Web Scraping. HTTP and Requests
|
|
|
- Dominic Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Web Scraping Lab Objective: Web Scraping is the process of gathering data from websites on the internet. Since almost everything rendered by an internet browser as a web page uses HTML, the rst step in web scraping is being able to extract information from HTML. In this lab, we introduce the requests library for scraping web pages, and BeautifulSoup, Python's canonical tool for eciently and cleanly navigating and parsing HTML. HTTP and Requests HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which is an application layer networking protocol. It is a higher level protocol than TCP, which we used to build a server in the Web Technologies lab, but uses TCP protocols to manage connections and provide network capabilities. The HTTP protocol is centered around a request and response paradigm, in which a client makes a request to a server and the server replies with a response. There are several methods, or requests, dened for HTTP servers, the three most common of which are GET, POST, and PUT. GET requests request information from the server, POST requests modify the state of the server, and PUT requests add new pieces of data to the server. The standard way to get the source code of a website using Python is via the requests library. 1 Calling requests.get() sends an HTTP GET request to a specied website. The website returns a response code, which indicates whether or not the request was received, understood, and accepted. If the response code is good, typically 200, then the response will also include the website source code as an HTML le. >>> import requests # Make a request and check the result. A status code of 200 is good. >>> response = requests.get(" >>> print(response.status_code, response.ok, response.reason) 200 True OK 1 Though requests is not part of the standard library, it is recognized as a standard tool in the data science community. See 1
2 2 Lab 1. Web Scraping # The HTML of the website is stored in the 'text' attribute. >>> print(response.text) <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" dir="ltr" prefix="content: content/ dc: foaf: og: rdfs: schema: sioc: sioct: /sioc/types# skos: xsd: w3.org/2001/xmlschema# " class=" "> <head> #... <meta charset="utf-8" /> Note that some websites aren't built to handle large amounts of trac or many repeated requests. Most are built to identify web scrapers or crawlers that initiate many consecutive GET requests without pauses, and retaliate or block them. When web scraping, always make sure to store the data that you receive in a le and include error checks to prevent retrieving the same data unnecessarily. This is especially important in larger applications. Problem 1. Use the requests library to get the HTML source for the website example.com. Save the source as a le called example.html. If the le already exists, make sure not to scrape the website, or overwrite the le. You will use this le later in the lab. Achtung! Scraping copyrighted information without the consent of the copyright owner can have severe legal consequences. Many websites, in their terms and conditions, prohibit scraping parts or all of the site. Websites that do allow scraping usually have a le called robots.txt (for example, that species which parts of the website are o-limits and how often requests can be made according to the robots exclusion standard. a Be careful and considerate when doing any sort of scraping, and take care when writing and testing code to avoid unintended behavior. It is up to the programmer to create a scraper that respects the rules found in the terms and conditions and in robots.txt. b a See and en.wikipedia.org/wiki/robots_exclusion_standard. b Python provides a parsing library called urllib.robotparser for reading robot.txt les. For more information, see HTML Hyper Text Markup Language, or HTML, is the standard markup language a language designed for the processing, denition, and presentation of textfor creating webpages. It structures a document using pairs of tags that surround and dene content. Opening tags have a tag name surrounded by angle brackets (<tag-name>). The companion closing tag looks the same, but with a forward
3 3 slash before the tag name (</tag-name>). A list of all current HTML tags can be found at http: //htmldog.com/reference/htmltags. Most tags can be combined with attributes to include more data about the content, help identify individual tags, and make navigating the document much simpler. In the following example, the <a> tag has id and href attributes. <html> <!-- Opening tags --> <body> <p> </body> </html> Click <a id='info' href=' for more information. </p> <!-- Closing tags --> In HTML, href stands for hypertext reference, a link to another website. Thus the above example would be rendered by a browser as a single line of text, with here being a clickable link to Click here for more information. Unlike Python, HTML does not enforce indentation (or any whitespace rules), though indentation generally makes HTML more readable. The previous example can be written in a single line. <html><body><p>click <a id='info' href=' for more information.</p></body></html> Special tags, which don't contain any text or other tags, are written without a closing tag and in a single pair of brackets. A forward slash is included between the name and the closing bracket. Examples of these include <hr/>, which describes a horizontal line, and <img/>, the tag for representing an image. Problem 2. Using the output from Problem 1, examine the HTML source code for http: // What tags are used? What is the value of the type attribute associated with the style tag? Write a function that returns the set of names of tags used in the website, and the value of the type attribute of the style tag (as a string). (Hint: there are ten unique tag names.) BeautifulSoup BeautifulSoup (bs4) is a package 2 that makes it simple to navigate and extract data from HTML documents. See for the full documentation. 2 BeautifulSoup is not part of the standard library; install it with conda install beautifulsoup4 or with pip install beautifulsoup4.
4 4 Lab 1. Web Scraping The bs4.beautifulsoup class accepts two parameters to its constructor: a string of HTML code and an HTML parser to use under the hood. The HTML parser is technically a keyword argument, but the constructor prints a warning if one is not specied. The standard choice for the parser is "html.parser", which means the object uses the standard library's html.parser module as the engine behind the scenes. Note Depending on project demands, a parser other than "html.parser" may be useful. A couple of other options are "lxml", an extremely fast parser written in C, and "html5lib", a slower parser that treats HTML in much the same way a web browser does, allowing for irregularities. Both must be installed independently; see bs4/doc/#installing-a-parser for more information. A BeautifulSoup object represents an HTML document as a tree. In the tree, each tag is a node with nested tags and strings as its children. The prettify() method returns a string that can be printed to represent the BeautifulSoup object in a readable format that reects the tree structure. >>> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup >>> small_example_html = """ <html><body><p> Click <a id='info' href=' for more information. </p></body></html> """ >>> small_soup = BeautifulSoup(small_example_html, 'html.parser') >>> print(small_soup.prettify()) <html> <body> <p> Click <a href=" id="info"> here </a> for more information. </p> </body> </html> Each tag in a BeautifulSoup object's HTML code is stored as a bs4.element.tag object, with actual text stored as a bs4.element.navigablestring object. Tags are accessible directly through the BeautifulSoup object. # Get the <p> tag (and everything inside of it). >>> small_soup.p
5 5 <p> Click <a href=" id="info">here</a> for more information. </p> # Get the <a> sub-tag of the <p> tag. >>> a_tag = small_soup.p.a >>> print(a_tag, type(a_tag), sep='\n') <a href=" id="info">here</a> <class 'bs4.element.tag'> # Get just the name, attributes, and text of the <a> tag. >>> print(a_tag.name, a_tag.attrs, a_tag.string, sep="\n") a {'id': 'info', 'href': ' here Attribute name attrs string strings stripped_strings text Description The name of the tag A dictionary of the attributes The single string contained in the tag Generator for strings of children tags Generator for strings of children tags, stripping whitespace Concatenation of strings from all children tags Table 1.1: Data attributes of the bs4.element.tag class. Problem 3. The BeautifulSoup class has a find_all() method that, when called with True as the only argument, returns a list of all tags in the HTML source code. Write a function that accepts a string of HTML code as an argument. Use BeautifulSoup to return a list of the names of the tags in the code. Use your function and the source code from (use the output from Problem 1) to check your answers from Problem 2. Navigating the Tree Structure Not all tags are easily accessible from a BeautifulSoup object. Consider the following example. >>> pig_html = """ <html><head><title>three Little Pigs</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>the Three Little Pigs</b></p> <p class="story">once upon a time, there were three little pigs named <a href=" class="pig" id="link1">larry,</a> <a href=" class="pig" id="link2">mo</a>, and <a href=" class="pig" id="link3">curly.</a>
6 6 Lab 1. Web Scraping <p>the three pigs had an odd fascination with experimental construction.</p> <p>...</p> </body></html> """ >>> pig_soup = BeautifulSoup(pig_html, "html.parser") >>> pig_soup.p <p class="title"><b>the Three Little Pigs</b></p> >>> pig_soup.a <a class="pig" href=" id="link1">larry,</a> Since the HTML in this example has several <p> and <a> tags, only the rst tag of each name is accessible directly from pig_soup. The other tags can be accessed by manually navigating through the HTML tree. Every HTML tag (except for the topmost tag, which is usually <html>) has a parent tag. Each tag also has zero or more sibling and children tags or text. Following a true tree structure, every bs4.element.tag in a soup has multiple attributes for accessing or iterating through parent, sibling, or child tags. Attribute parent parents next_sibling next_siblings previous_sibling previous_siblings contents children descendants Description The parent tag Generator for the parent tags up to the top level The tag immediately after to the current tag Generator for sibling tags after the current tag The tag immediately before the current tag Generator for sibling tags before the current tag A list of the immediate children tags Generator for immediate children tags Generator for all children tags (recursively) Table 1.2: Navigation attributes of the bs4.element.tag class. # Start at the first <a> tag in the soup. >>> a_tag = pig_soup.a >>> a_tag <a class="pig" href=" id="link1">larry,</a> # Get the names of all of <a>'s parent tags, traveling up to the top. # The name '[document]' means it is the top of the HTML code. >>> [par.name for par in a_tag.parents] # <a>'s parent is <p>, whose ['p', 'body', 'html', '[document]'] # parent is <body>, and so on. # Get the next siblings of <a>. >>> a_tag.next_sibling '\n' # The first sibling is just text. >>> a_tag.next_sibling.next_sibling # The second sibling is a tag. <a class="pig" href=" id="link2">mo</a>
7 7 %# Alternatively, get all siblings past <a> at once. %>>> list(a_tag.next_siblings) %['\n', % <a class="pig" href=" id="link2">mo</a>, % ', and\n', % <a class="pig" href=" id="link3">curly.</a>, % '\n', % <p>the three pigs had an odd fascination with experimental construction.</p>, % '\n', % <p>...</p>, % '\n'] Note carefully that newline characters are considered to be children of a parent tag. Therefore iterating through children or siblings often requires checking which entries are tags and which are just text. # Get to the <p> tag that has class="story". >>> p_tag = pig_soup.body.p.next_sibling.next_sibling >>> p_tag.attrs["class"] # Make sure it's the right tag. ['story'] # Iterate through the child tags of <p> and print hrefs whenever they exist. >>> for child in p_tag.children:... if hasattr(child, "attrs") and "href" in child.attrs:... print(child.attrs["href"]) Note that the "class" attribute of the <p> tag is a list. This is because the "class" attribute can take on several values at once; for example, the tag <p class="story book"> is of class 'story' and of class 'book'. The behavior of the string attribute of a bs4.element.tag object depends on the structure of the corresponding HTML tag. 1. If the tag has a string of text and no other child elements, then string is just that text. 2. If the tag has exactly one child tag and the child tag has only a string of text, then the tag has the same string as its child tag. 3. If the tag has more than one child, then string is None. In this case, use strings to iterate through the child strings. Alternatively, the get_text() method returns all text belonging to a tag and to all of its descendants. In other words, it returns anything inside a tag that isn't another tag. >>> pig_soup.head <head><title>three Little Pigs</title></head>
8 8 Lab 1. Web Scraping # Case 1: the <title> tag's only child is a string. >>> pig_soup.head.title.string 'Three Little Pigs' # Case 2: The <head> tag's only child is the <title> tag. >>> pig_soup.head.string 'Three Little Pigs' # Case 3: the <body> tag has several children. >>> pig_soup.body.string is None True >>> print(pig_soup.body.get_text().strip()) The Three Little Pigs Once upon a time, there were three little pigs named Larry, Mo, and Curly. The three pigs had an odd fascination with experimental construction.... Problem 4. Using the output from Problem 1, write a function that reads the le and loads the code into BeautifulSoup. Find the only <a> tag with a hyperlink, and return its text. Searching for Tags Navigating the HTML tree manually can be helpful for gathering data out of lists or tables, but these kinds of structures are usually buried deep in the tree. The find() and find_all() methods of the BeautifulSoup class identify tags that have distinctive characteristics, making it much easier to jump straight to a desired location in the HTML code. The find() method only returns the rst tag that matches a given criteria, while find_all() returns a list of all matching tags. Tags can be matched by name, attributes, and/or text. # Find the first <b> tag in the soup. >>> pig_soup.find(name='b') <b>the Three Little Pigs</b> # Find all tags with a class attribute of 'pig'. # Since 'class' is a Python keyword, use 'class_' as the argument. >>> pig_soup.find_all(class_="pig") [<a class="pig" href=" id="link1">larry,</a>, <a class="pig" href=" id="link2">mo</a>, <a class="pig" href=" id="link3">curly.</a>] # Find the first tag that matches several attributes. >>> pig_soup.find(attrs={"class": "pig", "href": " <a class="pig" href=" id="link2">mo</a>
9 9 # Find the first tag whose text is 'Mo'. >>> pig_soup.find(string='mo') 'Mo' # The result is the actual string, >>> pig_soup.find(string='mo').parent # so go up one level to get the tag. <a class="pig" href=" id="link2">mo</a> Problem 5. The le san_diego_weather.html contains the HTML source for an old page from Weather Underground. a Write a function that reads the le and loads it into Beautiful- Soup. Return a list of the following tags: 1. The tag containing the date Thursday, January 1, The tags which contain the links Previous Day and Next Day. 3. The tag which contains the number associated with the Actual Max Temperature. This HTML tree is signicantly larger than the previous examples. To get started, consider opening the le in a web browser. Find the element that you are searching for on the page, right click it, and select Inspect. This opens the HTML source at the element that the mouse clicked on. a See Diego&req_state=CA&req_statename=California&reqdb.zip=92101&reqdb.magic=1&reqdb.wmo=99999&MR=1 Advanced Search Techniques Consider the problem of nding the tag that is a link to the URL >>> pig_soup.find(href=" <a class="pig" href=" id="link3">curly.</a> This approach works, but it requires entering in the entire URL. To perform generalized searches, the find() and find_all() method also accept compiled regular expressions from the re module. This way, the methods locate tags whose name, attributes, and/or string matches a pattern. >>> import re # Find the first tag with an href attribute containing 'curly'. >>> pig_soup.find(href=re.compile(r"curly")) <a class="pig" href=" id="link3">curly.</a # Find the first tag with a string that starts with 'Cu'. >>> pig_soup.find(string=re.compile(r"^cu")).parent <a class="pig" href=" id="link3">curly.</a> # Find all tags with text containing 'Three'.
10 10 Lab 1. Web Scraping >>> [tag.parent for tag in pig_soup.find_all(string=re.compile(r"three"))] [<title>three Little Pigs</title>, <b>the Three Little Pigs</b>] Finally, to nd a tag that has a particular attribute, regardless of the actual value of the attribute, use True in place of search values. # Find all tags with an 'id' attribute. >>> pig_soup.find_all(id=true) [<a class="pig" href=" id="link1">larry,</a>, <a class="pig" href=" id="link2">mo</a>, <a class="pig" href=" id="link3">curly.</a>] # Final the names all tags WITHOUT an 'id' attribute. >>> [tag.name for tag in pig_soup.find_all(id=false)] ['html', 'head', 'title', 'body', 'p', 'b', 'p', 'p', 'p'] Problem 6. The le large_banks_index.html is an index of data about large banks, as recorded by the Federal Reserve. a Write a function that reads the le and loads the source into BeautifulSoup. Return a list of the tags containing the links to bank data from September 30, 2003 to December 31, 2014, where the dates are in reverse chronological order. a See Problem 7. The le large_banks_data.html is one of the pages from the index in Problem 6. a Write a function that reads the le and loads the source into BeautifulSoup. Create a single gure with two subplots: 1. A sorted bar chart of the seven banks with the most domestic branches. 2. A sorted bar chart of the seven banks with the most foreign branches. In the case of a tie, sort the banks alphabetically by name. a See
Scraping I: Introduction to BeautifulSoup
 5 Web Scraping I: Introduction to BeautifulSoup Lab Objective: Web Scraping is the process of gathering data from websites on the internet. Since almost everything rendered by an internet browser as a
5 Web Scraping I: Introduction to BeautifulSoup Lab Objective: Web Scraping is the process of gathering data from websites on the internet. Since almost everything rendered by an internet browser as a
BeautifulSoup. Lab 16 HTML. Lab Objective: Learn how to load HTML documents into BeautifulSoup and navigate the resulting BeautifulSoup object
 Lab 16 BeautifulSoup Lab Objective: Learn how to load HTML documents into BeautifulSoup and navigate the resulting BeautifulSoup object HTML HTML, or Hyper Text Markup Language is the standard markup language
Lab 16 BeautifulSoup Lab Objective: Learn how to load HTML documents into BeautifulSoup and navigate the resulting BeautifulSoup object HTML HTML, or Hyper Text Markup Language is the standard markup language
CIS192 Python Programming
 CIS192 Python Programming HTTP Requests and HTML Parsing Robert Rand University of Pennsylvania March 30, 2016 Robert Rand (University of Pennsylvania) CIS 192 March 30, 2016 1 / 19 Outline 1 HTTP Requests
CIS192 Python Programming HTTP Requests and HTML Parsing Robert Rand University of Pennsylvania March 30, 2016 Robert Rand (University of Pennsylvania) CIS 192 March 30, 2016 1 / 19 Outline 1 HTTP Requests
CIS192 Python Programming
 CIS192 Python Programming HTTP Requests and HTML Parsing Raymond Yin University of Pennsylvania October 12, 2016 Raymond Yin (University of Pennsylvania) CIS 192 October 12, 2016 1 / 22 Outline 1 HTTP
CIS192 Python Programming HTTP Requests and HTML Parsing Raymond Yin University of Pennsylvania October 12, 2016 Raymond Yin (University of Pennsylvania) CIS 192 October 12, 2016 1 / 22 Outline 1 HTTP
CIS192 Python Programming
 CIS192 Python Programming HTTP & HTML & JSON Harry Smith University of Pennsylvania November 1, 2017 Harry Smith (University of Pennsylvania) CIS 192 Lecture 10 November 1, 2017 1 / 22 Outline 1 HTTP Requests
CIS192 Python Programming HTTP & HTML & JSON Harry Smith University of Pennsylvania November 1, 2017 Harry Smith (University of Pennsylvania) CIS 192 Lecture 10 November 1, 2017 1 / 22 Outline 1 HTTP Requests
12. Web Spidering. These notes are based, in part, on notes by Dr. Raymond J. Mooney at the University of Texas at Austin.
 12. Web Spidering These notes are based, in part, on notes by Dr. Raymond J. Mooney at the University of Texas at Austin. 1 Web Search Web Spider Document corpus Query String IR System 1. Page1 2. Page2
12. Web Spidering These notes are based, in part, on notes by Dr. Raymond J. Mooney at the University of Texas at Austin. 1 Web Search Web Spider Document corpus Query String IR System 1. Page1 2. Page2
CIS 192: Lecture 8 HTML Parsing
 CIS 192: Lecture 8 HTML Parsing Lili Dworkin University of Pennsylvania HTTP Requests Use the requests library to make HTTP requests: >>> import requests >>> url = "http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis192/ spring2014/"
CIS 192: Lecture 8 HTML Parsing Lili Dworkin University of Pennsylvania HTTP Requests Use the requests library to make HTTP requests: >>> import requests >>> url = "http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~cis192/ spring2014/"
Web Scraping with Python
 Web Scraping with Python Carlos Hurtado Department of Economics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign hrtdmrt2@illinois.edu Dec 5th, 2017 C. Hurtado (UIUC - Economics) Numerical Methods On the Agenda
Web Scraping with Python Carlos Hurtado Department of Economics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign hrtdmrt2@illinois.edu Dec 5th, 2017 C. Hurtado (UIUC - Economics) Numerical Methods On the Agenda
HTML Processing in Python. 3. Construction of the HTML parse tree for further use and traversal.
 .. DATA 301 Introduction to Data Science Alexander Dekhtyar.. HTML Processing in Python Overview HTML processing in Python consists of three steps: 1. Download of the HTML file from the World Wide Web.
.. DATA 301 Introduction to Data Science Alexander Dekhtyar.. HTML Processing in Python Overview HTML processing in Python consists of three steps: 1. Download of the HTML file from the World Wide Web.
linkgrabber Documentation
 linkgrabber Documentation Release 0.2.6 Eric Bower Jun 08, 2017 Contents 1 Install 3 2 Tutorial 5 2.1 Quickie.................................................. 5 2.2 Documentation..............................................
linkgrabber Documentation Release 0.2.6 Eric Bower Jun 08, 2017 Contents 1 Install 3 2 Tutorial 5 2.1 Quickie.................................................. 5 2.2 Documentation..............................................
HTML. Mohammed Alhessi M.Sc. Geomatics Engineering. Internet GIS Technologies كلية اآلداب - قسم الجغرافيا نظم المعلومات الجغرافية
 HTML Mohammed Alhessi M.Sc. Geomatics Engineering Wednesday, February 18, 2015 Eng. Mohammed Alhessi 1 W3Schools Main Reference: http://www.w3schools.com/ 2 What is HTML? HTML is a markup language for
HTML Mohammed Alhessi M.Sc. Geomatics Engineering Wednesday, February 18, 2015 Eng. Mohammed Alhessi 1 W3Schools Main Reference: http://www.w3schools.com/ 2 What is HTML? HTML is a markup language for
Introduction to programming using Python
 Introduction to programming using Python Matthieu Choplin matthieu.choplin@city.ac.uk http://moodle.city.ac.uk/ Session 9 1 Objectives Quick review of what HTML is The find() string method Regular expressions
Introduction to programming using Python Matthieu Choplin matthieu.choplin@city.ac.uk http://moodle.city.ac.uk/ Session 9 1 Objectives Quick review of what HTML is The find() string method Regular expressions
Skills you will learn: How to make requests to multiple URLs using For loops and by altering the URL
 Chapter 9 Your First Multi-Page Scrape Skills you will learn: How to make requests to multiple URLs using For loops and by altering the URL In this tutorial, we will pick up from the detailed example from
Chapter 9 Your First Multi-Page Scrape Skills you will learn: How to make requests to multiple URLs using For loops and by altering the URL In this tutorial, we will pick up from the detailed example from
An Introduction to Web Scraping with Python and DataCamp
 An Introduction to Web Scraping with Python and DataCamp Olga Scrivner, Research Scientist, CNS, CEWIT WIM, February 23, 2018 0 Objectives Materials: DataCamp.com Review: Importing files Accessing Web
An Introduction to Web Scraping with Python and DataCamp Olga Scrivner, Research Scientist, CNS, CEWIT WIM, February 23, 2018 0 Objectives Materials: DataCamp.com Review: Importing files Accessing Web
HTML. Based mostly on
 HTML Based mostly on www.w3schools.com What is HTML? The standard markup language for creating Web pages HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML describes the structure of Web pages using markup
HTML Based mostly on www.w3schools.com What is HTML? The standard markup language for creating Web pages HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML describes the structure of Web pages using markup
CS109 Data Science Data Munging
 CS109 Data Science Data Munging Hanspeter Pfister & Joe Blitzstein pfister@seas.harvard.edu / blitzstein@stat.harvard.edu http://dilbert.com/strips/comic/2008-05-07/ Enrollment Numbers 377 including all
CS109 Data Science Data Munging Hanspeter Pfister & Joe Blitzstein pfister@seas.harvard.edu / blitzstein@stat.harvard.edu http://dilbert.com/strips/comic/2008-05-07/ Enrollment Numbers 377 including all
Regular Expressions. Regular Expression Syntax in Python. Achtung!
 1 Regular Expressions Lab Objective: Cleaning and formatting data are fundamental problems in data science. Regular expressions are an important tool for working with text carefully and eciently, and are
1 Regular Expressions Lab Objective: Cleaning and formatting data are fundamental problems in data science. Regular expressions are an important tool for working with text carefully and eciently, and are
Data Acquisition and Processing
 Data Acquisition and Processing Adisak Sukul, Ph.D., Lecturer,, adisak@iastate.edu http://web.cs.iastate.edu/~adisak/bigdata/ Topics http://web.cs.iastate.edu/~adisak/bigdata/ Data Acquisition Data Processing
Data Acquisition and Processing Adisak Sukul, Ph.D., Lecturer,, adisak@iastate.edu http://web.cs.iastate.edu/~adisak/bigdata/ Topics http://web.cs.iastate.edu/~adisak/bigdata/ Data Acquisition Data Processing
Revision for Grade 7 ASP in Unit :1&2 Design & Technology Subject
 Your Name:.... Grade 7 - SECTION 1 Matching :Match the terms with its explanations. Write the matching letter in the correct box. The first one has been done for you. (1 mark each) Term Explanation 1.
Your Name:.... Grade 7 - SECTION 1 Matching :Match the terms with its explanations. Write the matching letter in the correct box. The first one has been done for you. (1 mark each) Term Explanation 1.
Introduction to HTML & CSS. Instructor: Beck Johnson Week 2
 Introduction to HTML & CSS Instructor: Beck Johnson Week 2 today Week One review and questions File organization CSS Box Model: margin and padding Background images and gradients with CSS Make a hero banner!
Introduction to HTML & CSS Instructor: Beck Johnson Week 2 today Week One review and questions File organization CSS Box Model: margin and padding Background images and gradients with CSS Make a hero banner!
DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON
 DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON Common Use Python Module II Peter Lo Pandas Data Structures and Data Analysis tools 2 What is Pandas? Pandas is an open-source Python library providing highperformance,
DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON Common Use Python Module II Peter Lo Pandas Data Structures and Data Analysis tools 2 What is Pandas? Pandas is an open-source Python library providing highperformance,
Introduction to Web Scraping with Python
 Introduction to Web Scraping with Python NaLette Brodnax The Institute for Quantitative Social Science Harvard University January 26, 2018 workshop structure 1 2 3 4 intro get the review scrape tools Python
Introduction to Web Scraping with Python NaLette Brodnax The Institute for Quantitative Social Science Harvard University January 26, 2018 workshop structure 1 2 3 4 intro get the review scrape tools Python
Web Scrapping. (Lectures on High-performance Computing for Economists X)
 Web Scrapping (Lectures on High-performance Computing for Economists X) Jesús Fernández-Villaverde, 1 Pablo Guerrón, 2 and David Zarruk Valencia 3 December 20, 2018 1 University of Pennsylvania 2 Boston
Web Scrapping (Lectures on High-performance Computing for Economists X) Jesús Fernández-Villaverde, 1 Pablo Guerrón, 2 and David Zarruk Valencia 3 December 20, 2018 1 University of Pennsylvania 2 Boston
LABORATORY 117. Intorduction to VoiceXML
 LABORATORY 117 Intorduction to VoiceXML 1 TAC2000/2000 Outline XML VoiceXML Building your VoiceXML application on TellMe Studio 2 TAC2000/2000 XML Extensible Markup Language The de facto standard for defining
LABORATORY 117 Intorduction to VoiceXML 1 TAC2000/2000 Outline XML VoiceXML Building your VoiceXML application on TellMe Studio 2 TAC2000/2000 XML Extensible Markup Language The de facto standard for defining
IMPORTING DATA IN PYTHON. Importing flat files from the web
 IMPORTING DATA IN PYTHON Importing flat files from the web You re already great at importing! Flat files such as.txt and.csv Pickled files, Excel spreadsheets, and many others! Data from relational databases
IMPORTING DATA IN PYTHON Importing flat files from the web You re already great at importing! Flat files such as.txt and.csv Pickled files, Excel spreadsheets, and many others! Data from relational databases
INTRODUCTION TO WEB USING HTML What is HTML?
 Geoinformation and Sectoral Statistics Section (GiSS) INTRODUCTION TO WEB USING HTML What is HTML? HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
Geoinformation and Sectoral Statistics Section (GiSS) INTRODUCTION TO WEB USING HTML What is HTML? HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
Web Engineering (Lecture 01)
 Web Engineering (Lecture 01) By: Kamran Ullah Lecturer (CS) Class BS(CS)-5 th semester Web Engineering Definition 1: Web Engineering is the application of systematic and disciplined approaches to the design,
Web Engineering (Lecture 01) By: Kamran Ullah Lecturer (CS) Class BS(CS)-5 th semester Web Engineering Definition 1: Web Engineering is the application of systematic and disciplined approaches to the design,
Developing a Basic Web Page
 Developing a Basic Web Page Creating a Web Page for Stephen Dubé s Chemistry Classes 1 Objectives Review the history of the Web, the Internet, and HTML Describe different HTML standards and specifications
Developing a Basic Web Page Creating a Web Page for Stephen Dubé s Chemistry Classes 1 Objectives Review the history of the Web, the Internet, and HTML Describe different HTML standards and specifications
CSE 143: Computer Programming II Spring 2015 HW2: HTMLManager (due Thursday, April 16, :30pm)
 CSE 143: Computer Programming II Spring 2015 HW2: HTMLManager (due Thursday, April 16, 2015 11:30pm) This assignment focuses on using Stack and Queue collections. Turn in the following files using the
CSE 143: Computer Programming II Spring 2015 HW2: HTMLManager (due Thursday, April 16, 2015 11:30pm) This assignment focuses on using Stack and Queue collections. Turn in the following files using the
data analysis - basic steps Arend Hintze
 data analysis - basic steps Arend Hintze 1/13: Data collection, (web scraping, crawlers, and spiders) 1/15: API for Twitter, Reddit 1/20: no lecture due to MLK 1/22: relational databases, SQL 1/27: SQL,
data analysis - basic steps Arend Hintze 1/13: Data collection, (web scraping, crawlers, and spiders) 1/15: API for Twitter, Reddit 1/20: no lecture due to MLK 1/22: relational databases, SQL 1/27: SQL,
HTML OBJECTIVES WHAT IS HTML? BY FAITH BRENNER AN INTRODUCTION
 HTML AN INTRODUCTION BY FAITH BRENNER 1 OBJECTIVES BY THE END OF THIS LESSON YOU WILL: UNDERSTAND HTML BASICS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO WITH IT BE ABLE TO USE BASIC HTML TAGS BE ABLE TO USE SOME BASIC FORMATTING
HTML AN INTRODUCTION BY FAITH BRENNER 1 OBJECTIVES BY THE END OF THIS LESSON YOU WILL: UNDERSTAND HTML BASICS AND WHAT YOU CAN DO WITH IT BE ABLE TO USE BASIC HTML TAGS BE ABLE TO USE SOME BASIC FORMATTING
Make a Website. A complex guide to building a website through continuing the fundamentals of HTML & CSS. Created by Michael Parekh 1
 Make a Website A complex guide to building a website through continuing the fundamentals of HTML & CSS. Created by Michael Parekh 1 Overview Course outcome: You'll build four simple websites using web
Make a Website A complex guide to building a website through continuing the fundamentals of HTML & CSS. Created by Michael Parekh 1 Overview Course outcome: You'll build four simple websites using web
LECTURE 13. Intro to Web Development
 LECTURE 13 Intro to Web Development WEB DEVELOPMENT IN PYTHON In the next few lectures, we ll be discussing web development in Python. Python can be used to create a full-stack web application or as a
LECTURE 13 Intro to Web Development WEB DEVELOPMENT IN PYTHON In the next few lectures, we ll be discussing web development in Python. Python can be used to create a full-stack web application or as a
CSC148, Lab #4. General rules. Overview. Tracing recursion. Greatest Common Denominator GCD
 CSC148, Lab #4 This document contains the instructions for lab number 4 in CSC148H. To earn your lab mark, you must actively participate in the lab. We mark you in order to ensure a serious attempt at
CSC148, Lab #4 This document contains the instructions for lab number 4 in CSC148H. To earn your lab mark, you must actively participate in the lab. We mark you in order to ensure a serious attempt at
Introduction to Web Development
 Introduction to Web Development Lecture 1 CGS 3066 Fall 2016 September 8, 2016 Why learn Web Development? Why learn Web Development? Reach Today, we have around 12.5 billion web enabled devices. Visual
Introduction to Web Development Lecture 1 CGS 3066 Fall 2016 September 8, 2016 Why learn Web Development? Why learn Web Development? Reach Today, we have around 12.5 billion web enabled devices. Visual
Using Development Tools to Examine Webpages
 Chapter 9 Using Development Tools to Examine Webpages Skills you will learn: For this tutorial, we will use the developer tools in Firefox. However, these are quite similar to the developer tools found
Chapter 9 Using Development Tools to Examine Webpages Skills you will learn: For this tutorial, we will use the developer tools in Firefox. However, these are quite similar to the developer tools found
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML)
 11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
11. EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE (XML) Introduction Extensible Markup Language is a Meta language that describes the contents of the document. So these tags can be called as self-describing data tags. XML
Chapter 2 XML, XML Schema, XSLT, and XPath
 Summary Chapter 2 XML, XML Schema, XSLT, and XPath Ryan McAlister XML stands for Extensible Markup Language, meaning it uses tags to denote data much like HTML. Unlike HTML though it was designed to carry
Summary Chapter 2 XML, XML Schema, XSLT, and XPath Ryan McAlister XML stands for Extensible Markup Language, meaning it uses tags to denote data much like HTML. Unlike HTML though it was designed to carry
COMSC-030 Web Site Development- Part 1. Part-Time Instructor: Joenil Mistal
 COMSC-030 Web Site Development- Part 1 Part-Time Instructor: Joenil Mistal Chapter 1 1 HTML and Web Page Basics Are you interested in building your own Web pages? This chapter introduces you to basic HTML
COMSC-030 Web Site Development- Part 1 Part-Time Instructor: Joenil Mistal Chapter 1 1 HTML and Web Page Basics Are you interested in building your own Web pages? This chapter introduces you to basic HTML
INLEDANDE WEBBPROGRAMMERING MED JAVASCRIPT INTRODUCTION TO WEB PROGRAMING USING JAVASCRIPT
 INLEDANDE WEBBPROGRAMMERING MED JAVASCRIPT INTRODUCTION TO WEB PROGRAMING USING JAVASCRIPT ME152A L4: 1. HIGHER ORDER FUNCTIONS 2. REGULAR EXPRESSIONS 3. JAVASCRIPT - HTML 4. DOM AND EVENTS OUTLINE What
INLEDANDE WEBBPROGRAMMERING MED JAVASCRIPT INTRODUCTION TO WEB PROGRAMING USING JAVASCRIPT ME152A L4: 1. HIGHER ORDER FUNCTIONS 2. REGULAR EXPRESSIONS 3. JAVASCRIPT - HTML 4. DOM AND EVENTS OUTLINE What
Introduction, Notepad++, File Structure, 9 Tags, Hyperlinks 1
 Introduction, Notepad++, File Structure, 9 Tags, Hyperlinks 1 Introduction to HTML HTML, which stands for Hypertext Markup Language, is the standard markup language used to create web pages. HTML consists
Introduction, Notepad++, File Structure, 9 Tags, Hyperlinks 1 Introduction to HTML HTML, which stands for Hypertext Markup Language, is the standard markup language used to create web pages. HTML consists
Introduction to XML. XML: basic elements
 Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
What is XHTML? XHTML is the language used to create and organize a web page:
 XHTML Basics What is XHTML? XHTML is the language used to create and organize a web page: XHTML is newer than, but built upon, the original HTML (HyperText Markup Language) platform. XHTML has stricter
XHTML Basics What is XHTML? XHTML is the language used to create and organize a web page: XHTML is newer than, but built upon, the original HTML (HyperText Markup Language) platform. XHTML has stricter
Programmazione Web a.a. 2017/2018 HTML5
 Programmazione Web a.a. 2017/2018 HTML5 PhD Ing.Antonino Raucea antonino.raucea@dieei.unict.it 1 Introduzione HTML HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text
Programmazione Web a.a. 2017/2018 HTML5 PhD Ing.Antonino Raucea antonino.raucea@dieei.unict.it 1 Introduzione HTML HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text
Objectives. Introduction to HTML. Objectives. Objectives
 Objectives Introduction to HTML Developing a Basic Web Page Review the history of the Web, the Internet, and HTML. Describe different HTML standards and specifications. Learn about the basic syntax of
Objectives Introduction to HTML Developing a Basic Web Page Review the history of the Web, the Internet, and HTML. Describe different HTML standards and specifications. Learn about the basic syntax of
Announcements. 1. Class webpage: Have you been reading the announcements? Lecture slides and coding examples will be posted
 Announcements 1. Class webpage: Have you been reading the announcements? Lecture slides and coding examples will be posted 2. Campus is closed on Monday. 3. Install Komodo Edit on your computer this weekend.
Announcements 1. Class webpage: Have you been reading the announcements? Lecture slides and coding examples will be posted 2. Campus is closed on Monday. 3. Install Komodo Edit on your computer this weekend.
Web Design 101. What is HTML? HTML Tags. Web Browsers. <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>my First Heading</h1> <p>my first paragraph.
 What is HTML? Web Design 101 HTML is a language for describing web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is a markup language à A markup language is a set of markup tags The tags describe
What is HTML? Web Design 101 HTML is a language for describing web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is a markup language à A markup language is a set of markup tags The tags describe
Chapter 7: The Internet
 CSE1520.03 Glade Manual Chapter 7: The Internet Objectives This chapter introduces you to creating a web page that can be viewed on the Internet using a web browser such Firefox, Safari, Chrome or Internet
CSE1520.03 Glade Manual Chapter 7: The Internet Objectives This chapter introduces you to creating a web page that can be viewed on the Internet using a web browser such Firefox, Safari, Chrome or Internet
MODULE 2 HTML 5 FUNDAMENTALS. HyperText. > Douglas Engelbart ( )
 MODULE 2 HTML 5 FUNDAMENTALS HyperText > Douglas Engelbart (1925-2013) Tim Berners-Lee's proposal In March 1989, Tim Berners- Lee submitted a proposal for an information management system to his boss,
MODULE 2 HTML 5 FUNDAMENTALS HyperText > Douglas Engelbart (1925-2013) Tim Berners-Lee's proposal In March 1989, Tim Berners- Lee submitted a proposal for an information management system to his boss,
Announcements. 1. Class webpage: Have you been reading the announcements? Lecture slides and coding examples will be posted
 Announcements 1. Class webpage: Have you been reading the announcements? Lecture slides and coding examples will be posted 2. Install Komodo Edit on your computer right away. 3. Bring laptops to next class
Announcements 1. Class webpage: Have you been reading the announcements? Lecture slides and coding examples will be posted 2. Install Komodo Edit on your computer right away. 3. Bring laptops to next class
HTML: Introduction CISC 282. September 11, What is HTML?
 HTML: Introduction CISC 282 September 11, 2018 What is HTML? Hypertext Markup Language Markup language "Set of words or symbols" Assigns properties to text Not actually part of the text HTML specifies
HTML: Introduction CISC 282 September 11, 2018 What is HTML? Hypertext Markup Language Markup language "Set of words or symbols" Assigns properties to text Not actually part of the text HTML specifies
Glossary. advance: to move forward
 Computer Computer Skills Glossary Skills Glossary advance: to move forward alignment tab: the tab in the Format Cells dialog box that allows you to choose how the data in the cells will be aligned (left,
Computer Computer Skills Glossary Skills Glossary advance: to move forward alignment tab: the tab in the Format Cells dialog box that allows you to choose how the data in the cells will be aligned (left,
CSE 115. Introduction to Computer Science I
 CSE 115 Introduction to Computer Science I Road map Review Limitations of front-end sites Web servers Examples Review
CSE 115 Introduction to Computer Science I Road map Review Limitations of front-end sites Web servers Examples Review
Understanding structure Learning about markup Tags and elements. Structure COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 XX XX XX Understanding structure Learning about markup Tags and elements 1 Structure COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL We come across all kinds of documents every day of our lives. Newspapers, insurance forms, shop
XX XX XX Understanding structure Learning about markup Tags and elements 1 Structure COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL We come across all kinds of documents every day of our lives. Newspapers, insurance forms, shop
Objective % Select and utilize tools to design and develop websites.
 Objective 207.02 8% Select and utilize tools to design and develop websites. Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Basic framework for all web design. Written using tags that a web browser uses to interpret
Objective 207.02 8% Select and utilize tools to design and develop websites. Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) Basic framework for all web design. Written using tags that a web browser uses to interpret
Comp 426 Midterm Fall 2013
 Comp 426 Midterm Fall 2013 I have not given nor received any unauthorized assistance in the course of completing this examination. Name: PID: This is a closed book exam. This page left intentionally blank.
Comp 426 Midterm Fall 2013 I have not given nor received any unauthorized assistance in the course of completing this examination. Name: PID: This is a closed book exam. This page left intentionally blank.
LECTURE 13. Intro to Web Development
 LECTURE 13 Intro to Web Development WEB DEVELOPMENT IN PYTHON In the next few lectures, we ll be discussing web development in Python. Python can be used to create a full-stack web application or as a
LECTURE 13 Intro to Web Development WEB DEVELOPMENT IN PYTHON In the next few lectures, we ll be discussing web development in Python. Python can be used to create a full-stack web application or as a
Creating Web Pages Using HTML
 Creating Web Pages Using HTML HTML Commands Commands are called tags Each tag is surrounded by Some tags need ending tags containing / Tags are not case sensitive, but for future compatibility, use
Creating Web Pages Using HTML HTML Commands Commands are called tags Each tag is surrounded by Some tags need ending tags containing / Tags are not case sensitive, but for future compatibility, use
Uniform Resource Locators (URL)
 The World Wide Web Web Web site consists of simply of pages of text and images A web pages are render by a web browser Retrieving a webpage online: Client open a web browser on the local machine The web
The World Wide Web Web Web site consists of simply of pages of text and images A web pages are render by a web browser Retrieving a webpage online: Client open a web browser on the local machine The web
6.001 Notes: Section 15.1
 6.001 Notes: Section 15.1 Slide 15.1.1 Our goal over the next few lectures is to build an interpreter, which in a very basic sense is the ultimate in programming, since doing so will allow us to define
6.001 Notes: Section 15.1 Slide 15.1.1 Our goal over the next few lectures is to build an interpreter, which in a very basic sense is the ultimate in programming, since doing so will allow us to define
Web Development & Design Foundations with XHTML. Chapter 2 Key Concepts
 Web Development & Design Foundations with XHTML Chapter 2 Key Concepts Learning Outcomes In this chapter, you will learn about: XHTML syntax, tags, and document type definitions The anatomy of a web page
Web Development & Design Foundations with XHTML Chapter 2 Key Concepts Learning Outcomes In this chapter, you will learn about: XHTML syntax, tags, and document type definitions The anatomy of a web page
Hyper Text Markup Language
 Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is a markup language. It tells your browser how to structure the webpage. HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, or mark up different parts of
Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is a markup language. It tells your browser how to structure the webpage. HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, or mark up different parts of
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM Advanced Internet Technology Lab.
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 5049 Advanced Internet Technology Lab Lab # 1 Eng. Haneen El-masry February, 2015 Objective To be familiar with
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 5049 Advanced Internet Technology Lab Lab # 1 Eng. Haneen El-masry February, 2015 Objective To be familiar with
(1) I (2) S (3) P allow subscribers to connect to the (4) often provide basic services such as (5) (6)
 Collection of (1) Meta-network That is, a (2) of (3) Uses a standard set of protocols Also uses standards d for structuring t the information transferred (1) I (2) S (3) P allow subscribers to connect
Collection of (1) Meta-network That is, a (2) of (3) Uses a standard set of protocols Also uses standards d for structuring t the information transferred (1) I (2) S (3) P allow subscribers to connect
BeautifulSoup: Web Scraping with Python
 : Web Scraping with Python Andrew Peterson Apr 9, 2013 files available at: https://github.com/aristotle-tek/_pres Roadmap Uses: data types, examples... Getting Started downloading files with wget : in
: Web Scraping with Python Andrew Peterson Apr 9, 2013 files available at: https://github.com/aristotle-tek/_pres Roadmap Uses: data types, examples... Getting Started downloading files with wget : in
Adobe Campaign Standard
 Adobe Campaign Standard Overview This guide will walk you through how to setup your email campaigns with Adobe Campaign Standard [https://www.adobe.com/marketingcloud/campaign.html] using Branch Universal
Adobe Campaign Standard Overview This guide will walk you through how to setup your email campaigns with Adobe Campaign Standard [https://www.adobe.com/marketingcloud/campaign.html] using Branch Universal
Computer Applications Final Exam Study Guide
 Computer Applications Final Exam Study Guide Our final exam is based from the quizzes, tests, and from skills we have learned about Hardware, PPT, Word, Excel and HTML during our Computer Applications
Computer Applications Final Exam Study Guide Our final exam is based from the quizzes, tests, and from skills we have learned about Hardware, PPT, Word, Excel and HTML during our Computer Applications
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
Web scraping and social media scraping introduction
 Web scraping and social media scraping introduction Jacek Lewkowicz, Dorota Celińska University of Warsaw February 23, 2018 Motivation Definition of scraping Tons of (potentially useful) information on
Web scraping and social media scraping introduction Jacek Lewkowicz, Dorota Celińska University of Warsaw February 23, 2018 Motivation Definition of scraping Tons of (potentially useful) information on
Office Wo Office W r o d r 2007 Revi i ng and R d Refifini ng a D Document
 Office Word 2007 Lab 2 Revising i and Refining i a Document In this lab, the student will learn more about editing documents They will learn to use many more of the formatting features included in Office
Office Word 2007 Lab 2 Revising i and Refining i a Document In this lab, the student will learn more about editing documents They will learn to use many more of the formatting features included in Office
Developing Online Databases and Serving Biological Research Data
 Developing Online Databases and Serving Biological Research Data 1 Last Time HTML Hypertext Markup Language Used to build web pages Static, and can't change the way it presents itself based off of user
Developing Online Databases and Serving Biological Research Data 1 Last Time HTML Hypertext Markup Language Used to build web pages Static, and can't change the way it presents itself based off of user
(Refer Slide Time: 01:41) (Refer Slide Time: 01:42)
 Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #14 HTML -Part II We continue with our discussion on html.
Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #14 HTML -Part II We continue with our discussion on html.
Bonus Lesson: Working with Code
 15 Bonus Lesson: Working with Code In this lesson, you ll learn how to work with code and do the following: Select code elements in new ways Collapse and expand code entries Write code using code hinting
15 Bonus Lesson: Working with Code In this lesson, you ll learn how to work with code and do the following: Select code elements in new ways Collapse and expand code entries Write code using code hinting
Web Site Design and Development. CS 0134 Fall 2018 Tues and Thurs 1:00 2:15PM
 Web Site Design and Development CS 0134 Fall 2018 Tues and Thurs 1:00 2:15PM By the end of this course you will be able to Design a static website from scratch Use HTML5 and CSS3 to build the site you
Web Site Design and Development CS 0134 Fall 2018 Tues and Thurs 1:00 2:15PM By the end of this course you will be able to Design a static website from scratch Use HTML5 and CSS3 to build the site you
Web Publishing Basics I
 Web Publishing Basics I Jeff Pankin Information Services and Technology Contents Course Objectives... 2 Creating a Web Page with HTML... 3 What is Dreamweaver?... 3 What is HTML?... 3 What are the basic
Web Publishing Basics I Jeff Pankin Information Services and Technology Contents Course Objectives... 2 Creating a Web Page with HTML... 3 What is Dreamweaver?... 3 What is HTML?... 3 What are the basic
P3e REPORT WRITER CREATING A BLANK REPORT
 P3e REPORT WRITER CREATING A BLANK REPORT 1. On the Reports window, select a report, then click Copy. 2. Click Paste. 3. Click Modify. 4. Click the New Report icon. The report will look like the following
P3e REPORT WRITER CREATING A BLANK REPORT 1. On the Reports window, select a report, then click Copy. 2. Click Paste. 3. Click Modify. 4. Click the New Report icon. The report will look like the following
DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON
 DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON Advanced Data Structure and File Manipulation Peter Lo Linear Structure Queue, Stack, Linked List and Tree 2 Queue A queue is a line of people or things waiting
DATA STRUCTURE AND ALGORITHM USING PYTHON Advanced Data Structure and File Manipulation Peter Lo Linear Structure Queue, Stack, Linked List and Tree 2 Queue A queue is a line of people or things waiting
Assignment 4. Overview. Prof. Stewart Weiss. CSci 335 Software Design and Analysis III Assignment 4
 Overview This assignment combines several dierent data abstractions and algorithms that we have covered in class, including priority queues, on-line disjoint set operations, hashing, and sorting. The project
Overview This assignment combines several dierent data abstractions and algorithms that we have covered in class, including priority queues, on-line disjoint set operations, hashing, and sorting. The project
Basic Internet Skills
 The Internet might seem intimidating at first - a vast global communications network with billions of webpages. But in this lesson, we simplify and explain the basics about the Internet using a conversational
The Internet might seem intimidating at first - a vast global communications network with billions of webpages. But in this lesson, we simplify and explain the basics about the Internet using a conversational
Basics of Web Design, 3 rd Edition Instructor Materials Chapter 2 Test Bank
 Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer. 1. What element is used to configure a new paragraph? a. new b. paragraph c. p d. div 2. What element is used to create the largest heading? a. h1 b. h9 c. head
Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer. 1. What element is used to configure a new paragraph? a. new b. paragraph c. p d. div 2. What element is used to create the largest heading? a. h1 b. h9 c. head
A4: HTML Validator/Basic DOM Operation
 A4: HTML Validator/Basic DOM Operation Overview You are tasked with creating a basic HTML parser to perform a *very* limited subset of what a web browser does behind the scenes to setup the DOM for displaying
A4: HTML Validator/Basic DOM Operation Overview You are tasked with creating a basic HTML parser to perform a *very* limited subset of what a web browser does behind the scenes to setup the DOM for displaying
Index. alt, 38, 57 class, 86, 88, 101, 107 href, 24, 51, 57 id, 86 88, 98 overview, 37. src, 37, 57. backend, WordPress, 146, 148
 Index Numbers & Symbols (angle brackets), in HTML, 47 : (colon), in CSS, 96 {} (curly brackets), in CSS, 75, 96. (dot), in CSS, 89, 102 # (hash mark), in CSS, 87 88, 99 % (percent) font size, in CSS,
Index Numbers & Symbols (angle brackets), in HTML, 47 : (colon), in CSS, 96 {} (curly brackets), in CSS, 75, 96. (dot), in CSS, 89, 102 # (hash mark), in CSS, 87 88, 99 % (percent) font size, in CSS,
Learn how to login to Sitefinity and what possible errors you can get if you do not have proper permissions.
 USER GUIDE This guide is intended for users of all levels of expertise. The guide describes in detail Sitefinity user interface - from logging to completing a project. Use it to learn how to create pages
USER GUIDE This guide is intended for users of all levels of expertise. The guide describes in detail Sitefinity user interface - from logging to completing a project. Use it to learn how to create pages
Installation Guide. Sitecore Federated Experience Manager. Installation & Configuration Guide
 Sitecore Federated Experience Manager Installation Guide Rev: 23 August 2014 Sitecore Federated Experience Manager Installation Guide Installation & Configuration Guide Table of Contents Chapter 1 Overview...
Sitecore Federated Experience Manager Installation Guide Rev: 23 August 2014 Sitecore Federated Experience Manager Installation Guide Installation & Configuration Guide Table of Contents Chapter 1 Overview...
MARKING KEY The University of British Columbia MARKING KEY Computer Science 260 Midterm #2 Examination 12:30 noon, Thursday, March 15, 2012
 MARKING KEY The University of British Columbia MARKING KEY Computer Science 260 Midterm #2 Examination 12:30 noon, Thursday, March 15, 2012 Instructor: K. S. Booth Time: 70 minutes (one hour ten minutes)
MARKING KEY The University of British Columbia MARKING KEY Computer Science 260 Midterm #2 Examination 12:30 noon, Thursday, March 15, 2012 Instructor: K. S. Booth Time: 70 minutes (one hour ten minutes)
As we design and build out our HTML pages, there are some basics that we may follow for each page, site, and application.
 Extra notes - Client-side Design and Development Dr Nick Hayward HTML - Basics A brief introduction to some of the basics of HTML. Contents Intro element add some metadata define a base address
Extra notes - Client-side Design and Development Dr Nick Hayward HTML - Basics A brief introduction to some of the basics of HTML. Contents Intro element add some metadata define a base address
Introduction to Corpora
 Introduction to Max Planck Summer School 2017 Overview These slides describe the process of getting a corpus of written language. Input: Output: A set of documents (e.g. text les), D. A matrix, X, containing
Introduction to Max Planck Summer School 2017 Overview These slides describe the process of getting a corpus of written language. Input: Output: A set of documents (e.g. text les), D. A matrix, X, containing
Lecture 4: Data Collection and Munging
 Lecture 4: Data Collection and Munging Instructor: Outline 1 Data Collection and Scraping 2 Web Scraping basics In-Class Quizzes URL: http://m.socrative.com/ Room Name: 4f2bb99e Data Collection What you
Lecture 4: Data Collection and Munging Instructor: Outline 1 Data Collection and Scraping 2 Web Scraping basics In-Class Quizzes URL: http://m.socrative.com/ Room Name: 4f2bb99e Data Collection What you
Purpose, features and functionality
 Topic 6 Purpose, features and functionality In this topic you will look at the purpose, features, functionality and range of users that use information systems. You will learn the importance of being able
Topic 6 Purpose, features and functionality In this topic you will look at the purpose, features, functionality and range of users that use information systems. You will learn the importance of being able
CIT 590 Homework 5 HTML Resumes
 CIT 590 Homework 5 HTML Resumes Purposes of this assignment Reading from and writing to files Scraping information from a text file Basic HTML usage General problem specification A website is made up of
CIT 590 Homework 5 HTML Resumes Purposes of this assignment Reading from and writing to files Scraping information from a text file Basic HTML usage General problem specification A website is made up of
Attributes & Images 1 Create a new webpage
 Attributes & Images 1 Create a new webpage Open your test page. Use the Save as instructions from the last activity to save your test page as 4Attributes.html and make the following changes:
Attributes & Images 1 Create a new webpage Open your test page. Use the Save as instructions from the last activity to save your test page as 4Attributes.html and make the following changes:
Review of HTML. Chapter Pearson. Fundamentals of Web Development. Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar
 Review of HTML Chapter 3 Fundamentals of Web Development 2017 Pearson Fundamentals of Web Development http://www.funwebdev.com - 2 nd Ed. What Is HTML and Where Did It Come from? HTML HTML is defined as
Review of HTML Chapter 3 Fundamentals of Web Development 2017 Pearson Fundamentals of Web Development http://www.funwebdev.com - 2 nd Ed. What Is HTML and Where Did It Come from? HTML HTML is defined as
PHP. Interactive Web Systems
 PHP Interactive Web Systems PHP PHP is an open-source server side scripting language. PHP stands for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor One of the most popular server side languages Second most popular on GitHub
PHP Interactive Web Systems PHP PHP is an open-source server side scripting language. PHP stands for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor One of the most popular server side languages Second most popular on GitHub
Developing a Basic Web Site
 Developing a Basic Web Site Creating a Chemistry Web Site 1 Objectives Define links and how to use them Create element ids to mark specific locations within a document Create links to jump between sections
Developing a Basic Web Site Creating a Chemistry Web Site 1 Objectives Define links and how to use them Create element ids to mark specific locations within a document Create links to jump between sections
Quark XML Author September 2016 Update for Platform with Business Documents
 Quark XML Author 05 - September 06 Update for Platform with Business Documents Contents Getting started... About Quark XML Author... Working with the Platform repository... Creating a new document from
Quark XML Author 05 - September 06 Update for Platform with Business Documents Contents Getting started... About Quark XML Author... Working with the Platform repository... Creating a new document from
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES. XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
Hyper Text Markup Language
 Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is a markup language. It tells your browser how to structure the webpage. HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, or mark up different parts of
Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is a markup language. It tells your browser how to structure the webpage. HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, or mark up different parts of
HTML Overview. With an emphasis on XHTML
 HTML Overview With an emphasis on XHTML What is HTML? Stands for HyperText Markup Language A client-side technology (i.e. runs on a user s computer) HTML has a specific set of tags that allow: the structure
HTML Overview With an emphasis on XHTML What is HTML? Stands for HyperText Markup Language A client-side technology (i.e. runs on a user s computer) HTML has a specific set of tags that allow: the structure
Web Technology. COMP476 Networked Computer Systems. Hypertext and Hypermedia. Document Representation. Client-Server Paradigm.
 Web Technology COMP476 Networked Computer Systems - Paradigm The method of interaction used when two application programs communicate over a network. A server application waits at a known address and a
Web Technology COMP476 Networked Computer Systems - Paradigm The method of interaction used when two application programs communicate over a network. A server application waits at a known address and a
Anatomy of an HTML document
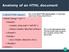 Anatomy of an HTML document hello World hello World This is the DOCTYPE declaration.
Anatomy of an HTML document hello World hello World This is the DOCTYPE declaration.
