The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals)
|
|
|
- Meryl Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented by a 2D set of discrete samples (pixels) Sampling can cause artifacts (=Aliasing) 2
3 Examples - Moiré Patterns 3
4 Examples - Jaggies Staircase effect at borders 4
5 Temporal Aliasing time real (continuous) motion sampled (perceived) motion 5
6 Aliasing in Computer Graphics Aliasing effects: loss of detail Moiré patterns jaggies Appear in texture mapping scan conversion of geometry raytracing 6
7 Sampling and Reconstruction 7
8 Example Point Sampling 8
9 Signal Processing Aliasing is well understood in signal processing Interpret images as 2D signals Aliasing = sampling of L 2 -functions below the Nyquist frequency u Nyquist = 2 u signal 9
10 Spectrum of an Image What is u signal of an image f(x,y)? Use Fourier analysis (1D first) Represent f(x) as a sum of harmonic waves: F j 2π u x f(x) = F(u)e du The amplitudes F(u) of waves with frequency u (spectrum) are computed as j 2π u x = f(x)e dx { f(x) } F(u) = 10
11 Avoiding Aliasing Let W be the maximum u for which F(u) >0 Either choose u sampling > 2W Or zero all F(u) for u > ½ u sampling i.e. low pass filter the signal Smoothing of image before sampling! e.g. Mip mapping: decreasing sampling rate, increased smoothing 11
12 1D Fourier Transform Fourier transform F Inverse transform F j 2π u x = f(x)e dx { f(x) } F(u) = -1 j 2π u x { F(u) } f(x) = = F(u)e du 12
13 1D Discrete Fourier Transform Discrete transform F(k) = 1 1 N N i= 0 f(i)e j 2π k i N Discrete inverse x = i x, u = k u N f(i) = = k 1 0 F(k)e Heisenberg resolution bounds j 2π k i N x u 1 4π 13
14 F F { f(x,y) } -1 Discrete setting = F(u,v) = { F(u,v) } = f(x,y) = 2D Fourier Transforms f(x,y)e f(x,y)e j 2π(u x+ v y) j 2π(u x+ v y) dx dy du dv F(u,v) = M N M N x= 0 y= 0 f(x,y)e u x v y j 2π( + M N ) f(x,y) = M 1 N 1 u= 0 v= 0 F(u,v)e u x v y j 2π( + M N ) 14
15 Example: 2D Fourier Transforms rect(x,y) sinc(x,y) sine cardinal: sinc( x) = 1 sin( x) / x x = 0 otherwise 15
16 Reconstruction f(i x) g(x) x x reconstruction filter x f(x) x f(x) N = i=1 f ( i x) g( x i x) x 16
17 Convolutions f(x)*g(x) = f(α) g(x α) dα f(x) g(x) x x f(α) g(x-α) x α 17
18 Convolutions f(x) δ(x) x x Discrete setting f(x)* δ (x) = f(α)δ(x α)dα = f(x) f(x)*g(x) = M 1 m= 0 f(m) g(x m) 18
19 Convolutions 2D convolution as a separable TP-extension f(x,y)*g(x,y) = f(α, β) g(x α,y β)dα dβ Discrete form f(x,y)*g(x,y) = M 1 N 1 m= 0 n= 0 f(m,n) g(x m,y n) 19
20 Convolutions Convolution theorem f(x)*g(x) F(u)G(u) f(x)g(x) F(u)*G(u) For function of finite energy (L 2 ) f 2 = f,f = f(x) dx 2 < 20
21 Aliasing Sampling = multiplication with sequence of delta functions (impulse train) 21
22 Aliasing Multiplication converts to convolution in Fourier domain 22
23 Aliasing Convolution with sequence of delta functions = periodization 23
24 Aliasing Overlap of Fourier transforms leads to aliasing 24
25 Aliasing Reconstruction = Low pass filtering 25
26 Aliasing-free Reconstruction Spatial Domain Frequency Domain Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 26
27 Occurrence of Aliasing Spatial Domain Frequency Domain Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 27
28 2D Sampling 2D impulse fields f(x,y) δ(x x0,y y0 )dx dy = f(x0,y0 ) 28
29 Periodic spectrum of band limited sampled function Fourier Domain 29
30 Reconstruction Antialiasing Windowing spectrum using filters Simple f(x,y) = G(u,v) [ S(u,v)*F(u,v) ] where G(u,v) = 1 0 (u,v) else within Bounding Box of R 30
31 2D Sampling Theorem Sampling rate is bounded by u v Finite, discrete setting = = x y 1 N x 1 N y 1 2W u 1 2W v 31
32 32
33 Spectral Analysis Geometry 33
34 Antialiasing Filters in Practice Properties of a good low pass filter 34
35 Antialiasing Filters B-Spline filters of order n x 1 1 sin ω/ 2 sin π f g (x) 2 1 = = = 0 x > 1 ω/ 2 π f 2 sin c f Increase order by repeated convolution g n (x) = g 1(x)*g 1(x)* *g 1(x) sin c n f 35
36 36 Antialiasing Filters Gaussian filters Sinc-filter > = = c c c c c g x x sin x sinc ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ω ) ( ) ( ) ( π π ) ( ) ( ) ( ω σ π ω π σ /σ / ω σ σ σ / σ g e G e x g x = = =
37 Filters and Fourier Transforms 37
38 Filtering in Texture Space and Screen Space 38
39 The Concept of Resampling Filters Perspective projection of a textured surface Non-uniform sampling pattern on screen Optimal resampling filter is spatially variant 39
40 Projection and Image Warping Affine Mapping Projective Mapping 40
41 Relations between Texture and Image Space Texture space Image space warp
42 Spatially Variant Filtering Screen Space Texture Space 42
43 Antialiasing in Raytracing Supersampling Pixel 43
44 Jittering Random Perturbation of Sampling Positions 44
45 Poisson Sampling vs. Jittering 45
46 Supersampling & Jittering 4 Rays/Pixel Jitter=0.3 46
47 Supersampling & Jittering Jitter=0.5 Jitter=1.0 47
48 Supersampling & Jittering 4 Rays/Pixel Jitter=0.3 48
49 Supersampling & Jittering Jitter=0.5 Jitter=1.0 49
50 Adaptive Supersampling 50
51 Adaptive Supersampling 51
Motivation. The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images. 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals)
 Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
To Do. Advanced Computer Graphics. Sampling and Reconstruction. Outline. Sign up for Piazza
 Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 63 [Spring 207], Lecture 3 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Sign up for Piazza To Do Assignment, Due Apr 28. Anyone need help finding partners? Any issues with
Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 63 [Spring 207], Lecture 3 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Sign up for Piazza To Do Assignment, Due Apr 28. Anyone need help finding partners? Any issues with
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Reading. 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory. Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
Aliasing. Can t draw smooth lines on discrete raster device get staircased lines ( jaggies ):
 (Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = 7 + 8 * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ; Aliasing Can t draw
(Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = 7 + 8 * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ; Aliasing Can t draw
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Fourier analysis and sampling theory
 Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Outline. Sampling and Reconstruction. Sampling and Reconstruction. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Outline Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Outline Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Aliasing and Antialiasing. ITCS 4120/ Aliasing and Antialiasing
 Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
Outline. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Computer Graphics. Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory. Hendrik Lensch. Computer Graphics WS07/08 Texturing
 Computer Graphics Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory Hendrik Lensch Overview Last time Texture Parameterization Procedural Shading Today Texturing Filtering 2D Texture Mapping Forward mapping Object surface
Computer Graphics Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory Hendrik Lensch Overview Last time Texture Parameterization Procedural Shading Today Texturing Filtering 2D Texture Mapping Forward mapping Object surface
Computer Graphics. Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing. Philipp Slusallek
 Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications
 Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Advanced Computer Graphics. Aliasing. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Advanced Computer Graphics Aliasing Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline motivation Fourier analysis filtering sampling reconstruction / aliasing antialiasing University
Advanced Computer Graphics Aliasing Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline motivation Fourier analysis filtering sampling reconstruction / aliasing antialiasing University
Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations
 #1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
#1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
Continuous Space Fourier Transform (CSFT)
 C. A. Bouman: Digital Image Processing - January 8, 8 Continuous Space Fourier Transform (CSFT) Forward CSFT: F(u,v) = Inverse CSFT: f(x,y) = f(x,y)e jπ(ux+vy) dxdy F(u,v)e jπ(ux+vy) dudv Space coordinates:.
C. A. Bouman: Digital Image Processing - January 8, 8 Continuous Space Fourier Transform (CSFT) Forward CSFT: F(u,v) = Inverse CSFT: f(x,y) = f(x,y)e jπ(ux+vy) dxdy F(u,v)e jπ(ux+vy) dudv Space coordinates:.
CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing
 Slide Credit: http://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/hypergraph/aliasing/alias0.htm CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing Qixing Huang February 12th 2018 Sampling and Aliasing Display is discrete
Slide Credit: http://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/hypergraph/aliasing/alias0.htm CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing Qixing Huang February 12th 2018 Sampling and Aliasing Display is discrete
Basics. Sampling and Reconstruction. Sampling and Reconstruction. Outline. (Spatial) Aliasing. Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010)
 Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) CS 283, Lecture 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Ravi Ramamoorthi http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs283/fa10 Some slides courtesy Thomas Funkhouser and Pat Hanrahan
Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) CS 283, Lecture 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Ravi Ramamoorthi http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs283/fa10 Some slides courtesy Thomas Funkhouser and Pat Hanrahan
Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration
 Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee2031) Digital Image Processing I
 Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling
 Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling
 Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Sampling: Application to 2D Transformations
 Sampling: Application to 2D Transformations University of the Philippines - Diliman August Diane Lingrand lingrand@polytech.unice.fr http://www.essi.fr/~lingrand Sampling Computer images are manipulated
Sampling: Application to 2D Transformations University of the Philippines - Diliman August Diane Lingrand lingrand@polytech.unice.fr http://www.essi.fr/~lingrand Sampling Computer images are manipulated
Phys. 428, Lecture 6
 Phys. 428, Lecture 6 Mid-Term & Weekly questions Since we are behind in the material, there will be no midterm Instead the final project will be subdivided into graded stages Class Project Pick: An imaging
Phys. 428, Lecture 6 Mid-Term & Weekly questions Since we are behind in the material, there will be no midterm Instead the final project will be subdivided into graded stages Class Project Pick: An imaging
Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Biomedical Image Analysis. Homomorphic Filtering and applications to PET
 Biomedical Image Analysis Homomorphic Filtering and applications to PET Contents: Image enhancement and correction Brightness normalization and contrast enhancement Applications to SPECT BMIA 15 V. Roth
Biomedical Image Analysis Homomorphic Filtering and applications to PET Contents: Image enhancement and correction Brightness normalization and contrast enhancement Applications to SPECT BMIA 15 V. Roth
Signals and Sampling. CMPT 461/761 Image Synthesis Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Möller
 Signals and Sampling CMPT 461/761 Image Synthesis Torsten Möller Reading Chapter 7 of Physically Based Rendering by Pharr&Humphreys Chapter 14.10 of CG: Principles & Practice by Foley, van Dam et al. Chapter
Signals and Sampling CMPT 461/761 Image Synthesis Torsten Möller Reading Chapter 7 of Physically Based Rendering by Pharr&Humphreys Chapter 14.10 of CG: Principles & Practice by Foley, van Dam et al. Chapter
Introduction to Computer Vision. Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino
 Introduction to Computer Vision Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Last Week! Image Sensing " Our eyes: rods and cones " CCD, CMOS, Rolling Shutter " Sensing brightness and sensing color! Projective
Introduction to Computer Vision Week 3, Fall 2010 Instructor: Prof. Ko Nishino Last Week! Image Sensing " Our eyes: rods and cones " CCD, CMOS, Rolling Shutter " Sensing brightness and sensing color! Projective
CoE4TN4 Image Processing. Chapter 5 Image Restoration and Reconstruction
 CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 5 Image Restoration and Reconstruction Image Restoration Similar to image enhancement, the ultimate goal of restoration techniques is to improve an image Restoration: a
CoE4TN4 Image Processing Chapter 5 Image Restoration and Reconstruction Image Restoration Similar to image enhancement, the ultimate goal of restoration techniques is to improve an image Restoration: a
COMP 9517 Computer Vision
 COMP 9517 Computer Vision Frequency Domain Techniques 1 Frequency Versus Spa
COMP 9517 Computer Vision Frequency Domain Techniques 1 Frequency Versus Spa
Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction
 Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction An Introduction Computer Overview Intro - Aliasing Problem definition, Examples Ad-hoc Solutions Sampling theory Fourier transform Convolution Reconstruction
Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction An Introduction Computer Overview Intro - Aliasing Problem definition, Examples Ad-hoc Solutions Sampling theory Fourier transform Convolution Reconstruction
1-D Sampling. Letf s = 1/T be the sampling frequency. What is the relationship between S(e jω ) and G(f)? S(e jω ) = 1. Intuition Scale frequencies
 C. A. Bouman: Digital Image Processing - January 12, 2015 1 1-D Sampling g(t) Continuous timeinput Sampler PeriodT s(n) = g(nt) Discrete timeoutput Letf s = 1/T be the sampling frequency. What is the relationship
C. A. Bouman: Digital Image Processing - January 12, 2015 1 1-D Sampling g(t) Continuous timeinput Sampler PeriodT s(n) = g(nt) Discrete timeoutput Letf s = 1/T be the sampling frequency. What is the relationship
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09. Interpolation. Interpolation techniques B splines
 EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Interpolation Interpolation techniques B splines What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image representation
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Interpolation Interpolation techniques B splines What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image representation
Image warping introduction
 Image warping introduction 1997-2015 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Warping 2015 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 22 Warping.. image
Image warping introduction 1997-2015 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Warping 2015 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 22 Warping.. image
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Biomedical Image Analysis. Spatial Filtering
 Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
DIGITAL IMAGE WARPING. abstract of Digital Image Warping. George Wolberg, IEEE Computer Society Press
 DIGITAL IMAGE WARPING abstract of Digital Image Warping George Wolberg, IEEE Computer Society Press R.A. van der Stelt 10 october 1996 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Spatial Transformations 3 2.1 Perspective
DIGITAL IMAGE WARPING abstract of Digital Image Warping George Wolberg, IEEE Computer Society Press R.A. van der Stelt 10 october 1996 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Spatial Transformations 3 2.1 Perspective
Sampling, Resampling, and Warping. COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser
 Sampling, Resampling, and Warping COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser Image Processing Goal: read an image, process it, write the result input.jpg output.jpg imgpro input.jpg output.jpg histogram_equalization
Sampling, Resampling, and Warping COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser Image Processing Goal: read an image, process it, write the result input.jpg output.jpg imgpro input.jpg output.jpg histogram_equalization
Image Warping: A Review. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Image Warping: A Review Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we review digital image warping: - Geometric transformations - Forward inverse
Image Warping: A Review Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we review digital image warping: - Geometric transformations - Forward inverse
CS4670: Computer Vision
 CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 9: Image alignment http://www.wired.com/gadgetlab/2010/07/camera-software-lets-you-see-into-the-past/ Szeliski: Chapter 6.1 Reading All 2D Linear Transformations
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 9: Image alignment http://www.wired.com/gadgetlab/2010/07/camera-software-lets-you-see-into-the-past/ Szeliski: Chapter 6.1 Reading All 2D Linear Transformations
Tutorial 5. Jun Xu, Teaching Asistant March 2, COMP4134 Biometrics Authentication
 Tutorial 5 Jun Xu, Teaching Asistant nankaimathxujun@gmail.com COMP4134 Biometrics Authentication March 2, 2017 Table of Contents Problems Problem 1: Answer The Questions Problem 2: Indeterminate Region
Tutorial 5 Jun Xu, Teaching Asistant nankaimathxujun@gmail.com COMP4134 Biometrics Authentication March 2, 2017 Table of Contents Problems Problem 1: Answer The Questions Problem 2: Indeterminate Region
Fourier Transform and Texture Filtering
 Fourier Transform and Texture Filtering Lucas J. van Vliet www.ph.tn.tudelft.nl/~lucas Image Analysis Paradigm scene Image formation sensor pre-processing Image enhancement Image restoration Texture filtering
Fourier Transform and Texture Filtering Lucas J. van Vliet www.ph.tn.tudelft.nl/~lucas Image Analysis Paradigm scene Image formation sensor pre-processing Image enhancement Image restoration Texture filtering
Fourier transform of images
 Fourier transform of images Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Methods for Image Processing academic year 2014 2015 Extension to bidimensional domain The concepts
Fourier transform of images Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Methods for Image Processing academic year 2014 2015 Extension to bidimensional domain The concepts
Computer Vision. Fourier Transform. 20 January Copyright by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved
 Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing
 Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Image preprocessing in spatial domain
 Image preprocessing in spatial domain Sampling theorem, aliasing, interpolation, geometrical transformations Revision:.4, dated: May 25, 26 Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical
Image preprocessing in spatial domain Sampling theorem, aliasing, interpolation, geometrical transformations Revision:.4, dated: May 25, 26 Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical
Image preprocessing in spatial domain
 Image preprocessing in spatial domain Sampling theorem, aliasing, interpolation, geometrical transformations Revision:.3, dated: December 7, 25 Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical
Image preprocessing in spatial domain Sampling theorem, aliasing, interpolation, geometrical transformations Revision:.3, dated: December 7, 25 Tomáš Svoboda Czech Technical University, Faculty of Electrical
Central Slice Theorem
 Central Slice Theorem Incident X-rays y f(x,y) R x r x Detected p(, x ) The thick line is described by xcos +ysin =R Properties of Fourier Transform F [ f ( x a)] F [ f ( x)] e j 2 a Spatial Domain Spatial
Central Slice Theorem Incident X-rays y f(x,y) R x r x Detected p(, x ) The thick line is described by xcos +ysin =R Properties of Fourier Transform F [ f ( x a)] F [ f ( x)] e j 2 a Spatial Domain Spatial
Computer Vision: 4. Filtering. By I-Chen Lin Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University
 Computer Vision: 4. Filtering By I-Chen Lin Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Computer Vision: 4. Filtering By I-Chen Lin Dept. of CS, National Chiao Tung University Outline Impulse response and convolution. Linear filter and image pyramid. Textbook: David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Filters and Fourier Transforms
 Filters and Fourier Transforms NOTE: Before reading these notes, see 15-462 Basic Raster notes: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15462/web/notes/notes.html OUTLINE: The Cost of Filtering Fourier
Filters and Fourier Transforms NOTE: Before reading these notes, see 15-462 Basic Raster notes: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15462/web/notes/notes.html OUTLINE: The Cost of Filtering Fourier
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
1. No calculators or other electronic devices are allowed during this exam.
 Version A Math 2E Spring 24 Midterm Exam Instructions. No calculators or other electronic devices are allowed during this exam. 2. You may use one page of notes, but no books or other assistance during
Version A Math 2E Spring 24 Midterm Exam Instructions. No calculators or other electronic devices are allowed during this exam. 2. You may use one page of notes, but no books or other assistance during
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Image Processing: Discrete Images
 7 Image Processing: Discrete Images In the previous chapter we explored linear, shift-invariant systems in the continuous two-dimensional domain. In practice, we deal with images that are both limited
7 Image Processing: Discrete Images In the previous chapter we explored linear, shift-invariant systems in the continuous two-dimensional domain. In practice, we deal with images that are both limited
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Image Processing Lecture 10
 Image Restoration Image restoration attempts to reconstruct or recover an image that has been degraded by a degradation phenomenon. Thus, restoration techniques are oriented toward modeling the degradation
Image Restoration Image restoration attempts to reconstruct or recover an image that has been degraded by a degradation phenomenon. Thus, restoration techniques are oriented toward modeling the degradation
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #16
 Lecture #16 Wiener Filters Constrained Least Squares Filter Computed Tomography Basics Reconstruction and the Radon Transform Fourier Slice Theorem Filtered Backprojections Fan Beams Motion Blurring Model
Lecture #16 Wiener Filters Constrained Least Squares Filter Computed Tomography Basics Reconstruction and the Radon Transform Fourier Slice Theorem Filtered Backprojections Fan Beams Motion Blurring Model
Image Acquisition Image Digitization Spatial domain Intensity domain Image Characteristics
 Image Acquisition Image Digitization Spatial domain Intensity domain Image Characteristics 1 What is an Image? An image is a projection of a 3D scene into a 2D projection plane. An image can be defined
Image Acquisition Image Digitization Spatial domain Intensity domain Image Characteristics 1 What is an Image? An image is a projection of a 3D scene into a 2D projection plane. An image can be defined
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING
 28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
Anti-aliasing and sampling
 Anti-aliasing and sampling 1996-2017 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Sampling 2017 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 34 Spatial and temporal
Anti-aliasing and sampling 1996-2017 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Sampling 2017 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 34 Spatial and temporal
Image Reconstruction from Projection
 Image Reconstruction from Projection Reconstruct an image from a series of projections X-ray computed tomography (CT) Computed tomography is a medical imaging method employing tomography where digital
Image Reconstruction from Projection Reconstruct an image from a series of projections X-ray computed tomography (CT) Computed tomography is a medical imaging method employing tomography where digital
Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain. By Dr. Rajeev Srivastava
 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain By Dr. Rajeev Srivastava CONTENTS Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Domain Methods 1. Point Processing Functions A. Gray Level Transformation functions for
Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain By Dr. Rajeev Srivastava CONTENTS Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Domain Methods 1. Point Processing Functions A. Gray Level Transformation functions for
The simplest and most obvious method to go from a continuous to a discrete image is by point sampling,
 Sampling our scenes are described with triangles giving a continuous 2d color field our images are digital/discrete made up of a grid of dots need to make a bridge between these two worlds else we will
Sampling our scenes are described with triangles giving a continuous 2d color field our images are digital/discrete made up of a grid of dots need to make a bridge between these two worlds else we will
3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory. Paula da Fonseca
 3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory Paula da Fonseca EM course 2017 - Agenda - Overview of: Introduction to Fourier analysis o o o o Sine waves Fourier transform (simple examples of 1D
3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory Paula da Fonseca EM course 2017 - Agenda - Overview of: Introduction to Fourier analysis o o o o Sine waves Fourier transform (simple examples of 1D
Image processing in frequency Domain
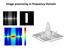 Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Image Restoration. Yao Wang Polytechnic Institute of NYU, Brooklyn, NY 11201
 Image Restoration Yao Wang Polytechnic Institute of NYU, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Partly based on A. K. Jain, Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing, and Gonzalez/Woods, Digital Image Processing Figures from
Image Restoration Yao Wang Polytechnic Institute of NYU, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Partly based on A. K. Jain, Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing, and Gonzalez/Woods, Digital Image Processing Figures from
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies"
 ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
Amortized Supersampling
 Amortized Supersampling LEI YANG H, DIEGO NEHAB M, PEDRO V. SANDER H, PITCHAYA SITTHI-AMORN V, JASON LAWRENCE V, HUGUES HOPPE M H M V Dec. 18, 2009, Pacifico Yokohama, Japan Outline 3/27 Problem Amortized
Amortized Supersampling LEI YANG H, DIEGO NEHAB M, PEDRO V. SANDER H, PITCHAYA SITTHI-AMORN V, JASON LAWRENCE V, HUGUES HOPPE M H M V Dec. 18, 2009, Pacifico Yokohama, Japan Outline 3/27 Problem Amortized
Overview. Spectral Processing of Point- Sampled Geometry. Introduction. Introduction. Fourier Transform. Fourier Transform
 Overview Spectral Processing of Point- Sampled Geometry Introduction Fourier transform Spectral processing pipeline Spectral filtering Adaptive subsampling Summary Point-Based Computer Graphics Markus
Overview Spectral Processing of Point- Sampled Geometry Introduction Fourier transform Spectral processing pipeline Spectral filtering Adaptive subsampling Summary Point-Based Computer Graphics Markus
Solutions to Midterm Exam
 05-76-0 Solutions to Midterm Exam. For the function: f [x] =sin[πx] RECT [x ] (a) Find expressions for the even and odd parts of f [x] (b) Sketch these even and odd parts. It will first be useful to sketch
05-76-0 Solutions to Midterm Exam. For the function: f [x] =sin[πx] RECT [x ] (a) Find expressions for the even and odd parts of f [x] (b) Sketch these even and odd parts. It will first be useful to sketch
Point and Spatial Processing
 Filtering 1 Point and Spatial Processing Spatial Domain g(x,y) = T[ f(x,y) ] f(x,y) input image g(x,y) output image T is an operator on f Defined over some neighborhood of (x,y) can operate on a set of
Filtering 1 Point and Spatial Processing Spatial Domain g(x,y) = T[ f(x,y) ] f(x,y) input image g(x,y) output image T is an operator on f Defined over some neighborhood of (x,y) can operate on a set of
PSD2B Digital Image Processing. Unit I -V
 PSD2B Digital Image Processing Unit I -V Syllabus- Unit 1 Introduction Steps in Image Processing Image Acquisition Representation Sampling & Quantization Relationship between pixels Color Models Basics
PSD2B Digital Image Processing Unit I -V Syllabus- Unit 1 Introduction Steps in Image Processing Image Acquisition Representation Sampling & Quantization Relationship between pixels Color Models Basics
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
Super-Resolution. Many slides from Miki Elad Technion Yosi Rubner RTC and more
 Super-Resolution Many slides from Mii Elad Technion Yosi Rubner RTC and more 1 Example - Video 53 images, ratio 1:4 2 Example Surveillance 40 images ratio 1:4 3 Example Enhance Mosaics 4 5 Super-Resolution
Super-Resolution Many slides from Mii Elad Technion Yosi Rubner RTC and more 1 Example - Video 53 images, ratio 1:4 2 Example Surveillance 40 images ratio 1:4 3 Example Enhance Mosaics 4 5 Super-Resolution
Rasterization. Rasterization (scan conversion) Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) Rasterizing a line. Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA)
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline: rasterization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline: rasterization
Visual Pathways to the Brain
 Visual Pathways to the Brain 1 Left half of visual field which is imaged on the right half of each retina is transmitted to right half of brain. Vice versa for right half of visual field. From each eye
Visual Pathways to the Brain 1 Left half of visual field which is imaged on the right half of each retina is transmitted to right half of brain. Vice versa for right half of visual field. From each eye
ELEC Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW
 ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Dynamic Range and Weber s Law HVS is capable of operating over an enormous dynamic range, However, sensitivity is far from uniform over this range Example:
ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Dynamic Range and Weber s Law HVS is capable of operating over an enormous dynamic range, However, sensitivity is far from uniform over this range Example:
CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images. Joshua Levine
 CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images Joshua Levine levinej@clemson.edu Lecture 19 Projective Warping and Bilinear Warping Nov. 3, 2015 Agenda EC Quiz Review PA06 out Refresher from Lec18 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/affine_transformation
CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images Joshua Levine levinej@clemson.edu Lecture 19 Projective Warping and Bilinear Warping Nov. 3, 2015 Agenda EC Quiz Review PA06 out Refresher from Lec18 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/affine_transformation
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
x' = c 1 x + c 2 y + c 3 xy + c 4 y' = c 5 x + c 6 y + c 7 xy + c 8
 1. Explain about gray level interpolation. The distortion correction equations yield non integer values for x' and y'. Because the distorted image g is digital, its pixel values are defined only at integer
1. Explain about gray level interpolation. The distortion correction equations yield non integer values for x' and y'. Because the distorted image g is digital, its pixel values are defined only at integer
Chapter6 Image Reconstruction
 Chapter6 Image Reconstruction Preview 61I 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Reconstruction by Fourier Inversion 6.3 Reconstruction by convolution and backprojection 6.4 Finite series-expansion 1 Preview Reconstruction
Chapter6 Image Reconstruction Preview 61I 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Reconstruction by Fourier Inversion 6.3 Reconstruction by convolution and backprojection 6.4 Finite series-expansion 1 Preview Reconstruction
Image Processing and Analysis
 Image Processing and Analysis 3 stages: Image Restoration - correcting errors and distortion. Warping and correcting systematic distortion related to viewing geometry Correcting "drop outs", striping and
Image Processing and Analysis 3 stages: Image Restoration - correcting errors and distortion. Warping and correcting systematic distortion related to viewing geometry Correcting "drop outs", striping and
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
Fourier Transform in Image Processing. CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012)
 Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) 1D: Common Transform Pairs Summary source FT Properties: Convolution See book DIP 4.2.5:
Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) 1D: Common Transform Pairs Summary source FT Properties: Convolution See book DIP 4.2.5:
Sampling II, Anti-aliasing, Texture Filtering
 ME-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2017 Jaakko Lehtinen Many slides from Frédo Durand Sampling II, Anti-aliasing, Texture Filtering 1 Sampling The process of mapping a function defined on a continuous domain
ME-C3100 Computer Graphics, Fall 2017 Jaakko Lehtinen Many slides from Frédo Durand Sampling II, Anti-aliasing, Texture Filtering 1 Sampling The process of mapping a function defined on a continuous domain
Image restoration. Lecture 14. Milan Gavrilovic Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University
 Image restoration Lecture 14 Milan Gavrilovic milan@cb.uu.se Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University Computer Assisted Image Analysis 2009-05-08 M. Gavrilovic (Uppsala University) L14 Image restoration
Image restoration Lecture 14 Milan Gavrilovic milan@cb.uu.se Centre for Image Analysis Uppsala University Computer Assisted Image Analysis 2009-05-08 M. Gavrilovic (Uppsala University) L14 Image restoration
To Do. Advanced Computer Graphics. Discrete Convolution. Outline. Outline. Implementing Discrete Convolution
 Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 163 [Spring 2018], Lecture 4 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir To Do Assignment 1, Due Apr 27. Please START EARLY This lecture completes all the material you
Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 163 [Spring 2018], Lecture 4 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir To Do Assignment 1, Due Apr 27. Please START EARLY This lecture completes all the material you
Fall CSCI 420: Computer Graphics. 7.1 Rasterization. Hao Li.
 Fall 2015 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 7.1 Rasterization Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Rendering Pipeline 2 Outline Scan Conversion for Lines Scan Conversion for Polygons Antialiasing 3 Rasterization
Fall 2015 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 7.1 Rasterization Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Rendering Pipeline 2 Outline Scan Conversion for Lines Scan Conversion for Polygons Antialiasing 3 Rasterization
Computer Graphics - Week 8
 Computer Graphics - Week 8 Bengt-Olaf Schneider IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Questions about Last Week? Comments about the Assignment Deadline for 2nd assignment extended to Friday March 12 at 5:30
Computer Graphics - Week 8 Bengt-Olaf Schneider IBM T.J. Watson Research Center Questions about Last Week? Comments about the Assignment Deadline for 2nd assignment extended to Friday March 12 at 5:30
Analysis of Planar Anisotropy of Fibre Systems by Using 2D Fourier Transform
 Maroš Tunák, Aleš Linka Technical University in Liberec Faculty of Textile Engineering Department of Textile Materials Studentská 2, 461 17 Liberec 1, Czech Republic E-mail: maros.tunak@tul.cz ales.linka@tul.cz
Maroš Tunák, Aleš Linka Technical University in Liberec Faculty of Textile Engineering Department of Textile Materials Studentská 2, 461 17 Liberec 1, Czech Republic E-mail: maros.tunak@tul.cz ales.linka@tul.cz
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler
 CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 2 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 2 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
Lecture 8: Jointly distributed random variables
 Lecture : Jointly distributed random variables Random Vectors and Joint Probability Distributions Definition: Random Vector. An n-dimensional random vector, denoted as Z = (Z, Z,, Z n ), is a function
Lecture : Jointly distributed random variables Random Vectors and Joint Probability Distributions Definition: Random Vector. An n-dimensional random vector, denoted as Z = (Z, Z,, Z n ), is a function
Texture. Outline. Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation
 Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Distribution Ray-Tracing. Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos
 Distribution Ray-Tracing Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Bibliography K. Suffern; Ray Tracing from the Ground Up, http://www.raytracegroundup.com Chapter 4, 5 for Anti-Aliasing Chapter 6 for Disc Sampling
Distribution Ray-Tracing Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Bibliography K. Suffern; Ray Tracing from the Ground Up, http://www.raytracegroundup.com Chapter 4, 5 for Anti-Aliasing Chapter 6 for Disc Sampling
