Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
|
|
|
- Aldous Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, and 2600 or any such combination can be used. Please refer to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. Perform the following steps on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
2 Step 1 Configure the routers On the routers, enter the global configuration mode and configure the hostname, console, virtual terminal and enable secret passwords. Next configure the interfaces and IP hostnames according to the chart. Do not configure the routing protocol until specifically told to. If there are any problems configuring the router basics, refer to the lab Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Router 1 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname Sydney Sydney(config)#enable secret class Sydney(config)#line console 0 Sydney(config-line)#password cisco Sydney(config-line)#login Sydney(config-line)#line vty 0 4 Sydney(config-line)#password cisco Sydney(config-line)#login Sydney(config-line)#exit Sydney(config)#interface loopback 0 Sydney(config-if)#ip address Sydney(config-if)#interface serial 0 Sydney(config-if)#ip address Sydney(config-if)#clockrate Sydney(config-if)#no shutdown Sydney(config-if)#interface ethernet 0 Sydney(config-if)#ip address Sydney(config-if)#no shutdown Sydney(config-if)#exit Sydney(config)#ip host Rome Sydney(config)#exit Router 2 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname Rome Rome(config)#enable secret class Rome(config)#line console 0 Rome(config-line)#password cisco Rome(config-line)#login Rome(config-line)#line vty 0 4 Rome(config-line)#password cisco Rome(config-line)#login Rome(config-line)#exit Rome(config)#interface loopback 0 Rome(config-if)#ip address Rome(config-if)#interface serial 0 Rome(config-if)#ip address Rome(config-if)#no shutdown Rome(config-if)#interface ethernet 0 Rome(config-if)#ip address Rome(config-if)#no shutdown Rome(config-if)#exit Rome(config)#ip host Sydney Rome(config)#exit CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3 Step 2 Save the configuration information from the privileged EXEC command mode Sydney#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [Enter] Rome#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [Enter] Why save the running configuration to the startup configuration? Saving the configuration will allow the router to keep the configuration after a reload or power down. Step 3 Configure the hosts with the proper IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway a. Each workstation should be able to ping the attached router. Troubleshoot as necessary. Remember to assign a specific IP address and default gateway to the workstation. If running Windows 9x/ME, check by using Start > Run > winipcfg. If running WindowsNT/2000/XP, check by using the ipconfig command in a DOS window. b. At this point the workstations will not be able to communicate with each other. The following steps will demonstrate the process required to get communication working using OSPF as the routing protocol. Host connected to router Sydney IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Host connected to router Rome IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Step 4 Verify connectivity a. On a router, ping the serial interface of the other router. b. What the ping successful? Yes c. If the ping was not successful, troubleshoot the router configurations, until the ping is successful. Step 5 Configure OSPF routing on both routers a. Configure OSPF routing on each router. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Refer to the lab, Configuring Loopback Interfaces for review on configuring OSPF routing if necessary. Sydney(config)#router ospf 1 Sydney(config-router)#network area 0 Sydney(config-router)#network area 0 Sydney(config-router)#end Rome(config)#router ospf 1 Rome(config-router)#network area 0 Rome(config-router)#network area 0 Rome(config-router)#end b. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes c. Show the routing table for the Sydney router. Sydney#show ip route CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
4 d. Are there any entries in the routing table? Yes Step 6 Test network connectivity Ping the Sydney host from the Rome host. Was it successful? Yes If not troubleshoot as necessary. Step 7 Observe OSPF traffic a. At the privileged EXEC mode type the command debug ip ospf events and observe the output. b. How frequently are Hello messages sent? Every 10 seconds c. Where are they coming from? Receive hello from area 0 from Serial d. Turn off debugging by typing no debug ip ospf events or undebug all. Step 8 Show interface timer information a. Show the hello and dead interval timers on the Sydney router Ethernet and Serial interfaces by entering the command show ip ospf interface in privileged EXEC mode. b. Record the Hello and Dead Interval timers for these interfaces c. Hello Interval: 10 d. Dead Interval: 40 e. What is the purpose of the dead interval? The amount of time when a hello interval is not received before flagging the router as being down. Step 9 Modify the OSPF timers a. Modify the Hello and Dead-Interval timers to smaller values to try to improve performance. On the Sydney router only enter the commands ip ospf hello-interval 5 and ip ospf dead-interval 20 for interface Serial 0. Sydney(config)#interface serial 0 Sydney(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 5 Sydney(config-if)#ip ospf dead-interval 20 b. Wait for a minute and then enter the command show ip ospf neighbor. c. Are there any OSPF neighbors? No Step 10 Examine the routing table a. Examine the Sydney router routing table by entering show ip route. b. Are there any OSPF routes in the table? No c. Can the Sydney Host ping the Rome host? No Step 11 Look at the OSPF data transmissions. a. Enter the command debug ip ospf events in privileged EXEC mode. b. Is there an issue that is identified? Yes c. If there is, what is the issue? Hello and Dead intervals are mismatched CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
5 Step 12 Check the Rome router routing table status. a. On the Rome router check the routing table by typing show ip route. b. Are there any OSPF routes in the table? No Step 13 Set the Rome router interval timers a. Match the timer values on the Rome Serial link with the Sydney router. Rome(config)#interface serial 0 Rome(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 5 Rome(config-if)#ip ospf dead-interval 20 b. Verify the OSPF neighbor by entering show ip ospf neighbor command. Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0 c. Show the routing table by typing show ip route. Rome#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C C C O /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets is directly connected, Loopback /24 is directly connected, Ethernet /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /30 is directly connected, Serial /25 [110/782] via , 00:00:12, Serial0 d. Are there OSPF routes in the table? Yes e. Ping the Rome host from Sydney. If this was not successful troubleshoot the configurations. Step 14 Reset the routers interval timers to the default values Use the no form of the ip ospf hello-interval and the ip ospf dead-interval to reset the OSPF timers back to their default values. Step 15 Verify the interval timers are returned to the default values a. Use the show ip ospf interface command to verify the timers are reset to their default values. b. Are the values back to the default? Yes c. If not, repeat step 13 and verify again CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
6 Once the previous steps are completed, logoff by typing exit and turn the router off. Then remove and store the cables and adapter CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
7 Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
8 Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Ethernet Serial Serial Interface #1 Interface #2 Interface #1 Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2600 FastEthernet 0/0 (FA0/0) FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
9 Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2600 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, and 2600 or any such combination can be used. Please refer to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. Perform the following steps on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
10 Step 1 Configure the routers On the routers, enter the global configuration mode and configure the hostname, console, virtual terminal and enable secret passwords. Next configure the interfaces and IP hostnames according to the chart. Do not configure the routing protocol until specifically told to. If there are any problems configuring the router basics, refer to the lab Review of Basic Router Configuration with RIP. Router 1 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname Sydney Sydney(config)#enable secret class Sydney(config)#line console 0 Sydney(config-line)#password cisco Sydney(config-line)#login Sydney(config-line)#line vty 0 4 Sydney(config-line)#password cisco Sydney(config-line)#login Sydney(config-line)#exit Sydney(config)#interface loopback 0 Sydney(config-if)#ip address Sydney(config-if)#interface serial 0/0 Sydney(config-if)#ip address Sydney(config-if)#clockrate Sydney(config-if)#no shutdown Sydney(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Sydney(config-if)#ip address Sydney(config-if)#no shutdown Sydney(config-if)#exit Sydney(config)#ip host Rome Sydney(config)#exit Router 2 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname Rome Rome(config)#enable secret class Rome(config)#line console 0 Rome(config-line)#password cisco Rome(config-line)#login Rome(config-line)#line vty 0 4 Rome(config-line)#password cisco Rome(config-line)#login Rome(config-line)#exit Rome(config)#interface loopback 0 Rome(config-if)#ip address Rome(config-if)#interface serial 0/0 Rome(config-if)#ip address Rome(config-if)#no shutdown Rome(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/0 Rome(config-if)#ip address Rome(config-if)#no shutdown Rome(config-if)#exit Rome(config)#ip host Sydney Rome(config)#exit Step 2 Save the configuration information from the privileged EXEC command mode CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
11 Sydney#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [Enter] Rome#copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [Enter] Why save the running configuration to the startup configuration? Saving the configuration will allow the router to keep the configuration after a reload or power down. Step 3 Configure the hosts with the proper IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway a. Each workstation should be able to ping the attached router. Troubleshoot as necessary. Remember to assign a specific IP address and default gateway to the workstation. If running Windows 9x/ME, check by using Start > Run > winipcfg. If running WindowsNT/2000/XP, check by using the ipconfig command in a DOS window. b. At this point the workstations will not be able to communicate with each other. The following steps will demonstrate the process required to get communication working using OSPF as the routing protocol. Host connected to router Sydney IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Host connected to router Rome IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Step 4 Verify connectivity a. On a router, ping the serial interface of the other router. b. What the ping successful? Yes c. If the ping was not successful, troubleshoot the router configurations, until the ping is successful. Step 5 Configure OSPF routing on both routers a. Configure OSPF routing on each router. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Refer to the lab, Configuring Loopback Interfaces for review on configuring OSPF routing if necessary. Sydney(config)#router ospf 1 Sydney(config-router)#network area 0 Sydney(config-router)#network area 0 Sydney(config-router)#end Rome(config)#router ospf 1 Rome(config-router)#network area 0 Rome(config-router)#network area 0 Rome(config-router)#end b. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes c. Show the routing table for the Sydney router. Sydney#show ip route CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
12 d. Are there any entries in the routing table? Yes Step 6 Test network connectivity Ping the Sydney host from the Rome host. Was it successful? Yes If not troubleshoot as necessary. Step 7 Observe OSPF traffic a. At the privileged EXEC mode type the command debug ip ospf events and observe the output. b. How frequently are Hello messages sent? Every 10 seconds c. Where are they coming from? Receive hello from area 0 from Serial0/ d. Turn off debugging by typing no debug ip ospf events or undebug all. Step 8 Show interface timer information a. Show the hello and dead interval timers on the Sydney router Ethernet and Serial interfaces by entering the command show ip ospf interface in privileged EXEC mode. b. Record the Hello and Dead Interval timers for these interfaces c. Hello Interval: 10 d. Dead Interval: 40 e. What is the purpose of the dead interval? The amount of time when a hello interval is not received before flagging the router as being down. Step 9 Modify the OSPF timers a. Modify the Hello and Dead-Interval timers to smaller values to try to improve performance. On the Sydney router only enter the commands ip ospf hello-interval 5 and ip ospf dead-interval 20 for interface Serial 0. Sydney(config)#interface serial 0/0 Sydney(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 5 Sydney(config-if)#ip ospf dead-interval 20 b. Wait for a minute and then enter the command show ip ospf neighbor. c. Are there any OSPF neighbors? No Step 10 Examine the routing table a. Examine the Sydney router routing table by entering show ip route. b. Are there any OSPF routes in the table? No c. Can the Sydney Host ping the Rome host? No Step 11 Look at the OSPF data transmissions. a. Enter the command debug ip ospf events in privileged EXEC mode. b. Is there an issue that is identified? Yes CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
13 c. If there is, what is the issue? Hello and Dead intervals are mismatched. Step 12 Check the Rome router routing table status. a. On the Rome router check the routing table by typing show ip route. b. Are there any OSPF routes in the table? No Step 13 Set the Rome router interval timers a. Match the timer values on the Rome Serial link with the Sydney router. Rome(config)#interface serial 0/0 Rome(config-if)#ip ospf hello-interval 5 Rome(config-if)#ip ospf dead-interval 20 b. Verify the OSPF neighbor by entering show ip ospf neighbor command. Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ - 00:00: Serial0/0 c. Show the routing table by typing show ip route. Rome#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets C is directly connected, Loopback0 C /24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C /30 is directly connected, Serial0/0 O /25 [110/782] via , 00:00:12, Serial0/0 d. Are there OSPF routes in the table? Yes e. Ping the Rome host from Sydney. If this was not successful troubleshoot the configurations. Step 14 Reset the routers interval timers to the default values Use the no form of the ip ospf hello-interval and the ip ospf dead-interval to reset the OSPF timers back to their default values. Step 15 Verify the interval timers are returned to the default values a. Use the show ip ospf interface command to verify the timers are reset to their default values. b. Are the values back to the default? Yes c. If not, repeat step 13 and verify again CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
14 Once the previous steps are completed, logoff by typing exit and turn the router off. Then remove and store the cables and adapter CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
15 Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
16 Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Ethernet Serial Serial Interface #1 Interface #2 Interface #1 Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2600 FastEthernet 0/0 (FA0/0) FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab Configuring the OSPF Routing Process
 Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab Troubleshooting RIP
 Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab Command Modes and Router Identification. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab Modifying OSPF Cost Metric
 Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab Configuring Router Passwords. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Lab Verifying PPP Configuration
 Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions
 Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab Configuring Dialer Profiles
 Lab 4.3.7 Configuring Dialer Profiles Objective Configure ISDN Dialer Profiles on the routers enabling a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to be made from two remote routers simultaneously into a central
Lab 4.3.7 Configuring Dialer Profiles Objective Configure ISDN Dialer Profiles on the routers enabling a dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to be made from two remote routers simultaneously into a central
Lab Verifying RIP v2 Configuration
 Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
Lab Using the Boot System Command. Objective. Background/Preparation
 Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab Configuring a Serial Interface
 Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring DHCP
 Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab Backing up Configuration Files
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the configuration with a text
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the configuration with a text
Lab Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface)
 Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router.
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Legacy DDR
 Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab 4.3.2 Configuring Legacy DDR Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a legacy dial-on-demand routing (DDR) call to another ISDN capable router. When the DDR connection is successfully made, augment
Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on
Module 9, Assignment 7
 Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
Lab Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500 Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 372-833 CCNA 2:
Lab 11.2.3b Simple DMZ Extended Access Lists Instructor Version 2500 Objective In this lab, the use of extended access lists to create a simple DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) will be learned. 372-833 CCNA 2:
Lab Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses
 Lab 6.2.6 Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Move a PC from one switch port to another and add a new PC to the switch. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.6 Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Move a PC from one switch port to another and add a new PC to the switch. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 9.3.6 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create a basic configuration
Lab 9.3.6 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create a basic configuration
Lab Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Lab Spanning-Tree Recalculation
 Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Lab Verifying VLAN Configurations
 Lab 8.2.4 Verifying VLAN Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create two VLANs. Name the VLANs and assign multiple member ports to them. Test functionality by moving
Lab 8.2.4 Verifying VLAN Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create two VLANs. Name the VLANs and assign multiple member ports to them. Test functionality by moving
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q
 Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an 802.1q trunk line between
Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an 802.1q trunk line between
Lab Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
Lab 2.2.9 Command Line Fundamentals Instructor Version 2500 Objective Log into a router and go to the user and privileged modes. Use several basic router commands to determine how the router is configured.
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab Selecting the Root Bridge
 Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test
 Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab Configuring Static VLANs
 Lab 8.2.3 Configuring Static VLANs Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine the switch firmware version. Create two VLANs, name them and assign member ports to them. Background/Preparation
Lab 8.2.3 Configuring Static VLANs Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine the switch firmware version. Create two VLANs, name them and assign member ports to them. Background/Preparation
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA ( )
 STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software
 Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab VTP Client and Server Configurations
 Lab 9.2.5 VTP Client and Server Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Configure the VTP
Lab 9.2.5 VTP Client and Server Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Configure the VTP
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab Configuring Static NAT
 Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
 Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Lab Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2900 Series Switches
 Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2900 Series Switches Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration verify it. Change passwords to the password recovery procedure be performed.
Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2900 Series Switches Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration verify it. Change passwords to the password recovery procedure be performed.
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Change passwords and use the password recovery procedure.
Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Change passwords and use the password recovery procedure.
Network Cable : Configure & Verifying Cross-Over Cable. Network Profile: Network Discovery, File and Printer sharing
 Lab # Lab 1 Lab 2 Lab 3 Lab 4 Lab 5 Lab 6 Lab 7 Lab 8 Lab 9 Lab 10 Lab 11 Lab 12 Lab 13 Lab 14 Lab 15 Lab 16 Lab 17 Lab 18 Lab 19 Lab 20 Lab 21 Lab 22 Lab 23 Topic LAN Card: Check Speed, Enable/Disable.
Lab # Lab 1 Lab 2 Lab 3 Lab 4 Lab 5 Lab 6 Lab 7 Lab 8 Lab 9 Lab 10 Lab 11 Lab 12 Lab 13 Lab 14 Lab 15 Lab 16 Lab 17 Lab 18 Lab 19 Lab 20 Lab 21 Lab 22 Lab 23 Topic LAN Card: Check Speed, Enable/Disable.
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files
 Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation Cable a network
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv2
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network
 LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
LAB MANUAL for Computer Network CSE-310 F Computer Network Lab L T P - - 3 Class Work : 25 Marks Exam : 25 MARKS Total : 50 Marks This course provides students with hands on training regarding the design,
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Antonio Cianfrani. Packet Tracer
 Antonio Cianfrani Packet Tracer Packet Tracer (1/2) Packet Tracer? Cisco Packet Tracer is a software able to emulate CISCO networking devices. Packet Tracer features: Allows to create network topologies
Antonio Cianfrani Packet Tracer Packet Tracer (1/2) Packet Tracer? Cisco Packet Tracer is a software able to emulate CISCO networking devices. Packet Tracer features: Allows to create network topologies
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
OSPF single area configuration lab on packet tracer
 OSPF single area configuration lab on packet tracer This OSPF lab is created in packet tracer and you will learn the OSPF single area configuration from this lab. Configuring the OSPF Routing Process This
OSPF single area configuration lab on packet tracer This OSPF lab is created in packet tracer and you will learn the OSPF single area configuration from this lab. Configuring the OSPF Routing Process This
Lab - Building a Switch and Router Network
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network
 CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
Lab Configuring Multi-Area Integrated IS-IS
 Lab 7.7.2 Configuring Multi-Area Integrated IS-IS Objective In this lab, multiarea Integrated IS-IS and level-specific routers will be configured. Scenario Previous tests demonstrated that Integrated IS-IS
Lab 7.7.2 Configuring Multi-Area Integrated IS-IS Objective In this lab, multiarea Integrated IS-IS and level-specific routers will be configured. Scenario Previous tests demonstrated that Integrated IS-IS
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
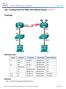 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500 Objective Recover a Cisco router stuck in ROM monitor (ROMmon) mode. Learn how to avoid having to use Xmodem to restore an
Lab 5.2.6b Managing IOS Images with ROMmon and Xmodem Instructor Version 2500 Objective Recover a Cisco router stuck in ROM monitor (ROMmon) mode. Learn how to avoid having to use Xmodem to restore an
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
CCNA Layer 2 switching. Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03
 CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
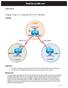 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute Topology Objectives Background Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
