<!DOCTYPE ichicsrack [ <!-- PUBLIC "-//ICHM2//DTD ICH ICSR Acknowledgment Vers. 1.1//EN" "ich-icsrack-v1.1.dtd" -->
|
|
|
- May Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A.7 ICH ICSR DTD <!DOCTYPE ichicsrack [ <!-- PUBLIC "-//ICHM2//DTD ICH ICSR Acknowledgment Vers. 1.1//EN" "ich-icsrack-v1.1.dtd" -- <!-- Individual Case Safety Report Acknowledgment Document Type Definition The DTD issued by the ICH M2 group and is public domain in nature. No one can claim copyright on this DTD. No commercial distribution is allowed. The ICH is not responsible for any damage or financial loss resulting from use of this DTD. This version is tentative in nature and changes are expected. This DTD is subject to the ICH M2 change control procedures. Version 1.0, Release 1.0 Version 1.1, Release 1.0, Date to be decided -- <!-- TECHNICAL NOTE ICH ICSR SGML Declaration To correctly parse an ICH ICSR SGML message requires the selection of the correct SGML declaration, along with this DTD, and the ICH ICSR SGML instance. This technical note provides guidance on which of several SGML declarations included with the ICH ICSR application to select based on the language and character set used within the ICH ICSR SGML instance. The method by which an SGML parser is told to use a specific declaration is parser specific. The three most common methods are: 1. Tell the parser via the command line which declaration to use. 2. Tell the parser via a specific environment variable which declaration to use. 3. If the parser supports SGML Open catalogs, within the catalog file is a command that can tell the parser which declaration to use. SGML catalog files are an industry standard way to tell a parser how to find all of the pieces (declaration, DTD, SGML document instance) needed to successfully parse. To cover all of the languages necessary to support the ICH ICSR application, ISO (UNICODE) would have to be used. If this were the case, then only one SGML declaration would be needed to support all ICH ICSR languages. Because UNICODE support is not available in all popular computer application programs, the ICH M2 EWG has recommended that a variety of character sets be used at this time, instead of a single UNICODE character encoding. For each of these different character encodings a different SGML declaration needs to be generated and used. 109
2 Five SGML declarations are included with the ICH ICSR distribution. They are described briefly below. ich-icsr-latin1.dcl - This SGML declaration supports the ISO (Latin 1) character set. This character set supports English, and most Western European languages. ich-icsr-latin7.dcl - This SGML declaration supports the ISO (Latin 7) character set. This character set supports Greek. ich-icsr-sjis.dcl - This SGML declaration supports the Shift JIS character set for encoding Japanese. ich-icsr-utf8.dcl - This SGML declaration supports the ISO (UNICODE) UTF-8 character set. This character set supports almost all of the worlds currently written languages. ich-icsr-mult.dcl - This SGML declaration will support all of the currently defined ICHICSR languages, and it doesn't require the use of UNICODE. It is however a "hack" that relies on a fortuitous characteristic of the languages currently being used within the ICH ICSR SGML application. This hack works because the character set documented within an SGML declaration is for the benefit of both the SGML parser, and the programmer who implements the SGML application. The programmer needs detailed knowledge of all the characters being used to correctly code an application. The parser only really needs to about some of the characters. In particular it needs to know which characters signify an SGML event. For instance that the "<" character starts an SGML open tag, and the "</" character sequence starts an SGML close tag. All told, the parser needs to know very little. Because of the particular combination of character sets being used within the ICH ICSR application, an SGML declaration can be defined that tells the parser just what it needs to know and still work across all of the different character sets. The catch is that this SGML declaration doesn't tell the programmer all that she or he needs to know to correctly code the rest of the application. If this declaration is used, the programmer will have to get this detailed information from another source. -- <!-- ================================================================== -- <!-- Entities -- <!-- ================================================================== -- <!-- Use the lang attribute to indicate the language of an elements content via an ISO 639 language Code. -- <!ENTITY % lang.att "lang CDATA #IMPLIED" <!-- Standard Character Entities to escape SGML special characters When "<", "", and "&" occur in text, they should be replaced by "<", ">", and "&" respectfully
3 <!-- Less Than "<" -- <!ENTITY lt "<" <!-- Greater Than "" -- <!ENTITY gt ">" <!-- Ampersand "&" -- <!ENTITY amp "&" <!-- ================================================================== -- <!-- Elements and Attributes -- <!-- ================================================================== -- <!ELEMENT ichicsrack - - (ichicsrmessageheader, acknowledgment) <!ATTLIST ichicsrack lang CDATA #REQUIRED <!-- M.1 ICH ICSR Message Header Information -- <!ELEMENT ichicsrmessageheader - - (messagetype, messageformatversion, messageformatrelease, messagenumb, messagesenderidentifier, messagereceiveridentifier, messagedateformat, messagedate) <!ATTLIST ichicsrmessageheader <!-- M.1.1 Message Type -- <!ELEMENT messagetype - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messagetype <!-- M.1.2 Message Format Version -- <!ELEMENT messageformatversion - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messageformatversion <!-- M.1.3 Message Format Release -- <!ELEMENT messageformatrelease - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messageformatrelease 111
4 <!-- M.1.4 Message Number -- <!ELEMENT messagenumb - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messagenumb <!-- M.1.5 Message Sender Identifier -- <!ELEMENT messagesenderidentifier - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messagesenderidentifier <!-- M.1.6 Message Receiver Identifier -- <!ELEMENT messagereceiveridentifier - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messagereceiveridentifier <!-- M.1.7a Message Date Format -- <!ELEMENT messagedateformat - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messagedateformat <!-- M.1.7b Message Date -- <!ELEMENT messagedate - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST messagedate <!-- A.1 ICSR Acknowledgment Message-- <!ELEMENT acknowledgment - - (messageacknowledgment, reportacknowledgment*) <!ATTLIST acknowledgment <!-- A.1 Message Acknowledgment -- <!ELEMENT messageacknowledgment - - (icsrmessagenumb, localmessagenumb?, icsrmessagesenderidentifier, icsrmessagereceiveridentifier, icsrmessagedateformat, icsrmessagedate, transmissionacknowledgmentcode, parsingerrormessage?) <!ATTLIST messageacknowledgment 112
5 <!-- A.1.1 ICSR Message Number -- <!ELEMENT icsrmessagenumb - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST icsrmessagenumb <!-- A.1.2 Local Message Number -- <!ELEMENT localmessagenumb - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST localmessagenumb <!-- A.1.3 ICSR Message Sender Identifier -- <!ELEMENT icsrmessagesenderidentifier - - <!ATTLIST icsrmessagesenderidentifier <!-- A.1.4 ICSR Message Receiver Identifier -- <!ELEMENT icsrmessagereceiveridentifier - - <!ATTLIST icsrmessagereceiveridentifier (#PCDATA) (#PCDATA) <!-- A.1.5a ICSR Message Date Format -- <!ELEMENT icsrmessagedateformat - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST icsrmessagedateformat <!-- A.1.5b ICSR Message Date -- <!ELEMENT icsrmessagedate - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST icsrmessagedate <!-- A.1.6 Transmission Acknowledgment -- <!ELEMENT transmissionacknowledgmentcode - - <!ATTLIST transmissionacknowledgmentcode (#PCDATA) <!-- A.1.7 Parsing Error Message -- <!ELEMENT parsingerrormessage - - <!ATTLIST parsingerrormessage (#PCDATA) <!-- B.1 Report Acknowledgment -- <!ELEMENT reportacknowledgment - - (safetyreportid, safetyreportversion?, localreportnumb?, 113
6 authoritynumb?, companynumb?, receiptdateformat?, receiptdate?, reportacknowledgmentcode, errormessagecomment?) <!ATTLIST reportacknowledgment <!-- B.1.1 Safety Report Identification -- <!ELEMENT safetyreportid - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST safetyreportid <!-- B.1.2 Safety Report Version -- <!ELEMENT safetyreportversion - - <!ATTLIST safetyreportversion (#PCDATA) <!-- B.1.3 Local Report Number -- <!ELEMENT localreportnumb - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST localreportnumb <!-- B.1.4 Regulatory authority's case report number (E2BM - A )-- <!ELEMENT authoritynumb - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST authoritynumb <!-- B.1.5 Other Sender s case report number (E2BM - A ) -- <!ELEMENT companynumb - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST companynumb <!-- B.1.7a Receipt Date Format -- <!ELEMENT receiptdateformat - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST receiptdateformat <!-- B.1.7b Date of receipt of the most recent information (E2BM - A.1.7) -- <!ELEMENT receiptdate - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST receiptdate <!-- B.1.8 Acknowledgment Code for a report -- <!ELEMENT reportacknowledgmentcode - - (#PCDATA) 114
7 <!ATTLIST reportacknowledgmentcode <!-- B.1.9 Error Message or Comment -- <!ELEMENT errormessagecomment - - (#PCDATA) <!ATTLIST errormessagecomment ] 115
Electronic Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports Message Specification (ICH ICSR DTD Version 2.1)
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH M2 EWG Electronic Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports Message Specification
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH M2 EWG Electronic Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports Message Specification
Chapter 5: Extended EudraVigilance Product Report Acknowledgement Message
 4 April 2014 EMA/718844/2011 Patient Health Protection Detailed guidance on the electronic submission of information on medicinal products for human use by marketing authorisation holders to the European
4 April 2014 EMA/718844/2011 Patient Health Protection Detailed guidance on the electronic submission of information on medicinal products for human use by marketing authorisation holders to the European
Introduction to XML. An Example XML Document. The following is a very simple XML document.
 Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
Introduction to XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) was standardized in 1998 after 2 years of work. However, it developed out of SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), a product of the 1970s and
XML and DTD. Mario Alviano A.Y. 2017/2018. University of Calabria, Italy 1 / 28
 1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
1 / 28 XML and DTD Mario Alviano University of Calabria, Italy A.Y. 2017/2018 Outline 2 / 28 1 Introduction 2 XML syntax 3 Namespace 4 Document Type Definition (DTD) 5 Exercises Outline 3 / 28 1 Introduction
XML Structures. Web Programming. Uta Priss ZELL, Ostfalia University. XML Introduction Syntax: well-formed Semantics: validity Issues
 XML Structures Web Programming Uta Priss ZELL, Ostfalia University 2013 Web Programming XML1 Slide 1/32 Outline XML Introduction Syntax: well-formed Semantics: validity Issues Web Programming XML1 Slide
XML Structures Web Programming Uta Priss ZELL, Ostfalia University 2013 Web Programming XML1 Slide 1/32 Outline XML Introduction Syntax: well-formed Semantics: validity Issues Web Programming XML1 Slide
Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda
 NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
NPRG036 XML Technologies Lecture 1 Introduction, XML, DTD 19. 2. 2018 Author: Irena Holubová Lecturer: Martin Svoboda http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/172-nprg036/ Lecture Outline Introduction
2009 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XML Syntax
 Data-centric XML XML Syntax 2 What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language Derived from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) Two goals: large-scale electronic publishing exchange of wide variety of data
Data-centric XML XML Syntax 2 What Is XML? Extensible Markup Language Derived from SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language) Two goals: large-scale electronic publishing exchange of wide variety of data
Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards
 Disclaimer: All words, pictures are adopted from Learning Web Design (3 rd eds.) by Jennifer Niederst Robbins, published by O Reilly 2007. Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards CSc2320 In this chapter
Disclaimer: All words, pictures are adopted from Learning Web Design (3 rd eds.) by Jennifer Niederst Robbins, published by O Reilly 2007. Chapter 10: Understanding the Standards CSc2320 In this chapter
Overview. Introduction. Introduction XML XML. Lecture 16 Introduction to XML. Boriana Koleva Room: C54
 Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
Overview Lecture 16 Introduction to XML Boriana Koleva Room: C54 Email: bnk@cs.nott.ac.uk Introduction The Syntax of XML XML Document Structure Document Type Definitions Introduction Introduction SGML
UNIT I. A protocol is a precise set of rules defining how components communicate, the format of addresses, how data is split into packets
 UNIT I Web Essentials: Clients, Servers, and Communication. The Internet- Basic Internet Protocols -The World Wide Web-HTTP request message-response message- Web Clients Web Servers-Case Study. Markup
UNIT I Web Essentials: Clients, Servers, and Communication. The Internet- Basic Internet Protocols -The World Wide Web-HTTP request message-response message- Web Clients Web Servers-Case Study. Markup
European Medicines Agency Post-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use
 European Medicines Agency Post-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 11 November 2009 Doc. Ref. EMEA/183240/2008 OVERVIEW OF COMMENTS RECEIVED ON DRAFT NOTE FOR GUIDANCE EUDRAVIGILANCE
European Medicines Agency Post-authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 11 November 2009 Doc. Ref. EMEA/183240/2008 OVERVIEW OF COMMENTS RECEIVED ON DRAFT NOTE FOR GUIDANCE EUDRAVIGILANCE
2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. Document Types
 Data-centric XML Document Types Purpose 2006 Martin v. Löwis Document Type Definitions define a vocabulary set of allowed element names set of attributes per element name data type given for each attribute
Data-centric XML Document Types Purpose 2006 Martin v. Löwis Document Type Definitions define a vocabulary set of allowed element names set of attributes per element name data type given for each attribute
Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa
 NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
NPFL092 Technology for Natural Language Processing Introduction to XML Zdeněk Žabokrtský, Rudolf Rosa November 28, 2018 Charles Univeristy in Prague Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Institute of Formal
Introduction to XML. XML: basic elements
 Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Introduction to XML XML: basic elements XML Trying to wrap your brain around XML is sort of like trying to put an octopus in a bottle. Every time you think you have it under control, a new tentacle shows
Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors
 Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors Topologi Technical Note. August 13, 2002 Rick Jelliffe SGML and XML Editing Concrete Syntax (ECS) This draft paper formalizes the lexical
Editor s Concrete Syntax (ECS): a Profile of SGML for Editors Topologi Technical Note. August 13, 2002 Rick Jelliffe SGML and XML Editing Concrete Syntax (ECS) This draft paper formalizes the lexical
XML. XML Syntax. An example of XML:
 XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. Defined in the XML 1.0 Specification
XML Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. Defined in the XML 1.0 Specification
SDPL : XML Basics 2. SDPL : XML Basics 1. SDPL : XML Basics 4. SDPL : XML Basics 3. SDPL : XML Basics 5
 2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
2 Basics of XML and XML documents 2.1 XML and XML documents Survivor's Guide to XML, or XML for Computer Scientists / Dummies 2.1 XML and XML documents 2.2 Basics of XML DTDs 2.3 XML Namespaces XML 1.0
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
Tutorial 2: Validating Documents with DTDs
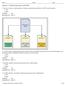 1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
1. One way to create a valid document is to design a document type definition, or DTD, for the document. 2. As shown in the accompanying figure, the external subset would define some basic rules for all
What is XML? XML is designed to transport and store data.
 What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
What is XML? XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML is designed to transport and store data. HTML was designed to display data. XML is a markup language much like HTML XML was designed to carry
XML. extensible Markup Language. Overview. Overview. Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema
 XML extensible Markup Language An introduction in XML and parsing XML Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema 3011 Compiler Construction 2 Overview Overview
XML extensible Markup Language An introduction in XML and parsing XML Overview XML Components Document Type Definition (DTD) Attributes and Tags An XML schema 3011 Compiler Construction 2 Overview Overview
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013
 Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Hamid Zarrabi-Zadeh Web Programming Fall 2013 2 Outline Introduction XML Structure Document Type Definition (DTD) XHMTL Formatting XML CSS Formatting XSLT Transformations
XML is a popular multi-language system, and XHTML depends on it. XML details languages
 1 XML XML is a popular multi-language system, and XHTML depends on it XML details languages XML 2 Many of the newer standards, including XHTML, are based on XML = Extensible Markup Language, so we will
1 XML XML is a popular multi-language system, and XHTML depends on it XML details languages XML 2 Many of the newer standards, including XHTML, are based on XML = Extensible Markup Language, so we will
The concept of DTD. DTD(Document Type Definition) Why we need DTD
 Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
Contents Topics The concept of DTD Why we need DTD The basic grammar of DTD The practice which apply DTD in XML document How to write DTD for valid XML document The concept of DTD DTD(Document Type Definition)
XML: Introduction. !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... Directive... 9:11
 !important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
!important Declaration... 9:11 #FIXED... 7:5 #IMPLIED... 7:5 #REQUIRED... 7:4 @import Directive... 9:11 A Absolute Units of Length... 9:14 Addressing the First Line... 9:6 Assigning Meaning to XML Tags...
On the Missing-Characters (Gaiji) of the Taisho Tripitaka Text Database Published by SAT
 On the Missing-Characters (Gaiji) of the Taisho Tripitaka Text Database Published by SAT Shigeki Moro The Association for the Computerization of Buddhist Texts, Japan 0 ABSTRACT In March of 1998, the Association
On the Missing-Characters (Gaiji) of the Taisho Tripitaka Text Database Published by SAT Shigeki Moro The Association for the Computerization of Buddhist Texts, Japan 0 ABSTRACT In March of 1998, the Association
웹기술및응용. XML Basics 2018 년 2 학기. Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering
 웹기술및응용 XML Basics 2018 년 2 학기 Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering 목차 q Introduction to XML q XML Document Structure and Basic Syntax 2 Introduction to XML XML (extensible
웹기술및응용 XML Basics 2018 년 2 학기 Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering 목차 q Introduction to XML q XML Document Structure and Basic Syntax 2 Introduction to XML XML (extensible
Introduction Syntax and Usage XML Databases Java Tutorial XML. November 5, 2008 XML
 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial November 5, 2008 Introduction Syntax and Usage Databases Java Tutorial Outline 1 Introduction 2 Syntax and Usage Syntax Well Formed and Valid Displaying
Version number: Published: Date of coming into force:
 5 January 2015 EMA/800577/2011 Information and Communications Technology Detailed guidance on the electronic submission of information on medicinal products for human use by marketing authorisation holders
5 January 2015 EMA/800577/2011 Information and Communications Technology Detailed guidance on the electronic submission of information on medicinal products for human use by marketing authorisation holders
Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML
 Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML Abstract John W. Shipman 2013-08-24 12:16 Describes the Document Type Definition notation for describing the schema of an SGML or XML document type.
Constructing a Document Type Definition (DTD) for XML Abstract John W. Shipman 2013-08-24 12:16 Describes the Document Type Definition notation for describing the schema of an SGML or XML document type.
XML. Part I XML Document and DTD
 XML Part I XML Document and DTD What is XML? XML = Extensible Markup Language A Mark up language Designed based on SGML with less complexity Goal: data interchange over the web What is XML? เป ด น อย HTML
XML Part I XML Document and DTD What is XML? XML = Extensible Markup Language A Mark up language Designed based on SGML with less complexity Goal: data interchange over the web What is XML? เป ด น อย HTML
XML, DTD: Exercises. A7B36XML, AD7B36XML: XML Technologies. Practical Classes 1 and 2: 3. and
 A7B36XML, AD7B36XML: XML Technologies Practical Classes 1 and 2: XML, DTD: Exercises 3. and 10. 3. 2017 Jiří Helmich helmich@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Martin Svoboda svoboda@ksi.mff.cuni.cz http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/2016-2-a7b36xml/
A7B36XML, AD7B36XML: XML Technologies Practical Classes 1 and 2: XML, DTD: Exercises 3. and 10. 3. 2017 Jiří Helmich helmich@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Martin Svoboda svoboda@ksi.mff.cuni.cz http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~svoboda/courses/2016-2-a7b36xml/
extensible Markup Language
 extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
extensible Markup Language XML is rapidly becoming a widespread method of creating, controlling and managing data on the Web. XML Orientation XML is a method for putting structured data in a text file.
Fundamentals of Web Programming a
 Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Introduction to XML. Chapter 133
 Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
Chapter 133 Introduction to XML A. Multiple choice questions: 1. Attributes in XML should be enclosed within. a. single quotes b. double quotes c. both a and b d. none of these c. both a and b 2. Which
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2
 Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
Java EE 7: Back-end Server Application Development 4-2 XML describes data objects called XML documents that: Are composed of markup language for structuring the document data Support custom tags for data
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar..
 .. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar.. XML in a Nutshell XML, extended Markup Language is a collection of rules for universal markup of data. Brief History
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 366: Database Modeling, Design and Implementation Alexander Dekhtyar.. XML in a Nutshell XML, extended Markup Language is a collection of rules for universal markup of data. Brief History
Outline. XML vs. HTML and Well Formed vs. Valid. XML Overview. CSC309 Tutorial --XML 4. Edward Xia
 CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
CSC309 Tutorial XML Edward Xia November 7, 2003 Outline XML Overview XML DOCTYPE Element Declarations Attribute List Declarations Entity Declarations CDATA Stylesheet PI XML Namespaces A Complete Example
Data Format Specifications for the Collection of PCT National Phase Information
 PCT IS Division Data Format Specifications for the Collection of PCT National Phase Information Version Number 3.0 May 14, 2007 WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERT Y ORGANI ZATION GENEVA Page: 1 Document Information
PCT IS Division Data Format Specifications for the Collection of PCT National Phase Information Version Number 3.0 May 14, 2007 WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERT Y ORGANI ZATION GENEVA Page: 1 Document Information
Solutions. a. Yes b. No c. Cannot be determined without the DTD. d. Schema. 9. Explain the term extensible. 10. What is an attribute?
 Chapter 7: Information Representation Method XML Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. XML was developed to overcome the limitations of the markup language. a. EDI b. SGML
Chapter 7: Information Representation Method XML Solutions Summative Assessment Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) 1. XML was developed to overcome the limitations of the markup language. a. EDI b. SGML
ICH E2B(R3) Expert Working Group. Backwards and Forwards Compatibility
 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 1 2 3 4 5 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH Expert Working
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 1 2 3 4 5 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH Expert Working
 XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
XML Introduction 1. XML Stands for EXtensible Mark-up Language (XML). 2. SGML Electronic Publishing challenges -1986 3. HTML Web Presentation challenges -1991 4. XML Data Representation challenges -1996
Data Presentation and Markup Languages
 Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
Data Presentation and Markup Languages MIE456 Tutorial Acknowledgements Some contents of this presentation are borrowed from a tutorial given at VLDB 2000, Cairo, Agypte (www.vldb.org) by D. Florescu &.
The Reality of Web Encoding Identification, or Lack Thereof
 The Reality of Web Encoding Identification, or Lack Thereof --- What to trust to determine the character encoding of a web page? --- KUROSAKA Teruhiko 1, Internationalization Architect, IONA Technologies
The Reality of Web Encoding Identification, or Lack Thereof --- What to trust to determine the character encoding of a web page? --- KUROSAKA Teruhiko 1, Internationalization Architect, IONA Technologies
Introduction to XML. When talking about XML, here are some terms that would be helpful:
 Introduction to XML XML stands for the extensible Markup Language. It is a new markup language, developed by the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), mainly to overcome limitations in HTML. HTML is an immensely
Introduction to XML XML stands for the extensible Markup Language. It is a new markup language, developed by the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium), mainly to overcome limitations in HTML. HTML is an immensely
This chapter describes the encoding scheme supported through the Java API.
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction This chapter describes the encoding scheme supported through the Java API. XML DTD Data exchanged between the client application and the Java API are encoded as an XML string. This
CHAPTER 3 Introduction This chapter describes the encoding scheme supported through the Java API. XML DTD Data exchanged between the client application and the Java API are encoded as an XML string. This
TagSoup: A SAX parser in Java for nasty, ugly HTML. John Cowan
 TagSoup: A SAX parser in Java for nasty, ugly HTML John Cowan (cowan@ccil.org) Copyright This presentation is: Copyright 2002 John Cowan Licensed under the GNU General Public License ABSOLUTELY WITHOUT
TagSoup: A SAX parser in Java for nasty, ugly HTML John Cowan (cowan@ccil.org) Copyright This presentation is: Copyright 2002 John Cowan Licensed under the GNU General Public License ABSOLUTELY WITHOUT
XML. extensible Markup Language. ... and its usefulness for linguists
 XML extensible Markup Language... and its usefulness for linguists Thomas Mayer thomas.mayer@uni-konstanz.de Fachbereich Sprachwissenschaft, Universität Konstanz Seminar Computerlinguistik II (Miriam Butt)
XML extensible Markup Language... and its usefulness for linguists Thomas Mayer thomas.mayer@uni-konstanz.de Fachbereich Sprachwissenschaft, Universität Konstanz Seminar Computerlinguistik II (Miriam Butt)
Chapter 1: Getting Started. You will learn:
 Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Chapter 1: Getting Started SGML and SGML document components. What XML is. XML as compared to SGML and HTML. XML format. XML specifications. XML architecture. Data structure namespaces. Data delivery,
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Overview. How the Web is Today. Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington
 Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Chapter 16: Introduction to XML and DTD Files
 Chapter 16: Introduction to XML and DTD Files The configuration files for the CRL desktop as well as for the inquiry and forms features are provided in XML format. In this chapter we provide the information
Chapter 16: Introduction to XML and DTD Files The configuration files for the CRL desktop as well as for the inquiry and forms features are provided in XML format. In this chapter we provide the information
XML Technologies XML, DTD
 XML Technologies XML, DTD Basic Structural Components of XML Documents (1/2)
XML Technologies XML, DTD Basic Structural Components of XML Documents (1/2)
Fundamentals of Web Programming a
 Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
Fundamentals of Web Programming a Introduction to XML Teodor Rus rus@cs.uiowa.edu The University of Iowa, Department of Computer Science a Copyright 2009 Teodor Rus. These slides have been developed by
M2 Glossary of Terms and Abbreviations
 M2 Glossary of Terms and Abbreviations 11 June 2015 M2: Electronic Standards for the Transfer of Regulatory Information Updated at ICH Expert Working Group meeting, Fukuoka, June 2015 Definitions... 2
M2 Glossary of Terms and Abbreviations 11 June 2015 M2: Electronic Standards for the Transfer of Regulatory Information Updated at ICH Expert Working Group meeting, Fukuoka, June 2015 Definitions... 2
Overview. Structured Data. The Structure of Data. Semi-Structured Data Introduction to XML Querying XML Documents. CMPUT 391: XML and Querying XML
 Database Management Systems Winter 2004 CMPUT 391: XML and Querying XML Lecture 12 Overview Semi-Structured Data Introduction to XML Querying XML Documents Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane University of Alberta Chapter
Database Management Systems Winter 2004 CMPUT 391: XML and Querying XML Lecture 12 Overview Semi-Structured Data Introduction to XML Querying XML Documents Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane University of Alberta Chapter
Session 23 XML. XML Reading and Reference. Reading. Reference: Session 23 XML. Robert Kelly, 2018
 Session 23 XML Reading XML Reading and Reference https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/xml Reference: XML in a Nutshell (Ch. 1-3), available in Safari On-line 2 1 Lecture Objectives Understand the goal of application
Session 23 XML Reading XML Reading and Reference https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/xml Reference: XML in a Nutshell (Ch. 1-3), available in Safari On-line 2 1 Lecture Objectives Understand the goal of application
Multilingual vi Clones: Past, Now and the Future
 THE ADVANCED COMPUTING SYSTEMS ASSOCIATION The following paper was originally published in the Proceedings of the FREENIX Track: 1999 USENIX Annual Technical Conference Monterey, California, USA, June
THE ADVANCED COMPUTING SYSTEMS ASSOCIATION The following paper was originally published in the Proceedings of the FREENIX Track: 1999 USENIX Annual Technical Conference Monterey, California, USA, June
XML 2 APPLICATION. Chapter SYS-ED/ COMPUTER EDUCATION TECHNIQUES, INC.
 XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
XML 2 APPLIATION hapter SYS-ED/ OMPUTER EDUATION TEHNIQUES, IN. Objectives You will learn: How to create an XML document. The role of the document map, prolog, and XML declarations. Standalone declarations.
Chapter 1: XML Syntax
 1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
Internet and Web Technologies. Sample Solutions 2013
 Internet and Web Technologies Sample Solutions 2013 1. (a) stream paradigm connection-oriented one-to-one communication sequence of individual bytes arbitrary length transfer used by most applications
Internet and Web Technologies Sample Solutions 2013 1. (a) stream paradigm connection-oriented one-to-one communication sequence of individual bytes arbitrary length transfer used by most applications
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is a text-based markup language derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML).
 About the Tutorial XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is a text-based markup language derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). This tutorial will teach you the basics of XML.
About the Tutorial XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is a text-based markup language derived from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). This tutorial will teach you the basics of XML.
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD
![Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD](/thumbs/72/67474201.jpg) Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
Session [2] Information Modeling with XSD and DTD September 12, 2000 Horst Rechner Q&A from Session [1] HTML without XML See Code HDBMS vs. RDBMS What does XDR mean? XML-Data Reduced Utilized in Biztalk
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
WAP Binary XML Content Format Proposed Version 15-Aug-1999
 WAP Binary XML Content Format Proposed Version 15-Aug-1999 Wireless Application Protocol Binary XML Content Format Specification Version 1.2 Disclaimer: This document is subject to change without notice.
WAP Binary XML Content Format Proposed Version 15-Aug-1999 Wireless Application Protocol Binary XML Content Format Specification Version 1.2 Disclaimer: This document is subject to change without notice.
Computer Science E-75 Building Dynamic Websites
 Computer Science E-75 Building Dynamic Websites Harvard Extension School http://www.cs75.net/ Lecture 3: XML David J. Malan dmalan@harvard.edu 0 1 XML element child element start tag end tag attribute
Computer Science E-75 Building Dynamic Websites Harvard Extension School http://www.cs75.net/ Lecture 3: XML David J. Malan dmalan@harvard.edu 0 1 XML element child element start tag end tag attribute
2011 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. Character Sets
 Data-centric XML Character Sets Character Sets: Rationale Computer stores data in sequences of bytes each byte represents a value in range 0..255 Text data are intended to denote characters, not numbers
Data-centric XML Character Sets Character Sets: Rationale Computer stores data in sequences of bytes each byte represents a value in range 0..255 Text data are intended to denote characters, not numbers
XML: and related technologies
 XML" XML: and related technologies extensible Markup Language (XML) Is a meta-language that describes the content of the document (self-describing data) XML does not specify the tag set or grammar of the
XML" XML: and related technologies extensible Markup Language (XML) Is a meta-language that describes the content of the document (self-describing data) XML does not specify the tag set or grammar of the
Oracle Argus Interchange
 Oracle Argus Interchange Japan User s Guide Release 8.1.1 E89439-01 September 2017 Oracle Argus Interchange Japan User's Guide, Release 8.1.1 E89439-01 Copyright 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All
Oracle Argus Interchange Japan User s Guide Release 8.1.1 E89439-01 September 2017 Oracle Argus Interchange Japan User's Guide, Release 8.1.1 E89439-01 Copyright 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All
2007 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. Character Sets
 Data-centric XML Character Sets Character Sets: Rationale Computer stores data in sequences of bytes each byte represents a value in range 0..255 Text data are intended to denote characters, not numbers
Data-centric XML Character Sets Character Sets: Rationale Computer stores data in sequences of bytes each byte represents a value in range 0..255 Text data are intended to denote characters, not numbers
SYBEX Sample Chapter. Chapter 4: Understanding and Creating Entities
 SYBEX Sample Chapter XML Complete Chapter 4: Understanding and Creating Entities Copyright 2001 SYBEX Inc., 1151 Marina Village Parkway, Alameda, CA 94501. World rights reserved. No part of this publication
SYBEX Sample Chapter XML Complete Chapter 4: Understanding and Creating Entities Copyright 2001 SYBEX Inc., 1151 Marina Village Parkway, Alameda, CA 94501. World rights reserved. No part of this publication
Introduction to XML. National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore. Shafiq Ur Rahman. Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing
 Introduction to XML Shafiq Ur Rahman Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore XMLXML DTDDTD Related Related Standards Overview What
Introduction to XML Shafiq Ur Rahman Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing National University of Computer and Emerging Sciences, Lahore XMLXML DTDDTD Related Related Standards Overview What
UTF and Turkish. İstinye University. Representing Text
 Representing Text Representation of text predates the use of computers for text Text representation was needed for communication equipment One particular commonly used communication equipment was teleprinter
Representing Text Representation of text predates the use of computers for text Text representation was needed for communication equipment One particular commonly used communication equipment was teleprinter
ONIX for Books Product Information Message. Application Note: Embedding HTML markup in ONIX 3.0 data elements
 ONIX for Books Product Information Message Application Note: Embedding HTML markup in ONIX 3.0 data elements In ONIX whether version 2.1 or 3.0 there are many common issues that arise when data providers
ONIX for Books Product Information Message Application Note: Embedding HTML markup in ONIX 3.0 data elements In ONIX whether version 2.1 or 3.0 there are many common issues that arise when data providers
Part II: Semistructured Data
 Inf1-DA 2011 2012 II: 22 / 119 Part II Semistructured Data XML: II.1 Semistructured data, XPath and XML II.2 Structuring XML II.3 Navigating XML using XPath Corpora: II.4 Introduction to corpora II.5 Querying
Inf1-DA 2011 2012 II: 22 / 119 Part II Semistructured Data XML: II.1 Semistructured data, XPath and XML II.2 Structuring XML II.3 Navigating XML using XPath Corpora: II.4 Introduction to corpora II.5 Querying
Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5. HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION
 Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5 HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION Objectives Explore the history of the Internet, the Web, and HTML Compare the different versions of HTML Study the syntax
Tutorial 1 Getting Started with HTML5 HTML, CSS, and Dynamic HTML 5 TH EDITION Objectives Explore the history of the Internet, the Web, and HTML Compare the different versions of HTML Study the syntax
A DTD-Syntax-Tree Based XML file Modularization Browsing Technique
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.6 No.2A, February 2006 127 A DTD-Syntax-Tree Based XML file Modularization Browsing Technique Zhu Zhengyu 1, Changzhi Li, Yuan
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.6 No.2A, February 2006 127 A DTD-Syntax-Tree Based XML file Modularization Browsing Technique Zhu Zhengyu 1, Changzhi Li, Yuan
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. Chapter 7 XML
 Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
Chapter 7 XML 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
Representing Characters and Text
 Representing Characters and Text cs4: Computer Science Bootcamp Çetin Kaya Koç cetinkoc@ucsb.edu Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.org Winter 2018 1 / 28 Representing Text Representation of text predates the
Representing Characters and Text cs4: Computer Science Bootcamp Çetin Kaya Koç cetinkoc@ucsb.edu Çetin Kaya Koç http://koclab.org Winter 2018 1 / 28 Representing Text Representation of text predates the
Chapter 1: XML Syntax
 1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
1. XML Syntax 1-1 Chapter 1: XML Syntax References: Boc DuCharme: XML The Annotated Specification. Prentice Hall, 1999. Tim Bray, Jean Paoli, C.M. Sperberg-McQueen: Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0,
XML: Managing with the Java Platform
 In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
In order to learn which questions have been answered correctly: 1. Print these pages. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this assessment with the answers via: a. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or b. Mail the answers
European Medicines Agency Standard Operating Procedure
 European Medicines Agency Standard Operating Procedure Title: Procedure to be followed by the EMEA in case of mechanical, programme, electronic or communication failure, which prevents a Sender from generating
European Medicines Agency Standard Operating Procedure Title: Procedure to be followed by the EMEA in case of mechanical, programme, electronic or communication failure, which prevents a Sender from generating
PART. Oracle and the XML Standards
 PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
PART I Oracle and the XML Standards CHAPTER 1 Introducing XML 4 Oracle Database 10g XML & SQL E xtensible Markup Language (XML) is a meta-markup language, meaning that the language, as specified by the
Computer Science S-75 Building Dynamic Websites
 Computer Science S-75 Building Dynamic Websites Harvard Summer School https://www.cs75.net/ Lecture 3: MVC, XML David J. Malan malan@harvard.edu 0 CS50 Appliance https://manual.cs50.net/appliance 1 MVC
Computer Science S-75 Building Dynamic Websites Harvard Summer School https://www.cs75.net/ Lecture 3: MVC, XML David J. Malan malan@harvard.edu 0 CS50 Appliance https://manual.cs50.net/appliance 1 MVC
Structured documents
 Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
Structured documents An overview of XML Structured documents Michael Houghton 15/11/2000 Unstructured documents Broadly speaking, text and multimedia document formats can be structured or unstructured.
XML. Objectives. Duration. Audience. Pre-Requisites
 XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
XML XML - extensible Markup Language is a family of standardized data formats. XML is used for data transmission and storage. Common applications of XML include business to business transactions, web services
7.1 Introduction. extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML
 7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
7.1 Introduction extensible Markup Language Developed from SGML A meta-markup language Deficiencies of HTML and SGML Lax syntactical rules Many complex features that are rarely used HTML is a markup language,
CSC Web Technologies, Spring Web Data Exchange Formats
 CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
CSC 342 - Web Technologies, Spring 2017 Web Data Exchange Formats Web Data Exchange Data exchange is the process of transforming structured data from one format to another to facilitate data sharing between
Part III: Survey of Internet technologies
 Part III: Survey of Internet technologies Content (e.g., HTML) kinds of objects we re moving around? References (e.g, URLs) how to talk about something not in hand? Protocols (e.g., HTTP) how do things
Part III: Survey of Internet technologies Content (e.g., HTML) kinds of objects we re moving around? References (e.g, URLs) how to talk about something not in hand? Protocols (e.g., HTTP) how do things
Web Services Part I. XML Web Services. Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009
 Web Services Part I Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 CS 437/637 Database-Backed Web Sites and Web Services 1 XML Web Services XML Web Services = Web Services A Web service is a different kind of Web
Web Services Part I Instructor: Dr. Wei Ding Fall 2009 CS 437/637 Database-Backed Web Sites and Web Services 1 XML Web Services XML Web Services = Web Services A Web service is a different kind of Web
extensible Markup Language (XML) Basic Concepts
 (XML) Basic Concepts Giuseppe Della Penna Università degli Studi di L Aquila dellapenna@univaq.it http://www.di.univaq.it/gdellape This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
(XML) Basic Concepts Giuseppe Della Penna Università degli Studi di L Aquila dellapenna@univaq.it http://www.di.univaq.it/gdellape This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Non-English Web Pages In Dreamweaver MX
 Non-English Web Pages In Dreamweaver MX The following describes how to use multiple languages in a web page using Dreamweaver MX for Microsoft Windows. The reader is assumed to have basic computer usage
Non-English Web Pages In Dreamweaver MX The following describes how to use multiple languages in a web page using Dreamweaver MX for Microsoft Windows. The reader is assumed to have basic computer usage
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CPT374 Tutorial-Laboratory Sheet Two
 CPT374 Tutorial-Laboratory Sheet Two Objectives: Understanding XML DTDs Tutorial Exercises Exercise 1 - An introduction to XML DTD Go to http://www.zvon.org/xxl/dtdtutorial/general/contents.html and read
CPT374 Tutorial-Laboratory Sheet Two Objectives: Understanding XML DTDs Tutorial Exercises Exercise 1 - An introduction to XML DTD Go to http://www.zvon.org/xxl/dtdtutorial/general/contents.html and read
INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL FOR HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE
 USER GUIDE Use of EDQM terminologies for Dose Forms and Routes of Administration for Individual Case Safety Reports in E2B(R3) message Version 1.0, 16 November 2017 Page 1 of 8 Document History Date of
USER GUIDE Use of EDQM terminologies for Dose Forms and Routes of Administration for Individual Case Safety Reports in E2B(R3) message Version 1.0, 16 November 2017 Page 1 of 8 Document History Date of
CSCI3030U Database Models
 CSCI3030U Database Models CSCI3030U RELATIONAL MODEL SEMISTRUCTURED MODEL 1 Content Design of databases. relational model, semistructured model. Database programming. SQL, XPath, XQuery. Not DBMS implementation.
CSCI3030U Database Models CSCI3030U RELATIONAL MODEL SEMISTRUCTURED MODEL 1 Content Design of databases. relational model, semistructured model. Database programming. SQL, XPath, XQuery. Not DBMS implementation.
XML: Basics. Paul V. Biron Permanente Clinical Systems Development Kaiser Permanente, Southern California
 XML: Basics Paul V. Biron Permanente Clinical Systems Development Kaiser Permanente, Southern California Paul.V.Biron@kp.org 09/15/98 1 Outline HTML, SGML and XML The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) HTML
XML: Basics Paul V. Biron Permanente Clinical Systems Development Kaiser Permanente, Southern California Paul.V.Biron@kp.org 09/15/98 1 Outline HTML, SGML and XML The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) HTML
Forthnet Mobile Platform - groupsms http interface v1.0 1 / 9
 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Requirements... 2 Connecting to Forthnet Mobile Platform... 2 Message submission... 3 Client Request... 3 Parameters... 4 Parameter user... 4 Parameter pass... 4 Parameter
Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Requirements... 2 Connecting to Forthnet Mobile Platform... 2 Message submission... 3 Client Request... 3 Parameters... 4 Parameter user... 4 Parameter pass... 4 Parameter
MRP/DCP Tracking Table Description Version 1.0. May 2008
 MRP/DCP Tracking Table Description Version 1.0 May 2008 Document Control Change Record Version Date Author(s) Comments 0.1 (RC1) May, 2008 Laurent Desqueper Draft 0.1 (RC2) May, 2008 Laurent Desqueper
MRP/DCP Tracking Table Description Version 1.0 May 2008 Document Control Change Record Version Date Author(s) Comments 0.1 (RC1) May, 2008 Laurent Desqueper Draft 0.1 (RC2) May, 2008 Laurent Desqueper
Informatique de Gestion 3 èmes Bachelier Groupes 230x
 Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique de Gestion 3 èmes Bachelier Groupes 230x Année Académique 2014 2015 21/10/14 07:53 Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique
Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique de Gestion 3 èmes Bachelier Groupes 230x Année Académique 2014 2015 21/10/14 07:53 Catégorie Technique XML Basics XML Ludovic Kuty Informatique
