MT90870 Flexible 12 k Digital Switch (F12kDX)
|
|
|
- Christine Chase
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
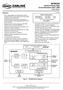
1 Flexible 12 k Digital Switch (F12kDX) Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching matrix with 48 stream inputs and 48 stream outputs 8,192-channel x 4,096-channel blocking Backplane to Local stream switch 4,096-channel x 8,192-channel non-blocking Local to Backplane stream switch 8,192-channel x 8,192-channel non-blocking Backplane input to Backplane output switch 4,096-channel x 4,096-channel non-blocking Local input to Local output stream switch Rate conversion on all data paths, Backplane to Local, Local to Backplane, Backplane to Backplane and Local to Local streams Backplane port accepts 32 ST-BUS streams with data rates of Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s in any combination, or a fixed allocation of 16 streams at Mb/s Ordering Information December 2010 MT90870AG 272 Ball PBGA Trays MT90870AG2 272 Ball PBGA* Trays *Pb Free Tin/Silver/Copper -40 to +85 o C *Note: the package thickness is different than the MT90870AG (see drawing at the end of the data sheet). Local port accepts 16 ST-BUS streams with data rates of Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s, in any combination Per-stream channel and bit delay for Local input streams Per-stream channel and bit delay for Backplane input streams Per-stream advancement for Local output streams Per-stream advancement for Backplane output streams V DD_IO V DD_CORE V SS (GND) RESET ODE BSTi0-31 Backplane Data Memories (8,192 channels) Local Interface LSTi0-15 BSTo0-31 Backplane Interface Backplane Connection Memory (8,192 locations) Local Connection Memory (4,096 locations) Local Interface LSTo0-15 BCST0-3 BORS Local Data Memories (4,096 channels) LCST0-1 LORS FP8i Backplane Timing Unit Local Timing Unit FP8o FP16o C8o C16o C8i PLL Microprocessor Interface and Internal Registers Test Port V DD_PLL DS CS R/W A14-A0 DTA D15-D0 TMS TDi TDo TCK TRST Figure 1 - MT90870 Functional Block Diagram 1 Zarlink, ZL and the Zarlink Semiconductor logo are trademarks of Copyright , All Rights Reserved.
2 Constant throughput delay for frame integrity Per-channel high impedance output control for Local and Backplane streams Per-channel driven-high output control for Local and Backplane streams High impedance-control outputs for external drivers on Backplane and Local port Per-channel message mode for Local and Backplane output streams Connection memory block programming for fast device initialization Automatic selection between ST-BUS and GCI-BUS operation Non-multiplexed Motorola microprocessor interface BER testing for Local and Backplane ports Conforms to the mandatory requirements of the IEEE (JTAG) standard Memory Built-In-Self-Test (BIST), controlled via microprocessor registers 1.8 V core supply voltage 3.3 V I/O supply voltage 5 V tolerant inputs, outputs and I/Os Per streams subrate switching at 4 bit, 2 bit and 1 bit depending on stream data rate Applications Central Office Switches (Class 5) Mediation Switches Class-independent switches Access Concentrators Scalable TDM-Based Architectures Digital Loop Carriers Device Overview The MT90870 has two data ports, the Backplane and the Local port. The Backplane port has two modes of operation, either 32 input and 32 output streams operated at Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s, in any combination, or 16 input and 16 output streams operated at Mb/s. The Local port has 16 input and 16 output streams operated at Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s, in any combination. The MT90870 contains two data memory blocks (Backplane and Local) to provide the following switching path configurations: Backplane-to-Local, supporting 8 K x 4 K data switching, Local-to-Backplane, supporting 4 K x 8 K data switching, Backplane-to-Backplane, supporting 8 K x 8 K data switching. Local-to-Local, supporting 4 K x 4 K data switching. The device contains two connection memory blocks, one for the Backplane output and one for the Local output. Data to be output on the serial streams may come from either of the data memories (Connection Mode) or directly from the connection memory contents (Message Mode). 2
3 In Connection Mode the contents of the connection memory defines, for each output stream and channel, the source stream and channel (stored in data memory) to be switched. In Message Mode, microprocessor data can be written to the connection memory for broadcast on the output streams on a per channel basis. This feature is useful for transferring control and status information to external circuits or other ST-BUS devices. The device uses a master frame pulse (FP8i) and master clock (C8i) to define the frame boundary and timing for both the Backplane port and the Local port. The device will automatically detect whether an ST-BUS or a GCI-BUS style frame pulse is being used. There is a two frame delay from the time RESET is de-asserted to the establishment of full switch functionality. During this period the frame format is determined before switching begins. The device provides FP8o, FP16o, C8o and C16o outputs to support external devices connected to the Local port. Subrate switching is accomplished by oversampling (i.e., 1 bit switching can be accomplished by sampling a 2 Mb/s stream at 16 Mbps). Refer to MSAN-175. A non-multiplexed Motorola microprocessor port allows programming of the various device operation modes and switching configurations. The microprocessor port provides access for Register read/write, Connection Memory read/write and Data Memory read-only operations. The port has a 15-bit address bus, 16-bit data bus and 4 control signals. The microprocessor may monitor channel data in the Backplane and Local data memories. The mandatory requirements of the IEEE (JTAG) standard are fully supported via a dedicated test port. The MT90870 is manufactured in a 27 mm x 27 mm body, 1.27 mm ball-pitch, 272-PBGA to JEDEC standard MS-034 BAL-2 Iss. A. 3
4 Table of Contents 1.0 Bidirectional and Unidirectional Applications Flexible Configuration Functional Description Switching Configurations Backplane-to-Local Path Local-to-Backplane Path Backplane-to-Backplane Path Local-to-Local Path Uni-directional Switch Port Data Rate Modes and Selection Local Port Rate Selection Local Input Port Local Output Port Backplane Port Rate Selection Backplane Input Port Backplane Output Port Backplane Frame Pulse Input and Master Input Clock Timing Backplane Frame Pulse Input and Local Frame Pulse Output Alignment Input and Output Offset Programming Input Channel Delay Programming (Backplane and Local Input Streams) Input Bit Delay Programming (Backplane and Local Input Streams) Output Advancement Programming (Backplane and Local Output Streams) Local Output Advancement Programming Backplane Output Advancement Programming Port High Impedance Control Local Port High Impedance Control LORS Set LOW Backplane High Impedance Control BORS Set LOW, Non-32 Mb/s Mode BORS Set LOW, 32 Mb/s Mode BORS Set HIGH Data Delay Through the Switching Paths Connection Memory Description Local Connection Memory Backplane Connection Memory Connection Memory Block Programming Memory Block Programming Procedure Microprocessor Port Device Power-up, Initialization and Reset Power-Up Sequence Initialization Reset Bit Error Rate Test Memory Built-In-Self-Test (BIST) Mode JTAG Port Test Access Port (TAP) TAP Registers Test Instruction Register Test Data Registers The Boundary-Scan Register The Bypass Register
5 Table of Contents The Device Identification Register Boundary Scan Description Language (BSDL) File Memory Address Mappings Backplane Data Memory Bit Definition Local Data Memory Bit Definition Local Connection Memory Bit Definition Backplane Connection Memory Bit Definition Internal Register Mappings Detailed Register Description Control Register (CR) Block Programming Register (BPR) Bit Error Rate Test Control Register (BERCR) Local Input Channel Delay Registers (LCDR0 to LCDR15) Local Channel Delay Bits 7-0 (LCD7 - LCD0) Local Input Bit Delay Registers (LIDR0 to LIDR15) Local Input Delay Bits 4-0 (LID4 - LID0) Backplane Input Channel Delay Registers (BCDR0 to BCDR31) Backplane Channel Delay Bits 8-0 (BCDn8 - BCDn0) Backplane Input Bit Delay Registers (BIDR0 to BIDR31) Backplane Input Delay Bits 4-0 (BID4 - BID0) Local Output Advancement Registers (LOAR0 to LOAR15) Local Output Advancement Bits 1-0 (LOA1-LOA0) Backplane Output Advancement Registers (BOAR0-31) Backplane Output Advancement Bits 1-0 (BOA1-BOA0) Local Bit Error Rate (BER) Registers Local BER Start Send Register (LBSSR) Local Transmit BER Length Register (LTXBLR) Local Receive BER Length Register (LRXBLR) Local BER Start Receive Register (LBSRR) Local BER Count Register (LBCR) Backplane Bit Error Rate (BER) Registers Backplane BER Start Send Register (BBSSR) Backplane Transmit BER Length Register (BTXBLR) Backplane Receive BER Length Register (BRXBLR) Backplane BER Start Receive Register (BBSRR) Backplane BER Count Register (BBCR) Local Bit Rate Registers Local Input Bit Rate Registers (LIBRR0-15) Local Output Bit Rate Resisters (LOBRR0-15) Backplane Bit Rate Registers Backplane Input Bit Rate Registers (BIBRR0-31) Backplane Output Bit Rate Registers (BOBRR0-31) Memory BIST Register Revision Control Register
6 List of Figures Figure 1 - MT90870 Functional Block Diagram Figure 2 - MT90870 PBGA Connections (272 PBGA) Pin Diagram Figure 3-8,192 x 4,096 Channels (16 Mb/s), Bidirectional Switching Figure 4-12,288 x 12,288 Channels (16 Mb/s), Unidirectional Switching Figure 5-6 K x 6 K Non-Blocking Configuration Figure 6 - Local Port Timing Diagram for 2,4,8 and 16 Mb/s stream rates Figure 7 - Backplane Port Timing Diagram for 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 Mb/s stream rates Figure 8 - Backplane and Local Frame Pulse Alignment for Data Rates of 2 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 8 Mb/s and 16 Mb/s. 24 Figure 9 - Backplane and Local Input Channel Delay Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s) Figure 10 - Backplane and Local Input Bit Delay Timing Diagram for Data Rate of 16 Mb/s Figure 11 - Backplane and Local Input Bit Delay Timing Diagram for Data Rate of 8 Mb/s Figure 12 - Backplane and Local Output Advancement Timing diagram for Data Rate of 16 Mb/s Figure 13 - Local Port External High Impedance Control Bit Timing (ST-Bus Mode) Figure 14 - Backplane Port External High Impedance Control Bit Timing (Non-32 Mb/s mode) Figure 15 - Backplane Port External High Impedance Control Timing (32 Mb/s Mode) Figure 16 - Constant Switch Delay: Examples of Different Stream Rates and Routing Figure 17 - Examples of BER transmission channels Figure 18 - Frame Boundary Conditions, ST- BUS Operation Figure 19 - Frame Boundary Conditions, GCI - BUS Operation Figure 20 - Backplane and Local Clock Timing Diagram for ST-BUS Figure 21 - Backplane and Local Clock Timing for GCI-BUS Figure 22 - ST-BUS Backplane Data Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 2 Mb/s) Figure 23 - ST-BUS Backplane Data Timing Diagram (32 Mb/s, 16 Mb/s) Figure 24 - GCI BUS Backplane Data Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 2 Mb/s) Figure 25 - GCI BUS Backplane Data Timing Diagram (32 Mb/s, 16 Mb/s) Figure 26 - ST-BUS Local Timing Diagram (16 Mb/s) Figure 27 - ST-BUS Local Data Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 2 Mb/s) Figure 28 - Serial Output and External Control Figure 29 - Output Driver Enable (ODE) Figure 30 - Motorola Non-Multiplexed Bus Timing
7 List of Tables Table 1 - Per-stream Data-Rate Selection: Backplane and Local, Non-32 Mb/s Mode and 32 Mb/s Mode Table 2 - LCSTo Allocation of Channel Control Bits to the Output Streams Table 3 - BCSTo Allocation of Channel Control Bits to the Output Streams (Non-32 Mb/s Mode) Table 4 - BCSTo Allocation of Channel Control Bits to the Output Streams (32 Mb/s Mode) Table 5 - Local and Backplane Connection Memory Configuration Table 6 - Local Connection Memory in Block Programming Mode Table 7 - Backplane Connection Memory in Block Programming Mode Table 8 - Address Map for Data and Connection Memory Locations (A14=1) Table 9 - Backplane Data Memory (BDM) Bits Table 10 - Local Data Memory (LDM) Bits Table 11 - LCM Bits for Local-to-Local and Backplane (Non-32 Mb/s Mode)-to-Local Switching Table 12 - LCM Bits for Backplane(32 Mb/s Mode)-to-Local Switching Table 13 - BCM Bits for Local-to-Backplane and Backplane-to-Backplane Switching (Non-32 Mb/s Mode) Table 14 - BCM Bits for Backplane-to-Backplane Switching (32 Mb/s mode) Table 15 - Address Map for Register (A14 = 0) Table 16 - Control Register Bits Table 18 - Bit Error Rate Test Control Register (BERCR) Bits Table 17 - Block Programming Register Bits Table 19 - Local Channel Delay Register (LCDRn) Bits Table 20 - Local Input Channel Delay Programming Table Table 21 - Local Channel Delay Register (LIDRn) Bits Table 22 - Local Input Bit Delay Programming Table Table 23 - Backplane Channel Delay Register (BCDRn) Bits Table 24 - Backplane Input Channel Delay (BCD) Programming Table Table 25 - Backplane Input Bit Delay Register (BIDRn) Bits Table 26 - Backplane Input Bit Delay Programming Table Table 27 - Local Output Advancement Register (LOARn) Bits Table 28 - Local Output Advancement (LOAR) Programming Table Table 29 - Backplane Output Advancement Register (BOAR) Bits Table 30 - Backplane Output Advancement (BOAR) Programming Table Table 31 - Local BER Start Send Register (LBSSR) Bits Table 32 - Local Transmit BER Length Register (LTXBLR) Bits Table 33 - Local Receive BER Length Register (LRXBLR) Bits Table 34 - Local BER Start Receive Register (LBSRR) Bits Table 35 - Local BER Count Register (LBCR) Bits Table 36 - Backplane BER Start Send Register (BBSSR) Bits Table 37 - Backplane Transmit BER Length (BTXBLR) Bits Table 38 - Backplane Receive BER Length (BRXBLR) Bits Table 39 - Backplane BER Start Receive Register (BBSRR) Bits Table 40 - Backplane BER Count Register (BBCR) Bits Table 41 - Local Input Bit Rate Register (LIBRRn) Bits Table 42 - Local Input Bit Rate (LIBR) Programming Table Table 43 - Local Output Bit Rate Register (LOBRRn) Bits Table 44 - Output Bit Rate (LOBR) Programming Register Table 45 - Backplane Input Bit Rate Register (BIBRRn) Bits Table 46 - Backplane Input Bit Rate (BIBR) Programming Table
8 List of Tables Table 47 - Backplane Output Bit Rate Register (BOBRRn) Bits Table 49 - Memory BIST Register (MBISTR) Bits Table 50 - Revision Control Register (RCR) Bits
9 Changes Summary The following table captures the changes from the November 2005 issue. Page Item Change 85 Package Drawing Changed package Bill of Material with a thinner substrate thickness. The following table captures the changes from the December 2002 issue. Page Item Change 14 Pin Description, C8i The internal frame boundary alignment description is changed from the clock rising or falling edge to rising edge only. Also added description to specify setting the C8IPOL bit in the Control Register to one for clock rising edge alignment operation Figure 6, Local Port Timing Diagram for 2,4,8 and 16 Mb/s stream rates Figure 7, Backplane Port Timing Diagram for 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 Mb/s stream rates Section 2.3. Backplane Frame Pulse Input and Master Input Clock Timing Figure 8, Backplane and Local Frame Pulse Alignment for Data Rates of 2 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 8 Mb/s and 16 Mb/s Figure 9, Backplane and Local Input Channel Delay Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s) Figure 10, Backplane and Local Input Bit Delay Timing Diagram for Data Rate of 16 Mb/s Figure 11, Backplane and Local Input Bit Delay Timing Diagram for Data Rate of 8Mb/s Section Control Register (CR) Bit 6, C8IPOL Figure 18, Frame Boundary Conditions, ST- BUS Operation Figure 19, Frame Boundary Conditions, GCI - BUS Operation Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Removed the falling clock edge frame boundary alignment option. Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Changed FPo and C8o to FPi and C8i respectively and showing rising C8i frame boundary active edge. Changed FPo and C8o to FPi and C8i respectively and showing rising C8i frame boundary active edge. Changed FPo and C8o to FPi and C8i respectively. Changed description to specify Bit 6, C8IPOL must be set high for rising clock edge frame boundary alignment operation. Removed waveforms showing C8i falling edge frame boundary option. Removed waveforms showing C8i falling edge frame boundary option. 9
10 Page Item Change Backplane and Local Clock Timing: Item 2, Backplane Frame Pulse Setup Time before C8i clock falling edge Item 3, Backplane Frame Pulse Hold Time from C8i clock falling edge Figure 20, Backplane and Local Clock Timing Diagram for ST-BUS Figure 22, ST-BUS Backplane Data Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 2 Mb/s) Figure 23, ST-BUS Backplane Data Timing Diagram (32 Mb/s, 16 Mb/s) Figure 26, ST-BUS Local Timing Diagram (16 Mb/s) Figure 27, ST-BUS Local Data Timing Diagram (8 Mb/s, 4 Mb/s, 2 Mb/s) Item 2, Backplane Frame Pulse Setup Time before C8i clock falling edge changed to Backplane Frame Pulse Setup Time before C8i clock rising edge. Item 3, Backplane Frame Pulse Hold Time from C8i clock falling edge changed to Backplane Frame Pulse Hold Time from C8i clock rising edge. Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Changed C8i frame boundary active edge from falling to rising edge. Changed FPo and C8o to FPi and C8i respectively and shows rising C8i frame boundary active edge. 10
11 A B C D E F G H J K L M N P R T U V W Y GND IC BSTo5 BSTo4 BSTo2 A2 VDD_CORE A8 A11 A14 BSTo6 BSTo7 BSTo8 VDD_CORE BSTo1 IC A5 A7 A10 IC BSTo9 BSTo10 IC BSTo3 BSTo0 A1 A4 A6 IC A13 BSTo11 BSTo12 BSTo13 GND A0 VDD_IO A3 GND A9 A12 BSTo14 BSTo15 BSTo16 BSTo17 BSTo18 BSTo19 BSTo20 VDD_IO BSTo21 BSTo22 BSTo23 BSTo24 BSTo25 BSTo26 BSTo27 GND BSTo28 BSTo29 BSTo30 BSTo31 GND GND VDD_CORE BORS BSTi0 VDD_IO GND GND BSTi1 BSTi2 BSTi3 BSTi4 GND GND BSTi5 BSTi6 BSTi7 BSTi8 GND GND BSTi9 BSTi10 VDD_CORE GND BSTi11 BSTi12 BSTi13 BSTi14 BSTi15 BSTi16 BSTi17 VDD_IO BSTi18 BSTi19 BSTi20 BSTi21 BSTi22 IC IC GND BSTi28 VDD_IO D10 GND D4 VDD_IO VDD_CORE IC IC BSTi29 VDD_CORE D13 D9 D7 D3 D0 BSTi23 BSTi24 BSTi25 BSTi30 D15 D12 D8 D6 D2 IC BSTi26 BSTi27 IC BSTi31 D14 D11 VDD_CORE D5 D1 IC DS ODE DTA TCK BCSTo1 NC LSTo0 LSTo1 LSTo2 IC CS VDD_CORE TDi TRST BCSTo2 NC IC LSTo3 LSTo4 LSTo5 R/W RESET TDo BCSTo0 BCSTo3 LCSTo1 LCSTo0 LSTo6 LSTo7 LSTo8 VDD_IO TMS GND VDD_CORE VDD_IO IC GND LSTo9 LSTo10 LSTo11 LSTo12 LSTo13 LSTo14 LSTo15 VDD_IO IC IC IC IC IC IC IC GND IC IC IC GND GND IC IC IC IC GND GND IC IC LORS VDD_CORE VDD_IO LSTi0 LSTi1 LSTi2 GND GND LSTi3 LSTi4 LSTi5 LSTi6 GND GND GND LSTi7 LSTi8 LSTi9 LSTi10 VDD_CORE LSTi11 LSTi12 VDD_IO LSTi13 LSTi14 LSTi15 VDD_CORE IC IC IC GND VDD_PLL GND FP8i VDD_IO VDD_CORE GND IC IC IC IC IC C8o FP8o IC IC IC IC IC IC IC C8i C16o FP16o IC IC IC IC IC IC VDD_CORE NC NC VDD_CORE IC IC IC IC IC IC A B C D E F G H J K L M N P R T U V W Y A1 corner identified by metallized marking Figure 2 - MT90870 PBGA Connections (272 PBGA) Pin Diagram (as viewed through top of package) 11
12 Pin Description Name Package Coordinates Description V DD_IO D6, D11, D15, F4, F17, K4, L17, R4, R17, U6, U10, U15 V DD_CORE A7, B4, B12, D14, K1, K20, N3, P18, T17, U16, V1, V5, Y7, Y11, Y14 Power Supply for Periphery Circuits: +3.3 V Power Supply for Core Logic Circuits: +1.8 V V DD_PLL U12 Power Supply for Analog PLL: +1.8 V V SS (GND) A1, D4, D8, D13, D17, H4, H17, J9, J10, J11, J12, K9, K10, K11, K12, L9, L10, L11, L12, M9, M10, M11, M12, N4, N17, U4, U8, U11, U13, U17 BSTi0-15 K3, L1, L2, L3, L4, M1, M2, M3, M4, N1, N2, P1, P2, P3, P4, R1 Ground Backplane Serial Input Streams 0 to 15 (5 V Tolerant, Internal pulldown). In Non-32 Mb/s Mode, these pins accept serial TDM data streams at a data-rate of: Mb/s (with 256 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 128 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 64 channels per stream), or Mb/s (with 32 channels per stream). The data-rate is independently programmable for each input stream. In 32 Mb/s Mode, these pins accept serial TDM data streams at a fixed data-rate of Mb/s (with 512 channels per stream). BSTi16-31 R2, R3, T1, T2, T3, T4, U1,W1, W2, W3, Y1, Y2, U5, V4, W4, Y4 Backplane Serial Input Streams 16 to 31 (5 V Tolerant, Internal pulldown). In Non-32 Mb/s Mode, these pins accept serial TDM data streams at a data-rate of: Mb/s (with 256 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 128 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 64 channels per stream), or Mb/s (with 32 channels per stream). The data-rate is independently programmable for each input stream. In 32 Mb/s Mode, these pins are unused and should be externally connected to a defined logic level. 12
13 Pin Description (continued) Name Package Coordinates Description BSTo0-15 C5, B5, A5 C4, A4, A3, B1, B2, B3, C1, C2, D1, D2, D3, E1, E2 Backplane Serial Output Streams 0 to 15 (5 V Tolerant, Three-state Outputs). In Non-32 Mb/s Mode, these pins output serial TDM data streams at a data-rate of: Mb/s (with 256 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 128 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 64 channels per stream), or Mb/s (with 32 channels per stream). The data-rate is independently programmable for each output stream. In 32 Mb/s Mode, these pins output serial TDM data streams at a fixed data-rate of Mb/s (with 512 channels per stream). Refer to descriptions of the BORS and ODE pins for control of the output High or High-Impedance state. BSTo16-31 E3, E4, F1, F2, F3, G1, G2, G3, G4, H1, H2, H3, J1, J2, J3, J4 Backplane Serial Output Streams 16 to 31 (5 V Tolerant Three-state Outputs). In Non-32 Mb/s Mode, these pins output serial TDM data streams at a data-rate of: Mb/s (with 256 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 128 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 64 channels per stream), or Mb/s (with 32 channels per stream). The data-rate is independently programmable for each output stream. These pins are unused when the 32 Mb/s Mode is selected. Refer to descriptions of the BORS and ODE pins for control of the output High or High-Impedance state. 13
14 Pin Description (continued) Name Package Coordinates Description BCSTo0-3 C14, A15, B15, C15 Backplane Output Channel High Impedance Control (5 V Tolerant Three-state Outputs). Active high output enable which may be used to control external buffering individually for a set of Backplane output streams on a per channel basis. In non-32 Mb/s mode (stream rates 2 Mb/s to 16 Mb/s): BCSTo0 is the output enable for BSTo[0,4,8,12,16,20,24,28], BCSTo1 is the output enable for BSTo[1,5,9,13,17,21,25,29], BCSTo2 is the output enable for BSTo[2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30], BCSTo3 is the output enable for BSTo[3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31]. In 32 Mb/s mode (stream rate 32 Mb/s): BCSTo0 is the output enable for BSTo[0,4,8,12], BCSTo1 is the output enable for BSTo[1,5,9,13], BCSTo2 is the output enable for BSTo[2,6,10,14], BCSTo3 is the output enable for BSTo[3,7,11,15]. Refer to descriptions of the BORS and ODE pins for control of the output High or High-Impedance state. FP8i U14 Frame Pulse Input (5 V Tolerant). This pin accepts the Frame Pulse signal. The pulse width may be active for 122 ns or 244 ns at the frame boundary and the Frame Pulse Width bit (FPW) of the Control Register must be set Low (default) for a 122 ns and set High for a the 244 ns pulse condition.the device will automatically detect whether an ST-BUS or GCI- BUS style frame pulse is applied. C8i W12 Master Clock Input (5 V Tolerant). This pin accepts a MHz clock. The internal Frame Boundary is aligned with the rising edge of this clock. This rising edge frame boundary alignment is controlled by the C8IPOL bit in the Control Register as shown in Table 16 on page 52. The C8IPOL bit MUST be set to ONE for the rising edge frame boundary to be detected correctly. Falling C8i edge frame boundary alignment is not supported and should not be used. CS B11 Chip Select (5 V Tolerant). Active low input used by the microprocessor to enable the microprocessor port access. This input is internally set low during a device RESET. DS A11 Data Strobe (5 V Tolerant). This active low input works in conjunction with CS to enable the microprocessor port read and write operations. R/W C11 Read/Write (5 V Tolerant). This input controls the direction of the data bus lines (D0-D15) during a microprocessor access. A0 - A14 D5, C6, A6, D7, C7, B7, C8, B8, A8, D9, B9, A9, D10, C10, A10 Address 0-14 (5 V Tolerant). These pins form the 15-bit address bus to the internal memories and registers. (Address A0 = LSB). 14
15 Pin Description (continued) Name Package Coordinates Description D0 - D15 V10, Y9, W9, V9, U9, Y8, W8, V8, W7, V7, U7, Y6, W6, V6, Y5, W5 Data Bus 0-15 (5 V Tolerant). These pins form the 16-bit data bus of the microprocessor port. (Data D0 = LSB). DTA A13 Data Transfer Acknowledgment (5 V Tolerant). This active low output indicates that a data bus transfer is complete. A pull-up resistor is required to hold a HIGH level. (Max. I OL = 10mA). TMS D12 Test Mode Select (5 V Tolerant with internal pull-up). JTAG signal that controls the state transitions of the TAP controller. TCK A14 Test Clock (5 V Tolerant). Provides the clock to the JTAG test logic. TDi B13 Test Serial Data In (5 V Tolerant with internal pull-up). JTAG serial test instructions and data are shifted in on this pin. TDo C13 Test Serial Data Out (5 V Tolerant Three-state Output). JTAG serial data is output on this pin on the falling edge of TCK. This pin is held in high impedance state when JTAG is not enabled. TRST B14 Test Reset (5 V Tolerant with internal pull-up) Asynchronously initializes the JTAG TAP controller to the Test-Logic-Reset state. To be pulsed low during power-up for JTAG testing. This pin must be held LOW for normal functional operation of the device. RESET C12 Device Reset (5 V Tolerant with internal pull-up). This input (active LOW) asynchronously applies reset and synchronously releases reset to the device. In the reset state, the outputs LSTo0-15 and BSTo0-31 are set to a high or high impedance depending on the state of the LORS and BORS external control pins, respectively. It clears the device registers and internal counters. This pin must stay low for more than 2 cycles of input clock C8i for the reset to be invoked. LSTi0-15 L18, L19, L20, M17, M18, M19, M20, N18, N19, N20, P17, P19, P20, R18, R19, R20, Local Serial Input Streams 0 to 15 (5 V Tolerant with internal pulldown). These pins accept serial TDM data streams at a data-rate of: Mb/s (with 256 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 128 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 64 channels per stream), or Mb/s (with 32 channels per stream). The data-rate is independently programmable for each input stream. C16o W13 C16o Output Clock (Three-state Output). A MHz clock output. The clock falling edge or rising edge is aligned with the Local frame boundary, this is controlled by the COPOL bit of the Control Register. C8o V13 C8o Output Clock (Three-state Output). A MHz clock output. The clock falling edge or rising edge is aligned with the Local frame boundary, this is controlled by the COPOL bit of the Control Register. 15
16 Pin Description (continued) Name Package Coordinates Description FP16o W14 Frame Pulse Output (Three-state Output). Frame pulse output is active for 61 ns at the frame boundary. The frame pulse, running at a 8 KHz rate, will be the same format (ST-BUS or GCI-BUS) as the input frame pulse (FP8i). FP8o V14 Frame Pulse Output (Three-state Output). Frame pulse output is active for 122 ns at the frame boundary. The frame pulse, running at 8 KHz rate, will be the same style (ST-BUS or GCI-BUS) as the input frame pulse (FP8i). LSTo0-15 A17, A18, A19, B18, B19, B20, C18, C19, C20, D18, D19, D20, E17, E18, E19, E20, Local Serial Output Streams 0 to 15 (5 V Tolerant Three-state Outputs). These pins output serial TDM data streams at a data-rate of: Mb/s (with 256 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 128 channels per stream), Mb/s (with 64 channels per stream), or Mb/s (with 32 channels per stream). The data-rate is independently programmable for each output stream. Refer to descriptions of the LORS and ODE pins for control of the output High or High-Impedance state. LCSTo0-1 C17, C16 Local Output Channel High Impedance Control (5 V Tolerant Threestate Outputs). Active high output enable: used to control, on a per-channel basis, the external buffering of Local output streams. LCSTo0 is the output enable for streams: LSTo[0,2,4,6,8,10,12, and 14]. LCSTo1 is the output enable for streams: LSTo[1,3,5,7,9,11,13, and 15]. Refer to descriptions of the LORS and ODE pins for control of the output High or High-Impedance state. ODE A12 Output Drive Enable (5 V Tolerant, Internal pull-up). An asynchronous input providing Output Enable control to the BSTo0-31, LSTo0-15, BCSTo0-3 and LCSTo0-1 outputs. When LOW, the BSTo0-31 and LSTo0-31 outputs are driven high or high impedance (dependent on the BORS and LORS pin settings respectively) and the outputs BCSTo0-3 and LCSTo0-1 are driven low. When HIGH, the outputs BSTo0-31, LSTo0-15, BCSTo0-3 and LCSTo0-1 are enabled. 16
17 Pin Description (continued) Name Package Coordinates Description BORS K2 Backplane Output Reset State (5 V Tolerant, Internal pull-down). When this input is LOW the device will initialize with the BSTo0-31 outputs driven high, and the BCSTo0-3 outputs driven low. Following initialization, the Backplane stream outputs are always active and a high impedance state, if required on a per-channel basis, may be implemented with external buffers controlled by outputs BCSTo0-3. When this input is HIGH, the device will initialize with the BSTo0-31 outputs at high impedance and the BCSTo0-3 outputs driven low. Following initialization, the Backplane stream outputs may be set active or high impedance using the ODE pin, or on a per-channel basis with the BE bit of the Backplane Connection Memory. LORS K19 Local Output Reset State (5 V Tolerant, Internal pull-down). When this input is LOW, the device will initialize with the LSTo0-15 outputs driven high and the LCSTo0-1 outputs driven low. Following initialization, the Local stream outputs are always active and a high impedance state, if required on a per-channel basis, may be implemented with external buffers controlled by the LCSTo0-1 outputs. When this input is HIGH, the device will initialize with the LSTo0-15 outputs at high impedance and the LCSTo0-1 outputs driven low. Following initialization, the Local stream outputs may be set active or high impedance using the ODE pin, or on a per-channel basis with the LE bit of the Local Connection Memory. NC A16, B16, Y12, Y13 IC A2, A20, B6, B10, B17, C3, C9, D16, U2, U3, V2, V3, V11, V12, V15, V16, W10, W11, W15, W16, W17, W20, Y3, Y10, Y15, Y16, No Connect. No connection to be made. Internal Connects These inputs MUST be held LOW. T18, T19, T20, U18, U19, U20, V17, V18, V19, V20, W18, W19, Y20, Y17, Y18, Y19, F18, F19, F20, G17, G18, G19, G20, H18, H19, H20, J17, J18, J19, J20, K17, K18 17
18 1.0 Bidirectional and Unidirectional Applications The MT90870 has a maximum capacity of 12,288 input channels and 12,288 output channels. This is calculated from the maximum number of streams and channels: 48 input streams (32 Backplane, 16 Local) at Mb/s and 48 output streams (32 Backplane, 16 Local) at Mb/s. One typical mode of operation is to separate the Backplane and Local sides, as shown in Figure 3 below. BSTi streams LSTo streams BACKPLANE LOCAL BSTo streams LSTi streams MT90870 Figure 3-8,192 x 4,096 Channels (16 Mb/s), Bidirectional Switching In this system setup, the chip has a capacity of 8,192 input channels and 8,192 output channels on the Backplane side as well as 4,096 input channels and 4,096 output channels on the Local side. Note that some of the output channels on one side can come from the other side, i.e., Backplane input to Local output switching. Often a system design does not need to differentiate between Backplane and Local side, and merely needs maximum switching capacity. In this case, the MT90870 can be used as shown in Figure 4 to give the full 12,288 x 12,288 channel capacity. BSTi streams BSTo streams INPUT OUTPUT LSTi streams LSTo streams MT90870 Figure 4-12,288 x 12,288 Channels (16 Mb/s), Unidirectional Switching In this system, the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs are combined and the switch appears as a 48 stream input by 48 stream output switch. This style of operation is similar to older switch designs, such as the MT Note, in either configuration the Backplane may be operated in the 32 Mb/s Mode, providing 512 channels on each of the 16 available input and output streams (BSTi0-15 and BSTo0-15) operating at a data-rate of Mb/s, in conjunction with the Local streams (LSTi0-15 and LSTo0-15) operated at Mb/s. This allows data-rate conversion between Mb/s and Mb/s without loss to the switching capacity. 18
19 1.1 Flexible Configuration The F12KDX can be configured as an 8 K by 4 K blocking bi-directional digital switch, a 12 K by 12 K unidirectional non-blocking digital switch, and as a non-blocking switch with various switching capacities. A. Blocking Bi-directional Configuration (Typical System Configuration) 8,192-channel x 4,096-channel blocking switching from backplane to local streams 4,096-channel x 8,192-channel blocking switching from local to backplane streams 8,192-channel x 8,192-channel non-blocking switching from backplane input to backplane output streams 4,096-channel x 4,096-channel non-blocking switching from local input to local output streams B. Unidirectional Configuration Because the input and output drivers are synchronous, the user can combine input backplane streams and input local streams or output backplane streams and output local streams to increase the total number of input and output streams of the switch in a unidirectional configuration. 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking switching from input to output streams C. Non-Blocking Configuration The F12KDX can be configured as a non-blocking switch if it is an application requirement. For example, it can be configured as a 6 K by 6 K non-blocking switch: 6,144-channel x 6,144-channel non-blocking switching from "backplane" to "local" streams 6,144-channel x 6,144-channel non-blocking switching from "local" to "backplane" streams 6,144-channel x 6,144-channel non-blocking switching from "backplane" input to "backplane" output streams 6,144-channel x 6,144-channel non-blocking switching from local input to local output streams MT90870 LSTo0-15 BSTi0-23 BSTo K by 6 K 6 K by 6 K 6 K by 6 K 6 K by 6 K BSTo24-31 LSTi0-15 BSTi24-31 Total 24 input streams and 24 output streams Total 24 input streams and 24 output streams 2.0 Functional Description 2.1 Switching Configurations Figure 5-6 K x 6 K Non-Blocking Configuration The device supports five switching configurations. (1) Backplane-to-Local, (2) Local-to-Backplane, (3) Backplaneto-Backplane, (4) Local-to-Local, and (5) Uni-directional switch. The following sections describe the switching paths. The switch paths of Configurations (1) to (4) may be operated simultaneously and in all 5 cases the Backplane streams may be operated at a fixed data-rate of Mb/s on 16 input and 16 output streams, or optionally, at Mb/s or lower data-rates on 32 input and 32 output streams. The Local streams (16 input and 16 output) may be operated at Mb/s or lower data-rates. When the lower data-rates of 8.192, 4.096, and 19
20 2.048 Mb/s are included, there will be a corresponding reduction in switch capacity although conversion between differing rates will be maintained Backplane-to-Local Path The device can provide data switching between the Backplane input port (8192 channels) and the Local output port (4096 channels). The Local Connection Memory determines the switching configurations Local-to-Backplane Path The device can provide data switching between the Local input port (4096 channels) and the Backplane output port (8192 channels). The Backplane Connection Memory determines the switching configurations Backplane-to-Backplane Path The device can provide data switching between the Backplane input (8192 channels) and output (8192 channels) ports. The Backplane Connection Memory determines the switching configurations Local-to-Local Path The device can provide data switching between the Local input (4096 channels) and output (4096 channels) ports. The Local Connection Memory determines the switching configurations Uni-directional Switch The device may be optionally configured to provide a 12,288 x 12,288 uni-directional switch by grouping together Backplane and Local input and output streams. 2.2 Port Data Rate Modes and Selection The selection of individual stream data-rates is summarized in Table Local Port Rate Selection The Local port has 16 input (LSTi0-15) and 16 output (LSTo0-15) data streams. All input and output streams may be individually selected for operation at a data rate of either Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s. The timing of the input and output clocks and frame pulses are shown in Figure 6, Local Port Timing Diagram for 2,4,8 and 16 Mb/s stream rates Local Input Port The bit rate for each input stream is selected by writing to a dedicated Local Input Bit Rate Register (LIBRR0-15). Refer to Table 41, Local Input Bit Rate Register (LIBRRn) Bits. Stream Number Input stream - Backplane 0-15 (BSTi0-15) Input stream - Backplane (BSTi16-31) Output stream - Backplane 0-15 (BSTo0-15) Rate Selection Capability (for each individual stream) 2.048, 4.096, or Mb/s - Non-32 Mb/s Mode Mb/s - 32 Mb/s Mode 2.048, 4.096, or Mb/s - Non-32 Mb/s Mode Unused - 32 Mb/s Mode 2.048, 4.096, or Mb/s - Non-32 Mb/s Mode Mb/s - 32 Mb/s Mode 20
21 Stream Number Output stream - Backplane (BSTo16-31) Input stream - Local 0-15 (LSTi0-15) Output stream - Local 0-15 (LSTo0-15) Rate Selection Capability (for each individual stream) 2.048, 4.096, or Mb/s - Non-32 Mb/s Mode Unused - 32 Mb/s Mode 2.048, 4.096, or Mb/s 2.048, 4.096, or Mb/s Table 1 - Per-stream Data-Rate Selection: Backplane and Local, Non-32 Mb/s Mode and 32 Mb/s Mode FP8i (ST-BUS) (8 khz) C8i (ST-BUS) (8.192 MHz) FP8i (GCI) (8 khz) C8i (GCI) (8.192 MHz) LSTi/LSTo0-15 (16 Mb/s) ST LSTi/LSTo0-15 (16 Mb/s) GCI LSTi/LSTo0-15 (8 Mb/s) ST LSTi/LSTo0-15 (8 Mb/s) GCI LSTi/LSTo0-15 (4 Mb/s) ST LSTi/LSTo0-15 (4 Mb/s) GCI LSTi/LSTo0-15 (2 Mb/s) ST Channel 0 Channel Channel 0 Channel Channel 0 Channel 0 Channel Channel 0 Channel 0 Channel 0 7 Channel 127 Channel Channel Channel LSTi/LSTo0-15 (2 Mb/s) GCI 7 Channel 0 0 Channel Figure 6 - Local Port Timing Diagram for 2,4,8 and 16 Mb/s stream rates 21
22 Local Output Port The bit rate for each output stream is selected by writing to a dedicated Local Output Bit Rate Register (LOBRR0-15). Refer to Table 43, Local Output Bit Rate Register (LOBRRn) Bits. Operation of stream data in the Connection Mode or the Message Mode is determined by the state of the LMM bit, and the channel High-impedance state is controlled by the LE bit of the Local Connection Memory. The data source (i.e. from the Local or Backplane Data Memory) is determined by the LSRC bit of the Local Connection Memory. Refer to Section 6.1, Local Connection Memory, and Section 12.3, Local Connection Memory Bit Definition Backplane Port Rate Selection The Backplane streams may be operated in one of two modes, namely Non-32 Mb/s Mode and 32 Mb/s Mode. The Local stream data-rates are not affected by the operating mode of the Backplane. The operating mode of the Backplane is determined by setting the Control Register bit, MODE32. Setting the bit HIGH will invoke the 32 Mb/s Mode. Setting the bit LOW will invoke the Non-32 Mb/s mode. The default bit value on device Reset is LOW. The timing of the input and output clocks and frame pulses are shown in Figure 7, Backplane Port Timing Diagram for 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 Mb/s stream rates. Non-32 Mb/s Mode: Each of the 32 Backplane streams (BSTi0-31 and BSTo0-31) and Local streams (LSTi0-15 and LSTo0-15) can be independently programmed for a data-rate of Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s. 32 Mb/s Mode: 16 of the Backplane input streams (BSTi0-15) and 16 Backplane output (BSTo0-15) streams operate at a fixed rate of Mb/s. In this mode, the upper 16 input (BSTi16-31) and 16 output (BSTi16-31) streams are unused. All 32 Local streams can be independently programmed for a data-rate of Mb/s, Mb/s, Mb/s or Mb/s Backplane Input Port The bit rate for each input stream is selected by writing to a dedicated Backplane Input Bit Rate Register (BOBRR0-31). Refer to Table 45, Backplane Input Bit Rate Register (BIBRRn) Bits. If the 32 Mb/s mode is selected by writing to the Control Register bit (MODE32), the settings in BIBRRn are ignored Backplane Output Port The bit rate for each output stream is selected by writing to a dedicated Backplane Output Bit Rate Register (BOBRR0-31). Refer to Table 47, Backplane Output Bit Rate Register (BOBRRn) Bits. If the 32 Mb/s mode is selected by writing to the Control Register bit (MODE32), the settings in BOBRRn are ignored. Operation of stream data in the Connection Mode or the Message Mode is determined by the state of the BMM bit, and the channel High-impedance state is controlled by the BE bit of the Backplane Connection Memory. The data source (i.e., from the Local or Backplane Data Memory) is determined by the BSRC bit of the Backplane Connection Memory. Refer to Section 6.2, Backplane Connection Memory and Section 12.4, Backplane Connection Memory Bit Definition. 22
MT90869 Flexible 16 K Digital Switch (F16kDX)
 Flexible 16 K Digital Switch (F16kDX) Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching
Flexible 16 K Digital Switch (F16kDX) Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional switching.the Backplane and Local inputs and outputs can be combined to form a non-blocking switching
V SS (GND) RESET. Backplane Data Memories (8,192 channels) Local Connection Memory (4,096 locations) Backplane Connection Memory (8,192 locations)
 12 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 48 Inputs and 48 Outputs Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional
12 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 48 Inputs and 48 Outputs Features 12,288-channel x 12,288-channel non-blocking unidirectional
V SS (GND) Backplane Data Memories (8,192 channels) Backplane Connection Memory (8,192 locations) Local Connection Memory (8,192 locations)
 16 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 64 Inputs and 64 Outputs Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional
16 K-Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Per Stream Rate Conversion (2, 4, 8, 16, or 32 Mbps), and 64 Inputs and 64 Outputs Features 16,384-channel x 16,384-channel non-blocking unidirectional
Data Memory. Connection Memory. Output Timing. Microprocessor Interface and Control Registers D31-0 BERR R/W DTA D16B A18-0 SIZ1-0 WAIT
 Features ZL50073 32 K Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Rate Conversion per Group of 4 Streams (8, 16, 32 or 64 Mbps), and 128 Inputs and 128 Outputs January 2006 32,768 channel x 32,768
Features ZL50073 32 K Channel Digital Switch with High Jitter Tolerance, Rate Conversion per Group of 4 Streams (8, 16, 32 or 64 Mbps), and 128 Inputs and 128 Outputs January 2006 32,768 channel x 32,768
MT V Rate Conversion Digital Switch
 MT63 3 V Rate Conversion Digital Switch Features 2,4 52 and 52 x 52 switching among backplane and local streams Rate conversion between 2.4, 4.6 and.2 Mb/s Optional sub-rate switch configuration for 2.4
MT63 3 V Rate Conversion Digital Switch Features 2,4 52 and 52 x 52 switching among backplane and local streams Rate conversion between 2.4, 4.6 and.2 Mb/s Optional sub-rate switch configuration for 2.4
MT90826 Quad Digital Switch
 MT9826 Quad Digital Switch Features 4,96 4,96 channel non-blocking switching at 892 or 6384 Mbps Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Accepts 32 ST-BUS streams of 248 Mbps, 496 Mbps, 892 Mbps
MT9826 Quad Digital Switch Features 4,96 4,96 channel non-blocking switching at 892 or 6384 Mbps Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Accepts 32 ST-BUS streams of 248 Mbps, 496 Mbps, 892 Mbps
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT90820 Large Digital Switch
 CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT982 Large Digital Switch Features 2,48 2,48 channel non-blocking switching at 892 Mb/s Per-channel variable or cotant throughput delay Automatic identification of ST-BUS/GCI interfaces
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT982 Large Digital Switch Features 2,48 2,48 channel non-blocking switching at 892 Mb/s Per-channel variable or cotant throughput delay Automatic identification of ST-BUS/GCI interfaces
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 2,048 x 2,048
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 2,048 x 2,048 IDT72V90823 FEATURES: 2,048 x 2,048 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 2,048 x 2,048 IDT72V90823 FEATURES: 2,048 x 2,048 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic
FEATURES: DESCRIPTION: FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH WITH RATE MATCHING 16,384 X 16,384 CHANNELS IDT72V73263
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH WITH RATE MATCHING 16,384 16,384 CHANNELS IDT72V73263 FEATURES: Up to 64 serial input and output streams Maximum 16,384 x 16,384 channel non-blocking switching
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH WITH RATE MATCHING 16,384 16,384 CHANNELS IDT72V73263 FEATURES: Up to 64 serial input and output streams Maximum 16,384 x 16,384 channel non-blocking switching
Boundary Scan Implementation
 OpenCORES s Boundary Scan Implementation Abstract This document describes Boundary Scan Implementation (software and hardware solution. It is fully IEEE 1149.1 compliant. Date : August 6, 2000 Version:
OpenCORES s Boundary Scan Implementation Abstract This document describes Boundary Scan Implementation (software and hardware solution. It is fully IEEE 1149.1 compliant. Date : August 6, 2000 Version:
DESCRIPTION: FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM. 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 8,192 x 8,192 JUNE Internal Registers
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 8,192 x 8,192 IDT72V73250 FEATURES: 8K x 8K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 16 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 8,192 x 8,192 IDT72V73250 FEATURES: 8K x 8K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 16 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 16,384 X 16,384 GND RESET TX0 RX0. Data Memory MUX. Connection Memory. Internal Registers
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 16,384 X 16,384 IDT72V73260 FEATURES: 16K x 16K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 32 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 16,384 X 16,384 IDT72V73260 FEATURES: 16K x 16K non-blocking switching at 32.768Mb/s 32 serial input and output streams Accepts single-bit single-data streams
SECTION 11 JTAG PORT
 nc. SECTION JTAG PORT MOTOROLA DSP5662 User s Manual - nc.. INTRODUCTION....................................-3.2 JTAG PINS........................................-5.3 TAP CONTROLLER.................................-6.4
nc. SECTION JTAG PORT MOTOROLA DSP5662 User s Manual - nc.. INTRODUCTION....................................-3.2 JTAG PINS........................................-5.3 TAP CONTROLLER.................................-6.4
1.8V MULTI-QUEUE FLOW-CONTROL DEVICES (128 QUEUES) 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION 1,179,648 bits 2,359,296 bits 4,718,592 bits Q127 Q126 Q125
 1.8V MULTI-QUEUE FLOW-CONTROL DEVICES (128 QUEUES) 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION 1,179,648 bits 2,359,296 bits 4,718,592 bits ADVANCE INFORMATION IDT72P51749 IDT72P51759 IDT72P51769 FEATURES Choose from among
1.8V MULTI-QUEUE FLOW-CONTROL DEVICES (128 QUEUES) 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION 1,179,648 bits 2,359,296 bits 4,718,592 bits ADVANCE INFORMATION IDT72P51749 IDT72P51759 IDT72P51769 FEATURES Choose from among
ZL30132 OC-192/STM-64 SONET/SDH/10GbE Network Interface Synchronizer
 OC-192/STM-64 SONET/SDH/10bE Network Interface Synchronizer Features Synchronizes to standard telecom or Ethernet backplane clocks and provides jitter filtered output clocks for SONET/SDH, DH and Ethernet
OC-192/STM-64 SONET/SDH/10bE Network Interface Synchronizer Features Synchronizes to standard telecom or Ethernet backplane clocks and provides jitter filtered output clocks for SONET/SDH, DH and Ethernet
Aeroflex Colorado Springs Application Note
 Synchronous SRAM (SSRAM) JTAG Operation Table : Cross Reference of Applicable Products Product Name: Manufacturer Part Number SMD # Device Type Internal PIC #. Overview 64Mbit Synchronous SRAM UT8SP2M32
Synchronous SRAM (SSRAM) JTAG Operation Table : Cross Reference of Applicable Products Product Name: Manufacturer Part Number SMD # Device Type Internal PIC #. Overview 64Mbit Synchronous SRAM UT8SP2M32
IEEE JTAG Boundary Scan Standard
 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan Standard Bed-of-nails tester Motivation System view of boundary scan hardware Elementary scan cell Test Access Port (TAP) controller Boundary scan instructions Example *Joint
IEEE 1149.1 JTAG Boundary Scan Standard Bed-of-nails tester Motivation System view of boundary scan hardware Elementary scan cell Test Access Port (TAP) controller Boundary scan instructions Example *Joint
VC Look-Up Table. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory. Figure 1 - MT90528 Block Diagram
 28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
28-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-0078.000) Supports both Unstructured and
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT89L80 Digital Switch
 CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT89L8 Digital Switch Features 3.3 volt supply 5 V lerant inputs and TTL compatible outputs. 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Accepts serial streams at 2.48 Mb/s Per-channel
CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT89L8 Digital Switch Features 3.3 volt supply 5 V lerant inputs and TTL compatible outputs. 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Accepts serial streams at 2.48 Mb/s Per-channel
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 52 x 52 IDT72V70200 FEATURES: 52 x 52 channel non-blocking switching at 2.048 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 52 x 52 IDT72V70200 FEATURES: 52 x 52 channel non-blocking switching at 2.048 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
8. JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in MAX V Devices
 December 2 MV58-. 8. JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in MAX V Devices MV58-. This chapter describes the IEEE Std.49. (JTAG) boundary-scan testing for Altera MAX V devices. The IEEE Std. 49. BST circuitry available
December 2 MV58-. 8. JTAG Boundary-Scan Testing in MAX V Devices MV58-. This chapter describes the IEEE Std.49. (JTAG) boundary-scan testing for Altera MAX V devices. The IEEE Std. 49. BST circuitry available
Chapter 7 Debugging Support
 Chapter 7 Debugging Support The DSP563 modules and features for debugging applications during system development are as follows: JTAG Test Access Port (TAP): Provides the TAP and Boundary Scan functionality
Chapter 7 Debugging Support The DSP563 modules and features for debugging applications during system development are as follows: JTAG Test Access Port (TAP): Provides the TAP and Boundary Scan functionality
Connecting Spansion SPI Serial Flash to Configure Altera FPGAs
 Connecting SPI Serial Flash to Configure Altera s Application By Frank Cirimele 1. Introduction Altera s are programmable logic devices used for basic logic functions, chip-to-chip connectivity, signal
Connecting SPI Serial Flash to Configure Altera s Application By Frank Cirimele 1. Introduction Altera s are programmable logic devices used for basic logic functions, chip-to-chip connectivity, signal
A Research Paper on Designing a TAP(Test Access Port)
 A Research Paper on Designing a TAP(Test Access Port) 1 Mr. VISHWAS K. CHAUDHARY, 2 Mr. MANISH J. PATEL 1, 2 P. G. Students in M.E.(VLSI & ESD) Gujarat Technological University & Seer-Akademi Ahmedabad,
A Research Paper on Designing a TAP(Test Access Port) 1 Mr. VISHWAS K. CHAUDHARY, 2 Mr. MANISH J. PATEL 1, 2 P. G. Students in M.E.(VLSI & ESD) Gujarat Technological University & Seer-Akademi Ahmedabad,
SCANSTA111. SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE (JTAG) Port. Literature Number: SNLS060J
 SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port Literature Number: SNLS060J Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111
SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port Literature Number: SNLS060J Enhanced SCAN Bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111
SCANSTA111 Enhanced SCAN bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE (JTAG) Port
 Enhanced SCAN bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111 extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1 test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a multidrop
Enhanced SCAN bridge Multidrop Addressable IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Port General Description The SCANSTA111 extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1 test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a multidrop
13. Configuring Stratix & Stratix GX Devices
 13. Configuring Stratix & Stratix GX Devices S52013-2.0 Introduction You can configure Stratix TM and Stratix GX devices using one of several configuration schemes. All configuration schemes use either
13. Configuring Stratix & Stratix GX Devices S52013-2.0 Introduction You can configure Stratix TM and Stratix GX devices using one of several configuration schemes. All configuration schemes use either
2.5V SEQUENTIAL FLOW-CONTROL DEVICE 36 BIT WIDE CONFIGURATION For use with 128Mb to 256Mb DDR SDRAM. IDT72T6360 Sequential Flow Control Device.
 FEATURES Product to be used with single or multiple external DDR SDRAM to provide significant storage capability of up to 1Gb density 166MHz operation (6ns read/write cycle time) User selectable input
FEATURES Product to be used with single or multiple external DDR SDRAM to provide significant storage capability of up to 1Gb density 166MHz operation (6ns read/write cycle time) User selectable input
9. IEEE (JTAG) Boundary-Scan Testing for Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices
 SII529-3.3 9. IEEE 49. (JTAG) Boundary-Scan Testing for Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices Introduction As printed circuit boards (PCBs) become more complex, the need for thorough testing becomes increasingly
SII529-3.3 9. IEEE 49. (JTAG) Boundary-Scan Testing for Stratix II and Stratix II GX Devices Introduction As printed circuit boards (PCBs) become more complex, the need for thorough testing becomes increasingly
SCAN92LV090 9 Channel Bus LVDS Transceiver w/ Boundary SCAN
 9 Channel Bus LVDS Transceiver w/ Boundary SCAN General Description The SCAN92LV090A is one in a series of Bus LVDS transceivers designed specifically for the high speed, low power proprietary backplane
9 Channel Bus LVDS Transceiver w/ Boundary SCAN General Description The SCAN92LV090A is one in a series of Bus LVDS transceivers designed specifically for the high speed, low power proprietary backplane
Configuring Cyclone FPGAs
 Configuring Cyclone FPGAs March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 250 Introduction You can configure Cyclone TM FPGAs using one of several configuration schemes, including the new active serial (AS) configuration
Configuring Cyclone FPGAs March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 250 Introduction You can configure Cyclone TM FPGAs using one of several configuration schemes, including the new active serial (AS) configuration
18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM
 18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM 18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM Features Functional Description Supports bus operation up to 250 MHz Available speed grades are 250, 200, and 167 MHz Registered
18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM 18-Mbit (512K 36/1M 18) Pipelined SRAM Features Functional Description Supports bus operation up to 250 MHz Available speed grades are 250, 200, and 167 MHz Registered
Section 3. System Integration
 Section 3. System Integration This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 9, Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in the Cyclone III Device Family Chapter 10, Hot-Socketing
Section 3. System Integration This section includes the following chapters: Chapter 9, Configuration, Design Security, and Remote System Upgrades in the Cyclone III Device Family Chapter 10, Hot-Socketing
IDT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 256 x 256 EATURES: UNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
 TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 256 x 256 IDT728985 EATURES: 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Automatic signal identification (ST-BUS, GCI) 8 RX inputs 32 channels at 64 Kbit/s per serial line
TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 256 x 256 IDT728985 EATURES: 256 x 256 channel non-blocking switch Automatic signal identification (ST-BUS, GCI) 8 RX inputs 32 channels at 64 Kbit/s per serial line
Implementing LVDS in Cyclone Devices
 Implementing LVDS in Cyclone Devices March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 254 Introduction Preliminary Information From high-speed backplane applications to high-end switch boxes, LVDS is the technology
Implementing LVDS in Cyclone Devices March 2003, ver. 1.1 Application Note 254 Introduction Preliminary Information From high-speed backplane applications to high-end switch boxes, LVDS is the technology
SCANSTA112 7-Port Multidrop IEEE (JTAG) Multiplexer
 7-Port Multidrop IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Multiplexer General Description The SCANSTA112 extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1 test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a multidrop approach over
7-Port Multidrop IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Multiplexer General Description The SCANSTA112 extends the IEEE Std. 1149.1 test bus into a multidrop test bus environment. The advantage of a multidrop approach over
REV CHANGE DESCRIPTION NAME DATE. A Release B Increased +1.2V Capacitor Value & VDD12A Cap Requirement
 REV CHANGE DESCRIPTION NAME DATE A Release 8-1-16 B Increased +1.2V Capacitor Value & VDD12A Cap Requirement 1-16-17 Any assistance, services, comments, information, or suggestions provided by Microchip
REV CHANGE DESCRIPTION NAME DATE A Release 8-1-16 B Increased +1.2V Capacitor Value & VDD12A Cap Requirement 1-16-17 Any assistance, services, comments, information, or suggestions provided by Microchip
Preliminary Data MOS IC. Type Ordering Code Package SDA Q67100-H5096 P-DIP-8-1
 Nonvolatile Memory 4-Kbit E 2 PROM with I 2 C Bus Interface SDA 2546-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM)
Nonvolatile Memory 4-Kbit E 2 PROM with I 2 C Bus Interface SDA 2546-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM)
Preliminary Data MOS IC. Type Ordering Code Package SDA Q67100-H5092 P-DIP-8-1
 Nonvolatile Memory 1-Kbit E 2 PROM SDA 2516-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM) 128 8-bit organization Supply
Nonvolatile Memory 1-Kbit E 2 PROM SDA 2516-5 Preliminary Data MOS IC Features Word-organized reprogrammable nonvolatile memory in n-channel floating-gate technology (E 2 PROM) 128 8-bit organization Supply
Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 General Description The DS75 digital thermometer and thermostat provides 9, 10, 11, or 12-bit digital temperature readings over a -55 C to +125 C range with ±2 C accuracy over a -25 C to +100 C range.
General Description The DS75 digital thermometer and thermostat provides 9, 10, 11, or 12-bit digital temperature readings over a -55 C to +125 C range with ±2 C accuracy over a -25 C to +100 C range.
Configuring APEX 20K, FLEX 10K & FLEX 6000 Devices
 Configuring APEX 20K, FLEX 10K & FLEX 6000 Devices December 1999, ver. 1.02 Application Note 116 Introduction APEX TM 20K, FLEX 10K, and FLEX 6000 devices can be configured using one of six configuration
Configuring APEX 20K, FLEX 10K & FLEX 6000 Devices December 1999, ver. 1.02 Application Note 116 Introduction APEX TM 20K, FLEX 10K, and FLEX 6000 devices can be configured using one of six configuration
Boundary Scan. Sungho Kang. Yonsei University
 Boundary Scan Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outiline Introduction TAP Controller Instruction Register Test Data Registers Instructions Hardware Test Innovations PCB Test Conclusion 2 Boundary Scan Improve
Boundary Scan Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outiline Introduction TAP Controller Instruction Register Test Data Registers Instructions Hardware Test Innovations PCB Test Conclusion 2 Boundary Scan Improve
AT45DQ321. Features. 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory with Dual-I/O and Quad-I/O Support
 32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory with Dual-I/O and Quad-I/O Support Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
32-Mbit DataFlash (with Extra 1-Mbits), 2.3V Minimum SPI Serial Flash Memory with Dual-I/O and Quad-I/O Support Features Single 2.3V - 3.6V supply Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) compatible Supports
72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM
 72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 1334 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 667 MHz Read latency
72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV HP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 1334 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 667 MHz Read latency
VC Look-Up Table. Segmentation / Reassembly Circular Buffers. External Memory Controller. TX SAR Local Memory. Local Memory
 8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
8-Port Primary Rate Circuit Emulation AAL1 SAR Features AAL1 Segmentation and Reassembly device compliant with Circuit Emulation Services (CES) standard (af-vtoa-78.) Supports both Unstructured and Structured
72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM
 72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 2132 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 1066 MHz Read latency
72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM 72-Mbit QDR -IV XP SRAM Features Configurations 72-Mbit density (4M 18, 2M 36) Total Random Transaction Rate [1] of 2132 MT/s Maximum operating frequency of 1066 MHz Read latency
SECTION 2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
 SECTION 2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION Figure 2-1 displays the block diagram of the MCF5206 along with the signal interface. This section describes the MCF5206 input and output signals. The descriptions
SECTION 2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION Figure 2-1 displays the block diagram of the MCF5206 along with the signal interface. This section describes the MCF5206 input and output signals. The descriptions
Emulation Tech Note 8 Using SdConfigEx
 Spectrum Digital Document Revision 0.01 Emulation Tech Note 8 Using SdConfigEx Document Revision 0.01 Jan 30, 2006 Spectrum Digital 1. Introduction 3 2. Features and Differences 3 3. Installation 4 4.
Spectrum Digital Document Revision 0.01 Emulation Tech Note 8 Using SdConfigEx Document Revision 0.01 Jan 30, 2006 Spectrum Digital 1. Introduction 3 2. Features and Differences 3 3. Installation 4 4.
1 Megabit Serial Flash EEPROM SST45LF010
 EEPROM FEATURES: Single.0-.V Read and Write Operations Serial Interface Architecture SPI Compatible: Mode 0 and Mode Byte Serial Read with Single Command Superior Reliability Endurance: 00,000 Cycles (typical)
EEPROM FEATURES: Single.0-.V Read and Write Operations Serial Interface Architecture SPI Compatible: Mode 0 and Mode Byte Serial Read with Single Command Superior Reliability Endurance: 00,000 Cycles (typical)
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512
 3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512 IDT72V70800 FEATURES: 512 x 512 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
3.3 VOLT TIME SLOT INTERCHANGE DIGITAL SWITCH 512 x 512 IDT72V70800 FEATURES: 512 x 512 channel non-blocking switching at 8.192 Mb/s Per-channel variable or constant throughput delay Automatic identification
SSD1322. Product Preview. 480 x 128, Dot Matrix High Power OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1322 Product Preview 480 x 128, Dot Matrix High Power OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a product under
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1322 Product Preview 480 x 128, Dot Matrix High Power OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a product under
Micron MT54V512H18EF-10 9Mb QDR SRAM Circuit Analysis
 May 14, 2002 Micron MT54V512H18EF-10 9Mb QDR SRAM Circuit Analysis Table of Contents Introduction... Page 1 List of Figures... Page 4 Device Summary Sheet... Page 12 Top Level Diagram...Tab 1 Data Path...Tab
May 14, 2002 Micron MT54V512H18EF-10 9Mb QDR SRAM Circuit Analysis Table of Contents Introduction... Page 1 List of Figures... Page 4 Device Summary Sheet... Page 12 Top Level Diagram...Tab 1 Data Path...Tab
4-Megabit 2.7-volt Only Serial DataFlash AT45DB041. Features. Description. Pin Configurations
 Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Interface Architecture Page Program Operation Single Cycle Reprogram (Erase and Program) 2048 Pages (264 Bytes/Page) Main Memory Two 264-Byte SRAM Data Buffers
Features Single 2.7V - 3.6V Supply Serial Interface Architecture Page Program Operation Single Cycle Reprogram (Erase and Program) 2048 Pages (264 Bytes/Page) Main Memory Two 264-Byte SRAM Data Buffers
Organization Row Address Column Address Bank Address Auto Precharge 128Mx8 (1GB) based module A0-A13 A0-A9 BA0-BA2 A10
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Gigaram is ECC Registered Dual-Die DIMM with 1.25inch (30.00mm) height based on DDR2 technology. DIMMs are available as ECC modules in 256Mx72 (2GByte) organization and density,
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The Gigaram is ECC Registered Dual-Die DIMM with 1.25inch (30.00mm) height based on DDR2 technology. DIMMs are available as ECC modules in 256Mx72 (2GByte) organization and density,
Flexible MVIP Interface Circuit
 CMOS MT90810 Flexible MVIP Interface Circuit Features MVIP and ST-BUS compliant MVIP Enhanced Switching with 384x384 channel capacity (256 MVIP channels; 128 local channels) On-chip PLL for MVIP master/slave
CMOS MT90810 Flexible MVIP Interface Circuit Features MVIP and ST-BUS compliant MVIP Enhanced Switching with 384x384 channel capacity (256 MVIP channels; 128 local channels) On-chip PLL for MVIP master/slave
Amarjeet Singh. January 30, 2012
 Amarjeet Singh January 30, 2012 Website updated - https://sites.google.com/a/iiitd.ac.in/emsys2012/ Lecture slides, audio from last class Assignment-2 How many of you have already finished it? Final deadline
Amarjeet Singh January 30, 2012 Website updated - https://sites.google.com/a/iiitd.ac.in/emsys2012/ Lecture slides, audio from last class Assignment-2 How many of you have already finished it? Final deadline
DS75 Digital Thermometer and Thermostat
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature Measurements Require No External Components Measures Temperatures from -55 C to +125 C (-67 F to +257 F) 2 C Accuracy Over a -25 C to +100 C Range Thermometer Resolution
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Temperature Measurements Require No External Components Measures Temperatures from -55 C to +125 C (-67 F to +257 F) 2 C Accuracy Over a -25 C to +100 C Range Thermometer Resolution
24C08/24C16. Two-Wire Serial EEPROM. Preliminary datasheet 8K (1024 X 8)/16K (2048 X 8) General Description. Pin Configuration
 Two-Wire Serial EEPROM Preliminary datasheet 8K (1024 X 8)/16K (2048 X 8) Low-voltage Operation 1.8 (VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V) Operating Ambient Temperature: -40 C to +85 C Internally Organized 1024 X 8 (8K),
Two-Wire Serial EEPROM Preliminary datasheet 8K (1024 X 8)/16K (2048 X 8) Low-voltage Operation 1.8 (VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V) Operating Ambient Temperature: -40 C to +85 C Internally Organized 1024 X 8 (8K),
Introduction to I2C & SPI. Chapter 22
 Introduction to I2C & SPI Chapter 22 Issues with Asynch. Communication Protocols Asynchronous Communications Devices must agree ahead of time on a data rate The two devices must also have clocks that are
Introduction to I2C & SPI Chapter 22 Issues with Asynch. Communication Protocols Asynchronous Communications Devices must agree ahead of time on a data rate The two devices must also have clocks that are
Preliminary Data Sheet, DS 1, Nov SWITI Switching IC. Version 1.3. Wired Communications. Never stop thinking.
 Preliminary Data Sheet, DS 1, Nov. 2001 SWITI Switching IC PEF 20451 PEF 20471 PEF 24471 Version 1.3 HTSI HTSI-L HTSI-XL Wired Communications Never stop thinking. Edition 2001-11-16 Published by Infineon
Preliminary Data Sheet, DS 1, Nov. 2001 SWITI Switching IC PEF 20451 PEF 20471 PEF 24471 Version 1.3 HTSI HTSI-L HTSI-XL Wired Communications Never stop thinking. Edition 2001-11-16 Published by Infineon
JTAG TAP CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING USING FPGA BOARD
 JTAG TAP CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING USING FPGA BOARD 1 MOHAMED JEBRAN.P, 2 SHIREEN FATHIMA, 3 JYOTHI M 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, HKBKCE, Bangalore-45. 3 Software Engineer, Imspired solutions,
JTAG TAP CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING USING FPGA BOARD 1 MOHAMED JEBRAN.P, 2 SHIREEN FATHIMA, 3 JYOTHI M 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, HKBKCE, Bangalore-45. 3 Software Engineer, Imspired solutions,
SSD1305. Advance Information. 132 x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1305 Advance Information 132 x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1305 Advance Information 132 x 64 Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Segment/Common Driver with Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications
AGM CPLD AGM CPLD DATASHEET
 AGM CPLD DATASHEET 1 General Description AGM CPLD family provides low-cost instant-on, non-volatile CPLDs, with densities from 256, 272 to 576 logic LUTs and non-volatile flash storage of 256Kbits. The
AGM CPLD DATASHEET 1 General Description AGM CPLD family provides low-cost instant-on, non-volatile CPLDs, with densities from 256, 272 to 576 logic LUTs and non-volatile flash storage of 256Kbits. The
Specifications USB-1408FS
 Document Revision 1.1, May, 2006 Copyright 2006, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design. Analog input Table
Document Revision 1.1, May, 2006 Copyright 2006, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design. Analog input Table
MMCLAB01 Logic Analyzer Board User s Manual
 nc. MMCLAB01 Logic Analyzer Board Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. Motorola does not assume any liability
nc. MMCLAB01 Logic Analyzer Board Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. Motorola does not assume any liability
HSP Histogrammer/Accumulating Buffer. Features. Applications. Ordering Information. Block Diagram FN Data Sheet July 2004
 HSP48410 Data Sheet July 2004 FN3185.3 Histogrammer/Accumulating Buffer The Intersil HSP48410 is an 84 lead Histogrammer IC intended for use in image and signal analysis. The on-board memory is configured
HSP48410 Data Sheet July 2004 FN3185.3 Histogrammer/Accumulating Buffer The Intersil HSP48410 is an 84 lead Histogrammer IC intended for use in image and signal analysis. The on-board memory is configured
Freescale Semiconductor, I. Ingress Cell Processing
 nc. Advance Information ATM Cell Processor Order this document by MC92501/D MC92501 The MC92501 is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Cell Processor layer device composed of dedicated high-performance
nc. Advance Information ATM Cell Processor Order this document by MC92501/D MC92501 The MC92501 is an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Cell Processor layer device composed of dedicated high-performance
FM24CL04 4Kb FRAM Serial Memory
 4Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Writes 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric Process
4Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 4K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 512 x 8 bits Unlimited Read/Writes 45 Year Data Retention NoDelay Writes Advanced High-Reliability Ferroelectric Process
Intel386 TM DX MICROPROCESSOR 32-BIT CHMOS MICROPROCESSOR WITH INTEGRATED MEMORY MANAGEMENT (PQFP SUPPLEMENT)
 Intel386 TM DX MICROPROCESSOR 32-BIT CHMOS MICROPROCESSOR WITH INTEGRATED MEMORY MANAGEMENT (PQFP SUPPLEMENT) Y Flexible 32-Bit Microprocessor 8 16 32-Bit Data Types 8 General Purpose 32-Bit Registers
Intel386 TM DX MICROPROCESSOR 32-BIT CHMOS MICROPROCESSOR WITH INTEGRATED MEMORY MANAGEMENT (PQFP SUPPLEMENT) Y Flexible 32-Bit Microprocessor 8 16 32-Bit Data Types 8 General Purpose 32-Bit Registers
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
 DATA SHEET MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT µpd6708 IEBus (Inter Equipment Bus ) PROTOCOL CONTROL LSI DESCRIPTION The µpd6708 is a peripheral LSI for microcontrollers that controls the protocol of the IEBus. This
DATA SHEET MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT µpd6708 IEBus (Inter Equipment Bus ) PROTOCOL CONTROL LSI DESCRIPTION The µpd6708 is a peripheral LSI for microcontrollers that controls the protocol of the IEBus. This
W25X40CL 2.5/3/3.3 V 4M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI. Publication Release Date: October 15, Revision E
 2.5/3/3.3 V 4M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision E Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 4 2. FEATURES... 4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 208-MIL, SOIC 150-MIL
2.5/3/3.3 V 4M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision E Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION... 4 2. FEATURES... 4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 208-MIL, SOIC 150-MIL
DM-OLED X 64 BLUE GRAPHIC OLED DISPLAY MODULE WITH SPI, I2C INTERFACE
 1.3 128 X 64 BLUE GRAPHIC OLED DISPLAY MODULE WITH SPI, I2C INTERFACE Contents Revision History Main Features Pin Description Panel Pin Description Module Pin Description Mechanical Drawing Panel Mechanical
1.3 128 X 64 BLUE GRAPHIC OLED DISPLAY MODULE WITH SPI, I2C INTERFACE Contents Revision History Main Features Pin Description Panel Pin Description Module Pin Description Mechanical Drawing Panel Mechanical
power supply Tamper Detect function will detect possible data modification from outside magnetic
 FEATURES High bandwidth Read and Write at 52MB/sec Quad I/O with the use of dual purpose pins to maintain a low pin count Operates in both standard, single SPI mode and high speed quad SPI mode Fast quad
FEATURES High bandwidth Read and Write at 52MB/sec Quad I/O with the use of dual purpose pins to maintain a low pin count Operates in both standard, single SPI mode and high speed quad SPI mode Fast quad
SN74V215, SN74V225, SN74V235, SN74V , , , DSP-SYNC FIRST-IN, FIRST-OUT MEMORIES
 512 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V215) 1024 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V225) 2048 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V235) 4096 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V245) 7.5-ns Read/Write Cycle Time 3.3-V
512 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V215) 1024 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V225) 2048 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V235) 4096 18-Bit Organization Array (SN74V245) 7.5-ns Read/Write Cycle Time 3.3-V
Fremont Micro Devices, Inc.
 FEATURES Low voltage and low power operations: FT24C02/04/08/16: V CC = 2.5V to 5.5V FT24C02A/04A/08A/16A: V CC = 1.8V to 5.5V Maximum Standby current < 1µA (typically 0.02µA and 0.06µA @ 1.8V and 5.5V
FEATURES Low voltage and low power operations: FT24C02/04/08/16: V CC = 2.5V to 5.5V FT24C02A/04A/08A/16A: V CC = 1.8V to 5.5V Maximum Standby current < 1µA (typically 0.02µA and 0.06µA @ 1.8V and 5.5V
DS1845 Dual NV Potentiometer and Memory
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Two linear taper potentiometers -010 one 10k, 100 position & one 10k, 256 position -050 one 10k, 100 position & one 50k, 256 postition -100 one 10k, 100 position & one 100k, 256
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Two linear taper potentiometers -010 one 10k, 100 position & one 10k, 256 position -050 one 10k, 100 position & one 50k, 256 postition -100 one 10k, 100 position & one 100k, 256
W25X05CL/10CL/20CL 2.5 / 3 / 3.3 V 512K / 1M / 2M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI
 2.5 / 3 / 3.3 V 512K / 1M / 2M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision B Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION...4 2. FEATURES...4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 150-MIL,
2.5 / 3 / 3.3 V 512K / 1M / 2M-BIT SERIAL FLASH MEMORY WITH 4KB SECTORS AND DUAL I/O SPI - 1 - Revision B Table of Contents 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION...4 2. FEATURES...4 3. PIN CONFIGURATION SOIC 150-MIL,
TOP VIEW CLOCK GENERATOR A1 A2 GND CPU SPEED SELECT
 Rev 0; 6/04 9-Bit I 2 C Nonvolatile General Description The is a 9-bit nonvolatile (NV) I/O expander with 64 bytes of NV user memory controlled by an I 2 C TM - compatible serial interface. The offers
Rev 0; 6/04 9-Bit I 2 C Nonvolatile General Description The is a 9-bit nonvolatile (NV) I/O expander with 64 bytes of NV user memory controlled by an I 2 C TM - compatible serial interface. The offers
FM24C Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features
 Preliminary FM24C512 512Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 512Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 65,536 x 8 bits High Endurance 10 Billion (10 10 ) Read/Writes 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes
Preliminary FM24C512 512Kb FRAM Serial Memory Features 512Kbit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 65,536 x 8 bits High Endurance 10 Billion (10 10 ) Read/Writes 45 year Data Retention NoDelay Writes
USB-1208LS Specifications
 Specifications Document Revision 1.1, February, 2010 Copyright 2010, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
Specifications Document Revision 1.1, February, 2010 Copyright 2010, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design.
FM24C16C-GTR. 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory. Features. Description. Pin Configuration NC NC NC VSS VDD WP SCL SDA. Ordering Information.
 Preliminary FM24C16C 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits High Endurance (10 12 ) Read/Write Cycles 36 year Data Retention at +75 C NoDelay
Preliminary FM24C16C 16Kb Serial 5V F-RAM Memory Features 16K bit Ferroelectric Nonvolatile RAM Organized as 2,048 x 8 bits High Endurance (10 12 ) Read/Write Cycles 36 year Data Retention at +75 C NoDelay
Specifications
 Specifications 18200-10 Cole-Parmer Instrument Company 625 East Bunker Court Vernon Hills, Illinois 60061-1844 (847) 549-7600 (847) 247-2929 (Fax) 800-323-4340 www.coleparmer.com e-mail: techinfo@coleparmer.com
Specifications 18200-10 Cole-Parmer Instrument Company 625 East Bunker Court Vernon Hills, Illinois 60061-1844 (847) 549-7600 (847) 247-2929 (Fax) 800-323-4340 www.coleparmer.com e-mail: techinfo@coleparmer.com
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. DS12887 Real Time Clock www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Drop in replacement for
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. DS12887 Real Time Clock www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Drop in replacement for
Universität Dortmund. IO and Peripheral Interfaces
 IO and Peripheral Interfaces Microcontroller System Architecture Each MCU (micro-controller unit) is characterized by: Microprocessor 8,16,32 bit architecture Usually simple in-order microarchitecture,
IO and Peripheral Interfaces Microcontroller System Architecture Each MCU (micro-controller unit) is characterized by: Microprocessor 8,16,32 bit architecture Usually simple in-order microarchitecture,
Low Voltage, 10-Bit Digital Temperature Sensor in 8-Lead MSOP AD7314
 a FEATURES 10-Bit Temperature-to-Digital Converter 35 C to +85 C Operating Temperature Range 2 C Accuracy SPI and DSP Compatible Serial Interface Shutdown Mode Space-Saving MSOP Package APPLICATIONS Hard
a FEATURES 10-Bit Temperature-to-Digital Converter 35 C to +85 C Operating Temperature Range 2 C Accuracy SPI and DSP Compatible Serial Interface Shutdown Mode Space-Saving MSOP Package APPLICATIONS Hard
JTAG and I 2 C on ELMB
 JTAG and I 2 C on ELMB Henk Boterenbrood NIKHEF, Amsterdam Nov 2000 Version 0.3 ABSTRACT The ELMB is designed as a general-purpose plug-on module for distributed monitoring and control applications in
JTAG and I 2 C on ELMB Henk Boterenbrood NIKHEF, Amsterdam Nov 2000 Version 0.3 ABSTRACT The ELMB is designed as a general-purpose plug-on module for distributed monitoring and control applications in
Specifications PMD-1208FS
 Document Revision 1.1, May, 2005 Copyright 2005, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design. Analog input section
Document Revision 1.1, May, 2005 Copyright 2005, Measurement Computing Corporation Typical for 25 C unless otherwise specified. Specifications in italic text are guaranteed by design. Analog input section
DSP56002 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
 nc. SECTION 2 DSP56002 PIN DESCRIPTIONS MOTOROLA 2-1 nc. SECTION CONTENTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION............................................. 2-3 2.2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS......................................
nc. SECTION 2 DSP56002 PIN DESCRIPTIONS MOTOROLA 2-1 nc. SECTION CONTENTS 2.1 INTRODUCTION............................................. 2-3 2.2 SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS......................................
FIN3385 FIN3383 Low Voltage 28-Bit Flat Panel Display Link Serializers
 October 2003 Revised January 2004 FIN3385 FIN3383 Low Voltage 28-Bit Flat Panel Display Link Serializers General Description The FIN3385 and FIN3383 transform 28 bit wide parallel LVTTL (Low Voltage TTL)
October 2003 Revised January 2004 FIN3385 FIN3383 Low Voltage 28-Bit Flat Panel Display Link Serializers General Description The FIN3385 and FIN3383 transform 28 bit wide parallel LVTTL (Low Voltage TTL)
P1149.1A Extensions to IEEE-STD
 AN-890 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note February 1994 Revised May 2001 P1149.1A Extensions to IEEE-STD-1149.1-1990 Abstract Since publication of IEEE-1149.1-1990/ANSI 1, 2, 3, extensions and requests
AN-890 Fairchild Semiconductor Application Note February 1994 Revised May 2001 P1149.1A Extensions to IEEE-STD-1149.1-1990 Abstract Since publication of IEEE-1149.1-1990/ANSI 1, 2, 3, extensions and requests
SPI 3-Wire Master (VHDL)
 SPI 3-Wire Master (VHDL) Code Download Features Introduction Background Port Descriptions Clocking Polarity and Phase Command and Data Widths Transactions Reset Conclusion Contact Code Download spi_3_wire_master.vhd
SPI 3-Wire Master (VHDL) Code Download Features Introduction Background Port Descriptions Clocking Polarity and Phase Command and Data Widths Transactions Reset Conclusion Contact Code Download spi_3_wire_master.vhd
16COM/80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 6COM/80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It is capable of displaying or 2 lines with
6COM/80SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION The is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It is capable of displaying or 2 lines with
OTP MATRIX 3-D MEMORY - 32PIN TSOP 16MB, 32MB, 64MB DATA SHEET DOCUMENT NUMBER: DS004 REVISION: 1.11 REVISION DATE:
 16MB, 32MB, 64MB DATA SHEET REVISION: 111 REVISION DATE: 06-24-05 REV 111 06/24/05 NOTICES: Copyright 2002, 2004, 2005 Matrix Semiconductor, Inc All rights reserved If you have received this document from
16MB, 32MB, 64MB DATA SHEET REVISION: 111 REVISION DATE: 06-24-05 REV 111 06/24/05 NOTICES: Copyright 2002, 2004, 2005 Matrix Semiconductor, Inc All rights reserved If you have received this document from
description STRB A0 A1 A2 R/W D1 D2 D3 GND D4 D5 RDY TDO TCK TMS TRST TDI RST TOE D7 CLKIN STRB R/W D0 D1 D2 D3 NC GND D4 D5
 Members of Texas Instruments (TI) Broad Family of Testability Products Supporting IEEE Std 1149.1-1990 (JTAG) Test Access Port () and Boundary-Scan Architecture Provide Built-In Access to IEEE Std 1149.1
Members of Texas Instruments (TI) Broad Family of Testability Products Supporting IEEE Std 1149.1-1990 (JTAG) Test Access Port () and Boundary-Scan Architecture Provide Built-In Access to IEEE Std 1149.1
DS1682 Total-Elapsed-Time Recorder with Alarm
 www.maxim-ic.com GENERAL DESCRIPTION The DS1682 is an integrated elapsed-time recorder containing a factory-calibrated, temperaturecompensated RC time base that eliminates the need for an external crystal.
www.maxim-ic.com GENERAL DESCRIPTION The DS1682 is an integrated elapsed-time recorder containing a factory-calibrated, temperaturecompensated RC time base that eliminates the need for an external crystal.
SSD1329. Advance Information. 128 x 128 OLED Segment / Common Driver with Controller Equips with 16 Gray Scale Levels and 64 Hard Icon Lines
 SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1329 Advance Information 128 x 128 OLED Segment / Common Driver with Controller Equips with 16 Gray Scale Levels and 64 Hard Icon Lines This document contains
SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA SSD1329 Advance Information 128 x 128 OLED Segment / Common Driver with Controller Equips with 16 Gray Scale Levels and 64 Hard Icon Lines This document contains
Z Z-280 MT8930, MT8992/3/4/5 MT8880 MT8888 MT8889 MT8980/1 MT8985, MT8986 (DIP-40) MT8986 (PLCC-44) MT8920B MT8952B
 MSAN-145 How to Interface Mitel Components to Parallel Bus CPUs TABL OF CONTNTS Introduction ISSU 1 August 1993 1.0 Group 1 Components 1.1 Interfacing to the 6802 1.2 Interfacing to the 6809 1.3 Interfacing
MSAN-145 How to Interface Mitel Components to Parallel Bus CPUs TABL OF CONTNTS Introduction ISSU 1 August 1993 1.0 Group 1 Components 1.1 Interfacing to the 6802 1.2 Interfacing to the 6809 1.3 Interfacing
16COM/40SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD
 6COM/4SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It can display, 2-line with 5 x 8 or 5 x dots
6COM/4SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR DOT MATRIX LCD INTRODUCTION is a dot matrix LCD driver & controller LSI which is fabricated by low power CMOS technology It can display, 2-line with 5 x 8 or 5 x dots
89HPES24T3G2 Hardware Design Guide
 89H Hardware Design Guide Notes Introduction This document provides system design guidelines for IDT 89H PCI Express (PCIe ) 2. base specification compliant switch device. The letters "G2" within the device
89H Hardware Design Guide Notes Introduction This document provides system design guidelines for IDT 89H PCI Express (PCIe ) 2. base specification compliant switch device. The letters "G2" within the device
+Denotes a lead(pb)-free/rohs-compliant package.
 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX7320 General Description The MAX7320 2-wire serial-interfaced peripheral features eight push-pull outputs with selectable power-up logic states. The +5.5V tolerant RST input
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX7320 General Description The MAX7320 2-wire serial-interfaced peripheral features eight push-pull outputs with selectable power-up logic states. The +5.5V tolerant RST input
