Testing Riverstone RS MPLS Interoperability with Cisco GSR and Juniper M Series Routers
|
|
|
- Scott Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 #127 TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPER Page: 1 of 40 Testing Riverstone RS MPLS Interoperability with Cisco GSR and Juniper M Series Routers Ray Qiu, Riverstone Networks ABSTRACT MPLS interoperability is an important concern for service providers deploying or considering the deployment of MPLS networks. This paper demonstrates the interoperability of the Riverstone RS Router s MPLS implementation with that of two important core routers: the Cisco Systems GSR and Juniper Networks M series routers. You can use the procedures in this paper to replicate the tests. The interoperability tests here described focus on two aspects of MPLS interoperability: the creation and use of Label Switch Paths (LSPs), and use of the control plane with RSVP-TE and LDP to setup LSPs and the forwarding plane that forwards packets through LSPs. IS-IS is used as the IGP in the tests, and IS-IS Traffic Engineering Extension interoperability is verified. Sample OSPF configurations are shown in Appendix D, which can be used to do the tests with OSPF as the IGP. Due to limitations of the GSR and M20, the tests do not include testing of L2 tunneling LSPs (based on the Martini draft). The GSR and M20 can only act as the LSR and not the LER in a Martini setup. For this reason the tests focus on LDP and RSVP-TE. The tests successfully demonstrate that the MPLS implementations of Riverstone Networks, Cisco Systems, and Juniper Networks are highly interoperable. TEST ENVIRONMENT The test environment consists of four routers in a fully meshed network topology as shown in Figure 1. All links between routers are Gigabit Ethernet. Hardware: 2 x Riverstone RS8000 with two MPLS GE modules each 1 x Cisco GSR with one 3-port GE module 1 x Juniper M20 with 3 GE ports
2 Page: 2 of 40 Software: Riverstone RS: ROS Cisco GSR 12008: IOS 12.0(18)ST Juniper M20: JUNOS 4.4R2.3 The appendix lists all of the configurations used in the tests. These tests do not include performance testing, as this is outside the scope of an interoperability test. CSCO Loopback0: /32 ISO: JNPR Loopback0: /32 ISO: gi4/ /30 gi4/0 gig4/ / ge-0/0/0.2 ge-0/1/0 M20.17 ge-0/2/ / / /30.14 gi gi gi gi.2.2 gi.3.1 gi.3.1 RS /30.22 RS8000 RSTN1 Loopback0: /32 ISO: RSTN2 Loopback0: /32 ISO: Figure 1 MPLS Interoperability Test Topology RSVP-TE INTEROPERABILITY TEST This test verifies the creation of LSPs across different paths using the RSVP-TE signaling protocol, and tests RSVP-TE interoperability. Parameters There are three different label switching router (LSR) functions: ingress, transit, and egress. In order to demonstrate interoperability over an arbitrary path, a set of permutations of possible paths are created as shown in Table 1. TABLE 1 Ingress Transit Egress RSTN1 CSCO RSTN2 RSTN1 JNPR RSTN2 RSTN1 RSTN2 CSCO RSTN1 RSTN2 JNPR RSTN1 JNPR CSCO CSCO RSTN2 JNPR JNPR RSTN1 CSCO RSTN1 CSCO, JNPR RSTN2
3 Page: 3 of 40 Results All LSPs were created and became operational. The testing, therefore, successfully demonstrates that the MPLS RSVP-TE implementations are interoperable. Specifically, the following RSVP objects are interoperable between Riverstone Networks, Cisco Systems, and Juniper Networks routers: " EXPLICIT_ROUTE " LABEL_REQUEST " LABEL " SESSION " RECORD_ROUTE Riverstone and Juniper both support RSVP hello extension, and the RSVP hello implementations are interoperable. Cisco does not support RSVP hello extensions at this time. All configurations and show output are listed in Appendix A. IS-IS TRAFFIC ENGINEERING INTEROPERABILITY TEST This test determines if the routers can interoperate to setup LSPs according to constraints. It determines whether the routers are sending correct information in the sub-tlvs in the new IS-IS extended IS reachability TLV (type 22). Parameters Riverstone Networks and Juniper Networks routers support creating administrative groups, while Cisco Systems routers assign the link color directly using a 32-bit affinity value. Administrative groups are created according to Table 2. The links between the routers are colored, that is, given different administrative groups as shown in Figure 2. All LSPs are created with administrative group constraints. LSP path selection is computed using CSPF. Administrative Groups TABLE 2 Administrative groups Riverstone Networks Juniper Networks Blue 0 0 Red 1 1 Yellow 2 2
4 Page: 4 of 40 CSCO Loopback0: /32 ISO: gi4/ /30 ge-0/0/0 JNPR Loopback0: /32 ISO: gi4/1 gig4/ / ge-0/1/0.17 ge-0/2/ / / /30.14 gi gi gi gi.2.2 gi.3.1 gi.3.1 RS /30.22 RS8000 RSTN1 Loopback0: /32 ISO: RSTN2 Loopback0: /32 ISO: Figure 2: Topology with Link Colors Results All LSPs are correctly created and become operational. The testing demonstrates that the administrative group and the ISIS-TE implementations are interoperable. The following sub-tlvs are successfully exchanged. These sub-tlvs comprise the entire set as described in the I-D "draft-ietf-isis-traffic-03.txt". TABLE 3 IS-IS sub-tlvs exchanged Sub-TLV number Sub-TLV name 3 Administrative group (color) 6 IPv4 interface address 8 IPv4 neighbor address 9 Maximum link bandwidth 10 Reservable link bandwidth 11 Unreserved bandwidth 18 TE Default metric All configurations and show output are listed in Appendix B.
5 Page: 5 of 40 Administrative Group Implementation Differences Please note that the administrative group implementations are the same between Riverstone Networks and Juniper Networks, but are different with Cisco Systems. In Riverstone s ROS and Juniper s JUNOS, you can place circuits in different administrative groups, that is, color circuits. LSPs without constraints can traverse circuits of any colors including uncolored circuits. LSPs constrained to include circuits of specified colors are only allowed to traverse circuits of at least one of the included colors. This selection is a logical OR. LSPs constrained to exclude circuits of a specified color are not allowed to traverse the circuits that contain the color. In Cisco s IOS, you can also color circuits and constrain the LSPs to a set of colors. However, the default behaviors are different. LSPs with no constraints can traverse only uncolored circuits. Cisco IOS uses a logical AND, rather than a logical OR. Cisco s implementation also uses affinity bits and masks to constrain circuits and LSPs to administrative groups. Table 4 identifies the differences of the administrative group implementations in detail. TABLE 4 Differences in administrative groups Riverstone/Juniper Cisco Description Include/exclude Affinity bits and masks Include group 0 Include group 0 Exclude group 2 Exclude group 1 Exclude all Include group 0,2 Exclude group 1 No equivalent 0x1 mask 0x1 0x1 mask 0x5 0x0 mask 0x2 0x0 mask 0xFFFFFFFF No equivalent 0x7 mask 0xFFFFFFFF Include circuits that contain group 0. The circuits can contain other groups. Include circuits that contain group 0 and that do not contain group 2. The circuits can contain other groups. Exclude circuits that contain group 1. The circuits can contain other groups. Uncolored circuits. Include circuits that contain group 0 or 2 and that do not contain group 1. Include circuits that contain group 0, 1 and 2. The circuits can not contain other groups.
6 Page: 6 of 40 LDP INTEROPERABILITY TEST This test determines if the routers can interoperate to setup LSPs using LDP. It also determines whether the routers can correctly use the LSPs as in BGP next-hop resolution. Parameters Riverstone Networks, Juniper Networks, and Cisco Systems routers support unsolicited LDP by default. That is, the MPLS labels are provided by the downstream LDP peers automatically. In this test, the circuit between the two RS routers are disabled. All routers are assigned to AS The two RS routers run IBGP sessions between each other, but the Cisco GSR and Juniper M20 only run IS-IS as the IGP. The IS-IS metrics are set up so that RSTN1 will prefer to use CSCO to get to RSTN2, but RSTN2 will prefer to use JNPR to get back to RSTN1. RSTN1 and RSTN2 introduce some external routes into the AS which are not redistributed into IS-IS. So by verifying that RSTN1 and RSTN2 can access the external routes generated by the opposite remote peer, we know that the routers are using the LSPs to pass traffic. In this test, the BGP next-hop self option is set. The test topology is shown below in Figure 3. CSCO Loopback0: /32 ISO: JNPR Loopback0: /32 ISO: gi4/ /30 gi4/0 gig4/ / ge-0/0/0.2 ge-0/1/0 M20.17 ge-0/2/ / / / gi.2.1 gi gi gi.2.2 RS8000 RSTN1 Loopback0: /32 ISO: RS8000 RSTN2 Loopback0: /32 ISO: Figure 3: LDP Interoperability Test Topology Results The LDP prefix/label mappings are advertised correctly. RSTN1 and RSTN2 can access the external routes through the LDP LSPs. The testing demonstrates that the LDP implementations of Riverstone Networks, Juniper Networks, and Cisco Systems routers are interoperable. All configurations and show output are listed in Appendix C.
7 Page: 7 of 40 APPENDIX A: RSVP-TE TEST CONFIGURATIONS AND SHOW OUTPUT CSCO (Cisco GSR 12008) Configuration version 12.0 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname CSCO boot system flash slot0:gsr-p-mz st.bin enable password cisco ip subnet-zero no ip domain-lookup mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng signalling advertise implicit-null mpls traffic-eng reoptimize timers frequency 0 no tag-switching ip no tag-switching advertise-tags clns routing interface Loopback0 ip address ip router isis interface Tunnel0 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast tunnel destination tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 explicit identifier 1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng record-route interface GigabitEthernet4/0 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls traffic-eng tunnels no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth interface GigabitEthernet4/1 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls traffic-eng tunnels no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth interface GigabitEthernet4/2 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls traffic-eng tunnels no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth
8 Page: 8 of 40 router isis mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0 mpls traffic-eng level-1 net is-type level-1 metric-style wide ip classless no ip pim bidir-enable ip explicit-path identifier 1 enable next-address next-address next-address no cdp run line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 timeout login response 0 login ip netmask-format hexadecimal line aux 0 line vty 0 3 timeout login response 0 password cisco login line vty 4 access-class 1 in timeout login response 0 password cisco login autocommand show version end CSCO Show Output CSCO#show mpls traffic-eng tunnels Name: CSCO_t0 (Tunnel0) Destination: Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 1, type explicit 1 (Basis for Setup, path weight 15) Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x0/0xFFFF Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled(0/32) 0 Bandwidth Requested: 0 InLabel : - OutLabel : GigabitEthernet4/2, 18 RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 0, Tun_Instance 7 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
9 Page: 9 of 40 RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits History: Tunnel: Time since created: 52 minutes, 58 seconds Time since path change: 3 minutes, 59 seconds Current LSP: Uptime: 3 minutes, 59 seconds Selection: reoptimation Prior LSP: ID: path option 1 [6] Removal Trigger: path verification failed LSP Tunnel lsp1-jnpr-rstn1-csco is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/1, implicit-null OutLabel : - RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 27, Tun_Instance 1 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: NONE Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=inf RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=inf LSP Tunnel lsp1_rstn1-csco-rstn2 is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/1, 16 OutLabel : GigabitEthernet4/2, implicit-null RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 16392, Tun_Instance 205 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits LSP Tunnel lsp3_rstn1-rstn2-csco is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/2, implicit-null OutLabel : - RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 16393, Tun_Instance 204 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: NONE Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=inf LSP Tunnel lsp5_rstn1-csco-jnpr_rstn2 is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/1, 17 OutLabel : GigabitEthernet4/0, RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 16395, Tun_Instance 203 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits
10 Page: 10 of 40 RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits LSP Tunnel lsp6_rstn1-jnpr-csco is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/0, implicit-null OutLabel : - RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 16396, Tun_Instance 43 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: NONE Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=inf JNPR (Juniper M20) Configuration version 4.4R2.3; system { host-name JNPR; syslog { user * { any emergency; file messages { any notice; authorization info; interfaces { ge-0/0/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; ge-0/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; ge-0/2/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls;
11 Page: 11 of 40 lo0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /32; address /32; family iso { address ; routing-options { router-id ; protocols { rsvp { interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; mpls { label-switched-path lsp1-jnpr-rstn1-csco { to ; primary JNPR-RSTN1-CSCO { no-cspf; path JNPR-RSTN1-CSCO { ; ; interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; isis { level 2 disable; level 1 wide-metrics-only; interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; interface lo0.0; JNPR Show Output root@jnpr# run show mpls lsp detail Ingress LSP: 1 sessions From: , State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp1-jnpr-rstn1-csco ActivePath: JNPR-RSTN1-CSCO (primary) LoadBalance: Random *Primary JNPR-RSTN1-CSCO State: Up Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Egress LSP: 3 sessions
12 Page: 12 of From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: CSCO_t0 Resv style: 1 SE, Label in: 3, Label out: - Time left: 135, Since: Tue Aug 28 07:04: Tspec: rate 0bps size 8kbps peak 0bps m 0 M 0 Port number: sender 9 receiver 0 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/2/0.0) 38 pkts PATH sentto: localclient RESV rcvfrom: localclient From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp4_rstn1-rstn2- JNPR Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 3, Label out: - Time left: 33, Since: Tue Aug 28 07:20: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 215 receiver protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/2/0.0) 3 pkts PATH sentto: localclient RESV rcvfrom: localclient Record route: <self> From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp4_rstn1-rstn2- JNPR Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 3, Label out: - Time left: 138, Since: Tue Aug 28 07:22: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 216 receiver protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/2/0.0) 3 pkts PATH sentto: localclient RESV rcvfrom: localclient Record route: <self> Total 3 displayed, Up 3, Down 0 Transit LSP: 3 sessions From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp6_rstn1-jnpr- CSCO Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: , Label out: 3 Time left: 132, Since: Tue Aug 28 02:41: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 43 receiver protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/1/0.0) 563 pkts PATH sentto: (ge-0/0/0.0) 389 pkts RESV rcvfrom: (ge-0/0/0.0) 798 pkts Explct route: Record route: <self> From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp2_rstn1-jnpr- RSTN2 Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: , Label out: 3 Time left: 153, Since: Tue Aug 28 02:43: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 51 receiver protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/1/0.0) 560 pkts PATH sentto: (ge-0/2/0.0) 386 pkts RESV rcvfrom: (ge-0/2/0.0) 560 pkts Explct route: Record route: <self>
13 Page: 13 of From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp5_rstn1-csco- JNPR_RSTN2 Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: , Label out: 3 Time left: 154, Since: Tue Aug 28 07:03: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 203 receiver protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/0/0.0) 40 pkts PATH sentto: (ge-0/2/0.0) 29 pkts RESV rcvfrom: (ge-0/2/0.0) 41 pkts Explct route: Record route: <self> Total 3 displayed, Up 3, Down 0 RSTN1 (Riverstone RS8000) Configuration version 8.0 interface create ip to_csco address-netmask /30 port gi.2.1 interface create ip to_jnpr address-netmask /30 port gi.2.2 interface create ip to_rstn2 address-netmask /30 port gi.3.1 interface add ip lo0 address-netmask /32 ip-router global set router-id isis add area isis add interface to_csco isis add interface lo0 isis add interface to_jnpr isis add interface to_rstn2 isis set level 1 isis set traffic-engineering enable isis set wide-metrics-only isis set system-id isis start mpls add interface to_jnpr mpls add interface to_csco mpls add interface to_rstn2 mpls create path RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2 num-hops 3 mpls create path RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2 num-hops 3 mpls create path RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO num-hops 3 mpls create path RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR num-hops 3 mpls create path RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2 num-hops 4 mpls create path RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO num-hops 3 mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2 hop 1 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2 hop 2 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2 hop 3 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2 hop 1 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2 hop 2 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2 hop 3 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO hop 1 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO hop 2 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO hop 3 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR hop 1 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR hop 2 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR hop 3 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2 hop 1 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2 hop 2 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2 hop 3 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2 hop 4 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO hop 1 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO hop 2 ip-addr type strict mpls set path RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO hop 3 ip-addr type strict mpls create label-switched-path lsp1 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp2 to
14 Page: 14 of 40 mpls create label-switched-path lsp3 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp4 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp5 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp6 to mpls set label-switched-path lsp2 primary RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2 no-cspf mpls set label-switched-path lsp1 primary RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2 no-cspf mpls set label-switched-path lsp3 primary RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO no-cspf mpls set label-switched-path lsp4 primary RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR no-cspf mpls set label-switched-path lsp5 primary RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2 no-cspf mpls set label-switched-path lsp6 primary RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO no-cspf mpls start rsvp add interface to_jnpr rsvp add interface to_csco rsvp add interface to_rstn2 rsvp set interface to_jnpr hello-enable rsvp set interface to_rstn2 hello-enable rsvp start system set name RSTN1 system set idle-timeout serial 0 RSTN1 Show Output RSTN1# mpls show label-switched-paths all verbose Ingress LSP: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp6" state: Up lsp-id: 0x18 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: primary setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <PRI> Protection-Path "RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO": <Active, Primary> state: Up lsp-id: 0x4006 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> attributes: <STANDBY NO-CSPF> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 1 ref-count: 1 explicit-path: "RSTN1-JNPR-CSCO" num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp5" state: Up lsp-id: 0x17 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: primary setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <PRI>
15 Page: 15 of 40 Protection-Path "RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2": <Active, Primary> state: Up lsp-id: 0x4005 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> attributes: <STANDBY NO-CSPF> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 2 ref-count: 1 explicit-path: "RSTN1-CSCO-JNPR_RSTN2" num-hops: strict strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp4" state: Up lsp-id: 0x16 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: primary setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <PRI> Protection-Path "RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR": <Active, Primary> state: Up lsp-id: 0x4004 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> attributes: <STANDBY NO-CSPF> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 6 ref-count: 1 explicit-path: "RSTN1-RSTN2-JNPR" num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp3" state: Up lsp-id: 0x15 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: primary setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <PRI>
16 Page: 16 of 40 Protection-Path "RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO": <Active, Primary> state: Up lsp-id: 0x4003 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> attributes: <STANDBY NO-CSPF> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 5 ref-count: 1 explicit-path: "RSTN1-RSTN2-CSCO" num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp2" state: Up lsp-id: 0x14 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: primary setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <PRI> Protection-Path "RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2": <Active, Primary> state: Up lsp-id: 0x4001 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> attributes: <STANDBY NO-CSPF> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 4 ref-count: 1 explicit-path: "RSTN1-JNPR-RSTN2" num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp1" state: Up lsp-id: 0x13 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: primary setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <PRI> Protection-Path "RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2": <Active, Primary> state: Up lsp-id: 0x4002 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <>
17 Page: 17 of 40 Transit LSP: attributes: <STANDBY NO-CSPF> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 3 ref-count: 1 explicit-path: "RSTN1-CSCO-RSTN2" num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp1-jnpr-rstn1-csco" state: lsp-id: 27 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 17 label out: 3 path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Egress LSP: RSTN2 (Riverstone RS8000) Configuration version 8.0 interface create ip to_csco address-netmask /30 port gi.2.1 interface create ip to_jnpr address-netmask /30 port gi.2.2 interface create ip to_rstn1 address-netmask /30 port gi.3.1 interface add ip lo0 address-netmask /32 ip-router global set router-id isis add area isis add interface to_csco isis add interface lo0 isis add interface to_jnpr isis add interface to_rstn1 isis set level 1 isis set traffic-engineering enable isis set wide-metrics-only isis set system-id isis start mpls add interface to_jnpr mpls add interface to_csco mpls add interface to_rstn1 mpls start rsvp add interface to_jnpr rsvp add interface to_csco rsvp add interface to_rstn1 rsvp set interface to_jnpr hello-enable rsvp set interface to_rstn1 hello-enable rsvp start system set name RSTN2 system set idle-timeout serial 0
18 Page: 18 of 40 RSTN2 Show Output RSTN2# mpls show label-switched-paths all verbose Transit LSP: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp3_rstn1-rstn2-csco" state: lsp-id: to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 17 label out: 3 path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp4_rstn1-rstn2-jnpr" state: lsp-id: to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 18 label out: 3 path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "CSCO_t0" state: lsp-id: 0 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 7 label in: 17 label out: 3 path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: => Egress LSP: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp1_rstn1-csco-rstn2" state: lsp-id: to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp5_rstn1-csco-jnpr_rstn2" state: lsp-id: to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp2_rstn1-jnpr-rstn2" state: lsp-id: to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path:
19 Page: 19 of 40 APPENDIX B: IS-IS TE TEST CONFIGURATIONS AND SHOW OUTPUT CSCO Configuration version 12.0 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname CSCO boot system flash slot0:gsr-p-mz st.bin enable password cisco ip subnet-zero no ip domain-lookup mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng signalling advertise implicit-null mpls traffic-eng reoptimize timers frequency 0 no tag-switching ip no tag-switching advertise-tags clns routing interface Loopback0 ip address ip directed-broadcast ip router isis interface Tunnel0 no ip address no ip directed-broadcast tunnel destination tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng tunnel mpls traffic-eng affinity 0x1 mask 0x1 tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 1 dynamic interface GigabitEthernet4/0 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng attribute-flags 0x3 no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth interface GigabitEthernet4/1 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng attribute-flags 0x2 no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth
20 Page: 20 of 40 interface GigabitEthernet4/2 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls traffic-eng tunnels mpls traffic-eng attribute-flags 0x2 no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth router isis mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0 mpls traffic-eng level-1 net is-type level-1 metric-style wide ip classless no ip pim bidir-enable no cdp run line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 timeout login response 0 login ip netmask-format hexadecimal line aux 0 line vty 0 3 timeout login response 0 password cisco login line vty 4 access-class 1 in timeout login response 0 password cisco login autocommand show version end CSCO Show Output CSCO#show mpls tr tunnels Name: CSCO_t0 (Tunnel0) Destination: Status: Admin: up Oper: up Path: valid Signalling: connected path option 1, type dynamic (Basis for Setup, path weight 20) Config Parameters: Bandwidth: 0 kbps (Global) Priority: 7 7 Affinity: 0x1/0x1 Metric Type: TE (default) AutoRoute: disabled LockDown: disabled Loadshare: 0 bw-based auto-bw: disabled(0/159) 0 Bandwidth Requested: 0
21 Page: 21 of 40 InLabel : - OutLabel : GigabitEthernet4/0, RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 0, Tun_Instance 9 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: Record Route: NONE Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=1000 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: NONE Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits History: Tunnel: Time since created: 1 hours, 6 minutes Time since path change: 11 minutes, 3 seconds Current LSP: Uptime: 11 minutes, 3 seconds Prior LSP: ID: path option 1 [3] Removal Trigger: path verification failed LSP Tunnel JNPR-lsp1 is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/0, 17 OutLabel : GigabitEthernet4/2, implicit-null RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 31, Tun_Instance 1 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=inf RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate= kbits LSP Tunnel lsp2 is signalled, connection is up InLabel : GigabitEthernet4/1, 16 OutLabel : GigabitEthernet4/2, implicit-null RSVP Signalling Info: Src , Dst , Tun_Id 10, Tun_Instance 13 RSVP Path Info: My Address: Explicit Route: Record Route: Tspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits RSVP Resv Info: Record Route: Fspec: ave rate=0 kbits, burst=0 bytes, peak rate=0 kbits JNPR Configuration root@jnpr# show version 4.4R2.3; system { host-name JNPR; syslog { user * { any emergency; file messages { any notice; authorization info;
22 Page: 22 of 40 interfaces { ge-0/0/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; ge-0/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; ge-0/2/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; lo0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /32; address /32; family iso { address ; routing-options { router-id ; protocols { rsvp { interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; mpls { admin-groups { blue 0; red 1; yellow 2; label-switched-path JNPR-lsp1 { to ; admin-group { include red; exclude yellow;
23 Page: 23 of 40 interface ge-0/0/0.0 { admin-group [ blue red ]; interface ge-0/1/0.0 { admin-group [ red blue ]; interface ge-0/2/0.0 { admin-group blue; isis { level 2 disable; level 1 wide-metrics-only; interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; interface lo0.0; JNPR Show Output root@jnpr# run show mpls lsp detail Ingress LSP: 1 sessions From: , State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: JNPR-lsp1 ActivePath: (primary) LoadBalance: Random Include: red Exclude: yellow *Primary State: Up Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 20) S S Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Egress LSP: 1 sessions From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp5 Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: 3, Label out: - Time left: 142, Since: Tue Aug 28 08:47: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 10 receiver 14 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/1/0.0) 15 pkts PATH sentto: localclient RESV rcvfrom: localclient Record route: <self> Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0 Transit LSP: 2 sessions From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: CSCO_t0 Resv style: 1 SE, Label in: , Label out: 3 Time left: 154, Since: Tue Aug 28 08:41: Tspec: rate 0bps size 8kbps peak 0bps m 0 M 0 Port number: sender 9 receiver 0 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/0/0.0) 38 pkts PATH sentto: (ge-0/1/0.0) 18 pkts RESV rcvfrom: (ge-0/1/0.0) 25 pkts Explct route:
24 Page: 24 of From: , LSPstate: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: lsp3 Resv style: 1 FF, Label in: , Label out: 3 Time left: 142, Since: Tue Aug 28 08:47: Tspec: rate 0bps size 0bps peak 0bps m 20 M 1436 Port number: sender 12 receiver 11 protocol 0 PATH rcvfrom: (ge-0/1/0.0) 15 pkts PATH sentto: (ge-0/2/0.0) 11 pkts RESV rcvfrom: (ge-0/2/0.0) 15 pkts Explct route: Record route: <self> Total 2 displayed, Up 2, Down 0 RSTN1 Configuration version 8.0 interface create ip to_csco address-netmask /30 port gi.2.1 interface create ip to_jnpr address-netmask /30 port gi.2.2 interface create ip to_rstn2 address-netmask /30 port gi.3.1 interface add ip lo0 address-netmask /32 ip-router global set router-id isis add area isis add interface to_csco isis add interface lo0 isis add interface to_jnpr isis add interface to_rstn2 isis set level 1 isis set traffic-engineering enable isis set wide-metrics-only isis set system-id isis start mpls create admin-group blue group-value 0 mpls create admin-group red group-value 1 mpls create admin-group yellow group-value 2 mpls add interface to_jnpr mpls add interface to_csco mpls add interface to_rstn2 mpls set interface to_csco admin-group red mpls set interface to_jnpr admin-group blue,red mpls set interface to_rstn2 admin-group blue,red,yellow mpls create label-switched-path lsp1 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp2 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp3 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp4 to mpls create label-switched-path lsp5 to mpls set label-switched-path lsp2 include red exclude blue,yellow mpls set label-switched-path lsp3 include blue exclude yellow mpls set label-switched-path lsp4 include yellow mpls set label-switched-path lsp5 include blue,yellow mpls start rsvp add interface to_jnpr rsvp add interface to_csco rsvp add interface to_rstn2 rsvp set interface to_jnpr hello-enable rsvp set interface to_rstn2 hello-enable rsvp start system set name RSTN1 system set idle-timeout serial 0
25 Page: 25 of 40 RSTN1 Show Output RSTN1# mpls show label-switched-paths all verbose Ingress LSP: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp5" state: Up lsp-id: 0xe to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: none setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <INCLUDE> attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. include: blue yellow mtu: 1500 ott-index: 2 ref-count: 1 cspf-path: num-hops: strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp4" state: Up lsp-id: 0xc to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: none setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <INCLUDE> attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. include: yellow mtu: 1500 ott-index: 1 ref-count: 1 cspf-path: num-hops: strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp3" state: Up lsp-id: 0xb to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: none setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <EXCLUDE INCLUDE>
26 Page: 26 of 40 attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. include: blue exclude: yellow mtu: 1500 ott-index: 5 ref-count: 1 cspf-path: num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp2" state: Up lsp-id: 0xa to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: none setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <EXCLUDE INCLUDE> attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. include: red exclude: blue yellow mtu: 1500 ott-index: 4 ref-count: 1 cspf-path: num-hops: strict strict strict Label-Switched-Path: "lsp1" state: Up lsp-id: 0x9 to: from: proto: <rsvp> protection: none setup-pri: 7 hold-pri: 0 attributes: <> attributes: <> inherited-attributes: <> retry-limit: 5000 retry-int: 15 sec. retry-count: 5000 next_retry_int: sec. bps: 0 preference: 7 hop-limit: 255 opt-int: 600 sec. mtu: 1500 ott-index: 3 ref-count: 1 cspf-path: num-hops: strict strict
27 Page: 27 of 40 Transit LSP: Egress LSP: Label-Switched-Path: "CSCO_t0" state: lsp-id: 0 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 7 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: RSTN2 Configuration version 8.0 interface create ip to_csco address-netmask /30 port gi.2.1 interface create ip to_jnpr address-netmask /30 port gi.2.2 interface create ip to_rstn1 address-netmask /30 port gi.3.1 interface add ip lo0 address-netmask /32 ip-router global set router-id isis add area isis add interface to_csco isis add interface lo0 isis add interface to_jnpr isis add interface to_rstn1 isis set level 1 isis set traffic-engineering enable isis set wide-metrics-only isis set system-id isis start mpls create admin-group blue group-value 0 mpls create admin-group red group-value 1 mpls create admin-group yellow group-value 2 mpls add interface to_jnpr mpls add interface to_csco mpls add interface to_rstn1 mpls set interface to_csco admin-group red mpls set interface to_rstn1 admin-group blue,red,yellow mpls set interface to_jnpr admin-group blue mpls start rsvp add interface to_jnpr rsvp add interface to_csco rsvp add interface to_rstn1 rsvp set interface to_jnpr hello-enable rsvp set interface to_rstn1 hello-enable rsvp start system set name RSTN2 system set idle-timeout serial 0 RSTN2 Show Output RSTN2# mpls show label-switched-paths all verbose Transit LSP: Egress LSP: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp4" state: lsp-id: 12 to: from:
28 Page: 28 of 40 setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp3" state: lsp-id: 11 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp2" state: lsp-id: 10 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "lsp1" state: lsp-id: 9 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: Label-Switched-Path: "JNPR-lsp1" state: lsp-id: 31 to: from: setup-pri: 7 holding-pri: 0 label in: 3 label out: path recvfrom: path sendto: explicit-path: CSCO configuration version 12.0 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname CSCO boot system flash slot0:gsr-p-mz st.bin enable password cisco ip subnet-zero no ip domain-lookup mpls label protocol ldp no tag-switching advertise-tags tag-switching tdp router-id Loopback0 clns routing
29 Page: 29 of 40 interface Loopback0 ip address ip directed-broadcast ip router isis interface GigabitEthernet4/0 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls label protocol ldp tag-switching ip no cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/1 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls label protocol ldp tag-switching ip no cdp enable interface GigabitEthernet4/2 ip address no ip directed-broadcast ip router isis negotiation auto mpls label protocol ldp tag-switching ip no cdp enable router isis mpls traffic-eng router-id Loopback0 mpls traffic-eng level-1 net is-type level-1 metric-style wide ip classless no ip pim bidir-enable no cdp run line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 timeout login response 0 login ip netmask-format hexadecimal line aux 0 line vty 0 3 timeout login response 0 password cisco login line vty 4 access-class 1 in timeout login response 0 password cisco login autocommand show version end
30 Page: 30 of 40 APPENDIX C: LDP TEST CONFIGURATIONS CSCO Show Output CSCO#show mpls ip binding xFFFFFFFC in label: imp-null xFFFFFFFC in label: imp-null xFFFFFFFC in label: xFFFFFFFC in label: imp-null xFFFFFFFC in label: xFFFF0000 in label: imp-null xFFFFFF00 in label: imp-null xFFFFFFFF in label: imp-null out label: 2056 lsr: :0 out label: lsr: :0 out label: 2052 lsr: : xFFFFFFFF in label: 18 out label: imp-null lsr: :0 inuse out label: 2058 lsr: :0 out label: 2054 lsr: : xFFFFFFFF in label: 19 out label: imp-null lsr: :0 inuse out label: lsr: : xFFFFFFFF in label: 20 out label: 2057 lsr: :0 out label: imp-null lsr: :0 inuse out label: lsr: :0 CSCO#show mpls forwarding-table Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes tag Outgoing Next Hop tag tag or VC or Tunnel Id switched interface 16 Untagged xFFFFFFFC \ 0 Gi4/ Untagged xFFFFFFFC \ 0 Gi4/ Untagged xFFFFFFFC \ 0 Gi4/ Pop tag xFFFFFFFF \ 0 Gi4/ Pop tag xFFFFFFFF \ 0 Gi4/ Pop tag xFFFFFFFF \ 2950 Gi4/ CSCO#show ip ro Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area * - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR Gateway of last resort is not set
31 Page: 31 of 40 i L1 C C C i L1 C C i L1 i L1 i L xFF is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks xFFFFFFFC [115/20] via , GigabitEthernet4/0 [115/20] via , GigabitEthernet4/ xFFFFFFFC is directly connected, GigabitEthernet4/ xFFFFFFFC is directly connected, GigabitEthernet4/ xFFFFFFFC is directly connected, GigabitEthernet4/ xFFFFFFFC [115/15] via , GigabitEthernet4/ xFFFF0000 is directly connected, Ethernet xFFFFFFFF is subnetted, 4 subnets is directly connected, Loopback [115/10] via , GigabitEthernet4/ [115/10] via , GigabitEthernet4/ [115/10] via , GigabitEthernet4/2 JNPR Configuration version 4.4R2.3; system { host-name JNPR; syslog { user * { any emergency; file messages { any notice; authorization info; interfaces { ge-0/0/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; ge-0/1/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; ge-0/2/0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /30; family iso; family mpls; lo0 { unit 0 { family inet { address /32; address /32;
32 Page: 32 of 40 family iso { address ; routing-options { router-id ; protocols { rsvp { disable; interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; mpls { interface all; isis { level 2 disable; level 1 wide-metrics-only; interface ge-0/0/0.0; interface ge-0/1/0.0; interface ge-0/2/0.0; interface lo0.0; ldp { interface all; JNPR Show Output root@jnpr# run show ldp database Input label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / / /32 Output label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / / /32 Input label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / / /32 Output label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / / /32
33 Page: 33 of 40 Input label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / /32 Output label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / / /32 root@jnpr# run show route inet.0: 13 destinations, 13 routes (12 active, 0 holddown, 1 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both /30 *[Direct/0] 20:20:41 > via ge-0/0/ /32 *[Local/0] 1d 00:28:45 Local /30 *[IS-IS/15] 12:10:01, metric 20, tag 1 > to via ge-0/0/0.0 to via ge-0/2/ /30 *[Direct/0] 12:15:41 > via ge-0/1/ /32 *[Local/0] 21:40:23 Local /30 *[IS-IS/15] 01:03:31, metric 15, tag 1 > to via ge-0/1/ /30 *[Direct/0] 12:10:38 > via ge-0/2/ /32 *[Local/0] 21:44:11 Local /32 *[IS-IS/15] 20:20:20, metric 20, tag 1 > to via ge-0/0/ /32 *[Direct/0] 1d 00:33:54 > via lo /32 *[IS-IS/15] 12:15:09, metric 10, tag 1 > to via ge-0/1/ /32 *[IS-IS/15] 12:10:01, metric 10, tag 1 > to via ge-0/2/0.0 inet.3: 3 destinations, 3 routes (3 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both /32 *[LDP/9] 01:29:10, metric 1 > to via ge-0/0/ /32 *[LDP/9] 01:29:00, metric 1 > to via ge-0/1/ /32 *[LDP/9] 00:55:37, metric 1 > to via ge-0/2/0.0 iso.0: 1 destinations, 1 routes (1 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both /80 *[Direct/0] 21:29:57 > via lo0.0 mpls.0: 8 destinations, 8 routes (8 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) + = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
34 Page: 34 of 40 0 *[MPLS/0] 21:00:26, metric 1 Receive 1 *[MPLS/0] 21:00:26, metric 1 Receive *[LDP/9] 01:29:10, metric 1 > to via ge-0/0/0.0, Pop (S=0) *[LDP/9] 01:29:10, metric 1 > to via ge-0/0/0.0, Pop *[LDP/9] 01:29:00, metric 1 > to via ge-0/1/0.0, Pop (S=0) *[LDP/9] 01:29:00, metric 1 > to via ge-0/1/0.0, Pop *[LDP/9] 00:55:37, metric 1 > to via ge-0/2/0.0, Pop (S=0) *[LDP/9] 00:55:37, metric 1 > to via ge-0/2/0.0, Pop RSTN1 Configuration version 8.0 port disable gi.3.1 force-link-down interface create ip to_csco address-netmask /30 port gi.2.1 interface create ip to_jnpr address-netmask /30 port gi.2.2 interface create ip et11 address-netmask /24 port et.1.1 interface add ip lo0 address-netmask /32 ip-router global set router-id ip-router global set autonomous-system ip-router policy redistribute from-proto aggregate to-proto bgp target-as network /16 bgp create peer-group ibgp autonomous-system type routing bgp add peer-host group ibgp bgp set peer-group ibgp local-address bgp set peer-group ibgp next-hop-self bgp start isis add area isis add interface to_csco isis add interface lo0 isis add interface to_jnpr isis set level 1 isis set traffic-engineering enable isis set wide-metrics-only isis set system-id isis set interface to_csco l1-metric 5 isis start mpls add interface to_jnpr mpls add interface to_csco mpls start ldp add interface to_jnpr ldp add interface to_csco ldp start system set name RSTN1 system set idle-timeout serial 0 ip-router policy summarize route /16 type aggregate RSTN1 Show Output RSTN1# ldp show database Input label database, : :0 Label Prefix / / / /32
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab. Part 2 of 7
 CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
CCIE Service Provider Sample Lab Part 2 of 7 SP Sample Lab Main Topology R13 S2/1.135.13/24 Backbone Carrier SP AS 1002 S2/1 PPP E0/1.69.6/24 R6 Customer Carrier SP ABC Site 5 AS 612 E1/0 ISIS.126.6/24
MPLS Traffic Engineering over Bridge Domain Interfaces
 MPLS Traffic Engineering over Bridge Domain Interfaces The MPLS Traffic Engineering(TE) over Bridge Domain Interfaces(BDI) feature enables MPLS traffic engineering over Bridge Domain Interfaces. Prerequisites
MPLS Traffic Engineering over Bridge Domain Interfaces The MPLS Traffic Engineering(TE) over Bridge Domain Interfaces(BDI) feature enables MPLS traffic engineering over Bridge Domain Interfaces. Prerequisites
Signaling Methods and Object Association for Flex LSPs
 Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example RSVP LSP Tunnels Modified: 2016-12-14 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All rights reserved. Juniper
Network Configuration Example RSVP LSP Tunnels Modified: 2016-12-14 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All rights reserved. Juniper
Configure IOS XR Traffic Controller (XTC)
 IOS XR Traffic Controller (XTC) provides stateful path computation element (PCE) functionality by exting the existing IOS-XR PCE functionality with additional capabilities. The current IOS-XR PCE function
IOS XR Traffic Controller (XTC) provides stateful path computation element (PCE) functionality by exting the existing IOS-XR PCE functionality with additional capabilities. The current IOS-XR PCE function
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN
 Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Segment Routing On Demand Next Hop for L3/L3VPN When redistributing routing information across domains, provisioning of multi-domain services (L2VPN & L3VPN) has its own complexity and scalability issues.
Signaling Methods and Object Association for Flex LSPs
 Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
Flex LSP also known as Associated Bidirectional LSPs is the combination of static bidirectional MPLS-TP and dynamic MPLS-TE. Flex LSP provides bidirectional label switched paths (LSPs) set up dynamically
Junos OS. RSVP LSP Tunnels Feature Guide. Release Published: Copyright 2011, Juniper Networks, Inc.
 Junos OS RSVP LSP Tunnels Feature Guide Release 11.4 Published: 2011-11-08 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net This product includes
Junos OS RSVP LSP Tunnels Feature Guide Release 11.4 Published: 2011-11-08 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net This product includes
mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes
 mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes To create or modify a label switched path (LSP) attribute list, use the mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes command in global configuration mode.
mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes To create or modify a label switched path (LSP) attribute list, use the mpls traffic-eng lsp attributes command in global configuration mode.
Junos OS. MPLS LSP Link Protection and Node Link Protection Feature Guide. Release Published: Copyright 2011, Juniper Networks, Inc.
 Junos OS MPLS LSP Link Protection and Node Link Protection Feature Guide Release 11.4 Published: 2011-11-08 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Junos OS MPLS LSP Link Protection and Node Link Protection Feature Guide Release 11.4 Published: 2011-11-08 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1194 North Mathilda Avenue Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
MPLS Traffic Engineering
 8 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T MPLS Traffic Engineering This online supplement of Chapter 8 deals with a few advanced traffic engineering (TE) topics. Ensure that you have read Chapter 8 in the book
8 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T MPLS Traffic Engineering This online supplement of Chapter 8 deals with a few advanced traffic engineering (TE) topics. Ensure that you have read Chapter 8 in the book
Configuring MPLS, MPLS VPN, MPLS OAM, and EoMPLS
 CHAPTER 43 Configuring MPLS, MPLS VPN, MPLS OAM, and EoMPLS This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Cisco ME 3800X and ME 3600X
CHAPTER 43 Configuring MPLS, MPLS VPN, MPLS OAM, and EoMPLS This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Cisco ME 3800X and ME 3600X
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
MPLS VPN C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T. BGP Advertising IPv4 Prefixes with a Label
 7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering
 9/27/16 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) Cisco Public Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter- Domain Traffic Engineering
9/27/16 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) Cisco Public Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter- Domain Traffic Engineering
MPLS Embedded Management LSP Ping/Traceroute and AToM VCCV
 MPLS Embedded Management LSP Ping/Traceroute and AToM VCCV As Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) deployments increase and the traffic types they carry increase, the ability of service providers to monitor
MPLS Embedded Management LSP Ping/Traceroute and AToM VCCV As Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) deployments increase and the traffic types they carry increase, the ability of service providers to monitor
MPLS Traffic Engineering Inter-AS TE
 MPLS Traffic Engineering Inter-AS TE Last Updated: November 22, 2011 The MPLS Traffic Engineering: Inter-AS TE feature provides Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) node protection, loose path reoptimization,
MPLS Traffic Engineering Inter-AS TE Last Updated: November 22, 2011 The MPLS Traffic Engineering: Inter-AS TE feature provides Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) node protection, loose path reoptimization,
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example GMPLS Modified: 2016-12-14 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All rights reserved. Juniper Networks, Junos,
Network Configuration Example GMPLS Modified: 2016-12-14 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All rights reserved. Juniper Networks, Junos,
Segment Routing On Demand for L2VPN/VPWS
 On-Demand Next Hop (ODN) for Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) creates a segment routing (SR) traffic-engineering (TE) auto-tunnel and uses the auto-tunnel for pseudowire dataplane. Restrictions
On-Demand Next Hop (ODN) for Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) creates a segment routing (SR) traffic-engineering (TE) auto-tunnel and uses the auto-tunnel for pseudowire dataplane. Restrictions
SR-TE On Demand LSP. The SR TE On demand LSP feature provides the ability to connect Metro access rings via a static route to the
 The SR TE On demand LSP feature provides the ability to connect Metro access rings via a static route to the destination. The static route is mapped to an explicit path and that will trigger an on demand
The SR TE On demand LSP feature provides the ability to connect Metro access rings via a static route to the destination. The static route is mapped to an explicit path and that will trigger an on demand
Dynamic PCC. Information About Dynamic PCC. Path Computation Element Protocol Functions
 The Stateful Path Computation Element Protocol(PCEP) enables a router to report and optionally delegate Label Switched Paths (LSPs) which is established using either Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
The Stateful Path Computation Element Protocol(PCEP) enables a router to report and optionally delegate Label Switched Paths (LSPs) which is established using either Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
MPLS Command Line Reference for E-Series ExaScale
 MPLS Line Reference for E-Series ExaScale December 21, 2009 MPLS This chapter contains the following sections: MPLS Traffic Engineering s on page 2 RSVP Traffic Engineering s on page 14 RSVP Fast-reroute
MPLS Line Reference for E-Series ExaScale December 21, 2009 MPLS This chapter contains the following sections: MPLS Traffic Engineering s on page 2 RSVP Traffic Engineering s on page 14 RSVP Fast-reroute
What You Will Learn By the end of this appendix, you should know and be able to explain the following:
 What You Will Learn By the end of this appendix, you should know and be able to explain the following: What static MPLS labels are and how they can be used The difference between static MPLS bindings and
What You Will Learn By the end of this appendix, you should know and be able to explain the following: What static MPLS labels are and how they can be used The difference between static MPLS bindings and
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
CONTENTS. Introduction
 CONTENTS Introduction MP-1 Multiprotocol Label Switching Commands MP-3 address-family MP-4 affinity (LSP Attributes) MP-6 append-after MP-8 auto-bw (LSP Attributes) MP-9 bandwidth (LSP Attributes) MP-11
CONTENTS Introduction MP-1 Multiprotocol Label Switching Commands MP-3 address-family MP-4 affinity (LSP Attributes) MP-6 append-after MP-8 auto-bw (LSP Attributes) MP-9 bandwidth (LSP Attributes) MP-11
You cannot configure prefix-sids on transit links at this time. Support for this feature may be introduced in later code versions.
 8.1 Segment Routing Segment Routing (SR) is a relatively new technology pioneered by Cisco that is meant to reduce state in MPLS core networks. One can use SR to replace LDP and RSVP-TE wholesale provided
8.1 Segment Routing Segment Routing (SR) is a relatively new technology pioneered by Cisco that is meant to reduce state in MPLS core networks. One can use SR to replace LDP and RSVP-TE wholesale provided
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Traffic Engineering
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Traffic Engineering Feature Overview Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) traffic engineering software enables an MPLS backbone to replicate and expand upon the traffic
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Traffic Engineering Feature Overview Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) traffic engineering software enables an MPLS backbone to replicate and expand upon the traffic
Router Lab Reference
 KTHNOC Router Lab Reference Juniper version Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 2 Reference: Workstation...3 2.1 Configuring network access...3 2.2 Connecting to your router...4 3 Reference: Basic commands...4
KTHNOC Router Lab Reference Juniper version Table of Contents 1 Introduction...3 2 Reference: Workstation...3 2.1 Configuring network access...3 2.2 Connecting to your router...4 3 Reference: Basic commands...4
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support
 Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF
 LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 05 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND LABEL DISTRIBUTION PROTOCOL (LDP) 1 by Xantaro IP Routing In IP networks, each router makes an independent
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 05 MULTIPROTOCOL LABEL SWITCHING (MPLS) AND LABEL DISTRIBUTION PROTOCOL (LDP) 1 by Xantaro IP Routing In IP networks, each router makes an independent
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Configuring GMPLS UNI
 The primary function of Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching (GMPLS) User Network Interface (UNI) is to create circuit connection between two clients (UNI-C) of an optical network. This is achieved
The primary function of Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching (GMPLS) User Network Interface (UNI) is to create circuit connection between two clients (UNI-C) of an optical network. This is achieved
ECMP Load Balancing. MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) 1
 Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Deploy MPLS Traffic Engineering. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS Traffic Engineering APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Acknowledgement Cisco Systems 2 Overview of MPLS TE 3 Why MPLS Traffic Engineering? Handling
Deploy MPLS Traffic Engineering APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Acknowledgement Cisco Systems 2 Overview of MPLS TE 3 Why MPLS Traffic Engineering? Handling
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
BrainDumps.4A0-103,230.Questions
 BrainDumps.4A0-103,230.Questions Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 11.02 http://www.gratisexam.com/ A "brain dump," as it relates to the certification exams, is a source
BrainDumps.4A0-103,230.Questions Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 11.02 http://www.gratisexam.com/ A "brain dump," as it relates to the certification exams, is a source
JNCIE Juniper Networks Certified Internet Expert
 JNCIE Juniper Networks Certified Internet Expert Study Guide - Chapter 2 by Harry Reynolds This book was originally developed by Juniper Networks Inc. in conjunction with Sybex Inc. It is being offered
JNCIE Juniper Networks Certified Internet Expert Study Guide - Chapter 2 by Harry Reynolds This book was originally developed by Juniper Networks Inc. in conjunction with Sybex Inc. It is being offered
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
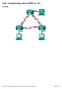 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone TEST. 26 April 2016 AN. Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC PBB-TE VPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS GMPLS SR RSVP-TE OSPF-TE PCEP
 Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP FEC VPLS PBB-TE MPLS etc.. MPLS is not alone LDP MPLS-TE LABEL MP-BGP LSP TAG H-VPLS 26 April 2016 AN TEST GMPLS SR T-MPLS ISIS-TE MPƛS OSPF-TE PCEP Multi-Protocol
Establishing MPLS LSPs Across Multiple Autonomous Systems for Next-Gen Multicast VPNs
 Establishing MPLS LSPs Across Multiple Autonomous Systems for Next-Gen Multicast VPNs Configuration Example October 2016 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Establishing MPLS LSPs Across Multiple Autonomous Systems for Next-Gen Multicast VPNs Configuration Example October 2016 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
MPLS LSP Ping, Traceroute, and AToM VCCV
 As Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) deployments increase and the traffic types they carry increase, the ability of service providers to monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate MPLS
As Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) deployments increase and the traffic types they carry increase, the ability of service providers to monitor label switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate MPLS
RR> RR> RR>en RR# RR# RR# RR# *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 RR#
 RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
RR> RR> RR>en *Oct 2 04:57:03.684: %AMDP2_FE-6-EXCESSCOLL: Ethernet0/2 TDR=0, TRC=0 term len 0 show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2568 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
MPLS Traffic Engineering - Fast Reroute Link Protection
 MPLS Traffic Engineering - Fast Reroute Link Protection This feature module describes the Fast Reroute (FRR) link protection and Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)-triggered FRR feature of Multiprotocol
MPLS Traffic Engineering - Fast Reroute Link Protection This feature module describes the Fast Reroute (FRR) link protection and Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)-triggered FRR feature of Multiprotocol
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS Configuration 3 Configuration Example
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] BGP-LS Configuration 3 Configuration Example
Testking.4A0-103,249.QA 4A Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching
 Testking.4A0-103,249.QA Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-103 Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching 1. These are the most accurate
Testking.4A0-103,249.QA Number: 4A0-103 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 6.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-103 Alcatel-Lucent Multi Protocol Label Switching 1. These are the most accurate
Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Label Distribution Protocol 2
Label Distribution Protocol and Basic MPLS Configuration APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Label Distribution Protocol 2
HP FlexFabric Switch Series
 HP FlexFabric 12900 Switch Series MPLS Command Reference Part number: 5998-7274 Software version: R103x Document version: 6W100-20150116 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development
HP FlexFabric 12900 Switch Series MPLS Command Reference Part number: 5998-7274 Software version: R103x Document version: 6W100-20150116 Legal and notice information Copyright 2015 Hewlett-Packard Development
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS
 CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
CCIE R&S Techtorial MPLS Ing. Tomáš Kelemen Partner Systems Engineer CCIE #24395 Ing. Peter Mesjar Systems Engineer CCIE #17428 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda Introduction to MPLS
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : JN0-661 Title : Service Provider Routing and Switching Vendor : Juniper Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid JN0-661 Exam's
PASS4TEST \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : JN0-661 Title : Service Provider Routing and Switching Vendor : Juniper Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid JN0-661 Exam's
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
MPLS LDP Graceful Restart
 MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Last Updated: November 23, 2011 When a router is configured with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) Graceful Restart (GR), it assists a neighboring
MPLS LDP Graceful Restart Last Updated: November 23, 2011 When a router is configured with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) Graceful Restart (GR), it assists a neighboring
Configuring Virtual Private LAN Services
 Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
Virtual Private LAN Services (VPLS) enables enterprises to link together their Ethernet-based LANs from multiple sites via the infrastructure provided by their service provider. This module explains VPLS
MPLS LDP. Agenda. LDP Overview LDP Protocol Details LDP Configuration and Monitoring 9/27/16. Nurul Islam Roman
 MPLS LDP Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) 1 Agenda LDP Overview LDP Protocol Details LDP Configuration and Monitoring 1 Label Distribution Protocol Overview MPLS nodes need to exchange label information
MPLS LDP Nurul Islam Roman (nurul@apnic.net) 1 Agenda LDP Overview LDP Protocol Details LDP Configuration and Monitoring 1 Label Distribution Protocol Overview MPLS nodes need to exchange label information
Configuring Integrated IS-IS Protocol Shutdown Support Maintaining Configuration Parameters
 Configuring Integrated IS-IS Protocol Shutdown Support Maintaining Configuration Parameters The Integrated IS-IS Protocol Shutdown Support Maintaining Configuration Parameters feature allows you to disable
Configuring Integrated IS-IS Protocol Shutdown Support Maintaining Configuration Parameters The Integrated IS-IS Protocol Shutdown Support Maintaining Configuration Parameters feature allows you to disable
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
RIP. Table of Contents. General Information. Summary. Specifications
 RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents
RIP Document revision 1 (Wed Mar 24 12:32:12 GMT 2004) This document applies to V2.8 Table of Contents Table of Contents General Information Summary Specifications Related Documents Additional Documents
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Interconnecting a Layer 2 Circuit with a Layer 3 VPN Modified: 2017-01-19 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net
Network Configuration Example Interconnecting a Layer 2 Circuit with a Layer 3 VPN Modified: 2017-01-19 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering
 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter-Domain Traffic Engineering General Deployment Considerations 2 Technology Overview
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter-Domain Traffic Engineering General Deployment Considerations 2 Technology Overview
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN
 Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Practice exam questions for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam
 Practice exam questions for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam The following questions will test your knowledge and prepare you for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam. Compare your responses with the Answer
Practice exam questions for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam The following questions will test your knowledge and prepare you for the Nokia NRS II Composite Exam. Compare your responses with the Answer
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Configure Segment Routing for IS-IS Protocol
 Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is a standards-based Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The Cisco IOS XR software implements the IP routing
Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS), Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is a standards-based Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The Cisco IOS XR software implements the IP routing
IP Router Command Reference
 IP Router Configuration IP Router Command Reference Command Hierarchies Configuration Commands Router Commands on page 94 Router L2TP Commands on page 96 Router Interface Commands on page 99 Router Interface
IP Router Configuration IP Router Command Reference Command Hierarchies Configuration Commands Router Commands on page 94 Router L2TP Commands on page 96 Router Interface Commands on page 99 Router Interface
2D1490 p MPLS, RSVP, etc. Olof Hagsand KTHNOC/NADA
 2D1490 p4 2007 MPLS, RSVP, etc Olof Hagsand KTHNOC/NADA Literature Handouts: MPLS-Enabled applications (Minei, Lucek). Parts of Section 1. JunOS Cookbook: Chapter 14 Background MPLS - Multiprotocol Label
2D1490 p4 2007 MPLS, RSVP, etc Olof Hagsand KTHNOC/NADA Literature Handouts: MPLS-Enabled applications (Minei, Lucek). Parts of Section 1. JunOS Cookbook: Chapter 14 Background MPLS - Multiprotocol Label
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF
 LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 07 - MPLS BASED LAYER 2 SERVICES 1 by Xantaro MPLS BASED LAYER 2 VPNS USING MPLS FOR POINT-TO-POINT LAYER 2 SERVICES 2 by Xantaro Why are Layer-2
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING LECTURE BY SEBASTIAN GRAF MODULE 07 - MPLS BASED LAYER 2 SERVICES 1 by Xantaro MPLS BASED LAYER 2 VPNS USING MPLS FOR POINT-TO-POINT LAYER 2 SERVICES 2 by Xantaro Why are Layer-2
Configuring MPLS and EoMPLS
 37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. MPLS is a packet-switching technology that integrates
37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) and Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) on the Catalyst 3750 Metro switch. MPLS is a packet-switching technology that integrates
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem
 How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
How to Configure a Cisco Router Behind a Non-Cisco Cable Modem Document ID: 19268 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
MPLS Traffic Engineering--Scalability Enhancements
 MPLS Traffic Engineering--Scalability Enhancements The MPLS Traffic Engineering--Scalability Enhancement feature improves scalability performance for large numbers of traffic engineering tunnels. These
MPLS Traffic Engineering--Scalability Enhancements The MPLS Traffic Engineering--Scalability Enhancement feature improves scalability performance for large numbers of traffic engineering tunnels. These
Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network
 Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
Anas Al-Selwi Multiprotocol Label Switching Virtual Private Network Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachelor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis 08 May 2013 Abstract Author(s)
MPLS Traffic Engineering BFD-triggered Fast Reroute
 MPLS Traffic Engineering BFD-triggered Fast Reroute The MPLS Traffic Engineering: BFD-triggered Fast Reroute feature allows you to obtain link and node protection by using the Bidirectional Forwarding
MPLS Traffic Engineering BFD-triggered Fast Reroute The MPLS Traffic Engineering: BFD-triggered Fast Reroute feature allows you to obtain link and node protection by using the Bidirectional Forwarding
MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) Configurable Path Calculation Metric for Tunnels
 MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) Configurable Path Calculation Metric for Tunnels Feature History Release 12.0(18)ST 12.2(11)S 12.0(22)S Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated
MPLS Traffic Engineering (TE) Configurable Path Calculation Metric for Tunnels Feature History Release 12.0(18)ST 12.2(11)S 12.0(22)S Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated
Segment Routing MPLS OAM Support
 Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
Segment Routing Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) helps service providers to monitor label-switched paths (LSPs) and quickly isolate forwarding problems to assist with fault detection and
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering
 Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter-Domain Traffic Engineering General Deployment Considerations 2 Technology Overview
Deploying MPLS Traffic Engineering Agenda Technology Overview Bandwidth optimization TE for QoS Traffic Protection Inter-Domain Traffic Engineering General Deployment Considerations 2 Technology Overview
Configuring MPLS and RSVP with CLI
 MPLS and RSVP Configuring MPLS and RSVP with CLI This section provides information to configure MPLS and RSVP using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: MPLS Configuration Overview
MPLS and RSVP Configuring MPLS and RSVP with CLI This section provides information to configure MPLS and RSVP using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: MPLS Configuration Overview
MPLS-TE Configuration Application
 CHAPTER 6 The contains the following tabs and subtabs: Global Tab, page 6-53 Labels Tab, page 6-54 Links Tab, page 6-55 General Subtab, page 6-56 Backup Tunnels Subtab, page 6-57 Tunnel Head Tab, page
CHAPTER 6 The contains the following tabs and subtabs: Global Tab, page 6-53 Labels Tab, page 6-54 Links Tab, page 6-55 General Subtab, page 6-56 Backup Tunnels Subtab, page 6-57 Tunnel Head Tab, page
MultiProtocol Label Switching - MPLS ( RFC 3031 )
 Outline MultiProtocol Label Switching - MPLS ( RFC 3031 ) 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? 2. What MPLS is used for? 3. Label Distribution Protocols 1 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? MPLS is
Outline MultiProtocol Label Switching - MPLS ( RFC 3031 ) 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? 2. What MPLS is used for? 3. Label Distribution Protocols 1 1. What is MPLS and how does it work? MPLS is
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
hapter 4 Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Summarize in OSPF at an ABR. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize in OSPF at an ASBR.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Optimal Route Reflection
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Optimal Route Reflection Contents Introduction Background Information Network Diagram Theory IOS-XR Implementation Configure Configuration Example MPLS Traffic-Engineering
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Optimal Route Reflection Contents Introduction Background Information Network Diagram Theory IOS-XR Implementation Configure Configuration Example MPLS Traffic-Engineering
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example
 FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
MPLS. 9 March 2018 AN
 MPLS 9 March 2018 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP MP-BGP H-VPLS OSPF-TE LIB MPLS is not alone LSP ISIS-TE EVPN GMPLS MPLS-TE T-MPLS LFIB LABEL LDP TAG Used in many (most?) provider networks to
MPLS 9 March 2018 AN Multi-Protocol Label Switching MPLS-TP MP-BGP H-VPLS OSPF-TE LIB MPLS is not alone LSP ISIS-TE EVPN GMPLS MPLS-TE T-MPLS LFIB LABEL LDP TAG Used in many (most?) provider networks to
mpls ldp atm vc-merge through mpls static binding ipv4
 mpls ldp atm vc-merge through mpls static binding ipv4 mpls ldp atm vc-merge, page 3 mpls ldp autoconfig, page 5 mpls ldp backoff, page 7 mpls ldp discovery, page 9 mpls ldp discovery transport-address,
mpls ldp atm vc-merge through mpls static binding ipv4 mpls ldp atm vc-merge, page 3 mpls ldp autoconfig, page 5 mpls ldp backoff, page 7 mpls ldp discovery, page 9 mpls ldp discovery transport-address,
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Monitor RSVP LSP Configure and monitor a LDP LSP Manipulate the default behavior of RSVP and LDP, depending on network requirements.
 Lab 1 MPLS Overview This lab demonstrates configuration and monitoring of Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) and Label Distribution (LDP) signalled label switched path (LSP) features on routers running
Lab 1 MPLS Overview This lab demonstrates configuration and monitoring of Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) and Label Distribution (LDP) signalled label switched path (LSP) features on routers running
BraindumpsQA. IT Exam Study materials / Braindumps
 BraindumpsQA http://www.braindumpsqa.com IT Exam Study materials / Braindumps Exam : JN0-660 Title : Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-SP) Vendor : Juniper Version : DEMO 1 /
BraindumpsQA http://www.braindumpsqa.com IT Exam Study materials / Braindumps Exam : JN0-660 Title : Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-SP) Vendor : Juniper Version : DEMO 1 /
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Ingress Replication for MVPN and for IP Multicast Using Next Gen MVPN Modified: 2016-12-20 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Network Configuration Example Ingress Replication for MVPN and for IP Multicast Using Next Gen MVPN Modified: 2016-12-20 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP
 Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
IPv6 Routing: IS-IS Support for IPv6
 This module describes how to configure Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) for IPv6. IS-IS is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that advertises link-state information throughout
This module describes how to configure Integrated Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) for IPv6. IS-IS is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that advertises link-state information throughout
Multicast in a VPN I. In This Chapter SR Advanced Configuration Guide Page 635
 Multicast in a VPN I In This Chapter This section provides information about multicast in a VPRN service. Topics in this section include: Applicability on page 636 Summary on page 637 Overview on page
Multicast in a VPN I In This Chapter This section provides information about multicast in a VPRN service. Topics in this section include: Applicability on page 636 Summary on page 637 Overview on page
RSVP-TE Point to Multi-Point (P2MP) Emulation Software
 RSVP-TE Point to Multi-Point (P2MP) Emulation Software Ixia's IxNetwork RSVP-TE (Resource reservation Protocol with Traffic Engineering) P2MP (Point to Multi-Point) Emulation Software is designed to analyze
RSVP-TE Point to Multi-Point (P2MP) Emulation Software Ixia's IxNetwork RSVP-TE (Resource reservation Protocol with Traffic Engineering) P2MP (Point to Multi-Point) Emulation Software is designed to analyze
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
internet technologies and standards
 Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2017 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching MPLS introduction
Institute of Telecommunications Warsaw University of Technology 2017 internet technologies and standards Piotr Gajowniczek Andrzej Bąk Michał Jarociński MPLS Multiprotocol Label Switching MPLS introduction
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
