Threads. Fundamentals of Computer Science
|
|
|
- June Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Threads Fundamentals of Computer Science
2 Outline Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core) Actually at the same time (multiple cores) Why? Get work done faster (on multi-core machines) Simplify code by splitting up work into parts Remain responsive to user input Threads in Java Creating, starting, sleeping Unpredictability Debugging
3 3 A Single-Threaded Program: Single Core public class Animal private String image; private String audio; public static void main(string [] args) 1 HashMap<String, Animal> map = new HashMap<String, Animal>(); 9 A 6 7 public Animal(String image, String audio) 3 this.image = image; 4 this.audio = audio; public void show() H StdDraw.picture(0.5, 0.5, image); I StdAudio.play(audio); Animal.java B map.put("dog", new Animal("dog.jpg", "dog.wav")); map.put("cat", new Animal("cat.jpg", "cat.wav")); map.put("cow", new Animal("cow.jpg", "cow.wav")); while (true) C D E F G J StdDraw.clear(); String name = StdIn.readLine(); Animal animal = map.get(name.tolowercase().trim()); if (animal!= null) animal.show(); StdDraw.show(100); AnimalMap.java A single core computer.
4 4 A Single-Threaded Program: Multi-Core public class Animal private String image; private String audio; public static void main(string [] args) 1 HashMap<String, Animal> map = new HashMap<String, Animal>(); 9 A 6 7 public Animal(String image, String audio) 3 this.image = image; 4 this.audio = audio; public void show() H StdDraw.picture(0.5, 0.5, image); I StdAudio.play(audio); Animal.java B map.put("dog", new Animal("dog.jpg", "dog.wav")); map.put("cat", new Animal("cat.jpg", "cat.wav")); map.put("cow", new Animal("cow.jpg", "cow.wav")); while (true) C D E F G J StdDraw.clear(); String name = StdIn.readLine(); Animal animal = map.get(name.tolowercase().trim()); if (animal!= null) animal.show(); StdDraw.show(100); AnimalMap.java A multi-core computer.
5 5 Multi-Threaded Animals New magic program: AnimalMapDeluxe.java Random spinning frogs! Frogs appear every second User can make requests: "dog", "cat", "cow" Even while frog is spinning
6 6 Creating and Starting a Thread Thread A separate path of execution Also: the name of a class in the Java API Program creates an object of type Thread Creating and starting a thread: Thread thread = new Thread(); thread.start(); Simple, but doesn't actually do anything: Thread is born Thread dies End of story
7 7 Making Work for a Thread Thread constructor can take an object Object must: implements Runnable Interface with a single method: run() run() may do work forever (e.g. random spinning frogs) run() may do something and exit (e.g. print a message) run() can call other methods, create objects, public class BlastOff implements Runnable public void run() for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) System.out.print(i + " "); System.out.println("BLAST OFF!");
8 8 Possible Code Execution Order #1 public class BlastOff implements Runnable public void run() for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) System.out.print(i + " "); System.out.println("BLAST OFF!"); public class Launch public static void main(string [] args) System.out.println("prepare for launch"); Thread thread = new Thread(new BlastOff()); thread.start(); System.out.println("done with launch"); % java Launch prepare for launch done with launch BLAST OFF!
9 9 Possible Code Execution Order #2 public class BlastOff implements Runnable public void run() for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) System.out.print(i + " "); System.out.println("BLAST OFF!"); public class Launch public static void main(string [] args) System.out.println("prepare for launch"); Thread thread = new Thread(new BlastOff()); thread.start(); System.out.println("done with launch"); % java Launch prepare for launch done with launch BLAST OFF! Different execution order: same output
10 10 Possible Code Execution Order #3 public class BlastOff implements Runnable public void run() for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) System.out.print(i + " "); System.out.println("BLAST OFF!"); public class Launch public static void main(string [] args) System.out.println("prepare for launch"); Thread thread = new Thread(new BlastOff()); thread.start(); System.out.println("done with launch"); % java Launch prepare for launch 10 done with launch BLAST OFF! Different execution order: different output
11 11 Possible Code Execution Order #4 public class BlastOff implements Runnable public void run() for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) System.out.print(i + " "); System.out.println("BLAST OFF!"); public class Launch public static void main(string [] args) System.out.println("prepare for launch"); Thread thread = new Thread(new BlastOff()); thread.start(); System.out.println("done with launch"); % java Launch prepare for launch 10 9 done with launch BLAST OFF! Lots more possible execution orders! Exact order depends on: thread scheduler
12 12 Thread States: Startup Thread t = new Thread(r); Just a normal object on the heap t.start(); Waiting to be selected by the thread scheduler Actually running on the CPU
13 13 Thread States
14 14 Launching Multiple Threads Main program: launch > 1 threads Split work into multiple parts public class MultiLaunch public static void main(string [] args) final int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); System.out.println("prepare for multi launch"); Thread [] threads = new Thread[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) threads[i] = new Thread(new BlastOff()); threads[i].start(); System.out.println("done launching"); % java MultiLaunch 3 prepare for multi launch done launching BLAST OFF! BLAST OFF! 1 BLAST OFF!
15 15 Important Thread Tricks Main thread can wait for workers e.g. Merge results from workers Alice Bob Carl Call join() on the thread object Passing data to/from a worker Thread() constructor is passed a Runnable object Add any instance variables / methods you want Input: send as parameters to constructor Output: add some get data method(s) But: you must keep track of object sent to Thread()
16 16 Parallel Fibonacci Calculator public class FibWorker implements Runnable private int num = 0; private long result = 0; public FibWorker(int num) this.num = num; public long getresult() return result; public void run() result = fib(num); private long fib(int n) if (n == 0) return 0; if (n == 1) return 1; return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2); Get the input, what we'll calculate once somebody says go! Somebody getting the output. Should only be called after the thread is known to be done. Method that runs when somebody call.start() on a Thread that has been passed this object.
17 17 Parallel Fibonacci Calculator public class FibLauncher public static void main(string [] args) Thread [] threads = new Thread[args.length]; FibWorker [] workers = new FibWorker[args.length]; for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) workers[i] = new FibWorker(Integer.parseInt(args[i])); threads[i] = new Thread(workers[i]); threads[i].start(); try for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) threads[i].join(); System.out.print("fib(" + args[i] + ") = "); System.out.println(workers[i].getResult()); catch (InterruptedException e) e.printstacktrace(); We must keep track of two parallel arrays, one for threads and one for worker objects. Setup worker with its job. Once a thread is done, we know it has a good output value.
18 18 Sleeping Making a thread take a nap Specify nap time in milliseconds Guaranteed to sleep at least this long Maybe longer though Allows other threads to enter running state Polite behavior when you've got nothing to do Thread.sleep(ms), but must catch an exception while (!StdDraw.hasNextKeyTyped()) // Burns an entire core to do nothing! char ch = StdDraw.nextKeyTyped(); while (!StdDraw.hasNextKeyTyped()) try Thread.sleep(10); catch (InterruptedException e) e.printstacktrace(); char ch = StdDraw.nextKeyTyped();
19 19 Naming Threads Threads can be given a name Helpful for debugging Second parameter to Thread() constructor Alice Bob Carl public class MultiLaunchSleep public static void main(string [] args) final int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); System.out.println("prepare for multi launch"); Thread [] threads = new Thread[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) threads[i] = new Thread(new BlastOff(), "B" + i); threads[i].start(); System.out.println("done launching");
20 20 A Sleepy Named Worker public class BlastOffSleep implements Runnable public void run() String myname = Thread.currentThread().getName(); for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--) System.out.print(i + "(" + myname + ") "); try Thread.sleep(1000); catch (InterruptedException e) e.printstacktrace(); System.out.println("BLAST OFF! (" + myname + ")"); % java MultiLaunchSleep 3 prepare for multi launch 10(B0) done launching 10(B2) 10(B1) 9(B0) 9(B1) 9(B2) 8(B0) 8(B1) 8(B2) 7(B0) 7(B1) 7(B2) 6(B1) 6(B0) 6(B2) 5(B0) 5(B2) 5(B1) 4(B0) 4(B1) 4(B2) 3(B0) 3(B1) 3(B2) 2(B0) 2(B1) 2(B2) 1(B0) 1(B1) 1(B2) BLAST OFF! (B0) BLAST OFF! (B1) BLAST OFF! (B2)
21 Summary Java Thread Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Really simultaneous (multiple cores) Simply seem that way (single core) Important thread skills: Implementing a worker class Starting a thread Making a thread sleep Waiting for a thread to finish Getting input to a thread Getting output from a thread
22 Your Turn Create a class that implements Runnable Draw something using StdDraw in unit box Sleep at least 500ms Change something about the drawing Repeat forever Don't worry about erasing Don't call StdDraw.clear() me your completed class I'll integrate into my ThreadZoo program Open Moodle, go to CSCI 136, Section 01 Open the dropbox for today Threads In-Class Asmt Drag and drop your program file to the Moodle dropbox You get: 1 point if you turn in something, 2 points if you turn in something that is correct.
Michele Van Dyne MUS 204B https://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136. Threads
 Michele Van Dyne MUS 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu https://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 Threads Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core) Actually at
Michele Van Dyne MUS 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu https://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 Threads Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core) Actually at
Concurrency. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Concurrency http://csunplugged.org/routing-and-deadlock Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core) Actually
Concurrency http://csunplugged.org/routing-and-deadlock Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core) Actually
Concurrency. CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen
 Concurrency http://csunplugged.org/routing-and-deadlock CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Overview Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly
Concurrency http://csunplugged.org/routing-and-deadlock CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Overview Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly
Michele Van Dyne MUS 204B https://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136. Concurrency Issues
 Michele Van Dyne MUS 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu https://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 Concurrency Issues Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core)
Michele Van Dyne MUS 204B mvandyne@mtech.edu https://katie.mtech.edu/classes/csci136 Concurrency Issues Multi-threaded programs Multiple simultaneous paths of execution Seemingly at once (single core)
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
Concurrent Computing CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development
 Concurrent Computing CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Outline Threads Multi-Threaded Code CPU Scheduling Program USC CSCI 201L Thread Overview Looking
Concurrent Computing CSCI 201 Principles of Software Development Jeffrey Miller, Ph.D. jeffrey.miller@usc.edu Outline Threads Multi-Threaded Code CPU Scheduling Program USC CSCI 201L Thread Overview Looking
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2012 Name: This exam consists of 5 problems on the following 8 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
Threads Chate Patanothai
 Threads Chate Patanothai Objectives Knowing thread: 3W1H Create separate threads Control the execution of a thread Communicate between threads Protect shared data C. Patanothai Threads 2 What are threads?
Threads Chate Patanothai Objectives Knowing thread: 3W1H Create separate threads Control the execution of a thread Communicate between threads Protect shared data C. Patanothai Threads 2 What are threads?
Stacks and Queues. Fundamentals of Computer Science.
 Stacks and Queues http://www.flickr.com/photos/mac-ash/4534203626/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/thowi/182298390/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Terminology Abstract Data Types ADT) Data structures
Stacks and Queues http://www.flickr.com/photos/mac-ash/4534203626/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/thowi/182298390/ Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Terminology Abstract Data Types ADT) Data structures
CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015
 CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
CSCI 136 Written Exam #2 Fundamentals of Computer Science II Spring 2015 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 6 pages. You may use your double- sided hand- written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet
Recursion. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Recursion Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Recursion A method calling itself All good recursion must come to an end A powerful tool in computer science Allows writing elegant and easy to understand
Recursion Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Recursion A method calling itself All good recursion must come to an end A powerful tool in computer science Allows writing elegant and easy to understand
7. MULTITHREDED PROGRAMMING
 7. MULTITHREDED PROGRAMMING What is thread? A thread is a single sequential flow of control within a program. Thread is a path of the execution in a program. Muti-Threading: Executing more than one thread
7. MULTITHREDED PROGRAMMING What is thread? A thread is a single sequential flow of control within a program. Thread is a path of the execution in a program. Muti-Threading: Executing more than one thread
Contents. 6-1 Copyright (c) N. Afshartous
 Contents 1. Classes and Objects 2. Inheritance 3. Interfaces 4. Exceptions and Error Handling 5. Intro to Concurrency 6. Concurrency in Java 7. Graphics and Animation 8. Applets 6-1 Copyright (c) 1999-2004
Contents 1. Classes and Objects 2. Inheritance 3. Interfaces 4. Exceptions and Error Handling 5. Intro to Concurrency 6. Concurrency in Java 7. Graphics and Animation 8. Applets 6-1 Copyright (c) 1999-2004
GRAPHICS AND SOUND. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 GRAPHICS AND SOUND Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline File Input Graphics StdDraw.java Audio Draw primitive shapes Draw images from a file Create animation loops Get keyboard input from users StdAudio.java
GRAPHICS AND SOUND Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline File Input Graphics StdDraw.java Audio Draw primitive shapes Draw images from a file Create animation loops Get keyboard input from users StdAudio.java
G51PGP Programming Paradigms. Lecture 009 Concurrency, exceptions
 G51PGP Programming Paradigms Lecture 009 Concurrency, exceptions 1 Reminder subtype polymorphism public class TestAnimals public static void main(string[] args) Animal[] animals = new Animal[6]; animals[0]
G51PGP Programming Paradigms Lecture 009 Concurrency, exceptions 1 Reminder subtype polymorphism public class TestAnimals public static void main(string[] args) Animal[] animals = new Animal[6]; animals[0]
Single processor CPU. Memory I/O
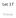 Lec 17 Threads Single processor CPU Memory I/O Multi processes Eclipse PPT iclicker Multi processor CPU CPU Memory I/O Multi-core Core Core Core Core Processor Memory I/O Logical Cores Multi-threaded
Lec 17 Threads Single processor CPU Memory I/O Multi processes Eclipse PPT iclicker Multi processor CPU CPU Memory I/O Multi-core Core Core Core Core Processor Memory I/O Logical Cores Multi-threaded
Stacks and queues. CSCI 135: Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen.
 Stacks and queues http://www.flickr.com/photos/mac-ash/4534203626/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/thowi/182298390/ CSCI 135: Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Terminology Overview Abstract
Stacks and queues http://www.flickr.com/photos/mac-ash/4534203626/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/thowi/182298390/ CSCI 135: Fundamentals of Computer Science Keith Vertanen Terminology Overview Abstract
Advanced Programming Methods. Lecture 6 - Concurrency in Java (1)
 Advanced Programming Methods Lecture 6 - Concurrency in Java (1) Overview Introduction Java threads Java.util.concurrent References NOTE: The slides are based on the following free tutorials. You may want
Advanced Programming Methods Lecture 6 - Concurrency in Java (1) Overview Introduction Java threads Java.util.concurrent References NOTE: The slides are based on the following free tutorials. You may want
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Threads and Concurrency
 CS 351 Design of Large Programs Threads and Concurrency Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Concurrency in Java Java has basic concurrency support built into the language. Also has high-level
CS 351 Design of Large Programs Threads and Concurrency Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Concurrency in Java Java has basic concurrency support built into the language. Also has high-level
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II. Threads in Java
 CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Threads in Java 1 Problem Multiple tasks for computer Draw & display images on screen Check keyboard & mouse input Send & receive data on network Read & write files
CMSC 132: Object-Oriented Programming II Threads in Java 1 Problem Multiple tasks for computer Draw & display images on screen Check keyboard & mouse input Send & receive data on network Read & write files
Enumerations. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Enumerations Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Avoiding magic numbers Variables takes on a small set of values Use descriptive names instead of literal values Java enumerations Using in a switch
Enumerations Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Avoiding magic numbers Variables takes on a small set of values Use descriptive names instead of literal values Java enumerations Using in a switch
Multiprocessing Threads/Lightweight objects Thread methods Concurrency Issues
 Concurrency Multiprocessing Threads/Lightweight objects Thread methods Concurrency Issues What is program execution? In order to run, a program must be loaded into memory and given an initial state. Code
Concurrency Multiprocessing Threads/Lightweight objects Thread methods Concurrency Issues What is program execution? In order to run, a program must be loaded into memory and given an initial state. Code
Animation Part 2: MoveableShape interface & Multithreading
 Animation Part 2: MoveableShape interface & Multithreading MoveableShape Interface In the previous example, an image was drawn, then redrawn in another location Since the actions described above can apply
Animation Part 2: MoveableShape interface & Multithreading MoveableShape Interface In the previous example, an image was drawn, then redrawn in another location Since the actions described above can apply
/** * Created Aug 19, 2012 */ package com.roguelogic.util;
 / Copyright 2012 Robert C. Ilardi Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
/ Copyright 2012 Robert C. Ilardi Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
System Programming. Practical Session 4: Threads and Concurrency / Safety
 System Programming Practical Session 4: Threads and Concurrency / Safety Using Threads - All the computer programs you've seen so far were sequential only one thing was performed at any given time - Sometimes
System Programming Practical Session 4: Threads and Concurrency / Safety Using Threads - All the computer programs you've seen so far were sequential only one thing was performed at any given time - Sometimes
Principles of Software Construction: Concurrency, Part 1
 Principles of Software Construction: Concurrency, Part 1 Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Midterm review tomorrow 7-9pm Midterm on Thursday If you re still looking for
Principles of Software Construction: Concurrency, Part 1 Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Midterm review tomorrow 7-9pm Midterm on Thursday If you re still looking for
CS61B, Spring 2003 Discussion #17 Amir Kamil UC Berkeley 5/12/03
 CS61B, Spring 2003 Discussion #17 Amir Kamil UC Berkeley 5/12/03 Topics: Threading, Synchronization 1 Threading Suppose we want to create an automated program that hacks into a server. Many encryption
CS61B, Spring 2003 Discussion #17 Amir Kamil UC Berkeley 5/12/03 Topics: Threading, Synchronization 1 Threading Suppose we want to create an automated program that hacks into a server. Many encryption
Network Programming COSC 1176/1179. Lecture 6 Concurrent Programming (2)
 Network Programming COSC 1176/1179 Lecture 6 Concurrent Programming (2) Threads Recall from last week Every line of Java code is part of a thread There can be one or more threads running in parallel Each
Network Programming COSC 1176/1179 Lecture 6 Concurrent Programming (2) Threads Recall from last week Every line of Java code is part of a thread There can be one or more threads running in parallel Each
CISC 4700 L01 Network & Client-Server Programming Spring Cowell Chapter 15: Writing Threaded Applications
 CISC 4700 L01 Network & Client-Server Programming Spring 2016 Cowell Chapter 15: Writing Threaded Applications Idea: application does simultaneous activities. Example: web browsers download text and graphics
CISC 4700 L01 Network & Client-Server Programming Spring 2016 Cowell Chapter 15: Writing Threaded Applications Idea: application does simultaneous activities. Example: web browsers download text and graphics
More on inheritance CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014
 More on inheritance CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Object hierarchies Overview Several classes inheriting from same base class Concrete versus abstract classes
More on inheritance CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Object hierarchies Overview Several classes inheriting from same base class Concrete versus abstract classes
Multithreaded Programming
 Multithreaded Programming Multithreaded programming basics Concurrency is the ability to run multiple parts of the program in parallel. In Concurrent programming, there are two units of execution: Processes
Multithreaded Programming Multithreaded programming basics Concurrency is the ability to run multiple parts of the program in parallel. In Concurrent programming, there are two units of execution: Processes
Chair of Software Engineering. Java and C# in Depth. Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer. Exercise Session 8. Nadia Polikarpova
 Chair of Software Engineering Java and C# in Depth Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session 8 Nadia Polikarpova Quiz 1: What is printed? (Java) class MyTask implements Runnable { «Everything is ok! public
Chair of Software Engineering Java and C# in Depth Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session 8 Nadia Polikarpova Quiz 1: What is printed? (Java) class MyTask implements Runnable { «Everything is ok! public
Definition: A thread is a single sequential flow of control within a program.
 What Is a Thread? All programmers are familiar with writing sequential programs. You've probably written a program that displays "Hello World!" or sorts a list of names or computes a list of prime numbers.
What Is a Thread? All programmers are familiar with writing sequential programs. You've probably written a program that displays "Hello World!" or sorts a list of names or computes a list of prime numbers.
Produced by. Design Patterns. MSc in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Design Patterns MSc in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie)! Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
Design Patterns MSc in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie)! Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
Threads & Timers. CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University
 Threads & Timers CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 Multi-tasking When you re working, how many different applications do you have open at one
Threads & Timers CSE260, Computer Science B: Honors Stony Brook University http://www.cs.stonybrook.edu/~cse260 Multi-tasking When you re working, how many different applications do you have open at one
CS 556 Distributed Systems
 CS 556 Distributed Systems Tutorial on 4 Oct 2002 Threads A thread is a lightweight process a single sequential flow of execution within a program Threads make possible the implementation of programs that
CS 556 Distributed Systems Tutorial on 4 Oct 2002 Threads A thread is a lightweight process a single sequential flow of execution within a program Threads make possible the implementation of programs that
Inheritance and objects
 Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket
Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2014 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket
Input and output thus far. Graphics and sound Input. New input/output capabilities. Output. StdDraw overview. StdDraw. StdAudio
 Graphics and sound Input Input and output thus far Parsing command line arguments Reading from a file using standard input Reading text typed by a user Output Display text to console Fundamentals of Computer
Graphics and sound Input Input and output thus far Parsing command line arguments Reading from a file using standard input Reading text typed by a user Output Display text to console Fundamentals of Computer
Program #3 - Airport Simulation
 CSCI212 Program #3 - Airport Simulation Write a simulation for a small airport that has one runway. There will be a queue of planes waiting to land and a queue of planes waiting to take off. Only one plane
CSCI212 Program #3 - Airport Simulation Write a simulation for a small airport that has one runway. There will be a queue of planes waiting to land and a queue of planes waiting to take off. Only one plane
Exercise Session Week 8
 Chair of Software Engineering Java and C# in Depth Carlo A. Furia, Marco Piccioni, Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session Week 8 Quiz 1: What is printed? (Java) class MyTask implements Runnable { public void
Chair of Software Engineering Java and C# in Depth Carlo A. Furia, Marco Piccioni, Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session Week 8 Quiz 1: What is printed? (Java) class MyTask implements Runnable { public void
Note: Each loop has 5 iterations in the ThreeLoopTest program.
 Lecture 23 Multithreading Introduction Multithreading is the ability to do multiple things at once with in the same application. It provides finer granularity of concurrency. A thread sometimes called
Lecture 23 Multithreading Introduction Multithreading is the ability to do multiple things at once with in the same application. It provides finer granularity of concurrency. A thread sometimes called
Java s Implementation of Concurrency, and how to use it in our applications.
 Java s Implementation of Concurrency, and how to use it in our applications. 1 An application running on a single CPU often appears to perform many tasks at the same time. For example, a streaming audio/video
Java s Implementation of Concurrency, and how to use it in our applications. 1 An application running on a single CPU often appears to perform many tasks at the same time. For example, a streaming audio/video
Principles of Software Construction: Concurrency, Part 1
 Principles of Software Construction: Concurrency, Part 1 Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Midterm review tomorrow 7-9pm, HH B103 Midterm on Thursday HW 5 team signup
Principles of Software Construction: Concurrency, Part 1 Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Midterm review tomorrow 7-9pm, HH B103 Midterm on Thursday HW 5 team signup
CSCD 330 Network Programming
 CSCD 330 Network Programming Lecture 12 More Client-Server Programming Winter 2019 Reading: References at end of Lecture 1 Introduction So far, Looked at client-server programs with Java Sockets TCP and
CSCD 330 Network Programming Lecture 12 More Client-Server Programming Winter 2019 Reading: References at end of Lecture 1 Introduction So far, Looked at client-server programs with Java Sockets TCP and
COE518 Lecture Notes Week 7 (Oct 17, 2011)
 coe518 (Operating Systems) Lecture Notes: Week 7 Page 1 of 10 COE518 Lecture Notes Week 7 (Oct 17, 2011) Topics multithreading in Java Note: Much of this material is based on http://download.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/concurrency/
coe518 (Operating Systems) Lecture Notes: Week 7 Page 1 of 10 COE518 Lecture Notes Week 7 (Oct 17, 2011) Topics multithreading in Java Note: Much of this material is based on http://download.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/concurrency/
Week 7. Concurrent Programming: Thread Synchronization. CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Week 7 Concurrent Programming: Thread Synchronization CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University Announcements Exam 1 tonight 6:30 pm - 7:30 pm MTHW 210 2 Outcomes Understand
Week 7 Concurrent Programming: Thread Synchronization CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University Announcements Exam 1 tonight 6:30 pm - 7:30 pm MTHW 210 2 Outcomes Understand
Exercise Session Week 8
 Chair of Software Engineering Java and C# in Depth Carlo A. Furia, Marco Piccioni, Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session Week 8 Java 8 release date Was early September 2013 Currently moved to March 2014 http://openjdk.java.net/projects/jdk8/milestones
Chair of Software Engineering Java and C# in Depth Carlo A. Furia, Marco Piccioni, Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session Week 8 Java 8 release date Was early September 2013 Currently moved to March 2014 http://openjdk.java.net/projects/jdk8/milestones
What is a Thread? Individual and separate unit of execution that is part of a process. multiple threads can work together to accomplish a common goal
 Java Threads What is a Thread? Individual and separate unit of execution that is part of a process multiple threads can work together to accomplish a common goal Video Game example one thread for graphics
Java Threads What is a Thread? Individual and separate unit of execution that is part of a process multiple threads can work together to accomplish a common goal Video Game example one thread for graphics
Java Threads. Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018
 Java Threads Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 9 of Learning Java, Fourth Edition by Niemeyer and Leuck, and other sources. Processes A process is an instance of a running program.
Java Threads Written by John Bell for CS 342, Spring 2018 Based on chapter 9 of Learning Java, Fourth Edition by Niemeyer and Leuck, and other sources. Processes A process is an instance of a running program.
Concurrency and Java Programming
 Concurrency and Java Programming What is Concurrent Programming? Concurrent programming involves using features of the Java VM that allow parts of your program to run in parallel with each other. This
Concurrency and Java Programming What is Concurrent Programming? Concurrent programming involves using features of the Java VM that allow parts of your program to run in parallel with each other. This
CSCD 330 Network Programming
 CSCD 330 Network Programming Lecture 12 More Client-Server Programming Winter 2016 Reading: References at end of Lecture 1 Introduction So far, Looked at client-server programs with Java Sockets TCP and
CSCD 330 Network Programming Lecture 12 More Client-Server Programming Winter 2016 Reading: References at end of Lecture 1 Introduction So far, Looked at client-server programs with Java Sockets TCP and
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
Multiprocessing Threads/Lightweight objects Thread methods Concurrency Issues
 Concurrency Multiprocessing Threads/Lightweight objects Thread methods Concurrency Issues What is program execution? In order to run, a program must be loaded into memory and given an initial state. Code
Concurrency Multiprocessing Threads/Lightweight objects Thread methods Concurrency Issues What is program execution? In order to run, a program must be loaded into memory and given an initial state. Code
The Java Programming Language Basics. Identifiers, Keywords, and Types. Object-Oriented Programming. Objects and Classes. Exception Handling
 Threads 13 Course Map This module covers multithreading, which allows a program to do multiple tasks at the same time. Getting Started The Java Programming Language Basics Identifiers, Keywords, and Types
Threads 13 Course Map This module covers multithreading, which allows a program to do multiple tasks at the same time. Getting Started The Java Programming Language Basics Identifiers, Keywords, and Types
COURSE 11 PROGRAMMING III OOP. JAVA LANGUAGE
 COURSE 11 PROGRAMMING III OOP. JAVA LANGUAGE PREVIOUS COURSE CONTENT Input/Output Streams Text Files Byte Files RandomAcessFile Exceptions Serialization NIO COURSE CONTENT Threads Threads lifecycle Thread
COURSE 11 PROGRAMMING III OOP. JAVA LANGUAGE PREVIOUS COURSE CONTENT Input/Output Streams Text Files Byte Files RandomAcessFile Exceptions Serialization NIO COURSE CONTENT Threads Threads lifecycle Thread
Computation Abstractions. Processes vs. Threads. So, What Is a Thread? CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2007
 CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2007 Threads and Synchronization May 8, 2007 Computation Abstractions t1 t1 t4 t2 t1 t2 t5 t3 p1 p2 p3 p4 CPU 1 CPU 2 A computer Processes
CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2007 Threads and Synchronization May 8, 2007 Computation Abstractions t1 t1 t4 t2 t1 t2 t5 t3 p1 p2 p3 p4 CPU 1 CPU 2 A computer Processes
Dynamic Arrays. Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Dynamic Arrays Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Dynamically sized arrays Java ArrayList Like an array but extra-powerful Has no fixed sized Add/remove elements dynamically as needed Contains objects
Dynamic Arrays Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline Dynamically sized arrays Java ArrayList Like an array but extra-powerful Has no fixed sized Add/remove elements dynamically as needed Contains objects
JAVA - MULTITHREADING
 JAVA - MULTITHREADING http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_multithreading.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Java is amultithreaded programming language which means we can develop mult it hreaded program
JAVA - MULTITHREADING http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_multithreading.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Java is amultithreaded programming language which means we can develop mult it hreaded program
/* Copyright 2012 Robert C. Ilardi
 / Copyright 2012 Robert C. Ilardi Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
/ Copyright 2012 Robert C. Ilardi Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
CS18000: Programming I
 CS18000: Programming I Synchronization 22 February, 2010 Prof. Chris Clifton Concurrency Example: Banking class ATM { public void withdrawcash(acct a) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int amount
CS18000: Programming I Synchronization 22 February, 2010 Prof. Chris Clifton Concurrency Example: Banking class ATM { public void withdrawcash(acct a) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int amount
Inheritance and objects
 Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Pu8ng similar objects in the same bucket Extremely
Inheritance and objects CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2013 Inheritance Overview Sharing code between related classes Pu8ng similar objects in the same bucket Extremely
Multithreading Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 1 23 Multithreading 2 23.1 Introduction Multithreading Provides application with multiple threads of execution Allows programs to perform tasks concurrently Often requires programmer to synchronize threads
1 23 Multithreading 2 23.1 Introduction Multithreading Provides application with multiple threads of execution Allows programs to perform tasks concurrently Often requires programmer to synchronize threads
CS360 Lecture 12 Multithreading
 CS360 Lecture 12 Multithreading Thursday, March 11, 2004 Reading Multithreading: Chapter 16 Thread States At any time, a thread can be in one of several thread states: - Born: this is the time when the
CS360 Lecture 12 Multithreading Thursday, March 11, 2004 Reading Multithreading: Chapter 16 Thread States At any time, a thread can be in one of several thread states: - Born: this is the time when the
Java Threads. 02/05/2007 CSCI 315 Operating Systems Design 1
 Java Threads Notice: The slides for this lecture have been largely based on those accompanying the textbook Operating Systems Concepts with Java, by Silberschatz, Galvin, and Gagne (2007). Many, if not
Java Threads Notice: The slides for this lecture have been largely based on those accompanying the textbook Operating Systems Concepts with Java, by Silberschatz, Galvin, and Gagne (2007). Many, if not
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING THREAD S BASICS. Introduction Thread basics. Thread states. Sequence diagrams
 SUMMARY CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING THREAD S BASICS PROGRAMMAZIONE CONCORRENTE E DISTR. Introduction Thread basics Thread properties Thread states Thread interruption Sequence diagrams Università degli Studi
SUMMARY CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING THREAD S BASICS PROGRAMMAZIONE CONCORRENTE E DISTR. Introduction Thread basics Thread properties Thread states Thread interruption Sequence diagrams Università degli Studi
Concurrent Programming: Threads. CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Concurrent Programming: Threads CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University Objectives This week we will get introduced to concurrent programming Creating a new thread of execution
Concurrent Programming: Threads CS 180 Sunil Prabhakar Department of Computer Science Purdue University Objectives This week we will get introduced to concurrent programming Creating a new thread of execution
INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Inheritance Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket Extremely common in modern OOP languages Managing
INHERITANCE AND OBJECTS Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Inheritance Sharing code between related classes Putting similar objects in the same bucket Extremely common in modern OOP languages Managing
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Software Practice 1 - Multithreading
 Software Practice 1 - Multithreading What is the thread Life cycle of thread How to create thread Thread method Lab practice Prof. Joonwon Lee T.A. Jaehyun Song Jongseok Kim T.A. Sujin Oh Junseong Lee
Software Practice 1 - Multithreading What is the thread Life cycle of thread How to create thread Thread method Lab practice Prof. Joonwon Lee T.A. Jaehyun Song Jongseok Kim T.A. Sujin Oh Junseong Lee
1 interface TemperatureSensor extends java.rmi.remote 2 { 3 public double gettemperature() throws java.rmi.remoteexception; 4 public void
 1 interface TemperatureSensor extends java.rmi.remote 2 { 3 public double gettemperature() throws java.rmi.remoteexception; 4 public void addtemperaturelistener ( TemperatureListener listener ) 5 throws
1 interface TemperatureSensor extends java.rmi.remote 2 { 3 public double gettemperature() throws java.rmi.remoteexception; 4 public void addtemperaturelistener ( TemperatureListener listener ) 5 throws
Java FX. Threads, Workers and Tasks
 Java FX Threads, Workers and Tasks Threads and related topics Lecture Overview...but first lets take a look at a good example of Model - View - Controler set up This and most of the lecture is taken from
Java FX Threads, Workers and Tasks Threads and related topics Lecture Overview...but first lets take a look at a good example of Model - View - Controler set up This and most of the lecture is taken from
Multithreaded Programming
 core programming Multithreaded Programming 1 2001-2003 Marty Hall, Larry Brown http:// 2 Multithreaded Programming Agenda Why threads? Approaches for starting threads Separate class approach Callback approach
core programming Multithreaded Programming 1 2001-2003 Marty Hall, Larry Brown http:// 2 Multithreaded Programming Agenda Why threads? Approaches for starting threads Separate class approach Callback approach
INF 212 ANALYSIS OF PROG. LANGS CONCURRENCY. Instructors: Crista Lopes Copyright Instructors.
 INF 212 ANALYSIS OF PROG. LANGS CONCURRENCY Instructors: Crista Lopes Copyright Instructors. Basics Concurrent Programming More than one thing at a time Examples: Network server handling hundreds of clients
INF 212 ANALYSIS OF PROG. LANGS CONCURRENCY Instructors: Crista Lopes Copyright Instructors. Basics Concurrent Programming More than one thing at a time Examples: Network server handling hundreds of clients
Multiple Choice Questions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. (15 marks)
 M257 MTA Spring2010 Multiple Choice Questions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. (15 marks) 1. If we need various objects that are similar in structure, but
M257 MTA Spring2010 Multiple Choice Questions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. (15 marks) 1. If we need various objects that are similar in structure, but
Synchronization synchronization.
 Unit 4 Synchronization of threads using Synchronized keyword and lock method- Thread pool and Executors framework, Futures and callable, Fork-Join in Java. Deadlock conditions 1 Synchronization When two
Unit 4 Synchronization of threads using Synchronized keyword and lock method- Thread pool and Executors framework, Futures and callable, Fork-Join in Java. Deadlock conditions 1 Synchronization When two
TDDB84: Lecture 5. Singleton, Builder, Proxy, Mediator. fredag 27 september 13
 TDDB84: Lecture 5 Singleton, Builder, Proxy, Mediator Creational Abstract Factory Singleton Builder Structural Composite Proxy Bridge Adapter Template method Behavioral Iterator Mediator Chain of responsibility
TDDB84: Lecture 5 Singleton, Builder, Proxy, Mediator Creational Abstract Factory Singleton Builder Structural Composite Proxy Bridge Adapter Template method Behavioral Iterator Mediator Chain of responsibility
THREADS AND CONCURRENCY
 THREADS AND CONCURRENCY Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2013 Graphs summary 2 Dijkstra: given a vertex v, finds shortest path from v to x for each vertex x in the graph Key idea: maintain a 5-part invariant on
THREADS AND CONCURRENCY Lecture 22 CS2110 Spring 2013 Graphs summary 2 Dijkstra: given a vertex v, finds shortest path from v to x for each vertex x in the graph Key idea: maintain a 5-part invariant on
Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011
 Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Recursion A method calling itself Overview A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming
Recursion CSCI 136: Fundamentals of Computer Science II Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Recursion A method calling itself Overview A new way of thinking about a problem Divide and conquer A powerful programming
Parallel Programming Languages COMP360
 Parallel Programming Languages COMP360 The way the processor industry is going, is to add more and more cores, but nobody knows how to program those things. I mean, two, yeah; four, not really; eight,
Parallel Programming Languages COMP360 The way the processor industry is going, is to add more and more cores, but nobody knows how to program those things. I mean, two, yeah; four, not really; eight,
BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I
![BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I BASIC COMPUTATION. public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I](/thumbs/81/83968367.jpg) BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
BASIC COMPUTATION x public static void main(string [] args) Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Using Eclipse Data Types Variables Primitive and Class Data Types Expressions Declaration Assignment
The Java Programming Language Basics. Identifiers, Keywords, and Types. Object-Oriented Programming. Objects and Classes. Exception Handling
 Threads 13 Course Map This module covers multithreading, which allows a program to do multiple tasks at the same time. Getting Started The Java Programming Language Basics Identifiers, Keywords, and Types
Threads 13 Course Map This module covers multithreading, which allows a program to do multiple tasks at the same time. Getting Started The Java Programming Language Basics Identifiers, Keywords, and Types
Java Programming Lecture 23
 Java Programming Lecture 23 Alice E. Fischer April 19, 2012 Alice E. Fischer () Java Programming - L23... 1/20 April 19, 2012 1 / 20 Outline 1 Thread Concepts Definition and Purpose 2 Java Threads Creation
Java Programming Lecture 23 Alice E. Fischer April 19, 2012 Alice E. Fischer () Java Programming - L23... 1/20 April 19, 2012 1 / 20 Outline 1 Thread Concepts Definition and Purpose 2 Java Threads Creation
Multithread Computing
 Multithread Computing About This Lecture Purpose To learn multithread programming in Java What You Will Learn ¾ Benefits of multithreading ¾ Class Thread and interface Runnable ¾ Thread methods and thread
Multithread Computing About This Lecture Purpose To learn multithread programming in Java What You Will Learn ¾ Benefits of multithreading ¾ Class Thread and interface Runnable ¾ Thread methods and thread
Programmazione Avanzata e Paradigmi Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche - UNIBO a.a 2013/2014 Lecturer: Alessandro Ricci
 v1.0 20130323 Programmazione Avanzata e Paradigmi Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche - UNIBO a.a 2013/2014 Lecturer: Alessandro Ricci [module lab 2.1] CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: INTRODUCTION 1 CONCURRENT
v1.0 20130323 Programmazione Avanzata e Paradigmi Ingegneria e Scienze Informatiche - UNIBO a.a 2013/2014 Lecturer: Alessandro Ricci [module lab 2.1] CONCURRENT PROGRAMMING IN JAVA: INTRODUCTION 1 CONCURRENT
Threads. 3 Two-Minute Drill. Certification Objectives. Q&A Self Test. Start New Threads. Write Code That Uses wait(), notify(), or notifyall()
 9 Threads Certification Objectives l l l Start New Threads Recognize Thread States and Transitions Use Object Locking to Avoid Concurrent Access l Write Code That Uses wait(), notify(), or notifyall()
9 Threads Certification Objectives l l l Start New Threads Recognize Thread States and Transitions Use Object Locking to Avoid Concurrent Access l Write Code That Uses wait(), notify(), or notifyall()
COMP 213. Advanced Object-oriented Programming. Lecture 23. Shared Variables and Synchronization
 COMP 213 Advanced Object-oriented Programming Lecture 23 Shared Variables and Synchronization Communicating Threads In the previous lecture, we saw an example of a multi-threaded program where three threads
COMP 213 Advanced Object-oriented Programming Lecture 23 Shared Variables and Synchronization Communicating Threads In the previous lecture, we saw an example of a multi-threaded program where three threads
TESTING AND DEBUGGING
 TESTING AND DEBUGGING zombie[1] zombie[3] Buuuuugs zombie[4] zombie[2] zombie[5] zombie[0] Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Debugging Types of Errors Syntax Errors Semantic Errors Logic Errors
TESTING AND DEBUGGING zombie[1] zombie[3] Buuuuugs zombie[4] zombie[2] zombie[5] zombie[0] Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Debugging Types of Errors Syntax Errors Semantic Errors Logic Errors
Threads Assistant Professor DCS Operating System Concepts
 Threads Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Assistant Professor COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Operating System Concepts Definitions Threads In the previous discussion, a process
Threads Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Assistant Professor COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Operating System Concepts Definitions Threads In the previous discussion, a process
Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 1 / 38 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 10: Threads and Multitasking Robots Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 2 / 38 Today Some more programming techniques that
1 / 38 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecture 10: Threads and Multitasking Robots Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool 2 / 38 Today Some more programming techniques that
Advanced Programming Concurrency
 Advanced Programming Concurrency Concurrent Programming Until now, a program was a sequence of operations, executing one after another. In a concurrent program, several sequences of operations may execute
Advanced Programming Concurrency Concurrent Programming Until now, a program was a sequence of operations, executing one after another. In a concurrent program, several sequences of operations may execute
Java Threads. What Are Threads? General-purpose solution for managing concurrency. Multiple independent execution streams. Shared state.
 Java Threads What Are Threads? Shared state (variables, files) Threads General-purpose solution for managing concurrency. Multiple independent execution streams Shared state SoftEng Group 1 What Are Threads
Java Threads What Are Threads? Shared state (variables, files) Threads General-purpose solution for managing concurrency. Multiple independent execution streams Shared state SoftEng Group 1 What Are Threads
Advanced Programming C# Lecture 13. dr inż. Małgorzata Janik
 Advanced Programming C# Lecture 13 dr inż. Małgorzata Janik majanik@if.pw.edu.pl Winter Semester 2017/2018 Project C# 2017/2018, Lecture 13 3 / 24 Project part III Final Date: 22.01.2018 (next week!) Today
Advanced Programming C# Lecture 13 dr inż. Małgorzata Janik majanik@if.pw.edu.pl Winter Semester 2017/2018 Project C# 2017/2018, Lecture 13 3 / 24 Project part III Final Date: 22.01.2018 (next week!) Today
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Chapter 4: Threads. Zhi Wang Florida State University
 COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Chapter 4: Threads Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Thread overview Multithreading models Thread libraries Threading issues Operating
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2015) Chapter 4: Threads Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Thread overview Multithreading models Thread libraries Threading issues Operating
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012
 CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
CSCI 135 Exam #1 Fundamentals of Computer Science I Fall 2012 Name: This exam consists of 6 problems on the following 7 pages. You may use your two-sided hand-written 8 ½ x 11 note sheet during the exam.
THREADS AND MULTITASKING ROBOTS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming techniques that will be helpful
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming techniques that will be helpful
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS
 ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 THREADS AND MULTITASKING ROBOTS comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming
ROBOTICS AND AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS Simon Parsons Department of Computer Science University of Liverpool LECTURE 10 THREADS AND MULTITASKING ROBOTS comp329-2013-parsons-lect10 2/37 Today Some more programming
EXCEPTIONS. Fundamentals of Computer Science I
 EXCEPTIONS Exception in thread "main" java.lang.numberformatexception: For input string: "3.5" at java.lang.numberformatexception.forinputstring(numberformatexception.java:48) at java.lang.integer.parseint(integer.java:458)
EXCEPTIONS Exception in thread "main" java.lang.numberformatexception: For input string: "3.5" at java.lang.numberformatexception.forinputstring(numberformatexception.java:48) at java.lang.integer.parseint(integer.java:458)
Question Points Score Total 100
 Midterm Exam #1 CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2014 March 13, 2014 Guidelines Put your name on each page before starting the exam. Write your answers directly on the exam
Midterm Exam #1 CMSC 433 Programming Language Technologies and Paradigms Spring 2014 March 13, 2014 Guidelines Put your name on each page before starting the exam. Write your answers directly on the exam
CS106A, Stanford Handout #25. Methods 2
 CS106A, Stanford Handout #25 Fall, 2004-05 Nick Parlante Methods 2 System.out.println() Console System.out is a standard system object. It implements a println() method that takes a String argument and
CS106A, Stanford Handout #25 Fall, 2004-05 Nick Parlante Methods 2 System.out.println() Console System.out is a standard system object. It implements a println() method that takes a String argument and
