A parallel computing framework and a modular collaborative cfd workbench in Java
|
|
|
- Michael Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 21 A parallel computing framework and a modular collaborative cfd workbench in Java S. Sengupta & K. P. Sinhamahapatra Department of Aerospace Engineering, IIT Kharagpur, India Abstract The aim of this study is to give the means for writing parallel programs and to transform sequential/shared memory programs into distributed programs, in an object-oriented environment and also to develop a parallel CFD workbench utilizing the framework. In this approach, the programmer controls the distribution of programs through control and data distribution. The authors have defined and implemented a parallel framework, including the expression of object distributions, and the transformations required to run a parallel program in a distributed environment. The authors provide programmers with a unified way to express parallelism and distribution by the use of collections storing active and passive objects. The distribution of classes/packages leads to the distribution of their elements and therefore to the generation of distributed programs. The authors have developed a full prototype to write parallel programs and to transform those programs into distributed programs with a host of about 12 functions. This prototype has been implemented with the Java language, and does not require any language extensions or modifications to the standard Java environment. The parallel program is utilized by developing a CFD workbench equipped with high end FEM unstructured mesh generation and flow solving tools with an easy-to-use GUI implemented entirely on the parallel framework. Keywords: Java, framework, parallel programming, program transformation, CFD, mesh. 1 Introduction The chief aim here is to provide a few tracks in the use and development of an environment or more specifically a programming framework for the development of CFD engineering software with parallel approaches. Many doi: /afm06003
2 22 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI authors have shown the strength of the approach in different fields of mechanics, including parallel and/or CFD computations: e.g. a study of a transient model of fluid mechanics fully coupled to an electrochemistry model in [1], some objectoriented techniques dedicated to CFD in [2], a finite element model for modeling heat and mass transfer using the Diffpack library in [3], domain decomposition techniques using pvm [4], [5]. In [6], the problem of the utilization of Java for numerical computation in the industrial real life problems is raised up, and no definitive response is brought probably because of lack of experiments in the domain. One aim of the present work is to give an example of large scale coding in java significantly more complex than sequential programming; the idea of this work is to develop a pure JAVA framework for finite elements or finite volume parallel computations. In this paper, the authors would like to describe some aspects of developing an application in Java for domain decomposition in CFD with examples and proves of data convergence and comparative speedups taking into account another problem of some computational complexity all along using the authors parallel framework.the paper, however, does not discuss the choices of the algorithms which will be done in a future paper, but to illustrate on complex algorithmic examples the opportunity to move to a new programming paradigm. To begin, the authors show some pure performance comparison tests between JAVA and C/C++ on a classical matrix/vector product and data convergence with a program written for calculating lift and drag over a NACA aerofoil (using Lifting-Line theory). Programming for multiprocessors computers is embedded in the JAVA environment. After a brief description of the basic features of JAVA, the authors introduce a simple way of writing a parallel matrix/vector product in Java implanted for SIMD/MIMD computers for solving large linear systems by the way of an iterative method. At last, the authors show a tentative development for a overlapping domain decomposition method for the Navier-Stokes problem implemented entirely on the framework to illustrate the fast development capabilities in JAVA for objectoriented finite elements and the emerging possibilities of the development of object-oriented distributed computing libraries for lucid programming. The library named JPE includes an easy and intuitive programming model based on distributed threads; object-based, message-passing APIs; and distributable data collection. JPE takes a class library-based approach to providing a distributed parallel programming environment. New classes and interfaces supporting distributed threads, message passing, and distributable data collections are included in this package. 2 Computational problems and the approach Roughly speaking, we distinguish the Java programming language from the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM is an interpreter that executes the program compiled to Java byte codes. The main consequence is that a program compiled on a system can be run on all systems. This very attractive aspect could hide a major drawback especially in CFD computation: the efficiency. Most computations in mechanics involve a large number of scalar products (elemental
3 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 23 contributions computation, Crout reduction in direct linear systems solvers, matrix/vector products in iterative linear system solvers). Here, the same code has been tested. (Java has a C++ syntax, only memory allocation) for computation of matrix/vector products, with a direct addressing and with an indirect addressing, i.e. code respectively corresponding to v[j] = A[i][j] * x[j] and v[j] = A[i][j] * x[table[j]], where table[] enables us to address the elements in the array x[]. It is worth noting that the code in C/C++ and JAVA are exactly the same. Various number of matrix/vector products are done, for various size of matrices. Results are shown on Figure 1. Results are similar on different platforms (Windows XP on a Pentium 845, Linux on a single-processor Intel- 845, Tru 64 Dec-Unix on a 4 processors EV6 Version and version for JAVA virtual machine and J2SDK1.4.2) and shows roughly speaking that Java is from 72% to 85% within the C compiled code with maximal optimization options for direct memory access, and from 65% to 82% with indirect addressing. It should be noted that with reference to Amdahl s law of speedup in parallel systems, the best results are obtained for large sized matrices. The drawn conclusion is that good performances rate can be achieved for computational tools in Java using threads. This efficiency is acceptable to develop tools for the fast design of numerical algorithms for large application on single processor systems using time-sharing. Figure 1: Comparison between C/C++ and Java code for matrix/vector multiplications using threads on single processor systems. 3 Parallel algorithm and approach 3.1 The parallel framework Looking at MPI which has been accepted as the standard for parallel computing on distributed platforms in C, the library comes with similar functions with almost similar syntax as well as functions. The use of non-blocking communication alleviates the need for buffering since a sending process may
4 24 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI progress after it has posted a send. Therefore the constraints of safe programming can be relaxed. However some amount of storage is consumed by a pending communication. At a minimum the communication subsystem needs to copy the parameters of a posted send or receive before the call returns. If this storage is exhausted then a call that posts a new communication will fail since post send or post receive calls are not allowed to block. A high quality implementation will consume only a fixed amount of storage per posted nonblocking communication thus supporting a large number of pending communications. The failure of a parallel program that exceeds the bounds on the number of pending non-blocking communications like the failure of a sequential program that exceeds the bound on stack size should be seen as a pathological case due either to a pathological program or a pathological JPE implementation. Table 1: Method specifications. int JPE_Init(int num_procs,string mother_machine) int JPE_getID(void) int JPE_Send(datatype[] data,int size,int hid) nt JPE_Recv(datatype[] data,int size,int hid) The first and foremost of the functions that has to be called to initialize the framework. Return value is 1 if successful else returns error code(0 to 7 except 1). This method returns the local id of the machine i.e. the integer id of the current processor. used to send data to another processor with id hid. (Overloaded) used to receive data from another processor with id hid. Is highly dependent on the machine identifier. Often used in identifying processors using ids and not machine id. The hid parameter must be correct to ensure data transfer. Available as both blocking and non-blocking. The hid parameter must be correct to ensure data transfer. Available as both blocking and non-blocking. int JPE_Bcast(datatype data,int size) used to send data to all another processors in the connection. Returns 1 if ok else 0-7 except 1 in case of errors. Comes in two formats blocking and non-blocking. Available as both blocking and non-blocking.
5 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 25 Table 1: Continued. int JPE_iAllReduce(int data,int operation int JPE_iReduce(int data,int operation,int hid) int JPE_Finalise() used to accumulate the results obtained as a result of certain computations in each processor by the operation parameter and saved in each processor. used to accumulate the results obtained as a result of certain computations in each processor by the operation parameter and saved in the target processor given by the parameter hid-> host id to receive final value. Returns 1 if ok else returns -1. Similar implementations exist for short, unsigned short, unsigned int, long, unsigned long, float, unsigned float, double, unsigned double as well as unsigned long double as well as for classes with applicable fields. Similar implementations exist for short, unsigned short, unsigned int, long, unsigned long, float, unsigned float, double, unsigned double as well as unsigned long double as well as for classes with applicable fields. Available as both blocking and nonblocking. Mandatory method. Figure 2: Comparison between data generated between serial and p=2,4 and 6 parallel algorithm.
6 26 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 4 Results 4.1 Data convergence Here to verify the convergence of the local and global solutions and to yield a satisfactory result that satisfies both advantages of time and space complexity, the authors have considered the computation of drag and lift (along with pressure) distribution on a NACA-0012 aerofoil at a given angle of attack, freestream conditions etc. making use of the thin aerofoil theory. Figure 2 shows the plot of lift coefficient along a NACA-0012 aerofoil for various numbers of processors against the serial code. Figure 3: Comparison between speed ups of various processors along with variation in data size. 4.2 Speed up In Java, parallel programming is embedded into the language. The key point of this kind of programming is the class JDC present in the package JPE. The question is then to check the performance of this class in the context of a CFD code. The test done here is to parallelize an unstructured mesh generation algorithm: the code being tested on Linux systems-intel-845. Figure 3 shows the speedup achieved over number of processors for a mesh size of 160,000 triangular elements. 4.3 The CFD workbench The workbench was written in Java and the GUI was implemented using the swing utility. The look and feel is set to platform default look by the Java code piece: UIManager.SetLookandFeel(default). The workbench provides users
7 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 27 with a canvas to draw arbitrary geometries as well as select certain standard features. The mesh button displays a dialog which prompts the user to select mesh fineness. Solve button displays a dialog prompting the equation to be solved and tolerance factors to be considers. The top-level menus include options to display pressure plots, streamlines and as well as vibration plots along time. Figure 4: Mesh generated around an arbitrary body. (2-D). Figure 5: Mesh generated by domain-decomposition around an arbitrary body. (2-D). Boundary lines indicate load-balancing across 4 processors by geometry distribution and inter-zonal boundaries.
8 28 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI Figure 6: Manager Worker model to distribute computational load. The mesh generation is achieved by decomposing the entire flow domain into sub-domains and distributing the computational load across participating processors. The method presented in this paper is geometry-based, in that the geometrical data of the boundary is used to create artificial inter-zonal boundaries. Figure 5 shows the artificial inter-zonal boundaries and figure 6 shows the approach taken to decompose the domain into parts which are separately distributed to the worker processors by the manager. 5 Conclusions The central point of this project is the development of a parallel framework for developing FEM components, FEM discretisations, adaptive ness and multi-grid solvers and their realisation in a CAD software package as shown, which directly includes tools for parallelism and hardware-adapted high-performance in low level kernel routines; completely platform independent. It is the special goal in this project to realize and to optimize the algorithmic concepts used internally in the environment for specific computers (Sun Solaris, Linux/Unix) and to adapt the mathematical components to complex configurations. In this paper we have presented an expressive parallel programming model implemented by a framework in the Java language. We have not made any extension to the language. The synchronization model is very simple and will be extended in order to enlarge the application domain of our programming model.
9 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 29 References [1] A. P. Peskin and G. R. Hardin, An object-oriented approach to general purpose fluid dynamics software, Computers & Chemical Engineering, Vol. 20, 1996, pp [2] O. Munthe and H. P. Langtangen, Finite elements and object-oriented implementation techniques in computational fluid dynamics, Computer Methods Applied Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 190, 2000, pp [3] S.-H. Sun and T. R. Marrero, An object-oriented programming approach for heat and mass transfer related analyses, Computers & Chemical Engineering, Vol. 22, 1998, pp [4] D. S. Kershaw, M. K. Prasad, M. J. Shaw and J. L. Milovich, 3D element Unstructured mesh ALE hydrodynamics, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, Vol. 158, 1998, pp [5] P. Krysl and T. Belytschko, Object-oriented parallelization of explicit structural dynamics with PVM, Computers & Structures, Vol. 66,1998, pp [6] M. Ginsberg, J. Hauser, J. E. Moreira, R. Morgan, J. C. Parsons and T. J. Wielenga, Panel session: future directions and challenges for Java implementations of numeric-intensive industrial applications, Advances in EngineeringSoftware, Vol.31, 2000,pp
CMSC 714 Lecture 6 MPI vs. OpenMP and OpenACC. Guest Lecturer: Sukhyun Song (original slides by Alan Sussman)
 CMSC 714 Lecture 6 MPI vs. OpenMP and OpenACC Guest Lecturer: Sukhyun Song (original slides by Alan Sussman) Parallel Programming with Message Passing and Directives 2 MPI + OpenMP Some applications can
CMSC 714 Lecture 6 MPI vs. OpenMP and OpenACC Guest Lecturer: Sukhyun Song (original slides by Alan Sussman) Parallel Programming with Message Passing and Directives 2 MPI + OpenMP Some applications can
CFDnet: Computational Fluid Dynamics on the Internet
 CFDnet: Computational Fluid Dynamics on the Internet F. E. Ham, J. Militzer and A. Bemfica Department of Mechanical Engineering Dalhousie University - DalTech Halifax, Nova Scotia Abstract CFDnet is computational
CFDnet: Computational Fluid Dynamics on the Internet F. E. Ham, J. Militzer and A. Bemfica Department of Mechanical Engineering Dalhousie University - DalTech Halifax, Nova Scotia Abstract CFDnet is computational
Introducing Overdecomposition to Existing Applications: PlasComCM and AMPI
 Introducing Overdecomposition to Existing Applications: PlasComCM and AMPI Sam White Parallel Programming Lab UIUC 1 Introduction How to enable Overdecomposition, Asynchrony, and Migratability in existing
Introducing Overdecomposition to Existing Applications: PlasComCM and AMPI Sam White Parallel Programming Lab UIUC 1 Introduction How to enable Overdecomposition, Asynchrony, and Migratability in existing
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems
 1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
1.2 Numerical Solutions of Flow Problems DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SIMPLIFIED FLOW PROBLEM Continuity equation for incompressible flow: 0 Momentum (Navier-Stokes) equations for a Newtonian
A Test Suite for High-Performance Parallel Java
 page 1 A Test Suite for High-Performance Parallel Java Jochem Häuser, Thorsten Ludewig, Roy D. Williams, Ralf Winkelmann, Torsten Gollnick, Sharon Brunett, Jean Muylaert presented at 5th National Symposium
page 1 A Test Suite for High-Performance Parallel Java Jochem Häuser, Thorsten Ludewig, Roy D. Williams, Ralf Winkelmann, Torsten Gollnick, Sharon Brunett, Jean Muylaert presented at 5th National Symposium
Program: Advanced Certificate Program
 Program: Advanced Certificate Program Course: CFD-Vehicle Aerodynamics Directorate of Training and Lifelong Learning #470-P, Peenya Industrial Area, 4th Phase Peenya, Bengaluru 560 058 www.msruas.ac.in
Program: Advanced Certificate Program Course: CFD-Vehicle Aerodynamics Directorate of Training and Lifelong Learning #470-P, Peenya Industrial Area, 4th Phase Peenya, Bengaluru 560 058 www.msruas.ac.in
computational Fluid Dynamics - Prof. V. Esfahanian
 Three boards categories: Experimental Theoretical Computational Crucial to know all three: Each has their advantages and disadvantages. Require validation and verification. School of Mechanical Engineering
Three boards categories: Experimental Theoretical Computational Crucial to know all three: Each has their advantages and disadvantages. Require validation and verification. School of Mechanical Engineering
AIRFOIL SHAPE OPTIMIZATION USING EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHMS
 AIRFOIL SHAPE OPTIMIZATION USING EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHMS Emre Alpman Graduate Research Assistant Aerospace Engineering Department Pennstate University University Park, PA, 6802 Abstract A new methodology
AIRFOIL SHAPE OPTIMIZATION USING EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHMS Emre Alpman Graduate Research Assistant Aerospace Engineering Department Pennstate University University Park, PA, 6802 Abstract A new methodology
Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies
 Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies Compiled by Mike Slack Ansys Technical Services 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Introduction Shape optimisation technologies
Shape optimisation using breakthrough technologies Compiled by Mike Slack Ansys Technical Services 2010 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Introduction Shape optimisation technologies
Multigrid Pattern. I. Problem. II. Driving Forces. III. Solution
 Multigrid Pattern I. Problem Problem domain is decomposed into a set of geometric grids, where each element participates in a local computation followed by data exchanges with adjacent neighbors. The grids
Multigrid Pattern I. Problem Problem domain is decomposed into a set of geometric grids, where each element participates in a local computation followed by data exchanges with adjacent neighbors. The grids
Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization
 Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Siva Nadarajah Antony Jameson Stanford University 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference
Studies of the Continuous and Discrete Adjoint Approaches to Viscous Automatic Aerodynamic Shape Optimization Siva Nadarajah Antony Jameson Stanford University 15th AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference
Fluent User Services Center
 Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING
 Review of the Air Force Academy No.3 (35)/2017 NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING Cvetelina VELKOVA Department of Technical Mechanics, Naval Academy Nikola Vaptsarov,Varna, Bulgaria (cvetelina.velkova1985@gmail.com)
Review of the Air Force Academy No.3 (35)/2017 NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING Cvetelina VELKOVA Department of Technical Mechanics, Naval Academy Nikola Vaptsarov,Varna, Bulgaria (cvetelina.velkova1985@gmail.com)
OPERATING SYSTEM. Chapter 4: Threads
 OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 4: Threads Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples Objectives To
OPERATING SYSTEM Chapter 4: Threads Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples Objectives To
Missile External Aerodynamics Using Star-CCM+ Star European Conference 03/22-23/2011
 Missile External Aerodynamics Using Star-CCM+ Star European Conference 03/22-23/2011 StarCCM_StarEurope_2011 4/6/11 1 Overview 2 Role of CFD in Aerodynamic Analyses Classical aerodynamics / Semi-Empirical
Missile External Aerodynamics Using Star-CCM+ Star European Conference 03/22-23/2011 StarCCM_StarEurope_2011 4/6/11 1 Overview 2 Role of CFD in Aerodynamic Analyses Classical aerodynamics / Semi-Empirical
The Finite Element Method
 The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
The Finite Element Method A Practical Course G. R. Liu and S. S. Quek Chapter 1: Computational modeling An overview 1 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION PHYSICAL PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING USING
Keisuke Sawada. Department of Aerospace Engineering Tohoku University
 March 29th, 213 : Next Generation Aircraft Workshop at Washington University Numerical Study of Wing Deformation Effect in Wind-Tunnel Testing Keisuke Sawada Department of Aerospace Engineering Tohoku
March 29th, 213 : Next Generation Aircraft Workshop at Washington University Numerical Study of Wing Deformation Effect in Wind-Tunnel Testing Keisuke Sawada Department of Aerospace Engineering Tohoku
Chapter 4: Threads. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
ANSYS FLUENT. Airfoil Analysis and Tutorial
 ANSYS FLUENT Airfoil Analysis and Tutorial ENGR083: Fluid Mechanics II Terry Yu 5/11/2017 Abstract The NACA 0012 airfoil was one of the earliest airfoils created. Its mathematically simple shape and age
ANSYS FLUENT Airfoil Analysis and Tutorial ENGR083: Fluid Mechanics II Terry Yu 5/11/2017 Abstract The NACA 0012 airfoil was one of the earliest airfoils created. Its mathematically simple shape and age
Flexible Hardware Mapping for Finite Element Simulations on Hybrid CPU/GPU Clusters
 Flexible Hardware Mapping for Finite Element Simulations on Hybrid /GPU Clusters Aaron Becker (abecker3@illinois.edu) Isaac Dooley Laxmikant Kale SAAHPC, July 30 2009 Champaign-Urbana, IL Target Application
Flexible Hardware Mapping for Finite Element Simulations on Hybrid /GPU Clusters Aaron Becker (abecker3@illinois.edu) Isaac Dooley Laxmikant Kale SAAHPC, July 30 2009 Champaign-Urbana, IL Target Application
Java Performance Analysis for Scientific Computing
 Java Performance Analysis for Scientific Computing Roldan Pozo Leader, Mathematical Software Group National Institute of Standards and Technology USA UKHEC: Java for High End Computing Nov. 20th, 2000
Java Performance Analysis for Scientific Computing Roldan Pozo Leader, Mathematical Software Group National Institute of Standards and Technology USA UKHEC: Java for High End Computing Nov. 20th, 2000
Modeling External Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Distributed Computing: PVM, MPI, and MOSIX. Multiple Processor Systems. Dr. Shaaban. Judd E.N. Jenne
 Distributed Computing: PVM, MPI, and MOSIX Multiple Processor Systems Dr. Shaaban Judd E.N. Jenne May 21, 1999 Abstract: Distributed computing is emerging as the preferred means of supporting parallel
Distributed Computing: PVM, MPI, and MOSIX Multiple Processor Systems Dr. Shaaban Judd E.N. Jenne May 21, 1999 Abstract: Distributed computing is emerging as the preferred means of supporting parallel
CFD-1. Introduction: What is CFD? T. J. Craft. Msc CFD-1. CFD: Computational Fluid Dynamics
 School of Mechanical Aerospace and Civil Engineering CFD-1 T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41 Msc CFD-1 Reading: J. Ferziger, M. Peric, Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics H.K. Versteeg, W. Malalasekara,
School of Mechanical Aerospace and Civil Engineering CFD-1 T. J. Craft George Begg Building, C41 Msc CFD-1 Reading: J. Ferziger, M. Peric, Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics H.K. Versteeg, W. Malalasekara,
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich
 Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics. Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4
 UMEÅ UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Claude Dion Olexii Iukhymenko May 15, 2015 Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics (5FY144) Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4!! Report requirements Computer labs must
UMEÅ UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Claude Dion Olexii Iukhymenko May 15, 2015 Strömningslära Fluid Dynamics (5FY144) Computer laboratories using COMSOL v4.4!! Report requirements Computer labs must
Multigrid Solvers in CFD. David Emerson. Scientific Computing Department STFC Daresbury Laboratory Daresbury, Warrington, WA4 4AD, UK
 Multigrid Solvers in CFD David Emerson Scientific Computing Department STFC Daresbury Laboratory Daresbury, Warrington, WA4 4AD, UK david.emerson@stfc.ac.uk 1 Outline Multigrid: general comments Incompressible
Multigrid Solvers in CFD David Emerson Scientific Computing Department STFC Daresbury Laboratory Daresbury, Warrington, WA4 4AD, UK david.emerson@stfc.ac.uk 1 Outline Multigrid: general comments Incompressible
Chapter 3: Processes. Operating System Concepts 8th Edition
 Chapter 3: Processes Chapter 3: Processes Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication Examples of IPC Systems Communication in Client-Server Systems 3.2 Objectives
Chapter 3: Processes Chapter 3: Processes Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication Examples of IPC Systems Communication in Client-Server Systems 3.2 Objectives
Transactions on Information and Communications Technologies vol 3, 1993 WIT Press, ISSN
 The implementation of a general purpose FORTRAN harness for an arbitrary network of transputers for computational fluid dynamics J. Mushtaq, A.J. Davies D.J. Morgan ABSTRACT Many Computational Fluid Dynamics
The implementation of a general purpose FORTRAN harness for an arbitrary network of transputers for computational fluid dynamics J. Mushtaq, A.J. Davies D.J. Morgan ABSTRACT Many Computational Fluid Dynamics
2008 International ANSYS Conference
 2008 International ANSYS Conference FEM AND FSI SIMULATIONS OF IMPACT LOADS ON GRP SUBSEA COMPOSITE COVERS Kjetil Rognlien, MSc Technical Consultant EDR AS, Norway 2008 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
2008 International ANSYS Conference FEM AND FSI SIMULATIONS OF IMPACT LOADS ON GRP SUBSEA COMPOSITE COVERS Kjetil Rognlien, MSc Technical Consultant EDR AS, Norway 2008 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
How to Enter and Analyze a Wing
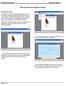 How to Enter and Analyze a Wing Entering the Wing The Stallion 3-D built-in geometry creation tool can be used to model wings and bodies of revolution. In this example, a simple rectangular wing is modeled
How to Enter and Analyze a Wing Entering the Wing The Stallion 3-D built-in geometry creation tool can be used to model wings and bodies of revolution. In this example, a simple rectangular wing is modeled
HARNESSING IRREGULAR PARALLELISM: A CASE STUDY ON UNSTRUCTURED MESHES. Cliff Woolley, NVIDIA
 HARNESSING IRREGULAR PARALLELISM: A CASE STUDY ON UNSTRUCTURED MESHES Cliff Woolley, NVIDIA PREFACE This talk presents a case study of extracting parallelism in the UMT2013 benchmark for 3D unstructured-mesh
HARNESSING IRREGULAR PARALLELISM: A CASE STUDY ON UNSTRUCTURED MESHES Cliff Woolley, NVIDIA PREFACE This talk presents a case study of extracting parallelism in the UMT2013 benchmark for 3D unstructured-mesh
Using Java for Scientific Computing. Mark Bul EPCC, University of Edinburgh
 Using Java for Scientific Computing Mark Bul EPCC, University of Edinburgh markb@epcc.ed.ac.uk Java and Scientific Computing? Benefits of Java for Scientific Computing Portability Network centricity Software
Using Java for Scientific Computing Mark Bul EPCC, University of Edinburgh markb@epcc.ed.ac.uk Java and Scientific Computing? Benefits of Java for Scientific Computing Portability Network centricity Software
HPX. High Performance ParalleX CCT Tech Talk Series. Hartmut Kaiser
 HPX High Performance CCT Tech Talk Hartmut Kaiser (hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu) 2 What s HPX? Exemplar runtime system implementation Targeting conventional architectures (Linux based SMPs and clusters) Currently,
HPX High Performance CCT Tech Talk Hartmut Kaiser (hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu) 2 What s HPX? Exemplar runtime system implementation Targeting conventional architectures (Linux based SMPs and clusters) Currently,
Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing
 Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing Mahantesh. HM 1, Prof. Anand. SN 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, East Point College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1 Associate
Estimation of Flow Field & Drag for Aerofoil Wing Mahantesh. HM 1, Prof. Anand. SN 2 P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, East Point College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka, India 1 Associate
Team 194: Aerodynamic Study of Airflow around an Airfoil in the EGI Cloud
 Team 194: Aerodynamic Study of Airflow around an Airfoil in the EGI Cloud CFD Support s OpenFOAM and UberCloud Containers enable efficient, effective, and easy access and use of MEET THE TEAM End-User/CFD
Team 194: Aerodynamic Study of Airflow around an Airfoil in the EGI Cloud CFD Support s OpenFOAM and UberCloud Containers enable efficient, effective, and easy access and use of MEET THE TEAM End-User/CFD
Outline. COMSOL Multyphysics: Overview of software package and capabilities
 COMSOL Multyphysics: Overview of software package and capabilities Lecture 5 Special Topics: Device Modeling Outline Basic concepts and modeling paradigm Overview of capabilities Steps in setting-up a
COMSOL Multyphysics: Overview of software package and capabilities Lecture 5 Special Topics: Device Modeling Outline Basic concepts and modeling paradigm Overview of capabilities Steps in setting-up a
6.1 Multiprocessor Computing Environment
 6 Parallel Computing 6.1 Multiprocessor Computing Environment The high-performance computing environment used in this book for optimization of very large building structures is the Origin 2000 multiprocessor,
6 Parallel Computing 6.1 Multiprocessor Computing Environment The high-performance computing environment used in this book for optimization of very large building structures is the Origin 2000 multiprocessor,
Abstract. Introduction
 EULER SOLUTIONS AS LIMIT OF INFINITE REYNOLDS NUMBER FOR SEPARATION FLOWS AND FLOWS WITH VORTICES Wolfgang Schmidt and Antony Jameson Dornier GmbH, D-7990 Friedrichshafen, FRG and Princeton University,
EULER SOLUTIONS AS LIMIT OF INFINITE REYNOLDS NUMBER FOR SEPARATION FLOWS AND FLOWS WITH VORTICES Wolfgang Schmidt and Antony Jameson Dornier GmbH, D-7990 Friedrichshafen, FRG and Princeton University,
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics. D. Murrin
 Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Chapter 4: Multithreaded
 Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating-System Examples 2009/10/19 2 4.1 Overview A thread is
Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating-System Examples 2009/10/19 2 4.1 Overview A thread is
VIEWZ 1.3 USER MANUAL
 VIEWZ 1.3 USER MANUAL 2007-08 Zeus Numerix ViewZ 1.3.0 User Manual Revision: 200806061429 The latest copy of this PDF may be downloaded from the website. An online (HTML) version is also available. Zeus
VIEWZ 1.3 USER MANUAL 2007-08 Zeus Numerix ViewZ 1.3.0 User Manual Revision: 200806061429 The latest copy of this PDF may be downloaded from the website. An online (HTML) version is also available. Zeus
Domain Decomposition: Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Domain Decomposition: Computational Fluid Dynamics July 11, 2016 1 Introduction and Aims This exercise takes an example from one of the most common applications of HPC resources: Fluid Dynamics. We will
Domain Decomposition: Computational Fluid Dynamics July 11, 2016 1 Introduction and Aims This exercise takes an example from one of the most common applications of HPC resources: Fluid Dynamics. We will
Numerical Simulations of Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems using MpCCI
 Numerical Simulations of Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems using MpCCI François Thirifay and Philippe Geuzaine CENAERO, Avenue Jean Mermoz 30, B-6041 Gosselies, Belgium Abstract. This paper reports
Numerical Simulations of Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems using MpCCI François Thirifay and Philippe Geuzaine CENAERO, Avenue Jean Mermoz 30, B-6041 Gosselies, Belgium Abstract. This paper reports
Parallel Computing. Slides credit: M. Quinn book (chapter 3 slides), A Grama book (chapter 3 slides)
 Parallel Computing 2012 Slides credit: M. Quinn book (chapter 3 slides), A Grama book (chapter 3 slides) Parallel Algorithm Design Outline Computational Model Design Methodology Partitioning Communication
Parallel Computing 2012 Slides credit: M. Quinn book (chapter 3 slides), A Grama book (chapter 3 slides) Parallel Algorithm Design Outline Computational Model Design Methodology Partitioning Communication
Using GPUs for unstructured grid CFD
 Using GPUs for unstructured grid CFD Mike Giles mike.giles@maths.ox.ac.uk Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford e-research Centre Schlumberger Abingdon Technology Centre, February 17th, 2011
Using GPUs for unstructured grid CFD Mike Giles mike.giles@maths.ox.ac.uk Oxford University Mathematical Institute Oxford e-research Centre Schlumberger Abingdon Technology Centre, February 17th, 2011
Chapter 5: Processes & Process Concept. Objectives. Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes. Communication in Client-Server Systems
 Chapter 5: Processes Chapter 5: Processes & Threads Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication Communication in Client-Server Systems, Silberschatz, Galvin and
Chapter 5: Processes Chapter 5: Processes & Threads Process Concept Process Scheduling Operations on Processes Interprocess Communication Communication in Client-Server Systems, Silberschatz, Galvin and
Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions. Milovan Perić
 Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions Milovan Perić Contents The need to couple STAR-CCM+ with other theoretical or numerical solutions Coupling approaches: surface and volume
Coupling of STAR-CCM+ to Other Theoretical or Numerical Solutions Milovan Perić Contents The need to couple STAR-CCM+ with other theoretical or numerical solutions Coupling approaches: surface and volume
Computational Fluid Dynamics using OpenCL a Practical Introduction
 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 Computational Fluid Dynamics using OpenCL a Practical Introduction T Bednarz
19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 Computational Fluid Dynamics using OpenCL a Practical Introduction T Bednarz
Parallel Semi Meshless Stencil Selection for Moving Geometry Simulations
 Parallel Semi Meshless Stencil Selection for Moving Geometry Simulations J. Angulo, D. J. Kennett, S. Timme and K. J. Badcock University of Liverpool, Liverpool, England L69 3BX, United Kingdom Computational
Parallel Semi Meshless Stencil Selection for Moving Geometry Simulations J. Angulo, D. J. Kennett, S. Timme and K. J. Badcock University of Liverpool, Liverpool, England L69 3BX, United Kingdom Computational
Chapter 4: Threads. Chapter 4: Threads
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Parallelization Principles. Sathish Vadhiyar
 Parallelization Principles Sathish Vadhiyar Parallel Programming and Challenges Recall the advantages and motivation of parallelism But parallel programs incur overheads not seen in sequential programs
Parallelization Principles Sathish Vadhiyar Parallel Programming and Challenges Recall the advantages and motivation of parallelism But parallel programs incur overheads not seen in sequential programs
Chapter 4: Threads. Operating System Concepts 9 th Edition
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues Operating System Examples
Commercial Implementations of Optimization Software and its Application to Fluid Dynamics Problems
 Commercial Implementations of Optimization Software and its Application to Fluid Dynamics Problems Szymon Buhajczuk, M.A.Sc SimuTech Group Toronto Fields Institute Optimization Seminar December 6, 2011
Commercial Implementations of Optimization Software and its Application to Fluid Dynamics Problems Szymon Buhajczuk, M.A.Sc SimuTech Group Toronto Fields Institute Optimization Seminar December 6, 2011
Performance of Implicit Solver Strategies on GPUs
 9. LS-DYNA Forum, Bamberg 2010 IT / Performance Performance of Implicit Solver Strategies on GPUs Prof. Dr. Uli Göhner DYNAmore GmbH Stuttgart, Germany Abstract: The increasing power of GPUs can be used
9. LS-DYNA Forum, Bamberg 2010 IT / Performance Performance of Implicit Solver Strategies on GPUs Prof. Dr. Uli Göhner DYNAmore GmbH Stuttgart, Germany Abstract: The increasing power of GPUs can be used
Lecture 13: Memory Consistency. + a Course-So-Far Review. Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming CMU , Spring 2013
 Lecture 13: Memory Consistency + a Course-So-Far Review Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Today: what you should know Understand the motivation for relaxed consistency models Understand the
Lecture 13: Memory Consistency + a Course-So-Far Review Parallel Computer Architecture and Programming Today: what you should know Understand the motivation for relaxed consistency models Understand the
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2016) Chapter 3: Process. Zhi Wang Florida State University
 COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2016) Chapter 3: Process Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Process concept Process scheduling Operations on processes Inter-process communication
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2016) Chapter 3: Process Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Process concept Process scheduling Operations on processes Inter-process communication
Introduction to CFX. Workshop 2. Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. WS2-1. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
Workshop 2 Transonic Flow Over a NACA 0012 Airfoil. Introduction to CFX WS2-1 Goals The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the user to modelling flow in high speed external aerodynamic applications.
PARALLELIZATION OF POTENTIAL FLOW SOLVER USING PC CLUSTERS
 Proceedings of FEDSM 2000: ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 11-15,2000, Boston, MA FEDSM2000-11223 PARALLELIZATION OF POTENTIAL FLOW SOLVER USING PC CLUSTERS Prof. Blair.J.Perot Manjunatha.N.
Proceedings of FEDSM 2000: ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 11-15,2000, Boston, MA FEDSM2000-11223 PARALLELIZATION OF POTENTIAL FLOW SOLVER USING PC CLUSTERS Prof. Blair.J.Perot Manjunatha.N.
Communication and Optimization Aspects of Parallel Programming Models on Hybrid Architectures
 Communication and Optimization Aspects of Parallel Programming Models on Hybrid Architectures Rolf Rabenseifner rabenseifner@hlrs.de Gerhard Wellein gerhard.wellein@rrze.uni-erlangen.de University of Stuttgart
Communication and Optimization Aspects of Parallel Programming Models on Hybrid Architectures Rolf Rabenseifner rabenseifner@hlrs.de Gerhard Wellein gerhard.wellein@rrze.uni-erlangen.de University of Stuttgart
CS420: Operating Systems
 Threads James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Threads A thread is a basic unit of processing
Threads James Moscola Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania Based on Operating System Concepts, 9th Edition by Silberschatz, Galvin, Gagne Threads A thread is a basic unit of processing
3D ADI Method for Fluid Simulation on Multiple GPUs. Nikolai Sakharnykh, NVIDIA Nikolay Markovskiy, NVIDIA
 3D ADI Method for Fluid Simulation on Multiple GPUs Nikolai Sakharnykh, NVIDIA Nikolay Markovskiy, NVIDIA Introduction Fluid simulation using direct numerical methods Gives the most accurate result Requires
3D ADI Method for Fluid Simulation on Multiple GPUs Nikolai Sakharnykh, NVIDIA Nikolay Markovskiy, NVIDIA Introduction Fluid simulation using direct numerical methods Gives the most accurate result Requires
Introduction to ANSYS CFX
 Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
I. INTRODUCTION FACTORS RELATED TO PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
 Performance Analysis of Java NativeThread and NativePthread on Win32 Platform Bala Dhandayuthapani Veerasamy Research Scholar Manonmaniam Sundaranar University Tirunelveli, Tamilnadu, India dhanssoft@gmail.com
Performance Analysis of Java NativeThread and NativePthread on Win32 Platform Bala Dhandayuthapani Veerasamy Research Scholar Manonmaniam Sundaranar University Tirunelveli, Tamilnadu, India dhanssoft@gmail.com
GPGPU LAB. Case study: Finite-Difference Time- Domain Method on CUDA
 GPGPU LAB Case study: Finite-Difference Time- Domain Method on CUDA Ana Balevic IPVS 1 Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method Numerical computation of solutions to partial differential equations Explicit
GPGPU LAB Case study: Finite-Difference Time- Domain Method on CUDA Ana Balevic IPVS 1 Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method Numerical computation of solutions to partial differential equations Explicit
A study of mesh sensitivity for crash simulations: comparison of manually and batch meshed models
 4. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 25 Modellierung A study of mesh sensitivity for crash simulations: comparison of manually and batch meshed models Marc Ratzel*, Paul Du Bois +, Lars A. Fredriksson*, Detlef
4. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 25 Modellierung A study of mesh sensitivity for crash simulations: comparison of manually and batch meshed models Marc Ratzel*, Paul Du Bois +, Lars A. Fredriksson*, Detlef
Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate
 Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate Summary... Problem Statement Geometry and Mesh Creation Problem Setup Solution. Results Validation......... Mesh Refinement.. Summary This ANSYS FLUENT tutorial
Module D: Laminar Flow over a Flat Plate Summary... Problem Statement Geometry and Mesh Creation Problem Setup Solution. Results Validation......... Mesh Refinement.. Summary This ANSYS FLUENT tutorial
Vehicle thermal safety with THESEUS-FE. Author: Dr. Daniel Koester
 Author: Dr. Daniel Koester Date: September 4, 2014 Workflow for Underhood Simulations ANSA or other CAD/meshing software CAD cleanup and meshing: either CAD geometry description or NASTRAN-style FE meshes
Author: Dr. Daniel Koester Date: September 4, 2014 Workflow for Underhood Simulations ANSA or other CAD/meshing software CAD cleanup and meshing: either CAD geometry description or NASTRAN-style FE meshes
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil
 1. Purpose Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew
1. Purpose Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew
Study Of Overloading Effects, In A Refrigerated Display Case
 Study Of Overloading Effects, In A Refrigerated Display Case Sandeep Palaksha Senior CAE Engineer HUSSMANN Basavanagudi Bangalore 04, India p.sandeep@hussmann.com Narasimhamurthy CAE Engineer HUSSMANN
Study Of Overloading Effects, In A Refrigerated Display Case Sandeep Palaksha Senior CAE Engineer HUSSMANN Basavanagudi Bangalore 04, India p.sandeep@hussmann.com Narasimhamurthy CAE Engineer HUSSMANN
Benchmarking the CGNS I/O performance
 46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit 7-10 January 2008, Reno, Nevada AIAA 2008-479 Benchmarking the CGNS I/O performance Thomas Hauser I. Introduction Linux clusters can provide a viable and
46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit 7-10 January 2008, Reno, Nevada AIAA 2008-479 Benchmarking the CGNS I/O performance Thomas Hauser I. Introduction Linux clusters can provide a viable and
Processes and Threads
 TDDI04 Concurrent Programming, Operating Systems, and Real-time Operating Systems Processes and Threads [SGG7] Chapters 3 and 4 Copyright Notice: The lecture notes are mainly based on Silberschatz s, Galvin
TDDI04 Concurrent Programming, Operating Systems, and Real-time Operating Systems Processes and Threads [SGG7] Chapters 3 and 4 Copyright Notice: The lecture notes are mainly based on Silberschatz s, Galvin
A Comparison of Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-Array Fortran. The purpose of this paper is to compare Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-
 Shaun Lindsay CS425 A Comparison of Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-Array Fortran The purpose of this paper is to compare Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co- Array Fortran s methods of parallelism
Shaun Lindsay CS425 A Comparison of Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-Array Fortran The purpose of this paper is to compare Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co- Array Fortran s methods of parallelism
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Ibrahim Sezai Department of Mechanical Engineering Eastern Mediterranean University Fall 2009-2010 What is CFD? CFD is the simulation of fluids engineering systems using modeling
Chapter 1 Introduction Ibrahim Sezai Department of Mechanical Engineering Eastern Mediterranean University Fall 2009-2010 What is CFD? CFD is the simulation of fluids engineering systems using modeling
Chapter 4: Threads. Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Windows XP Threads Linux Threads
 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Chapter 4: Threads Objectives To introduce the notion of a
Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues Operating System Examples Windows XP Threads Linux Threads Chapter 4: Threads Objectives To introduce the notion of a
Efficient Multi-GPU CUDA Linear Solvers for OpenFOAM
 Efficient Multi-GPU CUDA Linear Solvers for OpenFOAM Alexander Monakov, amonakov@ispras.ru Institute for System Programming of Russian Academy of Sciences March 20, 2013 1 / 17 Problem Statement In OpenFOAM,
Efficient Multi-GPU CUDA Linear Solvers for OpenFOAM Alexander Monakov, amonakov@ispras.ru Institute for System Programming of Russian Academy of Sciences March 20, 2013 1 / 17 Problem Statement In OpenFOAM,
The Public Shared Objects Run-Time System
 The Public Shared Objects Run-Time System Stefan Lüpke, Jürgen W. Quittek, Torsten Wiese E-mail: wiese@tu-harburg.d400.de Arbeitsbereich Technische Informatik 2, Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg
The Public Shared Objects Run-Time System Stefan Lüpke, Jürgen W. Quittek, Torsten Wiese E-mail: wiese@tu-harburg.d400.de Arbeitsbereich Technische Informatik 2, Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Pre-Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew Opyd, Dong-Hwan
Simulation of Turbulent Flow around an Airfoil ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transfer Processes CFD Pre-Lab 2 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Nov. 7, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Andrew Opyd, Dong-Hwan
Outline. Threads. Single and Multithreaded Processes. Benefits of Threads. Eike Ritter 1. Modified: October 16, 2012
 Eike Ritter 1 Modified: October 16, 2012 Lecture 8: Operating Systems with C/C++ School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK 1 Based on material by Matt Smart and Nick Blundell Outline 1 Concurrent
Eike Ritter 1 Modified: October 16, 2012 Lecture 8: Operating Systems with C/C++ School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, UK 1 Based on material by Matt Smart and Nick Blundell Outline 1 Concurrent
Grid. Apr 09, 1998 FLUENT 5.0 (2d, segregated, lam) Grid. Jul 31, 1998 FLUENT 5.0 (2d, segregated, lam)
 Tutorial 2. Around an Airfoil Transonic Turbulent Flow Introduction: The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a non-zero angle of attack. You will use the
Tutorial 2. Around an Airfoil Transonic Turbulent Flow Introduction: The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a non-zero angle of attack. You will use the
Techniques for Optimizing FEM/MoM Codes
 Techniques for Optimizing FEM/MoM Codes Y. Ji, T. H. Hubing, and H. Wang Electromagnetic Compatibility Laboratory Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Missouri-Rolla Rolla, MO
Techniques for Optimizing FEM/MoM Codes Y. Ji, T. H. Hubing, and H. Wang Electromagnetic Compatibility Laboratory Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Missouri-Rolla Rolla, MO
Virtual EM Inc. Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA
 Functional Description of the Architecture of a Special Purpose Processor for Orders of Magnitude Reduction in Run Time in Computational Electromagnetics Tayfun Özdemir Virtual EM Inc. Ann Arbor, Michigan,
Functional Description of the Architecture of a Special Purpose Processor for Orders of Magnitude Reduction in Run Time in Computational Electromagnetics Tayfun Özdemir Virtual EM Inc. Ann Arbor, Michigan,
Chapter 4: Threads. Chapter 4: Threads. Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues
 Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues 4.2 Silberschatz, Galvin
Chapter 4: Threads Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2013 Chapter 4: Threads Overview Multicore Programming Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Implicit Threading Threading Issues 4.2 Silberschatz, Galvin
Analysis, extensions and applications of the Finite-Volume Particle Method (FVPM) PN-II-RU-TE Synthesis of the technical report -
 Analysis, extensions and applications of the Finite-Volume Particle Method (FVPM) PN-II-RU-TE-2011-3-0256 - Synthesis of the technical report - Phase 1: Preparation phase Authors: Delia Teleaga, Eliza
Analysis, extensions and applications of the Finite-Volume Particle Method (FVPM) PN-II-RU-TE-2011-3-0256 - Synthesis of the technical report - Phase 1: Preparation phase Authors: Delia Teleaga, Eliza
Process. Program Vs. process. During execution, the process may be in one of the following states
 What is a process? What is process scheduling? What are the common operations on processes? How to conduct process-level communication? How to conduct client-server communication? Process is a program
What is a process? What is process scheduling? What are the common operations on processes? How to conduct process-level communication? How to conduct client-server communication? Process is a program
Effect of Position of Wall Mounted Surface Protrusion in Drag Characteristics At Low Reynolds Number
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 11 November 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Effect of Position of Wall Mounted Surface Protrusion in Drag Characteristics
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 11 November 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Effect of Position of Wall Mounted Surface Protrusion in Drag Characteristics
BioIRC solutions. CFDVasc manual
 BioIRC solutions CFDVasc manual Main window of application is consisted from two parts: toolbar - which consist set of button for accessing variety of present functionalities image area area in which is
BioIRC solutions CFDVasc manual Main window of application is consisted from two parts: toolbar - which consist set of button for accessing variety of present functionalities image area area in which is
LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA.
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2014) Chapter 3: Process. Zhi Wang Florida State University
 COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2014) Chapter 3: Process Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Process concept Process scheduling Operations on processes Inter-process communication
COP 4610: Introduction to Operating Systems (Spring 2014) Chapter 3: Process Zhi Wang Florida State University Contents Process concept Process scheduling Operations on processes Inter-process communication
Process Description and Control
 Process Description and Control 1 Process:the concept Process = a program in execution Example processes: OS kernel OS shell Program executing after compilation www-browser Process management by OS : Allocate
Process Description and Control 1 Process:the concept Process = a program in execution Example processes: OS kernel OS shell Program executing after compilation www-browser Process management by OS : Allocate
Operating System: Chap2 OS Structure. National Tsing-Hua University 2016, Fall Semester
 Operating System: Chap2 OS Structure National Tsing-Hua University 2016, Fall Semester Outline OS Services OS-Application Interface OS Structure Chapter2 OS-Structure Operating System Concepts NTHU LSA
Operating System: Chap2 OS Structure National Tsing-Hua University 2016, Fall Semester Outline OS Services OS-Application Interface OS Structure Chapter2 OS-Structure Operating System Concepts NTHU LSA
MPI Casestudy: Parallel Image Processing
 MPI Casestudy: Parallel Image Processing David Henty 1 Introduction The aim of this exercise is to write a complete MPI parallel program that does a very basic form of image processing. We will start by
MPI Casestudy: Parallel Image Processing David Henty 1 Introduction The aim of this exercise is to write a complete MPI parallel program that does a very basic form of image processing. We will start by
Parallel Performance Studies for COMSOL Multiphysics Using Scripting and Batch Processing
 Parallel Performance Studies for COMSOL Multiphysics Using Scripting and Batch Processing Noemi Petra and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore
Parallel Performance Studies for COMSOL Multiphysics Using Scripting and Batch Processing Noemi Petra and Matthias K. Gobbert Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore
Accelerating Implicit LS-DYNA with GPU
 Accelerating Implicit LS-DYNA with GPU Yih-Yih Lin Hewlett-Packard Company Abstract A major hindrance to the widespread use of Implicit LS-DYNA is its high compute cost. This paper will show modern GPU,
Accelerating Implicit LS-DYNA with GPU Yih-Yih Lin Hewlett-Packard Company Abstract A major hindrance to the widespread use of Implicit LS-DYNA is its high compute cost. This paper will show modern GPU,
Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming. Operating System Concepts 8 th Edition,
 Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues 4.2 Silberschatz, Galvin
Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming, Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne 2009 Chapter 4: Multithreaded Programming Overview Multithreading Models Thread Libraries Threading Issues 4.2 Silberschatz, Galvin
An Overview of Computational Fluid Dynamics
 An Overview of Computational Fluid Dynamics Dr. Nor Azwadi bin Che Sidik Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS 1 What is CFD? C computational
An Overview of Computational Fluid Dynamics Dr. Nor Azwadi bin Che Sidik Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia INSPIRING CREATIVE AND INNOVATIVE MINDS 1 What is CFD? C computational
Acknowledgments. Amdahl s Law. Contents. Programming with MPI Parallel programming. 1 speedup = (1 P )+ P N. Type to enter text
 Acknowledgments Programming with MPI Parallel ming Jan Thorbecke Type to enter text This course is partly based on the MPI courses developed by Rolf Rabenseifner at the High-Performance Computing-Center
Acknowledgments Programming with MPI Parallel ming Jan Thorbecke Type to enter text This course is partly based on the MPI courses developed by Rolf Rabenseifner at the High-Performance Computing-Center
OzenCloud Case Studies
 OzenCloud Case Studies Case Studies, April 20, 2015 ANSYS in the Cloud Case Studies: Aerodynamics & fluttering study on an aircraft wing using fluid structure interaction 1 Powered by UberCloud http://www.theubercloud.com
OzenCloud Case Studies Case Studies, April 20, 2015 ANSYS in the Cloud Case Studies: Aerodynamics & fluttering study on an aircraft wing using fluid structure interaction 1 Powered by UberCloud http://www.theubercloud.com
Handling Parallelisation in OpenFOAM
 Handling Parallelisation in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak hrvoje.jasak@fsb.hr Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture University of Zagreb, Croatia Handling Parallelisation in OpenFOAM p. 1 Parallelisation
Handling Parallelisation in OpenFOAM Hrvoje Jasak hrvoje.jasak@fsb.hr Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture University of Zagreb, Croatia Handling Parallelisation in OpenFOAM p. 1 Parallelisation
