Formal Support for Model Evolution
|
|
|
- Marilynn Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Formal Support for Model Evolution Tom Mens Software Engineering Lab University of Mons-Hainaut Belgium
2 Introduction - Model Evolution More and better tool support needed for model evolution Formalisms can be helpful for some of these tools Description logics Graph transformation Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 2
3 Model Inconsistency Management Using Description Logics joint work with Ragnhild Van Der Straeten Vrije Universiteit Brussel
4 Model Inconsistency Management Model consistency ensuring that all models/software artifacts are consistent internal consistency of each model mutual consistency between different models consistency maintenance is essential especially in the context of co-evolution where different models may evolve in parallel examples evolution of class diagrams, sequence diagrams and state diagrams evolution of design models and source code Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 4
5 Model Transformation Dimensions Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 5
6 Classification of Inconsistencies Specification specification conflicts Specification - instance conflicts Instance - instance conflicts Behavioural Invocation inconsistency Observation inconsistency Incompatible definition Invocation inconsistency Observation inconsistency Incompatible behaviour inconsistency Structural Dangling type reference Inherited association inconsistency Role specification missing Instance specification missing Disconnected model Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 6
7 Description Logics Decidable two-variable fragment of first-order predicate logics Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 7
8 Description Logics: TBox and ABox Terminological Knowledge (TBox) TBox reasoning Concept satisfiability Concept subsumption mechanism ABox Assertions a : C (a, b) : R ABox reasoning ABox satisfiability instantiation testing Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 8
9 DL versus FOL (1) [ESSLI02] Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 9
10 DL versus FOL (2) [ESSLI02] Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 10
11 Metamodel translation Direct correspondence of UML metamodel and DL concepts classes concepts associations roles attributes roles ore concrete domain attributes (primitive types) inheritance subsumption and transitive closure Manual translation of UML metamodel (define-primitive-role allattribute :domain classifier :range property :inverse owningclassifier :parent featuremembers) (implies-role redefinedattribute redefinitioncontext) (define-primitive-role ownedattribute :domain class :range property :inverse owningclass :parents(ownedmember allattribute)) (implies-role owningclass redefinedattribute) (implies property (and structuralfeature (some definedtype (or class primitivetype)))) (define-primitive-role ownedoperation :domain class :range operation :inverse ownedclass :parents(featuremembers ownedmember)) Automatic translation of UML models Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 11
12 Model translation Automatic translation of UML models Class diagrams (instance atm class) (instance printingatm class) (instance asciiprintingatm class) (instance gen1 generalization) (instance gen2 generalization) (instance controls association) (instance atmend property) (instance asciiend property) (related atm gen1 generalization) (related printingatm gen1 generalization) (related printingatm gen2 generalization) (related asciiprintingatm gen2 generalization) (related atm printingatm direct-superclass) (related printingatm asciiprintingatm direct-superclass) (related gen1 atm general) (related gen2 printingatm general) (related atm asciiend ownedattribute) Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 12
13 Model translation Automatic translation of UML models Sequence diagrams (define-concept m1 (and (all op checkifcashavailable) (exactly 1 op))) (define-concept m2 (and (all op ejectcard) (exactly 1 op)))) (define-concept m3 (and (all op dispensecash) (exactly 1 op))) (implies m1 (some r m2)) (implies m2 (some r m3)) (implies m3 (some r m4)) Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 13
14 Model translation Automatic translation of UML models State-transition diagrams (define-concept t1 (and (all op verifyaccount) (exactly 1 op))) (define-concept t2 (and (all op checkifcashavailable) (exactly 1 op))) (define-concept t3 (and (all op dispensecash) (exactly 1 op))) (define-concept t4 (and (all op ejectcard) (exactly 1 op))) (equivalent (and (some valid_pin) t1) (some r t2))) (equivalent t2 (some r t3)) (equivalent t3 (some r t4)) Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 14
15 Model Inconsistency Management Internal consistency of ATM 1.0 Refinement consistency between ATM 1.0 and its subclass CardChargingATM 1.1 Behavioural preservation between CardChargingATM versions 1.2 and 1.3 Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 15
16 Exemple Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 16
17 Model Inconsistency Management Internal consistency of ATM 1.0 class each sequence of the ATM sequence diagram is contained in the set of call sequences of the ATM state machine diagram Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 17
18 Model Inconsistency Management Internal consistency of ATM 1.0 class each sequence of the ATM sequence diagram is contained in the set of call sequences of the ATM state machine diagram Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 18
19 Model Inconsistency Management Refinement consistency behavioural consistency between class ATM 1.0 and its subclass CardChargingATM 1.1 each sequence of the ATM 1.0 sequence diagram should be contained in the set of sequences of the CardChargingATM 1.1 state machine diagram Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 19
20 Model Inconsistency Management Refinement consistency [Ebert&Engels 1997] Observation inheritance consistency each sequence of calls which is observable with respect to a subclass must result (under the projection of the methods known) in an observable sequence of its corresponding superclass. Invocation inheritance consistency any sequence of operations invocable on the superclass can also be invoked on the subclass. Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 20
21 Model Inconsistency Management Evolution consistency Refactoring of CardChargingATM version 1.2 to 1.3 should preserve behaviour Observation call preservation each sequence of calls which is observable with respect to a refactored class must result (under the projection of the methods known) in an observable sequence of its original class. Invocation call preservation any sequence of operations invocable on the original class can also be invoked on the refactored class. Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 21
22 Model Inconsistency Management Evolution consistency Refactoring state machine of CardChargingATM version 1.2 to CardChargingATM version 1.3 should preserve behaviour Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 22
23 Model Inconsistency Management Evolution consistency Refactoring state machine of CardChargingATM version 1.2 to CardChargingATM version 1.3 should preserve behaviour Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 23
24 Model Inconsistency Management Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 24
25 Model Refactoring Using Graph Transformation joint work with Gabi Taentzer Technical University of Berlin
26 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Graph transformation theory offers many theoretical results that can help during analysis of model refactorings type graph, negative application conditions, parallel and sequential (in)dependence, confluence and critical pair analysis Graph transformation tools allow us to perform concrete experiments AGG (in collaboration with Berlin) Current focus Analysing dependencies between class diagram refactorings Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 26
27 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Concrete Scenario: Suggest refactoring opportunities What are the alternatives of a selected refactoring? Which other refactorings need to be applied first in order to make the selected refactoring applicable? Which other refactorings are still applicable after applying the selected refactoring? Goal: Automate the detection of mutual exclusion relationships between refactorings sequential dependencies between refactorings Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 27
28 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Example Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 28
29 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Refactoring opportunities T1 Rename Method print in PrintServer to process T2 Rename Method save in FileServer to process T3 Create Superclass Server for PrintServer and FileServer T4 Pull Up Method accept from PrintServer and FileServer to Server T5 Move Method accept from PrintServer to Packet T6 Move Method accept from FileServer to Packet T7 Encapsulate Variable receiver in Packet T8 Add Parameter p of type Packet to method print in PrintServer T9 Add Parameter p of type Packet to method save in FileServer Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 29
30 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 T1 >> T2 >> T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 T9 Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 30
31 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Approach: Use critical pair analysis in AGG T 1 and T 2 form a critical pair if they can both be applied to the same initial graph G but applying T 1 prohibits application of T 2 and/or vice versa T 1 G H 1 T 2 X T 2 H 2 T 1 X Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 31
32 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Step 1: Express object-oriented metamodel as (attributed) type graph Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 32
33 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Step 2: Express refactorings as (typed attributed) graph transformations Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 33
34 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Step 3: Detect critical pairs between refactoring transformations Potential conflicts between refactorings Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 34
35 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Step 4: Fine-tune critical pairs in context of concrete input graph Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 35
36 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 36
37 Model Refactoring with Graph transformation Step 5: Perform sequential dependency analysis To identify dependencies between refactorings that are applicable Tom Mens, 18/4/2005, Dagstuhl, Transformation Techniques in Software Engineering 37
Formal tool support for software evolution
 Service de Génie Logiciel Formal tool support for software evolution Tom Mens staff.umh.ac.be/mens.tom/ www.umh.ac.be/~genlog Université de Mons-Hainaut Problem statement More and better tool support needed
Service de Génie Logiciel Formal tool support for software evolution Tom Mens staff.umh.ac.be/mens.tom/ www.umh.ac.be/~genlog Université de Mons-Hainaut Problem statement More and better tool support needed
2nd Belgian-Dutch workshop on Software Evolution
 2nd Belgian-Dutch workshop on Software Evolution BENEVOL 2004 8-9 July 2004 University of Antwerp Belgium Problem statement More and better tool support needed for software evolution traceability management
2nd Belgian-Dutch workshop on Software Evolution BENEVOL 2004 8-9 July 2004 University of Antwerp Belgium Problem statement More and better tool support needed for software evolution traceability management
Detecting Structural Refactoring Conflicts Using Critical Pair Analysis
 SETra 2004 Preliminary Version Detecting Structural Refactoring Conflicts Using Critical Pair Analysis Tom Mens 1 Software Engineering Lab Université de Mons-Hainaut B-7000 Mons, Belgium Gabriele Taentzer
SETra 2004 Preliminary Version Detecting Structural Refactoring Conflicts Using Critical Pair Analysis Tom Mens 1 Software Engineering Lab Université de Mons-Hainaut B-7000 Mons, Belgium Gabriele Taentzer
A Formal Approach to Model Refactoring and Model Refinement
 Software and Systems Modeling manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) A Formal Approach to Model Refactoring and Model Refinement Ragnhild Van Der Straeten, Viviane Jonckers, Tom Mens 2 System
Software and Systems Modeling manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) A Formal Approach to Model Refactoring and Model Refinement Ragnhild Van Der Straeten, Viviane Jonckers, Tom Mens 2 System
A formal approach to model refactoring and model refinement
 Softw Syst Model DOI 101007/s10270-006-0025-9 SPECIAL ISSUE PAPER A formal approach to model refactoring and model refinement Ragnhild Van Der Straeten Viviane Jonckers Tom Mens Received: 4 February 2005
Softw Syst Model DOI 101007/s10270-006-0025-9 SPECIAL ISSUE PAPER A formal approach to model refactoring and model refinement Ragnhild Van Der Straeten Viviane Jonckers Tom Mens Received: 4 February 2005
Detecting and Resolving Model Inconsistencies Using Transformation Dependency Analysis
 Detecting and Resolving Model Inconsistencies Using Transformation Dependency Analysis Tom Mens 1, Ragnhild Van Der Straeten 2, and Maja D Hondt 3 1 Software Engineering Lab, Université de Mons-Hainaut
Detecting and Resolving Model Inconsistencies Using Transformation Dependency Analysis Tom Mens 1, Ragnhild Van Der Straeten 2, and Maja D Hondt 3 1 Software Engineering Lab, Université de Mons-Hainaut
Towards using OWL DL as a metamodelling framework for ATL
 Towards using OWL DL as a metamodelling framework for ATL Dennis Wagelaar Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussels, Belgium dennis.wagelaar@vub.ac.be Abstract. Ontologies have become increasingly
Towards using OWL DL as a metamodelling framework for ATL Dennis Wagelaar Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussels, Belgium dennis.wagelaar@vub.ac.be Abstract. Ontologies have become increasingly
Inconsistency Detection between UML Models Using RACER and nrql
 Inconsistency Detection between UML Models Using RACER and nrql Ragnhild Van Der Straeten SSEL, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, Brussels, Belgium rvdstrae@vub.ac.be Abstract An object-oriented
Inconsistency Detection between UML Models Using RACER and nrql Ragnhild Van Der Straeten SSEL, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlaan 2, Brussels, Belgium rvdstrae@vub.ac.be Abstract An object-oriented
Features and Feature Interactions in Software Engineering using Logic
 Features and Feature Interactions in Software Engineering using Logic Ragnhild Van Der Straeten rvdstrae@vub.ac.be System and Software Engineering Lab Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Belgium Johan Brichau
Features and Feature Interactions in Software Engineering using Logic Ragnhild Van Der Straeten rvdstrae@vub.ac.be System and Software Engineering Lab Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Belgium Johan Brichau
Chapter 7. Modular Refactoring. 7.1 Introduction to Modular Refactoring
 Chapter 7 Modular Refactoring I n this chapter, the role of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams and Object Constraint Language (OCL) expressions in modular refactoring have been explained. It has
Chapter 7 Modular Refactoring I n this chapter, the role of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams and Object Constraint Language (OCL) expressions in modular refactoring have been explained. It has
Inductively Generated Pointcuts to Support Refactoring to Aspects
 Inductively Generated Pointcuts to Support Refactoring to Aspects Tom Tourwé Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica P.O. Box 94079, NL-1090 GB Amsterdam The Netherlands Email: tom.tourwe@cwi.nl Andy Kellens
Inductively Generated Pointcuts to Support Refactoring to Aspects Tom Tourwé Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica P.O. Box 94079, NL-1090 GB Amsterdam The Netherlands Email: tom.tourwe@cwi.nl Andy Kellens
Graph-Transformation Based Support for Model Evolution
 Graph-Transformation Based Support for Model Evolution Tom Mens 1 Software Engineering Lab, Université de Mons-Hainaut Av. du champ de Mars 6, 7000 Mons, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be Abstract. During model-driven
Graph-Transformation Based Support for Model Evolution Tom Mens 1 Software Engineering Lab, Université de Mons-Hainaut Av. du champ de Mars 6, 7000 Mons, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be Abstract. During model-driven
Conformance Relations between Business Processes
 Conformance Relations between usiness Processes Ragnhild Van Der Straeten System and Software Engineering Lab Vrije Universiteit russel Pleinlaan 2, 1050 russel, elgium rvdstrae@vub.ac.be bstract. This
Conformance Relations between usiness Processes Ragnhild Van Der Straeten System and Software Engineering Lab Vrije Universiteit russel Pleinlaan 2, 1050 russel, elgium rvdstrae@vub.ac.be bstract. This
Reuse Contracts: Managing the Evolution of Reusable Assets
 VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT BRUSSEL Vrije Universiteit Brussel Faculteit Wetenschappen SCI EN T I A V INCERE T ENE BRA S Reuse Contracts: Managing the Evolution of Reusable Assets Patrick Steyaert, Carine Lucas,
VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT BRUSSEL Vrije Universiteit Brussel Faculteit Wetenschappen SCI EN T I A V INCERE T ENE BRA S Reuse Contracts: Managing the Evolution of Reusable Assets Patrick Steyaert, Carine Lucas,
Representing Product Designs Using a Description Graph Extension to OWL 2
 Representing Product Designs Using a Description Graph Extension to OWL 2 Henson Graves Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company Fort Worth Texas, USA henson.graves@lmco.com Abstract. Product development requires
Representing Product Designs Using a Description Graph Extension to OWL 2 Henson Graves Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company Fort Worth Texas, USA henson.graves@lmco.com Abstract. Product development requires
On the Use of Graph Transformations for Model Refactoring
 On the Use of Graph Transformations for Model Refactoring Tom Mens Service de Génie Logiciel Université de Mons-Hainaut, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be http://w3.umh.ac.be/genlog Abstract. Model-driven software
On the Use of Graph Transformations for Model Refactoring Tom Mens Service de Génie Logiciel Université de Mons-Hainaut, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be http://w3.umh.ac.be/genlog Abstract. Model-driven software
Challenges in Model Refactoring
 Challenges in Model Refactoring Tom Mens, University of Mons-Hainaut, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be Gabriele Taentzer, Dirk Müller, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Germany {taentzer,dmueller}@mathematik.uni-marburg.de
Challenges in Model Refactoring Tom Mens, University of Mons-Hainaut, Belgium tom.mens@umh.ac.be Gabriele Taentzer, Dirk Müller, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Germany {taentzer,dmueller}@mathematik.uni-marburg.de
Using Graph Rewriting Models for Object-Oriented Oriented Software Evolution
 Using Graph Rewriting Models for Object-Oriented Oriented Software volution om Mens tom.mens@vub.ac.be rogramming echnology ab epartment of Computer Science Vrije Universiteit Brussel Object-oriented software
Using Graph Rewriting Models for Object-Oriented Oriented Software volution om Mens tom.mens@vub.ac.be rogramming echnology ab epartment of Computer Science Vrije Universiteit Brussel Object-oriented software
A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conflicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modifications
 A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conflicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modifications Hartmut Ehrig 1, Claudia Ermel 1 and Gabriele Taentzer 2 1 Technische Universität Berlin, Germany
A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conflicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modifications Hartmut Ehrig 1, Claudia Ermel 1 and Gabriele Taentzer 2 1 Technische Universität Berlin, Germany
Inheritance (Chapter 7)
 Inheritance (Chapter 7) Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Pree Department of Computer Science University of Salzburg cs.uni-salzburg.at Inheritance the soup of the day?! Inheritance combines three aspects: inheritance
Inheritance (Chapter 7) Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Pree Department of Computer Science University of Salzburg cs.uni-salzburg.at Inheritance the soup of the day?! Inheritance combines three aspects: inheritance
Motivation: Model-driven. driven Engineering. Semantics of Model Transformation. Reiko Heckel University of Leicester, UK
 Semantics of Model Transformation Reiko Heckel University of Leicester, UK, University of Birmingham, 1 March 2007 Motivation: Model-driven driven Engineering Focus and primary artifacts are models instead
Semantics of Model Transformation Reiko Heckel University of Leicester, UK, University of Birmingham, 1 March 2007 Motivation: Model-driven driven Engineering Focus and primary artifacts are models instead
SERG. An Extensive Catalog of Operators for the Coupled Evolution of Metamodels and Models
 Delft University of Technology Software Engineering Research Group Technical Report Series An Extensive Catalog of Operators for the Coupled Evolution of Metamodels and Models Markus Herrmannsdoerfer,
Delft University of Technology Software Engineering Research Group Technical Report Series An Extensive Catalog of Operators for the Coupled Evolution of Metamodels and Models Markus Herrmannsdoerfer,
Forschungsberichte der Fakultät IV Elektrotechnik und Informatik
 Forschungsberichte der Fakultät IV Elektrotechnik und Informatik A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modications Hartmut Ehrig 1 Claudia Ermel 1 Gabriele
Forschungsberichte der Fakultät IV Elektrotechnik und Informatik A Formal Resolution Strategy for Operation-Based Conicts in Model Versioning Using Graph Modications Hartmut Ehrig 1 Claudia Ermel 1 Gabriele
Consistency-Preserving Edit Scripts in Model Versioning
 Consistency-Preserving Edit Scripts in Model Versioning Technical Report 2013-11-12 Timo Kehrer, Udo Kelter Department Elektrotechnik und Informatik Universität Siegen, Germany Gabriele Taentzer Fachbereich
Consistency-Preserving Edit Scripts in Model Versioning Technical Report 2013-11-12 Timo Kehrer, Udo Kelter Department Elektrotechnik und Informatik Universität Siegen, Germany Gabriele Taentzer Fachbereich
Chapter 8: Enhanced ER Model
 Chapter 8: Enhanced ER Model Subclasses, Superclasses, and Inheritance Specialization and Generalization Constraints and Characteristics of Specialization and Generalization Hierarchies Modeling of UNION
Chapter 8: Enhanced ER Model Subclasses, Superclasses, and Inheritance Specialization and Generalization Constraints and Characteristics of Specialization and Generalization Hierarchies Modeling of UNION
Case study: Class diagram restructuring
 Case study: Class diagram restructuring K. Lano, S. Kolahdouz-Rahimi Dept. of Informatics, King s College London, Strand, London, UK This case study is an update-in-place refactoring transformation on
Case study: Class diagram restructuring K. Lano, S. Kolahdouz-Rahimi Dept. of Informatics, King s College London, Strand, London, UK This case study is an update-in-place refactoring transformation on
A Taxonomy of Model Transformation
 Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 152 (2006) 125 142 www.elsevier.com/locate/entcs A Taxonomy of Model Transformation Tom Mens 1 Software Engineering Lab Université de Mons-Hainaut Mons,
Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 152 (2006) 125 142 www.elsevier.com/locate/entcs A Taxonomy of Model Transformation Tom Mens 1 Software Engineering Lab Université de Mons-Hainaut Mons,
Reuse Contracts As Component Interface. Descriptions. Koen De Hondt, Carine Lucas, and Patrick Steyaert. Programming Technology Lab
 Reuse Contracts As Component Interface Descriptions Koen De Hondt, Carine Lucas, and Patrick Steyaert Programming Technology Lab Computer Science Department Vrije Universiteit Brussel Pleinlaan 2, B-1050
Reuse Contracts As Component Interface Descriptions Koen De Hondt, Carine Lucas, and Patrick Steyaert Programming Technology Lab Computer Science Department Vrije Universiteit Brussel Pleinlaan 2, B-1050
Rekayasa Perangkat Lunak 2 (IN043): Pertemuan 6. Moving on to Design
 Rekayasa Perangkat Lunak 2 (IN043): Pertemuan 6 Moving on to Design Analysis versus Design The purpose of analysis is to figure out what the business needs are. To achieve this, the analysis activities
Rekayasa Perangkat Lunak 2 (IN043): Pertemuan 6 Moving on to Design Analysis versus Design The purpose of analysis is to figure out what the business needs are. To achieve this, the analysis activities
Implementing evolution: Refactoring
 2IS55 Software Evolution Sources Implementing evolution: Refactoring Alexander Serebrenik / SET / W&I 17-5-2010 PAGE 1 Last week Problem: changing code is difficult Assignment 6 Deadline: Today Assignment
2IS55 Software Evolution Sources Implementing evolution: Refactoring Alexander Serebrenik / SET / W&I 17-5-2010 PAGE 1 Last week Problem: changing code is difficult Assignment 6 Deadline: Today Assignment
Model-Driven Software Refactoring
 Model-Driven Software Refactoring Tom Mens, University of Mons-Hainaut, Belgium, tom.mens@umh.ac.be Gabriele Taentzer, Dirk Müller, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Germany, {taentzer,dmueller}@mathematik.uni-marburg.de
Model-Driven Software Refactoring Tom Mens, University of Mons-Hainaut, Belgium, tom.mens@umh.ac.be Gabriele Taentzer, Dirk Müller, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Germany, {taentzer,dmueller}@mathematik.uni-marburg.de
A Survey of Software Refactoring
 126 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SOFTWARE ENGINEERING, VOL. 30, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2004 A Survey of Software Refactoring Tom Mens, Member, IEEE, and Tom Tourwé Abstract This paper provides an extensive overview of
126 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SOFTWARE ENGINEERING, VOL. 30, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2004 A Survey of Software Refactoring Tom Mens, Member, IEEE, and Tom Tourwé Abstract This paper provides an extensive overview of
A Rule-Based Change Impact Analysis Approach in Software Architecture for Requirements Changes
 A Rule-Based Change Impact Analysis Approach in Software Architecture for Requirements Changes ARDA GOKNIL 1, IVAN KURTEV 2, KLAAS VAN DEN BERG 3 1 SnT Centre, University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg 2 Altran,
A Rule-Based Change Impact Analysis Approach in Software Architecture for Requirements Changes ARDA GOKNIL 1, IVAN KURTEV 2, KLAAS VAN DEN BERG 3 1 SnT Centre, University of Luxembourg, Luxembourg 2 Altran,
SDC Design patterns GoF
 SDC Design patterns GoF Design Patterns The design pattern concept can be viewed as an abstraction of imitating useful parts of other software products. The design pattern is a description of communicating
SDC Design patterns GoF Design Patterns The design pattern concept can be viewed as an abstraction of imitating useful parts of other software products. The design pattern is a description of communicating
Department of Computer
 Department of Computer Science @VUB Department of Computer Science 80+ Researchers 10 professors 15 post-doc s 55 pre-doc s Software and Programming Language Engineering PROG SSEL Web- and Information
Department of Computer Science @VUB Department of Computer Science 80+ Researchers 10 professors 15 post-doc s 55 pre-doc s Software and Programming Language Engineering PROG SSEL Web- and Information
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 9: Generalization/Specialization 1 Analysis Workflow: Analyze a Use Case The analysis workflow consists of the following activities: Architectural
Object-Oriented Design Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 9: Generalization/Specialization 1 Analysis Workflow: Analyze a Use Case The analysis workflow consists of the following activities: Architectural
A Generic Visual Language Technique for DSVL Model Refactoring to Patterns
 ECEASST A Generic Visual Language Technique for DSVL Model Refactoring to Patterns Karen Li 1, John Hosking 1, and John Grundy 2 1 {k.li, j.hosking}@auckland.ac.nz Departments of Computer Science, University
ECEASST A Generic Visual Language Technique for DSVL Model Refactoring to Patterns Karen Li 1, John Hosking 1, and John Grundy 2 1 {k.li, j.hosking}@auckland.ac.nz Departments of Computer Science, University
l A family of logic based KR formalisms l Distinguished by: l Decidable fragments of FOL l Closely related to Propositional Modal & Dynamic Logics
 What Are Description Logics? Description Logics l A family of logic based KR formalisms Descendants of semantic networks and KL-ONE Describe domain in terms of concepts (classes), roles (relationships)
What Are Description Logics? Description Logics l A family of logic based KR formalisms Descendants of semantic networks and KL-ONE Describe domain in terms of concepts (classes), roles (relationships)
State-Based Testing Part B Error Identification. Generating test cases for complex behaviour
 State-Based Testing Part B Error Identification Generating test cases for complex behaviour Reference: Robert V. Binder Testing Object-Oriented Systems: Models, Patterns, and Tools Addison-Wesley, 2000,
State-Based Testing Part B Error Identification Generating test cases for complex behaviour Reference: Robert V. Binder Testing Object-Oriented Systems: Models, Patterns, and Tools Addison-Wesley, 2000,
For 100% Result Oriented IGNOU Coaching and Project Training Call CPD TM : ,
 Course Code : MCS-032 Course Title : Object Oriented Analysis and Design Assignment Number : MCA (3)/032/Assign/2014-15 Assignment Marks : 100 Weightage : 25% Last Dates for Submission : 15th October,
Course Code : MCS-032 Course Title : Object Oriented Analysis and Design Assignment Number : MCA (3)/032/Assign/2014-15 Assignment Marks : 100 Weightage : 25% Last Dates for Submission : 15th October,
Using Description Logic to Maintain Consistency between UML Models
 Using Description Logic to Maintain Consistency between UML Models Ragnhild Van Der Straeten 1, Tom Mens 2, Jocelyn Simmonds 1, and Viviane Jonckers 1 1 Systems and Software Engineering Lab Department
Using Description Logic to Maintain Consistency between UML Models Ragnhild Van Der Straeten 1, Tom Mens 2, Jocelyn Simmonds 1, and Viviane Jonckers 1 1 Systems and Software Engineering Lab Department
Formalizing Software Refactoring in the Distributed Environment by aednlc Graph Grammar
 Formalizing Software Refactoring in the Distributed Environment by aednlc Graph Grammar Leszek Kotulski, Adrian Nowak Institute of Computer Science, Jagiellonian University Nawojki 11, 30-072 Kraków, Poland
Formalizing Software Refactoring in the Distributed Environment by aednlc Graph Grammar Leszek Kotulski, Adrian Nowak Institute of Computer Science, Jagiellonian University Nawojki 11, 30-072 Kraków, Poland
Extracting Ontologies from Standards: Experiences and Issues
 Extracting Ontologies from Standards: Experiences and Issues Ken Baclawski, Yuwang Yin, Sumit Purohit College of Computer and Information Science Northeastern University Eric S. Chan Oracle Abstract We
Extracting Ontologies from Standards: Experiences and Issues Ken Baclawski, Yuwang Yin, Sumit Purohit College of Computer and Information Science Northeastern University Eric S. Chan Oracle Abstract We
Semantic Web Test
 Semantic Web Test 24.01.2017 Group 1 No. A B C D 1 X X X 2 X X 3 X X 4 X X 5 X X 6 X X X X 7 X X 8 X X 9 X X X 10 X X X 11 X 12 X X X 13 X X 14 X X 15 X X 16 X X 17 X 18 X X 19 X 20 X X 1. Which statements
Semantic Web Test 24.01.2017 Group 1 No. A B C D 1 X X X 2 X X 3 X X 4 X X 5 X X 6 X X X X 7 X X 8 X X 9 X X X 10 X X X 11 X 12 X X X 13 X X 14 X X 15 X X 16 X X 17 X 18 X X 19 X 20 X X 1. Which statements
Beyond the Refactoring Browser: Advanced Tool Support for Software Refactoring
 Beyond the Refactoring Browser: Advanced Tool Support for Software Refactoring Tom Mens Tom Tourwé Francisca Muñoz Programming Technology Lab Vrije Universiteit Brussel Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussel, Belgium
Beyond the Refactoring Browser: Advanced Tool Support for Software Refactoring Tom Mens Tom Tourwé Francisca Muñoz Programming Technology Lab Vrije Universiteit Brussel Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussel, Belgium
A Comparison of Software Refactoring Tools
 A Comparison of Software Refactoring Tools Jocelyn Simmonds Ecole des Mines de Nantes jocelyn.simmonds@eleve.emn.fr Tom Mens Vrije Universiteit Brussel tom.mens@vub.ac.be November 25, 2002 Abstract The
A Comparison of Software Refactoring Tools Jocelyn Simmonds Ecole des Mines de Nantes jocelyn.simmonds@eleve.emn.fr Tom Mens Vrije Universiteit Brussel tom.mens@vub.ac.be November 25, 2002 Abstract The
Using Component-oriented Process Models for Multi-Metamodel Applications
 Using Component-oriented Process Models for Multi-Metamodel Applications Fahad R. Golra Université Européenne de Bretagne Institut Télécom / Télécom Bretagne Brest, France Email: fahad.golra@telecom-bretagne.eu
Using Component-oriented Process Models for Multi-Metamodel Applications Fahad R. Golra Université Européenne de Bretagne Institut Télécom / Télécom Bretagne Brest, France Email: fahad.golra@telecom-bretagne.eu
OMG Modeling Glossary B
 OMG Modeling Glossary B This glossary defines the terms that are used to describe the Unified Modeling Language (UML) and the Meta Object Facility (MOF). In addition to UML and MOF specific terminology,
OMG Modeling Glossary B This glossary defines the terms that are used to describe the Unified Modeling Language (UML) and the Meta Object Facility (MOF). In addition to UML and MOF specific terminology,
Specifying Coherent Refactoring of Software Artefacts with Distributed Graph Transformations i
 Specifying Coherent Refactoring of Software Artefacts with Distributed Graph Transformations i Paolo Bottoni 1, Francesco Parisi-Presicce 1,2, Gabriele Taentzer 3 1 University of Rome La Sapienza, 2 George
Specifying Coherent Refactoring of Software Artefacts with Distributed Graph Transformations i Paolo Bottoni 1, Francesco Parisi-Presicce 1,2, Gabriele Taentzer 3 1 University of Rome La Sapienza, 2 George
Chapter 8: Class and Method Design
 Chapter 8: Class and Method Design Objectives Become familiar with coupling, cohesion, and connascence. Be able to specify, restructure, and optimize object designs. Be able to identify the reuse of predefined
Chapter 8: Class and Method Design Objectives Become familiar with coupling, cohesion, and connascence. Be able to specify, restructure, and optimize object designs. Be able to identify the reuse of predefined
Module Outline. What is Object-Oriented? Some Possible Definitions. Why Object-oriented? Fundamentals of Object Orientation
 Module Outline Fundamentals of Object Positioning Object Oriented Analysis Fundamentals of Object 1. Encapsulation 2. Abstraction 3. Inheritance 4. Polymorphism The need of Modeling Unified modeling language
Module Outline Fundamentals of Object Positioning Object Oriented Analysis Fundamentals of Object 1. Encapsulation 2. Abstraction 3. Inheritance 4. Polymorphism The need of Modeling Unified modeling language
Topics in Object-Oriented Design Patterns
 Software design Topics in Object-Oriented Design Patterns Material mainly from the book Design Patterns by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides; slides originally by Spiros Mancoridis;
Software design Topics in Object-Oriented Design Patterns Material mainly from the book Design Patterns by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides; slides originally by Spiros Mancoridis;
OO design. Classes, Responsibilities, Collaborations (CRC) 13/9/1999 COSC
 OO design Classes, Responsibilities, Collaborations (CRC) 1 bank accounts the system to be modelled: bank accounts with differing fee structures purpose: evaluate different account types with respect to
OO design Classes, Responsibilities, Collaborations (CRC) 1 bank accounts the system to be modelled: bank accounts with differing fee structures purpose: evaluate different account types with respect to
Optimised Classification for Taxonomic Knowledge Bases
 Optimised Classification for Taxonomic Knowledge Bases Dmitry Tsarkov and Ian Horrocks University of Manchester, Manchester, UK {tsarkov horrocks}@cs.man.ac.uk Abstract Many legacy ontologies are now being
Optimised Classification for Taxonomic Knowledge Bases Dmitry Tsarkov and Ian Horrocks University of Manchester, Manchester, UK {tsarkov horrocks}@cs.man.ac.uk Abstract Many legacy ontologies are now being
Ontologies and OWL. Riccardo Rosati. Knowledge Representation and Semantic Technologies
 Knowledge Representation and Semantic Technologies Ontologies and OWL Riccardo Rosati Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Informatica Sapienza Università di Roma 2016/2017 The Semantic Web Tower Ontologies
Knowledge Representation and Semantic Technologies Ontologies and OWL Riccardo Rosati Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Informatica Sapienza Università di Roma 2016/2017 The Semantic Web Tower Ontologies
Introduction to Protégé. Federico Chesani, 18 Febbraio 2010
 Introduction to Protégé Federico Chesani, 18 Febbraio 2010 Ontologies An ontology is a formal, explicit description of a domain of interest Allows to specify: Classes (domain concepts) Semantci relation
Introduction to Protégé Federico Chesani, 18 Febbraio 2010 Ontologies An ontology is a formal, explicit description of a domain of interest Allows to specify: Classes (domain concepts) Semantci relation
UML Specification and Correction of Object-Oriented Anti-patterns
 UML Specification and Correction of Object-Oriented Anti-patterns Maria Teresa Llano and Rob Pooley School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh, United Kingdom {mtl4,rjpooley}@hwacuk
UML Specification and Correction of Object-Oriented Anti-patterns Maria Teresa Llano and Rob Pooley School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh, United Kingdom {mtl4,rjpooley}@hwacuk
! model construction
 Logics of Image Interpretation 1 Describing Image Interpretation in Logical Terms In 2D images (with possible occlusions) we never see the complete 3D reality.? deduction! model construction "from the
Logics of Image Interpretation 1 Describing Image Interpretation in Logical Terms In 2D images (with possible occlusions) we never see the complete 3D reality.? deduction! model construction "from the
Directives for Composing Aspect-Oriented Design Class Models
 Directives for Composing Aspect-Oriented Design Class Models Y. R. Reddy, S. Ghosh, R. B. France, G. Straw, J. M. Bieman, N. McEachen, E. Song, G. Georg Contact Email: ghosh@cs.colostate.edu Computer Science
Directives for Composing Aspect-Oriented Design Class Models Y. R. Reddy, S. Ghosh, R. B. France, G. Straw, J. M. Bieman, N. McEachen, E. Song, G. Georg Contact Email: ghosh@cs.colostate.edu Computer Science
Chapter 8 The Enhanced Entity- Relationship (EER) Model
 Chapter 8 The Enhanced Entity- Relationship (EER) Model Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 8 Outline Subclasses, Superclasses, and Inheritance Specialization
Chapter 8 The Enhanced Entity- Relationship (EER) Model Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 8 Outline Subclasses, Superclasses, and Inheritance Specialization
Simplified Approach for Representing Part-Whole Relations in OWL-DL Ontologies
 Simplified Approach for Representing Part-Whole Relations in OWL-DL Ontologies Pace University IEEE BigDataSecurity, 2015 Aug. 24, 2015 Outline Ontology and Knowledge Representation 1 Ontology and Knowledge
Simplified Approach for Representing Part-Whole Relations in OWL-DL Ontologies Pace University IEEE BigDataSecurity, 2015 Aug. 24, 2015 Outline Ontology and Knowledge Representation 1 Ontology and Knowledge
ATL Transformation. Catalogue of Model Transformations
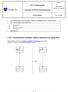 1. ATL TRANSFORMATION EXAMPLE: REPLACE INHERITANCE BY ASSOCIATION... 1 2. ATL TRANSFORMATION OVERVIEW... 2 2.1. DESCRIPTION... 2 2.2. PURPOSE... 2 2.3. RULES SPECIFICATION... 2 2.4. ATL CODE... 3 3. REFERENCES...
1. ATL TRANSFORMATION EXAMPLE: REPLACE INHERITANCE BY ASSOCIATION... 1 2. ATL TRANSFORMATION OVERVIEW... 2 2.1. DESCRIPTION... 2 2.2. PURPOSE... 2 2.3. RULES SPECIFICATION... 2 2.4. ATL CODE... 3 3. REFERENCES...
Abstraction. Design fundamentals in OO Systems. Fundamental Software Development Principles
 Abstraction Design fundamentals in OO Systems Tool for abstraction: object Object structure: properties and values for those properties operations to query and update those properties We refer to the collection
Abstraction Design fundamentals in OO Systems Tool for abstraction: object Object structure: properties and values for those properties operations to query and update those properties We refer to the collection
Specifying Coherent Refactoring of Software Artefacts with Distributed Graph Transformations i
 Specifying Coherent Refactoring of Software Artefacts with Distributed Graph Transformations i Paolo Bottoni 1, Francesco Parisi-Presicce 1,2, Gabriele Taentzer 3 1 University of Rome «La Sapienza», 2
Specifying Coherent Refactoring of Software Artefacts with Distributed Graph Transformations i Paolo Bottoni 1, Francesco Parisi-Presicce 1,2, Gabriele Taentzer 3 1 University of Rome «La Sapienza», 2
Overview. COMP 4200: Expert Systems. Knowledge Representation 2. Knowledge Representation 1
 Overview COMP 4200: Expert Systems Dr. Christel Kemke Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Knowledge Representation for XPS Associative Nets and Frame Systems (Jackson, Chapter 6) Object-oriented
Overview COMP 4200: Expert Systems Dr. Christel Kemke Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Knowledge Representation for XPS Associative Nets and Frame Systems (Jackson, Chapter 6) Object-oriented
Model driven Engineering & Model driven Architecture
 Model driven Engineering & Model driven Architecture Prof. Dr. Mark van den Brand Software Engineering and Technology Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica Technische Universiteit Eindhoven Model driven software
Model driven Engineering & Model driven Architecture Prof. Dr. Mark van den Brand Software Engineering and Technology Faculteit Wiskunde en Informatica Technische Universiteit Eindhoven Model driven software
Tiger EMF Model Transformation Framework (EMT)
 Tiger EMF Model Transformation Framework (EMT) Version 1.2.0 User Manual TU Berlin EMT Project Team: Enrico Biermann, Karsten Ehrig, Claudia Ermel, Christian Köhler, Günter Kuhns, Gabi Taentzer Email:
Tiger EMF Model Transformation Framework (EMT) Version 1.2.0 User Manual TU Berlin EMT Project Team: Enrico Biermann, Karsten Ehrig, Claudia Ermel, Christian Köhler, Günter Kuhns, Gabi Taentzer Email:
Object-Oriented Concepts and Principles (Adapted from Dr. Osman Balci)
 Object-Oriented Concepts and Principles (Adapted from Dr. Osman Balci) Sung Hee Park Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Virginia State University September 18, 2012 The Object-Oriented Paradigm
Object-Oriented Concepts and Principles (Adapted from Dr. Osman Balci) Sung Hee Park Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Virginia State University September 18, 2012 The Object-Oriented Paradigm
CHAPTER 9 DESIGN ENGINEERING. Overview
 CHAPTER 9 DESIGN ENGINEERING Overview A software design is a meaningful engineering representation of some software product that is to be built. Designers must strive to acquire a repertoire of alternative
CHAPTER 9 DESIGN ENGINEERING Overview A software design is a meaningful engineering representation of some software product that is to be built. Designers must strive to acquire a repertoire of alternative
XRay Views: Understanding the Internals of Classes
 XRay Views: Understanding the Internals of Classes Gabriela Arévalo, Stéphane Ducasse, Oscar Nierstrasz Software Composition Group University of Bern (Switzerland) {arevalo, ducasse, oscar}@iam.unibe.ch
XRay Views: Understanding the Internals of Classes Gabriela Arévalo, Stéphane Ducasse, Oscar Nierstrasz Software Composition Group University of Bern (Switzerland) {arevalo, ducasse, oscar}@iam.unibe.ch
CHAPTER 1. Topic: UML Overview. CHAPTER 1: Topic 1. Topic: UML Overview
 CHAPTER 1 Topic: UML Overview After studying this Chapter, students should be able to: Describe the goals of UML. Analyze the History of UML. Evaluate the use of UML in an area of interest. CHAPTER 1:
CHAPTER 1 Topic: UML Overview After studying this Chapter, students should be able to: Describe the goals of UML. Analyze the History of UML. Evaluate the use of UML in an area of interest. CHAPTER 1:
02291: System Integration
 02291: System Integration Introduction to UML Hubert Baumeister huba@dtu.dk DTU Compute Technical University of Denmark Spring 2019 What is the UML? Unified Modelling Language (UML) Family of graphical
02291: System Integration Introduction to UML Hubert Baumeister huba@dtu.dk DTU Compute Technical University of Denmark Spring 2019 What is the UML? Unified Modelling Language (UML) Family of graphical
Contents. I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses. Topic 04 - Inheritance
 Contents Topic 04 - Inheritance I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses - Inheritance Hierarchies Controlling Access to Members (public, no modifier, private, protected) Calling constructors of superclass
Contents Topic 04 - Inheritance I. Classes, Superclasses, and Subclasses - Inheritance Hierarchies Controlling Access to Members (public, no modifier, private, protected) Calling constructors of superclass
Metamodeling with Metamodels. Using. UML/MOF including OCL
 Metamodeling with Metamodels Using UML/MOF including OCL Introducing Metamodels (Wikipedia) A metamodel is a model of a model An instantiation of metamodel gives a model Metamodeling is the process of
Metamodeling with Metamodels Using UML/MOF including OCL Introducing Metamodels (Wikipedia) A metamodel is a model of a model An instantiation of metamodel gives a model Metamodeling is the process of
A Graphical Specification of Model Composition With Triple Graph Grammars
 A Graphical Specification of Model Composition With Triple Graph Grammars Adil Anwar 1, Amine Benelallam 2, Akram Idani 3, Bernard Coulette 4, and Mahmoud Nassar 2 1 Siweb, Computer Science Department,
A Graphical Specification of Model Composition With Triple Graph Grammars Adil Anwar 1, Amine Benelallam 2, Akram Idani 3, Bernard Coulette 4, and Mahmoud Nassar 2 1 Siweb, Computer Science Department,
Object-Oriented Programming
 Object-Oriented Programming 3/18/14 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Object-Oriented
Object-Oriented Programming 3/18/14 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Object-Oriented
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 14: Design Workflow Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology 1 UP iterations and workflow Workflows Requirements Analysis Phases Inception Elaboration
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 14: Design Workflow Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology 1 UP iterations and workflow Workflows Requirements Analysis Phases Inception Elaboration
09. Component-Level Design
 09. Component-Level Design Division of Computer Science, College of Computing Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2017 What is Component OMG UML Specification defines a component as OO view a
09. Component-Level Design Division of Computer Science, College of Computing Hanyang University ERICA Campus 1 st Semester 2017 What is Component OMG UML Specification defines a component as OO view a
UNIT II. Syllabus. a. An Overview of the UML: Visualizing, Specifying, Constructing, Documenting
 UNIT II Syllabus Introduction to UML (08 Hrs, 16 Marks) a. An Overview of the UML: Visualizing, Specifying, Constructing, Documenting b. Background, UML Basics c. Introducing UML 2.0 A Conceptual Model
UNIT II Syllabus Introduction to UML (08 Hrs, 16 Marks) a. An Overview of the UML: Visualizing, Specifying, Constructing, Documenting b. Background, UML Basics c. Introducing UML 2.0 A Conceptual Model
Automated Behavioral Testing of Refactoring Engines
 Automated Behavioral Testing of Refactoring Engines Gustavo Soares Federal University of Campina Grande, Campina Grande, PB, Brazil gsoares@dsc.ufcg.edu.br Abstract Refactoring is a transformation that
Automated Behavioral Testing of Refactoring Engines Gustavo Soares Federal University of Campina Grande, Campina Grande, PB, Brazil gsoares@dsc.ufcg.edu.br Abstract Refactoring is a transformation that
An ontology for the Business Process Modelling Notation
 An ontology for the Business Process Modelling Notation Marco Rospocher Fondazione Bruno Kessler, Data and Knowledge Management Unit Trento, Italy rospocher@fbk.eu :: http://dkm.fbk.eu/rospocher joint
An ontology for the Business Process Modelling Notation Marco Rospocher Fondazione Bruno Kessler, Data and Knowledge Management Unit Trento, Italy rospocher@fbk.eu :: http://dkm.fbk.eu/rospocher joint
Contents Contents 1 Introduction Entity Types... 37
 1 Introduction...1 1.1 Functions of an Information System...1 1.1.1 The Memory Function...3 1.1.2 The Informative Function...4 1.1.3 The Active Function...6 1.1.4 Examples of Information Systems...7 1.2
1 Introduction...1 1.1 Functions of an Information System...1 1.1.1 The Memory Function...3 1.1.2 The Informative Function...4 1.1.3 The Active Function...6 1.1.4 Examples of Information Systems...7 1.2
SUMMARY: MODEL DRIVEN SECURITY
 SUMMARY: MODEL DRIVEN SECURITY JAN-FILIP ZAGALAK, JZAGALAK@STUDENT.ETHZ.CH Model Driven Security: From UML Models to Access Control Infrastructres David Basin, Juergen Doser, ETH Zuerich Torsten lodderstedt,
SUMMARY: MODEL DRIVEN SECURITY JAN-FILIP ZAGALAK, JZAGALAK@STUDENT.ETHZ.CH Model Driven Security: From UML Models to Access Control Infrastructres David Basin, Juergen Doser, ETH Zuerich Torsten lodderstedt,
A Tool for Storing OWL Using Database Technology
 A Tool for Storing OWL Using Database Technology Maria del Mar Roldan-Garcia and Jose F. Aldana-Montes University of Malaga, Computer Languages and Computing Science Department Malaga 29071, Spain, (mmar,jfam)@lcc.uma.es,
A Tool for Storing OWL Using Database Technology Maria del Mar Roldan-Garcia and Jose F. Aldana-Montes University of Malaga, Computer Languages and Computing Science Department Malaga 29071, Spain, (mmar,jfam)@lcc.uma.es,
Institute of Automatics AGH University of Science and Technology, POLAND. Hybrid Knowledge Engineering.
 Institute of Automatics AGH University of Science and Technology, POLAND Hybrid Knowledge Engineering http://hekate.ia.agh.edu.pl and the process and (AGH-UST) 1 / 57 Outline 1 2 3 4 and the process and
Institute of Automatics AGH University of Science and Technology, POLAND Hybrid Knowledge Engineering http://hekate.ia.agh.edu.pl and the process and (AGH-UST) 1 / 57 Outline 1 2 3 4 and the process and
Understading Refactorings
 Understading Refactorings Ricardo Terra terra@dcc.ufmg.br Marco Túlio Valente mtov@dcc.ufmg.br UFMG, 2010 UFMG, 2010 Understanding Refactorings 1 / 36 Agenda 1 Overview 2 Refactoring 3 Final Considerations
Understading Refactorings Ricardo Terra terra@dcc.ufmg.br Marco Túlio Valente mtov@dcc.ufmg.br UFMG, 2010 UFMG, 2010 Understanding Refactorings 1 / 36 Agenda 1 Overview 2 Refactoring 3 Final Considerations
Announcement. Agenda 7/31/2008. Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Interface. The class will continue on Tuesday, 12 th August
 Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Interface 2 4 pm Thursday 7/31/2008 @JD2211 1 Announcement Next week is off The class will continue on Tuesday, 12 th August 2 Agenda Review Inheritance Abstract Array
Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Interface 2 4 pm Thursday 7/31/2008 @JD2211 1 Announcement Next week is off The class will continue on Tuesday, 12 th August 2 Agenda Review Inheritance Abstract Array
Chapter No. 2 Class modeling CO:-Sketch Class,object models using fundamental relationships Contents 2.1 Object and Class Concepts (12M) Objects,
 Chapter No. 2 Class modeling CO:-Sketch Class,object models using fundamental relationships Contents 2.1 Object and Class Concepts (12M) Objects, Classes, Class Diagrams Values and Attributes Operations
Chapter No. 2 Class modeling CO:-Sketch Class,object models using fundamental relationships Contents 2.1 Object and Class Concepts (12M) Objects, Classes, Class Diagrams Values and Attributes Operations
Object-Oriented Software Engineering. Chapter 2: Review of Object Orientation
 Object-Oriented Software Engineering Chapter 2: Review of Object Orientation 2.1 What is Object Orientation? Procedural paradigm: Software is organized around the notion of procedures Procedural abstraction
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Chapter 2: Review of Object Orientation 2.1 What is Object Orientation? Procedural paradigm: Software is organized around the notion of procedures Procedural abstraction
Software Engineering with Objects and Components Open Issues and Course Summary
 Software Engineering with Objects and Components Open Issues and Course Summary Massimo Felici Software Engineering with Objects and Components Software development process Lifecycle models and main stages
Software Engineering with Objects and Components Open Issues and Course Summary Massimo Felici Software Engineering with Objects and Components Software development process Lifecycle models and main stages
Applying a Model Transformation Taxonomy to Graph Transformation Technology
 Replace this file with prentcsmacro.sty for your meeting, or with entcsmacro.sty for your meeting. Both can be found at the ENTCS Macro Home Page. Applying a Model Transformation Taxonomy to Graph Transformation
Replace this file with prentcsmacro.sty for your meeting, or with entcsmacro.sty for your meeting. Both can be found at the ENTCS Macro Home Page. Applying a Model Transformation Taxonomy to Graph Transformation
26. Interfaces. Java. Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini
 26. Interfaces Java Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Definition The Comparable Interface Interfaces vs. Abstract Classes Creating Custom Interfaces References Definition Definition Single
26. Interfaces Java Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Definition The Comparable Interface Interfaces vs. Abstract Classes Creating Custom Interfaces References Definition Definition Single
SEMANTICS. Retrieval by Meaning
 SEMANTICS 1 Retrieval by Meaning Query: "Accident of a Mercedes" Retrieved image: Methods for retrieval by meaning: high-level image understanding beyond state-of-the-art except easy cases natural language
SEMANTICS 1 Retrieval by Meaning Query: "Accident of a Mercedes" Retrieved image: Methods for retrieval by meaning: high-level image understanding beyond state-of-the-art except easy cases natural language
Modellistica Medica. Maria Grazia Pia, INFN Genova. Scuola di Specializzazione in Fisica Sanitaria Genova Anno Accademico
 Modellistica Medica Maria Grazia Pia INFN Genova Scuola di Specializzazione in Fisica Sanitaria Genova Anno Accademico 2002-2003 Lezione 9 OO modeling Design Patterns Structural Patterns Behavioural Patterns
Modellistica Medica Maria Grazia Pia INFN Genova Scuola di Specializzazione in Fisica Sanitaria Genova Anno Accademico 2002-2003 Lezione 9 OO modeling Design Patterns Structural Patterns Behavioural Patterns
Presented By Aditya R Joshi Neha Purohit
 Presented By Aditya R Joshi Neha Purohit Pellet What is Pellet? Pellet is an OWL- DL reasoner Supports nearly all of OWL 1 and OWL 2 Sound and complete reasoner Written in Java and available from http://
Presented By Aditya R Joshi Neha Purohit Pellet What is Pellet? Pellet is an OWL- DL reasoner Supports nearly all of OWL 1 and OWL 2 Sound and complete reasoner Written in Java and available from http://
Goals of Lecture. Lecture 27: OO Design Patterns. Pattern Resources. Design Patterns. Cover OO Design Patterns. Pattern Languages of Programming
 Goals of Lecture Lecture 27: OO Design Patterns Cover OO Design Patterns Background Examples Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI 6448 - Spring Semester, 2001 April 24, 2001 Kenneth
Goals of Lecture Lecture 27: OO Design Patterns Cover OO Design Patterns Background Examples Kenneth M. Anderson Object-Oriented Analysis and Design CSCI 6448 - Spring Semester, 2001 April 24, 2001 Kenneth
EMF Model Refactoring based on Graph Transformation Concepts
 Page 29 EMF Model Refactoring based on Graph Transformation Concepts Enrico Biermann *, Karsten Ehrig **, Christian Köhler *, Günter Kuhns *, Gabriele Taentzer *, Eduard Weiss * *Department of Computer
Page 29 EMF Model Refactoring based on Graph Transformation Concepts Enrico Biermann *, Karsten Ehrig **, Christian Köhler *, Günter Kuhns *, Gabriele Taentzer *, Eduard Weiss * *Department of Computer
Vol. 5, No. 5 May 2014 ISSN Journal of Emerging Trends in Computing and Information Sciences CIS Journal. All rights reserved.
 Description of Consistency Rules in Software Design Models 1 Sadia Sahar, 2 Tasleem Mustafa, 3 Farnaz Usman, 4 Aasma Khalid, 5 Nadia Aslam, 6 Sidra Hafeez 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Dept. of Computer Science, University
Description of Consistency Rules in Software Design Models 1 Sadia Sahar, 2 Tasleem Mustafa, 3 Farnaz Usman, 4 Aasma Khalid, 5 Nadia Aslam, 6 Sidra Hafeez 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Dept. of Computer Science, University
02. (Conceptual) Modeling. F. Dalpiaz & J. Mylopoulos -- OIS Slide 1
 02. (Conceptual) Modeling F. Dalpiaz & J. Mylopoulos -- OIS 2011-12 Slide 1 Updates about the exam Assignment 1 is due April 20th (was, April 15th) After receiving feedback from the TA, students have 2
02. (Conceptual) Modeling F. Dalpiaz & J. Mylopoulos -- OIS 2011-12 Slide 1 Updates about the exam Assignment 1 is due April 20th (was, April 15th) After receiving feedback from the TA, students have 2
Exam in TDDB84: Design Patterns,
 Exam in TDDB84: Design Patterns, 2014-10-24 14-18 Information Observe the following, or risk subtraction of points: 1) Write only the answer to one task on one sheet. Use only the front side of the sheets
Exam in TDDB84: Design Patterns, 2014-10-24 14-18 Information Observe the following, or risk subtraction of points: 1) Write only the answer to one task on one sheet. Use only the front side of the sheets
