Testking Cisco _formatted
|
|
|
- Sarah Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Testking Cisco _formatted Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0
2 Exam A QUESTION 1 Which two statements about the Cisco Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) are true? (Select two) A. The Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) profile manager feature can create and manage only one profile for the wireless client adapter. B. The Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) can support only one wireless client adapter installed and used at a time. C. The Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) can be used to establish the association between the client adapter and the access point, manage authentication to the wireless network, and enable encryption. D. The Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) and the Microsoft Wireless Configuration Manager can be used at the same time to configure the wireless client adapter. Correct Answer: BC /Reference: : You can configure your Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Client Adapter through the Cisco ADU or a third-party tool, such as the Microsoft Wireless Configuration Manager. Because third-party tools may not provide all the functionality available in ADU, Cisco recommends that you use ADU. The Aironet Desktop Utility (ADU) can support only one wireless client adapter as well as Aironet Desktop Utility establish the association between the client adapter and Access Point, allows to authenticate wireless client, allows to configure encryption by setting static WEP, WPA/WPA2 passphrase. Section 3: Perform routine IOS device maintenance (0 Questions) Section 4: Isolate sub-optimal internetwork operation at the correctly defined OSI Model layer (2 Questions) QUESTION 2 At which layer of the OSI model does the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) operate at? A. Layer 5 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 2 B. Layer 4 C. Layer 3 D. Layer 2 E. Layer 1 Correct Answer: D /Reference: : Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 (L2) protocol designed to run on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is called 802.1d. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not run into a loop situation when you have redundant paths in your network. Loops are deadly to a network. QUESTION 3 In computer networking a multicast address is an identifier for a group of hosts that have joined a multicast group. Multicast addressing can be used in the Link Layer (OSI Layer 2), such as Ethernet Multicast, as well as at the Internet Layer (OSI Layer 3) as IPv4 or IPv6 Multicast. Which two descriptions are correct regarding multicast addressing?
3 A. The first 23 bits of the multicast MAC address are 0x E. This is a reserved value that indicates a multicast application. B. The last 3 bytes (24 bits) of the multicast MAC address are 0x E. This is a reserved value that indicates a multicast application. C. To calculate the Layer 2 multicast address, the host maps the last 23 bits of the IP address into the last 24 bits of the MAC address. The high-order bit is set to 0. D. The first 3 bytes (24 bits) of the multicast MAC address are 0x E. This is a reserved value that indicates a multicast application. Correct Answer: CD /Reference: : The point of this question is the form of multicast MAC address, and the conversion between the multicast MAC address and IP address. The multicast MAC address is 6 bytes(48 bits), the first 3 bytes (24 bits) of the multicast MAC address are 0x E, the last 3 bytes(24 bits) of the multicast MAC address = bit(the last 23 bit of the IP address). "0x E" is a reserved value that indicates a multicast application. So option B and D are correct. QUESTION 4 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 3 EIGRP is being used as the routing protocol on the company network. While troubleshooting some network connectivity issues, you notice a large number of EIGRP SIA (Stuck in Active) messages. What causes these SIA routes? (Select two) A. The neighboring router stops receiving ACK packets from this router. B. The neighboring router starts receiving route updates from this router. C. The neighboring router is too busy to answer the query (generally caused by high CPU utilization). D. The neighboring router is having memory problems and cannot allocate the memory to process the query or build the reply packet. Correct Answer: CD /Reference: : SIA routes are due to the fact that reply packets are not received. This could be caused by a router which is unable to send reply packets. The router could have reached the limit of its capacity, or it could be malfunctioning. Incorrect Answers: A: Missing replies, not missing ACKs, cause SIA.
4 B: Routes updates do not cause SIA.Notes: If a router does not receive a reply to all outstanding queries within 3 minutes, the route goes to the stuck in active (SIA) state. The router then resets the neighbors that fail to reply by going active on all routes known through that neighbor, and it re- advertises all routes to that neighbor.reference: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocolhttp:// eigrp3.html QUESTION 5 Part of the routing table of router R1 is displayed below: S /24 [1/0] via /32 is subnetted, 1 subnets D EX [170/ ] via , 06:47:28, Serial0/0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks D EX /24 [170/27316] via , 09:52:10, FastEthernet11/0/0 [170/27316] via , 09:52:10, FastEthernet11/0/ /24 [90/ ] via , 10:33:13, Serial0/0/ [90/ ] via , 10:33:13, Serial0/0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 12 subnets, 2 masks D /32 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 4 [90/ ] via , 10:33:13, FastEthernet1/0/0 [90/ ] via , 10:33:13, FastEthernet1/0/0 S* /0 [1/0] via From analyzing the above command output, what is the administrative distance of the external EIGRP routes? A. 24 B. 32 C. 90 D. 170 E F. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: D /Reference: : By default an external EIGRP route has a value of 170. By examining the exhibit we see that this default value of the external EIGRP routes (see D-EX in exhibit) indeed is set to 170. The first value within the brackets display the AD, so with a value of [170/27316] the AD is 170 and the metric of the route is Incorrect Answers: A: This is the subnet mask used for some of the routes in the table. B: This is the subnet mask used for some of the routes in the table. C: This is the AD of the internal EIGRP routes, which is the default E: This is the EIGRP metric of the external EIGRP routes.reference: What Is Administrative Distance? QUESTION 6 The network is shown below, along with the relevant router configurations:
5 R1# show run interface Loopback0 ip address ! interface Ethernet0 ip address media-type 10BaseT "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 5!! router eigrp 999 redistribute connected network auto-summary no eigrp log-neighbor-changes! ip classless no ip http server R2# show run interface Ethernet0 ip address media-type 10BaseT! interface Ethernet1 ip address media-type 10BaseT! router eigrp 999 network network ! ip classless no ip http server R3# show run interface Ethernet1/0 ip address ! router eigrp 999 network auto-summary no eigrp log-neighbor-changes! ip classless ip http server With the topology found in the graphic, what will the R1 loopback 0 be in the R3 routing table?
6 A. It will show up in the routing table as D /8. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 6 B. It will show up in the routing table as D EX /8. C. It will show up in the routing table as D /24. D. It will not show up in R3 routing table because there is no network command on R1. Correct Answer: B /Reference: : Because router R1 is configured with route redistribution, it will redistribute the connected loopback network into EIGRP. Because redistributed routes will show up as external EIGRP routes in the routing table, choice B is correct. Although the loopback interface is using a /24 subnet mask, EIGRP summarizes at network boundaries by default so the network will appear as the class A network of /8 in the routing table of the other routers. Incorrect Answers: A: The route will be external, since it was redistributed into EIGRP. C: It will be external because of redistribution, and it will also be summarized since that is the default behavior of EIGRP. D: Although it was not configured under the EIGRP network command, it would be redistributed because it is a connected route. QUESTION 7 The EIGRP network is displayed in the following topology diagram: You work as a network technician. Study the exhibits carefully. If the command "variance 3" was added to the EIGRP configuration of R5, which path or paths would be chosen to route traffic from R5 to network X? A. R5-R2-R1 B. R5-R2-R1 and R5-R3-R1. C. R5-R3-R1 and R5-R4-R1.
7 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 7 D. R5-R2-R1,R5-R3-R1, and R5-R4-R1. Correct Answer: B /Reference: : Every routing protocol supports equal cost path load balancing. In addition, Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) and EIGRP also support unequal cost path load balancing. Use the variance n command in order to instruct the router to include routes with a metric of less than n times the minimum metric route for that destination. The variable n can take a value between 1 and 128. The default is 1, which means equal cost load balancing. Traffic is also distributed among the links with unequal costs, proportionately, with respect to the metric. In this question the variance 3 command is used. In this instance, R5 can get to Net X using the path R5-R3 = metric of 10, and R3-R1 = 10 as well with the FD between R5 - R1 being = 20. Therefore, we can load balance on any route that had an FD of 3x the successor, or 3x20, which is 60 Important Note: If a path does not meet the feasibility condition, the path is not used in load balancing. This is why chose D is wrong as this path has an Advertised Distance of 25 which is greater than the successors FD. The link below refers to an example that is nearly identical to the example in this question, except theirs used a variance of 2 and this question used a variance of 3. Reference: QUESTION 8 The following command was issued on Router 2: Given the above output shown above, which statement is true? A is a redistributed route into EIGRP. B is a summarized route. C is a static route. D is equal path load balancing with E. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: A /Reference: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 8 :
8 When EIGRP learns the routing information from the different routing protocol it uses D EX symbol to indicate that this routing information has learned from other routing protocol. QUESTION 9 A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP connection between RouterA, IP address , and RouterB, IP address Given the debug output on RouterA, which two statements are true? A. RouterA received a hello packet with mismatched metric-calculation mechanisms. B. RouterA received a hello packet with mismatched authentication parameters. C. RouterA will form an adjacency with RouterB. D. RouterA received a hello packet with mismatched autonomous system numbers. E. RouterA received a hello packet with mismatched hello timers. F. RouterA will not form an adjacency with RouterB. Correct Answer: AF /Reference: : Metrics are the mathematics used to select a route. The higher the metric associated with a route, the less desirable it is. For EIGRP, the Bellman-Ford algorithm uses the following equation and creates the overall 24-bit metric assigned to a route: (reliability + K4)] The elements in this equation are as follows: * By default, K1 = K3 = 1, K2 = K4 = K5 = 0. Therefore, by default, the metric formula reduces to: metric = bandwidth + delay K Values should be same to become the EIGRP neighbors. QUESTION 10 Study the exhibit below carefully: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 9
9 If the configuration shown below is added to Router1, which three route entries will EIGRP advertise to neighboring routers? (Select three) router eigrp 10 network eigrp stub A /24 B /24 C /24 D /24 E /8 Correct Answer: CDE /Reference: : The Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Stub Routing feature improves network stability, reduces resource utilization, and simplifies stub router configuration. Stub routing is commonly used in a hub and spoke network topology. In a hub and spoke network, one or more end (stub) networks are connected to a remote router (the spoke) that is connected to one or more distribution routers (the hub). The remote router is adjacent only to one or more distribution routers. The only route for IP traffic to follow into the remote router is through a distribution router. This type of configuration is commonly used in WAN topologies where the distribution router is directly connected to a WAN. The distribution router can be connected to many more remote routers. Often, the distribution router will be connected to 100 or more remote routers. In a hub and spoke topology, the remote router must forward all nonlocal traffic to a distribution router, so it becomes unnecessary for the remote router to hold a complete routing table. Generally, the distribution router need not send anything more than a default route to the remote router. When using the EIGRP Stub Routing feature, you need to configure the distribution and remote routers to use EIGRP, and to configure only the remote router as a stub. Only specified routes are propagated from the remote (stub) router. The router responds to queries for summaries, connected routes, redistributed static routes, external routes, and internal routes with the message "inaccessible." A router that is configured as a stub will send a special peer information packet to all neighboring routers to report its status as a stub router. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 10 Any neighbor that receives a packet informing it of the stub status will not query the stub router for any routes, and a router that has a stub peer will not query that peer. The stub router will depend on the distribution router to send the proper updates to all peers. QUESTION 11 Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP has been configured on routers R1 and R2. However, R1 does not show R2 as a neighbor and does not accept routing updates from R2. What could be the cause of the problem?
10 A. The no auto-summary command has not been issued under the EIGRP process on both routers. B. Interface E0 on router R1 has not been configured with a secondary IP address of /24. C. EIGRP cannot exchange routing updates with a neighbor's router interface that is configured with two IP addresses. D. EIGRP cannot form neighbor relationship and exchange routing updates with a secondary address. Correct Answer: D /Reference: : Remember that simple distance vector routers do not establish any relationship with their neighbors. RIP and IGRP routers merely broadcast or multicast updates on configured interfaces. In contrast, EIGRP routers actively establish relationships with their neighbors, much the same way that OSPF routers do. EIGRP routers establish adjacencies with neighbor routers by using small hello packets. Hellos "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 11 are sent by default every five seconds. An EIGRP router assumes that as long as it is receiving hello packets from known neighbors, those neighbors (and their routes) remain viable. By forming adjacencies, EIGRP routers do the following: Dynamically learn of new routes that join their network Identify routers that become either unreachable or inoperable Rediscover routers that had previously been unreachable QUESTION 12
11 While troubleshooting an EIGRP routing problem you notice that one of the company routers have generated a large number of SIA messages. What are two possible causes for EIGRP Stuck-In- Active routes? (Select two) A. Some query or reply packets are lost between the routers. B. The neighboring router starts receiving route updates from this router. C. A failure causes traffic on a link between two neighboring routers to flow in only one direction (unidirectional link). D. The neighboring router stops receiving ACK packets from this router. Correct Answer: AC /Reference: : The acknowledgement does not reach the destination or they are too delayed. This is normally due to too many routing topology changes, or a router with insufficient memory. Note: In some circumstances, it takes a very long time for a query to be answered. So long, in fact, that the router that issued the query gives up and clears its connection to the router that isn't answering, effectively restarting the neighbor session. This is known as a stuck in active (SIA) route. The most basic SIA routes occur when it simply takes too long for a query to reach the other end of the network and for a reply to travel back. Incorrect Answers: B: Does not apply to SIA. This is the normal operation of EIGRP. D: Ack packets don't reply to Queries, only Reply do.reference: QUESTION 13 EIGRP uses five generic packet types (hello, updates, queries, replies, acknowledgements). If you wished to view the statistics for these packets, which IOS command should you use? A. debug eigrp packets B. show ip eigrp traffic C. show ip eigrp topology "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 12 D. show ip eigrp neighbors Correct Answer: B /Reference: : The show ip eigrp traffic command displays the number of Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) packets sent and received. Example: The following is sample output from the show ip eigrp traffic command: Router# show ip eigrp traffic IP-EIGRP Traffic Statistics for process 77 Hellos sent/received: 218/205 Updates sent/received: 7/23 Queries sent/received: 2/0 Replies sent/received: 0/2 Acks sent/received: 21/14 Reference
12 : a00800ca5a9.html#wp QUESTION 14 While troubleshooting a routing problem on the company EIGRP network you discover that one of the routers is failing to establish adjacencies with its neighbor. What is a likely cause of this problem between neighbors? (Select two) A. The K-values do not match. B. The hold times do not match. C. The hello times do not match. D. The AS numbers do not match. Correct Answer: AD /Reference: : Peer relationships and adjacencies between routers will not be formed between EIGRP routers if the neighbor resides in a different autonomous system or if the metric-calculation mechanism (K values) is misaligned for that link. Incorrect Answers: B: It is possible for two routers to become EIGRP neighbors even though the hello and hold timers do not match.section 2: Troubleshoot OSPF(9 Questions) C: It is possible for two routers to become EIGRP neighbors even though the hello and hold timers "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 13 do not match.section 2: Troubleshoot OSPF(9 Questions) QUESTION 15 A. B. C. D. Correct Answer: /Reference: QUESTION 16 Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the information presented, which statement is true?
13 A. OSPF router is an ABR. B. Network /8 was learned from an OSPF neighbor within the area. C. The default route is learned from an OSPF neighbor. D. A default route is configured on the local router. Correct Answer: B /Reference: : In this example, the network /8 shows that it was leaned via IA, or Inter-area. Since this came from a neighbor in a different area, then the neighbor router at must be an ABR. The various route types used by OSPF are: QUESTION 17 DR (Designated Router) is for environments where many routers on the same network such as Ethernet. In the following presented network, all routers are reloaded simultaneously, and DR is selected as expected. What is the CK-RTC status? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 14
14 A. 2WAY/BDR B. FULL/BDR C. 2WAY/DROTHER D. 2WAY/DR E. FULL/DROTHER F. FULL/DR G. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: E /Reference: : How OSPF Forms Its Neighbors : In this example topology, all routers are running Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) over the Ethernet network:
15 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 15 This is sample output of the show ip ospf neighbor command on R7 and R8: R7# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface WAY/DROTHER 00:00: Ethernet WAY/DROTHER 00:00: Ethernet FULL/DR 00:00: Ethernet FULL/BDR 00:00: Ethernet0 Notice that R7 establishes full adjacency only with the Designated Router (DR) and the Backup Designated Router (BDR). All other routers have a two-way adjacency established. This is normal behavior for OSPF. In this case, the "show ip ospf neighbor"is performed on R4. R4 is the DR (due to higher router ID)so it will have FULL adjacency with all routers including R2. If the "show ip ospf neighbor" had been performed on R1, then it would show 2way/drother with R2. Router4# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/DROTHER 00:00: FastEthernet0/ FULL/DROTHER 00:00: FastEthernet0/ FULL/ BDR 00:00: FastEthernet0/0 Router1# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface WAY/DROTHER 00:00: FastEthernet0/ FULL/BDR 00:00: FastEthernet0/ FULL/DR 00:00: FastEthernet0/0 Reference: QUESTION 18 While troubleshooting some connectivity issues, you issue the "show ip ospf database" in order to examine the link state database. Which three of the statements below are true regarding the OSPF link state database? (Select three) A. Each router has an identical link state database. B. External routes are imported into a separate link state database. C. Synchronization of link state databases is maintained via flooding of LSAs. D. Information in the link state database is used to build a routing table by calculating a shortest- path tree. E. By default, link state databases are refreshed every 10 minutes in the absence of topology changes. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 16 Correct Answer: ACD
16 /Reference: : The Link state database is a collection of link state advertisement for all routers and networks. Each router in the OSPF network maintains an identical database. LSA flooding occurs whenever there is a change in the OSPF topology, ensuring that the databases are synchronized. OSPF also uses the SPF algorithm to build the database tables. Incorrect Answers: B: Only one link state database is maintained, and it is used for all OSPF routes. E: The default refresh time is 30 minutes.reference: Building Scalable Cisco Networks (Cisco Press) page 178. QUESTION 19 Which command should you use to verify what networks are being routed by a given OSPF process? A. show ip ospf B. show ip route C. show ip protocol D. show ip ospf database E. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: C /Reference: : The information displayed by the show ip protocols command is useful in debugging routing operations. Information in the Routing Information Sources field of the show ip protocols output can help you identify a router suspected of delivering bad routing information. For OSPF routers, this command will display the routed networks. Incorrect Answers: A: To display general information about Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing processes, use the show ip ospf command in EXEC mode. This command will display the areas assigned and other useful information, but not the networks being routed.example:r1# show ip ospfrouting Process "ospf 201" with ID Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routeit is an area border and autonomous system boundary routerredistributing External Routes from, igrp 200 with metric mapped to 2, includes subnets in redistribution rip with metric mapped to 2 igrp 2 with metric mapped to 100 igrp 32 with metric mapped to 1Number of areas in this router is 3Area Number of interfaces in this area is 1 Area has simple password authentication SPF algorithm executed 6 times B: This will display the active routing table, but not the networks that are being routed. D: The OSPF database does not display the networks being routed. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 17 QUESTION 20 You have a multi-area OSPF network and you're concerned because one of the sites is having connectivity problem to resources in a different area. Which IOS privileged mode command would you enter to confirm that your network: A) has a path to its ABR, B) has a path to its ASBR, and C) the SPF calculation is functional? A. show ip protocols B. show running-config C. show ip ospf neighbor D. show ip ospf border-routers
17 Correct Answer: D /Reference: : The show ip ospf border-routers command displays the internal OSPF routing table entries to an area border router (ABR) and autonomous system boundary router (ASBR). The SPF No in the output is the internal number of SPF calculation that installs this route. Example: Router R# show ip ospf border-routers OSPF Process 109 internal Routing Table Destination Next Hop Cost Type Rte Type Area SPF No ABR INTRA ABR INTRA ASBR INTER ASBR INTER Incorrect Answers: A: The show ip protocols command only displays routing protocol parameters and current timer values. B: The show running-config command displays the currently used configuration mode. The required information will not be displayed. C: The show ip ospf neighbor command displays OSPF-neighbor information on a per-interface basis. It does not include ABR, ASBR or SPF information. QUESTION 21 An OSPF link can be in multiple states at any given moment (ie. Exstart, exchange, full). Which two IOS commands let you view the state of the link? (Select two) "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 18 A. show ip ospf B. show ip protocols C. show ip ospf neighbor D. show ip ospf interface Correct Answer: CD /Reference: : The link state exstart is an OSPF link state (see note below). We need retrieve OSPF link state information. C: The output of the show ip ospf neighbor command is used To display OSPF-neighbor information on a perinterface basis. It includes link state information. D: The show ip ospf interface command is used to display OSPF-related interface information for a particular interface. This includes the link state of the specified interface. Note: exstart state: After two OSPF neighboring routers establish bi-directional communication and complete DR/BDR election (on multi-access networks), the routers transition to the exstart state. Incorrect Answers: A: The show ip ospf command is used to display general information about OSPF routing processes. However, it does not include any link state information.b: The command "show ip protocols" displays the parameters and current state of the active routing protocol process. It does not show any link state information.
18 QUESTION 22 Which command would display OSPF parameters such as filters, default metric, maximum paths, and number of areas configured on a router? A. show ip protocol B. show ip route C. show ip ospf interface D. show ip ospf E. show ip interface F. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: A /Reference: : The "show ip protocol" command displays values about routing timers and network information associated with the entire router. This includes, the AS number associated with the routing process, number of areas configured on the router, the metric, and the maximum paths. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 19 QUESTION 23 Exhibit: You work as a network technician. You trainee shows you the IOS command output displayed in the exhibit. What command did Tess use to produce this output? A. show ip RIP B. show ipv6 ospf C. show ip ospf
19 D. show ip ospf interface E. show ipv6 ospf interface F. show ipv4 ospf G. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: B /Reference: : In this case we can see that OSPFv3 is being used, and since OSPFv3 is used exclusively for IPv6 networks we know that the correct answer must be "show ipv6 ospf." To display general information about Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing processes, use the show ipv6 ospf command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode. Example: The following is sample output from the show ipv6 ospf command: Router# show ipv6 ospf Routing Process "ospfv3 1" with ID SPF schedule delay 5 secs, Hold time between two SPFs 10 secs "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 20 Minimum LSA interval 5 secs. Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs LSA group pacing timer 240 secs Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa Area BACKBONE(0) Number of interfaces in this area is 1 MD5 Authentication, SPI 1000 SPF algorithm executed 2 times Number of LSA 5. Checksum Sum 0x02A005 Number of DCbitless LSA 0 Number of indication LSA 0 Number of DoNotAge LSA 0 Flood list length 0 Reference: QUESTION 24 Which IOS command would you use to find out which networks are routed by a particular OSPF process? A. show ospf B. show ip route C. show ip protocols D. show ip ospf database E. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: C /Reference:
20 : The show ip protocols command display current routing protocols. It displays the parameters and current state of the active routing protocol process. The output includes a list of the networks routing for individual ospf processes. Sample output: Rt Router # show ip protocols Routing Protocol is "ospf 200" Sending updates every 0 seconds Invalid after 0 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 0 Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 21 Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Redistributing: ospf 200 Routing for Networks: /32 Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update Distance: (default is 110) Incorrect Answers: A: The show ospf command displays summary information regarding the global OSPF configuration. B: The show ip route command displays the IP routing table. D: The show ip ospf database command displays the contents of the topological database maintained by the router. The command also shows the router ID and the OSPF process ID. However, the output does not include the networks routing for individual ospf processes.section 3: Troubleshoot ebgp(21 Questions) QUESTION 25 A problem was reported that the /24 prefix was not injected into the local BGP table on a Company router named R1. The following information is available from this router: R1 Configuration: router bgp network neighbor remote-as no auto-summary Routing table information: show ip route include 10 O /24 [110/11] via , 2d00h, Ethernet0/0 Why is this prefix not in the local BGP table of the R1? A. The neighbor is down. B. The prefix /24 is not a 'connected' route. C. This route is not a BGP learned route. D. The network command is wrong. E. None of the other alternatives apply "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 22 Correct Answer: D
21 /Reference: : The network command is used with IGPs, such as RIP, to determine the interfaces on which to send and receive updates. The command also indicates which directly connected networks to advertise. However, when configuring BGP, the network command does not affect what interfaces BGP runs on. Therefore, configuring just a network statement will not establish a BGP neighbor relationship. This is a major difference between BGP and IGPs. The network statement follows this syntax: Router(config-router)# network network-number [ mask network-mask ] In BGP, the network command tells the BGP process what locally learned networks to advertise. The networks can be connected routes, static routes, or routes learned by way of a dynamic routing protocol, such as RIP. These networks must also exist in the routing table of the local router or they will not be sent out in updates. The mask keyword can be used with the network command to specify individual subnets. Routes learned by the BGP process are propagated by default but are often filtered by a routing policy. In this example, the correct syntax should be "network mask " under the BGP routing process. Without the correct subnet mask specified, the route will not get injected into the BGP routing table, even if it is learned via an IGP. In this case, the route is known via OSPF. QUESTION 26 Which IOS command would you enter if you wanted to view a list of IBGP and EBGP neighbor relationships that are configured? A. show ip bgp B. show ip bgp paths C. show ip bgp peers D. show ip bgp summary E. show ip bgp protocols Correct Answer: D /Reference: : The show ip bgp summary command displays the status of all BGP connections. Neighbors with corresponding AS values will be listed; both interior and external. Incorrect Answers: A: The show ip bgp command displays routes in the BGP routing table, not the neighbors. B: The show ip bgp paths command is used to display all the BGP paths in the database. However, it does not list the neighbors. C: There is no such command.reference: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 23 _r/1rprt1/1rbgp.htm E: There is no such command.reference: _r/1rprt1/1rbgp.htm QUESTION 27 Which two of the following descriptions are correct according to the displayed output of the command show ip bgp summary? (Choose two.)
22 A. The BGP session to the neighbor is established. B. The router is trying to create a BGP peering session with the neighbor. C. The BGP session to the neighbor is created, but the router received no BGP routing updates from the neighbor. D. The router is attempting to establish a BGP peering session with the neighbor. Correct Answer: AD /Reference: : Show ip bgp summary command displays the summary of all BGP connections. The six states of the BGP FSM are described as follows: * Idle - Idle is the first state of a BGP connection. BGP is waiting for a start event. It is normally initiated by an administrator or a network event. At the start event, BGP initializes its resources and resets a connect retry timer. Then it starts listening for a TCP notice that BGP can transition back to Idle from any other state in case of errors. * Connect - In the Connect state, BGP is waiting for the TCP connection to be completed. If the TCP connection is successful, the state transitions to OpenSent. If the TCP connection fails, the state transitions to the Active state, and the router tries to connect again. If the connect retry timer expires, the state remains in the Connect state, the timer is reset, and a TCP connection is initiated. In case of any other event, initiated by the system or the administrator, the state returns to Idle. * Active - In the Active state, BGP is trying to acquire a peer by initiating a TCP connection. If it is successful, it transitions to OpenSent. If the connect retry timer expires, BGP restarts the connect timer and returns to the Connect state. While active, BGP is still listening for a connection "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 24 that may be initiated from another peer. The state may go back to Idle in case of other events, such as a stop event initiated by the system or the operator. In general, a neighbor state that is switching between "Connect" and "Active" is an indication that something is wrong and that there are problems with the TCP connection. It could be because of many TCP retransmissions, or the incapability of a neighbor to reach the IP address of its peer. * OpenSent - In the OpenSent state, BGP is waiting for an open message from its peer. The open message is checked for correctness. In case of errors, such as an incompatible version number or an unacceptable AS, the system sends an error notification message and goes back to idle. If there are no errors, BGP starts sending keepalive messages and resets the keepalive timer. At this stage, the hold time is negotiated and the smaller value is taken. If the negotiated hold time is zero (0), the hold timer and the keepalive timer are not restarted. At the OpenSent state, BGP recognizes whether the peer belongs to the same AS or to a different AS. BGP does this by comparing its AS number to the AS number of its peer. A same AS is an IBGP peer and a different AS is an EBGP peer.
23 When a TCP disconnect is detected, the state falls back to Active. For any other errors, such as an expiration of the hold timer, BGP sends a notification message with the corresponding error code. Then it returns to the Idle state. * OpenConfirm - While in OpenConfirm state, BGP is waiting for a keepalive or notification message. If a keepalive message is received, the state goes to the Established state, and the neighbor negotiation is complete. If the system receives an update or keepalive message, it restarts the hold time, assuming that the negotiated hold time is not zero. If a notification message is received, the state falls back to Idle. The system sends periodic keepalive messages at the rate set by the keepalive timer. In the case of any TCP disconnect or in response to any stop event, initiated by the system or the administrator, the state returns to Idle. In response to any other event, the system sends a notification message with an FSM error code and returns to the Idle state. * Established - Established is the final state in the neighbor negotiation. BGP starts exchanging update packets with its peers. If it is non-zero, the hold timer is restarted at the receipt of an update or keepalive message. QUESTION 28 The "show ip bgp" command was issued on a Router as shown below: Based on the Router2 output, which statement is true? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 25 A. The best path to reach the prefix is via B. The and prefixes were learned via EBGP from the and EBGP neighbors. C. The best path to reach the prefix is via both and ; BGP will automatically load balance between the two. D. The best path to reach the prefix is via E. None of the other alternatives apply. Correct Answer: D /Reference: : The best path to any given destination is noted by the ">" in the IP BGP table. In this case, the best path to is via next hop due to the fact that the weight is higher (101) than the path via the alternative next hop. Weight is a Cisco proprietary method for path determination and the weight value is used above all other values. Within a router, the path with the highest weight will be preferred. QUESTION 29 While verifying BGP operation on the Company router, you issue the "show ip bgp" command as shown below: routerr>show ip bgp BGP table version is , local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal Origin codes: i - IGP, e EGP,? -incomplete
24 Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * > * * * From the information above, which path will the network prefer to take to exit the AS? A B C D E. All of the above will be used in a round robin fashion. Correct Answer: A /Reference: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 26 : Local preference (LocPref) is a well-known discretionary attribute that provides an indication to routers in the AS about which path is preferred to exit the AS. A path with a higher local preference is more preferred. In this scenario the following entry has the highest local preference value of 400. Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path * > The preferred exit path of the AS is therefore , as noted by the">" which refers to the best path for this destination. QUESTION 30 Refer to the exhibit. Router RTR is attempting to establish BGP neighbor relationships with routers RT1 and RT3. On the basis of the information that is presented in the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
25 A. RTR has a BGP password set but neighbor does not. B. Neighbor has a BGP password set but RTR does not. C. RTR has a BGP password set but neighbor does not. D. RTR has a BGP password set but neighbor has an incorrect password set. E. Neighbor has a BGP password set but RTR does not. F. RTR has a BGP password set but neighbor has an incorrect password set. Correct Answer: AF /Reference: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 27 : The above log message means that there is an invalid MD5 password on one neighbor, where the other neighbor is configured for authentication while the other is not. If both sides were configured and there was a password mismatch, the error message would indicated "Bad MD5 digest" not "No MD5 digest." Only one configuration step is required to use BGP password authentication; that step is enabling password authentication on a peer-by-peer basis using the neighbor ip-address password password command. neighbor {ip-address peer-group} password [0-7] password-string
26 QUESTION 31 A company has a BGP network and a BGP route of /24 that should be propagated to all of the devices. The route is not now in any of the routing tables. The administrator determines that an access list is the cause of the problem. The administrator changes the access list to allow this route, but the route still does not appear in any of the routing tables. What should be done to propagate this route? A. Clear the BGP session. B. Change both the inbound and outbound policy related to this route. C. Use the service-policy command to adjust the QOS policy to allow the route to propagate. D. Use the release BGP routing command. Correct Answer: A /Reference: : When configuring BGP, changes made to an existing configuration may not appear immediately. In order to force BGP to clear its table and reset BGP sessions, use the clear ip bgp * command : Router# clear ip bgp * The asterisk (*) is a wildcard that matches all table entries. Therefore, all BGP routes are lost while the neighbor relationships are reset. This is expedient and very useful in a lab situation, but caution should be exercised when issuing this command on a production router. On an Internet backbone router, it may be more appropriate to use this command with a specific IP address, as shown in the following: Router# clear ip bgp QUESTION 32 Refer to the exhibit. Routers RTA and RTB are running BGP but the session is active. What command needs to be added to establish the BGP session? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 28
27 A. ip route s0/0 ip route s0/1 B. network C. no synchronization D. neighbor next-hop-self Correct Answer: A /Reference: : When BGP is running between routers in different autonomous systems, it is called External BGP (EBGP). When BGP is running between routers in the same AS, it is called Internal BGP (IBGP). BGP allows the path that packets take to be manipulated by the AS, as described in this module. It is important to understand how BGP works to avoid creating problems for your AS as a result of running BGP. A static route can be used to form an adjacency between EBGP neighbors. QUESTION 33 Refer to the exhibit. Router RT3 discovers network via BGP. Which one of these statements is true? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 29
28 A. RT1 advertised network /24 with a metric of 782. B. RT3 is directly connected to RT1 using subnet C. RT3 has an IGP metric of 782 to reach D. RT3 has a BGP metric of 782 to reach E. RT1 advertised network /24 with a metric of F. RT3 has an IGP metric of 1782 to reach /24. Correct Answer: C /Reference: : QUESTION 34 Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the information in the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Choose two.) "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 30
29 A. When traffic is sent from the ISP to autonomous system 64512, the traffic will be forwarded to SanJose2 because of the higher MED value of SanJose2. B. The serial 0/0/1 interface on the ISP router has been configured with the set metric 50 command. C. The output was generated by entering the show ip bgp command on the SanJose1 router. D. The output was generated by entering the show ip bgp command on the ISP router. E. The serial 0/0/1 interface on the ISP router has been configured with the set metric 75 command. F. When traffic is sent from the ISP to autonomous system 64512, the traffic will be forwarded to SanJose1 because of the lower MED value of SanJose1. Correct Answer: DF /Reference: : The "show ip route bgp" command will display any BGP-learned routes that make it into the IP routing table, the command "show ip bgp" is required to display the contents of the actual BGP routing table. This output was seen on ISP because the local router ID is (ISP). Since we know that this output must have been seen by ISP, we know the serial 0/0/1 interface has been configured with a metric of 75, as this is the metric to the peer with IP address (the other side of the serial 0/0/1 interface).
30 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 31 QUESTION 35 Refer to the exhibit. All routers are configured for BGP. EBGP routes received on router R2 show up in the BGP table on routers R1 and R3 but not in their IP routing tables. What would cause this? A. EBGP multihop is not configured on routers R1 and R3. B. Routers R1 and R3 do not receive the same routes via an IGP. C. Synchronization in autonomous system 100 is turned is on. D. The BGP routers in autonomous system 100 are not logically fully-meshed. E. Synchronization in autonomous system 100 is turned is off. Correct Answer: BC /Reference: : If your AS passes traffic from another AS to a third AS, BGP should not advertise a route before all routers in your AS learn about the route via IGP. BGP waits until IGP propagates the route within the AS and then advertises it to external peers. A BGP router with synchronization enabled does not install ibgp learned routes into its routing table if it is not able to validate those routes in its IGP. Issue the no synchronization command under router bgp in order to disable synchronization. This prevents BGP from validating ibgp routes in IGP. In this scenario, the routers must learn of the same route via an IGP, or synchronization should be turned off. Since this AS does not appear to be a transit AS, the best solution would be to disable synchronization. Reference: BGP Case Studies, QUESTION 36 The network consists of two separate autonomous systems as shown below: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 32
31 You need to configure Router R2 as a BGP route reflector and Router R1 as the client. Assuming that Router R3 isn't running BGP, which two of the commands below would you enter on R2 to satisfy your goals? (Select two) A. neighbor remote-as B. neighbor remote-as C. neighbor route-reflector-client D. neighbor route reflector-client Correct Answer: BD /Reference: : B: RouterR2(config-router)# neighbor remote-as We configure router R1 ( ) as a neighbor in AS D: RouterR2(config-router)# neighbor route-reflector-client Configures the router R2 as a BGP route reflector and configures the specified neighbor R1 ( ) as its client. Incorrect Answers: A: We must specify router R1 as neighbor, not R2 itself ( ). Furthermore, we should use the local AS (64000), not the remote AS C: We must specify router R1 as route reflector client, not R2 itself ( ). QUESTION 37 The network consists of a series of routers that are all configured for IBGP. Which one of the following IBGP characteristics is true? A. The IBGP routers must always be fully meshed. B. The IBGP routers can be in a different AS. C. The IBGP routers must be directly connected. D. The IBGP routers do not need to be directly connected. E. None of the other alternatives apply are true. Correct Answer: D
32 /Reference: "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 33 : The IBGP routers do not have to be directly connected. The remote IBGP peers need only be reachable via a TCP connection. For example, if the network is also running an interior routing protocol such as EIGRP or OSPF, the remote IBGP router could be many hops away, as long as it is reachable via the IGP that is being used. Incorrect Answers: A: Using route reflectors or confederations a full mesh topology is not necessary. B: The IBGP routers must be placed in the same AS. Peers that are in different autonomous systems are using EBGP, not IBGP. C: The IBGP routers do not have to be directly connected. QUESTION 38 A BGP router is configured as shown below: interface ethernet 0 ip address ! int serial 0 ip address ! router bgp neighbor remote-as Based on the above configuration, which of the following BGP statements would inject the /16 prefix into the BGP routing table? A. network B. network mask C. network mask D. network mask E. network mask Correct Answer: B /Reference: : The /16 mask is equal to , so answer choice B matches the address and the mask. To specify the route as classless, the mask keyword should be included or the network will be summarized at the network boundary. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 34 QUESTION 39 Router R-1 is configured for BGP routing as shown below: router bgp network neighbor remote-as 65300
33 From the perspective of router R-1, what kind of router is the router with IP address ? A. A peer router running IBGP B. A peer router running EBGP C. A community member running IBGP D. A peer group member running IBGP E. A peer group member running EBGP Correct Answer: A /Reference: : Both the local and remote router is configured with the same autonomous system number so they are peer routers running IBGP. QUESTION 40 The BGP routing table consists of the following network routes: What is the correct command to summarize these prefixes into a single summary prefix of /22 while also allowing for the advertisement of the more specific prefixes? A. network mask B. network mask C. network D. aggregate-address E. aggregate-address summary-only F. aggregate-address as-set "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 35 Correct Answer: D /Reference: :
34 To summarize BGP prefixes into one aggregated route, use the "aggregate-address" command. When used alone, this will advertise the aggregate route, along with the individual specific routing entries. To advertise only the aggregated route, use the "summary-only" keyword, as specified in choice E. QUESTION 41 Router R1 needs to be configured to advertise a specific network. Which of the following commands would you use if you wanted to advertise the subnet to the EBGP neighbors on your subnet? A. Router (config-router)#network B. Router (config-router)#network C. Router (config-router)#network-advertise D. Router (config-router)#network mask E. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: D /Reference: : The network command is used to specify the networks to be advertised by the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and multiprotocol BGP routing processes. Syntax: network network-number [ mask network-mask ] [ route-map map-name ] Mask and route-map are optional. If the mask keyword is configured, then an exact match must exist in the routing table. Incorrect Answers: A: If we do not specify the subnet mask then additional networks are allowed to be advertised. The classful subnet mask of is a Class B network. B: This is using the incorrect IP address, as well as a missing subnet mask. C: The network-advertise is an invalid command. QUESTION 42 You are the administrator of a company with BGP connections to multiple ISP's. How could you configure BGP to make it favor one particular ISP for outbound traffic? A. Configure weight B. Enable route reflector "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 36 C. Create a distribute list D. Enable the Longer Autonomous System path option. E. All of the above. Correct Answer: A /Reference: : If the router learns about more than one route to the same destination, the route with the highest weight will be preferred. Weight is a Cisco BGP parameter that is local to the router. When terminating multiple ISP connections into the same router, weight can be used to affect which path is chosen for outbound traffic. Incorrect Answers: B: A route reflector cannot be used to influence outbound traffic. A route reflector modifies the BGP split horizon rule by allowing the router configured as the route reflector to propagate routes learned by IBGP to other IBGP peers. This saves on the number of BGP TCP sessions that must be maintained, and also reduces the BGP routing traffic.
35 C: Distribute lists restrict the routing information that the router learns or advertises. By itself a distribute list cannot make routes from one ISP be preferred to routers from another ISP. D: This choice describes ASD path pre-pending, which would be used to influence the path that incoming traffic takes, not outgoing. QUESTION 43 An ISP is running a large IBPG network with 25 routers. The full mesh topology that is currently in place is inefficiently using up bandwidth from all of the BGP traffic. What can the administrator configure to reduce the number of BGP neighbor relationships within the AS? A. Route reflectors B. Route maps C. Route redistribution D. Peer groups E. Aggregate addresses Correct Answer: A /Reference: : In general, all IBGP peers must be configured to be fully meshed. If they are not, then all of the IBGP routers will not have the updated information from the external BGP routers. There are two ways to overcome the scalability issues of a full IBGP mesh: route reflectors and confederations. With route reflectors, internal BGP routers peer only with the route reflector, and then the route reflectors connect with each other. This can considerably reduce the number of IBGP sessions. Another solution to the scalability problem of IBGP is the use of confederations. With confederations, the AS is broken up into smaller, more manageable sub autonomous systems. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 37 QUESTION 44 What are the two reasons for the appearance of as the next hop for a network when using the "show ip bgp" command? (Choose two) A. The network was originated via redistribution of an interior gateway protocol into BGP. B. The network was defined by a static route. C. The network was learned via IBGP. D. The network was learned via EBGP. E. The network was originated via a network or aggregate command. Correct Answer: AE /Reference: : From BGP FAQ on : Q. What does a next hop of mean in the show ip bgp command output? A. A network in the BGP table with a next hop address of means that the network is locally originated via redistribution of Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) into BGP, or via a network or aggregate command in the
36 BGP configuration. Reference: o QUESTION 45 Refer to the exhibit diagram and configuration. RTB is summarizing its networks from AS with the aggregate-address command. However, the show ip route command on RTA reveals the RTB individual networks as well as its summary route. Which option would ensure that only the summary route would appear in the routing table of RTA? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 38 A. Add a static route with a prefix of pointing to the null0 interface. B. Create a route map permitting only the summary address. C. Delete the four network statements and leave only the aggregate-address statement in the BGP configuration. D. Add the keyword summary-only to the aggregate-address command. Correct Answer: D /Reference: : The aggregate-address <address> <netmask> command advertises the summary address as well as theadvertisement of the more specific routes. The purpose of aggregate-address <network> <netmask> summary-only command is to suppress the
37 advertisement of more specific routes. QUESTION 46 Refer to the exhibit. BGP has been configured on the routers in the network. However, the IBGP peers in autonomous system have not converged. In addition, this console message was generated on router R2: *Mar 1 03:09:07.729: %TCP-6-BADAUTH No MD5 digest from (179) to (11002) On the basis of the information that is provided, what is the cause of the problem? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 39 A. OSPF must be configured with the same MD5 authentication. B. BGP authentication can be used on ibgp peers when the connection is configured between the loopback interfaces. C. BGP authentication can be used on ebgp peers only. D. The password that is used for BGP authentication on both BGP peers in autonomous system must be the same. Correct Answer: D /Reference: : The above log message is relating the invalid MD5 password on neighbor. Both peers need to use the same password for MD5 authentication.
38 QUESTION 47 Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct? (Choose two.) A. All the routes were redistributed into BGP from an IGP. B. All the routes were originated by BGP with the network command. C. All six routes will be installed in the routing table. "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 40 D. Four routes will be installed in the routing table. E. Two routes will be installed in the routing table. Correct Answer: AD /Reference: : Because the AS paths shown all end with a? we know that all of the routes had beed redistributed into BGP. The four best paths, as noted with the > sign, will all be inserted into the routing table. Section 4: Troubleshoot routing redistribution solution (5 Questions) QUESTION 48 During a redistribution of routes from OSPF into EIGRP, the administrator notices that none of the OSPF routes are showing up in EIGRP. What are two possible causes? (Choose two.) A. Incorrect distribute lists have been configured B. Missing ip classless command C. CEF not enabled D. No default metric configured for EIGRP Correct Answer: AD /Reference: : Possible reasons for OSPF routes not showing up include the use of distribute lists to control routing and no metric is configured either with the redistribute command or with default-metric. Remember while redistributing into RIP or EIGRP, you should provide the metric. Here are the default seed metrics for various protocols:
39 RIP : Infinity EIGRP : Infinity OSPF : 20 IS-IS: 0 QUESTION 49 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 41 Refer to the exhibit and the partial configuration on router R2. On router R4 all RIP routes are redistributed into the OSPF domain. A second redistribution is configured on router R2 using a route map. Based on the configuration on router R2, which EIGRP external routes will be present in the routing table of R1? Select the best response. A. There will be no EIGRP external routes in the routing table of R1. B. The routes originating from the RIP routing domain. C. Only routes originating in the OSPF routing domain. D. All routes originating from RIP and OSPF routing domains. E. None of the other alternatives apply. Correct Answer: C
40 /Reference: : The route-map command is used to configure policy routing, which is often a complicated task. A route map is defined using the syntax shown in the figure. Syntax: RouterA(Config)#route-map map-tag [permit deny ] <Sequence Number> RouterA(Config-map-router)# The map-tag is the name, or ID, of the route map. This map-tag can be set to something easily recognizable name. The route-map command changes the mode on the router to the route-map configuration mode, from there conditions can be configured for the route map. Route maps operate similar to access lists, by examining one line at a time and when a match is found, action is taken. Route maps are different from numbered access lists because they can be modified without changing the entire list. Each route map statement is given a number. If a "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 42 sequence number is not specified, the first route map condition will automatically be numbered as ten (10). The second condition will automatically be numbered as 20, and so on. The optional sequence number can be used to indicate the position that a new route map is to have in the list of route maps already configured with the same name. In this exhibit an access-list is created to deny from and (RIP Domain) and that is called by route-map ABC. While redistributing OSPF routes into EIGRP the RED rout-map is used; and it denies advertising the RIP domain network into EIGRP. QUESTION 50 Refer to the exhibit. The routing protocols EIGRP and OSPF have been configured as indicated in the exhibit. Given the partial configuration of router R2, which network will be present in the routing table of R4? A. Network B B. Network A and Network B C. Network A
41 D. neither Network A nor Network B "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 43 Correct Answer: A /Reference: : In this exhibit the OSPF domain is redistributed into the EIGRP 100 domain so Network B will present into Router R4. However, the Network A network will not be seen on router R4 (The bottom router which is improperly labeled Network B) because EIGRP 50 was not redistributed into EIGRP 100. QUESTION 51 Refer to the network shown below: R1 and R2 belong to the RIP routing domain that includes the networks /16 and /16. R3 and R4 are performing two-way route redistribution between OSPF and RIP. A network administrator has discovered that R2 is receiving OSPF routes for the networks /16 and /16 and a routing loop has occurred. Which action will correct this problem? A. Set the OSPF default metric to 20. B. Apply an inbound ACL to the R2 serial interface. C. Configure distribute-lists on R3 and R4. D. Change the RIP administrative distance on R3 to 110. E. Change the OSPF administrative distance on R3 to 110. F. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: C /Reference: : Use the distribute-list command to pick and choose which routing updates a router will send or receive. By referencing an access list, the distribute-list creates a route filter. This is a set of rules that precisely controls what routes a router will send or receive in a routing update. This command is available for all IP routing protocols and can be applied to either inbound or outbound routing updates. When applied to inbound updates, the syntax for configuring a route filter is as follows: Router(config-router)# distribute-list access-list-number in [ interface-name ] When applied to outbound updates, the syntax can be more complicated as shown in the following:
42 "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 44 Router(config-router)# distribute-list access-list-number out [ interface-name routing-process as-number ] The routing-process and as-number options are invoked when exchanging routes between different routing protocols. QUESTION 52 RIP and OSPF are configured on the routers as shown in the exhibit. R2 is configured with a two- way redistribution between RIP and OSPF domains. All routers can ping each other, but R1 cannot see any of the OSPF routes in its routing table. What could the problem be? A. OSPF and RIP use the same major network Therefore, the keyword subnets is not required to redistribute protocols into OSPF. B. Because OSPF has a longer mask for the same major network than RIP and because RIP version 1 is being used, none of the routes learned from OSPF will be advertised into RIP. C. The metric for the OSPF routes that are redistributed into RIP is too low, a fact that prevents OSPF routes from being advertised into RIP. D. The process of redistribution of RIP into OSPF does not require any metric conversion, so there is no need to define the metric using the default-metric command during the redistribution. Correct Answer: B
43 /Reference: : The subnets keyword tells OSPF to redistribute all subnet routes. Without the subnets keyword, only networks that are not subnetted are redistributed by OSPF. Example: Router A(config)# router ospf 109 Router A(config-router)# redistribute rip subnets Router "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 45 A(config-router)# network area 0 Router A(config-router)# network area 0 Section 5: Troubleshoot a DHCP client and server solution (13 Questions) QUESTION 53 What is the purpose of configuring router R1 with the "IP Helper address" command? A. IP Helper is used to direct BOOTP clients to a BOOTP server. B. IP Helper is used to prevent the router form forwarding IP broadcasts. C. IP Helper is used to allow IPX clients to communicate with IP-based servers. D. IP Helper is used to accommodate compatibility routers using different IP routing protocols. E. None of the other alternatives apply Correct Answer: A /Reference: : The ip helper-address command is used to have the Cisco IOS software forward User Datagram Protocol (UDP) broadcasts, including BOOTP, received on an interface. DHCP protocol information is carried inside of BOOTP packets. To enable BOOTP broadcast forwarding for a set of clients, configure a helper address on the router interface closest to the client. The helper address should specify the address of the DHCP server. Note: A DHCP server can be considered to be a BOOTP server, even though a DHCP server is more advanced. Incorrect Answers: B: Combined with the ip forward-protocol global configuration command, the ip helper-address command allows you to control which broadcast packets and which protocols are forwarded. However, the main purpose of the IP helper feature is not to prevent the router from forwarding IP broadcasts. C: IP helper does not use IPX. D: This is false. QUESTION 54 When you execute the "ip helper-address" command on a router, which three UDP ports get enabled automatically by default? (Select three) A. 53 (DNS) "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 46 B. 69 (TFTP) C. 515 (LPR) D. 161 (SNMP) E. 49 (TACACS)
44 Correct Answer: ABE /Reference: : To forward the BootP/DHCP request from the client to the DHCP server, the ip helper-address interface command is used. The IP helper-address can be configured to forward any UDP broadcast based on UDP port number. By default, the IP helper-address will forward the following UDP broadcasts: DNS (port 53), time service (port 37) Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) (port 69) Terminal Access Control Access Control System (TACACS) service (port 49) NetBIOS name server (port 137) NetBIOS datagram server (port 138) Boot Protocol (DHCP/BootP) client and server datagrams (ports 67 and 68) IEN-116 name service (port 42) Reference: Understanding and Troubleshooting DHCP in Catalyst Switch or Enterprise Networks QUESTION 55 Refer to the exhibit. Router RTA has been configured as a DHCP server. The two debug commands will generate output on RTA when Host A requests an IP address. Which set of DHCPD debug messages is in the correct sequence? "Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - Guaranteed 47 A. DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client DHCPD: Sending DHCPACK to client B. DHCPD: DHCPDISCOVER received from client DHCPD: DHCPREQUEST received from client DHCPD: Sending DHCPOFFER to client
Exam Code : Version: Free Demo. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!
 Vendor : Cisco Exam Code : 642-832 Version: Free Demo IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way Cheat-Test.us - The Worldwide Renowned IT Certification Material Provider The safer, easier way to help you
Vendor : Cisco Exam Code : 642-832 Version: Free Demo IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way Cheat-Test.us - The Worldwide Renowned IT Certification Material Provider The safer, easier way to help you
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min.
 300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Cisco Building Scaleable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Practice Test. Version https://certkill.com
 Cisco 642-901 642-901 Building Scaleable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Practice Test Version 2.12 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 642-901: Practice Exam A company has a BGP network and a BGP route of 196.27.125.0/24
Cisco 642-901 642-901 Building Scaleable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Practice Test Version 2.12 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 642-901: Practice Exam A company has a BGP network and a BGP route of 196.27.125.0/24
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing
 Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
CertifyMe. CertifyMe
 CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Configuring BGP. Cisco s BGP Implementation
 Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Configuring BGP This chapter describes how to configure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For a complete description of the BGP commands in this chapter, refer to the BGP s chapter of the Network Protocols
Introduction. Keith Barker, CCIE #6783. YouTube - Keith6783.
 Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
Module 6 Implementing BGP
 Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name Score Grade Question Answer Question Answer
 CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-5-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
exam. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: Cisco
 300-101.exam Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 Cisco 300-101 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version 1.0 Exam A QUESTION 1 Company A recently acquired Company
300-101.exam Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 1.0 Cisco 300-101 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version 1.0 Exam A QUESTION 1 Company A recently acquired Company
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min.
 300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Company A recently acquired Company B and the network infrastructures are being merged. Both organizations used non-overlapping
300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Company A recently acquired Company B and the network infrastructures are being merged. Both organizations used non-overlapping
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training
 REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-8-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 8 Exam Answers
This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics:
 Appendix C BGP Supplement This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics: BGP Route Summarization Redistribution with IGPs Communities Route
Appendix C BGP Supplement This appendix contains supplementary Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) information and covers the following topics: BGP Route Summarization Redistribution with IGPs Communities Route
Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP
 Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Section 6. Implementing EIGRP ICND2
 ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1
 IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Fast IP Convergence. Section 4. Period from when a topology change occurs, to the moment when all the routers have a consistent view of the network.
 Fast IP Convergence Section 4 2899_05_2001_c1 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 IP Convergence Convergence Time Period from when a topology change occurs, to the moment when all the routers
Fast IP Convergence Section 4 2899_05_2001_c1 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 IP Convergence Convergence Time Period from when a topology change occurs, to the moment when all the routers
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 642-901 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks Vendors : Cisco Version
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 642-901 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks Vendors : Cisco Version
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
EIGRP Stub Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About EIGRP Stub Routing. EIGRP Stub Routing
 The EIGRP stub routing feature improves network stability, reduces resource utilization, and simplifies the stub device configuration. Stub routing is commonly used in hub-and-spoke network topologies.
The EIGRP stub routing feature improves network stability, reduces resource utilization, and simplifies the stub device configuration. Stub routing is commonly used in hub-and-spoke network topologies.
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4
 Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4 This chapter provides details on how to configure Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP4) on HP products using the CLI and the Web management interface. BGP4 is supported on
Chapter 13 Configuring BGP4 This chapter provides details on how to configure Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGP4) on HP products using the CLI and the Web management interface. BGP4 is supported on
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Hands-On ROUTE Implementing Cisco IP Routing CCNP Course 1
 Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
Hands-On CCNP Course 1 Course Description Revised CCNP Curriculum and Exams Cisco has redesigned the CCNP courses and exams to reflect the evolving job tasks of global network professionals. Course 1 ROUTE
The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Exam : : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Title. Ver :
 Exam : 642-801 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver : 03-22-05 QUESTION 1 A packet that needs to be forwarded arrives on an interface of a router. In order for a router to route data,
Exam : 642-801 Title : Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI) Ver : 03-22-05 QUESTION 1 A packet that needs to be forwarded arrives on an interface of a router. In order for a router to route data,
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Quickest Way To Get Certified (BSCI ) TestKing's Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks. Version 20.
 WWW.REAL-EXAMS.NET The Quickest Way To Get Certified 642-801 (BSCI ) TestKing's Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks Version 20.1 WWW.REAL-EXAMS.NET Please Read Carefully This Study Guide has been carefully
WWW.REAL-EXAMS.NET The Quickest Way To Get Certified 642-801 (BSCI ) TestKing's Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks Version 20.1 WWW.REAL-EXAMS.NET Please Read Carefully This Study Guide has been carefully
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent. Exam Code: 4A Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability.
 Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-101 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Version: Demo QUESTION 1 When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-101 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Version: Demo QUESTION 1 When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match
Internet Routing Protocols Tuba Saltürk
 Internet Routing Protocols 15505068 Tuba Saltürk Outline Internet Routers Routing Protocol Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) Distance- Vector Routing Protocol Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Interior
Internet Routing Protocols 15505068 Tuba Saltürk Outline Internet Routers Routing Protocol Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) Distance- Vector Routing Protocol Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Interior
Implementing Cisco IP Routing E-Learning
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing E-Learning Duration: 1 Day Course Code: E-ROUTE Overview: In this course, administrators of medium-to-large network sites will learn to use advanced routing to provide scalability
Implementing Cisco IP Routing E-Learning Duration: 1 Day Course Code: E-ROUTE Overview: In this course, administrators of medium-to-large network sites will learn to use advanced routing to provide scalability
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Part II. Chapter 3. Determining IP Routes
 Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Part II Chapter 3 Routers perform two main functions: switching and routing. The switching function is the process of moving packets from an inbound interface to an outbound interface. The switching function
Operation Manual Routing Protocol. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IP Routing Protocol Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to IP Route and Routing Table... 1-1 1.1.1 IP Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Routing Table... 1-1 1.2 Routing Management
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IP Routing Protocol Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to IP Route and Routing Table... 1-1 1.1.1 IP Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Routing Table... 1-1 1.2 Routing Management
ABR (Area Border Router), 206, 216 access, dedicated networks, 23 access layer, three-layer hierarchical design model, 6
 1358_fmi.book Page 460 Thursday, May 27, 2004 2:21 PM A ABR (Area Border Router), 206, 216 access, dedicated networks, 23 access layer, three-layer hierarchical design model, 6 access lists, scalable networks,
1358_fmi.book Page 460 Thursday, May 27, 2004 2:21 PM A ABR (Area Border Router), 206, 216 access, dedicated networks, 23 access layer, three-layer hierarchical design model, 6 access lists, scalable networks,
Two types of routing protocols are used in internetworks: interior gateway protocols (IGPs) and exterior gateway protocols (EGPs).
 Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF
 Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands
 Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Building Scalable
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNP: Building Scalable
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
 ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
 The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
CCNP 1: Advanced Routing
 Scope and Sequence CCNP 1: Advanced Routing Cisco Networking Academy Program Version 3.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CCNP 1: ADVANCED ROUTING...1 TARGET AUDIENCE...3 PREREQUISITES...3 COURSE DESCRIPTION...3 COURSE
Scope and Sequence CCNP 1: Advanced Routing Cisco Networking Academy Program Version 3.1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CCNP 1: ADVANCED ROUTING...1 TARGET AUDIENCE...3 PREREQUISITES...3 COURSE DESCRIPTION...3 COURSE
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Link State. 1 Flooding of link-state information. 5 Routing Table. 3 SPF Algorithm. 2 Building a Topological Database. 4 SPF Tree
 Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Configuring BGP community 43 Configuring a BGP route reflector 44 Configuring a BGP confederation 44 Configuring BGP GR 45 Enabling Guard route
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
8. Refer to the exhibit. The ORL router is unable to form a neighbor relationship with the JAX router. What is a possible cause of this problem?
 1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
Real4Test. Real IT Certification Exam Study materials/braindumps
 Real4Test http://www.real4test.com Real IT Certification Exam Study materials/braindumps Exam : 400-101 Title : CCIE Routing and Switching Written Exam v5.1 Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
Real4Test http://www.real4test.com Real IT Certification Exam Study materials/braindumps Exam : 400-101 Title : CCIE Routing and Switching Written Exam v5.1 Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
OSPFv3 Commands. address-family (OSPFv3), page 4. authentication (OSPFv3), page 7
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
Overview. Information About Layer 3 Unicast Routing. Send document comments to CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter introduces the basic concepts for Layer 3 unicast routing protocols in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About Layer 3 Unicast Routing, page
CHAPTER 1 This chapter introduces the basic concepts for Layer 3 unicast routing protocols in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About Layer 3 Unicast Routing, page
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7
 EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Exam : Title : Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert. Ver :
 Exam : 350-001 Title : Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert Ver : 11-26-07 QUESTION 1: Under the OSPF process of your router's configuration, you type in "redistribute igrp 25 metric 35 subnets" in order
Exam : 350-001 Title : Cisco Certified Internetworking Expert Ver : 11-26-07 QUESTION 1: Under the OSPF process of your router's configuration, you type in "redistribute igrp 25 metric 35 subnets" in order
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Passit4Sure.4A Questions 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
 Passit4Sure.4A0-101.300Questions Number: 4A0-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
Passit4Sure.4A0-101.300Questions Number: 4A0-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
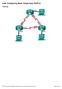 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
BGP can also be used for carrying routing information for IPv6 prefix over IPv6 networks.
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Border Gateway Protocol (). About, page 1 Guidelines for, page
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Border Gateway Protocol (). About, page 1 Guidelines for, page
COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route Duration: 40 Hours
 COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route 300-101 Duration: 40 Hours CCNP Route Training Day 1: Connecting Remote Locations Principles of Static Routing Configuring an IPv4 Static Route Configuring a Static Default
COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route 300-101 Duration: 40 Hours CCNP Route Training Day 1: Connecting Remote Locations Principles of Static Routing Configuring an IPv4 Static Route Configuring a Static Default
FiberstoreOS. IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
OSPF. OSPF processs can be enabled on 2 levels
 OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Routing Protocols. Autonomous System (AS)
 Routing Protocols Two classes of protocols: 1. Interior Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) 2. Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous System (AS) What is an AS?
Routing Protocols Two classes of protocols: 1. Interior Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) 2. Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous System (AS) What is an AS?
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
EIGRP. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9. Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech
 Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
Implementing cisco ip routing
 Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
Cisco 642-902 Implementing cisco ip routing Version Demo Topic 1: Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements QUESTION 1 Which three statements about the EIGRP routing
