Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
|
|
|
- Junior Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India ABSTRACT. In this paper, we will explore and visualize various centres of a triangle using Geogebra. We will discuss basic facts about triangle first and then see how we can locate centres related to triangle. 1. Introduction Mark three non-collinear point P, Q and R on a paper. Join these pints in all possible ways. The segments are PQ, QR and RP. A simple close curve formed by these three segments is called a triangle. A triangle is a 3-sided polygon. Every triangle has three sides and three angles, some of which may be have equal measurements. The sides of a triangle are given special names in the case of a right triangle, the side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse and the other two sides being known as the legs. All triangles are convex. The portion of the plane enclosed by the triangle is called the triangle interior, while the remainder is the exterior. Some basic facts about a triangle are Construction of a triangle is possible only when the sum of lengths of two sides is greater than the third side. The sum of angles in a triangle is 180. If a triangle PQR satisfies PQ = PR then PRQ = PQR. Conversely, if PRQ = PQR then PQ = PR. Triangles which satisfy these conditions are called isosceles triangles. If a triangle ABC satisfies AB = BC = CA then ACB = BAC = CBA. Conversely, if ACB = BAC = CBA then AB = BC = CA. Triangles which satisfy these conditions are called equilateral triangles. If a triangle has its three sides of unequal lengths then it is called a scalene triangle. Let us go through the introduction of Geogebra.
2 2. Introduction to Geogebra GeoGebra is an educational software for exploring and demonstrating Geometry and Algebra. It is an open source application and is freely available. It is capable of representing mathematical objects (at present 2-dimensional) algebraically and geometrically. For example, f(x) = x 2 4x+2, a quadratic function, is represented by a parabola in graphical view and by an equation in algebraic window. A variable in Geogebra is represented by a slider. You can draw an object with the help of tools or by entering command in the input bar of GeoGebra window. 3. Centers of Triangle On every triangle there are points where special lines or circles intersect, and those points usually have very interesting geometrical properties. Such points are called triangle centers. Some examples of triangle centers are incenter, orthocenter, centroid, circumcenter, excenters, Feuerbach point, Fermat points, etc. Concurrent Lines : Three lines are concurrent if there is a point P such that P lies on all three of the lines. The point P is called the point of concurrency. Three segments are concurrent if they have an interior point in common. Two arbitrary lines will intersect in a point unless the lines happen to be parallel. It is rare that three lines should have a point in common. One of the surprising and beautiful aspects of advanced Euclidean geometry is the fact that so many triples of lines determined by triangles are concurrent. Each of the triangle centers in this chapter is an example of that phenomenon. a. Centroid A median of a triangle is a line segment that joins any vertex of the triangle to the mid point of the opposite side. There are three medians of a triangle. Three medians of the triangle meet at a point i.e. they are concurrent. This point of concurrency is knows as the centroid of the triangle. Each median divides the triangle into two smaller triangles of equal areas. One of the basic ideas known about the centroid is that it it divides the medians into a 2:1 ratio. The part of the median near to the vertex is always twice as long as the part near the midpoint of the side. If the coordinates of the triangle are known, then the coordinates of the centroid are the averages of the coordinates of the vertices. If we call the three vertices A(x 1,y 1 ), B(x 2,y 2 ) and C(x 3,y 3 ) then the ( x1 x2 x3)( y1 y2 y3) coordinates of the centroid are , 3 3 In the following figure 1, points D, E and F are respectively the mid points of sides BC, CA and AB of triangle ABC. AD, BE and CF are the medians of triangle and G is its centroid.
3 Centroid of triangle always remains inside the triangle irrespective of its type (scalene, isosceles or equilateral) Figure -1 Centroid (G) of a Triangle b. Circumcenter A perpendicular bisector of a side of a triangle is a line which is perpendicular to the side and also passes through its mid point. There are three perpendicular bisectors of a triangle. Figure 2 Perpendicular Bisectors of a Triangle Three perpendicular bisectors of a triangle meet at a point i.e. they are concurrent. This point is called circumcenter of the triangle. It is called circumcenter because it is the centre of the circle circumscribing the triangle. (a circle passing through the three vertices of the triangle). The distance of circumcenter from three vertices is equal and is the radius of the circumcircle.
4 For an acute triangle the circumcenter is inside the triangle, for obtuse triangle it lies outside and for a right triangle it lies at the mid point of the hypotenuse of the triangle. Figure 3 Circumcenter (C ) of an acute triangle Figure 4 Circumcenter (C ) of an obtuse triangle
5 Figure 5 Circumcenter (C ) of a right triangle c. Incenter An angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects an angle of the triangle. Figure 6 Angle Bisectors There are three angle bisectors of a triangle. Three angle bisectors of a triangle meet at a point or they are concurrent. This point is called incenter of the triangle. It is called the incenter because it is the centre of the circle inscribed (the largest circle that will fit inside the triangle) in the triangle. Centroid of triangle always remains inside the triangle irrespective of its type (scalene, isosceles or equilateral)
6 Figure 7 Incenter (I) of a triangle d. Orthocenter The altitude of a triangle is a line which passes through a vertex of the triangle and is perpendicular to the opposite side. There are therefore three altitudes possible, one from each vertex. Figure 8 Altitudes of a Triangle AF, BE and CF are three altitudes of triangle ABC. The altitudes (perpendiculars from the vertices to the opposite sides) of a triangle meet at a point i.e. they are concurrent. This point is called orthocenter of the triangle.
7 For an acute triangle the orthocenter is inside the triangle, for obtuse triangle it lies outside and for a right triangle it lies at the vertex of the triangle where right angle is formed. Figure 9 Orthocenter (O) of an acute triangle There is a very interesting fact, If the orthocenter of triangle ABC is O, then the orthocenter of triangle OBC is A, the orthocenter of triangle OCA is B and the orthocenter of triangle OAB is C. Figure 10 Orthocenter (O) of an obtuse triangle
8 Figure 11 Orthocenter (O) of a right triangle e. Euler Line The orthocenter O, the circumcenter C, and the centroid G of any triangle are collinear. Furthermore, G is between O and C (unless the triangle is equilateral, in which case the three points coincide) and OG = 2GC. The line through O, C, and G is called the Euler line of the triangle. Figure 12 Euler Line
9 f. Nine Point Circle If ABC is any triangle, then the midpoints of the sides of ABC, the feet of the altitudes of ABC, and the midpoints of the segments joining the orthocenter of ABC to the three vertices of ABC all lie on single circle and this circle is called the nine point circle. Centre of nine point circle always lies on the Euler line, and is the mid point of the line segment joining orthocentre and circumcentre. In an equilateral triangle, the Orthocenter, centroid, and circumcenter conicide, so that the Euler line has a length of 0. Further, the altitiudes and medians are concurrent, so the 9-point circle now contains only 6 points. Figure 13 Nine Point Circle (Scalene Triangle)
10 Nine Point Circle in an Isosceles Triangle In an isosceles triangle the Euler line is collinear with the median from the vertex to the base. The altitude and perpendicular bisectors to the base are the same, so the intersection of those two lines with the base of the triangle is a coincident point. Thus our 9-point circle intersects 8 distinct points. The obtuse isosceles triangle also has 8 points in its 9-point circle. Figure 14 Nine Point Circle (Isosceles Triangle) 4. Conclusion In this study we used Dynamic Geometric Software GeoGebra, to visualize various centers of a triangle. There are many centers of a triangle, we explored four out of them viz Centroid,Circumcenter, Incenter and Orthocenter. We also explored that Centroid, Circumcenter and Orthocenter of a triangle lie on a line called the Euler Line. We also visualized that the distance of the Centroid from the Orthocenter is twice its distance from Circumcenter. In the end we visualized that the mid point of line segment joining Orthocenter and Circumcenter is the center of a circle passing through nine points (feet of the altitudes, the midpoints of the segments joining the orthocenter to the three vertices of the triangle and the midpoints of the sides of the triangle). This circle is called the nine point circle of the triangle. Reference : 1. Notes on Triangle Center
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments
 Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011
 MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
Type of Triangle Definition Drawing. Name the triangles below, and list the # of congruent sides and angles:
 Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
Name: Triangles Test Type of Triangle Definition Drawing Right Obtuse Acute Scalene Isosceles Equilateral Number of congruent angles = Congruent sides are of the congruent angles Name the triangles below,
3. Radius of incenter, C. 4. The centroid is the point that corresponds to the center of gravity in a triangle. B
 1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
1. triangle that contains one side that has the same length as the diameter of its circumscribing circle must be a right triangle, which cannot be acute, obtuse, or equilateral. 2. 3. Radius of incenter,
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Term: Definition: Picture:
 10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric Activities
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 6 Geometric ctivities ompass can be used to construct lengths, angles and many geometric figures. (eg. Line, cirvle, angle, triangle et s you are going through the activities,
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
H.Geometry Chapter 3 Definition Sheet
 Section 3.1 Measurement Tools Construction Tools Sketch Draw Construct Constructing the Duplicate of a Segment 1.) Start with a given segment. 2.) 3.) Constructing the Duplicate of an angle 1.) Start with
Section 3.1 Measurement Tools Construction Tools Sketch Draw Construct Constructing the Duplicate of a Segment 1.) Start with a given segment. 2.) 3.) Constructing the Duplicate of an angle 1.) Start with
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
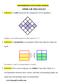 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
If B is the If two angles are
 If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Investigating Properties of Kites
 Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Investigating Properties of Kites Definition: Kite a quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of consecutive equal sides (Figure 1). Construct and Investigate: 1. Determine three ways to construct a kite
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence
 Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
TImath.com. Geometry. Special Segments in Triangles
 Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
Unit 1 Unit 1 A M. M.Sigley, Baker MS. Unit 1 Unit 1. 3 M.Sigley, Baker MS
 A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles
 Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles ***This is different than on your notetaking guide*** PART 1 - VOCABULARY Perpendicular Angle Median Altitude Circumcenter Incenter Centroid Orthocenter A line
Lesson 27/28 Special Segments in Triangles ***This is different than on your notetaking guide*** PART 1 - VOCABULARY Perpendicular Angle Median Altitude Circumcenter Incenter Centroid Orthocenter A line
Exterior Region Interior Region
 Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect and Angle Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Student Outcomes: ~Students learn how to bisect an angle as well as how to copy an angle
How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.)
 Geometric Constructions How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.) Construct a perpendicular line to each side of this triangle. Find the intersection of the three perpendicular lines. This point
Geometric Constructions How to Construct a Perpendicular to a Line (Cont.) Construct a perpendicular line to each side of this triangle. Find the intersection of the three perpendicular lines. This point
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Warm-Up. Find the domain and range:
 Warm-Up Find the domain and range: Geometry Vocabulary & Notation Point Name: Use only the capital letter, without any symbol. Line Name: Use any two points on the line with a line symbol above. AB Line
Warm-Up Find the domain and range: Geometry Vocabulary & Notation Point Name: Use only the capital letter, without any symbol. Line Name: Use any two points on the line with a line symbol above. AB Line
5.4 Medians and Altitudes in Triangles
 5.4. Medians and Altitudes in Triangles www.ck12.org 5.4 Medians and Altitudes in Triangles Learning Objectives Define median and find their point of concurrency in a triangle. Apply medians to the coordinate
5.4. Medians and Altitudes in Triangles www.ck12.org 5.4 Medians and Altitudes in Triangles Learning Objectives Define median and find their point of concurrency in a triangle. Apply medians to the coordinate
S56 (5.3) Higher Straight Line.notebook June 22, 2015
 Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
You MUST know the big 3 formulas!
 Name: Geometry Pd. Unit 3 Lines & Angles Review Midterm Review 3-1 Writing equations of lines. Determining slope and y intercept given an equation Writing the equation of a line given a graph. Graphing
Name: Geometry Pd. Unit 3 Lines & Angles Review Midterm Review 3-1 Writing equations of lines. Determining slope and y intercept given an equation Writing the equation of a line given a graph. Graphing
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
CLASSICAL THEOREMS IN PLANE GEOMETRY. September 2007 BC 1 AC 1 CA 1 BA 1 = 1.
 SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
SSI THEORES I E GEOETRY ZVEZEI STKOV September 2007 ote: ll objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual plane. We say that several points are collinear if they lie on a line. Similarly,
G.CO.C.10: Centroid, Orthocenter, Incenter and Circumcenter
 1 Which geometric principle is used in the construction shown below? 2 In the diagram below of ABC, CD is the bisector of BCA, AE is the bisector of CAB, and BG is drawn. 1) The intersection of the angle
1 Which geometric principle is used in the construction shown below? 2 In the diagram below of ABC, CD is the bisector of BCA, AE is the bisector of CAB, and BG is drawn. 1) The intersection of the angle
Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles
 1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Warm Up. Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes
 Unit 4 Review Warm Up Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes TRIANGLE Definition: A Triangle is a three-sided polygon Characteristics: Has three sides and three angles
Unit 4 Review Warm Up Grab a gold square from the front of the room and fold it into four boxes TRIANGLE Definition: A Triangle is a three-sided polygon Characteristics: Has three sides and three angles
Name. 1) If Q is the vertex angle of isosceles PQR, and RA is a median, find m QR Q. 4 inches A. 2) Which side is the dot closest to?
 enters of Triangles acket 1 Name 1) If Q is the vertex angle of isosceles QR, and R is a median, find m QR Q 4 inches R 2) Which side is the dot closest to? an you draw a point that is the same distance
enters of Triangles acket 1 Name 1) If Q is the vertex angle of isosceles QR, and R is a median, find m QR Q 4 inches R 2) Which side is the dot closest to? an you draw a point that is the same distance
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Centres of a Triangle. Teacher Notes
 Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
Introduction Centres of a Triangle Teacher Notes Centres of a Triangle The aim of this activity is to investigate some of the centres of a triangle and to discover the Euler Line. The activity enables
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
An Approach to Geometry (stolen in part from Moise and Downs: Geometry)
 An Approach to Geometry (stolen in part from Moise and Downs: Geometry) Undefined terms: point, line, plane The rules, axioms, theorems, etc. of elementary algebra are assumed as prior knowledge, and apply
An Approach to Geometry (stolen in part from Moise and Downs: Geometry) Undefined terms: point, line, plane The rules, axioms, theorems, etc. of elementary algebra are assumed as prior knowledge, and apply
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
Geometry Midterm Review
 Geometry Midterm Review **Look at Study Guide and old tests The Midterm covers: Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Parts of Chapter 6 Chapter 1 1.1 point: - has no dimension - represented
Geometry Midterm Review **Look at Study Guide and old tests The Midterm covers: Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Parts of Chapter 6 Chapter 1 1.1 point: - has no dimension - represented
CONSTRUCTIONS Introduction Division of a Line Segment
 216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
216 MATHEMATICS CONSTRUCTIONS 11 111 Introduction In Class IX, you have done certain constructions using a straight edge (ruler) and a compass, eg, bisecting an angle, drawing the perpendicular bisector
Let s Get This Started!
 Lesson. Skills Practice Name Date Let s Get This Started! Points, Lines, Planes, Rays, and Line Segments Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement.. A geometric figure created without
Lesson. Skills Practice Name Date Let s Get This Started! Points, Lines, Planes, Rays, and Line Segments Vocabulary Write the term that best completes each statement.. A geometric figure created without
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson
 Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
University of Sioux Falls. MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry
 University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004. Kay, David, College Geometry: A
University of Sioux Falls MATH 303 Foundations of Geometry Concepts addressed: Geometry Texts Cited: Hvidsten, Michael, Exploring Geometry, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004. Kay, David, College Geometry: A
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Semester Test Topic Review. Correct Version
 Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Chapter 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Undefined Terms: A point has no size but is often represented by a dot and usually named by a capital letter.. A A line extends in two directions without ending. Lines
Unit 2 Triangles Part 1
 Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
Constructions with Compass and Straightedge - Part 2
 Name: Constructions with Compass and Straightedge - Part 2 Original Text By Dr. Bradley Material Supplemented by Mrs.de Nobrega 4.8 Points of Concurrency in a Triangle Our last four constructions are our
Name: Constructions with Compass and Straightedge - Part 2 Original Text By Dr. Bradley Material Supplemented by Mrs.de Nobrega 4.8 Points of Concurrency in a Triangle Our last four constructions are our
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
1) If a point lies on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
 5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given: l
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
First Quarter Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter Unit 1: Geometry Basics
 Document Definitions Geometry/Geometry Honors Pacing Guide Focus: Second Quarter First Quarter Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter Unit 1: Geometry Basics 2.5 weeks/6 blocks Unit 2: Logic and Reasoning
Document Definitions Geometry/Geometry Honors Pacing Guide Focus: Second Quarter First Quarter Second Quarter Third Quarter Fourth Quarter Unit 1: Geometry Basics 2.5 weeks/6 blocks Unit 2: Logic and Reasoning
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA
 GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
Name: Geometry Honors Unit 5 Notes Packet Triangles Properties & More Proofs
 Name: Geometry Honors Unit 5 Notes Packet Triangles Properties & More Proofs 1 Negations, Contradictions, & Intro to Indirect Proof Writing an Indirect Proof: 1 state as an assumption the opposite (negation)
Name: Geometry Honors Unit 5 Notes Packet Triangles Properties & More Proofs 1 Negations, Contradictions, & Intro to Indirect Proof Writing an Indirect Proof: 1 state as an assumption the opposite (negation)
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders
 GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1
 Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Elementary Planar Geometry
 Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Elementary Planar Geometry What is a geometric solid? It is the part of space occupied by a physical object. A geometric solid is separated from the surrounding space by a surface. A part of the surface
Teacher: Mr. Samuels. Name: 1. 2
 Teacher: Mr. Samuels Name: 1. 2 As shown in the diagram below of ΔABC, a compass is used to find points D and E, equidistant from point A. Next, the compass is used to find point F, equidistant from points
Teacher: Mr. Samuels Name: 1. 2 As shown in the diagram below of ΔABC, a compass is used to find points D and E, equidistant from point A. Next, the compass is used to find point F, equidistant from points
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
Geometry CP Pen Argyl Area High School 2018
 Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Midpoint of a Line Segment Pg. 78 # 1, 3, 4-6, 8, 18. Classifying Figures on a Cartesian Plane Quiz ( )
 UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
Curriki Geometry Glossary
 Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
Curriki Geometry Glossary The following terms are used throughout the Curriki Geometry projects and represent the core vocabulary and concepts that students should know to meet Common Core State Standards.
1) If a point lies on the bisector of an angle, then the point is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
 5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s l Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given:
5.1 and 5.2 isectors in s l Theorems about perpendicular bisectors 1) If a point lies on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then the point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment. Given:
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes.
 1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes. A book, a birthday cap and a dice are some examples of 3-D shapes. 1) Write two examples of 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes. A book, a birthday cap and a dice are some examples of 3-D shapes. 1) Write two examples of 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes
Geometry Curriculum Map
 Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Downloaded from Class XI Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Maths
 A point is on the axis. What are its coordinates and coordinates? If a point is on the axis, then its coordinates and coordinates are zero. A point is in the XZplane. What can you say about its coordinate?
A point is on the axis. What are its coordinates and coordinates? If a point is on the axis, then its coordinates and coordinates are zero. A point is in the XZplane. What can you say about its coordinate?
Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Program of Studies TJ Math 1
 Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
For all questions, E. NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.
 For all questions, means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.. In the diagram, given m = 57, m = (x+ ), m = (4x 5). Find the degree measure of the smallest angle. 5. The
For all questions, means none of the above answers is correct. Diagrams are NOT drawn to scale.. In the diagram, given m = 57, m = (x+ ), m = (4x 5). Find the degree measure of the smallest angle. 5. The
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of 4 Congruence
 Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron (solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex)
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Winter March 29, 2015 Mathematical Analysis of Tetrahedron solid angle subtended by any tetrahedron at its vertex) Harish Chandra Rajpoot Rajpoot,
Plane Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2011
 lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
lane Geometry aul Yiu epartment of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2011 NTENTS 101 Theorem 1 If a straight line stands on another straight line, the sum of the adjacent angles so formed is
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry
 8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
