ROLE OF WEB BROWSING LAYOUT ENGINE EVALUATION IN DEVELOPMENT
|
|
|
- Todd Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES ROLE OF WEB BROWSING LAYOUT ENGINE EVALUATION IN DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OF MORE USABLE WEB INFORMATION SYSTEM Gatis Vitols, Latvia University of Agriculture Abstract. This paper focuses on evaluation of Web browsing layout engines used as a backbone in Web browsing software. Study of commonly used Web browsers and Web information system developing languages has been performed. The role of Web browsing layout engine evaluation in Web information system development process is identified as a critical matter for bringing business processes online in a form of usable and accessible information system. By analyzing Web browsing layout engines as a tool that renders elements on a particular Web page of Web information system, key tendencies and emphasis for Web information system developers are revealed and discussed. Key words: Web browser, Web browsing layout engine, Hyper Text Markup Language, Web information system. Introduction Bringing everyday business processes online has become a consistently growing tendency that goes side by side with developing possibilities of the Web (Lane et al., 2008). A key tool to carry out business process online is to develop information systems that are able to work online serving large number of users. Web users typically are not restricted by geographic location and specific accessibility environments (Taniar and Rahayu, 2004). One of the key software solutions for accessing Web services, including Web information systems, are Web browsers. Web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web (William, 2009). When users read a specific page on Web information system, it means, they use some type of Web browser. Most browsers that are available on the market have a common nuance: browsers read Hypertext Markup Language, HTML and Cascading Style Sheets, CSS codes and interpret them to data which are more understandable to users in a form of visual layout. HTML, CSS and other commonly met Web page development languages, such as JavaScript, are clientside languages (Scott, 2006). It means in a client server architecture, which is a core architecture in the Web, most of operations are processed in the client - user side (see Figure 1.). In the client side information processing model, for example, if a mathematics statement such as 1+1 is made, the server will not perform the calculation. In such a model, the server does not interact with data. The server s main function is to send data to the client side. The main interaction, in Figure 1 example is made on a client computer. In such interaction Web browser has a huge impact on how the server sent information is processed. The browser receives data then performs operation taking into account the client hardware and software environment and displays the result. Opposite to the client-side information processing, server-side processing is performed on the server. Data are processed and then the result is sent to the client. In such a model, the client does not know how the data, which are sent by the server, are processed. In this model, the main task for the client is to receive and display data. Each model with according languages has its main targeted tasks in the Web information system development. Sometimes the tasks can overlap, which requires developer skills to choose the solution for specific problems. One of the key factors in information system accessibility and usability is the designed presentation of information. System users usually are not interested how the information is processed or by which algorithm the task is completed. Most attention is paid on how the information system can be used in Figure 1. Client side information processing in the client-server architecture. 197
2 Role of WEB browsing layout engine Gatis Vitols, an effective, easy and beneficial way. It is seen that in order to meet such demands, focus on the client side information processing process examination has to be put. The aim of this paper is to evaluate commonly used Web browsing layout engines and bring forward tendencies for more accessible and usable Web information system design. To reach the aim the following tasks have been brought forward: 1. Determine Web browsing layout engine diversity in various Web browsers. 2. Evaluate commonly used Web browsing layout engine similarities and differences regarding processing Hypertext Markup Language tags. 3. Identify tendencies and factors in Web browsers for information system developers that could allow creating more accessible and usable Web information systems. Materials and Methods When the analysis and summary of the leading Web standardization organization W3C provided browser usage statistics are made, it is seen, that in the year 2009, three leading Web browsers were Mozilla Firefox 3.x (46.94%), Microsoft Internet Explorer 6-8.x (40.52%) and Google Chrome 3-4.x (6.28%) which all together make 93.74% from all browser usage. In the beginning of the year 2010, tendencies remain the same and companies Mozilla, Microsoft and Google are developing and own most widely used Web browsers. According to published data (World Wide Web Consortium, 2010), there is an obvious tendency that popularity of Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox has slightly increased, while Microsoft Internet Explorer has lost its stable position in the market. For example, Google browser popularity has increased for more than 5% in January 2010 compared with December 2009 (World Wide Web Consortium, 2010). Next in a queue for the three most used Web browsers is Apple owned Web browser Safari, whose popularity increases with its integration into company manufactured, popularity gaining products, such as ipod portable music player and iphone model mobile phones. Web browser market consists of more than 10 universal, widely known Web browsers, not including many locally known or existing in developmental stage. For this research three named Web browsers with corresponding layout engines were chosen: Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0, Mozilla Firefox 3.5 and Google Chrome 4.0. To examine the role of Web browser layout engine in development of accessible and usable Web information system, one of the backbone client side languages of the Web - Hypertext Markup Language was chosen. Since creation of HTML, this language has been updated to various versions. In the year 2000, HTML language version 4.01 specification (World Wide Web Consortium, 2009) was published as an ISO/IEC international standard ISO/IEC 15445:2000(E) with a title Information technology Document description and processing languages Hyper Text Markup Language (International Standards for Business, Government and Society, 2006). This is the latest approved version of HTML, (Johansson, 2010) however, there is an intense work at HTML 5.0 version development which specification still, until February 2010 appears to be in a draft version, and possibly will be released during the year 2010 or 2011 (Johansson, 2010). When using HTML 4.01, there is a need to define the format subtypes of a language usage or more precisely DOCTYPEs, such as Strict and Transitional. Usage of document types relates to the Web browser rendering methods. If the Strict is used, rendering will be more precise and close to the language fundamental aim. If Transitional is chosen, exceptions in HTML document formatting are allowed. (Johansson, 2005) As the Strict document type promotes, a Web page separation in structure and presentation, which makes more usable and easier accessible Web page (Johansson, 2005) to design, the document type Strict is used for research published in this paper. The test of HTML 4.01 Strict specification tag usage possibilities and Web browsers layout engine rendering have been performed. A sample page of Web information system containing each of elements across chosen browsers has been created and tested. Browsers use the following Web layout engines: Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 use Trident unversioned, Mozilla Firefox 3.5 use Gecko and Google Chrome 4.0 use WebKit unversioned. There are 91 markup tags named in HTML 4.01 specification (Holzsschlag, 2004; World Wide Web Consortium, 2009). As the Trident layout engine is fully available only in Microsoft Windows operation system (Lane et al., 2008), an operation system for testing Web browsers, Windows family operating system version XP SP2 were chosen. Rendering results on chosen Web browsers are ordered in a HTML tag functional groups. Results and Discussion HTML top level elements can be described by tags - body, frameset, head and html. Execution and rendering examination results show that each top level element is supported by all three analyzed Web layout engines. HTML head elements can be described by tags base, isindex, link, meta, script, style and title. Execution and rendering examination results show that only isindex element is not supported by any of three analyzed Web layout engines. Unsupported isindex element relates to the chosen document type Strict. Specification of Strict describes this element as deprecated or not supported by document type specification. Therefore, Web developers should avoid using isindex element. HTML generic block-level elements execution results are summarized in Table
3 Gatis Vitols, Role of WEB browsing layout engine Table 1 Layout engine evaluation based on block-level elements rendering examination on various Web browsers address Contact information for a document blockquote Quotations center Center alignment -* -* -* del Defines text that has been deleted from a document div Generic language container h1 Used to define HTML headings, largest size h2 Used to define HTML headings, size h3 Used to define HTML headings, size h4 Used to define HTML headings, size h5 Used to define HTML headings, size h6 Used to define HTML headings, smallest size hr Horizontal rule ins Defines the text that has been inserted into a document isindex Creates a single-line text input control -* -* -* noscript Alternate content container for non script rendering p Paragraph pre Pre-formatted text From the results included in Table 1 is seen, that from HTML block-level elements, only center and isindex are not supported. Mark + shows that the browser layout engine supports element rendering, but the mark -* means that the element rendering in document type Strict, is deprecated. Deprecated elements may become obsolete in the future, but browsers continue to support deprecated elements for backward compatibility. (World Wide Web Consortium, 2009) HTML list elements execution results are summarized in Table 2. supports element rendering, but mark -* means that element rendering in document type Strict, is deprecated. Deprecated elements may become obsolete in the future, but browsers continue to support deprecated elements for backward compatibility (World Wide Web Consortium, 2009). HTML table elements execution results are summarized in Table 3. Table 2 Layout engine evaluation based on list elements rendering examination on various Web browsers dd Description of items in a definition list dir List directory titles -* -* -* dl Defines definition list dt Definition term li List item menu Menu list -* -* -* ol Ordered list ul Unordered list
4 Role of WEB browsing layout engine Gatis Vitols, Table 3 Layout engine evaluation based on table elements rendering examination on various Web browsers caption Table caption col Table column for formatting colgroup Table column group for formatting table Table definition tbody Table body definition td Table cell tfoot Table footer th Table header cell thead Table header tr Table row supports element rendering, but mark shows that a tag is neither supported nor rendered. From the rendering results in Table 3, it is seen that Web information system developers should avoid using col and colgroup tags, as they are only supported by Trident layout engine and can lead to distortion of the whole rendered table on Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome family Web browsers. HTML form elements execution was successful for all analyzed Web layout engines. All HTML form elements, including a button, fieldset, form, input, label, legend, optgroup, option, select and textarea, are supported by all three analyzed Web layout engines. HTML special inline elements execution results are summarized in Table 4. supports element rendering, but mark shows that the tag is neither supported nor rendered. Mark -* means that the element rendering in document type Strict, is deprecated. A deprecated element is one that has been outdated. Deprecated elements may become obsolete in future, but browsers continue to support deprecated elements for backward compatibility (World Wide Web Consortium, 2009). Table 4 Layout engine evaluation based on special inline elements rendering examination on various Web browsers a Anchor applet Allows designers to embed a Java applet -* -* -* basefont Specifies a default font attributes for text in a document -* -* -* bdo Specifies text direction, overriding the bidirectional algorithm br Line break font Specifies the font attributes -* -* -* iframe Defines inline frame -* -* -* img Embedded image map Defines image map object Generic embedded object param Named property value q Defines a short quotation script Defines a client-side script span Generic language container sub Subscript sup Superscript
5 Gatis Vitols, Role of WEB browsing layout engine Table 5 Layout engine evaluation based on phrase elements rendering examination on various Web browsers abbr Abbreviation acronym Acronym cite Defines a citation code Computer code fragment del Defines the text that has been deleted from a document dfn Defines a definition term em Emphasis ins Defines the text that has been inserted into a document kbd Defines keyboard text samp Defines sample computer code strong Strong emphasis var Defines a variable part of a text From the rendering results in Table 4, it is seen that inline elements support varies from used Web layout engines. Trident shows the poorest performance by not supporting quotation and object elements, unlike Google Chrome Webkit can render all non deprecated special inline elements. Web developers should pay attention to widely used elements, such as iframe and font. These elements are deprecated and should be avoided. HTML phrase elements execution results are summarized in Table 5. supports element rendering, but mark shows that tag is neither supported nor rendered. From the rendering results in Table 5, it is seen that Web developers should be aware of using abbreviation and definition tags in developing projects as they are only partly supported by analyzed Web layout engines. Gecko shows the best performance in phrase element execution as it supports all phrase tags. HTML font style elements execution results are summarized in Table 6. supports element rendering. Mark -* means that the element rendering in document type Strict, is deprecated. A deprecated element is one that has been outdated. Deprecated elements may become obsolete in the future, but browsers continue to support deprecated elements for backward compatibility (World Wide Web Consortium, 2009). From the rendering results in Table 6, it is seen that Web developers should avoid using strike-through and underlined text elements as they are deprecated. As an alternative Cascade Style Sheet font styles could be used. HTML frame elements execution was successful for all analyzed Web Layout engines. All HTML frame elements, including frame, frameset, noframes, are supported. Even if Web developers follow mentioned analysis of HTML element rendering, there can still be some sort of distortions that relate Web layout engine tag attribute rendering or specific non-html element rendering, so in the project development stage it is useful to test Web page on different browsers. Besides installing different Web browsers on a system, there are also other possibilities to test Web page against various Web layout engines. Table 6 Layout engine evaluation based on font style elements rendering examination on various Web browsers b Bold text big Larger text size i Italic text style s Strike-through text -* -* -* small Small text strike Strike-though text -* -* -* tt Teletype text u Underlined text -* -* -* 201
6 Role of WEB browsing layout engine Gatis Vitols, In the Web browser market, a research for solutions to make more universal Web browser that could work with multiple layout engines is in progress. There are solutions named Hybrid Web browsers. These browsers include multiple layout engines in one software product. For example, Lunascape Orion that includes triple Web layout engine support Trident, Gecko and Webkit (Lunascape Author Group, 2009). But until 2010, hybrid Web browsers are still in developmental stage. Also hybrid Web browsers face serious problems. It is known that parts of Web layout engine family are proprietary and owned by specific company which means that a hybrid Web browser cannot implement such layout engines without a license from its owners. For example, Opera and Microsoft Internet Explorer owns its own Web layout engines. So the fact that, for example, Lunascape Orion operational requirements are Windows operation system and Internet Explorer 6 or later (Lunascape Author Group, 2009) clearly shows that in order to support Trident in Lunascape, a user should have Internet Explorer installed on their devices. Evaluation also can be done by using some virtualization service that is provided on Web. Adobe BrowserLab (Adobe BrowserLab Author Group, 2009) is one of examples. This service allows testing Web pages in various browsers on different operation systems using one Web page opened in Web browser. Although testing service is limited by amount of browsers and operation systems, there are few options that can be helpful for Web developers. For example, Adobe Browser lab supports the so called Onion skinning (Adobe BrowserLab Author Group, 2009) feature that allows to overlay two different browser rendering results, identifies faults and evaluates offsets. These types of services usually require Flash technologies support and at least one particular version Web browser that is already functioning on a system (Adobe BrowserLab Author Group, 2009). Conclusions 1. Layout engines that are analyzed in this paper are not the only existing ones, but as the data by World Wide Web Consortium shows these are mostly used in the year From the layout engine analysis summarized in result tables, it is seen that two layout engines - Gecko and Webkit perform with similar results. Trident HTML tag rendering possibilities are more limited, although the main HTML elements can be executed and rendered properly. According to the information by Microsoft (Lane et al., 2008), Trident Web layout engine has been dramatically improved in future versions; unfortunately statistics and practices still show that Internet Explorer 6 with its corresponding layout engine is still widespread in use. 2. The fact that one has to take into consideration when designing Web information system and facing layout engine rendering testing, is that the creation of draft specifications of HTML 5 is also in progress. There is a need for Web developers to take into account and be aware of new possibilities which will be available by release of HTML 5.0 specification. There will be also a need to analyze and evaluate HTML 5.0 elements rendering on various layout engines in the nearest future. 3. Analysis in this research is not complete as it only covers HTML main element rendering results, not including, for example, attribute rendering evaluation. 4. Web developers should consider testing developing project on various browsers as a critical matter. For testing, the most stable method is installation of various browsers on a system, but alternatives as hybrid Web browsers and virtualization services can be considered. The tendency for hybrid Web layout engine development is still under a question mark and shows that market will remain scattered with existence of various stand-alone layout engines, but virtualization services such as Adobe BrowserLab, can be a good option for evaluation of Web layout engine performance. 5. In conclusion, it can be seen that Web browsing layout engine evaluation against programming language element execution has a serious role in Web information system development process. Web developers should practice testing Web pages of Web information system on various browsers, follow guidelines and published practices, as it directly addresses developed system accessibility and usability problems. Acknowledgements Funding support for this research is provided by Europe Social Fund program Support for Doctoral Studies in LUA, agreement 2009/0180/1DP/ /09/IPIA/ VIAA/017 References 1. Adobe BrowserLab Author Group (2009) Adobe Browser Lab: An Introduction. Available at: browserlab.adobe.com, 10 December Holzsschlag E.M. (2004) 250 HTML and Web Design Secrets, Willey Publishing, Inc. USA, pp International Standards for Business, Government and Society (2006) ISO/IEC 15445: Information technology - Document description and processing languages - HyperText Markup Language (HTML) Available at: 3 February Johansson R. (2005) Transitional vs. Strict Markup. Available at: 12 December Johansson R. (2010) Seven HTML related working drafts published. Available at: com/archive/201003/seven_html_related_working_drafts_published, 4 March
7 Gatis Vitols, Role of WEB browsing layout engine 6. Lane J., Moscovitz M. and Lewis R.J. (2008) Website Creation with CSS, XHTML, and JavaScript, Friendsof, Apress, USA, 362 p. 7. Lunascape Author Group (2009) Lunascape Orion 6: First triple engine browser. Available at: lunascape.tv/products/tabid/111/default.aspx, 3 January Scott M.L. (2006) Programming Language Pragmatics: Second Edition. Elsevier Inc., USA pp Taniar D. and Rahayu J.W. (2004) Web Information Systems, Idea Group Publishing, USA, 372 p. 10. William S. (2009) Web Browser History. Available at: 5 May World Wide Web Consortium (2009) Index of the HTML 4 Elements. Available at: html4/index/elements.html, 8 January World Wide Web Consortium (2010) Web Statistics and Trends. Available at: browsers/browsers_stats.asp, 14 February
HTML: Parsing Library
 HTML: Parsing Library Version 4.1.3 November 20, 2008 (require html) The html library provides functions to read html documents and structures to represent them. (read-xhtml port) html? port : input-port?
HTML: Parsing Library Version 4.1.3 November 20, 2008 (require html) The html library provides functions to read html documents and structures to represent them. (read-xhtml port) html? port : input-port?
HTML: Parsing Library
 HTML: Parsing Library Version 6.7 October 26, 2016 (require html) package: html-lib The html library provides functions to read conformant HTML4 documents and structures to represent them. Since html assumes
HTML: Parsing Library Version 6.7 October 26, 2016 (require html) package: html-lib The html library provides functions to read conformant HTML4 documents and structures to represent them. Since html assumes
HTML TAG SUMMARY HTML REFERENCE 18 TAG/ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION PAGE REFERENCES TAG/ATTRIBUTE DESCRIPTION PAGE REFERENCES MOST TAGS
 MOST TAGS CLASS Divides tags into groups for applying styles 202 ID Identifies a specific tag 201 STYLE Applies a style locally 200 TITLE Adds tool tips to elements 181 Identifies the HTML version
MOST TAGS CLASS Divides tags into groups for applying styles 202 ID Identifies a specific tag 201 STYLE Applies a style locally 200 TITLE Adds tool tips to elements 181 Identifies the HTML version
The [HTML] Element p. 61 The [HEAD] Element p. 62 The [TITLE] Element p. 63 The [BODY] Element p. 66 HTML Elements p. 66 Core Attributes p.
![The [HTML] Element p. 61 The [HEAD] Element p. 62 The [TITLE] Element p. 63 The [BODY] Element p. 66 HTML Elements p. 66 Core Attributes p. The [HTML] Element p. 61 The [HEAD] Element p. 62 The [TITLE] Element p. 63 The [BODY] Element p. 66 HTML Elements p. 66 Core Attributes p.](/thumbs/77/76655283.jpg) Acknowledgments p. xix Preface p. xxi Web Basics Introduction to HTML p. 3 Basic HTML Concepts p. 4 HTML: A Structured Language p. 7 Overview of HTML Markup p. 11 Logical and Physical HTML p. 13 What HTML
Acknowledgments p. xix Preface p. xxi Web Basics Introduction to HTML p. 3 Basic HTML Concepts p. 4 HTML: A Structured Language p. 7 Overview of HTML Markup p. 11 Logical and Physical HTML p. 13 What HTML
Certified HTML Designer VS-1027
 VS-1027 Certification Code VS-1027 Certified HTML Designer Certified HTML Designer HTML Designer Certification allows organizations to easily develop website and other web based applications which are
VS-1027 Certification Code VS-1027 Certified HTML Designer Certified HTML Designer HTML Designer Certification allows organizations to easily develop website and other web based applications which are
HTML Markup for Accessibility You Never Knew About
 HTML Markup for Accessibility You Never Knew About David Epler dcepler@dcepler.net June 27, 2004 HTML Revisions HTML 2.0 November 1995 Base version everyone learned HTML 3.2 January 1997 Tried to reconcile
HTML Markup for Accessibility You Never Knew About David Epler dcepler@dcepler.net June 27, 2004 HTML Revisions HTML 2.0 November 1995 Base version everyone learned HTML 3.2 January 1997 Tried to reconcile
Certified HTML5 Developer VS-1029
 VS-1029 Certified HTML5 Developer Certification Code VS-1029 HTML5 Developer Certification enables candidates to develop websites and web based applications which are having an increased demand in the
VS-1029 Certified HTML5 Developer Certification Code VS-1029 HTML5 Developer Certification enables candidates to develop websites and web based applications which are having an increased demand in the
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. Chapter 1: Creating Structured Documents 1
 59313ftoc.qxd:WroxPro 3/22/08 2:31 PM Page xi Introduction xxiii Chapter 1: Creating Structured Documents 1 A Web of Structured Documents 1 Introducing XHTML 2 Core Elements and Attributes 9 The
59313ftoc.qxd:WroxPro 3/22/08 2:31 PM Page xi Introduction xxiii Chapter 1: Creating Structured Documents 1 A Web of Structured Documents 1 Introducing XHTML 2 Core Elements and Attributes 9 The
Index. CSS directive, # (octothorpe), intrapage links, 26
 Holzschlag_.qxd 3/30/05 9:23 AM Page 299 Symbols @import CSS directive, 114-115 # (octothorpe), intrapage links, 26 A a element, 23, 163, 228 abbr element, 228 absolute keywords for font sizing, 144 absolute
Holzschlag_.qxd 3/30/05 9:23 AM Page 299 Symbols @import CSS directive, 114-115 # (octothorpe), intrapage links, 26 A a element, 23, 163, 228 abbr element, 228 absolute keywords for font sizing, 144 absolute
Oliver Pott HTML XML. new reference. Markt+Technik Verlag
 Oliver Pott HTML XML new reference Markt+Technik Verlag Inhaltsverzeichnis Übersicht 13 14 A 15 A 16 ABBR 23 ABBR 23 ACCEPT 26 ACCEPT-CHARSET
Oliver Pott HTML XML new reference Markt+Technik Verlag Inhaltsverzeichnis Übersicht 13 14 A 15 A 16 ABBR 23 ABBR 23 ACCEPT 26 ACCEPT-CHARSET
Evaluation of alignment methods for HTML parallel text 1
 Evaluation of alignment methods for HTML parallel text 1 Enrique Sánchez-Villamil, Susana Santos-Antón, Sergio Ortiz-Rojas, Mikel L. Forcada Transducens Group, Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics
Evaluation of alignment methods for HTML parallel text 1 Enrique Sánchez-Villamil, Susana Santos-Antón, Sergio Ortiz-Rojas, Mikel L. Forcada Transducens Group, Departament de Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics
5-Sep-16 Copyright 2016 by GemTalk Systems LLC 1
 So far we have identified the specific Seaside messages to create particular HTML constructs in an adhoc manner as needed for particular features. Now we will attempt a more systematic approach by looking
So far we have identified the specific Seaside messages to create particular HTML constructs in an adhoc manner as needed for particular features. Now we will attempt a more systematic approach by looking
UNIT II Dynamic HTML and web designing
 UNIT II Dynamic HTML and web designing HTML is a language for describing web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is not a programming language, it is a markup language A markup language
UNIT II Dynamic HTML and web designing HTML is a language for describing web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML is not a programming language, it is a markup language A markup language
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE New Selectors New Properties Animations 2D/3D Transformations Rounded Corners Shadow Effects Downloadable Fonts @ purgeru.deviantart.com WHAT IS HTML5? HTML5 is being developed as
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE New Selectors New Properties Animations 2D/3D Transformations Rounded Corners Shadow Effects Downloadable Fonts @ purgeru.deviantart.com WHAT IS HTML5? HTML5 is being developed as
Beginning Web Programming with HTML, XHTML, and CSS. Second Edition. Jon Duckett
 Beginning Web Programming with HTML, XHTML, and CSS Second Edition Jon Duckett Beginning Web Programming with HTML, XHTML, and CSS Introduction............................................... xxiii Chapter
Beginning Web Programming with HTML, XHTML, and CSS Second Edition Jon Duckett Beginning Web Programming with HTML, XHTML, and CSS Introduction............................................... xxiii Chapter
Chapter 2:- Introduction to XHTML. Compiled By:- Sanjay Patel Assistant Professor, SVBIT.
 Chapter 2:- Introduction to XHTML Compiled By:- Assistant Professor, SVBIT. Outline Introduction to XHTML Move to XHTML Meta tags Character entities Frames and frame sets Inside Browser What is XHTML?
Chapter 2:- Introduction to XHTML Compiled By:- Assistant Professor, SVBIT. Outline Introduction to XHTML Move to XHTML Meta tags Character entities Frames and frame sets Inside Browser What is XHTML?
A HTML document has two sections 1) HEAD section and 2) BODY section A HTML file is saved with.html or.htm extension
 HTML Website is a collection of web pages on a particular topic, or of a organization, individual, etc. It is stored on a computer on Internet called Web Server, WWW stands for World Wide Web, also called
HTML Website is a collection of web pages on a particular topic, or of a organization, individual, etc. It is stored on a computer on Internet called Web Server, WWW stands for World Wide Web, also called
Announcements. Paper due this Wednesday
 Announcements Paper due this Wednesday 1 Client and Server Client and server are two terms frequently used Client/Server Model Client/Server model when talking about software Client/Server model when talking
Announcements Paper due this Wednesday 1 Client and Server Client and server are two terms frequently used Client/Server Model Client/Server model when talking about software Client/Server model when talking
@namespace url(http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml); /* set default namespace to HTML */ /* bidi */
 / BEGIN LICENSE BLOCK Version: MPL 1.1/GPL 2.0/LGPL 2.1 The contents of this file are subject to the Mozilla Public License Version 1.1 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
/ BEGIN LICENSE BLOCK Version: MPL 1.1/GPL 2.0/LGPL 2.1 The contents of this file are subject to the Mozilla Public License Version 1.1 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
Inline Elements Karl Kasischke WCC INP 150 Winter
 Inline Elements 2009 Karl Kasischke WCC INP 150 Winter 2009 1 Inline Elements Emphasizing Text Increasing / Decreasing Text Size Quotes and Citations Code, Variables, and Sample Output Spanning Text Subscripts
Inline Elements 2009 Karl Kasischke WCC INP 150 Winter 2009 1 Inline Elements Emphasizing Text Increasing / Decreasing Text Size Quotes and Citations Code, Variables, and Sample Output Spanning Text Subscripts
Tutorial 2 - HTML basics
 Tutorial 2 - HTML basics Developing a Web Site The first phase in creating a new web site is planning. This involves determining the site s navigation structure, content, and page layout. It is only after
Tutorial 2 - HTML basics Developing a Web Site The first phase in creating a new web site is planning. This involves determining the site s navigation structure, content, and page layout. It is only after
WML2.0 TUTORIAL. The XHTML Basic defined by the W3C is a proper subset of XHTML, which is a reformulation of HTML in XML.
 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/wml/wml2_tutorial.htm WML2.0 TUTORIAL Copyright tutorialspoint.com WML2 is a language, which extends the syntax and semantics of the followings: XHTML Basic [ XHTMLBasic ]
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/wml/wml2_tutorial.htm WML2.0 TUTORIAL Copyright tutorialspoint.com WML2 is a language, which extends the syntax and semantics of the followings: XHTML Basic [ XHTMLBasic ]
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. Introduction. Chapter 1: Structuring Documents for the Web 1
 Introduction Chapter 1: Structuring Documents for the Web 1 A Web of Structured Documents 1 Introducing HTML and XHTML 2 Tags and Elements 4 Separating Heads from Bodies 5 Attributes Tell Us About Elements
Introduction Chapter 1: Structuring Documents for the Web 1 A Web of Structured Documents 1 Introducing HTML and XHTML 2 Tags and Elements 4 Separating Heads from Bodies 5 Attributes Tell Us About Elements
Canvas & Brush Reference. Source: stock.xchng, Maarten Uilenbroek
 Canvas & Brush Reference Source: stock.xchng, Maarten Uilenbroek Canvas Hierarchy WACanvas WAHtmlCanvas WARenderCanvas WAStaticHtmlCanvas Brush Hierarchy WABrush WACompound WADateInput WATimeInput WATagBrush
Canvas & Brush Reference Source: stock.xchng, Maarten Uilenbroek Canvas Hierarchy WACanvas WAHtmlCanvas WARenderCanvas WAStaticHtmlCanvas Brush Hierarchy WABrush WACompound WADateInput WATimeInput WATagBrush
Wireframe :: tistory wireframe tistory.
 Page 1 of 45 Wireframe :: tistory wireframe tistory Daum Tistory GO Home Location Tags Media Guestbook Admin 'XHTML+CSS' 7 1 2009/09/20 [ ] XHTML CSS - 6 (2) 2 2009/07/23 [ ] XHTML CSS - 5 (6) 3 2009/07/17
Page 1 of 45 Wireframe :: tistory wireframe tistory Daum Tistory GO Home Location Tags Media Guestbook Admin 'XHTML+CSS' 7 1 2009/09/20 [ ] XHTML CSS - 6 (2) 2 2009/07/23 [ ] XHTML CSS - 5 (6) 3 2009/07/17
Basics of Web Design, 3 rd Edition Instructor Materials Chapter 2 Test Bank
 Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer. 1. What element is used to configure a new paragraph? a. new b. paragraph c. p d. div 2. What element is used to create the largest heading? a. h1 b. h9 c. head
Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer. 1. What element is used to configure a new paragraph? a. new b. paragraph c. p d. div 2. What element is used to create the largest heading? a. h1 b. h9 c. head
HTML Summary. All of the following are containers. Structure. Italics Bold. Line Break. Horizontal Rule. Non-break (hard) space.
 HTML Summary Structure All of the following are containers. Structure Contains the entire web page. Contains information
HTML Summary Structure All of the following are containers. Structure Contains the entire web page. Contains information
CPET 499/ITC 250 Web Systems. Topics
 CPET 499/ITC 250 Web Systems Lecture on HTML and XHTML, Web Browsers, and Web Servers References: * Fundamentals of Web Development, 2015 ed., by Randy Connolly and Richard Hoar, from Pearson *Chapter
CPET 499/ITC 250 Web Systems Lecture on HTML and XHTML, Web Browsers, and Web Servers References: * Fundamentals of Web Development, 2015 ed., by Randy Connolly and Richard Hoar, from Pearson *Chapter
Advanced Web Programming C2. Basic Web Technologies
 Politehnica University of Timisoara Advanced Web Programming C2. Basic Web Technologies 2013 UPT-AC Assoc.Prof.Dr. Dan Pescaru HTML Originally developed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990 at CERN (Conseil Européen
Politehnica University of Timisoara Advanced Web Programming C2. Basic Web Technologies 2013 UPT-AC Assoc.Prof.Dr. Dan Pescaru HTML Originally developed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990 at CERN (Conseil Européen
Symbols INDEX. !important rule, rule, , 146, , rule,
 Symbols!important rule, 209 @import rule, 140-144, 146, 155-156, 157 @media rule, 155-156 A element. See anchors abbr attribute, 36-37 element, 87, 90-91 absolute positioning, 177, 178, 182,
Symbols!important rule, 209 @import rule, 140-144, 146, 155-156, 157 @media rule, 155-156 A element. See anchors abbr attribute, 36-37 element, 87, 90-91 absolute positioning, 177, 178, 182,
Designing UI. Mine mine-cetinkaya-rundel
 Designing UI Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel @minebocek mine-cetinkaya-rundel mine@stat.duke.edu - Web application UI is ultimately HTML/CSS/JavaScript - Let R users write user interfaces using a simple, familiar-looking
Designing UI Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel @minebocek mine-cetinkaya-rundel mine@stat.duke.edu - Web application UI is ultimately HTML/CSS/JavaScript - Let R users write user interfaces using a simple, familiar-looking
HTML BEGINNING TAGS. HTML Structure <html> <head> <title> </title> </head> <body> Web page content </body> </html>
 HTML BEGINNING TAGS HTML Structure Web page content Structure tags: Tags used to give structure to the document.
HTML BEGINNING TAGS HTML Structure Web page content Structure tags: Tags used to give structure to the document.
HTML TUTORIAL ONE. Understanding What XHTML is Not
 HTML TUTORIAL ONE Defining Blended HTML, XHTML and CSS HTML: o Language used to create Web pages o Create code to describe structure of a Web page XHTM: o Variation of HTML o More strictly defines how
HTML TUTORIAL ONE Defining Blended HTML, XHTML and CSS HTML: o Language used to create Web pages o Create code to describe structure of a Web page XHTM: o Variation of HTML o More strictly defines how
HTML and CSS COURSE SYLLABUS
 HTML and CSS COURSE SYLLABUS Overview: HTML and CSS go hand in hand for developing flexible, attractively and user friendly websites. HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language) is used to show content on the page
HTML and CSS COURSE SYLLABUS Overview: HTML and CSS go hand in hand for developing flexible, attractively and user friendly websites. HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language) is used to show content on the page
"utf-8";
 http://salsa-copacabana.com/css/import.css @charset "Shift_JIS"; /* ------------------------------------------ File name: import.css Style Info: CSS screen Windwos IE4 ------------------------------------------
http://salsa-copacabana.com/css/import.css @charset "Shift_JIS"; /* ------------------------------------------ File name: import.css Style Info: CSS screen Windwos IE4 ------------------------------------------
Chapter 1 Self Test. LATIHAN BAB 1. tjetjeprb{at}gmail{dot}com. webdesign/favorites.html :// / / / that houses that information. structure?
 LATIHAN BAB 1 Chapter 1 Self Test 1. What is a web browser? 2. What does HTML stand for? 3. Identify the various parts of the following URL: http://www.mcgrawhill.com/books/ webdesign/favorites.html ://
LATIHAN BAB 1 Chapter 1 Self Test 1. What is a web browser? 2. What does HTML stand for? 3. Identify the various parts of the following URL: http://www.mcgrawhill.com/books/ webdesign/favorites.html ://
c122jan2714.notebook January 27, 2014
 Internet Developer 1 Start here! 2 3 Right click on screen and select View page source if you are in Firefox tells the browser you are using html. Next we have the tag and at the
Internet Developer 1 Start here! 2 3 Right click on screen and select View page source if you are in Firefox tells the browser you are using html. Next we have the tag and at the
Name Related Elements Type Default Depr. DTD Comment
 Legend: Deprecated, Loose DTD, Frameset DTD Name Related Elements Type Default Depr. DTD Comment abbr TD, TH %Text; accept-charset FORM %Charsets; accept FORM, INPUT %ContentTypes; abbreviation for header
Legend: Deprecated, Loose DTD, Frameset DTD Name Related Elements Type Default Depr. DTD Comment abbr TD, TH %Text; accept-charset FORM %Charsets; accept FORM, INPUT %ContentTypes; abbreviation for header
A Brief Introduction to HTML
 A P P E N D I X HTML SuMMAry J A Brief Introduction to HTML A web page is written in a language called HTML (Hypertext Markup Language). Like Java code, HTML code is made up of text that follows certain
A P P E N D I X HTML SuMMAry J A Brief Introduction to HTML A web page is written in a language called HTML (Hypertext Markup Language). Like Java code, HTML code is made up of text that follows certain
INTRODUCTION TO HTML5! HTML5 Page Structure!
 INTRODUCTION TO HTML5! HTML5 Page Structure! What is HTML5? HTML5 will be the new standard for HTML, XHTML, and the HTML DOM. The previous version of HTML came in 1999. The web has changed a lot since
INTRODUCTION TO HTML5! HTML5 Page Structure! What is HTML5? HTML5 will be the new standard for HTML, XHTML, and the HTML DOM. The previous version of HTML came in 1999. The web has changed a lot since
CSC 121 Computers and Scientific Thinking
 CSC 121 Computers and Scientific Thinking Fall 2005 HTML and Web Pages 1 HTML & Web Pages recall: a Web page is a text document that contains additional formatting information in the HyperText Markup Language
CSC 121 Computers and Scientific Thinking Fall 2005 HTML and Web Pages 1 HTML & Web Pages recall: a Web page is a text document that contains additional formatting information in the HyperText Markup Language
Duke Library Website Preliminary Accessibility Assessment
 Duke Library Website Preliminary Accessibility Assessment RAW OUTPUT FROM CYNTHIASAYS December 15, 2011 Michael Daul, Digital Projects Developer Digital Experience Services HiSoftware Cynthia Says - Web
Duke Library Website Preliminary Accessibility Assessment RAW OUTPUT FROM CYNTHIASAYS December 15, 2011 Michael Daul, Digital Projects Developer Digital Experience Services HiSoftware Cynthia Says - Web
Deccansoft Software Services
 Deccansoft Software Services (A Microsoft Learning Partner) HTML and CSS COURSE SYLLABUS Module 1: Web Programming Introduction In this module you will learn basic introduction to web development. Module
Deccansoft Software Services (A Microsoft Learning Partner) HTML and CSS COURSE SYLLABUS Module 1: Web Programming Introduction In this module you will learn basic introduction to web development. Module
Winwap Technologies Oy. WinWAP Browser. Application Environment
 Winwap Technologies Oy WinWAP Browser Application Environment WinWAP Browser version 4.0 WAP Specification version 2.0 Wireless Markup Language Specification version 2.0 Document dated: 26 Mar 2007 Notice
Winwap Technologies Oy WinWAP Browser Application Environment WinWAP Browser version 4.0 WAP Specification version 2.0 Wireless Markup Language Specification version 2.0 Document dated: 26 Mar 2007 Notice
Chapter 1 Getting Started with HTML 5 1. Chapter 2 Introduction to New Elements in HTML 5 21
 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Getting Started with HTML 5 1 Introduction to HTML 5... 2 New API... 2 New Structure... 3 New Markup Elements and Attributes... 3 New Form Elements and Attributes... 4 Geolocation...
Table of Contents Chapter 1 Getting Started with HTML 5 1 Introduction to HTML 5... 2 New API... 2 New Structure... 3 New Markup Elements and Attributes... 3 New Form Elements and Attributes... 4 Geolocation...
13.8 How to specify alternate text
 13.8 How to specify alternate text Attribute definitions alt = text [p.50] [CS] [p.49] For user agents that cannot display images, forms, or applets, this attribute specifies alternate text. The language
13.8 How to specify alternate text Attribute definitions alt = text [p.50] [CS] [p.49] For user agents that cannot display images, forms, or applets, this attribute specifies alternate text. The language
recall: a Web page is a text document that contains additional formatting information in the HyperText Markup Language (HTML)
 HTML & Web Pages recall: a Web page is a text document that contains additional formatting information in the HyperText Markup Language (HTML) HTML specifies formatting within a page using tags in its
HTML & Web Pages recall: a Web page is a text document that contains additional formatting information in the HyperText Markup Language (HTML) HTML specifies formatting within a page using tags in its
1.264 Lecture 12. HTML Introduction to FrontPage
 1.264 Lecture 12 HTML Introduction to FrontPage HTML Subset of Structured Generalized Markup Language (SGML), a document description language SGML is ISO standard Current version of HTML is version 4.01
1.264 Lecture 12 HTML Introduction to FrontPage HTML Subset of Structured Generalized Markup Language (SGML), a document description language SGML is ISO standard Current version of HTML is version 4.01
CSC Web Programming. Introduction to HTML
 CSC 242 - Web Programming Introduction to HTML Semantic Markup The purpose of HTML is to add meaning and structure to the content HTML is not intended for presentation, that is the job of CSS When marking
CSC 242 - Web Programming Introduction to HTML Semantic Markup The purpose of HTML is to add meaning and structure to the content HTML is not intended for presentation, that is the job of CSS When marking
Html basics Course Outline
 Html basics Course Outline Description Learn the essential skills you will need to create your web pages with HTML. Topics include: adding text any hyperlinks, images and backgrounds, lists, tables, and
Html basics Course Outline Description Learn the essential skills you will need to create your web pages with HTML. Topics include: adding text any hyperlinks, images and backgrounds, lists, tables, and
HTML CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications
 HTML CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications 1 Anatomy of (Basic) Website Your content + HTML + CSS = Your website structure presentation A website is a way to present your content to the world,
HTML CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications 1 Anatomy of (Basic) Website Your content + HTML + CSS = Your website structure presentation A website is a way to present your content to the world,
Web Designing HTML5 NOTES
 Web Designing HTML5 NOTES HTML Introduction What is HTML? HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML describes the structure of Web pages
Web Designing HTML5 NOTES HTML Introduction What is HTML? HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML describes the structure of Web pages
HTML Cheat Sheet for Beginners
 HTML Cheat Sheet for Beginners HTML Cheat Sheet for Beginners Trying to remember every HTML element is like trying to remember all of your personal information, credit card, bank account numbers and your
HTML Cheat Sheet for Beginners HTML Cheat Sheet for Beginners Trying to remember every HTML element is like trying to remember all of your personal information, credit card, bank account numbers and your
CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0
 WEB TECHNOLOGIES A COMPUTER SCIENCE PERSPECTIVE CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0 Modified by Ahmed Sallam Based on original slides by Jeffrey C. Jackson reserved. 0-13-185603-0 HTML HELLO WORLD! Document
WEB TECHNOLOGIES A COMPUTER SCIENCE PERSPECTIVE CHAPTER 2 MARKUP LANGUAGES: XHTML 1.0 Modified by Ahmed Sallam Based on original slides by Jeffrey C. Jackson reserved. 0-13-185603-0 HTML HELLO WORLD! Document
Web Programming and Design. MPT Senior Cycle Tutor: Tamara Week 1
 Web Programming and Design MPT Senior Cycle Tutor: Tamara Week 1 What will we cover? HTML - Website Structure and Layout CSS - Website Style JavaScript - Makes our Website Dynamic and Interactive Plan
Web Programming and Design MPT Senior Cycle Tutor: Tamara Week 1 What will we cover? HTML - Website Structure and Layout CSS - Website Style JavaScript - Makes our Website Dynamic and Interactive Plan
GRAPHIC WEB DESIGNER PROGRAM
 NH128 HTML Level 1 24 Total Hours COURSE TITLE: HTML Level 1 COURSE OVERVIEW: This course introduces web designers to the nuts and bolts of HTML (HyperText Markup Language), the programming language used
NH128 HTML Level 1 24 Total Hours COURSE TITLE: HTML Level 1 COURSE OVERVIEW: This course introduces web designers to the nuts and bolts of HTML (HyperText Markup Language), the programming language used
Co. Louth VEC & Co. Monaghan VEC. Programme Module for. Web Authoring. leading to. Level 5 FETAC. Web Authoring 5N1910
 Co. Louth VEC & Co. Monaghan VEC Programme Module for Web Authoring leading to Level 5 FETAC Web Authoring 5N1910 Web Authoring 5N1910 1 Introduction This programme module may be delivered as a standalone
Co. Louth VEC & Co. Monaghan VEC Programme Module for Web Authoring leading to Level 5 FETAC Web Authoring 5N1910 Web Authoring 5N1910 1 Introduction This programme module may be delivered as a standalone
HTML Hyper Text Markup Language
 HTML Hyper Text Markup Language Home About Services index.html about.html services.html Homepage = index.html site root index.html about.html services.html images headshot.jpg charlie.jpg A webpage built
HTML Hyper Text Markup Language Home About Services index.html about.html services.html Homepage = index.html site root index.html about.html services.html images headshot.jpg charlie.jpg A webpage built
1/6/ :28 AM Approved New Course (First Version) CS 50A Course Outline as of Fall 2014
 1/6/2019 12:28 AM Approved New Course (First Version) CS 50A Course Outline as of Fall 2014 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: CS 50A Title: WEB DEVELOPMENT 1 Full Title: Web Development 1 Last Reviewed:
1/6/2019 12:28 AM Approved New Course (First Version) CS 50A Course Outline as of Fall 2014 CATALOG INFORMATION Dept and Nbr: CS 50A Title: WEB DEVELOPMENT 1 Full Title: Web Development 1 Last Reviewed:
NEW WEBMASTER HTML & CSS FOR BEGINNERS COURSE SYNOPSIS
 NEW WEBMASTER HTML & CSS FOR BEGINNERS COURSE SYNOPSIS LESSON 1 GETTING STARTED Before We Get Started; Pre requisites; The Notepad++ Text Editor; Download Chrome, Firefox, Opera, & Safari Browsers; The
NEW WEBMASTER HTML & CSS FOR BEGINNERS COURSE SYNOPSIS LESSON 1 GETTING STARTED Before We Get Started; Pre requisites; The Notepad++ Text Editor; Download Chrome, Firefox, Opera, & Safari Browsers; The
BACKGROUND. HTTP is a 2-phase protocol used by most web applications and all web browsers. The response is usually an HTML document
 HTML 2 BACKGROUND HTTP is a 2-phase protocol used by most web applications and all web browsers REQUEST: a client/browser asks a server for a resource RESPONSE: the server responds with the resource The
HTML 2 BACKGROUND HTTP is a 2-phase protocol used by most web applications and all web browsers REQUEST: a client/browser asks a server for a resource RESPONSE: the server responds with the resource The
Chapter 2 Creating and Editing a Web Page
 Chapter 2 Creating and Editing a Web Page MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. is a basic text editor installed with Windows that you can use for simple documents or for creating Web pages using HTML. a. Microsoft Word
Chapter 2 Creating and Editing a Web Page MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. is a basic text editor installed with Windows that you can use for simple documents or for creating Web pages using HTML. a. Microsoft Word
introduction to XHTML
 introduction to XHTML XHTML stands for Extensible HyperText Markup Language and is based on HTML 4.0, incorporating XML. Due to this fusion the mark up language will remain compatible with existing browsers
introduction to XHTML XHTML stands for Extensible HyperText Markup Language and is based on HTML 4.0, incorporating XML. Due to this fusion the mark up language will remain compatible with existing browsers
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E
 A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 2 HTML and Web Pages 1 HTML & Web Pages recall: a Web page is
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 2 HTML and Web Pages 1 HTML & Web Pages recall: a Web page is
Cascading Style Sheet
 Extra notes - Markup Languages Dr Nick Hayward CSS - Basics A brief introduction to the basics of CSS. Contents Intro CSS syntax rulesets comments display Display and elements inline block-level CSS selectors
Extra notes - Markup Languages Dr Nick Hayward CSS - Basics A brief introduction to the basics of CSS. Contents Intro CSS syntax rulesets comments display Display and elements inline block-level CSS selectors
<page> 1 Document Summary Document Information <page> 2 Document Structure Text Formatting <page> 3 Links Images <page> 4
 Document Summary Document Information Document Structure Text Formatting Links Images Lists Forms Input Type Attributes Select Attributes Option Attributes Table Formatting Objects and iframes iframe Attributes
Document Summary Document Information Document Structure Text Formatting Links Images Lists Forms Input Type Attributes Select Attributes Option Attributes Table Formatting Objects and iframes iframe Attributes
Revision for Grade 7 ASP in Unit :1&2 Design & Technology Subject
 Your Name:.... Grade 7 - SECTION 1 Matching :Match the terms with its explanations. Write the matching letter in the correct box. The first one has been done for you. (1 mark each) Term Explanation 1.
Your Name:.... Grade 7 - SECTION 1 Matching :Match the terms with its explanations. Write the matching letter in the correct box. The first one has been done for you. (1 mark each) Term Explanation 1.
Web Design and Application Development
 Yarmouk University Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees (PFISR) Web Design and Application Development Dr. Abdel-Karim Al-Tamimi altamimi@yu.edu.jo Lecture 02 A. Al-Tamimi 1 Lecture Overview
Yarmouk University Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees (PFISR) Web Design and Application Development Dr. Abdel-Karim Al-Tamimi altamimi@yu.edu.jo Lecture 02 A. Al-Tamimi 1 Lecture Overview
Skill Area 323: Design and Develop Website. Multimedia and Web Design (MWD)
 Skill Area 323: Design and Develop Website Multimedia and Web Design (MWD) 323.2 Work with Text and Hypertext (7 hrs) 323.2.1 Add headings, subheadings and body text 323.2.2 Format text according to specifications
Skill Area 323: Design and Develop Website Multimedia and Web Design (MWD) 323.2 Work with Text and Hypertext (7 hrs) 323.2.1 Add headings, subheadings and body text 323.2.2 Format text according to specifications
Web Development & Design Foundations with HTML5 & CSS3 Instructor Materials Chapter 2 Test Bank
 Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer. 1. What tag pair is used to create a new paragraph? a. b. c. d. 2. What tag pair
Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer. 1. What tag pair is used to create a new paragraph? a. b. c. d. 2. What tag pair
Web Development & Design Foundations with XHTML. Chapter 2 Key Concepts
 Web Development & Design Foundations with XHTML Chapter 2 Key Concepts Learning Outcomes In this chapter, you will learn about: XHTML syntax, tags, and document type definitions The anatomy of a web page
Web Development & Design Foundations with XHTML Chapter 2 Key Concepts Learning Outcomes In this chapter, you will learn about: XHTML syntax, tags, and document type definitions The anatomy of a web page
Web Programming Week 2 Semester Byron Fisher 2018
 Web Programming Week 2 Semester 1-2018 Byron Fisher 2018 INTRODUCTION Welcome to Week 2! In the next 60 minutes you will be learning about basic Web Programming with a view to creating your own ecommerce
Web Programming Week 2 Semester 1-2018 Byron Fisher 2018 INTRODUCTION Welcome to Week 2! In the next 60 minutes you will be learning about basic Web Programming with a view to creating your own ecommerce
Static Webpage Development
 Dear Student, Based upon your enquiry we are pleased to send you the course curriculum for PHP Given below is the brief description for the course you are looking for: - Static Webpage Development Introduction
Dear Student, Based upon your enquiry we are pleased to send you the course curriculum for PHP Given below is the brief description for the course you are looking for: - Static Webpage Development Introduction
Text and Layout. Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition Nigel Chapman & Jenny Chapman Chapter 11. This presentation 2004, MacAvon Media Productions
 Text and Layout Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition Nigel Chapman & Jenny Chapman Chapter 11 This presentation 344 345 Text in Graphics Maximum flexibility obtained by treating text as graphics and manipulating
Text and Layout Digital Multimedia, 2nd edition Nigel Chapman & Jenny Chapman Chapter 11 This presentation 344 345 Text in Graphics Maximum flexibility obtained by treating text as graphics and manipulating
As we design and build out our HTML pages, there are some basics that we may follow for each page, site, and application.
 Extra notes - Client-side Design and Development Dr Nick Hayward HTML - Basics A brief introduction to some of the basics of HTML. Contents Intro element add some metadata define a base address
Extra notes - Client-side Design and Development Dr Nick Hayward HTML - Basics A brief introduction to some of the basics of HTML. Contents Intro element add some metadata define a base address
Study Guide 2 - HTML and CSS - Chap. 6,8,10,11,12 Name - Alexia Bernardo
 Study Guide 2 - HTML and CSS - Chap. 6,8,10,11,12 Name - Alexia Bernardo Note: We skipped Study Guide 1. If you d like to review it, I place a copy here: https:// people.rit.edu/~nbbigm/studyguides/sg-1.docx
Study Guide 2 - HTML and CSS - Chap. 6,8,10,11,12 Name - Alexia Bernardo Note: We skipped Study Guide 1. If you d like to review it, I place a copy here: https:// people.rit.edu/~nbbigm/studyguides/sg-1.docx
HTML+ CSS PRINCIPLES. Getting started with web design the right way
 HTML+ CSS PRINCIPLES Getting started with web design the right way HTML : a brief history ❶ 1960s : ARPANET is developed... It is the first packet-switching network using TCP/IP protocol and is a precursor
HTML+ CSS PRINCIPLES Getting started with web design the right way HTML : a brief history ❶ 1960s : ARPANET is developed... It is the first packet-switching network using TCP/IP protocol and is a precursor
HTML HTML/XHTML HTML / XHTML HTML HTML: XHTML: (extensible HTML) Loose syntax Few syntactic rules: not enforced by HTML processors.
 HTML HTML/XHTML HyperText Mark-up Language Basic language for WWW documents Format a web page s look, position graphics and multimedia elements Describe document structure and formatting Platform independent:
HTML HTML/XHTML HyperText Mark-up Language Basic language for WWW documents Format a web page s look, position graphics and multimedia elements Describe document structure and formatting Platform independent:
Creating Accessible Web Sites with EPiServer
 Creating Accessible Web Sites with EPiServer Abstract This white paper describes how EPiServer promotes the creation of accessible Web sites. Product version: 4.50 Document version: 1.0 2 Creating Accessible
Creating Accessible Web Sites with EPiServer Abstract This white paper describes how EPiServer promotes the creation of accessible Web sites. Product version: 4.50 Document version: 1.0 2 Creating Accessible
Programmazione Web a.a. 2017/2018 HTML5
 Programmazione Web a.a. 2017/2018 HTML5 PhD Ing.Antonino Raucea antonino.raucea@dieei.unict.it 1 Introduzione HTML HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text
Programmazione Web a.a. 2017/2018 HTML5 PhD Ing.Antonino Raucea antonino.raucea@dieei.unict.it 1 Introduzione HTML HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML stands for Hyper Text
Internet publishing HTML (XHTML) language. Petr Zámostný room: A-72a phone.:
 Internet publishing HTML (XHTML) language Petr Zámostný room: A-72a phone.: 4222 e-mail: petr.zamostny@vscht.cz Essential HTML components Element element example Start tag Element content End tag
Internet publishing HTML (XHTML) language Petr Zámostný room: A-72a phone.: 4222 e-mail: petr.zamostny@vscht.cz Essential HTML components Element element example Start tag Element content End tag
HTML. Based mostly on
 HTML Based mostly on www.w3schools.com What is HTML? The standard markup language for creating Web pages HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML describes the structure of Web pages using markup
HTML Based mostly on www.w3schools.com What is HTML? The standard markup language for creating Web pages HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language HTML describes the structure of Web pages using markup
Hyper Text Markup Language HTML: A Tutorial
 Hyper Text Markup Language HTML: A Tutorial Ahmed Othman Eltahawey December 21, 2016 The World Wide Web (WWW) is an information space where documents and other web resources are located. Web is identified
Hyper Text Markup Language HTML: A Tutorial Ahmed Othman Eltahawey December 21, 2016 The World Wide Web (WWW) is an information space where documents and other web resources are located. Web is identified
Bok, Jong Soon
 HTML 5 Grouping Contents Bok, Jong Soon jongsoon.bok@gmail.com www.javaexpert.co.kr Defines a paragraph. Browsers automatically add some space (margin) before and after each element. Differences
HTML 5 Grouping Contents Bok, Jong Soon jongsoon.bok@gmail.com www.javaexpert.co.kr Defines a paragraph. Browsers automatically add some space (margin) before and after each element. Differences
Appendix A. XHTML 1.1 Module Reference
 Appendix A XHTML 1.1 Module Reference 2 How to Do Everything with HTML & XHTML XHTML 1.1 represents a major step by the W3C in moving away from the often-disorderly world of HTML to the organized and orderly
Appendix A XHTML 1.1 Module Reference 2 How to Do Everything with HTML & XHTML XHTML 1.1 represents a major step by the W3C in moving away from the often-disorderly world of HTML to the organized and orderly
Web development using PHP & MySQL with HTML5, CSS, JavaScript
 Web development using PHP & MySQL with HTML5, CSS, JavaScript Static Webpage Development Introduction to web Browser Website Webpage Content of webpage Static vs dynamic webpage Technologies to create
Web development using PHP & MySQL with HTML5, CSS, JavaScript Static Webpage Development Introduction to web Browser Website Webpage Content of webpage Static vs dynamic webpage Technologies to create
Web Publishing Basics I
 Web Publishing Basics I Jeff Pankin Information Services and Technology Contents Course Objectives... 2 Creating a Web Page with HTML... 3 What is Dreamweaver?... 3 What is HTML?... 3 What are the basic
Web Publishing Basics I Jeff Pankin Information Services and Technology Contents Course Objectives... 2 Creating a Web Page with HTML... 3 What is Dreamweaver?... 3 What is HTML?... 3 What are the basic
Bridges To Computing
 Bridges To Computing General Information: This document was created for use in the "Bridges to Computing" project of Brooklyn College. You are invited and encouraged to use this presentation to promote
Bridges To Computing General Information: This document was created for use in the "Bridges to Computing" project of Brooklyn College. You are invited and encouraged to use this presentation to promote
Aleph - Web Opac Accessibility. Accessibility in Aleph500 Web OPAC
 Accessibility in Aleph500 Web OPAC 1 CHANGE CONTROL Version Date Author Description 0.1 29.05.2007 Initial draft - v16 1.0 12.06.2007 Version for release - v16 1.1 15.06.2006 Updates v18 initial draft
Accessibility in Aleph500 Web OPAC 1 CHANGE CONTROL Version Date Author Description 0.1 29.05.2007 Initial draft - v16 1.0 12.06.2007 Version for release - v16 1.1 15.06.2006 Updates v18 initial draft
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Markup Languages: XHTML 1.0
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Markup Languages: XHTML 1.0 HTML Hello World! Document Type Declaration Document Instance Guy-Vincent Jourdan :: CSI 3140 :: based on Jeffrey C. Jackson
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Markup Languages: XHTML 1.0 HTML Hello World! Document Type Declaration Document Instance Guy-Vincent Jourdan :: CSI 3140 :: based on Jeffrey C. Jackson
Make a Website. A complex guide to building a website through continuing the fundamentals of HTML & CSS. Created by Michael Parekh 1
 Make a Website A complex guide to building a website through continuing the fundamentals of HTML & CSS. Created by Michael Parekh 1 Overview Course outcome: You'll build four simple websites using web
Make a Website A complex guide to building a website through continuing the fundamentals of HTML & CSS. Created by Michael Parekh 1 Overview Course outcome: You'll build four simple websites using web
Next... Next... Handling the past What s next - standards and browsers What s next - applications and technology
 Next... Handling the past What s next - standards and browsers What s next - applications and technology Next... Handling the past What s next - standards and browsers What s next - applications and technology
Next... Handling the past What s next - standards and browsers What s next - applications and technology Next... Handling the past What s next - standards and browsers What s next - applications and technology
Review of HTML. Chapter Pearson. Fundamentals of Web Development. Randy Connolly and Ricardo Hoar
 Review of HTML Chapter 3 Fundamentals of Web Development 2017 Pearson Fundamentals of Web Development http://www.funwebdev.com - 2 nd Ed. What Is HTML and Where Did It Come from? HTML HTML is defined as
Review of HTML Chapter 3 Fundamentals of Web Development 2017 Pearson Fundamentals of Web Development http://www.funwebdev.com - 2 nd Ed. What Is HTML and Where Did It Come from? HTML HTML is defined as
Programming of web-based systems Introduction to HTML5
 Programming of web-based systems Introduction to HTML5 Agenda 1. HTML5 as XML 2. Basic body elements 3. Text formatting and blocks 4. Tables 5. File paths 6. Head elements 7. Layout elements 8. Entities
Programming of web-based systems Introduction to HTML5 Agenda 1. HTML5 as XML 2. Basic body elements 3. Text formatting and blocks 4. Tables 5. File paths 6. Head elements 7. Layout elements 8. Entities
Structure Bars. Tag Bar
 C H E A T S H E E T / / F L A R E 2 0 1 8 Structure Bars The XML Editor provides structure bars above and to the left of the content area in order to provide a visual display of the topic tags and structure.
C H E A T S H E E T / / F L A R E 2 0 1 8 Structure Bars The XML Editor provides structure bars above and to the left of the content area in order to provide a visual display of the topic tags and structure.
White Paper. elcome to Nokia s WAP 2.0 XHTML browser for small devices. Advantages of XHTML for Wireless Data
 elcome to Nokia s WAP 2.0 XHTML browser for small devices. Advantages of XHTML for Wireless Data Contents Introduction: WAP 2.0 is XHTML 2 XHTML Basic: Key Features and Capabilities 2 Well-Formed XML 3
elcome to Nokia s WAP 2.0 XHTML browser for small devices. Advantages of XHTML for Wireless Data Contents Introduction: WAP 2.0 is XHTML 2 XHTML Basic: Key Features and Capabilities 2 Well-Formed XML 3
!Accessibility Issues Found
 WCG2- accessibility report for http://www.messiah.edu 207-07-28!ccessibility Issues Found (6,838,98 unique issues affecting 7,45 pages) Overall accessibility compliance Done 53 issues done issues to fix/review
WCG2- accessibility report for http://www.messiah.edu 207-07-28!ccessibility Issues Found (6,838,98 unique issues affecting 7,45 pages) Overall accessibility compliance Done 53 issues done issues to fix/review
Internet Explorer HTML 4.01 Standards Support Document
 [MS-HTML401]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
[MS-HTML401]: Intellectual Property Rights Notice for Open Specifications Documentation Technical Documentation. Microsoft publishes Open Specifications documentation ( this documentation ) for protocols,
Fundamentals: Client/Server
 Announcements Class Web Site: http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/passport/classes/summer2008/ You can find this link at the end of the main passport site http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/passport/webpage/ E-mail
Announcements Class Web Site: http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/passport/classes/summer2008/ You can find this link at the end of the main passport site http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/passport/webpage/ E-mail
WCAG2-AAA accessibility report for
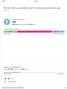 WCG2- accessibility report for http://www.messiah.edu 207-07-3 ccessibility Issues Found 30 (7,98,760 unique issues a ecting 7,629 pages) Overall accessibility compliance Done 38 issues done 30 issues
WCG2- accessibility report for http://www.messiah.edu 207-07-3 ccessibility Issues Found 30 (7,98,760 unique issues a ecting 7,629 pages) Overall accessibility compliance Done 38 issues done 30 issues
