Tools, Tips, and Workflows Breaklines, Part 4 Applying Breaklines to Enforce Constant Elevation
|
|
|
- Godwin Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Breaklines, Part 4 Applying Breaklines to l Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 In the last edition of LP360 News, we discussed the creation of 3D breaklines. Recall that, for our purposes, a 3D breakline is a vector that has an elevation value (Z) associated with each vertex. Generally, 3D breaklines can be divided into two categories those with the same elevation for each vertex (used for flat water bodies, for example) and those with the ability to store a different elevation value for each vertex (a down-stream flow polyline, for example). In this edition, let s look at a constant Z example such as a flat water body. A common method of collecting flat water bodies is to use heads-up digitizing from an orthophoto for the X, Y (planimetric) aspects of the construction and to store the desired (and single-valued) elevation in an attribute table. I like this storage approach as compared to using a pure 3D vector (where Z is stored on each vertex) since it saves 1/3 of the storage. Why store a Z value at each polygon vertex when all Zs are the same? In Figure 1 is depicted a water body in the Boulder, Colorado area. This figure is rendered as points, colorized in gray by the LIDAR return intensity. These data have not been classified, yet it is obvious that this is a water body. LP360 Basic Edition ArcGIS QCoherent Software LLC LP360 Standard Edition Windows Page 1 of 8 LP360 suas Edition GeoCue (phone) LP360 Advanced Edition (fax)
2 Figure 1: A water body shown rendered by intensity In Figure 2 is depicted the lake rendered as an elevation color-coded triangulated irregular network (TIN), modulated by intensity. Notice several features of this water body. First of all, the water body is not flat as is evident by the shaded relief triangle facets that appear on the lake surface. Secondly, note the water points that are showing in the profile view. Due to vertical noise in the LIDAR and potentially wave action on the water body, these water points will not exhibit the same vertical values and hence will distort a TIN rendering of the surface. Finally, note (from the profile graticule) that the elevation of this lake is about 1,872 meters above the datum. Thus, while we expect a water body to be flat, we do not (at least in general) expect the elevation to be at zero. Lewis Graham Page 2 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
3 Figure 2: Lake rendered as a TIN with water points shown in the profile window To flatten this water body, we must do several things: Construct a polygon that denotes the land-water boundary Provide a single elevation value to be used for designating the elevation of the water body Either remove all interior points from inclusion in the TIN or set their elevation values to the chosen water body elevation When following best practices in LIDAR data processing, the values of X, Y and/or Z coordinates are never changed once past the rigorous geometric correction phase. Therefore, we will eliminate the use of the interior water points rather than change their coordinate values (in fact, there is not a tool in LP360 that will allow you to change point coordinates!). The polygon (for LP360 for ArcGIS) will be either a 2D or 3D ArcMap feature. As previously mentioned, there is no need to use a 3D feature for a flat surface since each vertex Z will be set to the same value. I will provide an example of extracting the Z value from the LIDAR as the method of resolving the elevation value to use for the lake surface. The Summarize Z method of conflation is used for this task (see Figure 3). Lewis Graham Page 3 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
4 Figure 3: The Summarize Z dialog Note in Figure 4 that there are a number of methods of computing the Z value. If you know the value that you would like to use, you can simply check the Constant Z option and key in this value. You can also use statistics of points either within a range of the vertices or completely within the polygon that is to be drawn. I have set the method to use points completely within the polygon that I will draw. I chose this method since a visual inspection of the lake revealed that the interior points were relatively flat and should provide a reasonable estimate of the water surface level. Note that other methods are available that allow you to set a radius around each point and compute the statistics by including all points within the circle. Note that I have elected to compute a single set of values and store these in the attribute table. This means that I must add the attributes to the attribute table prior to running the conflation method. I have chosen to compute Mean, Min, Max and Standard Deviation since, by examining the results, I can quickly detect if I have anomalies in the data that will affect the result. Lewis Graham Page 4 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
5 Figure 4: Computing the Z value I now simply digitize the lake shore from the LIDAR TIN rendering. Note that LP360 combines the profile view with the Map View to allow you to easily see the true shore line. This is activated by pressing the P key while digitizing a breakline. A white vertical line is displayed in the profile view at the location where a point will be digitized in the Map View (see Figure 5). Lewis Graham Page 5 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
6 Figure 5: Digitizing the shoreline (note the vertical white line in the profile view) The resultant breakline and collected statistics are depicted in Figure 6. Note that the system computed a mean Z value of 1, m with a standard deviation of m. Due to the relatively small standard deviation, I am satisfied with this result and will apply the Mean Z as the elevation to use for the flattening operation. The next step is to classify all of the interior points as Water points. Note that I could have done this concurrently with digitizing the breakline. However, I like to keep this as a separate Classify by Feature step in case I make a mistake in breakline digitizing and have to modify the feature. The interior points are reclassified to Water by using the Classify by Feature tool in LP360. I set the source class to All and the destination class to Water (see the LP360 online help for details on this and the other operations in this article). Lewis Graham Page 6 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
7 Figure 6: Breakline with collected statistics I am now ready to enforce my new breakline. In the breakline enforcement dialog, I set the Buffer Class to Water so that the water points are not included in the TIN surface. The result is depicted in Figure 7. Notice that the water surface is perfectly flat (in the TIN rendering) and that none of the contours cross the breakline. To create a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with the breaklines enforced, I simply use the Export Wizard in LP360, setting the breakline option the same as I have in this exercise. The result will be a gridded elevation model with flat water surfaces. In the next edition of LP360 News, we will examine breaklines where the Z component varies from vertex to vertex. If you have any problems with breakline concepts, just post a note to our new Google Group, LP360. Lewis Graham Page 7 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
8 Figure 7: The enforced breakline Lewis Graham Page 8 of 8 QCoherent Software LLC
Tools, Tips and Workflows LP360 Under the Hood - The Conflation Point Cloud Task LP360
 Tools, Tips and Workflows LP360 Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 l In the January issue of GeoCue News, we discussed the new Point (PCT) overhaul that we released in LP360 2013.2. The focus of the last article
Tools, Tips and Workflows LP360 Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 l In the January issue of GeoCue News, we discussed the new Point (PCT) overhaul that we released in LP360 2013.2. The focus of the last article
Tools, Tips, and Workflows LP360 Under the Hood: Cross-sections LP360
 LP360 Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 l As we outlined in a previous LP360 Under the Hood, we have added volumetric analysis to LP360. This feature was first released with 2013.2 at the end of last year with
LP360 Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 l As we outlined in a previous LP360 Under the Hood, we have added volumetric analysis to LP360. This feature was first released with 2013.2 at the end of last year with
Tools, Tips, and Workflows Exporting Final Product LP360
 LP360 Support Revision 1.0 l Final products can be exported from LIDAR data using either LP360 command line executables or the LP360 Export Wizard. Some export functions and resulting products include,
LP360 Support Revision 1.0 l Final products can be exported from LIDAR data using either LP360 command line executables or the LP360 Export Wizard. Some export functions and resulting products include,
l GeoCue Group Support 2/8/2016 Revision 1.0
 , Tips, and Workflows LP360, versions 2015.1 and above l GeoCue Group Support 2/8/2016 Revision 1.0 Ground Classification After LIDAR data has been collected and delivered to the processing office one
, Tips, and Workflows LP360, versions 2015.1 and above l GeoCue Group Support 2/8/2016 Revision 1.0 Ground Classification After LIDAR data has been collected and delivered to the processing office one
Tools, Tips, and Workflows Automatic Building Extraction
 l Andrew Walker Revision 1.0 Last month s tool tip discussed using the Planar Point Filter to filter buildings from point cloud data. This month s tool tip discusses building extraction, essentially the
l Andrew Walker Revision 1.0 Last month s tool tip discussed using the Planar Point Filter to filter buildings from point cloud data. This month s tool tip discusses building extraction, essentially the
Tools, Tips and Workflows Thinning Feature Vertices in LP360 LP360,
 LP360, 2017.1 l L. Graham 7 January 2017 We have lot of LP360 customers with a variety of disparate feature collection and editing needs. To begin to address these needs, we introduced a completely new
LP360, 2017.1 l L. Graham 7 January 2017 We have lot of LP360 customers with a variety of disparate feature collection and editing needs. To begin to address these needs, we introduced a completely new
Tools River Flattening in TerraModeler TerraModeler, versions 12.xxx and above
 TerraModeler, versions 12.xxx and above GeoCue Group Support 1/12/2016 Hydro-flattening is a common requirement when it comes to delivering surface models to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) National
TerraModeler, versions 12.xxx and above GeoCue Group Support 1/12/2016 Hydro-flattening is a common requirement when it comes to delivering surface models to the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) National
Tools, Tips, and Workflows Automatic Ground Classification of Dense Point Clouds in LP360
 Automatic Ground Classification of Dense Point Clouds LP360, versions 2014.1 and above Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 The density of point clouds (usually expressed as points per square meter) is increasing
Automatic Ground Classification of Dense Point Clouds LP360, versions 2014.1 and above Lewis Graham Revision 1.0 The density of point clouds (usually expressed as points per square meter) is increasing
The 3D Analyst extension extends ArcGIS to support surface modeling and 3- dimensional visualization. 3D Shape Files
 NRM 435 Spring 2016 ArcGIS 3D Analyst Page#1 of 9 0B3D Analyst Extension The 3D Analyst extension extends ArcGIS to support surface modeling and 3- dimensional visualization. 3D Shape Files Analogous to
NRM 435 Spring 2016 ArcGIS 3D Analyst Page#1 of 9 0B3D Analyst Extension The 3D Analyst extension extends ArcGIS to support surface modeling and 3- dimensional visualization. 3D Shape Files Analogous to
Tools, Tips, and Workflows An Introduction to LAS File Analyst LP360
 LP360 l In 2016 we added a very powerful new tool to LP360 (standalone version) called Feature Analyst. This is a tabular-driven tool that synchronizes a table view of Features, Feature Parts and Vertices
LP360 l In 2016 we added a very powerful new tool to LP360 (standalone version) called Feature Analyst. This is a tabular-driven tool that synchronizes a table view of Features, Feature Parts and Vertices
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
LP360 for ArcGIS Tool Guide
 Common ArcMap Tools Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) Add Data Zoom In Measure Point Cloud Tasks Tab Identify Zoom Out Select Features ArcToolbox Pan Full LAS Files Tab ArcCatalog LP360 Basic
Common ArcMap Tools Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) Add Data Zoom In Measure Point Cloud Tasks Tab Identify Zoom Out Select Features ArcToolbox Pan Full LAS Files Tab ArcCatalog LP360 Basic
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
Tools, Tips and Workflows Colorized Point Clouds take on Role of 3D Image
 l Karrie-Sue Simmers, Darrick Wagg 1-15-2013 Revision 1.0 In a visual world an image is easily recognizable to viewers when compared to a monochrome point cloud and can be one of the biggest challenges
l Karrie-Sue Simmers, Darrick Wagg 1-15-2013 Revision 1.0 In a visual world an image is easily recognizable to viewers when compared to a monochrome point cloud and can be one of the biggest challenges
Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor
 Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor Written by Rick Guritz Alaska Satellite Facility Nov. 24, 2015 Contents
Alaska Department of Transportation Roads to Resources Project LiDAR & Imagery Quality Assurance Report Juneau Access South Corridor Written by Rick Guritz Alaska Satellite Facility Nov. 24, 2015 Contents
Tools Control Point Comparison QA-QC Analysis
 l Darrick Wagg, Support Services Manager 8/15/2012 Revision 1.0 By Darrick Wagg, Support Services Manager An important evaluation to make when performing a QAQC analysis of a LIDAR data set is a control
l Darrick Wagg, Support Services Manager 8/15/2012 Revision 1.0 By Darrick Wagg, Support Services Manager An important evaluation to make when performing a QAQC analysis of a LIDAR data set is a control
Introduction to GIS 2011
 Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
Introduction to GIS 2011 Digital Elevation Models CREATING A TIN SURFACE FROM CONTOUR LINES 1. Start ArcCatalog from either Desktop or Start Menu. 2. In ArcCatalog, create a new folder dem under your c:\introgis_2011
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
Tools, Tips, and Workflows LP360 Rail Extraction Tools LP360, versions and above
 , Tips, and Workflows LP360, versions 2016.1 and above l 06 March 2017 L. Graham Overview LP360 includes tools to automatically extract a rail alignment (centerline) feature as a polyline as well as classify
, Tips, and Workflows LP360, versions 2016.1 and above l 06 March 2017 L. Graham Overview LP360 includes tools to automatically extract a rail alignment (centerline) feature as a polyline as well as classify
SMS v D Summary Table. SRH-2D Tutorial. Prerequisites. Requirements. Time. Objectives
 SMS v. 12.3 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives Learn the process of making a summary table to compare the 2D hydraulic model results with 1D hydraulic model results. This tutorial introduces a method of presenting
SMS v. 12.3 SRH-2D Tutorial Objectives Learn the process of making a summary table to compare the 2D hydraulic model results with 1D hydraulic model results. This tutorial introduces a method of presenting
Spatial Density Distribution
 GeoCue Group Support Team 5/28/2015 Quality control and quality assurance checks for LIDAR data continue to evolve as the industry identifies new ways to help ensure that data collections meet desired
GeoCue Group Support Team 5/28/2015 Quality control and quality assurance checks for LIDAR data continue to evolve as the industry identifies new ways to help ensure that data collections meet desired
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
The following sections provide step by step guidance on using the Toe Extractor. 2.1 Creating an Instance of the Toe Extractor Point Cloud Task
 , Tips, and Workflows LP360, versions 2015.1 and above l support@lp360.com 11/8/2016 Revision 1.0 1 Introduction LP360 includes a Point Cloud Task (PCT) that will automatically digitize the toe of a clean
, Tips, and Workflows LP360, versions 2015.1 and above l support@lp360.com 11/8/2016 Revision 1.0 1 Introduction LP360 includes a Point Cloud Task (PCT) that will automatically digitize the toe of a clean
UNDERSTAND HOW TO SET UP AND RUN A HYDRAULIC MODEL IN HEC-RAS CREATE A FLOOD INUNDATION MAP IN ARCGIS.
 CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
CE 412/512, Spring 2017 HW9: Introduction to HEC-RAS and Floodplain Mapping Due: end of class, print and hand in. HEC-RAS is a Hydrologic Modeling System that is designed to describe the physical properties
A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM
 A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM Sagar Deshpande 1 and Alper Yilmaz 2 1 Surveying Engineering, Ferris State University 2 Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geodetic
A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM Sagar Deshpande 1 and Alper Yilmaz 2 1 Surveying Engineering, Ferris State University 2 Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geodetic
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 3D Data: Modeling with ArcGIS 3D Analyst and Google Earth Introduction to 3D Data is a self - study tutorial workbook that teaches you how to create data and maps with ESRI s
The Reference Library Generating Low Confidence Polygons
 GeoCue Support Team In the new ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data, low confidence areas within LIDAR data are defined to be where the bare earth model might not meet the overall
GeoCue Support Team In the new ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data, low confidence areas within LIDAR data are defined to be where the bare earth model might not meet the overall
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document
 City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
City of La Crosse Online Mapping Website Help Document This document was created to assist in using the new City of La Crosse online mapping sites. When the website is first opened, a map showing the City
Objectives Learn how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters can be used for interpolation in GMS.
 v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives Learn how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters can be used for interpolation
v. 9.1 GMS 9.1 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives Learn how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters can be used for interpolation
Improved Applications with SAMB Derived 3 meter DTMs
 Improved Applications with SAMB Derived 3 meter DTMs Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 20 April 2005 This report sums up the processes used to create several products from the Lorado 7
Improved Applications with SAMB Derived 3 meter DTMs Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 20 April 2005 This report sums up the processes used to create several products from the Lorado 7
Vector Data Analysis Working with Topographic Data. Vector data analysis working with topographic data.
 Vector Data Analysis Working with Topographic Data Vector data analysis working with topographic data. 1 Triangulated Irregular Network Triangulated Irregular Network 2 Triangulated Irregular Networks
Vector Data Analysis Working with Topographic Data Vector data analysis working with topographic data. 1 Triangulated Irregular Network Triangulated Irregular Network 2 Triangulated Irregular Networks
v Introduction to WMS Become familiar with the WMS interface WMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 s v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Read files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Read files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
MODULE 1 BASIC LIDAR TECHNIQUES
 MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
MODULE SCENARIO One of the first tasks a geographic information systems (GIS) department using lidar data should perform is to check the quality of the data delivered by the data provider. The department
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
QUALITY CONTROL METHOD FOR FILTERING IN AERIAL LIDAR SURVEY
 QUALITY CONTROL METHOD FOR FILTERING IN AERIAL LIDAR SURVEY Y. Yokoo a, *, T. Ooishi a, a Kokusai Kogyo CO., LTD.,Base Information Group, 2-24-1 Harumicho Fuchu-shi, Tokyo, 183-0057, JAPAN - (yasuhiro_yokoo,
QUALITY CONTROL METHOD FOR FILTERING IN AERIAL LIDAR SURVEY Y. Yokoo a, *, T. Ooishi a, a Kokusai Kogyo CO., LTD.,Base Information Group, 2-24-1 Harumicho Fuchu-shi, Tokyo, 183-0057, JAPAN - (yasuhiro_yokoo,
Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY
 LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
LAB #7 Creating TIN and 3D scenes (ArcScene) GISC, UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce and explore surface data analysis using a vector data model: TIN. We
Civil 3D Introduction
 Civil 3D Introduction Points Overview Points are data collected by surveyors which represent existing site conditions (elevations, boundaries, utilities, etc.). Each point is numbered (or named) and has
Civil 3D Introduction Points Overview Points are data collected by surveyors which represent existing site conditions (elevations, boundaries, utilities, etc.). Each point is numbered (or named) and has
Image Services for Elevation Data
 Image Services for Elevation Data Peter Becker Need for Elevation Using Image Services for Elevation Data sources Creating Elevation Service Requirement: GIS and Imagery, Integrated and Accessible Field
Image Services for Elevation Data Peter Becker Need for Elevation Using Image Services for Elevation Data sources Creating Elevation Service Requirement: GIS and Imagery, Integrated and Accessible Field
Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst
 2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
NEW HORIZONTAL ACCURACY ASSESSMENT TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES FOR LIDAR DATA INTRODUCTION
 NEW HORIZONTAL ACCURACY ASSESSMENT TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES FOR LIDAR DATA John A. Ray Ohio Department of Transportation Columbus, Ohio 43223 john.ray@dot.state.oh.us Lewis Graham GeoCue Corporation Madison,
NEW HORIZONTAL ACCURACY ASSESSMENT TOOLS AND TECHNIQUES FOR LIDAR DATA John A. Ray Ohio Department of Transportation Columbus, Ohio 43223 john.ray@dot.state.oh.us Lewis Graham GeoCue Corporation Madison,
INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE
 111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
111 Mulford Hall, College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley (510) 643-4539 INTRODUCTION TO GIS WORKSHOP EXERCISE This exercise is a survey of some GIS and spatial analysis tools for ecological and natural
LIDAR ESSENTIALS: Module 4
 LIDAR ESSENTIALS: Module 4 Alan Lulloff Association of State Floodplain Managers 575 D'Onofrio Drive, Suite 200 Madison, WI 53719 608-828-3000 alan@floods.org www.floods.org Lewis Graham GeoCue Corporation
LIDAR ESSENTIALS: Module 4 Alan Lulloff Association of State Floodplain Managers 575 D'Onofrio Drive, Suite 200 Madison, WI 53719 608-828-3000 alan@floods.org www.floods.org Lewis Graham GeoCue Corporation
LiDAR QA/QC - Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment report -
 LiDAR QA/QC - Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment report - CT T0009_LiDAR September 14, 2007 Submitted to: Roald Haested Inc. Prepared by: Fairfax, VA EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This LiDAR project covered approximately
LiDAR QA/QC - Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment report - CT T0009_LiDAR September 14, 2007 Submitted to: Roald Haested Inc. Prepared by: Fairfax, VA EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This LiDAR project covered approximately
3D Model - Data Transfer Guide
 Introduction 3D Model - The Leicester City model is a photogrammetric survey based 3D representation of 380ha of Leicester s Central Regeneration Area. The model is to be: Used for marketing and inward
Introduction 3D Model - The Leicester City model is a photogrammetric survey based 3D representation of 380ha of Leicester s Central Regeneration Area. The model is to be: Used for marketing and inward
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data
 Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Making Yield Contour Maps Using John Deere Data Exporting the Yield Data Using JDOffice 1. Data Format On Hard Drive 2. Start program JD Office. a. From the PC Card menu on the left of the screen choose
Masking Lidar Cliff-Edge Artifacts
 Masking Lidar Cliff-Edge Artifacts Methods 6/12/2014 Authors: Abigail Schaaf is a Remote Sensing Specialist at RedCastle Resources, Inc., working on site at the Remote Sensing Applications Center in Salt
Masking Lidar Cliff-Edge Artifacts Methods 6/12/2014 Authors: Abigail Schaaf is a Remote Sensing Specialist at RedCastle Resources, Inc., working on site at the Remote Sensing Applications Center in Salt
Field-Scale Watershed Analysis
 Conservation Applications of LiDAR Field-Scale Watershed Analysis A Supplemental Exercise for the Hydrologic Applications Module Andy Jenks, University of Minnesota Department of Forest Resources 2013
Conservation Applications of LiDAR Field-Scale Watershed Analysis A Supplemental Exercise for the Hydrologic Applications Module Andy Jenks, University of Minnesota Department of Forest Resources 2013
Lecture 06. Raster and Vector Data Models. Part (1) Common Data Models. Raster. Vector. Points. Points. ( x,y ) Area. Area Line.
 Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Lecture 06 Raster and Vector Data Models Part (1) 1 Common Data Models Vector Raster Y Points Points ( x,y ) Line Area Line Area 2 X 1 3 Raster uses a grid cell structure Vector is more like a drawn map
Tutorial (Intermediate level): Dense Cloud Classification and DTM generation with Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.1
 Tutorial (Intermediate level): Dense Cloud Classification and DTM generation with Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.1 This tutorial illustrates how to perform dense point cloud classification in manual and automatic
Tutorial (Intermediate level): Dense Cloud Classification and DTM generation with Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.1 This tutorial illustrates how to perform dense point cloud classification in manual and automatic
Esri International User Conference. July San Diego Convention Center. Lidar Solutions. Clayton Crawford
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Lidar Solutions Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Lidar Solutions Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density
Introduction to 3D Analysis. Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri
 Introduction to 3D Analysis Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri Area & Volume 3D Analyst Features Detect Change Determine Cut/Fill Calculate Surface Area & Volume Data Management Data Creation Data Conversion
Introduction to 3D Analysis Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri Area & Volume 3D Analyst Features Detect Change Determine Cut/Fill Calculate Surface Area & Volume Data Management Data Creation Data Conversion
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
The complete design environment for road planning & construction ANADELTA TESSERA.
 The complete design environment for road planning & construction Short Description Short Description ANADELTA TESSERA Tessera is the professional, standards-based road design solution helping civil engineers
The complete design environment for road planning & construction Short Description Short Description ANADELTA TESSERA Tessera is the professional, standards-based road design solution helping civil engineers
Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections. Summary. Coming up with a plan. Using the Point To Raster geoprocessing tool
 Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
Page 1 of 5 Creating raster DEMs and DSMs from large lidar point collections ArcGIS 10 Summary Raster, or gridded, elevation models are one of the most common GIS data types. They can be used in many ways
Tips for a Good Meshing Experience
 Tips for a Good Meshing Experience Meshes are very powerful and flexible for modeling 2D overland flows in a complex urban environment. However, complex geometries can be frustrating for many modelers
Tips for a Good Meshing Experience Meshes are very powerful and flexible for modeling 2D overland flows in a complex urban environment. However, complex geometries can be frustrating for many modelers
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models
 Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
CHAPTER 5 DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL AND 3D VISUALIZATION
 CHAPTER 5 DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL AND 3D VISUALIZATION A digital elevation model (DEM) is a digital model or 3D representation of a terrain's surface. A DEM can be represented as a raster (a grid of squares,
CHAPTER 5 DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL AND 3D VISUALIZATION A digital elevation model (DEM) is a digital model or 3D representation of a terrain's surface. A DEM can be represented as a raster (a grid of squares,
v CMS-Flow SMS Tutorials Requirements Time Prerequisites Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This lesson demonstrates how to prepare a grid and run a solution using. Prerequisites SMS Overview Requirements Map Module Cartesian Grid Module Scatter Module Time
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This lesson demonstrates how to prepare a grid and run a solution using. Prerequisites SMS Overview Requirements Map Module Cartesian Grid Module Scatter Module Time
Creating advanced shadedrelief maps and layer blending with Global Mapper software
 Creating advanced shadedrelief maps and layer blending with Global Mapper software J. Buck Ehler GIS Analyst/Cartographer Utah Geological Survey buckehler@utah.gov (801) 537-3343 SLUG Meeting August 11,
Creating advanced shadedrelief maps and layer blending with Global Mapper software J. Buck Ehler GIS Analyst/Cartographer Utah Geological Survey buckehler@utah.gov (801) 537-3343 SLUG Meeting August 11,
Surfaces CHAPTER INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES
 CHAPTER 4 Surfaces INTRODUCTION This chapter introduces the surface object. A surface is a triangulated or grid data net and represents a surface s elevations and slopes. Surface data can be points, nodes,
CHAPTER 4 Surfaces INTRODUCTION This chapter introduces the surface object. A surface is a triangulated or grid data net and represents a surface s elevations and slopes. Surface data can be points, nodes,
Recreating Hand Drawn Contour Maps using Didger and Surfer
 Recreating Hand Drawn Contour Maps using Didger and Surfer Have you ever had a scanned contour map that you wanted to convert into a digital version? You might want to do this to easily change contour
Recreating Hand Drawn Contour Maps using Didger and Surfer Have you ever had a scanned contour map that you wanted to convert into a digital version? You might want to do this to easily change contour
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data. A story of data, more data and some more data
 Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data A story of data, more data and some more data Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Introduction and Background
Reality Check: Processing LiDAR Data A story of data, more data and some more data Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Red River of the North Introduction and Background
Raster Data. James Frew ESM 263 Winter
 Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons attributes linked to feature ID explicit location every point has coordinates 2 Fields
Raster Data 1 Vector Data Review discrete objects geometry = points by themselves connected lines closed polygons attributes linked to feature ID explicit location every point has coordinates 2 Fields
v Getting Started An introduction to GMS GMS Tutorials Time minutes Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial An introduction to GMS Objectives This tutorial introduces GMS and covers the basic elements of the user interface. It is the first tutorial that new users should complete. Prerequisite
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial An introduction to GMS Objectives This tutorial introduces GMS and covers the basic elements of the user interface. It is the first tutorial that new users should complete. Prerequisite
AEC Logic. AEC Terrain. A program to manage earth works in a construction project. Yudhishtirudu Gaddipati 29-Jun-13
 AEC Logic AEC Terrain A program to manage earth works in a construction project Yudhishtirudu Gaddipati 29-Jun-13 Contents 1 Introduction:... 5 2 Program Launch... 5 2.1 How to Launch Program... 5 2.2
AEC Logic AEC Terrain A program to manage earth works in a construction project Yudhishtirudu Gaddipati 29-Jun-13 Contents 1 Introduction:... 5 2 Program Launch... 5 2.1 How to Launch Program... 5 2.2
Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Import, view, edit, convert, and digitize triangulated irregular networks Objectives Import survey data in an XYZ format. Digitize elevation points using contour imagery. Edit
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Education Curriculum Student Workbook Unit 2: Create Ground Data
 AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Education Curriculum Student Workbook Unit 2: Create Ground Data Lesson 3 Surfaces Overview In this lesson, you learn how to work with surfaces in AutoCAD Civil 3D. Surfaces are threedimensional
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2010 Education Curriculum Student Workbook Unit 2: Create Ground Data Lesson 3 Surfaces Overview In this lesson, you learn how to work with surfaces in AutoCAD Civil 3D. Surfaces are threedimensional
Overview of the SMS Interface for the CMS and New CIRP Additions: CIRP Wiki and CMS Discussion List
 Overview of the SMS Interface for the CMS and New Additions: Wiki and CMS Discussion List Mitch Brown Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Engineer Research and Development Center May 20, 2010 US Army Corps
Overview of the SMS Interface for the CMS and New Additions: Wiki and CMS Discussion List Mitch Brown Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Engineer Research and Development Center May 20, 2010 US Army Corps
Getting Started With LP360
 Getting Started With LP360 12/22/2015 1 Contents What is LP360?... 3 System Requirements... 3 Installing LP360... 4 How to Enable the LP360 Extension... 4 How to Display the LP360 Toolbar... 4 How to Import
Getting Started With LP360 12/22/2015 1 Contents What is LP360?... 3 System Requirements... 3 Installing LP360... 4 How to Enable the LP360 Extension... 4 How to Display the LP360 Toolbar... 4 How to Import
EXERCISE 2: GETTING STARTED WITH FUSION
 Document Updated: May, 2010 Fusion v2.8 Introduction In this exercise, you ll be using the fully-prepared example data to explore the basics of FUSION. Prerequisites Successful completion of Exercise 1
Document Updated: May, 2010 Fusion v2.8 Introduction In this exercise, you ll be using the fully-prepared example data to explore the basics of FUSION. Prerequisites Successful completion of Exercise 1
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
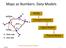 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Should Contours Be Generated from Lidar Data, and Are Breaklines Required? Lidar data provides the most
 Should Contours Be Generated from Lidar Data, and Are Breaklines Required? Lidar data provides the most accurate and reliable representation of the topography of the earth. As lidar technology advances
Should Contours Be Generated from Lidar Data, and Are Breaklines Required? Lidar data provides the most accurate and reliable representation of the topography of the earth. As lidar technology advances
Shading. Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann
 Shading Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann Reading Chapter 5.5 - Angel Chapter 6.3 - Hughes, van Dam, et al Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann 2 Shading Illumination
Shading Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann Reading Chapter 5.5 - Angel Chapter 6.3 - Hughes, van Dam, et al Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann 2 Shading Illumination
Overview of the Surface-water Modeling Software (SMS) GUI. Objective: This lecture will discuss the Surfacewater Modeling Software GUI.
 Overview of the Surface-water Modeling Software (SMS) GUI { Objective: This lecture will discuss the Surfacewater Modeling Software GUI. { Outline Outline Mesh Generation Interpolation Manning s n Coefficient
Overview of the Surface-water Modeling Software (SMS) GUI { Objective: This lecture will discuss the Surfacewater Modeling Software GUI. { Outline Outline Mesh Generation Interpolation Manning s n Coefficient
Lab 11: Terrain Analyses
 Lab 11: Terrain Analyses What You ll Learn: Basic terrain analysis functions, including watershed, viewshed, and profile processing. There is a mix of old and new functions used in this lab. We ll explain
Lab 11: Terrain Analyses What You ll Learn: Basic terrain analysis functions, including watershed, viewshed, and profile processing. There is a mix of old and new functions used in this lab. We ll explain
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Simplified Dam Break Learn how to run a dam break simulation and delineate its floodplain Objectives Setup a conceptual model of stream centerlines
v SMS Tutorials Working with Rasters Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives Learn how to import a Raster, view elevations at individual points, change display options for multiple views of the data, show the 2D profile plots, and interpolate
If you are relying on someone else to provide existing ground data to you, use the guidelines below to ensure you receive the best data available.
 That CAD Girl J ennifer dib ona Website: www.thatcadgirl.com Email: thatcadgirl@aol.com Phone: (919) 417-8351 Fax: (919) 573-0351 Basics of Existing Ground Surface Generation The accuracy of an existing
That CAD Girl J ennifer dib ona Website: www.thatcadgirl.com Email: thatcadgirl@aol.com Phone: (919) 417-8351 Fax: (919) 573-0351 Basics of Existing Ground Surface Generation The accuracy of an existing
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
v CMS-Wave Analysis SMS 12.2 Tutorial Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This workshop gives a brief introduction to the CMS-Wave interface and model. This model is similar to STWAVE and the tutorial for the models is similar. As with the
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This workshop gives a brief introduction to the CMS-Wave interface and model. This model is similar to STWAVE and the tutorial for the models is similar. As with the
Creating Surfaces. Steve Kopp Steve Lynch
 Steve Kopp Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to store them Emphasis on surface interpolation Learn the interpolation workflow Understand how interpolators work
Steve Kopp Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to store them Emphasis on surface interpolation Learn the interpolation workflow Understand how interpolators work
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples. Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford
 Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Lidar and GIS: Applications and Examples Dan Hedges Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density Creating raster DEMs and DSMs Data area
Geographical Information Systems Institute. Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University. LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap
 Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Harvard University Introduction to ArcMap Geographical Information Systems Institute Center for Geographic Analysis, Harvard University LAB EXERCISE 1: Basic Mapping in ArcMap Individual files (lab instructions,
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings
 Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
LAB 9: Buffering and Overlay in ArcGIS - ArcMAP
 LAB 9: Buffering and Overlay in ArcGIS - ArcMAP What You ll Learn: to apply the concepts of buffering and overlay, two common cartographic operations. You should read chapter 9 in the GIS Fundamentals
LAB 9: Buffering and Overlay in ArcGIS - ArcMAP What You ll Learn: to apply the concepts of buffering and overlay, two common cartographic operations. You should read chapter 9 in the GIS Fundamentals
Exercise One: Creating A Map Of Species Distribution For A Publication
 --- Chapter three --- Exercise One: Creating A Map Of Species Distribution For A Publication One of the first, and most common, tasks you will want to do in using GIS is to produce maps for use in presentations,
--- Chapter three --- Exercise One: Creating A Map Of Species Distribution For A Publication One of the first, and most common, tasks you will want to do in using GIS is to produce maps for use in presentations,
Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using rasters for interpolation and visualization in GMS Objectives This tutorial teaches how GMS uses rasters to support all kinds of digital elevation models and how rasters
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling DEM Delineation Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to delineate a watershed using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives Read a digital elevation model, compute flow directions, and delineate a watershed and sub-basins
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader
 Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
Combine Yield Data From Combine to Contour Map Ag Leader Exporting the Yield Data Using SMS Program 1. Data format On Hard Drive. 2. Start program SMS Basic. a. In the File menu choose Open. b. Click on
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering. Dr. Celso Ferreira
 George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Exercise Topic: HEC GeoRAS Post-Processing Objectives: This tutorial is designed to walk you
George Mason University Department of Civil, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering Dr. Celso Ferreira Exercise Topic: HEC GeoRAS Post-Processing Objectives: This tutorial is designed to walk you
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
MARS v Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds and )
 MARS v2018.0 Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds 8302.01 8302.18 and 8350.00 8352.00) Contents New Features:... 2 Enhancements:... 6 List of Bug Fixes... 13 1 New Features: LAS Up-Conversion prompts
MARS v2018.0 Release Notes Revised: May 23, 2018 (Builds 8302.01 8302.18 and 8350.00 8352.00) Contents New Features:... 2 Enhancements:... 6 List of Bug Fixes... 13 1 New Features: LAS Up-Conversion prompts
CALPUFF View. Graphical Interface for the US EPA Approved Long Range Transport Model - CALPUFF
 CALPUFF View Graphical Interface for the US EPA Approved Long Range Transport Model - CALPUFF These release notes cover CALPUFF View Version 3.0.0. They provide: New Features Resolved Issues Tel: (519)
CALPUFF View Graphical Interface for the US EPA Approved Long Range Transport Model - CALPUFF These release notes cover CALPUFF View Version 3.0.0. They provide: New Features Resolved Issues Tel: (519)
LP360 (Advanced) Planar Point Filter
 LP360 (Advanced) Planar Point Filter L. Graham 23 May 2013 Introduction: This is an overview discussion of setting parameters for the Planar Point Filter Point Cloud Task (PCT) in LP360 (Advanced level).
LP360 (Advanced) Planar Point Filter L. Graham 23 May 2013 Introduction: This is an overview discussion of setting parameters for the Planar Point Filter Point Cloud Task (PCT) in LP360 (Advanced level).
Draping Overview Drape Vertices CHAPTER 13. Drape elements onto a triangulated model. Feature / Function Tools
 CHAPTER 13 Draping 13.1 Overview Feature / Function Tools Drape elements onto a triangulated model. DTM Menu Bar Drape > Vertices, Vectors GEOPAK provides tools to drape MicroStation elements onto a triangulated
CHAPTER 13 Draping 13.1 Overview Feature / Function Tools Drape elements onto a triangulated model. DTM Menu Bar Drape > Vertices, Vectors GEOPAK provides tools to drape MicroStation elements onto a triangulated
