Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500
|
|
|
- Jennifer West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were achieved. The company home office in Gadsden (GAD) provides services to branch offices such as the Birmingham (BHM) office. These offices have some minor security and performance concerns. A Standard ACL needs to be implemented as a simple and effective tool to control traffic CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
2 Infrastructure Host #3 represents the kiosk station that needs to have its access limited to the local network. Host #4 represents another host in the BHM office and the Loopback 0 interface on the GAD router represents the Internet. Step 1 Basic Router Interconnection a. Interconnect the routers as shown in the diagram. Step 2 Basic Configuration a. The router may contain configurations from a previous use. For this reason, erase the startup configuration and reload the router to remove any residual configurations. Refer to the table on the first page and setup the router and host configurations. Verify reachability by pinging all systems and routers from each system. b. To simulate the Internet, add the following configuration to the GAD router. GAD(config)#interface loopback0 GAD(config-if)#address GAD(config-if)#exit GAD(config)#router rip GAD(config-router)#network GAD(config-if)#^z Step 3 Establish Access List Requirements a. The kiosk station (host 3) needs to have its access limited to the local network. It is determined that a standard access list needs to be created to prevent traffic from this host from reaching any other networks. The access control list should block traffic from this host and not affect other traffic from this network. A standard IP ACL satisfies this requirement as it filters based on the source address to any destination. What source address of the kiosk? Step 4 Plan the Access List Requirements a. As with any project, the most important part of the process is the planning. First, define the information needed to create the ACL. Remember that statements are added sequentially to an ACL. Therefore, the order of the statements needs to be planned carefully. b. It has been determined that this ACL will require 2 logical steps. Each of these steps can be accomplished with one statement each. As a planning tool, a text editor like Notepad can be used to organize the logic and then write the list. In the text editor enter the logic by typing: stop traffic from host 3 permit all other traffic CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3 c. From this logic the actual ACL will be written. Using the tables below, document the information for each statement. stop traffic from host 3 List # permit or deny Source address Wildcard mask 1 Deny permit all other traffic List # permit or deny Source address Wildcard mask 1 Permit d. What would be the result of not including a statement to permit all other source addresses? Every packet going into that interface would be denied due to the implicit deny any any statement. e. What would be the result of reversing the order of the 2 statements in the list? The ACL tests packets in the order in which the ACL was written. Therefore, if the packet is sent past the permit any any statement first, the deny statement does not take place. f. Why are both statements using the same ACL number? They are both part of the incoming ACL. And since there are only two ACLs allowed per interface, the statements must be listed with each other in the same ACL. g. The final step in the planning process is to determine the best location for the access list and the direction the list should be applied. Examine the internetwork diagram and choose the appropriate interface and direction. Document this in the table below: Router Interface Direction BHM E0 in* Note:* This may also be applied to S0 out to stop traffic to the GAD. Step 5 Write and Apply the ACL a. Using the previously constructed logic and information of the access list, complete the commands in the text editor. The list syntax should look similar to: stop traffic from host 3 access-list # deny address wildcard permit all other traffic access-list # permit address wildcard b. Add to this text file the configuration statements to apply the list. The configuration statements take the form of: interface type #/# ip access-group # {in, out} CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
4 c. Now the text file configuration needs to be applied to the router. Enter the configuration mode on the appropriate router and copy and paste the configuration. Observe the CLI display to ensure no errors were encountered. Step 6 Verify the ACL Now that the ACL is completed, the ACL needs to be confirmed and tested. a. The first step is to check the list to see if it was configured properly on the router. To check the ACL logic use the show access-lists command. Record the output. BHM#show ip access-lists Standard IP access list 1 deny permit any b. Next, verify that the access list was applied to the proper interface and in the correct direction. To do this examine the interface with the show ip interface command. Look at the output from each interface and record the lists applied to the interface. Interface E0 Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 1 Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /24 Broadcast address is Address determined by setup command MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 1 <output omitted> c. Finally, test the functionality of the ACL by trying to send packets from the source host and verify that is to be permitted or denied as appropriate. In this case, ping will be used to test this. [ x ] verify that host 3 CAN ping host 4 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping host 1 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping host 2 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping GAD Fa0/0E0 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping GAD LO0 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping host 1 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping host 2 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping GAD Fa0/0E0 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping GAD LO0 Step 7 Document the ACL a. As a part of all network management, documentation needs to be created. Using the text file created for the configuration, add additional comments. This file should also contain output from the show access-lists and the show ip interface commands. b. The file should be saved with other network documentation. The file naming convention should reflect the function of the file and the date of implementation CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
5 That should complete the ACL project. This is to stop access from the kiosk and is applied to Fa0 in access-list 1 deny access-list 1 permit any interface Ethernet0 ip access-group 1 in access list applied to stop kiosk traffic Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /24 Broadcast address is Address determined by setup command MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 1 <output omitted> BHM#show ip access-lists Standard IP access list 1 deny permit any c. Once finished, erase the start-up configuration on routers, remove and store the cables and adapter. Also logoff and turn the router off CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
6 Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If class does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started Press Enter. The router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed. Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Interface #1 Ethernet Interface #2 Serial Interface #1 Serial Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2600 FastEthernet 0/0 (FA0/0) FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) Interface # CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
7 In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify the type of router as well as how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
8 BHM#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname BHM ip subnet-zero ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 process-max-time 200 interface Ethernet0 ip address ip access-group 1 in interface Serial0 ip address no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue clockrate interface Serial1 no ip address shutdown router rip network network ip classless no ip http server access-list 1 deny access-list 1 permit any line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 no scheduler allocate end CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
9 GAD#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname GAD memory-size iomem 10 ip subnet-zero ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 process-max-time 200 interface Loopback0 ip address interface Ethernet0 ip address interface Serial0 ip address no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue interface Serial1 no ip address shutdown router rip network network network ip classless no ip http server line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 no scheduler allocate end CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
10 Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2600 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were achieved. The company home office in Gadsden (GAD) provides services to branch offices such as the Birmingham (BHM) office. These offices have some minor security and performance concerns. A Standard ACL needs to be implemented as a simple and effective tool to control traffic CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
11 Infrastructure Host #3 represents the kiosk station that needs to have its access limited to the local network. Host #4 represents another host in the BHM office and the Loopback 0 interface on the GAD router represents the Internet. Step 1 Basic Router Interconnection a. Interconnect the routers as shown in the diagram. Step 2 Basic Configuration a. The router may contain configurations from a previous use. For this reason, erase the startup configuration and reload the router to remove any residual configurations. Refer to the table on the first page and setup the router and host configurations. Verify reachability by pinging all systems and routers from each system. b. To simulate the Internet, add the following configuration to the GAD router. GAD(config)#interface loopback0 GAD(config-if)#address GAD(config-if)#exit GAD(config)#router rip GAD(config-router)#network GAD(config-if)#^z Step 3 Establish Access List Requirements a. The kiosk station (host 3) needs to have its access limited to the local network. It is determined that a standard access list needs to be created to prevent traffic from this host from reaching any other networks. The access control list should block traffic from this host and not affect other traffic from this network. A standard IP ACL satisfies this requirement as it filters based on the source address to any destination. What source address of the kiosk? Step 4 Plan the Access List Requirements a. As with any project, the most important part of the process is the planning. First, define the information needed to create the ACL. Remember that statements are added sequentially to an ACL. Therefore, the order of the statements needs to be planned carefully. b. It has been determined that this ACL will require 2 logical steps. Each of these steps can be accomplished with one statement each. As a planning tool, a text editor like Notepad can be used to organize the logic and then write the list. In the text editor enter the logic by typing: stop traffic from host 3 permit all other traffic CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
12 c. From this logic the actual ACL will be written. Using the tables below, document the information for each statement. stop traffic from host 3 List # permit or deny Source address Wildcard mask 1 Deny permit all other traffic List # permit or deny Source address Wildcard mask 1 Permit d. What would be the result of not including a statement to permit all other source addresses? Every packet going into that interface would be denied due to the implicit deny any any statement. e. What would be the result of reversing the order of the 2 statements in the list? The ACL tests packets in the order in which the ACL was written. Therefore, if the packet is sent past the permit any any statement first, the deny statement does not take place. f. Why are both statements using the same ACL number? They are both part of the incoming ACL. Since there are only two ACLs allowed per interface, the statements must be listed with each other in the same ACL. g. The final step in the planning process is to determine the best location for the access list and the direction the list should be applied. Examine the internetwork diagram and choose the appropriate interface and direction. Document this in the table below: Router Interface Direction BHM FA0/0 in* Note: * This may also be applied to S0 out to stop traffic to GAD. Step 5 Write and Apply the ACL a. Using the previously constructed logic and information of the access list, complete the commands in the text editor. The list syntax should look similar to: stop traffic from host 3 access-list # deny address wildcard permit all other traffic access-list # permit address wildcard b. Add to this text file the configuration statements to apply the list. The configuration statements take the form of: interface type #/# ip access-group # {in, out} CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
13 c. Now the text file configuration needs to be applied to the router. Enter the configuration mode on the appropriate router and copy and paste the configuration. Observe the CLI display to ensure no errors were encountered. Step 6 Verify the ACL Now that the ACL is completed, the ACL needs to be confirmed and tested. a. The first step is to check the list to see if it was configured properly on the router. To check the ACL logic use the show access-lists command. Record the output. BHM#show ip access-lists Standard IP access list 1 deny permit any b. Next, verify that the access list was applied to the proper interface and in the correct direction. To do this examine the interface with the show ip interface command. Look at the output from each interface and record the lists applied to the interface. Interface FA0/0 Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 1 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /24 Broadcast address is Address determined by setup command MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 1 <output omitted> c. Finally, test the functionality of the ACL by trying to send packets from the source host and verify that is to be permitted or denied as appropriate. In this case, ping will be used to test this. [ x ] verify that host 3 CAN ping host 4 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping host 1 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping host 2 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping GAD Fa0/0 [ x ] verify that host 3 CANNOT ping GAD LO0 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping host 1 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping host 2 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping GAD Fa0/0 [ x ] verify that host 4 CAN ping GAD LO0 Step 7 Document the ACL a. As a part of all network management, documentation needs to be created. Using the text file created for the configuration, add additional comments. This file should also contain output from the show access-lists and the show ip interface commands. b. The file should be saved with other network documentation. The file naming convention should reflect the function of the file and the date of implementation CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
14 That should complete the ACL project. This is to stop access from the kiosk and is applied to Fa0 in access-list 1 deny access-list 1 permit any interface FastEthernet0/0 ip access-group 1 in access list applied to stop kiosk traffic FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /24 Broadcast address is Address determined by setup command MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is 1 <output omitted> BHM#show ip access-lists Standard IP access list 1 deny permit any c. Once finished, erase the start-up configuration on routers, remove and store the cables and adapter. Also logoff and turn the router off CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
15 BHM#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname BHM ip subnet-zero ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 process-max-time 200 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address ip access-group 1 in interface Serial0/0 ip address no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue clockrate interface Serial0/1 no ip address shutdown router rip network network ip classless no ip http server access-list 1 deny access-list 1 permit any line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 no scheduler allocate end CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
16 GAD#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.0 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname GAD memory-size iomem 10 ip subnet-zero ip audit notify log ip audit po max-events 100 process-max-time 200 interface Loopback0 ip address interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address interface Serial0/0 ip address no ip mroute-cache no fair-queue interface Serial0/1 no ip address shutdown router rip network network network ip classless no ip http server line con 0 transport input none line aux 0 line vty 0 4 no scheduler allocate end CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v Lab b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab Troubleshooting RIP
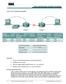 Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab Configuring a Serial Interface
 Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab Verifying RIP v2 Configuration
 Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab Backing up Configuration Files
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the configuration with a text
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the configuration with a text
Lab b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500 Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 372-833 CCNA 2:
Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500 Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 372-833 CCNA 2:
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab b Simple Extended Access Lists
 Lab 11.2.2b Simple Extended Access Lists 1-7 CCNA 2: Simple Extended Access Lists v 3.1 - Lab 11.2.2b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Scenario In this lab, configuring extended access lists
Lab 11.2.2b Simple Extended Access Lists 1-7 CCNA 2: Simple Extended Access Lists v 3.1 - Lab 11.2.2b Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Scenario In this lab, configuring extended access lists
Lab Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions
 Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab Command Modes and Router Identification. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab Configuring Router Passwords. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab Using the Boot System Command. Objective. Background/Preparation
 Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
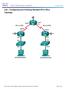 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Lab Configuring the OSPF Routing Process
 Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router.
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab Verifying PPP Configuration
 Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab Modifying OSPF Cost Metric
 Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface)
 Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab Configuring DHCP
 Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab c Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists
 Lab 11.2.3c Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Objective In this lab, the use extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 1-9 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.0
Lab 11.2.3c Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Objective In this lab, the use extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 1-9 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.0
Lab b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists
 Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 1-9 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics
Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 1-9 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab Configuring Dialer Profiles
 Lab 4.3.7 Configuring Dialer Profiles Objective Configure ISDN Dialer Profiles on the routers enabling a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to be made from two remote routers simultaneously into a central
Lab 4.3.7 Configuring Dialer Profiles Objective Configure ISDN Dialer Profiles on the routers enabling a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to be made from two remote routers simultaneously into a central
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
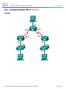 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software
 Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Solution)
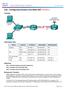 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Lab Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Static Routes (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab Configuring Port Address Translation (PAT) (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab - Building a Switch and Router Network
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
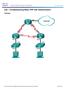 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
WCCPv2 and WCCP Enhancements
 WCCPv2 and WCCP Enhancements Release 12.0(11)S June 20, 2000 This feature module describes the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) Enhancements feature and includes information on the benefits of the
WCCPv2 and WCCP Enhancements Release 12.0(11)S June 20, 2000 This feature module describes the Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) Enhancements feature and includes information on the benefits of the
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers %
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
Skills Assessment Student Training
 Skills Assessment Student Training Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (6 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (33 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure Switch
Skills Assessment Student Training Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (6 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (33 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure Switch
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500 Objective Recover a Cisco router stuck in ROM monitor (ROMmon) mode. Learn how to avoid having to use Xmodem to restore an
Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500 Objective Recover a Cisco router stuck in ROM monitor (ROMmon) mode. Learn how to avoid having to use Xmodem to restore an
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1: Getting Started and Building Start.TXT
 1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1: Getting Started and Building Start.TXT Objective This lab introduces the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new to you. This introductory activity also
1.4.1 Introductory Lab 1: Getting Started and Building Start.TXT Objective This lab introduces the CCNP lab equipment and certain IOS features that might be new to you. This introductory activity also
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall
 Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall Document ID: 43068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Configuring Dynamic Multipoint VPN Using GRE Over IPsec With OSPF, NAT, and Cisco IOS Firewall Document ID: 43068 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 on a Router (Solution)
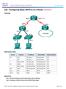 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.2.253
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.2.253
cable modem dhcp proxy nat on Cisco Cable Modems
 cable modem dhcp proxy nat on Cisco Cable Modems Document ID: 12176 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dynamic NAT Versus Static NAT Configuration Using cable
cable modem dhcp proxy nat on Cisco Cable Modems Document ID: 12176 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Dynamic NAT Versus Static NAT Configuration Using cable
Lab Configuring Switch Security Features Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC 172.16.99.3
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC 172.16.99.3
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Enchilada Solutions
 Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: Solutions Cisco Press CCIE Practical Studies CCIE Practice Lab: LAB Book Chapter Book Page The 18 1161 Overview... 3 Technical Details... 3 Table 54-1:
1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services?
 CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
Lab - Configuring IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Antonio Cianfrani. Access Control List (ACL) Part I
 Antonio Cianfrani Access Control List (ACL) Part I Index ACL? How to configure Standard ACL Extended ACL Named ACL Limiting the vty access ACL (1/3) Control lists applied to traffic incoming in / outgoing
Antonio Cianfrani Access Control List (ACL) Part I Index ACL? How to configure Standard ACL Extended ACL Named ACL Limiting the vty access ACL (1/3) Control lists applied to traffic incoming in / outgoing
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Lab Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
