Note. Out of town Thursday afternoon. Willing to meet before 1pm, me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office
|
|
|
- Virginia Poole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 raphs and Trees
2 Note Out of town Thursday afternoon Willing to meet before pm, me if you want to meet then so I know to be in my office
3 few extra remarks about recursion If you can write it recursively you can also write it iteratively, and vice versa hurch-turing Thesis ut why pick one method over the other?
4 xample: ibonacci numbers int fib(int n) { if(n == n == 0) return ; else return fib(n-)+fib(n-) } int fib(int n) { int current = ; int previous = ; int temp; if(n == 0 n == ) return ; for(int i = ; i < n; i++) { temp = current + previous; previous = current; current = temp; } return current; }
5 Results... Recursive may be easier, but may not be the best way Work out the best way before moving forward
6 raphs and Trees Represents a lot of things ormally a graph is a pair of sets, = (V,) V - The set of vertices - the set of edges ach edge connects vertices together
7 Terminology Lots of terminology surrounding graphs, tons of types, specific patterns, etc Tip: lways read the description of graphs carefully - they describe a lot in just a few words
8 raph terminology Undirected - you can travel along an edge in either direction irected (igraph) - One-way travel only (but still possible to have edges!) Note: ll undirected graphs can be converted into directed graphs, but not the other way around! Unweighted - dges have no value associated with them Weighted - dges have a value associated with them xamples on board
9 Yet more terminology ycle - set of edges that forms a loop yclic - raph contains a cycle cyclic - No cycles allowed in the graph - irected cyclic raph Self-loop: n edge from a vertex to itself (yes, this counts as a cycle) Simple raph - Shorthand for Undirected Unweighted No-self-loops graph
10 Yes, there s still more egree (undirected only): The number of edges connected to a vertex In/Out-degree (directed only): The number of edges entering/leaving a graph Regular - ll vertices have the same degree (Simple) Path - sequence of (distinct) edges going from u to v onnected - or any two vertices there exists a path between them irected graphs - strongly connected components
11 Special graphs lique (K n ) - graph will all possible edges on n vertices ipartite - graph with two sets of vertices. dges only allowed between sets omplete ipartite (K n,m ) - bipartite graph with all possible edges mpty graph - No vertices or edges ycle raph - One giant cycle, no other edges allowed Path raph - ll linked in a line
12 nd... Tree: ny acyclic graph with n vertices and n- edges. Or.. n acyclic directed graph where there is only one path between any two vertices orest - collection of trees
13 raph representations djacency Matrix - a V x V matrix where [u][v] represents the existence and weight of an edge from u to v ood for dense graphs, easy to work with O(n ) memory djacency list - list of lists. ach list represents a vertex, and contains the vertices it is connected to ood for sparse graphs, harder to work with O(n + m) memory xample on board
14 Trees Used in a lot of more complex data structures Often a single vertex is designated as the root Root is on top. Not on bottom llows a natural direction for edges
15 Tree terminology Root - The top of the tree hildren - Those connected one layer below escendant - an get to these nodes by only moving downward ncestor - Node that can be reached by following parents
16 Minimum Spanning Trees onsider a weighted graph ind a set of edges that forms a tree (or forest, if is not connected) within in such a way that the sum of the edges is minimized ssentially, find the cheapest possible spanning tree that you can
17 Prim s lgorithm Idea: Take a greedy approach to making a MST Two versions: dj. Matrix and dj. List Matrix - O(n ) List - O(m log n) [O( log V)] ist: Pick a starting point. Repeatedly add the closest edge to the current tree to the tree until you re done
18
19 Start with. ind closest vertex to tree
20 Start with. ind closest vertex to tree
21 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
22 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
23 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
24 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
25 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
26 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree rbitrary tiebreaker: lphabetical order
27 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
28 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
29 Repeatedly find the closest vertex to the tree
30 ll N nodes in the tree. one!
31 Kruskals algorithm Repeatedly pick the smallest edge that has not been visited If it does not make a cycle, add it to the tree Initialized as a forest of singletons Tree is stored as a Union ind. ives us the runtimes we want
32 Pick edges, if there is no cycle, add to tree
33 Pick edges, if there is no cycle, add to tree
34 Pick edges, if there is no cycle, add to tree
35 Pick edges, if there is no cycle, add to tree
36 Pick edges, if there is no cycle, add to tree
37 Pick edges, if there is no cycle, add to tree
38 ll vertices connected. one
39 ycle case
40 ycle case
41 ycle case
42 ycle case
Spanning Tree. Lecture19: Graph III. Minimum Spanning Tree (MSP)
 Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths
 Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Prim's algorithm ijkstra's algorithm November, 017 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Recall: S spanning tree Starting from vertex 16 9 1 6 10 13 4 3 17 5 11 7 16 13
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Prim's algorithm ijkstra's algorithm November, 017 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Recall: S spanning tree Starting from vertex 16 9 1 6 10 13 4 3 17 5 11 7 16 13
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths
 Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Kruskal's lgorithm Prim's lgorithm Shortest Paths pril 04, 018 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Kruskal's algorithm ata types for implementation Kruskalslgorithm()
Minimum Spanning Trees and Shortest Paths Kruskal's lgorithm Prim's lgorithm Shortest Paths pril 04, 018 inda eeren / eoffrey Tien 1 Kruskal's algorithm ata types for implementation Kruskalslgorithm()
Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Karen Daniels
 UMass Lowell omputer Science 91.404 nalysis of lgorithms Prof. Karen aniels Spring, 2013 hapter 22: raph lgorithms & rief Introduction to Shortest Paths [Source: ormen et al. textbook except where noted]
UMass Lowell omputer Science 91.404 nalysis of lgorithms Prof. Karen aniels Spring, 2013 hapter 22: raph lgorithms & rief Introduction to Shortest Paths [Source: ormen et al. textbook except where noted]
Chapter 9. Greedy Algorithms: Spanning Trees and Minimum Spanning Trees
 msc20 Intro to lgorithms hapter. Greedy lgorithms: Spanning Trees and Minimum Spanning Trees The concept is relevant to connected undirected graphs. Problem: Here is a diagram of a prison for political
msc20 Intro to lgorithms hapter. Greedy lgorithms: Spanning Trees and Minimum Spanning Trees The concept is relevant to connected undirected graphs. Problem: Here is a diagram of a prison for political
Week 9 Student Responsibilities. Mat Example: Minimal Spanning Tree. 3.3 Spanning Trees. Prim s Minimal Spanning Tree.
 Week 9 Student Responsibilities Reading: hapter 3.3 3. (Tucker),..5 (Rosen) Mat 3770 Spring 01 Homework Due date Tucker Rosen 3/1 3..3 3/1 DS & S Worksheets 3/6 3.3.,.5 3/8 Heapify worksheet ttendance
Week 9 Student Responsibilities Reading: hapter 3.3 3. (Tucker),..5 (Rosen) Mat 3770 Spring 01 Homework Due date Tucker Rosen 3/1 3..3 3/1 DS & S Worksheets 3/6 3.3.,.5 3/8 Heapify worksheet ttendance
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 S 101, Winter 2018 esign and nalysis of lgorithms Lecture 3: onnected omponents lass URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ nd of Lecture 2: s, Topological Order irected cyclic raph.g., Vertices
S 101, Winter 2018 esign and nalysis of lgorithms Lecture 3: onnected omponents lass URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse101-w18/ nd of Lecture 2: s, Topological Order irected cyclic raph.g., Vertices
L10 Graphs. Alice E. Fischer. April Alice E. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 April / 37
 L10 Graphs lice. Fischer pril 2016 lice. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 pril 2016 1 / 37 Outline 1 Graphs efinition Graph pplications Graph Representations 2 Graph Implementation 3 Graph lgorithms Sorting
L10 Graphs lice. Fischer pril 2016 lice. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 pril 2016 1 / 37 Outline 1 Graphs efinition Graph pplications Graph Representations 2 Graph Implementation 3 Graph lgorithms Sorting
Spanning Trees. CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 17: Minimum Spanning Trees. Motivation. Observations. Spanning tree via DFS
 Spanning Trees S: ata Structures & lgorithms Lecture : Minimum Spanning Trees simple problem: iven a connected undirected graph =(V,), find a minimal subset of edges such that is still connected graph
Spanning Trees S: ata Structures & lgorithms Lecture : Minimum Spanning Trees simple problem: iven a connected undirected graph =(V,), find a minimal subset of edges such that is still connected graph
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal
 CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
Graphs: Definitions and Representations (Chapter 9)
 oday s Outline Graphs: efinitions and Representations (hapter 9) dmin: HW #4 due hursday, Nov 10 at 11pm Memory hierarchy Graphs Representations SE 373 ata Structures and lgorithms 11/04/2011 1 11/04/2011
oday s Outline Graphs: efinitions and Representations (hapter 9) dmin: HW #4 due hursday, Nov 10 at 11pm Memory hierarchy Graphs Representations SE 373 ata Structures and lgorithms 11/04/2011 1 11/04/2011
ALGORITHM DESIGN GREEDY ALGORITHMS. University of Waterloo
 ALORITHM DSIN RDY ALORITHMS University of Waterloo LIST OF SLIDS - List of Slides reedy Approaches xample: Making Change 4 Making Change (cont.) 5 Minimum Spanning Tree 6 xample 7 Approaches that Don t
ALORITHM DSIN RDY ALORITHMS University of Waterloo LIST OF SLIDS - List of Slides reedy Approaches xample: Making Change 4 Making Change (cont.) 5 Minimum Spanning Tree 6 xample 7 Approaches that Don t
Today s Outline CSE 221: Algorithms and Data Structures Graphs (with no Axes to Grind)
 Today s Outline S : lgorithms and ata Structures raphs (with no xes to rind) Steve Wolfman 0W Topological Sort: etting to Know raphs with a Sort raph T and raph Representations raph Terminology (a lot
Today s Outline S : lgorithms and ata Structures raphs (with no xes to rind) Steve Wolfman 0W Topological Sort: etting to Know raphs with a Sort raph T and raph Representations raph Terminology (a lot
Graphs: Definitions and Representations (Chapter 9)
 oday s Outline Graphs: efinitions and Representations (hapter 9) SE 373 ata Structures and lgorithms dmin: Homework #4 - due hurs, Nov 8 th at 11pm Midterm 2, ri Nov 16 Memory hierarchy Graphs Representations
oday s Outline Graphs: efinitions and Representations (hapter 9) SE 373 ata Structures and lgorithms dmin: Homework #4 - due hurs, Nov 8 th at 11pm Midterm 2, ri Nov 16 Memory hierarchy Graphs Representations
A region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that is divided up by the network.
 Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Math 135 Networks and graphs Key terms Vertex (Vertices) ach point of a graph dge n edge is a segment that connects two vertices. Region region is each individual area or separate piece of the plane that
Chapter 9. Greedy Technique. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Greedy Technique Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Greedy Technique Constructs a solution to an optimization problem piece by piece through a sequence of choices that
Chapter 9 Greedy Technique Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Greedy Technique Constructs a solution to an optimization problem piece by piece through a sequence of choices that
Minimum-Spanning-Tree problem. Minimum Spanning Trees (Forests) Minimum-Spanning-Tree problem
 Minimum Spanning Trees (Forests) Given an undirected graph G=(V,E) with each edge e having a weight w(e) : Find a subgraph T of G of minimum total weight s.t. every pair of vertices connected in G are
Minimum Spanning Trees (Forests) Given an undirected graph G=(V,E) with each edge e having a weight w(e) : Find a subgraph T of G of minimum total weight s.t. every pair of vertices connected in G are
Greedy Algorithms. At each step in the algorithm, one of several choices can be made.
 Greedy Algorithms At each step in the algorithm, one of several choices can be made. Greedy Strategy: make the choice that is the best at the moment. After making a choice, we are left with one subproblem
Greedy Algorithms At each step in the algorithm, one of several choices can be made. Greedy Strategy: make the choice that is the best at the moment. After making a choice, we are left with one subproblem
TCOM 501: Networking Theory & Fundamentals. Lecture 11 April 16, 2003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis
 TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
TOM 50: Networking Theory & undamentals Lecture pril 6, 2003 Prof. Yannis. Korilis 2 Topics Routing in ata Network Graph Representation of a Network Undirected Graphs Spanning Trees and Minimum Weight
Chapter 9: Elementary Graph Algorithms Basic Graph Concepts
 hapter 9: Elementary Graph lgorithms asic Graph oncepts msc 250 Intro to lgorithms graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different situations objects and processes: Linked list Tree (partial
hapter 9: Elementary Graph lgorithms asic Graph oncepts msc 250 Intro to lgorithms graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different situations objects and processes: Linked list Tree (partial
Campus Tour. 1/18/2005 4:08 AM Campus Tour 1
 ampus Tour //00 :0 M ampus Tour Outline and Reading Overview of the assignment Review djacency matrix structure (..) Kruskal s MST algorithm (..) Partition T and implementation (..) The decorator pattern
ampus Tour //00 :0 M ampus Tour Outline and Reading Overview of the assignment Review djacency matrix structure (..) Kruskal s MST algorithm (..) Partition T and implementation (..) The decorator pattern
CAD Algorithms. Shortest Path
 lgorithms Shortest Path lgorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor epartment September 00 Shortest Path Problem: ind the best way of getting from s to t where s and t are vertices in a graph. est: Min (sum of the
lgorithms Shortest Path lgorithms Mohammad Tehranipoor epartment September 00 Shortest Path Problem: ind the best way of getting from s to t where s and t are vertices in a graph. est: Min (sum of the
11/26/17. directed graphs. CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10. undirected graphs
 directed graphs S 220: iscrete Structures and their pplications collection of vertices and directed edges graphs zybooks chapter 10 collection of vertices and edges undirected graphs What can this represent?
directed graphs S 220: iscrete Structures and their pplications collection of vertices and directed edges graphs zybooks chapter 10 collection of vertices and edges undirected graphs What can this represent?
Reading. Graph Introduction. What are graphs? Graphs. Motivation for Graphs. Varieties. Reading. CSE 373 Data Structures Lecture 18
 Reading Graph Introduction Reading Section 9.1 S 373 ata Structures Lecture 18 11/25/02 Graph Introduction - Lecture 18 2 What are graphs? Yes, this is a graph. Graphs Graphs are composed of Nodes (vertices)
Reading Graph Introduction Reading Section 9.1 S 373 ata Structures Lecture 18 11/25/02 Graph Introduction - Lecture 18 2 What are graphs? Yes, this is a graph. Graphs Graphs are composed of Nodes (vertices)
Reading. Graph Terminology. Graphs. What are graphs? Varieties. Motivation for Graphs. Reading. CSE 373 Data Structures. Graphs are composed of.
 Reading Graph Reading Goodrich and Tamassia, hapter 1 S 7 ata Structures What are graphs? Graphs Yes, this is a graph. Graphs are composed of Nodes (vertices) dges (arcs) node ut we are interested in a
Reading Graph Reading Goodrich and Tamassia, hapter 1 S 7 ata Structures What are graphs? Graphs Yes, this is a graph. Graphs are composed of Nodes (vertices) dges (arcs) node ut we are interested in a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Campus Tour Goodrich, Tamassia. Campus Tour 1
 ampus Tour 00 oodrich, Tamassia ampus Tour raph ssignment oals Learn and implement the adjacency matrix structure an Kruskal s minimum spanning tree algorithm Understand and use the decorator pattern and
ampus Tour 00 oodrich, Tamassia ampus Tour raph ssignment oals Learn and implement the adjacency matrix structure an Kruskal s minimum spanning tree algorithm Understand and use the decorator pattern and
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Lesson 22: Basic Graph Concepts
 Lesson 22: asic Graph oncepts msc 175 iscrete Mathematics 1. Introduction graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different relations between objects and processes: Linked list Flowchart of
Lesson 22: asic Graph oncepts msc 175 iscrete Mathematics 1. Introduction graph is a mathematical object that is used to model different relations between objects and processes: Linked list Flowchart of
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Minimum Spanning Tree Kostas Alexis The Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm A telecommunication company wants to connect all the blocks in a new neighborhood. However,
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Minimum Spanning Tree Kostas Alexis The Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm A telecommunication company wants to connect all the blocks in a new neighborhood. However,
What is a minimal spanning tree (MST) and how to find one
 What is a minimal spanning tree (MST) and how to find one A tree contains a root, the top node. Each node has: One parent Any number of children A spanning tree of a graph is a subgraph that contains all
What is a minimal spanning tree (MST) and how to find one A tree contains a root, the top node. Each node has: One parent Any number of children A spanning tree of a graph is a subgraph that contains all
Introduction to Algorithms. Minimum Spanning Tree. Chapter 23: Minimum Spanning Trees
 Introdction to lgorithms oncrete example Imagine: Yo wish to connect all the compters in an office bilding sing the least amont of cable - ach vertex in a graph G represents a compter - ach edge represents
Introdction to lgorithms oncrete example Imagine: Yo wish to connect all the compters in an office bilding sing the least amont of cable - ach vertex in a graph G represents a compter - ach edge represents
CS 5114: Theory of Algorithms. Graph Algorithms. A Tree Proof. Graph Traversals. Clifford A. Shaffer. Spring 2014
 epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
Lecture 4 Greedy algorithms
 dvanced lgorithms loriano Zini ree University of ozen-olzano aculty of omputer Science cademic Year 203-20 Lecture Greedy algorithms hess vs Scrabble In chess the player must think ahead winning strategy
dvanced lgorithms loriano Zini ree University of ozen-olzano aculty of omputer Science cademic Year 203-20 Lecture Greedy algorithms hess vs Scrabble In chess the player must think ahead winning strategy
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 19: Introduction to Graphs. Ruth Anderson Autumn 2018
 SE 332: ata Structures & Parallelism Lecture 19: Introduction to Graphs Ruth nderson utumn 2018 Today Graphs Intro & efinitions 11/19/2018 2 Graphs graph is a formalism for representing relationships among
SE 332: ata Structures & Parallelism Lecture 19: Introduction to Graphs Ruth nderson utumn 2018 Today Graphs Intro & efinitions 11/19/2018 2 Graphs graph is a formalism for representing relationships among
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
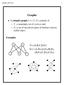 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree. Example
 Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree weighted connected undirected graph spanning tree cost of spanning tree is sum of edge costs find spanning tree that has minimum cost Example 2 4 12 6 3 Network has 10 edges.
Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree weighted connected undirected graph spanning tree cost of spanning tree is sum of edge costs find spanning tree that has minimum cost Example 2 4 12 6 3 Network has 10 edges.
Example. Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree. Edge Selection Greedy Strategies. Edge Selection Greedy Strategies
 Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree weighted connected undirected graph spanning tree cost of spanning tree is sum of edge costs find spanning tree that has minimum cost Example 2 4 12 6 3 Network has 10 edges.
Minimum-Cost Spanning Tree weighted connected undirected graph spanning tree cost of spanning tree is sum of edge costs find spanning tree that has minimum cost Example 2 4 12 6 3 Network has 10 edges.
CSE 332: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture 22: Minimum Spanning Trees. Ruth Anderson Winter 2018
 SE 33: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture : Minimum Spanning Trees Ruth nderson Winter 08 Minimum Spanning Trees iven an undirected graph =(V,E), find a graph =(V, E ) such that: E is a subset of E
SE 33: Data Structures & Parallelism Lecture : Minimum Spanning Trees Ruth nderson Winter 08 Minimum Spanning Trees iven an undirected graph =(V,E), find a graph =(V, E ) such that: E is a subset of E
Introduction to Graphs. common/notes/ppt/
 Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
Outline and Reading. Minimum Spanning Tree. Minimum Spanning Tree. Cycle Property. Minimum Spanning Trees ( 12.7)
 Outline and Reading Minimum Spanning Tree PV 1 1 1 1 JK 1 15 SO 11 1 LX 15 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) efinitions crucial fact Prim-Jarnik s lgorithm ( 1..) Kruskal s lgorithm ( 1..1) 111 // :1 PM Minimum
Outline and Reading Minimum Spanning Tree PV 1 1 1 1 JK 1 15 SO 11 1 LX 15 Minimum Spanning Trees ( 1.) efinitions crucial fact Prim-Jarnik s lgorithm ( 1..) Kruskal s lgorithm ( 1..1) 111 // :1 PM Minimum
Agenda. Graph Representation DFS BFS Dijkstra A* Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp
 Graph Charles Lin genda Graph Representation FS BFS ijkstra * Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp Graph Representation djacency Matrix bool way[100][100];
Graph Charles Lin genda Graph Representation FS BFS ijkstra * Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp Graph Representation djacency Matrix bool way[100][100];
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Lecture 13. Reading: Weiss, Ch. 9, Ch 8 CSE 100, UCSD: LEC 13. Page 1 of 29
 Lecture 13 Connectedness in graphs Spanning trees in graphs Finding a minimal spanning tree Time costs of graph problems and NP-completeness Finding a minimal spanning tree: Prim s and Kruskal s algorithms
Lecture 13 Connectedness in graphs Spanning trees in graphs Finding a minimal spanning tree Time costs of graph problems and NP-completeness Finding a minimal spanning tree: Prim s and Kruskal s algorithms
COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms
 COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Algorithms for MSTs Sections 4.5 (KT) 1 Minimum Spanning Tree Minimum spanning tree. Given a connected graph G = (V, E) with realvalued edge weights c e, an MST is a subset
COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Algorithms for MSTs Sections 4.5 (KT) 1 Minimum Spanning Tree Minimum spanning tree. Given a connected graph G = (V, E) with realvalued edge weights c e, an MST is a subset
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Graphs II. Lecture 27. Prof.
 242 ata Structures and lgorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/242/ Graphs II Lecture 27 Prof. ric Polizzi Summary Previous Lecture omposed of vertices (nodes) and edges vertex or node edges
242 ata Structures and lgorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/242/ Graphs II Lecture 27 Prof. ric Polizzi Summary Previous Lecture omposed of vertices (nodes) and edges vertex or node edges
Week 11: Minimum Spanning trees
 Week 11: Minimum Spanning trees Agenda: Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s Algorithm Reading: Textbook : 61-7 1 Week 11: Minimum Spanning trees Minimum spanning tree (MST) problem: Input: edge-weighted (simple,
Week 11: Minimum Spanning trees Agenda: Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s Algorithm Reading: Textbook : 61-7 1 Week 11: Minimum Spanning trees Minimum spanning tree (MST) problem: Input: edge-weighted (simple,
GRAPH THEORY. What are graphs? Why graphs? Graphs are usually used to represent different elements that are somehow related to each other.
 GRPH THEORY Hadrian ng, Kyle See, March 2017 What are graphs? graph G is a pair G = (V, E) where V is a nonempty set of vertices and E is a set of edges e such that e = {a, b where a and b are vertices.
GRPH THEORY Hadrian ng, Kyle See, March 2017 What are graphs? graph G is a pair G = (V, E) where V is a nonempty set of vertices and E is a set of edges e such that e = {a, b where a and b are vertices.
Data Structures Lecture 14
 Fall 2018 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. ept. Management Information Systems, National hengchi University ata Structures Lecture 14 Graphs efinition, Implementation and Traversal Graphs Formally speaking,
Fall 2018 Fang Yu Software Security Lab. ept. Management Information Systems, National hengchi University ata Structures Lecture 14 Graphs efinition, Implementation and Traversal Graphs Formally speaking,
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS Dijkstra s Algorithm: Questions Initialize the graph: Give all vertices a dist of INFINITY, set all done flags to false Start at s; give s dist = 0 and set prev field to -1 Enqueue
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS Dijkstra s Algorithm: Questions Initialize the graph: Give all vertices a dist of INFINITY, set all done flags to false Start at s; give s dist = 0 and set prev field to -1 Enqueue
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 0 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Weighted Graphs July 0, 07 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 0 July 0, 07 / Weighted Graphs Each edge has a weight (cost) Edge-weighted graphs Mostly we consider only
CS 0 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Weighted Graphs July 0, 07 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 0 July 0, 07 / Weighted Graphs Each edge has a weight (cost) Edge-weighted graphs Mostly we consider only
Minimum Spanning Tree
 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Minimum Spanning Tree Autumn 018 Shrirang (Shri) Mare shri@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Kasey Champion, Ben Jones, Adam Blank, Michael Lee, Evan McCarty, Robbie Weber,
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Minimum Spanning Tree Autumn 018 Shrirang (Shri) Mare shri@cs.washington.edu Thanks to Kasey Champion, Ben Jones, Adam Blank, Michael Lee, Evan McCarty, Robbie Weber,
What are graphs? (Take 1)
 Lecture 22: Let s Get Graphic Graph lgorithms Today s genda: What is a graph? Some graphs that you already know efinitions and Properties Implementing Graphs Topological Sort overed in hapter 9 of the
Lecture 22: Let s Get Graphic Graph lgorithms Today s genda: What is a graph? Some graphs that you already know efinitions and Properties Implementing Graphs Topological Sort overed in hapter 9 of the
CHAPTER 14 GRAPH ALGORITHMS ORD SFO LAX DFW
 SO OR HPTR 1 GRPH LGORITHMS LX W KNOWLGMNT: THS SLIS R PT ROM SLIS PROVI WITH T STRUTURS N LGORITHMS IN JV, GOORIH, TMSSI N GOLWSSR (WILY 16) 6 OS MINIMUM SPNNING TRS SO 16 PV OR 1 1 16 61 JK 1 1 11 WI
SO OR HPTR 1 GRPH LGORITHMS LX W KNOWLGMNT: THS SLIS R PT ROM SLIS PROVI WITH T STRUTURS N LGORITHMS IN JV, GOORIH, TMSSI N GOLWSSR (WILY 16) 6 OS MINIMUM SPNNING TRS SO 16 PV OR 1 1 16 61 JK 1 1 11 WI
Decreasing a key FIB-HEAP-DECREASE-KEY(,, ) 3.. NIL. 2. error new key is greater than current key 6. CASCADING-CUT(, )
 Decreasing a key FIB-HEAP-DECREASE-KEY(,, ) 1. if >. 2. error new key is greater than current key 3.. 4.. 5. if NIL and.
Decreasing a key FIB-HEAP-DECREASE-KEY(,, ) 1. if >. 2. error new key is greater than current key 3.. 4.. 5. if NIL and.
Greedy Approach: Intro
 Greedy Approach: Intro Applies to optimization problems only Problem solving consists of a series of actions/steps Each action must be 1. Feasible 2. Locally optimal 3. Irrevocable Motivation: If always
Greedy Approach: Intro Applies to optimization problems only Problem solving consists of a series of actions/steps Each action must be 1. Feasible 2. Locally optimal 3. Irrevocable Motivation: If always
Tree. number of vertices. Connected Graph. CSE 680 Prof. Roger Crawfis
 Tree Introduction to lgorithms Spanning Trees CSE Prof. Roger Crawfis We call an undirected graph a tree if the graph is connected and contains no cycles. Trees: Not Trees: Not connected Has a cycle Number
Tree Introduction to lgorithms Spanning Trees CSE Prof. Roger Crawfis We call an undirected graph a tree if the graph is connected and contains no cycles. Trees: Not Trees: Not connected Has a cycle Number
CSE 21: Mathematics for Algorithms and Systems Analysis
 CSE 21: Mathematics for Algorithms and Systems Analysis Week 10 Discussion David Lisuk June 4, 2014 David Lisuk CSE 21: Mathematics for Algorithms and Systems Analysis June 4, 2014 1 / 26 Agenda 1 Announcements
CSE 21: Mathematics for Algorithms and Systems Analysis Week 10 Discussion David Lisuk June 4, 2014 David Lisuk CSE 21: Mathematics for Algorithms and Systems Analysis June 4, 2014 1 / 26 Agenda 1 Announcements
An Early Problem in Graph Theory. Clicker Question 1. Konigsberg and the River Pregel
 raphs Topic " Hopefully, you've played around a bit with The Oracle of acon at Virginia and discovered how few steps are necessary to link just about anybody who has ever been in a movie to Kevin acon,
raphs Topic " Hopefully, you've played around a bit with The Oracle of acon at Virginia and discovered how few steps are necessary to link just about anybody who has ever been in a movie to Kevin acon,
Graphs and Network Flows ISE 411. Lecture 7. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Graphs and Network Flows ISE 411 Lecture 7 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 411 Lecture 7 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Chapter 20 References AMO Chapter 13 CLRS Chapter 23 ISE 411 Lecture 7 2 Minimum
Graphs and Network Flows ISE 411 Lecture 7 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 411 Lecture 7 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Chapter 20 References AMO Chapter 13 CLRS Chapter 23 ISE 411 Lecture 7 2 Minimum
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS GREEDY METHOD
 1 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT II Objectives GREEDY METHOD Explain and detail about greedy method Explain the concept of knapsack problem and solve the problems in knapsack Discuss the applications
1 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT II Objectives GREEDY METHOD Explain and detail about greedy method Explain the concept of knapsack problem and solve the problems in knapsack Discuss the applications
Eulerian Cycle (2A) Young Won Lim 5/11/18
 ulerian ycle (2) opyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the NU ree ocumentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
ulerian ycle (2) opyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the NU ree ocumentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Shortest Paths and Minimum Spanning Trees
 /9/ hortest Paths and Minimum panning Trees dmin avid Kauchak cs0 pring 0 ijkstra s algorithm What about ijkstra s on? 0-0 /9/ What about ijkstra s on? ijkstra s algorithm only works for positive edge
/9/ hortest Paths and Minimum panning Trees dmin avid Kauchak cs0 pring 0 ijkstra s algorithm What about ijkstra s on? 0-0 /9/ What about ijkstra s on? ijkstra s algorithm only works for positive edge
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees Overview Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads. A road connects and only houses. A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: Repair enough (and
Minimum Spanning Trees Overview Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads. A road connects and only houses. A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: Repair enough (and
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Graphs - I CS 2110, Spring 2016
 Graphs - I CS 2110, Spring 2016 Announcements Reading: Chapter 28: Graphs Chapter 29: Graph Implementations These aren t the graphs we re interested in These aren t the graphs we re interested in This
Graphs - I CS 2110, Spring 2016 Announcements Reading: Chapter 28: Graphs Chapter 29: Graph Implementations These aren t the graphs we re interested in These aren t the graphs we re interested in This
Minimum Spanning Trees My T. UF
 Introduction to Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees @ UF Problem Find a low cost network connecting a set of locations Any pair of locations are connected There is no cycle Some applications: Communication
Introduction to Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees @ UF Problem Find a low cost network connecting a set of locations Any pair of locations are connected There is no cycle Some applications: Communication
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
Applications of BFS and DFS
 pplications of S and S S all // : PM Some pplications of S and S S o find the shortest path from a vertex s to a vertex v in an unweighted graph o find the length of such a path o construct a S tree/forest
pplications of S and S S all // : PM Some pplications of S and S S o find the shortest path from a vertex s to a vertex v in an unweighted graph o find the length of such a path o construct a S tree/forest
CS 5114: Theory of Algorithms. Graph Algorithms. A Tree Proof. Graph Traversals. Clifford A. Shaffer. Spring 2014
 epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
epartment of omputer Science Virginia Tech lacksburg, Virginia opyright c 04 by lifford. Shaffer : Theory of lgorithms Title page : Theory of lgorithms lifford. Shaffer Spring 04 lifford. Shaffer epartment
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees 0 OS SO LX PV OR 0 JK 0 WI 00 W MI 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
Minimum Spanning Trees 0 OS SO LX PV OR 0 JK 0 WI 00 W MI 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Spanning subgraph Subgraph of a graph G containing all the vertices of G Spanning
Chapter 23. Minimum Spanning Trees
 Chapter 23. Minimum Spanning Trees We are given a connected, weighted, undirected graph G = (V,E;w), where each edge (u,v) E has a non-negative weight (often called length) w(u,v). The Minimum Spanning
Chapter 23. Minimum Spanning Trees We are given a connected, weighted, undirected graph G = (V,E;w), where each edge (u,v) E has a non-negative weight (often called length) w(u,v). The Minimum Spanning
Homework 5: Graphs, Minimum Spanning Trees, and Dijkstra Shortest-Path
 Homework 5: Graphs, Minimum Spanning Trees, and Dijkstra Shortest-Path 1. (4 points) A graph is Hamiltonian if there is a cycle in the graph visiting each vertex exactly once. Give an example of an Eulerian
Homework 5: Graphs, Minimum Spanning Trees, and Dijkstra Shortest-Path 1. (4 points) A graph is Hamiltonian if there is a cycle in the graph visiting each vertex exactly once. Give an example of an Eulerian
Digraphs ( 12.4) Directed Graphs. Digraph Application. Digraph Properties. A digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed.
 igraphs ( 12.4) irected Graphs OR OS digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed Short for directed graph pplications one- way streets flights task scheduling irected Graphs 1 irected Graphs 2 igraph
igraphs ( 12.4) irected Graphs OR OS digraph is a graph whose edges are all directed Short for directed graph pplications one- way streets flights task scheduling irected Graphs 1 irected Graphs 2 igraph
Info 2950, Lecture 16
 Info 2950, Lecture 16 28 Mar 2017 Prob Set 5: due Fri night 31 Mar Breadth first search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) Must have an ordering on the vertices of the graph. In most examples here, the
Info 2950, Lecture 16 28 Mar 2017 Prob Set 5: due Fri night 31 Mar Breadth first search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) Must have an ordering on the vertices of the graph. In most examples here, the
Minimum spanning trees
 Minimum spanning trees [We re following the book very closely.] One of the most famous greedy algorithms (actually rather family of greedy algorithms). Given undirected graph G = (V, E), connected Weight
Minimum spanning trees [We re following the book very closely.] One of the most famous greedy algorithms (actually rather family of greedy algorithms). Given undirected graph G = (V, E), connected Weight
Graph ADT. Lecture18: Graph II. Adjacency Matrix. Representation of Graphs. Data Vertices and edges. Methods
 Graph T S33: ata Structures (0) Lecture8: Graph II ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr ata Vertices and edges endvertices(e): an array of the two endvertices of e opposite(v,e): the vertex opposite
Graph T S33: ata Structures (0) Lecture8: Graph II ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr ata Vertices and edges endvertices(e): an array of the two endvertices of e opposite(v,e): the vertex opposite
looking ahead to see the optimum
 ! Make choice based on immediate rewards rather than looking ahead to see the optimum! In many cases this is effective as the look ahead variation can require exponential time as the number of possible
! Make choice based on immediate rewards rather than looking ahead to see the optimum! In many cases this is effective as the look ahead variation can require exponential time as the number of possible
Minimum Spanning Tree
 Minimum Spanning Tree 1 Minimum Spanning Tree G=(V,E) is an undirected graph, where V is a set of nodes and E is a set of possible interconnections between pairs of nodes. For each edge (u,v) in E, we
Minimum Spanning Tree 1 Minimum Spanning Tree G=(V,E) is an undirected graph, where V is a set of nodes and E is a set of possible interconnections between pairs of nodes. For each edge (u,v) in E, we
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
Minimum Spanning Tree (5A) Young Won Lim 5/11/18
 Minimum Spanning Tree (5A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Minimum Spanning Tree (5A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Graphs: Connectivity. A graph. Transportation systems. Social networks
 graph raphs: onnectivity ordi ortadella and ordi Petit epartment of omputer Science Source: Wikipedia The network graph formed by Wikipedia editors (edges) contributing to different Wikipedia language
graph raphs: onnectivity ordi ortadella and ordi Petit epartment of omputer Science Source: Wikipedia The network graph formed by Wikipedia editors (edges) contributing to different Wikipedia language
Problem Score Maximum MC 34 (25/17) = 50 Total 100
 Stony Brook University Midterm 2 CSE 373 Analysis of Algorithms November 22, 2016 Midterm Exam Name: ID #: Signature: Circle one: GRAD / UNDERGRAD INSTRUCTIONS: This is a closed book, closed mouth exam.
Stony Brook University Midterm 2 CSE 373 Analysis of Algorithms November 22, 2016 Midterm Exam Name: ID #: Signature: Circle one: GRAD / UNDERGRAD INSTRUCTIONS: This is a closed book, closed mouth exam.
The minimum spanning tree problem
 The minimum spanning tree problem MST is a minimum cost connection problem on graphs The graph can model the connection in a (hydraulic, electric, telecommunication) network: the nodes are the points that
The minimum spanning tree problem MST is a minimum cost connection problem on graphs The graph can model the connection in a (hydraulic, electric, telecommunication) network: the nodes are the points that
Announcements Problem Set 5 is out (today)!
 CSC263 Week 10 Announcements Problem Set is out (today)! Due Tuesday (Dec 1) Minimum Spanning Trees The Graph of interest today A connected undirected weighted graph G = (V, E) with weights w(e) for each
CSC263 Week 10 Announcements Problem Set is out (today)! Due Tuesday (Dec 1) Minimum Spanning Trees The Graph of interest today A connected undirected weighted graph G = (V, E) with weights w(e) for each
tree follows. Game Trees
 CPSC-320: Intermediate Algorithm Design and Analysis 113 On a graph that is simply a linear list, or a graph consisting of a root node v that is connected to all other nodes, but such that no other edges
CPSC-320: Intermediate Algorithm Design and Analysis 113 On a graph that is simply a linear list, or a graph consisting of a root node v that is connected to all other nodes, but such that no other edges
Understand graph terminology Implement graphs using
 raphs Understand graph terminology Implement graphs using djacency lists and djacency matrices Perform graph searches Depth first search Breadth first search Perform shortest-path algorithms Disjkstra
raphs Understand graph terminology Implement graphs using djacency lists and djacency matrices Perform graph searches Depth first search Breadth first search Perform shortest-path algorithms Disjkstra
22 Elementary Graph Algorithms. There are two standard ways to represent a
 VI Graph Algorithms Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees Single-Source Shortest Paths All-Pairs Shortest Paths 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms There are two standard ways to represent a graph
VI Graph Algorithms Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees Single-Source Shortest Paths All-Pairs Shortest Paths 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms There are two standard ways to represent a graph
22 Elementary Graph Algorithms. There are two standard ways to represent a
 VI Graph Algorithms Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees Single-Source Shortest Paths All-Pairs Shortest Paths 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms There are two standard ways to represent a graph
VI Graph Algorithms Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees Single-Source Shortest Paths All-Pairs Shortest Paths 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms There are two standard ways to represent a graph
Data Organization: Creating Order Out Of Chaos
 ata Organization: reating Order Out Of haos 3 Non-linear data structures 5-5 Principles of omputation, arnegie Mellon University - ORTIN Trees tree is a hierarchical (usually non-linear) data structure.
ata Organization: reating Order Out Of haos 3 Non-linear data structures 5-5 Principles of omputation, arnegie Mellon University - ORTIN Trees tree is a hierarchical (usually non-linear) data structure.
Minimum Spanning Trees
 CSMPS 2200 Fall Minimum Spanning Trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes and additions by Carola Wenk 11/6/ CMPS 2200 Intro. to Algorithms 1 Minimum spanning trees Input: A
CSMPS 2200 Fall Minimum Spanning Trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes and additions by Carola Wenk 11/6/ CMPS 2200 Intro. to Algorithms 1 Minimum spanning trees Input: A
Minimum Spanning Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Minimum Spanning Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Reading Chapter 3 Section 3.7 MSTs 2 Spanning Tree Given (connected) G(V,E) a spanning tree T(V,E ): Spans the graph (V = V) Forms a tree (no cycle); E has
Minimum Spanning Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Reading Chapter 3 Section 3.7 MSTs 2 Spanning Tree Given (connected) G(V,E) a spanning tree T(V,E ): Spans the graph (V = V) Forms a tree (no cycle); E has
Lecture 25 Notes Spanning Trees
 Lecture 25 Notes Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices
Lecture 25 Notes Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices
Parallel Graph Algorithms
 Parallel Graph Algorithms Design and Analysis of Parallel Algorithms 5DV050 Spring 202 Part I Introduction Overview Graphsdenitions, properties, representation Minimal spanning tree Prim's algorithm Shortest
Parallel Graph Algorithms Design and Analysis of Parallel Algorithms 5DV050 Spring 202 Part I Introduction Overview Graphsdenitions, properties, representation Minimal spanning tree Prim's algorithm Shortest
Multicast routing principles in Internet
 Multicast routing principles in Internet Motivation Recap on graphs Principles and algortihms Multicast1-1 Multicast capability has been and is under intensive development since the 1990 s Mone used to
Multicast routing principles in Internet Motivation Recap on graphs Principles and algortihms Multicast1-1 Multicast capability has been and is under intensive development since the 1990 s Mone used to
An Early Problem in Graph Theory
 raphs Topic 2 " Hopefully, you've played around a bit with The Oracle of acon at Virginia and discovered how few steps are necessary to link just about anybody who has ever been in a movie to Kevin acon,
raphs Topic 2 " Hopefully, you've played around a bit with The Oracle of acon at Virginia and discovered how few steps are necessary to link just about anybody who has ever been in a movie to Kevin acon,
Eulerian Cycle (2A) Young Won Lim 5/25/18
 ulerian ycle (2) opyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU ree ocumentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
ulerian ycle (2) opyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU ree ocumentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
