MOBILE CLIENT FOR ONLINE DICTIONARY. Constantin Lucian ALDEA 1. Abstract
|
|
|
- Sherilyn May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 4(53), No Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, MOBILE CLIENT FOR ONLINE DICTIONARY Constantin Lucian ALDEA 1 Abstract The Lexica dictionary is an online bilingual dictionary [5]. It provides contexts, translations, paradigms and structures for a large number of English words used in the terminology associated with European Community legal texts [4]. In this paper a software architecture that extends the web application to the mobile phones such that a user can also access the online web application using its mobile device is presented. For the proposed architecture a client program is developed with the Google s Android software. Mobile Lexica is a software project that uses the same database as the website, but removes the need of a browser. Using the http protocol and the JSON (Javascript Object Notation) serialization format, it transfers data from the web service to the mobile, and backwards Mathematics Subject Classification: 94A05, 94C30. Key words: mobile devices, online dictionary, web access. 1 Indroduction The Lexica dictionary is an online vocabulary [5]. It provides contexts, translations, paradigms and structures for a large number of English words. The user accesses the web site, enters a word and presses different search buttons to start a type of search (entire data, only paradigms, only translation etc.). After pressing the search button a request is sent to the web server that looks into the database for the proper data. The dictionary data was already added [4] and the purpose of this project is to present an Android client application project for the existing online dictionary. Figure 1: Lexica Web Architecture 1 Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Transilvania University of Braşov, Romania, costel.aldea@unitbv.ro
2 124 Constantin Lucian Aldea The project extends the application to mobile phones and it results in an application architecture which is further implemented using Google s Android software. Mobile Lexica is software that uses the same database as the website, but removes the need of a browser. Using the http protocol and the JSON serialization format, it transfers data from the web service to the mobile, and backwards. As presented in figure 1 for the current project two components for the application were developed: 1. the first component which is server side and it queries the database and intermediates the request formulated on the mobile device interface. This component was developed using php programming and is hosted on the Apache server auxiliary to the old web application. The old application part keeps its own functionality. 2. the second component which is installed on the mobile device and assures the interface between the user and the vocabulary data through the first component. This project part was implemented on the mobile device using the Android platform. 2 Android Framework Android programming is basically Java programming [3] and the developing platform uses a special type of application life cycle for the developed application [1]. Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications. The Android SDK provides the tools and APIs necessary to begin developing applications on the Android platform using the Java programming language [6]. The main components of the android framework are the following: 1. View - Views are user interface (UI) elements that form the basic building blocks of a user interface. Views are hierarchical and they know how to draw themselves. A view could be a button, a label,a text field or other kind of UI elements. 2. Activity - An activity is a user interface concept. An activity usually represents a single screen in the android application. It generally contains one or more views, but not necessarily. Moreover, other concepts in Android could better represent a viewless activity. 3. Intent - An intent generically defines an intention to do some work. Intents encapsulate several concepts. Intents can be used to perform the following tasks: (a) broadcast a message, (b) start a service, (c) launch an activity, (d) display a web page or a list of contacts, (e) dial a phone number or answer a phone call. 4. Content Provider - Data sharing among mobile applications on a device is common. Therefore, Android defines a standard mechanism for applications to share
3 Mobile client for online dictionary 125 data (such as a list of contacts) without exposing the underlying storage, structure, and implementation. Through content providers, data can be exposed to other applications. 5. Services in Android resemble services in Windows or other platformstheyre background processes that can potentially run for a long time. Android defines two types of services: local services and remote services. Local services are components that are only accessible through the application that is hosting the service. Conversely, remote services are services that are meant to be accessed remotely by other applications running on the device. 6. AndroidManifest.xml - is similar to the web.xml file in the J2EE world and defines the contents and behavior of the application. For example, it lists the applications activities and services, along with the permissions the application needs to run. 7. Android Virtual Devices - An Android Virtual Device (AVD) allows developers to test their applications without hooking up an actual Android phone. AVDs can be created in various configurations to emulate different types of real phones. 3 Mobile Lexica application use case When the application is opened, the screen from figure 2 will appear. It contains a field, where the user can type the word he wants to search for, then by pressing the OK button, a request is made to the server. The server will search in the database, and return the result, which will be displayed on the screen of the application. Figure 2: Mobile application screens It displays Contexts, Translations, Paradigms and Structures for the given word.
4 126 Constantin Lucian Aldea 3.1 Application classes As stated in the previous sections the proposed project consists of two parts which collaborate for solving the users requests. In the following table the classes used by the project by keeping the correspondences between them with regards to the mobile dictionary functionality are presented. Mobile client Web Server Description Context.java Context.php A class that represents Context data. Paradigm.java Paradigm.php A class that represents Paradigm data. Structure.java Structure.php A class that represents Structure data. Translation.java Translation.php A class that represents Translation data. WordContext.java WordContext.php A class that represents Word Context data. HttpAccess.java - A class that generates a http request. Utils.java - Class used to convert data from JSON to Java Objects. It also creates requests to the Web Server. Lexica.java - It is the main class of the mobile application. It creates the layout components. - Mysql.php Class used by the web server to communicate to database. - Lexica.php Receives requests from mobile clients and returns a result. 3.2 Application implementation The main part of the application is the Lexica class: 1 public class Lexica extends Activity { 2 / Called when the a c t i v i t y i s f i r s t c r e a t e d. / 4 public void oncreate ( Bundle savedinstancestate ) { 5 super. oncreate ( savedinstancestate ) ; 6 setcontentview ( R. layout. main ) ; 7 } 8 } It extends the Activity class, which means that it is the component that runs when the application is started. Here, by overriding the oncreate method, we gain access to the setcontentview method, with which we define the layout of the application. The file main.xml contains the definition of the applications layout. 1 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android=" http: // schemas. android. com / apk / res / android " 2 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t w i d t h=" fill_parent " 3 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t h e i g h t=" fill_parent " 4 a n d r o i d : p a d d i n g="10 px" 5 a n d r o i d : i d="@+id/ relativelayout "> 6 <TextView a n d r o i d : i d="@+id/ label " 7 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t w i d t h=" fill_parent " 8 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t h e i g h t=" wrap_content " 9 a n d r o i d : t e x / search " />
5 Mobile client for online dictionary <EditText a n d r o i d : i d="@+id/ entry " 11 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t w i d t h=" fill_parent " 12 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t h e i g h t=" wrap_content " 13 android: / editbox_background " 14 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t b e l o / label " /> 15 <Button a n d r o i d : i d="@+id/ok" 16 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t w i d t h=" wrap_content " 17 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t h e i g h t=" wrap_content " 18 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t b e l o / entry " 19 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t a l i g n P a r e n t R i g h t=" true " 20 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t m a r g i n L e f t="10 px" 21 a n d r o i d : t e x t="ok" /> 22 <S c r o l l V i e w a n d r o i d : i d="@+id/ scroll " 23 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t w i d t h=" fill_parent " 24 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t h e i g h t=" wrap_content " 25 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t b e l o /ok"> 26 <LinearLayout a n d r o i d : i d="@+id/ description " 27 a n d r o i d : o r i e n t a t i o n=" vertical " 28 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t w i d t h=" fill_parent " 29 a n d r o i d : l a y o u t h e i g h t=" wrap_content " /> 30 </ S c r o l l V i e w> 31 </ RelativeLayout> The root element of the visual hierarchy is an instance of the RelativeLayout class, which lets child views specify their position relative to parent view or to each other (specified by ID). Elements are rendered in the order given, so if the first element is centered in the screen, other elements aligning themselves to that element will be aligned relative to screen center. The TextView is used to display a label with the Search content. EditText will take the user input, and after clicking the ok button, the LinearLayout component will be filled with the data retrieved from the Lexica server. For each entity, there is a separate class: Context, Paradigm, Structure, Translation, and WordContext. All of them contain a method, which will convert the JSON string to the actual java object. 1 public static ArrayList<Context> getcontextsfromjsonobject ( String json ) throws JSONException { 2 ArrayList<Context> result = new ArrayList<Context >() ; 3 JSONArray jsonobj = null ; 4 5 try { 6 jsonobj = ( JSONArray ) new JSONTokener ( json ). nextvalue ( ) ; 7 } 8 catch ( Exception ex ) { 9 System. out. println ( ex. getmessage ( ) ) ; 10 return null ; 11 } 12 int size = jsonobj. length ( ) ; 13 int pos = 0 ; 14 while ( pos < size ) { 15 JSONObject o = ( JSONObject ) jsonobj. get ( pos ) ; 16 Context c = new Context ( o ) ; 17 result. add ( c ) ; 18 pos ++; 19 }
6 128 Constantin Lucian Aldea 20 return result ; 21 } Which uses the following constructor: 1 public Context ( JSONObject obj ) throws JSONException 2 { 3 setidcontext ( obj. getint ( " idcontext " ) ) ; 4 setcontext ( obj. getstring ( " context " ) ) ; 5 setfile ( obj. getstring ( "file" ) ) ; 6 } Communication with the Lexica service is done by using the Utils class, which makes a http post/get request. 1 HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet ( url ) ; 2 HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient ( ) ; 3 // Execute HTTP Get Request 4 HttpResponse response = httpclient. execute ( httpget ) ; 5 content = response. getentity ( ). getcontent ( ) ; 4 Conclusion The electronic society introduces new forms of communication [2]. As regards mobile devices culture imposes new models for web applications. This paper presents a model which can be further used for transferring the information and the computability power on to mobile devices and at the same time keeping the existing functionalities for the legacy applications. References [1] Wei-Meng, L., Beginning Android Application Development, Wiley Publishing, Inc., Indianapolis, [2] Aldea, C., L., Elemente de securitate în reţele de calculatoare, Transilvania University Publishing House, Braşov, [3] Sângeorzan L., Aldea, C., Dumitru, M., Java. Aplicaţii, Infomarket Publishing House, Braşov, [4] Sangeorzan, L., Burada, M., Kiss-Iakab, K., Designing a Text Parsing Programme for a Specialized Bilingual Online Dictionary, Recent Advances in Computer Engineering, Proc. of the 8 T H WSEAS International conf. on applied informatics and communications, Pts I and II, Greece, Aug , 2008, [5] [6]
Android User Interface
 Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 20. Oktober 2014 Outline 1 Android User Interface 2 Multi-Language Support 3 Summary Matthias Keil Android
Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 20. Oktober 2014 Outline 1 Android User Interface 2 Multi-Language Support 3 Summary Matthias Keil Android
Lab 3. Accessing GSM Functions on an Android Smartphone
 Lab 3 Accessing GSM Functions on an Android Smartphone 1 Lab Overview 1.1 Goals The objective of this practical exercise is to create an application for a smartphone with the Android mobile operating system,
Lab 3 Accessing GSM Functions on an Android Smartphone 1 Lab Overview 1.1 Goals The objective of this practical exercise is to create an application for a smartphone with the Android mobile operating system,
Android User Interface Android Smartphone Programming. Outline University of Freiburg
 Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 20. Oktober 2014 Outline 1 2 Multi-Language Support 3 Summary Matthias Keil 20. Oktober 2014 2 / 19 From
Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 20. Oktober 2014 Outline 1 2 Multi-Language Support 3 Summary Matthias Keil 20. Oktober 2014 2 / 19 From
Praktikum Entwicklung Mediensysteme. Implementing a User Interface
 Praktikum Entwicklung Mediensysteme Implementing a User Interface Outline Introduction Programmatic vs. XML Layout Common Layout Objects Hooking into a Screen Element Listening for UI Notifications Applying
Praktikum Entwicklung Mediensysteme Implementing a User Interface Outline Introduction Programmatic vs. XML Layout Common Layout Objects Hooking into a Screen Element Listening for UI Notifications Applying
The Suggest Example layout (cont ed)
 Using Web Services 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 7: Working with Web Services Android provides a full set of Java-standard networking APIs, such as the java.net package containing among
Using Web Services 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 7: Working with Web Services Android provides a full set of Java-standard networking APIs, such as the java.net package containing among
User Interface: Layout. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 User Interface: Layout Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://twitter.com/krunapon Agenda User Interface Declaring Layout Common Layouts User Interface
User Interface: Layout Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University http://twitter.com/krunapon Agenda User Interface Declaring Layout Common Layouts User Interface
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Web access to cloud system Author(s) Tao, Qingyi Citation Tao, Q. (2014). Web access to cloud system.
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Web access to cloud system Author(s) Tao, Qingyi Citation Tao, Q. (2014). Web access to cloud system.
Fragments were added to the Android API in Honeycomb, API 11. The primary classes related to fragments are: android.app.fragment
 FRAGMENTS Fragments An activity is a container for views When you have a larger screen device than a phone like a tablet it can look too simple to use phone interface here. Fragments Mini-activities, each
FRAGMENTS Fragments An activity is a container for views When you have a larger screen device than a phone like a tablet it can look too simple to use phone interface here. Fragments Mini-activities, each
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. David Drohan Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology
 Mobile Application Development Produced by David Drohan (ddrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie User Interface Design" & Development -
Mobile Application Development Produced by David Drohan (ddrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing & Mathematics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie User Interface Design" & Development -
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I)
 CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2015 Winter 2015 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2015 Winter 2015 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
Dependence Graph Considerering Resource for Automatic Sample Program Generation
 1 2 2 2 ( ) Google Android Dependence Graph Considerering Resource for Automatic Sample Program Generation Yoshimasa Fujiura, 1 Hirotaka Ohkubo, 1 Hideto Kasuya 1 and Shinichiro Yamamoto 1 This paper propose
1 2 2 2 ( ) Google Android Dependence Graph Considerering Resource for Automatic Sample Program Generation Yoshimasa Fujiura, 1 Hirotaka Ohkubo, 1 Hideto Kasuya 1 and Shinichiro Yamamoto 1 This paper propose
Introduction To Android
 Introduction To Android Mobile Technologies Symbian OS ios BlackBerry OS Windows Android Introduction to Android Android is an operating system for mobile devices such as smart phones and tablet computers.
Introduction To Android Mobile Technologies Symbian OS ios BlackBerry OS Windows Android Introduction to Android Android is an operating system for mobile devices such as smart phones and tablet computers.
Mobile Development Lecture 9: Android & RESTFUL Services
 Mobile Development Lecture 9: Android & RESTFUL Services Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Elgayyar.weebly.com What is a RESTFUL Web Service REST stands for REpresentational State Transfer. In
Mobile Development Lecture 9: Android & RESTFUL Services Mahmoud El-Gayyar elgayyar@ci.suez.edu.eg Elgayyar.weebly.com What is a RESTFUL Web Service REST stands for REpresentational State Transfer. In
This lecture. The BrowserIntent Example (cont d)
 This lecture 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 10: Working with the Web Browser Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos Android provides a full-featured web browser based on the Chromium open source
This lecture 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 10: Working with the Web Browser Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos Android provides a full-featured web browser based on the Chromium open source
Mobile Programming Lecture 1. Getting Started
 Mobile Programming Lecture 1 Getting Started Today's Agenda About the Android Studio IDE Hello, World! Project Android Project Structure Introduction to Activities, Layouts, and Widgets Editing Files in
Mobile Programming Lecture 1 Getting Started Today's Agenda About the Android Studio IDE Hello, World! Project Android Project Structure Introduction to Activities, Layouts, and Widgets Editing Files in
Diploma in Android Programming (DAP)
 Diploma in Android Programming (DAP) Duration: 01 Year Total credit: 32 1 st Semester (DAP) Theory Course Course Title (T-L-P) Credit Code CSP-80 Operating Systems T 04 CSP-45 Programing in JAVA T 04 CSP-46
Diploma in Android Programming (DAP) Duration: 01 Year Total credit: 32 1 st Semester (DAP) Theory Course Course Title (T-L-P) Credit Code CSP-80 Operating Systems T 04 CSP-45 Programing in JAVA T 04 CSP-46
Building User Interface for Android Mobile Applications II
 Building User Interface for Android Mobile Applications II Mobile App Development 1 MVC 2 MVC 1 MVC 2 MVC Android redraw View invalidate Controller tap, key pressed update Model MVC MVC in Android View
Building User Interface for Android Mobile Applications II Mobile App Development 1 MVC 2 MVC 1 MVC 2 MVC Android redraw View invalidate Controller tap, key pressed update Model MVC MVC in Android View
Android for Ubiquitous Computing Researchers. Andrew Rice University of Cambridge 17-Sep-2011
 Android for Ubiquitous Computing Researchers Andrew Rice University of Cambridge 17-Sep-2011 Getting started Website for the tutorial: http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~acr31/ubicomp/ Contains links to downloads
Android for Ubiquitous Computing Researchers Andrew Rice University of Cambridge 17-Sep-2011 Getting started Website for the tutorial: http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/~acr31/ubicomp/ Contains links to downloads
1. Implementation of Inheritance with objects, methods. 2. Implementing Interface in a simple java class. 3. To create java class with polymorphism
 ANDROID TRAINING COURSE CONTENT SECTION 1 : INTRODUCTION Android What it is? History of Android Importance of Java language for Android Apps Other mobile OS-es Android Versions & different development
ANDROID TRAINING COURSE CONTENT SECTION 1 : INTRODUCTION Android What it is? History of Android Importance of Java language for Android Apps Other mobile OS-es Android Versions & different development
Answers to Exercises
 Answers to Exercises CHAPTER 1 ANSWERS 1. What is an AVD? Ans: An AVD is an Android Virtual Device. It represents an Android emulator, which emulates a particular configuration of an actual Android device.
Answers to Exercises CHAPTER 1 ANSWERS 1. What is an AVD? Ans: An AVD is an Android Virtual Device. It represents an Android emulator, which emulates a particular configuration of an actual Android device.
Android Programming (5 Days)
 www.peaklearningllc.com Android Programming (5 Days) Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse tools. This Android
www.peaklearningllc.com Android Programming (5 Days) Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse tools. This Android
Android development. Outline. Android Studio. Setting up Android Studio. 1. Set up Android Studio. Tiberiu Vilcu. 2.
 Outline 1. Set up Android Studio Android development Tiberiu Vilcu Prepared for EECS 411 Sugih Jamin 15 September 2017 2. Create sample app 3. Add UI to see how the design interface works 4. Add some code
Outline 1. Set up Android Studio Android development Tiberiu Vilcu Prepared for EECS 411 Sugih Jamin 15 September 2017 2. Create sample app 3. Add UI to see how the design interface works 4. Add some code
A Crash Course to Android Mobile Platform
 Enterprise Application Development using J2EE Shmulik London Lecture #2 A Crash Course to Android Mobile Platform Enterprise Application Development Using J2EE / Shmulik London 2004 Interdisciplinary Center
Enterprise Application Development using J2EE Shmulik London Lecture #2 A Crash Course to Android Mobile Platform Enterprise Application Development Using J2EE / Shmulik London 2004 Interdisciplinary Center
BCA 6. Question Bank
 BCA 6 030010601 : Introduction to Mobile Application Development Question Bank Unit 1: Introduction to Android and Development tools Short questions 1. What kind of tool is used to simulate Android application?
BCA 6 030010601 : Introduction to Mobile Application Development Question Bank Unit 1: Introduction to Android and Development tools Short questions 1. What kind of tool is used to simulate Android application?
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I)
 CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2018 Winter 2018 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
CS260 Intro to Java & Android 05.Android UI(Part I) Winter 2018 Winter 2018 CS250 - Intro to Java & Android 1 User Interface UIs in Android are built using View and ViewGroup objects A View is the base
Mobile User Interfaces
 Mobile User Interfaces CS 2046 Mobile Application Development Fall 2010 Announcements Next class = Lab session: Upson B7 Office Hours (starting 10/25): Me: MW 1:15-2:15 PM, Upson 360 Jae (TA): F 11:00
Mobile User Interfaces CS 2046 Mobile Application Development Fall 2010 Announcements Next class = Lab session: Upson B7 Office Hours (starting 10/25): Me: MW 1:15-2:15 PM, Upson 360 Jae (TA): F 11:00
CMSC436: Fall 2013 Week 3 Lab
 CMSC436: Fall 2013 Week 3 Lab Objectives: Familiarize yourself with the Activity class, the Activity lifecycle, and the Android reconfiguration process. Create and monitor a simple application to observe
CMSC436: Fall 2013 Week 3 Lab Objectives: Familiarize yourself with the Activity class, the Activity lifecycle, and the Android reconfiguration process. Create and monitor a simple application to observe
Questions and Answers. Q.1) Which of the following is the most ^aeuroeresource hungry ^aeuroepart of dealing with activities on android?
 Q.1) Which of the following is the most ^aeuroeresource hungry ^aeuroepart of dealing with activities on android? A. Closing an app. B. Suspending an app C. Opening a new app D. Restoring the most recent
Q.1) Which of the following is the most ^aeuroeresource hungry ^aeuroepart of dealing with activities on android? A. Closing an app. B. Suspending an app C. Opening a new app D. Restoring the most recent
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE GAME
 ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE GAME Application Components Hold the content of a message (E.g. convey a request for an activity to present an image) Lecture 2: Android Layout and Permission Present
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE GAME Application Components Hold the content of a message (E.g. convey a request for an activity to present an image) Lecture 2: Android Layout and Permission Present
Real-Time Embedded Systems
 Real-Time Embedded Systems DT8025, Fall 2016 http://goo.gl/azfc9l Lecture 8 Masoumeh Taromirad m.taromirad@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Technology 1 / 51 Smart phones
Real-Time Embedded Systems DT8025, Fall 2016 http://goo.gl/azfc9l Lecture 8 Masoumeh Taromirad m.taromirad@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Technology 1 / 51 Smart phones
CS 4518 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Introduction to Android Programming. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4518 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Android Apps: Big Picture UI Design using XML UI design code (XML) separate from the program (Java) Why?
CS 4518 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Android Apps: Big Picture UI Design using XML UI design code (XML) separate from the program (Java) Why?
SQLite. 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 6: Working with Databases. What is a Database Server. Advantages of SQLite
 SQLite 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 6: Working with Databases Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos SQLite is a tiny yet powerful database engine. Besides Android, it can be found in: Apple iphone
SQLite 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 6: Working with Databases Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos SQLite is a tiny yet powerful database engine. Besides Android, it can be found in: Apple iphone
Aim behind client server architecture Characteristics of client and server Types of architectures
 QA Automation - API Automation - All in one course Course Summary: In detailed, easy, step by step, real time, practical and well organized Course Not required to have any prior programming knowledge,
QA Automation - API Automation - All in one course Course Summary: In detailed, easy, step by step, real time, practical and well organized Course Not required to have any prior programming knowledge,
Intro to XML. Borrowed, with author s permission, from:
 Intro to XML Borrowed, with author s permission, from: http://business.unr.edu/faculty/ekedahl/is389/topic3a ndroidintroduction/is389androidbasics.aspx Part 1: XML Basics Why XML Here? You need to understand
Intro to XML Borrowed, with author s permission, from: http://business.unr.edu/faculty/ekedahl/is389/topic3a ndroidintroduction/is389androidbasics.aspx Part 1: XML Basics Why XML Here? You need to understand
Mobile Application Development Android
 Mobile Application Development Android Lecture 2 MTAT.03.262 Satish Srirama satish.srirama@ut.ee Android Lecture 1 -recap What is Android How to develop Android applications Run & debug the applications
Mobile Application Development Android Lecture 2 MTAT.03.262 Satish Srirama satish.srirama@ut.ee Android Lecture 1 -recap What is Android How to develop Android applications Run & debug the applications
Required Core Java for Android application development
 Required Core Java for Android application development Introduction to Java Datatypes primitive data types non-primitive data types Variable declaration Operators Control flow statements Arrays and Enhanced
Required Core Java for Android application development Introduction to Java Datatypes primitive data types non-primitive data types Variable declaration Operators Control flow statements Arrays and Enhanced
MC Android Programming
 MC1921 - Android Programming Duration: 5 days Course Price: $3,395 Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse
MC1921 - Android Programming Duration: 5 days Course Price: $3,395 Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse
Android App Development. Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology
 Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
Beginning Android 4 Application Development
 Beginning Android 4 Application Development Lee, Wei-Meng ISBN-13: 9781118199541 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION xxi CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED WITH ANDROID PROGRAMMING 1 What Is Android? 2 Android Versions
Beginning Android 4 Application Development Lee, Wei-Meng ISBN-13: 9781118199541 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION xxi CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED WITH ANDROID PROGRAMMING 1 What Is Android? 2 Android Versions
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL II)
 ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL II) Lecture 6: Notification and Web Services Notification A notification is a user interface element that you display outside your app's normal
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL II) Lecture 6: Notification and Web Services Notification A notification is a user interface element that you display outside your app's normal
ANDROID BASED WS SECURITY AND MVC BASED UI REPRESENTATION OF DATA
 ANDROID BASED WS SECURITY AND MVC BASED UI REPRESENTATION OF DATA Jitendra Ingale, Parikshit mahalle SKNCOE pune,maharashtra,india Email: jits.ingale@gmail.com ABSTRACT: Google s Android is open source;
ANDROID BASED WS SECURITY AND MVC BASED UI REPRESENTATION OF DATA Jitendra Ingale, Parikshit mahalle SKNCOE pune,maharashtra,india Email: jits.ingale@gmail.com ABSTRACT: Google s Android is open source;
INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID
 INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID 1 Niv Voskoboynik Ben-Gurion University Electrical and Computer Engineering Advanced computer lab 2015 2 Contents Introduction Prior learning Download and install Thread Android
INTRODUCTION TO ANDROID 1 Niv Voskoboynik Ben-Gurion University Electrical and Computer Engineering Advanced computer lab 2015 2 Contents Introduction Prior learning Download and install Thread Android
CORE JAVA& ANDROID SYLLABUS
 CORE JAVA& ANDROID SYLLABUS AAvhdvchdvchdvhdh CORE JAVA Assignment s Introduction Programming language Types and Paradigms Why Java? Flavors of Java Java Designing Goal Role of Java Programmer in Industry
CORE JAVA& ANDROID SYLLABUS AAvhdvchdvchdvhdh CORE JAVA Assignment s Introduction Programming language Types and Paradigms Why Java? Flavors of Java Java Designing Goal Role of Java Programmer in Industry
Android Basics. - Bhaumik Shukla Android Application STEALTH FLASH
 Android Basics - Bhaumik Shukla Android Application Developer @ STEALTH FLASH Introduction to Android Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key
Android Basics - Bhaumik Shukla Android Application Developer @ STEALTH FLASH Introduction to Android Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key
The drawable/tile empty.xml file
 The X and O Symbols 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 3: Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe Game: The Interface Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos Create them with the filenames x blue.png and o red.png in an
The X and O Symbols 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 3: Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe Game: The Interface Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos Create them with the filenames x blue.png and o red.png in an
Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001
 Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001 http://goo.gl/ydeczu Lecture 8 Mohammad Mousavi m.r.mousavi@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering
Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001 http://goo.gl/ydeczu Lecture 8 Mohammad Mousavi m.r.mousavi@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering
COMP4521 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS SOFTWARE
 COMP4521 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS SOFTWARE LAB 1: DEVELOPING SIMPLE APPLICATIONS FOR ANDROID INTRODUCTION Android is a mobile platform/os that uses a modified version of the Linux kernel. It was initially developed
COMP4521 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS SOFTWARE LAB 1: DEVELOPING SIMPLE APPLICATIONS FOR ANDROID INTRODUCTION Android is a mobile platform/os that uses a modified version of the Linux kernel. It was initially developed
Android Beginners Workshop
 Android Beginners Workshop at the M O B IL E M O N D AY m 2 d 2 D E V E L O P E R D A Y February, 23 th 2010 Sven Woltmann, AndroidPIT Sven Woltmann Studied Computer Science at the TU Ilmenau, 1994-1999
Android Beginners Workshop at the M O B IL E M O N D AY m 2 d 2 D E V E L O P E R D A Y February, 23 th 2010 Sven Woltmann, AndroidPIT Sven Woltmann Studied Computer Science at the TU Ilmenau, 1994-1999
ES E 3 3 L a L b 5 Android development
 ES3 Lab 5 Android development This Lab Create a simple Android interface Use XML interface layouts Access the filesystem Play media files Info about Android development can be found at http://developer.android.com/index.html
ES3 Lab 5 Android development This Lab Create a simple Android interface Use XML interface layouts Access the filesystem Play media files Info about Android development can be found at http://developer.android.com/index.html
Debugging Arts of the Ninja Masters. Justin Mattson Developer Advocate Android Google 28/5/2009
 Debugging Arts of the Ninja Masters Justin Mattson Developer Advocate Android Team @ Google 28/5/2009 Agenda Tool tour logcat traceview hierarchyviewer Real world usage Pop quiz! Q&A (pop quiz for me)
Debugging Arts of the Ninja Masters Justin Mattson Developer Advocate Android Team @ Google 28/5/2009 Agenda Tool tour logcat traceview hierarchyviewer Real world usage Pop quiz! Q&A (pop quiz for me)
Lab 1 - Setting up the User s Profile UI
 Lab 1 - Setting up the User s Profile UI Getting started This is the first in a series of labs that allow you to develop the MyRuns App. The goal of the app is to capture and display (using maps) walks
Lab 1 - Setting up the User s Profile UI Getting started This is the first in a series of labs that allow you to develop the MyRuns App. The goal of the app is to capture and display (using maps) walks
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Introduction to Android Programming. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Editting in Android Studio Recall: Editting Android Can edit apps in: Text View: edit XML directly Design
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Editting in Android Studio Recall: Editting Android Can edit apps in: Text View: edit XML directly Design
ECOM 5341 Mobile Computing(Android) Eng.Ruba A. Salamah
 ECOM 5341 Mobile Computing(Android) 1 Eng.Ruba A. Salamah Lecture # 2 Android Tools Objectives Understand Android Tools Setup Android Development Environment Create HelloWorld Application Understand HelloWorld
ECOM 5341 Mobile Computing(Android) 1 Eng.Ruba A. Salamah Lecture # 2 Android Tools Objectives Understand Android Tools Setup Android Development Environment Create HelloWorld Application Understand HelloWorld
ListView Containers. Resources. Creating a ListView
 ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
Programming Android UI. J. Serrat Software Design December 2017
 Programming Android UI J. Serrat Software Design December 2017 Preliminaries : Goals Introduce basic programming Android concepts Examine code for some simple examples Limited to those relevant for the
Programming Android UI J. Serrat Software Design December 2017 Preliminaries : Goals Introduce basic programming Android concepts Examine code for some simple examples Limited to those relevant for the
06. Advanced Widget. DKU-MUST Mobile ICT Education Center
 06. Advanced Widget DKU-MUST Mobile ICT Education Center Goal Learn how to deal with advanced widget. Learn how the View Container and its applications Learn how to set the AndroidManiFest.xml Page 2 1.
06. Advanced Widget DKU-MUST Mobile ICT Education Center Goal Learn how to deal with advanced widget. Learn how the View Container and its applications Learn how to set the AndroidManiFest.xml Page 2 1.
Android App Development. Ahmad Tayeb
 Android App Development Ahmad Tayeb Ahmad Tayeb Lecturer @ Department of Information Technology, Faculty of Computing and Information Technology, KAU Master degree from Information Sciences and Technologies,
Android App Development Ahmad Tayeb Ahmad Tayeb Lecturer @ Department of Information Technology, Faculty of Computing and Information Technology, KAU Master degree from Information Sciences and Technologies,
Android - JSON Parser Tutorial
 Android - JSON Parser Tutorial JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation.It is an independent data exchange format and is the best alternative for XML. This chapter explains how to parse the JSON file
Android - JSON Parser Tutorial JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation.It is an independent data exchange format and is the best alternative for XML. This chapter explains how to parse the JSON file
University of Stirling Computing Science Telecommunications Systems and Services CSCU9YH: Android Practical 1 Hello World
 University of Stirling Computing Science Telecommunications Systems and Services CSCU9YH: Android Practical 1 Hello World Before you do anything read all of the following red paragraph! For this lab you
University of Stirling Computing Science Telecommunications Systems and Services CSCU9YH: Android Practical 1 Hello World Before you do anything read all of the following red paragraph! For this lab you
The Internet. CS 2046 Mobile Application Development Fall Jeff Davidson CS 2046
 The Internet CS 2046 Mobile Application Development Fall 2010 Announcements HW2 due Monday, 11/8, at 11:59pm If you want to know what it means to root your phone, or what this does, see Newsgroup HW1 grades
The Internet CS 2046 Mobile Application Development Fall 2010 Announcements HW2 due Monday, 11/8, at 11:59pm If you want to know what it means to root your phone, or what this does, see Newsgroup HW1 grades
Android Workshop: Model View Controller ( MVC):
 Android Workshop: Android Details: Android is framework that provides java programmers the ability to control different aspects of smart devices. This interaction happens through the Android SDK (Software
Android Workshop: Android Details: Android is framework that provides java programmers the ability to control different aspects of smart devices. This interaction happens through the Android SDK (Software
Android Application Development 101. Jason Chen Google I/O 2008
 Android Application Development 101 Jason Chen Google I/O 2008 Goal Get you an idea of how to start developing Android applications Introduce major Android application concepts Provide pointers for where
Android Application Development 101 Jason Chen Google I/O 2008 Goal Get you an idea of how to start developing Android applications Introduce major Android application concepts Provide pointers for where
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
PROCE55 Mobile: Web API App. Web API. https://www.rijksmuseum.nl/api/...
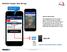 PROCE55 Mobile: Web API App PROCE55 Mobile with Test Web API App Web API App Example This example shows how to access a typical Web API using your mobile phone via Internet. The returned data is in JSON
PROCE55 Mobile: Web API App PROCE55 Mobile with Test Web API App Web API App Example This example shows how to access a typical Web API using your mobile phone via Internet. The returned data is in JSON
O X X X O O X O X. Tic-Tac-Toe. 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 2: The Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe Game
 Tic-Tac-Toe 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 2: The Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe Game Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos O X X X O O X O X The Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe: Rules of the Game Dimitris C. Dracopoulos
Tic-Tac-Toe 5COSC005W MOBILE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT Lecture 2: The Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe Game Dr Dimitris C. Dracopoulos O X X X O O X O X The Ultimate Tic-Tac-Toe: Rules of the Game Dimitris C. Dracopoulos
Lecture 7: Data Persistence : shared preferences. Lecturer : Ali Kadhim Al-Bermani Mobile Fundamentals and Programming
 University of Babylon College of Information Technology Department of Information Networks Mobile Fundamentals and Programming Lecture 7: Data Persistence : shared preferences Lecturer : Ali Kadhim Al-Bermani
University of Babylon College of Information Technology Department of Information Networks Mobile Fundamentals and Programming Lecture 7: Data Persistence : shared preferences Lecturer : Ali Kadhim Al-Bermani
User Interface Design & Development
 User Interface Design & Development Lecture Intro to Android João Pedro Sousa SWE 632, Fall 2011 George Mason University features multitasking w/ just-in-time compiler for Dalvik-VM bytecode storage on
User Interface Design & Development Lecture Intro to Android João Pedro Sousa SWE 632, Fall 2011 George Mason University features multitasking w/ just-in-time compiler for Dalvik-VM bytecode storage on
Mobile Programming Lecture 2. Layouts, Widgets, Toasts, and Event Handling
 Mobile Programming Lecture 2 Layouts, Widgets, Toasts, and Event Handling Lecture 1 Review How to edit XML files in Android Studio? What holds all elements (Views) that appear to the user in an Activity?
Mobile Programming Lecture 2 Layouts, Widgets, Toasts, and Event Handling Lecture 1 Review How to edit XML files in Android Studio? What holds all elements (Views) that appear to the user in an Activity?
Java Training Center - Android Application Development
 Java Training Center - Android Application Development Android Syllabus and Course Content (3 months, 2 hour Daily) Introduction to Android Android and it's feature Android releases and Versions Introduction
Java Training Center - Android Application Development Android Syllabus and Course Content (3 months, 2 hour Daily) Introduction to Android Android and it's feature Android releases and Versions Introduction
Android. Mobile operating system developed by Google A complete stack. Based on the Linux kernel Open source under the Apache 2 license
 Android Android Mobile operating system developed by Google A complete stack OS, framework A rich set of applications Email, calendar, browser, maps, text messaging, contacts, camera, dialer, music player,
Android Android Mobile operating system developed by Google A complete stack OS, framework A rich set of applications Email, calendar, browser, maps, text messaging, contacts, camera, dialer, music player,
Android Application Development
 Android Application Development Octav Chipara What is Android A free, open source mobile platform A Linux-based, multiprocess, multithreaded OS Android is not a device or a product It s not even limited
Android Application Development Octav Chipara What is Android A free, open source mobile platform A Linux-based, multiprocess, multithreaded OS Android is not a device or a product It s not even limited
LECTURE NOTES OF APPLICATION ACTIVITIES
 Department of Information Networks The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF APPLICATION ACTIVITIES By College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@inet.uobabylon.edu.iq The
Department of Information Networks The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF APPLICATION ACTIVITIES By College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@inet.uobabylon.edu.iq The
Using Eclipse for Android Development
 3 Using Eclipse for Android Development This chapter is an introduction to building a complete Android app. The chapter includes creating a new app project, exploring the components of an Android app,
3 Using Eclipse for Android Development This chapter is an introduction to building a complete Android app. The chapter includes creating a new app project, exploring the components of an Android app,
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces. More About Layouts. Scott MacKenzie. York University. Overview (Review)
 EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
CS 234/334 Lab 1: Android Jump Start
 CS 234/334 Lab 1: Android Jump Start Distributed: January 7, 2014 Due: Friday, January 10 or Monday, January 13 (in-person check off in Mobile Lab, Ry 167). No late assignments. Introduction The goal of
CS 234/334 Lab 1: Android Jump Start Distributed: January 7, 2014 Due: Friday, January 10 or Monday, January 13 (in-person check off in Mobile Lab, Ry 167). No late assignments. Introduction The goal of
Eventually, you'll be returned to the AVD Manager. From there, you'll see your new device.
 Let's get started! Start Studio We might have a bit of work to do here Create new project Let's give it a useful name Note the traditional convention for company/package names We don't need C++ support
Let's get started! Start Studio We might have a bit of work to do here Create new project Let's give it a useful name Note the traditional convention for company/package names We don't need C++ support
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces. More About Layouts. Scott MacKenzie. York University
 EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
CS378 -Mobile Computing. User Interface Basics
 CS378 -Mobile Computing User Interface Basics User Interface Elements View Control ViewGroup Layout Widget (Compound Control) Many pre built Views Button, CheckBox, RadioButton TextView, EditText, ListView
CS378 -Mobile Computing User Interface Basics User Interface Elements View Control ViewGroup Layout Widget (Compound Control) Many pre built Views Button, CheckBox, RadioButton TextView, EditText, ListView
CS 403X Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 5: Web Services, Broadcast Receivers, Tracking Location, SQLite Databases Emmanuel Agu
 CS 403X Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 5: Web Services, Broadcast Receivers, Tracking Location, SQLite Databases Emmanuel Agu Web Services What are Web Services? Means to call a remote method
CS 403X Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 5: Web Services, Broadcast Receivers, Tracking Location, SQLite Databases Emmanuel Agu Web Services What are Web Services? Means to call a remote method
Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB)
 Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB) In this exercise, we will create a simple Android application that uses IBM Bluemix Cloudant NoSQL DB. The application
Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB) In this exercise, we will create a simple Android application that uses IBM Bluemix Cloudant NoSQL DB. The application
Course Learning Outcomes (CLO): Student Outcomes (SO):
 Course Coverage Course Learning Outcomes (CLO): 1. Understand the technical limitations and challenges posed by current mobile devices and wireless communications; be able to evaluate and select appropriate
Course Coverage Course Learning Outcomes (CLO): 1. Understand the technical limitations and challenges posed by current mobile devices and wireless communications; be able to evaluate and select appropriate
Hello World. Lesson 1. Android Developer Fundamentals. Android Developer Fundamentals. Layouts, and. NonCommercial
 Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Syllabus- Java + Android. Java Fundamentals
 Introducing the Java Technology Syllabus- Java + Android Java Fundamentals Key features of the technology and the advantages of using Java Using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Introducing
Introducing the Java Technology Syllabus- Java + Android Java Fundamentals Key features of the technology and the advantages of using Java Using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Introducing
Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 2
 Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 2 Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 3 Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 4
Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 2 Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 3 Develop Mobile Front Ends Using Mobile Application Framework A - 4
Android Help. Section 8. Eric Xiao
 Android Help Section 8 Eric Xiao The Midterm That happened Any residual questions? New Assignment! Make a low-fi prototype Must be interactive Use balsamiq or paper Test it with users 3 tasks Test task
Android Help Section 8 Eric Xiao The Midterm That happened Any residual questions? New Assignment! Make a low-fi prototype Must be interactive Use balsamiq or paper Test it with users 3 tasks Test task
CMSC436: Fall 2013 Week 4 Lab
 CMSC436: Fall 2013 Week 4 Lab Objectives: Familiarize yourself with Android Permission and with the Fragment class. Create simple applications using different Permissions and Fragments. Once you ve completed
CMSC436: Fall 2013 Week 4 Lab Objectives: Familiarize yourself with Android Permission and with the Fragment class. Create simple applications using different Permissions and Fragments. Once you ve completed
izzati Documentation Release Gustav Hansen
 izzati Documentation Release 1.0.0 Gustav Hansen Sep 03, 2017 Contents: 1 Why? 3 1.1 Features.................................................. 3 2 Quickstart - Backend 5 2.1 Installation................................................
izzati Documentation Release 1.0.0 Gustav Hansen Sep 03, 2017 Contents: 1 Why? 3 1.1 Features.................................................. 3 2 Quickstart - Backend 5 2.1 Installation................................................
Applications. Marco Ronchetti Università degli Studi di Trento
 Applications Marco Ronchetti Università degli Studi di Trento Android Applications An Android application typically consists of one or more related, loosely bound activities for the user to interact with.
Applications Marco Ronchetti Università degli Studi di Trento Android Applications An Android application typically consists of one or more related, loosely bound activities for the user to interact with.
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Cisco StadiumVision Mobile API for Google Android
 CHAPTER 2 Cisco StadiumVision Mobile API for Google Android Revised: October 31, 2013 This chapter describes the Cisco StadiumVision Mobile SDK Release 1.3 for Google Android, and contains the following
CHAPTER 2 Cisco StadiumVision Mobile API for Google Android Revised: October 31, 2013 This chapter describes the Cisco StadiumVision Mobile SDK Release 1.3 for Google Android, and contains the following
A view is a widget that has an appearance on screen. A view derives from the base class android.view.view.
 LAYOUTS Views and ViewGroups An activity contains Views and ViewGroups. A view is a widget that has an appearance on screen. A view derives from the base class android.view.view. One or more views can
LAYOUTS Views and ViewGroups An activity contains Views and ViewGroups. A view is a widget that has an appearance on screen. A view derives from the base class android.view.view. One or more views can
ANDROID SYLLABUS. Advanced Android
 Advanced Android 1) Introduction To Mobile Apps I. Why we Need Mobile Apps II. Different Kinds of Mobile Apps III. Briefly about Android 2) Introduction Android I. History Behind Android Development II.
Advanced Android 1) Introduction To Mobile Apps I. Why we Need Mobile Apps II. Different Kinds of Mobile Apps III. Briefly about Android 2) Introduction Android I. History Behind Android Development II.
Android Programming Lecture 2 9/7/2011
 Android Programming Lecture 2 9/7/2011 Creating a first app 1. Create a new Android project (a collection of source code and resources for the app) from the Eclipse file menu 2. Choose a project name (can
Android Programming Lecture 2 9/7/2011 Creating a first app 1. Create a new Android project (a collection of source code and resources for the app) from the Eclipse file menu 2. Choose a project name (can
Building MyFirstApp Android Application Step by Step. Sang Shin Learn with Passion!
 Building MyFirstApp Android Application Step by Step. Sang Shin www.javapassion.com Learn with Passion! 1 Disclaimer Portions of this presentation are modifications based on work created and shared by
Building MyFirstApp Android Application Step by Step. Sang Shin www.javapassion.com Learn with Passion! 1 Disclaimer Portions of this presentation are modifications based on work created and shared by
Activities and Fragments
 Activities and Fragments 21 November 2017 Lecture 5 21 Nov 2017 SE 435: Development in the Android Environment 1 Topics for Today Activities UI Design and handlers Fragments Source: developer.android.com
Activities and Fragments 21 November 2017 Lecture 5 21 Nov 2017 SE 435: Development in the Android Environment 1 Topics for Today Activities UI Design and handlers Fragments Source: developer.android.com
User Interface Development. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr.
 User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
Intro to Android Development 3. Accessibility Capstone Dec 10, 2010
 Intro to Android Development 3 Accessibility Capstone Dec 10, 2010 Using Web Services HTTP Request HTTP Response Using Web Services HTTP Request HTTP Response webserver some program Why use a web service?
Intro to Android Development 3 Accessibility Capstone Dec 10, 2010 Using Web Services HTTP Request HTTP Response Using Web Services HTTP Request HTTP Response webserver some program Why use a web service?
Web Services and Enterprise Games
 Web Services and Enterprise Games COSTEL ALDEA 1, LIVIA SANGEORZAN 2, ALINA ALDEA 3 1 Department of Computer Science 2 Department of Computer Science 2 Library University Transilvania of Brasov Iuliu Maniu,
Web Services and Enterprise Games COSTEL ALDEA 1, LIVIA SANGEORZAN 2, ALINA ALDEA 3 1 Department of Computer Science 2 Department of Computer Science 2 Library University Transilvania of Brasov Iuliu Maniu,
Understand applications and their components. activity service broadcast receiver content provider intent AndroidManifest.xml
 Understand applications and their components activity service broadcast receiver content provider intent AndroidManifest.xml Android Application Written in Java (it s possible to write native code) Good
Understand applications and their components activity service broadcast receiver content provider intent AndroidManifest.xml Android Application Written in Java (it s possible to write native code) Good
ANDROID USER INTERFACE
 1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
