack module HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL Revision 1.0 JANUARY, 2008 This Document shall not be duplicated, nor its contents used for any purpose,
IP-THERMISTOR 6 CHANNELS TEMPERATURE 8-CHANNEL VOLTAGE Industry Pack module HARDWARE REFERENCE MANUAL Revision 1.0 JANUARY, 2008 This Document shall not be duplicated, nor its contents used for any purpose,
DS1302. Trickle Charge Timekeeping Chip FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT PIN DESCRIPTION
 DS132 Trickle Charge Timekeeping Chip FEATURES Real time clock counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap year compensation valid up to 21 31 x 8 RAM
DS132 Trickle Charge Timekeeping Chip FEATURES Real time clock counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap year compensation valid up to 21 31 x 8 RAM
2. List the five interrupt pins available in INTR, TRAP, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5.
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6502- MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT I: 8085 PROCESSOR PART A 1. What is the need for ALE signal in
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6502- MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS UNIT I: 8085 PROCESSOR PART A 1. What is the need for ALE signal in
Configuring Cyclone FPGAs
 Configuring Cyclone FPGAs March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 250 Introduction You can configure Cyclone TM FPGAs using one of several configuration schemes, including the new active serial (AS) configuration
Configuring Cyclone FPGAs March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 250 Introduction You can configure Cyclone TM FPGAs using one of several configuration schemes, including the new active serial (AS) configuration
512-Kilobit 2.7-volt Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory AT25BCM512B. Preliminary
 Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Compatible Supports SPI Modes and 3 7 MHz Maximum Operating Frequency Clock-to-Output (t V ) of 6 ns Maximum Flexible, Optimized Erase
Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Compatible Supports SPI Modes and 3 7 MHz Maximum Operating Frequency Clock-to-Output (t V ) of 6 ns Maximum Flexible, Optimized Erase
DP8420V 21V 22V-33 DP84T22-25 microcmos Programmable 256k 1M 4M Dynamic RAM Controller Drivers
 DP8420V 21V 22V-33 DP84T22-25 microcmos Programmable 256k 1M 4M Dynamic RAM Controller Drivers General Description The DP8420V 21V 22V-33 DP84T22-25 dynamic RAM controllers provide a low cost single chip
DP8420V 21V 22V-33 DP84T22-25 microcmos Programmable 256k 1M 4M Dynamic RAM Controller Drivers General Description The DP8420V 21V 22V-33 DP84T22-25 dynamic RAM controllers provide a low cost single chip
DS1243Y 64K NV SRAM with Phantom Clock
 19-6076; Rev 11/11 DS1243Y 64K NV SRAM with Phantom Clock FEATURES Real-Time Clock Keeps Track of Hundredths of Seconds, Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Days, Date of the Month, Months, and Years 8K x 8 NV SRAM
19-6076; Rev 11/11 DS1243Y 64K NV SRAM with Phantom Clock FEATURES Real-Time Clock Keeps Track of Hundredths of Seconds, Seconds, Minutes, Hours, Days, Date of the Month, Months, and Years 8K x 8 NV SRAM
AT45DB321E. Features. 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory
 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS operation
32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS operation
PRELIMINARY DATASHEET
 AT45DB321E 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V or 2.5V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features PRELIMINARY DATASHEET See Errata Section 30. Single 2.3V - 3.6V or 2.5V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral
AT45DB321E 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V or 2.5V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features PRELIMINARY DATASHEET See Errata Section 30. Single 2.3V - 3.6V or 2.5V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral
Z Z-280 MT8930, MT8992/3/4/5 MT8880 MT8888 MT8889 MT8980/1 MT8985, MT8986 (DIP-40) MT8986 (PLCC-44) MT8920B MT8952B
 MSAN-145 How to Interface Mitel Components to Parallel Bus CPUs TABL OF CONTNTS Introduction ISSU 1 August 1993 1.0 Group 1 Components 1.1 Interfacing to the 6802 1.2 Interfacing to the 6809 1.3 Interfacing
MSAN-145 How to Interface Mitel Components to Parallel Bus CPUs TABL OF CONTNTS Introduction ISSU 1 August 1993 1.0 Group 1 Components 1.1 Interfacing to the 6802 1.2 Interfacing to the 6809 1.3 Interfacing
8. JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in MAX V Devices
 December 2 MV58-. 8. JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in MAX V Devices MV58-. This chapter describes the IEEE Std.49. (JTAG) boundary-scan testing for Altera MAX V devices. The IEEE Std. 49. BST circuitry available
December 2 MV58-. 8. JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in MAX V Devices MV58-. This chapter describes the IEEE Std.49. (JTAG) boundary-scan testing for Altera MAX V devices. The IEEE Std. 49. BST circuitry available
DS1846 NV Tri-Potentiometer, Memory, and MicroMonitor
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Three linear taper potentiometers Two 10k, 100-position One 100k, 256-position 248 bytes of user EEPROM memory Monitors microprocessor power supply, voltage sense, and external
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Three linear taper potentiometers Two 10k, 100-position One 100k, 256-position 248 bytes of user EEPROM memory Monitors microprocessor power supply, voltage sense, and external
Introduction Testing analog integrated circuits including A/D and D/A converters, requires a special digital interface to a main controller. The digit
 FPGA Interface for Signal Handling (FISH) Mohsen Moussavi Catena Networks April 2000 Introduction Testing analog integrated circuits including A/D and D/A converters, requires a special digital interface
FPGA Interface for Signal Handling (FISH) Mohsen Moussavi Catena Networks April 2000 Introduction Testing analog integrated circuits including A/D and D/A converters, requires a special digital interface
DS1682 Total-Elapsed-Time Recorder with Alarm
 www.maxim-ic.com GENERAL DESCRIPTION The DS1682 is an integrated elapsed-time recorder containing a factory-calibrated, temperaturecompensated RC time base that eliminates the need for an external crystal.
www.maxim-ic.com GENERAL DESCRIPTION The DS1682 is an integrated elapsed-time recorder containing a factory-calibrated, temperaturecompensated RC time base that eliminates the need for an external crystal.
16COM/40SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 6COM/4SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It can display, 2-line with 5 x 8 or 5 x dots
6COM/4SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It can display, 2-line with 5 x 8 or 5 x dots
Instructions Involve a Segment Register (SR-field)
 BYTE 1 = 11000111 2 = C7 16 BYTE 2 = (MOD)000(R/M) = 100000112 = 83 16 BYTE 3 = 34 16 and BYTE 4 = 12 16 BYTE 5 = CD 16 and BYTE 6 = AB 16 The machine code for the instruction is: MOV [BP+DI+1234H], 0ABCDH
BYTE 1 = 11000111 2 = C7 16 BYTE 2 = (MOD)000(R/M) = 100000112 = 83 16 BYTE 3 = 34 16 and BYTE 4 = 12 16 BYTE 5 = CD 16 and BYTE 6 = AB 16 The machine code for the instruction is: MOV [BP+DI+1234H], 0ABCDH
中显液晶 技术资料 中显控制器使用说明书 2009年3月15日 北京市海淀区中关村大街32号和盛大厦811室 电话 86 010 52926620 传真 86 010 52926621 企业网站.zxlcd.com
 http://wwwzxlcdcom 4 SEG / 6 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June 2 Ver Contents in this document are subject to change without notice No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted
http://wwwzxlcdcom 4 SEG / 6 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD June 2 Ver Contents in this document are subject to change without notice No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted
Micron MT54V512H18EF-10 9Mb QDR SRAM Circuit Analysis
 May 14, 2002 Micron MT54V512H18EF-10 9Mb QDR SRAM Circuit Analysis Table of Contents Introduction... Page 1 List of Figures... Page 4 Device Summary Sheet... Page 12 Top Level Diagram...Tab 1 Data Path...Tab
May 14, 2002 Micron MT54V512H18EF-10 9Mb QDR SRAM Circuit Analysis Table of Contents Introduction... Page 1 List of Figures... Page 4 Device Summary Sheet... Page 12 Top Level Diagram...Tab 1 Data Path...Tab
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers
 CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Notes Lecture 19 CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 1 THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Chapter 4 68000 interface
CPE/EE 421 Microcomputers THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Instructor: Dr Aleksandar Milenkovic Lecture Notes Lecture 19 CPE/EE 421/521 Microcomputers 1 THE 68000 CPU HARDWARE MODEL Chapter 4 68000 interface
SSD1355. Advance Information. 128 RGB x 160 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1355 Advance Information 128 RGB x 160 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1355 Advance Information 128 RGB x 160 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications
DS1625. Digital Thermometer and Thermostat FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT
 DS1625 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from 55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent is 67 F to
DS1625 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from 55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent is 67 F to
E Flash Program Procedure via JTAG AN 0136 Jun 15, 2015
 1 Scope This document describes flash access procedures via JTAG interface. The compliance of the rules below guaranties the reliable programming of the E520.32. TEN TEN LN24 D5 JTAG MASTER TCK TDI +5V
1 Scope This document describes flash access procedures via JTAG interface. The compliance of the rules below guaranties the reliable programming of the E520.32. TEN TEN LN24 D5 JTAG MASTER TCK TDI +5V
AT45DB041E. 4-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 128-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory. Features
 4-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 128-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS
4-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 128-Kbits), 1.65V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory Features Single 1.65V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports SPI modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. DS12887 Real Time Clock www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Drop in replacement for
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. DS12887 Real Time Clock www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Drop in replacement for
Preliminary Data MOS IC. Type Ordering Code Package SDA Q67100-H5096 P-DIP-8-1
 Nonvolatile Memory 4-Kbit E 2 PROM with I 2 C Bus Interface SDA 2546-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM)
Nonvolatile Memory 4-Kbit E 2 PROM with I 2 C Bus Interface SDA 2546-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM)
64-megabit 2.7V Dual-interface DataFlash
 Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Dual-interface Architecture RapidS Serial Interface: 66MHz Maximum Clock Frequency SPI Compatible Modes 0 and 3 Rapid8 8-bit Interface: 50MHz Maximum Clock Frequency
Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Dual-interface Architecture RapidS Serial Interface: 66MHz Maximum Clock Frequency SPI Compatible Modes 0 and 3 Rapid8 8-bit Interface: 50MHz Maximum Clock Frequency
ORDERING INFORMATION. OPERATION Measuring Temperature A block diagram of the DS1621 is shown in Figure 1. DESCRIPTION ORDERING PACKAGE
 AVAILABLE Digital Thermometer and Thermostat FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from -55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent is -67
AVAILABLE Digital Thermometer and Thermostat FEATURES Temperature measurements require no external components Measures temperatures from -55 C to +125 C in 0.5 C increments. Fahrenheit equivalent is -67
VC Look-Up Table. Segmentation / Reassembly Circular Buffers. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory
 8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
PIN DIAGRAM. Richa Upadhyay Prabhu. NMIMS s MPSTME January 19, 2016
 PIN DIAGRAM Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu January 19, 2016 Richa Upadhyay Prabhu (MPSTME) 8080 Microprocessor January 19, 2016 1 / 51 Pin Diagram of 8086 Richa Upadhyay
PIN DIAGRAM Richa Upadhyay Prabhu NMIMS s MPSTME richa.upadhyay@nmims.edu January 19, 2016 Richa Upadhyay Prabhu (MPSTME) 8080 Microprocessor January 19, 2016 1 / 51 Pin Diagram of 8086 Richa Upadhyay
16COM / 80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 INTRODUCTION KS0070B is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology. It is capable of displaying 1 or 2 lines with the 5 7 format or 1 line with the 5 10 dots
INTRODUCTION KS0070B is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology. It is capable of displaying 1 or 2 lines with the 5 7 format or 1 line with the 5 10 dots
ISO-CMOS ST-BUS FAMILY MT8920B ST-BUS Parallel Access Circuit
 ISO- ST-BUS FAMILY ST-BUS Parallel Access Circuit Features High speed parallel access to the serial ST-BUS Parallel bus optimized for 68 µp (mode ) Fast dual-port RAM access (mode 2) Access time: 2 nsec
ISO- ST-BUS FAMILY ST-BUS Parallel Access Circuit Features High speed parallel access to the serial ST-BUS Parallel bus optimized for 68 µp (mode ) Fast dual-port RAM access (mode 2) Access time: 2 nsec
Preliminary Data MOS IC. Type Ordering Code Package SDA Q67100-H5092 P-DIP-8-1
 Nonvolatile Memory 1-Kbit E 2 PROM SDA 2516-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM) 128 8-bit organization Supply
Nonvolatile Memory 1-Kbit E 2 PROM SDA 2516-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM) 128 8-bit organization Supply
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. APPLICATION NOTE A V A I L A B L E AN61 16K X25160 2K x 8 Bit SPI Serial
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. APPLICATION NOTE A V A I L A B L E AN61 16K X25160 2K x 8 Bit SPI Serial
DS1345W 3.3V 1024k Nonvolatile SRAM with Battery Monitor
 19-5587; Rev 10/10 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Power supply monitor resets processor when
19-5587; Rev 10/10 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES 10 years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Power supply monitor resets processor when
RW1026G Revision History Version Date Description
 RW1026G Revision History Version Date Description 0.1 2010/9/3 Add I/O Pin ITO Resistance Limitation 0.2 2010/9/15 Modify storage temperature -40 o C to 80 o C change to -50 o C to 125 o C and operation
RW1026G Revision History Version Date Description 0.1 2010/9/3 Add I/O Pin ITO Resistance Limitation 0.2 2010/9/15 Modify storage temperature -40 o C to 80 o C change to -50 o C to 125 o C and operation
16-Megabit 2.3V or 2.7V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory
 Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V or 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Compatible Supports SPI Modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS Operation Supports Dual-Input Program and Dual-Output Read Very
Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V or 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Compatible Supports SPI Modes 0 and 3 Supports RapidS Operation Supports Dual-Input Program and Dual-Output Read Very
32-Megabit 2.7-volt Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory AT25DF321A Preliminary
 BDTIC www.bdtic.com/atmel Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Compatible Supports SPI Modes and 3 Supports RapidS Operation Supports Dual-Input Program and Dual-Output
BDTIC www.bdtic.com/atmel Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Compatible Supports SPI Modes and 3 Supports RapidS Operation Supports Dual-Input Program and Dual-Output
DS1845 Dual NV Potentiometer and Memory
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Two linear taper potentiometers -010 one 10k, 100 position & one 10k, 256 position -050 one 10k, 100 position & one 50k, 256 postition -100 one 10k, 100 position & one 100k, 256
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Two linear taper potentiometers -010 one 10k, 100 position & one 10k, 256 position -050 one 10k, 100 position & one 50k, 256 postition -100 one 10k, 100 position & one 100k, 256
SSD1329. Advance Information. 128 x 128 OLED Segment / Common Driver with Controller Equips with 16 Gray Scale Levels and 64 Hard Icon Lines
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1329 Advance Information 128 x 128 OLED Segment / Common Driver with Controller Equips with 16 Gray Scale Levels and 64 Hard Icon Lines This document contains
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1329 Advance Information 128 x 128 OLED Segment / Common Driver with Controller Equips with 16 Gray Scale Levels and 64 Hard Icon Lines This document contains
8. SED1565 Series. (Rev. 1.2)
 8. (Rev. 1.2) Contents GENERAL DESCRIPTION...8-1 FEATURES...8-1 BLOCK DIAGRAM...8-3 PIN DIMENSIONS...8-4 PIN DESCRIPTIONS...8-2 DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTIONS...8-24 COMMANDS...8-48 COMMAND DESCRIPTION...8-57
8. (Rev. 1.2) Contents GENERAL DESCRIPTION...8-1 FEATURES...8-1 BLOCK DIAGRAM...8-3 PIN DIMENSIONS...8-4 PIN DESCRIPTIONS...8-2 DESCRIPTION OF FUNCTIONS...8-24 COMMANDS...8-48 COMMAND DESCRIPTION...8-57
