Designing Multi-Dimensional User Interaction for a Virtual Museum System
|
|
|
- Adrian George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol. 4, No. 3, December 2016, pp. 649 ~ 654 DOI: /ijeecs.v4.i3.pp Designing Multi-Dimensional User Interaction for a Virtual Museum System Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook* 1, Noraidah Ashaari 2, Normala Rahim 3 1,2, Centre for Software Technology and Management, Faculty of Information Science and Technology, UKM Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia 3 Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin, Faculty of Informatics and Computing, Besut, Terengganu, Malaysia *Corresponding author, tsm@ukm.edu.my Abstract The focus of this study is to improve the display platform for the State of Terengganu Virtual Museum System (muziummaya.terengganu.gov.my). The existing virtual museum can be displayed via desktop computing system where information is displayed on-line using features for searching, browsing, and manipulating artifacts and galleries. However, presentation of information on mobile device screens cannot be viewed effectively and is difficult to navigate due to the user's cognitive load. Therefore, this study will establish effective interaction design, taking into account the multi-dimensional context for the design of a user interface via a mobile device in the hopes that users who are students, curators, researchers, and the public can access the virtual museum system via desktop as well as from their mobile devices. This study was conducted in three stages i.e. user requirements analysis, interface design, and usability evaluation. The result of this research is the design of a multi-dimensional user interaction context that meets the display requirements and navigation information for mobile devices. Keywords: user interaction, information presentation, designing mobile interface, virtual museum Copyright 2016 Institute of Advanced Engineering and Science. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction The presentation of information should be displayed via a multi-dimensional user interaction context, which is not only limited to the computer screen but should also include small screen displays such as the ones on mobile devices. However, the challenges in designing a user interface include cognitive load and information presentation. Cognitive load issues occur when the user is forced to simultaneously divide his or her attention between certain tasks on a small display. Besides that, an excess of information presentation at any one time could result in information overload. Interface design for mobile devices should assist users to access relevant information without having to rely on their memory and strong visual attention on said interface. Zhang et al [1] stated that the main issue that interface designers face is how to present a lot of information on a small screen for effective and simple navigation, so as not to tax user memory load. The work of [2] showed users experienced a change in emotions when they visited the virtual museum as a result of information overload on the small screen of mobile devices. Users need a mobile application that can access and display the gallery panorama including the artifact hotspots in the gallery. Wook T [3] also suggests that the gallery display technique (floorplan and panorama) be used in the existing virtual museum, as it can optimise the screen space of mobile devices, which have smaller screens than computers, and thus, access and display artifact information in 3D. Each user has different personalities and attitudes when surfing for information on the Internet. This proves that user behaviour is important factors, which, besides information content display (gallery, artifact, and information), also involves interaction. The user interaction context via mobile devices calls for meticulous design and entails different requirements than desktop computing displays [4]. The design of information on mobile device displays must be more attractive to engage users to search for information and to increase the fun factor. Since information searching in the virtual museum environment allows for 360 exploration and 3D image display, emotions that can induce sensitive memories would also be indirectly Received September ; Revised November 10, 2016; Accepted November 30, 2016
2 650 ISSN: involved [5]. If sensitive memory is integrated with user usability context, a richer experience could be attained compared to visitation via computer desktop displays. Therefore, this study will create a multi-dimensional user interface context based on user requirements, which can easily and effectively increase the usage of the virtual museum system among its visitors. 2. Related Studies Design based on the multi-dimensional user interaction context is important to estimate the design challenges involving the use of mobile devices [6]. There are a few elements that can affect user interaction when using mobile devices including movement, various physical parameters, sound and light, limited screen size, and other external factors. Chen and Kotz [7] define these factors as an environment that can markedly change the way users interact with mobile devices. All these parameters can be grouped into the concept of multi-dimensional context. According to [8] context can be defined as usable information that can explain the condition of an entity. The entity should be regarded as the subject that relates to the interaction between the user and the application such as a person, place, or object, including the user and application itself. In general terms, context refers to location, identity and culture, group, and physical and computing objects. Adipat et al [9] suggested three techniques to present information so as to avoid information overload on mobile device screens. These include information visualisation (IV), an adaptive interface, and multimodal displays. The information visualisation technique presents graphics supported by the computer system that display data in a meaningful and intelligent way via four categories: Presentation Optimisation, Semantic Changes, the Zoom Method, and the Focus and Context Approach. This technique can be used separately or in tandem with other techniques to provide an effective information presentation on mobile device. Besides that [9] also states that the taxonomy of context visualisation involves context dimensions i.e. 1D content contains text documents only, 2D is made up of images, maps, and schedules, whereas 3D includes the virtual reality of an actual object. An adaptive interface is the dynamic re-configuration of presentation according to user actions. The use of an adaptive interface in a mobile environment could benefit the user in two ways i.e. in the provision of additional information that is known to be of interest to the user, and the style adjustment and format presentation according to user preferences and characteristics [10]. The characteristic of an adaptive interface is controllability, predictability and transparency, and non-distruptive. Controllability refers to the extent to which the user could control the execution of an action. Predictability is the extent to which the user could predict an outcome after executing an action. Transparency means the extent to which the user understands the system behaviour or has a clear picture of how the system functions. Lastly, non-distruptive refers to the extent to which the user can focus on a task without having to pay attention to the interface [10]. Based on their study, [11] suggest that mobile cloud computing be used to present multimedia content based on the existing limitations of mobile devices, such as space storage, computing power, and broadband strength, in support of an adaptive interface. Cloud computing can be visualised as a new paradigm for mobile applications whereby the processing and storage of data could be transferred from the mobile device to a powerful computing platform centred on a cloud. This centred application could be accessed via wireless connectivity from the web browser on mobile devices. In this way, mobile devices would not require power-heavy configurations (e.g. CPU speed and memory capacity) because all complex computing modules can be processed on the cloud [12]. On the other hand, the multimodal interface offers an interface that behaves naturally (Natural User Interface, NUI) via gesture interaction. These gestures involve natural user behaviour via the hand, shoulders, face or body gestures, to communicate information to the computer [13]. The gesture interface includes manipulative and communicative gestures where each can be used to interact with an object (direct gesture with the screen such as tap ) and for communication purposes i.e. using speech. Both these gestures can be executed using direct manipulation, making the interaction with the multimodal NUI more realistic such as the emulation of actual human communication in the real world. The research findings on the design of multi-dimensional user interaction context when designing a user interface for mobile devices have shown that a design that fulfills user IJEECS Vol. 4, No. 3, December 2016:
3 IJEECS ISSN: requirements could be realised from a transparent interface that is able to integrate desktop computing and naturally adapt it to the interaction design on mobile devices. Therefore, this study has conducted a Virtul Museum System (VMS) interface design process via application of the IV technique based on the visualisation taxonomy involving 1D, 2D, and 3D content dimensions. This technique will help the study to visualise a set of data from an image that is generated. Besides that, the application of the IV technique could contribute to an in-depth understanding for the user when using a system that is equipped with simple controllability and effective information presentation. 3. Method The research methodology involves three stages i.e. requirement analysis, interface design, and usability testing Requirement Analysis The requirement analysis was conducted via the interview technique with seven respondents consisting of public users. The aim of this analysis is to determine actual user requirements. The respondents were briefed on the desktop VMS and the following questions were asked: 1) What kind of functions would they require if they had to use a virtual museum tour mobile application? 2) Would they need a directory to direct them in the museum? 3) What kind of interactions is easiest for the user to determine artifact information? 4) What kind of interactions is easiest for navigation in the museum? Arrow or swipe screen? 5) How do they prefer to choose the galleries? Floor map or tree map? 3.2. Interface Design This study generated the VMS interface prototype design based on the user requirement analysis. Two activities were conducted i.e. the storyboard sketch followed by highfidelity prototype development. The storyboard sketch was created to visualise the user requirements i.e. 360 exploration with map directory and tree map guidance, swipe feature, and application of the minimalism principal. Next, the prototype design was developed to achieve the user requirement objective consisting of information (gallery and artifact) and navigation function, swipe, links, access, and manipulation. At this stage, the protoype is nearly identical to the final product but is still incomplete Interface Design Usability testing was conducted using the Cognitive Walkthrough evaluation technique, involving five respondents that are experts or are literate in determining the learnability aspects of the system. This technique extracts the perception of user experiential successes and failures when using the VMS prototype via task completion provided during testing. Subsequently, this perception is used to enhance the usability of the interface design. Four questions were addressed to the respondents: Q1. Is the effect of current action the same as the user s goal? Q2. Is the action visible? This relates to the visibility and understandability of actions on the interface. Q3. Will the user recognise the action as the correct one? Users often use the "labelfollowing" strategy, which leads them to select an action if the label for that action matches the task description. Q4. Will the user understand the feedback? This is to check the system feedback after the user executes the action. 4. Result and Discussion 4.1. Requirement Analysis Results The analysis results show 100% respondent agreement that it is good if the museum could be browsed in a 360 environment but the directory is still needed as a guide to the Designing Multi-Dimensional User Interaction for (Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook)
4 652 ISSN: museum. 57% of the respondents chose the floor map directory whilst the rest preferred the tree map for choosing the galleries they wanted to visit. The interaction element gained 100% respondent agreement i.e. they liked the swipe feature on the screen compared to touching the arrow icons for navigation. Besides that, the respondents liked the minimalist interface more, as it was easy to use and to remember during interaction Interface Design Results The findings for interface design include a visual storyboard sketch and a prototype. The storyboard that was created is a conceptual sketch of the user requirement and layout design display without any functionality. Figure 1 illustrates the storyboard that visualises the directory map and tree map guidance used for the interface. Figure 1. Storyboard 4.3 Usability Testing Results Figure 3 shows the usability testing results using the Cognitive Walkthrough technique based on the four questions presented in Section 3(C). 100% of the respondents agree that the navigation function worked well and was easy to use. However, for Question 4, only 85% agreed that the button to access more detailed information about the artifacts was easy to use. After the evaluation, all user feedbacks were taken into account. Overall, most of the users agreed that all the functionalities of the system worked well and the icons were easily recognisable except for the star button used to represent the information button. The users left some comments about this icon, i.e. it was too small and not visible at first glance. Other than that, the users could not recognise the star icon as representing artifact information. Besides that, the users also suggested ideas on adding a zoom function so that they would be able to see the artifact more closely and clearly. IJEECS Vol. 4, No. 3, December 2016:
5 IJEECS ISSN: Figure 2. Prototype Figure 3. Cognitive Walkthrough Chart Designing Multi-Dimensional User Interaction for (Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook)
6 654 ISSN: In order to make the application more accessible, some improvements were implemented based on the feedback obtained. The improvements are: 1) The star icons were changed into the standard icon for information, which is the i icon, to make the icon more visible and easier for users to understand. 2) The zoom function was added for the user to be able to see the artifacts up close. 5. Conclusion This study concludes that the VMS interface design in a mobile device environment, which applies the IV technique, could optimise the small screen space of mobile devices for accessing and displaying artifact information in 3D. The study s findings on multi-dimensional interface design context based on user requirements could effectively and easily enhance the usability of the virtual museum system among its visitors. Acknowledgements This work was supported by Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Faculty of Information Science and Technology, Center for Software Technology and Management, Multimedia Software and Usability Research Group and FRGS/2/2014/ICT05/UKM/02/1 research grant. References [1] Zhang, D Jangam, A Zhou, L Yakut I. Context-Aware Multimedia Content Adaptation for Mobile Web. International Journal of Networked and Distributed Computing. 2015; 3(1): [2] Noraidah Sahari, Hazura Hohamed, Hairulliza Mohamad Judi. Pemeriksaan Pakar Terhadap Kebolehgunaan Muzium Maya (Expert Usability Inspection toward Virtual Museum), Kelestarian Warisan Budaya Melalui Teknologi Maklumat dan Komunikasi. Bangi: Penerbitan Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. 2016: [3] Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook, Siti Fadzilah Mat Nor, Nor Azan Mat Zin, Hazura Mohamed, Noraidah Ashaari, Hairulliza Mohd Judi, Zurina Muda, Noorazean Mohd Ali, Amirah Ismail, Zuraidah Abdullah, Lailatul Qadri Zakaria, Normala Rahim. Tugas dan Gaya Interaksi Pengguna dalam Persekitaran Muzium Maya (User Interaction Style and Task in Virtual Museum Environment). Prosiding Teknologi Maklumat dan Komunikasi dalam Warisan Budaya (SICTH 16). 2016: [4] Mardhiah Ibrahim, Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook, Norleyza Jailani. Interface designs model of location-aware mobile commerce for songket. Jurnal Teknologi (Sciences and Engineering). 2014; 68(1): [5] Raptis D, Tselios N, Kjeldskov J, Skov M. Does size matter? Investigating the impact of mobile phone screen size on users perceived usability, effectiveness and efficiency. MobileHCI. 2013: [6] Ginige, A, Romano, M, Sebillo, M, Vitiello, G Di Giovanni P. Spatial data and mobile applications: general solutions for interface design. Proceedings of the International Working Conference on Advanced Visual Interfaces. 2012: [7] Chen, G Kotz D. A Survey of Context-Aware Mobile Computing Research. Technical Report, Dartmouth Computer Science Department, TR : 381. [8] Dix, A, Rodden, T, Davies, N, Trevor, J, Friday, A, Palfreyman K. Exploiting Space and Location as a Design Framework for Interactive Mobile Systems. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction (TOCHI). 2000; 7(3): [9] Adipat B, Zhang D, Zhou L. The effects of tree-view based presentation adaptation on mobile web browsing. Mis Quarterly. 2011; 35(1): [10] Adipat B, Zhang D. Interface design for mobile applications. AMCIS 2005 Proceedings, 2005: 494. [11] Karadimce A, Davcev D. Adaptive multimedia learning delivered in mobile cloud computing environment. The Fourth International Conference on Cloud Computing, GRIDs, and Virtualization, Valencia. 2013: [12] Warhekar, SP, Gaikwad, VT, Datir, HN. Development and evaluation mobile multimedia cloud application. International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing. 2014; 3(4): [13] Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook, Nor Hidayah Hussain, Juliati Jumahad. Preliminary study of an adaptive multimodal interface design for student's digital library. Computational Science and Technology (ICCST) International Conference. 2014: 1-5. IJEECS Vol. 4, No. 3, December 2016:
Development of Emulation Network Analyzer Tool for Computer Network Planning
 Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics ISSN: 2302-9285 Vol. 5, No. 2, June 2016, pp. 219~229, DOI: 10.11591/eei.v5i2.557 219 Development of Emulation Network Analyzer Tool for Computer Network
Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics ISSN: 2302-9285 Vol. 5, No. 2, June 2016, pp. 219~229, DOI: 10.11591/eei.v5i2.557 219 Development of Emulation Network Analyzer Tool for Computer Network
HOMEPAGE USABILITY: MULTIPLE CASE STUDIES OF TOP 5 IPTA S HOMEPAGE IN MALAYSIA Ahmad Khairul Azizi Ahmad 1 UniversitiTeknologi MARA 1
 HOMEPAGE USABILITY: MULTIPLE CASE STUDIES OF TOP 5 IPTA S HOMEPAGE IN MALAYSIA Ahmad Khairul Azizi Ahmad 1 UniversitiTeknologi MARA 1 khairulazizi@perak.uitm.edu.my Anwar Fikri Abdullah 2 UniversitiTeknologi
HOMEPAGE USABILITY: MULTIPLE CASE STUDIES OF TOP 5 IPTA S HOMEPAGE IN MALAYSIA Ahmad Khairul Azizi Ahmad 1 UniversitiTeknologi MARA 1 khairulazizi@perak.uitm.edu.my Anwar Fikri Abdullah 2 UniversitiTeknologi
Course Outline. Department of Computing Science Faculty of Science. COMP 3450 Human Computer Interaction Design (3,1,0) Fall 2015
 Course Outline Department of Computing Science Faculty of Science COMP 3450 Human Computer Interaction Design (3,1,0) Fall 2015 Instructor: Office: Phone/Voice Mail: E-Mail: Course Description Students
Course Outline Department of Computing Science Faculty of Science COMP 3450 Human Computer Interaction Design (3,1,0) Fall 2015 Instructor: Office: Phone/Voice Mail: E-Mail: Course Description Students
Aalborg Universitet. Just-In-Place Information for Mobile Device Interfaces Kjeldskov, Jesper. Published in: Paterno, F. (ed.)
 Aalborg Universitet Just-In-Place Information for Mobile Device Interfaces Kjeldskov, Jesper Published in: Paterno, F. (ed.) DOI (link to publication from Publisher): 10.1007/3-540-45756-9_21 Publication
Aalborg Universitet Just-In-Place Information for Mobile Device Interfaces Kjeldskov, Jesper Published in: Paterno, F. (ed.) DOI (link to publication from Publisher): 10.1007/3-540-45756-9_21 Publication
Real Time Break Point Detection Technique (RBPD) in Computer Mouse Trajectory
 TELKOMNIKA, Vol. 11, No. 5, May 2013, pp. 2710 ~ 2715 ISSN: 2302-4046 2710 Real Time Break Point Detection Technique (RBPD) in Computer Mouse Trajectory Seyed Yashar Banihashem 1, Nor Azan Mat Zin* 1,
TELKOMNIKA, Vol. 11, No. 5, May 2013, pp. 2710 ~ 2715 ISSN: 2302-4046 2710 Real Time Break Point Detection Technique (RBPD) in Computer Mouse Trajectory Seyed Yashar Banihashem 1, Nor Azan Mat Zin* 1,
Designing for Multimedia
 1 ing for Multi Phil Gray Outline What s Special about Multi? A Method Based on the City Method Developed by Alistair Sutcliffe and Stephanie Wilson Evaluation 2 What s Special About Multi? Rich forms
1 ing for Multi Phil Gray Outline What s Special about Multi? A Method Based on the City Method Developed by Alistair Sutcliffe and Stephanie Wilson Evaluation 2 What s Special About Multi? Rich forms
Heuristic Evaluation of a Learning Management System
 Heuristic Evaluation of a Learning Management System atrah Abdullah 1, and oor Hafizah Che Ali 2 1 Universiti Teknologi Mara, Shah Alam, Malaysia, natrah@tmsk.uitm.edu.my 2 Universiti Teknologi Mara, Shah
Heuristic Evaluation of a Learning Management System atrah Abdullah 1, and oor Hafizah Che Ali 2 1 Universiti Teknologi Mara, Shah Alam, Malaysia, natrah@tmsk.uitm.edu.my 2 Universiti Teknologi Mara, Shah
AN APPROACH FOR GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE DEVELOPMENT FOR STEREOSCOPIC VISUALIZATION SYSTEM
 AN APPROACH FOR GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE DEVELOPMENT FOR STEREOSCOPIC VISUALIZATION SYSTEM Rositsa R. Radoeva St. Cyril and St. Methodius University of Veliko Tarnovo, ABSTRACT Human-computer interaction
AN APPROACH FOR GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE DEVELOPMENT FOR STEREOSCOPIC VISUALIZATION SYSTEM Rositsa R. Radoeva St. Cyril and St. Methodius University of Veliko Tarnovo, ABSTRACT Human-computer interaction
AN IMAGE STEGANOGRAPHY ALGORITHM BASED ON LOGICAL CONNECTIVE
 AN IMAGE STEGANOGRAPHY ALGORITHM BASED ON LOGICAL CONNECTIVE 1 SITI DHALILA MOHD SATAR, 1 NAZIRAH ABD HAMID, 1 FATIMAH GHAZALI, 1 ROSLINDA MUDA, 1 MOHAMAD AFENDEE MOHAMED 1 Faculty of Informatics and Computing,
AN IMAGE STEGANOGRAPHY ALGORITHM BASED ON LOGICAL CONNECTIVE 1 SITI DHALILA MOHD SATAR, 1 NAZIRAH ABD HAMID, 1 FATIMAH GHAZALI, 1 ROSLINDA MUDA, 1 MOHAMAD AFENDEE MOHAMED 1 Faculty of Informatics and Computing,
3d: Usability Testing Review
 Balance Ryan Parsons, Chad Price, Jia Reese, Alex Vassallo 3d: Usability Testing Review Usability Test #1 Our first usability testing participant, Mary, was an undergraduate student in Computer Science
Balance Ryan Parsons, Chad Price, Jia Reese, Alex Vassallo 3d: Usability Testing Review Usability Test #1 Our first usability testing participant, Mary, was an undergraduate student in Computer Science
DESIGNING A TOOL TO MAP UML CLASS DIAGRAM INTO RELATIONAL DATABASE
 DESIGNING A TOOL TO MAP UML CLASS DIAGRAM INTO RELATIONAL DATABASE Mohd Khalid Awang 1 and Nur Lian Labadu 2 Faculty of Informatics University of Sultan Zainal Abidin (UniSZA) Gong Badak Campus, Kuala
DESIGNING A TOOL TO MAP UML CLASS DIAGRAM INTO RELATIONAL DATABASE Mohd Khalid Awang 1 and Nur Lian Labadu 2 Faculty of Informatics University of Sultan Zainal Abidin (UniSZA) Gong Badak Campus, Kuala
A Heuristic Evaluation of Ohiosci.org
 A Heuristic Evaluation of Ohiosci.org Executive Summary Site evaluated: Goal: Method: The Ohio Academy of Science http://www.ohiosci.org/ The goal of this heuristic evaluation is to test the overall usability
A Heuristic Evaluation of Ohiosci.org Executive Summary Site evaluated: Goal: Method: The Ohio Academy of Science http://www.ohiosci.org/ The goal of this heuristic evaluation is to test the overall usability
Evaluation of Electronic Guidebook Mobile Web Resources
 Evaluation of Electronic Guidebook Mobile Web Resources Executive Summary The Electronic Guidebook research project began in 1998 at The Exploratorium, an interactive science museum in San Francisco, in
Evaluation of Electronic Guidebook Mobile Web Resources Executive Summary The Electronic Guidebook research project began in 1998 at The Exploratorium, an interactive science museum in San Francisco, in
Level 4 Diploma in Computing
 Level 4 Diploma in Computing 1 www.lsib.co.uk Objective of the qualification: It should available to everyone who is capable of reaching the required standards It should be free from any barriers that
Level 4 Diploma in Computing 1 www.lsib.co.uk Objective of the qualification: It should available to everyone who is capable of reaching the required standards It should be free from any barriers that
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14915-1 First edition 2002-11-01 Software ergonomics for multimedia user interfaces Part 1: Design principles and framework Ergonomie des logiciels pour les interfaces utilisateur
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 14915-1 First edition 2002-11-01 Software ergonomics for multimedia user interfaces Part 1: Design principles and framework Ergonomie des logiciels pour les interfaces utilisateur
Usability Evaluation of Cell Phones for Early Adolescent Users
 Yassierli*, Melati Gilang Industrial Management Research Division, Faculty of Industrial Technology, Bandung Institute of Technology Jl. Ganesa 10 Bandung 40134 Indonesia ABSTRACT:. The increasing number
Yassierli*, Melati Gilang Industrial Management Research Division, Faculty of Industrial Technology, Bandung Institute of Technology Jl. Ganesa 10 Bandung 40134 Indonesia ABSTRACT:. The increasing number
Conceptualizing User Satisfaction toward a Library Quality at Malaysia Nuclear Agency Library
 Conceptualizing User Satisfaction toward a Library Quality at Malaysia Nuclear Agency Library Nurul Nadia Badrol Amin Faculty of Information Management, University Teknologi MARA (UiTM) Selangor MALAYSIA
Conceptualizing User Satisfaction toward a Library Quality at Malaysia Nuclear Agency Library Nurul Nadia Badrol Amin Faculty of Information Management, University Teknologi MARA (UiTM) Selangor MALAYSIA
UXD. using the elements: structure
 using the elements: structure defining structure you are here structure essentially defines how users get to a given screen and where they can go when they re done. structure also defines categories of
using the elements: structure defining structure you are here structure essentially defines how users get to a given screen and where they can go when they re done. structure also defines categories of
CS Human Computer Interaction
 Part A 1. Define HCI CS6008 - Human Computer Interaction UNIT-I Question Bank FOUNDATIONS OF HCI 2. What are the basic requirements of an Successful Interactive System? 3. What is STM & LTM? 4. List out
Part A 1. Define HCI CS6008 - Human Computer Interaction UNIT-I Question Bank FOUNDATIONS OF HCI 2. What are the basic requirements of an Successful Interactive System? 3. What is STM & LTM? 4. List out
Session 3 Presentation and Dialogue Design. Presentation Techniques. Design for Attention. Planning thematic threads through several media
 Session 3 Presentation and Dialogue Design Planning thematic threads through several media Presentation layout: sequential or concurrent Drawing attention to key facts especially in image Specifying explicit
Session 3 Presentation and Dialogue Design Planning thematic threads through several media Presentation layout: sequential or concurrent Drawing attention to key facts especially in image Specifying explicit
Development of a guidance system for tourism by using archived data
 Journal of Global Tourism Research, Volume 3, Number 1, 2018 Development of a guidance system for tourism by using archived data Original Article Mari Endo (Faculty of Information Design and Sociology,
Journal of Global Tourism Research, Volume 3, Number 1, 2018 Development of a guidance system for tourism by using archived data Original Article Mari Endo (Faculty of Information Design and Sociology,
Knowledge Organiser Digital Information Technology. Year 10: Unit 1, User Interface, Learning Aim A, B & C
 Knowledge Organiser Digital Information Technology Year 10: Unit 1, User Interface, Learning Aim A, B & C Enquiry Questions A1 What is a user interface? What is a user interface and how do they vary across
Knowledge Organiser Digital Information Technology Year 10: Unit 1, User Interface, Learning Aim A, B & C Enquiry Questions A1 What is a user interface? What is a user interface and how do they vary across
Ryan Parsons Chad Price Jia Reese Alex Vassallo
 Ryan Parsons - Paper Prototype, Writing Chad Price - Paper Prototype, Digital Mockup Jia Reese - Paper Prototype, Usability Testing Alex Vassallo - Usability Testing, Writing All we have to decide is what
Ryan Parsons - Paper Prototype, Writing Chad Price - Paper Prototype, Digital Mockup Jia Reese - Paper Prototype, Usability Testing Alex Vassallo - Usability Testing, Writing All we have to decide is what
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition
 Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition Learning Objectives Describe the difference between user interfaces and system interfaces Explain why the user interface is the system to
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition Learning Objectives Describe the difference between user interfaces and system interfaces Explain why the user interface is the system to
AN EVALUATION OF TIMELINE VISUALIZATION AND TREE VIEWER IN CRIME NEWS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 12, No. 9 (2017) 2426-2437 School of Engineering, Taylor s University AN EVALUATION OF TIMELINE VISUALIZATION AND TREE VIEWER IN CRIME NEWS NAZLENA MOHAMAD
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 12, No. 9 (2017) 2426-2437 School of Engineering, Taylor s University AN EVALUATION OF TIMELINE VISUALIZATION AND TREE VIEWER IN CRIME NEWS NAZLENA MOHAMAD
A Tagging Approach to Ontology Mapping
 A Tagging Approach to Ontology Mapping Colm Conroy 1, Declan O'Sullivan 1, Dave Lewis 1 1 Knowledge and Data Engineering Group, Trinity College Dublin {coconroy,declan.osullivan,dave.lewis}@cs.tcd.ie Abstract.
A Tagging Approach to Ontology Mapping Colm Conroy 1, Declan O'Sullivan 1, Dave Lewis 1 1 Knowledge and Data Engineering Group, Trinity College Dublin {coconroy,declan.osullivan,dave.lewis}@cs.tcd.ie Abstract.
Prototyping. Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994.
 Prototyping Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994. 1 What is prototyping? producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your
Prototyping Readings: Dix et al: Chapter 5.8 Marc Rettig: Prototyping for tiny fingers, Communications of the ACM, April 1994. 1 What is prototyping? producing cheaper, less accurate renditions of your
A Development Of A Web-Based Application System Of QR Code Location Generator and Scanner named QR- Location
 UTM Computing Proceedings Innovations in Computing Technology and Applications Volume 2 Year: 2017 ISBN: 978-967-0194-95-0 1 A Development Of A Web-Based Application System Of QR Code Location Generator
UTM Computing Proceedings Innovations in Computing Technology and Applications Volume 2 Year: 2017 ISBN: 978-967-0194-95-0 1 A Development Of A Web-Based Application System Of QR Code Location Generator
Visualisation of ergonomic guidelines
 Visualisation of ergonomic guidelines Widell Blomé, Mikael; Odenrick, Per; Andersson, M; Svensson, S Published: 2002-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Blomé, M., Odenrick,
Visualisation of ergonomic guidelines Widell Blomé, Mikael; Odenrick, Per; Andersson, M; Svensson, S Published: 2002-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Blomé, M., Odenrick,
Multimedia Content Delivery in Mobile Cloud: Quality of Experience model
 Multimedia Content Delivery in Mobile Cloud: Quality of Experience model Aleksandar Karadimce Danco Davcev Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering University Ss Cyril and Methodius, Skopje, R. Macedonia
Multimedia Content Delivery in Mobile Cloud: Quality of Experience model Aleksandar Karadimce Danco Davcev Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering University Ss Cyril and Methodius, Skopje, R. Macedonia
Scroll Display: Pointing Device for Palmtop Computers
 Asia Pacific Computer Human Interaction 1998 (APCHI 98), Japan, July 15-17, 1998, pp. 243-248, IEEE Computer Society, ISBN 0-8186-8347-3/98 $10.00 (c) 1998 IEEE Scroll Display: Pointing Device for Palmtop
Asia Pacific Computer Human Interaction 1998 (APCHI 98), Japan, July 15-17, 1998, pp. 243-248, IEEE Computer Society, ISBN 0-8186-8347-3/98 $10.00 (c) 1998 IEEE Scroll Display: Pointing Device for Palmtop
GeoFARA (Geography Fieldwork Augmented Reality Application): design, development and evaluation
 GeoFARA (Geography Fieldwork Augmented Reality Application): design, development and evaluation Xiaoling Wang, Corné P.J.M. van Elzakker, Menno-Jan Kraak, Barend Köbben ICC 2017, 5 July, 2017 Washington,
GeoFARA (Geography Fieldwork Augmented Reality Application): design, development and evaluation Xiaoling Wang, Corné P.J.M. van Elzakker, Menno-Jan Kraak, Barend Köbben ICC 2017, 5 July, 2017 Washington,
SMK SEKSYEN 5,WANGSAMAJU KUALA LUMPUR FORM
 SMK SEKSYEN 5,WANGSAMAJU 53300 KUALA LUMPUR FORM 5 LEARNING AREA 4 MULTIMEDIA Ramadan, SMK Pekan 2007 MULTIMEDIA LESSON 21 MULTIMEDIA CONCEPTS DEFINITION OF MULTIMEDIA Multimedia has been used in many
SMK SEKSYEN 5,WANGSAMAJU 53300 KUALA LUMPUR FORM 5 LEARNING AREA 4 MULTIMEDIA Ramadan, SMK Pekan 2007 MULTIMEDIA LESSON 21 MULTIMEDIA CONCEPTS DEFINITION OF MULTIMEDIA Multimedia has been used in many
Electronic Portfolios in the Classroom
 Electronic Portfolios in the Classroom What are portfolios? Electronic Portfolios are a creative means of organizing, summarizing, and sharing artifacts, information, and ideas about teaching and/or learning,
Electronic Portfolios in the Classroom What are portfolios? Electronic Portfolios are a creative means of organizing, summarizing, and sharing artifacts, information, and ideas about teaching and/or learning,
Tap Input as an Embedded Interaction Method for Mobile Devices
 Tap Input as an Embedded Interaction Method for Mobile Devices By Sami Ronkainen, Jonna Häkkilä, Saana Kaleva, Ashley Colley & Jukka Linjama (presentation) Nokia, Finland Presentation in TEI 07, Conference
Tap Input as an Embedded Interaction Method for Mobile Devices By Sami Ronkainen, Jonna Häkkilä, Saana Kaleva, Ashley Colley & Jukka Linjama (presentation) Nokia, Finland Presentation in TEI 07, Conference
RETRACTED ARTICLE. Web-Based Data Mining in System Design and Implementation. Open Access. Jianhu Gong 1* and Jianzhi Gong 2
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2014, 6, 1907-1911 1907 Web-Based Data Mining in System Design and Implementation Open Access Jianhu
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2014, 6, 1907-1911 1907 Web-Based Data Mining in System Design and Implementation Open Access Jianhu
Web Designers Opinions on Visual Elements in Educational Website
 Advanced Journal of Technical and Vocational Education, (): 4-47, 8 e-issn: 55-74 RMP Publications, 8 DOI:.6666/rmp.ajtve.8..7 Web Designers Opinions on Visual Elements in Educational Website Hafizah Abdullah@Ali,
Advanced Journal of Technical and Vocational Education, (): 4-47, 8 e-issn: 55-74 RMP Publications, 8 DOI:.6666/rmp.ajtve.8..7 Web Designers Opinions on Visual Elements in Educational Website Hafizah Abdullah@Ali,
Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University
 Human Computer Interface Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Today s Topics UI development and Trends NUI Discussion Today s Topics UI development and Trends Development Trends
Human Computer Interface Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Today s Topics UI development and Trends NUI Discussion Today s Topics UI development and Trends Development Trends
Multi-disciplinary User Interface Construction: Case FESTO Flexible Assembly Unit
 Multi-disciplinary User Interface Construction: Case FESTO Flexible Assembly Unit Marko Nieminen, Toni Koskinen, Lauri Repokari Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Information Ergonomics Research
Multi-disciplinary User Interface Construction: Case FESTO Flexible Assembly Unit Marko Nieminen, Toni Koskinen, Lauri Repokari Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Information Ergonomics Research
Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping
 Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping Course announcements Deadlines Individual assignment (extended) deadline: today (June 7) 8:00 am by email User testing summary for paper prototype testing- Thursday June
Seng310 Lecture 8. Prototyping Course announcements Deadlines Individual assignment (extended) deadline: today (June 7) 8:00 am by email User testing summary for paper prototype testing- Thursday June
User Experience and Emotions for Accessibility (UEE4A)
 User Experience and Emotions for Accessibility (UEE4A) User Experience & Emotions for Accessibility Introduction to the Special Thematic Session Yehya Mohamad (&), Gaby Nordbrock, Henrike Gappa, and Carlos
User Experience and Emotions for Accessibility (UEE4A) User Experience & Emotions for Accessibility Introduction to the Special Thematic Session Yehya Mohamad (&), Gaby Nordbrock, Henrike Gappa, and Carlos
BOOK TRANSACTION SYSTEM
 BOOK TRANSACTION SYSTEM NORHAFIZAL AHMAD Faculty of Computer Universiti Teknologi Malaysia hafizal@um.edu.my SITI WARDAH ABDUL HAMID Faculty of Computer Universiti Teknologi Malaysia ctwardah@um.edu.my
BOOK TRANSACTION SYSTEM NORHAFIZAL AHMAD Faculty of Computer Universiti Teknologi Malaysia hafizal@um.edu.my SITI WARDAH ABDUL HAMID Faculty of Computer Universiti Teknologi Malaysia ctwardah@um.edu.my
What is interaction design? What is Interaction Design? Example of bad and good design. Goals of interaction design
 What is interaction design? What is Interaction Design? Designing interactive products to support people in their everyday and working lives Sharp, Rogers and Preece (2002) The design of spaces for human
What is interaction design? What is Interaction Design? Designing interactive products to support people in their everyday and working lives Sharp, Rogers and Preece (2002) The design of spaces for human
Identify how the use of different browsers and devices affects the look of a webpage. Competencies
 1 Strand 2. IT Fundamentals Learners apply fundamental principles of IT, including the history of IT and its impact on society, common industry terms, systems theory, information storage and retrieval,
1 Strand 2. IT Fundamentals Learners apply fundamental principles of IT, including the history of IT and its impact on society, common industry terms, systems theory, information storage and retrieval,
Implementing Games User Research Processes Throughout Development: Beyond Playtesting
 Implementing Games User Research Processes Throughout Development: Beyond Playtesting Graham McAllister Founder, Player Research @grmcall Introduction Founder - Player Research, a User Research studio
Implementing Games User Research Processes Throughout Development: Beyond Playtesting Graham McAllister Founder, Player Research @grmcall Introduction Founder - Player Research, a User Research studio
Design and User Evaluation of Augmented-Reality Interfaces Topic Usability Evaluation Methods. Payel Bandyopadhyay MSc Student University of Helsinki
 Design and User Evaluation of Augmented-Reality Interfaces Topic Usability Evaluation Methods Payel Bandyopadhyay MSc Student University of Helsinki Outline Introduction Lab based usability testing Procedure
Design and User Evaluation of Augmented-Reality Interfaces Topic Usability Evaluation Methods Payel Bandyopadhyay MSc Student University of Helsinki Outline Introduction Lab based usability testing Procedure
Applying Usability to elearning
 Applying Usability to elearning 6 December 08 John Wooden, PhD Director of Usability Services Fredrickson Communications jwooden@fredcomm.com We make information useful! About Fredrickson Communications
Applying Usability to elearning 6 December 08 John Wooden, PhD Director of Usability Services Fredrickson Communications jwooden@fredcomm.com We make information useful! About Fredrickson Communications
(Milano Lugano Evaluation Method) A systematic approach to usability evaluation. Part I LAB HCI prof. Garzotto - HOC-POLITECNICO DI MILANO a.a.
 (Milano Lugano Evaluation Method) A systematic approach to usability evaluation Part I LAB HCI prof. Garzotto - HOC-POLITECNICO DI MILANO a.a. 04-05 1 ABOUT USABILITY 1. WHAT IS USABILITY? Ë Usability
(Milano Lugano Evaluation Method) A systematic approach to usability evaluation Part I LAB HCI prof. Garzotto - HOC-POLITECNICO DI MILANO a.a. 04-05 1 ABOUT USABILITY 1. WHAT IS USABILITY? Ë Usability
Table of contents. TOOLKIT for Making Written Material Clear and Effective
 TOOLKIT for Making Written Material Clear and Effective Table of contents U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Table of contents Overview of the Toolkit The
TOOLKIT for Making Written Material Clear and Effective Table of contents U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Table of contents Overview of the Toolkit The
A Grid-Based Extension to an Assistive Multimodal Interface
 Pre-print: Strain, P., McAllister, G., Murphy, E., Kuber, R. & Yu, W. 2007: A Grid-Based Extension to an Assistive Multimodal Interface. In Extended Abstracts of on Human Factors in Computing Systems -
Pre-print: Strain, P., McAllister, G., Murphy, E., Kuber, R. & Yu, W. 2007: A Grid-Based Extension to an Assistive Multimodal Interface. In Extended Abstracts of on Human Factors in Computing Systems -
TOWARDS THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TEMPORAL-BASED SOFTWARE VERSION MANAGEMENT AT UNIVERSITI DARUL IMAN MALAYSIA
 TOWARDS THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TEMPORAL-BASED SOFTWARE VERSION MANAGEMENT AT UNIVERSITI DARUL IMAN MALAYSIA M Nordin A Rahman, Azrul Amri Jamal and W Dagang W Ali Faculty of Informatics Universiti Darul
TOWARDS THE IMPLEMENTATION OF TEMPORAL-BASED SOFTWARE VERSION MANAGEMENT AT UNIVERSITI DARUL IMAN MALAYSIA M Nordin A Rahman, Azrul Amri Jamal and W Dagang W Ali Faculty of Informatics Universiti Darul
Interaction Style Categories. COSC 3461 User Interfaces. What is a Command-line Interface? Command-line Interfaces
 COSC User Interfaces Module 2 Interaction Styles What is a Command-line Interface? An interface where the user types commands in direct response to a prompt Examples Operating systems MS-DOS Unix Applications
COSC User Interfaces Module 2 Interaction Styles What is a Command-line Interface? An interface where the user types commands in direct response to a prompt Examples Operating systems MS-DOS Unix Applications
A Top-Down Visual Approach to GUI development
 A Top-Down Visual Approach to GUI development ROSANNA CASSINO, GENNY TORTORA, MAURIZIO TUCCI, GIULIANA VITIELLO Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università di Salerno Via Ponte don Melillo 84084
A Top-Down Visual Approach to GUI development ROSANNA CASSINO, GENNY TORTORA, MAURIZIO TUCCI, GIULIANA VITIELLO Dipartimento di Matematica e Informatica Università di Salerno Via Ponte don Melillo 84084
Cognitive Analysis of Software Interfaces
 2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Cognitive Analysis of Software Interfaces B.Venkata Raju, Ph.D Scholar, Reg.No.2004199506
2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Cognitive Analysis of Software Interfaces B.Venkata Raju, Ph.D Scholar, Reg.No.2004199506
Visual Appeal vs. Usability: Which One Influences User Perceptions of a Website More?
 1 of 9 10/3/2009 9:42 PM October 2009, Vol. 11 Issue 2 Volume 11 Issue 2 Past Issues A-Z List Usability News is a free web newsletter that is produced by the Software Usability Research Laboratory (SURL)
1 of 9 10/3/2009 9:42 PM October 2009, Vol. 11 Issue 2 Volume 11 Issue 2 Past Issues A-Z List Usability News is a free web newsletter that is produced by the Software Usability Research Laboratory (SURL)
CSCE 315 Fall Team Project 3
 CSCE 315 Fall 2017 Team Project 3 Project Goal Your team is to build a system that puts together different existing web components in an application that provides a quality user interface to the joined
CSCE 315 Fall 2017 Team Project 3 Project Goal Your team is to build a system that puts together different existing web components in an application that provides a quality user interface to the joined
User s Guide. Attainment s. GTN v4.11
 Attainment s User s Guide A printable PDF of this user guide is available from the Attainment Company website: https://www.attainmentcompany.com/gotalk-now Contents 1 Getting Started with GoTalk NOW 1
Attainment s User s Guide A printable PDF of this user guide is available from the Attainment Company website: https://www.attainmentcompany.com/gotalk-now Contents 1 Getting Started with GoTalk NOW 1
PG Certificate Web Design and Development. Course Structure. Course Overview. Web Development and User Experience - ARMC243S7 Overview
 PG Certificate Web Design and Development Course Overview This course focuses on a user-based approach to designing websites and implementation through standards-based, accessible code. It is also suitable
PG Certificate Web Design and Development Course Overview This course focuses on a user-based approach to designing websites and implementation through standards-based, accessible code. It is also suitable
Information Systems Interfaces (Advanced Higher) Information Systems (Advanced Higher)
 National Unit Specification: general information NUMBER DV51 13 COURSE Information Systems (Advanced Higher) SUMMARY This Unit is designed to develop knowledge and understanding of the principles of information
National Unit Specification: general information NUMBER DV51 13 COURSE Information Systems (Advanced Higher) SUMMARY This Unit is designed to develop knowledge and understanding of the principles of information
Getting Started for Moderators Quick Reference Guide
 Practice before leading your first session. Become familiar with the session content. Open web pages, applications needed for application sharing and screen captures before session begins. Load multimedia
Practice before leading your first session. Become familiar with the session content. Open web pages, applications needed for application sharing and screen captures before session begins. Load multimedia
Interaction design. The process of interaction design. Requirements. Data gathering. Interpretation and data analysis. Conceptual design.
 Interaction design The process of interaction design Requirements Data gathering Interpretation and data analysis Conceptual design Prototyping Physical design Conceptual design Introduction It aims to
Interaction design The process of interaction design Requirements Data gathering Interpretation and data analysis Conceptual design Prototyping Physical design Conceptual design Introduction It aims to
A Multimodal Mobile Museum Guide for All
 A Multimodal Mobile Museum Guide for All Carmen Santoro, Fabio Paternò, Giulia Ricci, Barbara Leporini ISTI-CNR Via G. Moruzzi 1 Pisa, Italy {carmen.santoro, fabio.paterno, giulia.ricci, barbara.leporini}@isti.cnr.it
A Multimodal Mobile Museum Guide for All Carmen Santoro, Fabio Paternò, Giulia Ricci, Barbara Leporini ISTI-CNR Via G. Moruzzi 1 Pisa, Italy {carmen.santoro, fabio.paterno, giulia.ricci, barbara.leporini}@isti.cnr.it
Overview In this lab you will Explore some of the features of the new Windows 8 Interface.
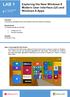 LAB 1 No Programming Experience Exploring the New Windows 8 Modern User Interface (UI) and Windows 8 Apps Overview In this lab you will Explore some of the features of the new Windows 8 Interface. Requirements
LAB 1 No Programming Experience Exploring the New Windows 8 Modern User Interface (UI) and Windows 8 Apps Overview In this lab you will Explore some of the features of the new Windows 8 Interface. Requirements
ScienceDirect. STA Data Model for Effective Business Process Modelling
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 11 ( 2013 ) 1218 1222 The 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI 2013) STA Data Model
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 11 ( 2013 ) 1218 1222 The 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI 2013) STA Data Model
INTRODUCTION USER POPULATION
 iscreen Usability Cognitive Walkthrough Report Christine Wania George Abraham INTRODUCTION Context and motivation The College of IST recently installed an interactive kiosk called iscreen, designed to
iscreen Usability Cognitive Walkthrough Report Christine Wania George Abraham INTRODUCTION Context and motivation The College of IST recently installed an interactive kiosk called iscreen, designed to
Website Redesign. Arkadiusz Kolodziej. Instructor D. Fluckiger Section 01 Fall 2015
 Website Redesign Interaction Design Instructor D. Fluckiger Section 01 Fall 2015 Introduction Introduction Requirements Design the interface for a university library website. Design the homepage, search
Website Redesign Interaction Design Instructor D. Fluckiger Section 01 Fall 2015 Introduction Introduction Requirements Design the interface for a university library website. Design the homepage, search
INTRODUCING THE UNIFIED E-BOOK FORMAT AND A HYBRID LIBRARY 2.0 APPLICATION MODEL BASED ON IT. 1. Introduction
 Преглед НЦД 14 (2009), 43 52 Teo Eterović, Nedim Šrndić INTRODUCING THE UNIFIED E-BOOK FORMAT AND A HYBRID LIBRARY 2.0 APPLICATION MODEL BASED ON IT Abstract: We introduce Unified e-book Format (UeBF)
Преглед НЦД 14 (2009), 43 52 Teo Eterović, Nedim Šrndić INTRODUCING THE UNIFIED E-BOOK FORMAT AND A HYBRID LIBRARY 2.0 APPLICATION MODEL BASED ON IT Abstract: We introduce Unified e-book Format (UeBF)
Chapter 6: Interfaces and interactions
 Chapter 6: Interfaces and interactions Overview Introduce the notion of a paradigm Provide an overview of the many different interface paradigms highlight the main design and research issues for each Consider
Chapter 6: Interfaces and interactions Overview Introduce the notion of a paradigm Provide an overview of the many different interface paradigms highlight the main design and research issues for each Consider
Interface Designs Model of Location-Aware Mobile Commerce for Songket
 Jurnal Teknologi Full paper Interface Designs Model of Location-Aware Mobile Commerce for Songket Mardhiah Ibrahim *, Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook, Norleyza Jailani Faculty of Information Science and
Jurnal Teknologi Full paper Interface Designs Model of Location-Aware Mobile Commerce for Songket Mardhiah Ibrahim *, Tengku Siti Meriam Tengku Wook, Norleyza Jailani Faculty of Information Science and
Chapter 15. User Interface Design. Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 15 Slide 1
 Chapter 15 User Interface Design Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 15 Slide 1 Topics covered User interface design principles User interaction Information presentation User
Chapter 15 User Interface Design Ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th edition. Chapter 15 Slide 1 Topics covered User interface design principles User interaction Information presentation User
User-Centered Analysis & Design
 User-Centered Analysis & Design Section Topic Slides Study Guide Quick References (QR) Introduction UCA vs. UT 1-26 12 Comparing Analysis and Testing Approaches ROI 1-29 7 Formulas for Calculating ROI
User-Centered Analysis & Design Section Topic Slides Study Guide Quick References (QR) Introduction UCA vs. UT 1-26 12 Comparing Analysis and Testing Approaches ROI 1-29 7 Formulas for Calculating ROI
A Content Based Image Retrieval System Based on Color Features
 A Content Based Image Retrieval System Based on Features Irena Valova, University of Rousse Angel Kanchev, Department of Computer Systems and Technologies, Rousse, Bulgaria, Irena@ecs.ru.acad.bg Boris
A Content Based Image Retrieval System Based on Features Irena Valova, University of Rousse Angel Kanchev, Department of Computer Systems and Technologies, Rousse, Bulgaria, Irena@ecs.ru.acad.bg Boris
Methods for Policy Conflict Detection and Resolution in Pervasive Computing Environments
 Methods for Policy Conflict Detection and Resolution in Pervasive Computing Environments Evi Syukur SCSSE, Monash University, Australia evis@csse.monash.edu.au Seng Wai Loke SCSSE, Monash University, Australia
Methods for Policy Conflict Detection and Resolution in Pervasive Computing Environments Evi Syukur SCSSE, Monash University, Australia evis@csse.monash.edu.au Seng Wai Loke SCSSE, Monash University, Australia
How to make CAD tools more useful to designers through re- representation
 How to make CAD tools more useful to designers through re- representation John S Gero and Nick Kelly Key Centre of Design Computing and Cognition, University of Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT: This paper describes
How to make CAD tools more useful to designers through re- representation John S Gero and Nick Kelly Key Centre of Design Computing and Cognition, University of Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT: This paper describes
6 Designing Interactive Systems
 6 Designing Interactive Systems 6.1 Design vs. Requirements 6.2 Paradigms, Styles and Principles of Interaction 6.3 How to Create a Conceptual Model 6.4 Activity-Based Design of Interactive Systems 6.5
6 Designing Interactive Systems 6.1 Design vs. Requirements 6.2 Paradigms, Styles and Principles of Interaction 6.3 How to Create a Conceptual Model 6.4 Activity-Based Design of Interactive Systems 6.5
15/16 CSY2041 Quality and User-Centred Systems
 15/16 CSY2041 Quality and User-Centred Systems INTERACTION DESIGN 1 Heuristic evaluation and walkthroughs 2 1 Aims: Describe the key concepts associated with inspection methods. Explain how to do heuristic
15/16 CSY2041 Quality and User-Centred Systems INTERACTION DESIGN 1 Heuristic evaluation and walkthroughs 2 1 Aims: Describe the key concepts associated with inspection methods. Explain how to do heuristic
Improving Touch Based Gesture Interfaces Ridhô Jeftha University of Cape Town Computer Science Student Rondebosch Cape Town 03 July 2012
 Improving Touch Based Gesture Interfaces Ridhô Jeftha University of Cape Town Computer Science Student Rondebosch Cape Town 03 July 2012 mail@ridhojeftha.com ABSTRACT The lack of affordance in gesture
Improving Touch Based Gesture Interfaces Ridhô Jeftha University of Cape Town Computer Science Student Rondebosch Cape Town 03 July 2012 mail@ridhojeftha.com ABSTRACT The lack of affordance in gesture
IOS SAFETY APPLICATION FOR UITM
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Special Issue on ICE & ICIE 2015, April (2016) 97-105 School of Engineering, Taylor s University IOS SAFETY APPLICATION FOR UITM MOHAMAD FAHMI HUSSIN*, W AHMAD
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Special Issue on ICE & ICIE 2015, April (2016) 97-105 School of Engineering, Taylor s University IOS SAFETY APPLICATION FOR UITM MOHAMAD FAHMI HUSSIN*, W AHMAD
LATIHAN Identify the use of multimedia in various fields.
 LATIHAN 4.1 1. Define multimedia. Multimedia is the presentation of information by using a combination of text, audio, graphic, video and animation. Multimedia has played an important role in other fields,
LATIHAN 4.1 1. Define multimedia. Multimedia is the presentation of information by using a combination of text, audio, graphic, video and animation. Multimedia has played an important role in other fields,
INTEGRATION AND TESTING OF THE WEB BASED SPATIAL DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM
 Annex: 28 INTEGRATION AND TESTING OF THE WEB BASED SPATIAL DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM Test plan report and procedures 1 SUMMARY 1 OVERALL DESCRIPTION... 3 2 TEST PLAN REPORT AND PROCEDURES... 4 2.1 INTRODUCTION...
Annex: 28 INTEGRATION AND TESTING OF THE WEB BASED SPATIAL DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM Test plan report and procedures 1 SUMMARY 1 OVERALL DESCRIPTION... 3 2 TEST PLAN REPORT AND PROCEDURES... 4 2.1 INTRODUCTION...
DISABILITY LAW SERVICE BEST PRACTICES FOR AN ACCESSIBLE AND USABLE WEBSITE
 DISABILITY LAW SERVICE BEST PRACTICES FOR AN ACCESSIBLE AND USABLE WEBSITE February 2018 1 FOREWORD This guide aims to provide organisations with essential information for compliance with modern website
DISABILITY LAW SERVICE BEST PRACTICES FOR AN ACCESSIBLE AND USABLE WEBSITE February 2018 1 FOREWORD This guide aims to provide organisations with essential information for compliance with modern website
Section 6 HCI & the Web 02/01/2013 1
 Section 6 HCI & the Web 02/01/2013 1 Web Site Planning Main questions to address when planning a web site: What do I want the site to accomplish, sell, or promote? Who are my users and what do they want
Section 6 HCI & the Web 02/01/2013 1 Web Site Planning Main questions to address when planning a web site: What do I want the site to accomplish, sell, or promote? Who are my users and what do they want
evision Review Project - Engagement Simon McLean, Head of Web & IT Support Information & Data Services.
 evision Review Project - Engagement Monitoring Simon McLean, Head of Web & IT Support Information & Data Services. What is Usability? Why Bother? Types of usability testing Usability Testing in evision
evision Review Project - Engagement Monitoring Simon McLean, Head of Web & IT Support Information & Data Services. What is Usability? Why Bother? Types of usability testing Usability Testing in evision
Fingertips Tracking based on Gradient Vector
 Int. J. Advance Soft Compu. Appl, Vol. 7, No. 3, November 2015 ISSN 2074-8523 Fingertips Tracking based on Gradient Vector Ahmad Yahya Dawod 1, Md Jan Nordin 1, and Junaidi Abdullah 2 1 Pattern Recognition
Int. J. Advance Soft Compu. Appl, Vol. 7, No. 3, November 2015 ISSN 2074-8523 Fingertips Tracking based on Gradient Vector Ahmad Yahya Dawod 1, Md Jan Nordin 1, and Junaidi Abdullah 2 1 Pattern Recognition
Human-Computer Interaction: An Overview. CS2190 Spring 2010
 Human-Computer Interaction: An Overview CS2190 Spring 2010 There must be a problem because What is HCI? Human-Computer interface Where people meet or come together with machines or computer-based systems
Human-Computer Interaction: An Overview CS2190 Spring 2010 There must be a problem because What is HCI? Human-Computer interface Where people meet or come together with machines or computer-based systems
cs465 principles of user interface design, implementation and evaluation
 cs465 principles of user interface design, implementation and evaluation Karrie G. Karahalios 24. September 2008 1. Heuristic Evaluation 2. Cognitive Walkthrough 3. Discuss Homework 3 4. Discuss Projects
cs465 principles of user interface design, implementation and evaluation Karrie G. Karahalios 24. September 2008 1. Heuristic Evaluation 2. Cognitive Walkthrough 3. Discuss Homework 3 4. Discuss Projects
Application development process. Interaction Design Principles
 Application development process Interaction Design Principles Overview Good/Bad UI Design Interaction Design Principles Screen layouts Navigation Patterns Screen Flows Prototyping Preview of UI Analysis/Design
Application development process Interaction Design Principles Overview Good/Bad UI Design Interaction Design Principles Screen layouts Navigation Patterns Screen Flows Prototyping Preview of UI Analysis/Design
Instructions for Download and Installation of CTAS Version 8.2 Full Install
 Instructions for Download and Installation of CTAS Version 8.2 Full Install Office of the State Auditor Website: http://www.osa.state.mn.us/ NOTE: Some pictures and screenshots in these instructions refer
Instructions for Download and Installation of CTAS Version 8.2 Full Install Office of the State Auditor Website: http://www.osa.state.mn.us/ NOTE: Some pictures and screenshots in these instructions refer
User interface design
 User interface design Objectives To suggest some general design principles for user interface design To explain different interaction styles and their use To explain when to use graphical and textual information
User interface design Objectives To suggest some general design principles for user interface design To explain different interaction styles and their use To explain when to use graphical and textual information
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT. BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT. March 2017 PRINCIPLES OF USER INTERFACE DESIGN
 BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT March 2017 PRINCIPLES OF USER INTERFACE DESIGN EXAMINERS REPORT General Comments Candidates should focus
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 5 Diploma in IT March 2017 PRINCIPLES OF USER INTERFACE DESIGN EXAMINERS REPORT General Comments Candidates should focus
Why User Interface Design? What
 Why User Interface Design? What Prof. Giuseppe Riccardi Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Scienza dell Informazione University of Trento riccardi@dit.unitn.it Spring 2013 1 UI guidelines in Android Spring 2013
Why User Interface Design? What Prof. Giuseppe Riccardi Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Scienza dell Informazione University of Trento riccardi@dit.unitn.it Spring 2013 1 UI guidelines in Android Spring 2013
Designing Software Usability Measurement Using Fuzzy Set Conjoint Model
 2011 International Conference on Computer Communication and Management Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Designing Software Usability Measurement Using Fuzzy Set Conjoint Model Yuhanim
2011 International Conference on Computer Communication and Management Proc.of CSIT vol.5 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Designing Software Usability Measurement Using Fuzzy Set Conjoint Model Yuhanim
CS 4317: Human-Computer Interaction
 September 8, 2017 Tentative Syllabus CS 4317: Human-Computer Interaction Spring 2017 Tuesday & Thursday, 9:00-10:20, Psychology Building, room 308 Instructor: Nigel Ward Office: CCS 3.0408 Phone: 747-6827
September 8, 2017 Tentative Syllabus CS 4317: Human-Computer Interaction Spring 2017 Tuesday & Thursday, 9:00-10:20, Psychology Building, room 308 Instructor: Nigel Ward Office: CCS 3.0408 Phone: 747-6827
1. Norman Stages of Action (28 points)
 Questions 1. Norman Stages of Action (28 points) Part A (14 points) What are the seven stages of action? Provide examples of the seven stages of action. The seven stages of action are forming a goal, forming
Questions 1. Norman Stages of Action (28 points) Part A (14 points) What are the seven stages of action? Provide examples of the seven stages of action. The seven stages of action are forming a goal, forming
3 Evaluating Interactive Systems
 3 Evaluating Interactive Systems Viktoria Pammer-Schindler March 23, 2015 Evaluate 1 Android Sensing Tutorial Day on April 23 Save the Date!!! Evaluate 2 Days and Topics March 11 March 16 Intro Designing
3 Evaluating Interactive Systems Viktoria Pammer-Schindler March 23, 2015 Evaluate 1 Android Sensing Tutorial Day on April 23 Save the Date!!! Evaluate 2 Days and Topics March 11 March 16 Intro Designing
User-Centred Evaluation Criteria for a Mixed Reality Authoring Application
 User-Centred Evaluation Criteria for a Mixed Reality Authoring Application Marjaana Träskbäck, Toni Koskinen, Marko Nieminen Helsinki University of Technology, Software Business and Engineering Institute
User-Centred Evaluation Criteria for a Mixed Reality Authoring Application Marjaana Träskbäck, Toni Koskinen, Marko Nieminen Helsinki University of Technology, Software Business and Engineering Institute
MAT-225 Informational Brief & Questionnaire
 MAT 225 MAT-225 Informational Brief & Questionnaire Instructor: Leigh Cotnoir Media Arts & Technologies MiraCosta College T 760-757-2121 x6451 lcotnoir@miracosta.edu learn.leighcotnoir.com Table of Contents
MAT 225 MAT-225 Informational Brief & Questionnaire Instructor: Leigh Cotnoir Media Arts & Technologies MiraCosta College T 760-757-2121 x6451 lcotnoir@miracosta.edu learn.leighcotnoir.com Table of Contents
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CSE COURSE PLAN Course Code : CS0430 Course Title : HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION Semester : VIII
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CSE COURSE PLAN Course Code : CS0430 Course Title : HUMAN COMPUTER INTERACTION Semester : VIII
New Media Production week 3
 New Media Production week 3 Multimedia ponpong@gmail.com What is Multimedia? Multimedia = Multi + Media Multi = Many, Multiple Media = Distribution tool & information presentation text, graphic, voice,
New Media Production week 3 Multimedia ponpong@gmail.com What is Multimedia? Multimedia = Multi + Media Multi = Many, Multiple Media = Distribution tool & information presentation text, graphic, voice,
Integrating User Evaluation into Software Development Environments
 Integrating User Evaluation into Software Development Environments Yael Dubinsky, Tiziana Catarci, Shah Rukh Humayoun, and Stephen Kimani Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica Università di Roma "La
Integrating User Evaluation into Software Development Environments Yael Dubinsky, Tiziana Catarci, Shah Rukh Humayoun, and Stephen Kimani Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica Università di Roma "La
