Compass and Straight Edge. Compass/Straight Edge. Constructions with some proofs.
|
|
|
- Malcolm McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Compass and Straight Edge Compass/Straight Edge Constructions with some proofs.
2 To Construct the Perpendicular isector of a line. 1. Place compass at, set over halfway and draw 2 arcs. 2. Place compass at, with same distance set and draw 2 arcs to intersect first two. 3. Draw the perpendicular bisector through the points of intersection. Perpendicular
3 1. Place compass at, and draw an arc crossing and C. Constructions To Construct the ngle isector of a given angle. 2. Place compass at intersections and (with the same distance set) draw 2 arcs that intersect. 3. Draw the angle bisector from through the point of intersection. C ngle
4 To Construct an Equilateral Triangle. 1. Draw base line of any length. 2. Place compass at, set to distance and draw arc. 3. Place compass at, with same distance set, draw an arc to intersect first one. 4. Join intersection point to and to form an equilateral triangle. Eq Tri
5 1. Draw base line of any length. Constructions To Construct an angle of 60 o. 2. Place compass at, set to distance and draw arc. 3. Place compass at, with same distance set and draw an arc to intersect first one. 4. Draw straight line from through point of intersection. ngle C = 60 o. C 60 deg
6 To Construct an angle of 30 o. 1. Draw base line of any length. 2. Construct an angle of 60 o at. 3. isect angle C. 4. ngle D = 30 o C 30 deg D
7 To draw a perpendicular to a given point on a line. 1. Place compass at P and with distance P set, draw arc at C. 2. With compass at and distance set greater than P, draw arc above line. 3. Repeat with compass at C and same distance set. 4. Draw line through intersection of arcs to P. This line is perpendicular to P. D P C Perp Point
8 To Construct an angle of 45 o at any point P on a straight line. 1. Draw base line of any length. 2. Mark a point P anywhere on. 3. Construct the perpendicular to P. 4. isect angle PD. 5. ngle PE = 45 o. D E P C 45 deg
9 To Construct a line through a given point P, parallel to a given line. 1. Mark off any 2 points on line. 2. With centre P and radius CD draw an arc adjacent to P. 3. With centre D and radius PC draw an arc to intersect the first one. 4. The line through P and the point of intersection is parallel to. P C D Parallel
10 To construct the perpendicular to a given line from a given point, not on the line. 1. With centre P, draw an arc of a circle that intersects at 2 points. 2. With centre C and compass set over ½ distance CD draw arc below. 3. With centre D and same distance set, draw an arc to intersect the previous one. 4. The line through P and the intersecting arcs is perpendicular to. P D C
11 To divide a straight line into any number of parts. (Example is into 5 parts) 1. Draw line C at any angle to. 2. Use compass to mark off 5 equal line segments of any length along C. 3. Join point of intersection on last arc to point. 4. Draw other lines from points of intersection on C parallel to C to meet. 5. is now divided into 5 equal parts. C Division
12 Compass and ruler/protractor Compass/Protractor/Ruler constructions of triangles.
13 To Construct a triangle, given 3 sides. Example 1: To construct a triangle of sides 8 cm, 7cm and 6 cm. 1. Draw line 8cm long and use as base of triangle. 2. Set compass to 7 cm, place at and draw an arc. 3. Set compass to 6 cm, place at and draw an arc to intersect the first one. 4. Draw straight lines from and to point of intersection. 7 cm 6 cm Tri 3 sides 8 cm
14 Explain why a triangle with sides 2 cm,10 cm and 7 cm cannot be constructed. 7 cm 6 cm 8 cm Under what conditions can it be guaranteed that a triangle can be constructed from 3 given lengths? 7 cm 3½ cm 10 cm 7 cm 4 cm 9 cm The sum of the lengths of the smaller sides must exceed the length of the longest side.
15 The table below shows lengths of sides for constructing a triangle. Which ones cannot form a triangle? Side 1 Side 2 Side cm 8 cm 7 cm 2 9 cm 12 cm 4 cm 3 8 cm 15 cm 7 cm 4 18 cm 3 cm 20 cm 5 8 cm 8 cm 17 cm 6 19 cm 7 cm 13 cm cm 18 cm 7.2 cm 8 50 cm 26 cm 23 cm 9 40 cm 41 cm 82 cm cm 2 cm 100 cm
16 To construct a triangle, given 1 side and 2 angles. Example 1: To construct a triangle of side, 9 cm with angles of 35 o and 65 o. 1. Draw a straight line 9 cm long. 2. Use a protractor to draw angles of 35 o and 65 o on either end of line. 3. Draw straight lines from and to point of intersection to form the triangle. Tri 1 side/2 angles 9 cm
17 To construct a triangle, given 1 side and 2 angles. Example 1: To construct a triangle of side, 9 cm with angles of 35 o and 65 o. 1. Draw a straight line 9 cm long. 2. Use a protractor to draw angles of 35 o and 65 o on either end of line. 3. Draw straight lines from and to point of intersection to form the triangle. 35 o 65 o 9 cm
18 To construct a triangle, given 2 sides and an angle. Example 1: To construct a triangle of sides, 9 cm and 7cm with an angle of 40 o. 1. Draw a straight line 9 cm long. 2. Use a protractor to draw an angle of 40 o on either end of line. 3. Mark off a length of 7 cm. Tri 2 sides/1 angle 9 cm
19 To construct a triangle, given 2 sides and an angle. Example 1: To construct a triangle of sides, 9 cm and 7cm with an angle of 40 o. 1. Draw a straight line 9 cm long. 2. Use a protractor to draw an angle of 40 o on either end of line. 3. Mark off a length of 7 cm. 4. Join end points to form the required triangle. 7 cm 40 o 9 cm
20 To Construct the Circumscribed Circle of a given triangle. The perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle are co-incident at the circumcentre. C Circumscribed isect any two sides of the triangle to find the circumcentre (In this case and C). Place compass at circumcentre and draw circumcircle through each vertex.
21 To Construct the Inscribed Circle for any given triangle. The angle bisectors of a triangle are co-incident at the Incentre. C Inscribed Find the incentre by taking the angle bisector of any two angles. (C and C in this case). Place compass at incentre and draw circle inside triangle.
Mid-point & Perpendicular Bisector of a line segment AB
 Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Mid-point & Perpendicular isector of a line segment Starting point: Line Segment Midpoint of 1. Open compasses so the points are approximately ¾ of the length of apart point 3. y eye - estimate the midpoint
Constructions Quiz Review November 29, 2017
 Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Using constructions to copy a segment 1. Mark an endpoint of the new segment 2. Set the point of the compass onto one of the endpoints of the initial line segment 3. djust the compass's width to the other
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
AJ has been constructed as the angle bisector of BAD. B. AJ is the of BD.
 im #9: How do we construct a perpendicular bisector? Do Now: Using the angle below: 1. isect the angle. Label the bisector D. 2. Construct a copy of DC using vertex '. CC Geometry H C ' Relevant Vocabulary
im #9: How do we construct a perpendicular bisector? Do Now: Using the angle below: 1. isect the angle. Label the bisector D. 2. Construct a copy of DC using vertex '. CC Geometry H C ' Relevant Vocabulary
Construction Instructions. Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment.
 Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Construction Instructions Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment. Or, construct the midpoint of a line segment. 1.) Begin with line segment XY. 2.) Place the compass at point X. Adjust
Geometric Constructions
 Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Materials: Compass, Straight Edge, Protractor Construction 1 Construct the perpendicular bisector of a line segment; Or construct the midpoint of a line segment. Construction 2 Given a point on a line,
Common Core State Standards High School Geometry Constructions
 ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS
 MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
CONSTRUCTING CONGRUENT LINE SEGMENTS
 NME: 1. Given: Task: Construct a segment congruent to. CONSTRUCTING CONGRUENT LINE SEGMENTS B a) Draw a new, longer segment with your straightedge. b) Place an endpoint on the left side of the new segment
NME: 1. Given: Task: Construct a segment congruent to. CONSTRUCTING CONGRUENT LINE SEGMENTS B a) Draw a new, longer segment with your straightedge. b) Place an endpoint on the left side of the new segment
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method. Goals:
 Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
ME 111: Engineering Drawing. Geometric Constructions
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
Geometry: Traditional Pathway
 GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
GEOMETRY: CONGRUENCE G.CO Prove geometric theorems. Focus on validity of underlying reasoning while using variety of ways of writing proofs. G.CO.11 Prove theorems about parallelograms. Theorems include:
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines
 Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines Tangent lines are useful in calculating distances as well as diagramming in the professions of construction, architecture, and landscaping. Geometry construction
Unit 6, Lesson 3.1 Constructing Tangent Lines Tangent lines are useful in calculating distances as well as diagramming in the professions of construction, architecture, and landscaping. Geometry construction
Mth 97 Winter 2013 Sections 4.3 and 4.4
 Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
Section 4.3 Problem Solving Using Triangle Congruence Isosceles Triangles Theorem 4.5 In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent. A Given: ABC with AB AC Prove: B C
Construction: Draw a ray with its endpoint on the left. Label this point B.
 Name: Ms. Ayinde Date: Geometry CC 1.13: Constructing Angles Objective: To copy angles and construct angle bisectors using a compass and straightedge. To construct an equilateral triangle. Copy an Angle:
Name: Ms. Ayinde Date: Geometry CC 1.13: Constructing Angles Objective: To copy angles and construct angle bisectors using a compass and straightedge. To construct an equilateral triangle. Copy an Angle:
Section Congruence Through Constructions
 Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Math 366 Chapter 12 Review Problems
 hapter 12 Math 366 hapter 12 Review Problems 1. ach of the following figures contains at least one pair of congruent triangles. Identify them and tell why they are congruent. a. b. G F c. d. e. f. 1 hapter
hapter 12 Math 366 hapter 12 Review Problems 1. ach of the following figures contains at least one pair of congruent triangles. Identify them and tell why they are congruent. a. b. G F c. d. e. f. 1 hapter
2) Draw a labeled example of : a) a ray b) a line c) a segment. 5) Which triangle congruency conjecture would be used for each of the following?
 eometry Semester Final Review Name Period ) raw an example of four collinear points. 2) raw a labeled example of : a) a ray b) a line c) a segment 3) Name this angle four ways: 4) raw a concave polygon
eometry Semester Final Review Name Period ) raw an example of four collinear points. 2) raw a labeled example of : a) a ray b) a line c) a segment 3) Name this angle four ways: 4) raw a concave polygon
Centres of a Triangle. Teacher Notes
 Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
2. A straightedge can create straight line, but can't measure. A ruler can create straight lines and measure distances.
 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
MATH 30 GEOMETRY UNIT OUTLINE AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by: Mr. F.
 1 MTH 30 GEMETRY UNIT UTLINE ND DEFINITINS Prepared by: Mr. F. Some f The Typical Geometric Properties We Will Investigate: The converse holds in many cases too! The Measure f The entral ngle Tangent To
1 MTH 30 GEMETRY UNIT UTLINE ND DEFINITINS Prepared by: Mr. F. Some f The Typical Geometric Properties We Will Investigate: The converse holds in many cases too! The Measure f The entral ngle Tangent To
You try: What is the definition of an angle bisector? You try: You try: is the bisector of ABC. BD is the bisector of ABC. = /4.MD.
 US Geometry 1 What is the definition of a midpoint? midpoint of a line segment is the point that bisects the line segment. That is, M is the midpoint of if M M. 1 What is the definition of an angle bisector?
US Geometry 1 What is the definition of a midpoint? midpoint of a line segment is the point that bisects the line segment. That is, M is the midpoint of if M M. 1 What is the definition of an angle bisector?
Study Guide - Geometry
 Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.)
 Geometric Constructions How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.) Construct a perpendicular line to each side of this triangle. Find the intersection of the three perpendicular lines. This point
Geometric Constructions How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.) Construct a perpendicular line to each side of this triangle. Find the intersection of the three perpendicular lines. This point
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task
 90 Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task For each of the following straightedge and compass constructions, illustrate or list the steps for completing the construction and give an eplanation
90 Construction Blueprints A Practice Understanding Task For each of the following straightedge and compass constructions, illustrate or list the steps for completing the construction and give an eplanation
Lesson 3: Rectangles Inscribed in Circles
 Classwork Opening Exercise Using only a compass and straightedge, find the location of the center of the circle below. Follow the steps provided. Draw chord. AAAA Construct a chord perpendicular to AAAA
Classwork Opening Exercise Using only a compass and straightedge, find the location of the center of the circle below. Follow the steps provided. Draw chord. AAAA Construct a chord perpendicular to AAAA
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Ideas beyond Number. Activity worksheets
 Ideas beyond Number Activity worksheets Activity sheet 1 Regular polygons and tesselation Which regular polygons tessellate? Square tiling is all around us, but are there any others? Questions 1. What
Ideas beyond Number Activity worksheets Activity sheet 1 Regular polygons and tesselation Which regular polygons tessellate? Square tiling is all around us, but are there any others? Questions 1. What
GEOMETRY. PARALLEL LINES Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal.
 GOMTRY RLLL LINS Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. Theorem 2: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then the alternate
GOMTRY RLLL LINS Theorems Theorem 1: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal. Theorem 2: If a pair of parallel lines is cut by a transversal, then the alternate
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Math-2. Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms And Isosceles Triangles
 Math-2 Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms nd Isosceles Triangles What sequence of angles would you link to prove m4 m9 3 1 4 2 13 14 16 15 lternate Interior Corresponding 8 5 7 6 9 10 12 11 What sequence
Math-2 Lesson 7-4 Properties of Parallelograms nd Isosceles Triangles What sequence of angles would you link to prove m4 m9 3 1 4 2 13 14 16 15 lternate Interior Corresponding 8 5 7 6 9 10 12 11 What sequence
(1) Find the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: mab, m BAF, m.
 (1) ind the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: m, m, m, m 100 9 90 (3) ind the length of the arc of a sector of in a circle
(1) ind the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: m, m, m, m 100 9 90 (3) ind the length of the arc of a sector of in a circle
7. 2 More Things Under. Construction. A Develop Understanding Task
 7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
February Regional Geometry Team: Question #1
 February Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 A = area of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 4. B = area of a square with a side length of 3. C = area of a regular hexagon with a side length
February Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 A = area of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 4. B = area of a square with a side length of 3. C = area of a regular hexagon with a side length
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths
 1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
1 Class IX Chapter 11 Constructions Maths 1: Exercise 11.1 Question Construct an angle of 90 at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction. Answer: The below given steps will be followed
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Elementary Planar Geometry
 Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Constructions. Constructions. Curriculum Ready.
 onstructions onstructions urriculum eady www.mathletics.com onstructions are all about creating precise, accurate mathematical diagrams. ompass encil ule/straight edge Equip yourself with these tools
onstructions onstructions urriculum eady www.mathletics.com onstructions are all about creating precise, accurate mathematical diagrams. ompass encil ule/straight edge Equip yourself with these tools
Workshop 1 on Minkowski Geometry using SketchPad
 Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Workshop 1 on Minkowski Geometry using Sketchad reliminary remarks: To perform geometrical constructions in Minkowski geometry, you need some hyperbolic drawing
Workshop at IME-10 July 2004 First part Workshop 1 on Minkowski Geometry using Sketchad reliminary remarks: To perform geometrical constructions in Minkowski geometry, you need some hyperbolic drawing
Segments and Angles. Name Period. All constructions done today will be with Compass and Straight-Edge ONLY.
 Segments and ngles Geometry 3.1 ll constructions done today will be with ompass and Straight-Edge ONLY. Duplicating a segment is easy. To duplicate the segment below: Draw a light, straight line. Set your
Segments and ngles Geometry 3.1 ll constructions done today will be with ompass and Straight-Edge ONLY. Duplicating a segment is easy. To duplicate the segment below: Draw a light, straight line. Set your
Constructing a square with given side length. -Extend a side perpendicular Bisector Measure lengths.
 Name Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral triangle-
Name Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral triangle-
A selection of Geometry constructions using ClassPad
 A selection of Geometry constructions using ClassPad Geoff Phillips Please note: These are unedited, very brief outlines only, but should contain enough detail to provide starting points for geometry investigations
A selection of Geometry constructions using ClassPad Geoff Phillips Please note: These are unedited, very brief outlines only, but should contain enough detail to provide starting points for geometry investigations
G7-3 Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 G7-3 Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles right angle acute angles obtuse angles 90 less than 90 more than 90 and less than 180 1. Without using a protractor, identify each angle as acute or obtuse.
G7-3 Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles right angle acute angles obtuse angles 90 less than 90 more than 90 and less than 180 1. Without using a protractor, identify each angle as acute or obtuse.
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking Deeply About Simple Things
 The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking eeply bout Simple Things University of Utah Teacher s Math ircle Monday, February 4 th, 2008 y Troy Jones Waterford School Important Terms (the word line may be
The Geometry of Piles of Salt Thinking eeply bout Simple Things University of Utah Teacher s Math ircle Monday, February 4 th, 2008 y Troy Jones Waterford School Important Terms (the word line may be
UNIT 3 CIRCLES AND VOLUME Lesson 2: Inscribed Polygons and Circumscribed Triangles Instruction
 UNIT 3 IRLES N VOLUME Lesson 2: Inscribed Polygons and ircumscribed Triangles Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: constructing a perpendicular bisector Introduction
UNIT 3 IRLES N VOLUME Lesson 2: Inscribed Polygons and ircumscribed Triangles Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: constructing a perpendicular bisector Introduction
Mathematics
 Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
edunepal_info
 facebook.com/edunepal.info @ edunepal_info Tangent Constructions Session 1 Drawing and designing logos Many symbols are constructed using geometric shapes. The following section explains common geometrical
facebook.com/edunepal.info @ edunepal_info Tangent Constructions Session 1 Drawing and designing logos Many symbols are constructed using geometric shapes. The following section explains common geometrical
Purpose. Using Problem Solving as a methodology to explore geometry construction in context. Geometry construction: connections within Strand 2 14:10
 Purpose Using Problem Solving as a methodology to explore geometry construction in context Geometry construction: connections within Strand 2 Section A: Geometry 2012/2013/2014 Foundation Constructions
Purpose Using Problem Solving as a methodology to explore geometry construction in context Geometry construction: connections within Strand 2 Section A: Geometry 2012/2013/2014 Foundation Constructions
Point A location in geometry. A point has no dimensions without any length, width, or depth. This is represented by a dot and is usually labelled.
 Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Extra Practice 1A. Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines. Name Date. 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b)
 Extra Practice 1A Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Draw line segment MN of length 8 cm. a) Use a ruler to draw a line segment parallel to
Extra Practice 1A Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Draw line segment MN of length 8 cm. a) Use a ruler to draw a line segment parallel to
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
5 km. 1. Open the sketch home.gsp provided by your teacher that shows the map above. * Construct a point P anywhere to represent James s home.
 uilding a Home Name James owns a small trout farm near the Drakensberg mountains, South frica, in the shape of a quadrilateral as shown. He wants to build his house so that it takes him the same time to
uilding a Home Name James owns a small trout farm near the Drakensberg mountains, South frica, in the shape of a quadrilateral as shown. He wants to build his house so that it takes him the same time to
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
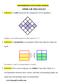 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, Glossary
 TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, 2003 2004 Glossary Absolute value The size of a number with its + or sign removed. The absolute value of 3.2 is 3.2, the absolute value of +4.6 is 4.6. We write this: 3.2 = 3.2
TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS, 2003 2004 Glossary Absolute value The size of a number with its + or sign removed. The absolute value of 3.2 is 3.2, the absolute value of +4.6 is 4.6. We write this: 3.2 = 3.2
3. Radius of incenter, C. 4. The centroid is the point that corresponds to the center of gravity in a triangle. B
 1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
1. Each interior angle of a polygon is 135. How many sides does it have? askiitians
 Class: VIII Subject: Mathematics Topic: Practical Geometry No. of Questions: 19 1. Each interior angle of a polygon is 135. How many sides does it have? (A) 10 (B) 8 (C) 6 (D) 5 (B) Interior angle =. 135
Class: VIII Subject: Mathematics Topic: Practical Geometry No. of Questions: 19 1. Each interior angle of a polygon is 135. How many sides does it have? (A) 10 (B) 8 (C) 6 (D) 5 (B) Interior angle =. 135
Ideas beyond Number. Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets
 Ideas beyond Number Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets Intended outcomes: Students will: extend their knowledge of geometrical objects, both 2D and 3D develop their skills in geometrical reasoning
Ideas beyond Number Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets Intended outcomes: Students will: extend their knowledge of geometrical objects, both 2D and 3D develop their skills in geometrical reasoning
S56 (5.3) Higher Straight Line.notebook June 22, 2015
 Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Day 1: Geometry Terms & Diagrams CC Geometry Module 1
 Name ate ay 1: Geometry Terms & iagrams Geometry Module 1 For #1-3: Identify each of the following diagrams with the correct geometry term. #1-3 Vocab. ank Line Segment Line Ray 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain why
Name ate ay 1: Geometry Terms & iagrams Geometry Module 1 For #1-3: Identify each of the following diagrams with the correct geometry term. #1-3 Vocab. ank Line Segment Line Ray 1. 2. 3. 4. Explain why
PASS. 5.2.b Use transformations (reflection, rotation, translation) on geometric figures to solve problems within coordinate geometry.
 Geometry Name Oklahoma cademic tandards for Oklahoma P PRCC odel Content Frameworks Current ajor Curriculum Topics G.CO.01 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle,
Geometry Name Oklahoma cademic tandards for Oklahoma P PRCC odel Content Frameworks Current ajor Curriculum Topics G.CO.01 Experiment with transformations in the plane. Know precise definitions of angle,
Chapter 6. Sir Migo Mendoza
 Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Circles Chapter 6 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Lesson 6.1 Sir Migo Mendoza Central Angles Definition 5.1 Arc An arc is a part of a circle. Types of Arc Minor Arc Major Arc Semicircle Definition 5.2
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever.
 Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles
 Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
( x 1) 2 + ( y 3) 2 = 25
 The locus of points 2 units from the x-axis. The question does not specify the direction of the 2 units so we must include all options. Therefore, the locus of points 2 units from the x-axis is a pair
The locus of points 2 units from the x-axis. The question does not specify the direction of the 2 units so we must include all options. Therefore, the locus of points 2 units from the x-axis is a pair
Review of 7 th Grade Geometry
 Review of 7 th Grade Geometry In the 7 th Grade Geometry we have covered: 1. Definition of geometry. Definition of a polygon. Definition of a regular polygon. Definition of a quadrilateral. Types of quadrilaterals
Review of 7 th Grade Geometry In the 7 th Grade Geometry we have covered: 1. Definition of geometry. Definition of a polygon. Definition of a regular polygon. Definition of a quadrilateral. Types of quadrilaterals
Angles. Problems: A.! Name the vertex of the angle. What rays are the sides of the angle? C.! Give three other names of LJK.
 ngles page # Problems:. ngles. Name the vertex of the angle.. What rays are the sides of the angle? J. Give three other names of LJK.. Name the following angles with three letters: = = N M The remaining
ngles page # Problems:. ngles. Name the vertex of the angle.. What rays are the sides of the angle? J. Give three other names of LJK.. Name the following angles with three letters: = = N M The remaining
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
NEW YORK GEOMETRY TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 POINTS, LINES, & PLANES {G.G.21, G.G.27} TOPIC A: Concepts Relating to Points, Lines, and Planes PART 1: Basic Concepts and Definitions...1 PART 2: Concepts
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Special Lines and Constructions of Regular Polygons
 Special Lines and Constructions of Regular Polygons A regular polygon with a center A is made up of congruent isosceles triangles with a principal angle A. The red line in the regular pentagon below is
Special Lines and Constructions of Regular Polygons A regular polygon with a center A is made up of congruent isosceles triangles with a principal angle A. The red line in the regular pentagon below is
Chapter 5 Practice Test
 hapter 5 Practice Test Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the value of x. The diagram is not to scale. 40 x 32 40 25 25 a. 32 b. 50 c.
hapter 5 Practice Test Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the value of x. The diagram is not to scale. 40 x 32 40 25 25 a. 32 b. 50 c.
Pi at School. Arindama Singh Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai , India
 Pi at School rindama Singh epartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai-600036, India Email: asingh@iitm.ac.in bstract: In this paper, an attempt has been made to define π by
Pi at School rindama Singh epartment of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai-600036, India Email: asingh@iitm.ac.in bstract: In this paper, an attempt has been made to define π by
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 Constructions Review
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 Constructions Review Complete all questions. Questions 7-18 must be completed on looseleaf paper. Constructions & Definitions to know: Altitudes Orthocenter Centers to know:
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 Constructions Review Complete all questions. Questions 7-18 must be completed on looseleaf paper. Constructions & Definitions to know: Altitudes Orthocenter Centers to know:
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Day 2 [Number Patterns 1.2A/Visual Patterns] Day 3 [Battleship Sample A in class together] [Number Patterns 1.2B/BS1
![Day 2 [Number Patterns 1.2A/Visual Patterns] Day 3 [Battleship Sample A in class together] [Number Patterns 1.2B/BS1 Day 2 [Number Patterns 1.2A/Visual Patterns] Day 3 [Battleship Sample A in class together] [Number Patterns 1.2B/BS1](/thumbs/74/69847188.jpg) Unit 1 Patterns Day 1 Inductive Reasoning 1.1 Define process of observing data, recognizing patterns, making generalizations (conjecture) Examples: meaning of hot, location of hot and cold faucets, Coincidence
Unit 1 Patterns Day 1 Inductive Reasoning 1.1 Define process of observing data, recognizing patterns, making generalizations (conjecture) Examples: meaning of hot, location of hot and cold faucets, Coincidence
Note: For all questions, answer (E) NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees.
 Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
14.2 Angles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals
 Name lass ate 14.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Explore G.12. pply theorems about circles, including
Name lass ate 14.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Explore G.12. pply theorems about circles, including
Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms
 Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Unit 1 asics of Geometry Objective- the students will be able to use undefined terms and definitions to work with points, lines and planes. Undefined Terms 1. Point has no dimension, geometrically looks
Geometry Mathematics Content Standards
 85 The geometry skills and concepts developed in this discipline are useful to all students. Aside from learning these skills and concepts, students will develop their ability to construct formal, logical
85 The geometry skills and concepts developed in this discipline are useful to all students. Aside from learning these skills and concepts, students will develop their ability to construct formal, logical
G12 Centers of Triangles
 Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
Summer 2006 I2T2 Geometry Page 45 6. Turn this page over and complete the activity with a different original shape. Scale actor 1 6 0.5 3 3.1 Perimeter of Original shape Measuring Perimeter Perimeter of
15.2 Angles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals
 Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Name lass ate 15.2 ngles in Inscribed Quadrilaterals Essential Question: What can you conclude about the angles of a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle? Resource Locker Explore Investigating Inscribed
Circumference of a Circle
 Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
1) If a point lies on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
 5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
