CSCI 1290: Comp Photo
|
|
|
- Kevin Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSCI 1290: Comp Photo Fall Brown University James Tompkin Many slides thanks to James Hays old CS 129 course, along with all of its acknowledgements.
2 What do we see? 3D world 2D image Point of observation Figures Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
3 What do we see? 3D world 2D image Point of observation Painted backdrop
4 On Simulating the Visual Experience Just feed the eyes the right data No one will know the difference! Philosophy: Ancient question: Does the world really exist? Science fiction: Many, many, many books on the subject, e.g. slowglass from Light of Other Days Latest take: The Matrix Physics: Slowglass might be possible? Computer Science: Virtual Reality To simulate we need to know: What does a person see?
5 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(l) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) l is wavelength Useful things: Light travels in straight lines In vacuum, radiance emitted = radiance arriving i.e. there is no transmission loss
6 The Plenoptic Function Figure by Leonard McMillan Q: What is the set of all things that we can ever see? A: The Plenoptic Function (Adelson & Bergen) Let s start with a stationary person and try to parameterize everything that he can see
7 Grayscale snapshot is intensity of light P(q,f) Seen from a single view point At a single time Averaged over the wavelengths of the visible spectrum (can also do P(x,y), but spherical coordinate are nicer)
8 Color snapshot is intensity of light P(q,f,l) Seen from a single view point At a single time As a function of wavelength
9 A movie is intensity of light P(q,f,l,t) Seen from a single view point Over time As a function of wavelength
10 Holographic movie is intensity of light Seen from ANY viewpoint Over time As a function of wavelength P(q,f,l,t,V X,V Y,V Z )
11 The Plenoptic Function P(q,f,l,t,V X,V Y,V Z ) Can reconstruct every possible view, at every moment, from every position, at every wavelength Contains every photograph, every movie, everything that anyone has ever seen! it completely captures our visual reality! Not bad for a function
12 Sampling Plenoptic Function (top view) Just lookup Google Street View
13 Model geometry or just capture images?
14 Ray Let s not worry about time and color: 5D 3D position 2D direction P(q,f,V X,V Y,V Z ) Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
15 How can we use this? Lighting No Change in Radiance Surface Camera
16 Ray Reuse Infinite line Assume light is constant (vacuum) 4D 2D direction 2D position non-dispersive medium Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
17 Only need plenoptic surface
18 Synthesizing novel views Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
19 Lumigraph / Lightfield Outside convex space 4D Empty Stuff Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
20 Lumigraph - Organization 2D position 2D direction q s Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
21 Lumigraph - Organization 2D position 2D position s u 2 plane parameterization Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
22 Lumigraph - Organization 2D position 2D position t s,t s,t u,v v 2 plane parameterization s u u,v Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
23 Lumigraph - Organization Hold s,t constant Let u,v vary An image s,t u,v Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
24 Lumigraph / Lightfield
25 Lumigraph - Capture Idea 1 Move camera carefully over s,t plane Gantry see Lightfield paper s,t u,v Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
26 Lumigraph - Capture Idea 2 Move camera anywhere Rebinning see Lumigraph paper s,t u,v Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
27 Lumigraph - Rendering For each output pixel determine s,t,u,v either use closest discrete RGB interpolate near values s u Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
28 Lumigraph - Rendering Nearest closest s closest u draw it Blend 16 nearest quadrilinear interpolation s u Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
29 Unstructured Light Field D4PA5plo
30 Stanford multi-camera array pixels 30 fps 128 cameras synchronized timing continuous streaming flexible arrangement
31 Light field photography using a handheld plenoptic camera Commercialized as Lytro Ren Ng, Marc Levoy, Mathieu Brédif, Gene Duval, Mark Horowitz and Pat Hanrahan
32 Conventional versus light field camera Marc Levoy
33 Marc Levoy Conventional versus light field camera uv-plane st-plane
34 Prototype camera Contax medium format camera Kodak 16-megapixel sensor Adaptive Optics microlens array 125μ square-sided microlenses pixels lenses = pixels per lens
35
36 Marc Levoy Digitally stopping-down the aperture Σ Σ stopping down = summing only the central portion of each microlens
37 Marc Levoy Digital refocusing Σ Σ refocusing = summing windows extracted from several microlenses
38 Example of digital refocusing Marc Levoy
39 Marc Levoy Digitally moving the observer Σ moving the observer = moving the window we extract from the microlenses Σ
40 Example of moving the observer Marc Levoy
41 P(x,t) by David Dewey
42 2D: Image What is an image? All rays through a point Panorama? Slide by Rick Szeliski and Michael Cohen
43 Image Image plane 2D position
44 Spherical Panorama See also: 2003 New Years Eve All light rays through a point form a ponorama Totally captured in a 2D array -- P(q,f) Where is the geometry???
45 Other ways to sample Plenoptic Function Moving in time: Spatio-temporal volume: P(q,f,t) Useful to study temporal changes Long an interest of artists: Claude Monet, Haystacks studies
46 Space-time images Other ways to slice the plenoptic function t y x
47 The Theatre Workshop Metaphor (Adelson & Pentland,1996) desired image Painter Lighting Designer Sheet-metal worker
48 Painter (images)
49 Lighting Designer (environment maps) Show Naimark SF MOMA video
50 Sheet-metal Worker (geometry) Let surface normals do all the work!
51 working together clever Italians Want to minimize cost Each one does what s easiest for him Geometry big things Images detail Lighting illumination effects
52 Link to other slide deck James Tompkin s section from here: VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN
53 Slides from Alexei A. Efros, James Hays, and others Modeling Light
54 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection? λ light source James Hays
55 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ light source James Hays
56 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffuse Reflection Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ light source James Hays
57 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Specular Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ light source James Hays
58 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ light source James Hays
59 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ light source James Hays
60 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ 2 λ 1 light source James Hays
61 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection λ light source James Hays
62 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection t=n t=1 light source James Hays
63 A photon s life choices Absorption Diffusion Reflection Transparency Refraction Fluorescence Subsurface scattering Phosphorescence Interreflection (Specular Interreflection) λ light source James Hays
64 Lambertian Reflectance In computer vision, surfaces are often assumed to be ideal diffuse reflectors with no dependence on viewing direction. Like in stereo depth estimation! James Hays
65 Fast Separation of Direct and Global Images Using High Frequency Illumination Shree K. Nayar Gurunandan G. Krishnan Columbia University Michael D. Grossberg City College of New York Ramesh Raskar MERL SIGGRAPH Conference Boston, July 2006 Support: ONR, NSF, MERL
66 Direct and Global Illumination participating medium surface source D B camera A E translucent surface P C A : Direct B : Interrelection C : Subsurface D : Volumetric E : Diffusion
67 Direct and Global Components: Interreflections source surface j i camera L[ c, i] = L [ c, i] L [ c, i] d + radiance direct global g L = g[ c, i] A[ i, j] L[ i, j] P BRDF and geometry
68 High Frequency Illumination Pattern source surface i camera + L [ c, i] = L [ c, i] L [ c, i] d + g fraction of activated source elements
69 High Frequency Illumination Pattern source surface i camera + L [ c, i] = L [ c, i] L [ c, i] d + - L [ c, i] = ( 1 ) L [ c, i] g g fraction of activated source elements
70 Separation from Two Images + L [ c, i] = L [ c, i] L [ c, i] d + - L [ c, i] = ( 1 ) L [ c, i] g g fraction of activated source elements = 1 : 2 L d = L max L min, L g = 2Lmin direct global
71 Diffuse Interreflections Specular Interreflections Diffusion Volumetric Scattering Subsurface Scattering
72 Scene
73 Scene Direct Global
74 High Frequency Illumination Pattern source surface i camera + L [ c, i] = L [ c, i] L [ c, i] d + - L [ c, i] = ( 1 ) L [ c, i] g g fraction of activated source elements
75 Pipeline projector surface 1. Actually use more unique chequerboard patterns Global effects from local lighting 2. Pick L_min and L_max from across all unique patterns for each pixel 3. Factor in projector s light floor camera i
76 More Real World Examples:
77 Eggs: Diffuse Interreflections Direct Global
78 Wooden Blocks: Specular Interreflections Direct Global
79 Kitchen Sink: Volumetric Scattering Volumetric Scattering: Chandrasekar 50, Ishimaru 78 Direct Global
80 Direct Global Peppers: Subsurface Scattering
81 Hand Skin: Hanrahan and Krueger 93, Uchida 96, Haro 01, Jensen et al. 01, Cula and Dana 02, Igarashi et al. 05, Weyrich et al. 05 Direct Global
82 Face: Without and With Makeup Without Makeup Direct Global With Makeup Direct Global
83 Blonde Hair Hair Scattering: Stamm et al. 77, Bustard and Smith 91, Lu et al. 00 Marschner et al. 03 Direct Global
84
Modeling Light. Slides from Alexei A. Efros and others
 Project 3 Results http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/jcmace/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/damoreno/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/taox/ Stereo
Project 3 Results http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/jcmace/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/damoreno/ http://www.cs.brown.edu/courses/cs129/results/proj3/taox/ Stereo
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Spring 2010 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R( ) is EMR, measured in units of
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Spring 2010 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R( ) is EMR, measured in units of
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2011
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2011 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2011 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 What is light? Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(λ) is EMR, measured in units of power
Light Field Spring
 Light Field 2015 Spring Recall: Light is Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(l) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) l is wavelength Useful things: Light travels in straight
Light Field 2015 Spring Recall: Light is Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) moving along rays in space R(l) is EMR, measured in units of power (watts) l is wavelength Useful things: Light travels in straight
Modeling Light. Michal Havlik : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007
 Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 The Plenoptic Function Figure by Leonard McMillan Q: What is the set of all things that we can ever see? A: The
Modeling Light Michal Havlik 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 The Plenoptic Function Figure by Leonard McMillan Q: What is the set of all things that we can ever see? A: The
Modeling Light. On Simulating the Visual Experience
 Modeling Light 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros On Simulating the Visual Experience Just feed the eyes the right data No one will know the difference! Philosophy: Ancient question: Does
Modeling Light 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros On Simulating the Visual Experience Just feed the eyes the right data No one will know the difference! Philosophy: Ancient question: Does
Matting, Transparency, and Illumination. Slides from Alexei Efros
 New course focus Done with texture, patches, and shuffling image content. Focus on light, specifically light models derived from multiple photos of the same scene. Matting, Transparency, and Illumination
New course focus Done with texture, patches, and shuffling image content. Focus on light, specifically light models derived from multiple photos of the same scene. Matting, Transparency, and Illumination
More computational light transport
 More computational light transport http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 23 Course announcements Sign-up for final project checkpoint
More computational light transport http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 23 Course announcements Sign-up for final project checkpoint
Computational light transport
 Computational light transport http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 19 Course announcements Homework 5 has been posted. - Due on
Computational light transport http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 19 Course announcements Homework 5 has been posted. - Due on
But, vision technology falls short. and so does graphics. Image Based Rendering. Ray. Constant radiance. time is fixed. 3D position 2D direction
 Computer Graphics -based rendering Output Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Research Synthetic Camera Model Computer Vision Combined Output Output Model Real Scene Synthetic Camera Model Real Cameras Real Scene
Computer Graphics -based rendering Output Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Research Synthetic Camera Model Computer Vision Combined Output Output Model Real Scene Synthetic Camera Model Real Cameras Real Scene
Image or Object? Is this real?
 Image or Object? Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Is this real? Photo by Patrick Jennings (patrick@synaptic.bc.ca), Copyright 1995, 96, 97 Whistler B. C. Canada Modeling, Rendering, and Lighting 1 A mental model?
Image or Object? Michael F. Cohen Microsoft Is this real? Photo by Patrick Jennings (patrick@synaptic.bc.ca), Copyright 1995, 96, 97 Whistler B. C. Canada Modeling, Rendering, and Lighting 1 A mental model?
Announcements. Light. Properties of light. Light. Project status reports on Wednesday. Readings. Today. Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.
 Announcements Project status reports on Wednesday prepare 5 minute ppt presentation should contain: problem statement (1 slide) description of approach (1 slide) some images (1 slide) current status +
Announcements Project status reports on Wednesday prepare 5 minute ppt presentation should contain: problem statement (1 slide) description of approach (1 slide) some images (1 slide) current status +
Image-Based Rendering
 Image-Based Rendering COS 526, Fall 2016 Thomas Funkhouser Acknowledgments: Dan Aliaga, Marc Levoy, Szymon Rusinkiewicz What is Image-Based Rendering? Definition 1: the use of photographic imagery to overcome
Image-Based Rendering COS 526, Fall 2016 Thomas Funkhouser Acknowledgments: Dan Aliaga, Marc Levoy, Szymon Rusinkiewicz What is Image-Based Rendering? Definition 1: the use of photographic imagery to overcome
Computational Photography
 Computational Photography Matthias Zwicker University of Bern Fall 2010 Today Light fields Introduction Light fields Signal processing analysis Light field cameras Application Introduction Pinhole camera
Computational Photography Matthias Zwicker University of Bern Fall 2010 Today Light fields Introduction Light fields Signal processing analysis Light field cameras Application Introduction Pinhole camera
Plenoptic camera and its Applications
 Aum Sri Sairam Plenoptic camera and its Applications Agenda: 1. Introduction 2. Single lens stereo design 3. Plenoptic camera design 4. Depth estimation 5. Synthetic refocusing 6. Fourier slicing 7. References
Aum Sri Sairam Plenoptic camera and its Applications Agenda: 1. Introduction 2. Single lens stereo design 3. Plenoptic camera design 4. Depth estimation 5. Synthetic refocusing 6. Fourier slicing 7. References
Light. Properties of light. What is light? Today What is light? How do we measure it? How does light propagate? How does light interact with matter?
 Light Properties of light Today What is light? How do we measure it? How does light propagate? How does light interact with matter? by Ted Adelson Readings Andrew Glassner, Principles of Digital Image
Light Properties of light Today What is light? How do we measure it? How does light propagate? How does light interact with matter? by Ted Adelson Readings Andrew Glassner, Principles of Digital Image
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 20: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Properties
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 20: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Properties
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering
 Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Richard Szeliski Microsoft Research IPAM Graduate Summer School: Computer Vision July 26, 2013 How far have we come? Light Fields / Lumigraph - 1996 Richard Szeliski
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Richard Szeliski Microsoft Research IPAM Graduate Summer School: Computer Vision July 26, 2013 How far have we come? Light Fields / Lumigraph - 1996 Richard Szeliski
Image-Based Modeling and Rendering
 Traditional Computer Graphics Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University COS 426 Guest Lecture Spring 2003 How would you model and render this scene? (Jensen) How about this
Traditional Computer Graphics Image-Based Modeling and Rendering Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University COS 426 Guest Lecture Spring 2003 How would you model and render this scene? (Jensen) How about this
Ligh%ng and Reflectance
 Ligh%ng and Reflectance 2 3 4 Ligh%ng Ligh%ng can have a big effect on how an object looks. Modeling the effect of ligh%ng can be used for: Recogni%on par%cularly face recogni%on Shape reconstruc%on Mo%on
Ligh%ng and Reflectance 2 3 4 Ligh%ng Ligh%ng can have a big effect on how an object looks. Modeling the effect of ligh%ng can be used for: Recogni%on par%cularly face recogni%on Shape reconstruc%on Mo%on
Focal stacks and lightfields
 Focal stacks and lightfields http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 11 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due October 12 th.
Focal stacks and lightfields http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 11 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due October 12 th.
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Light & Perception Announcements Quiz on Tuesday Project 3 code due Monday, April 17, by 11:59pm artifact due Wednesday, April 19, by 11:59pm Can we determine shape
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Light & Perception Announcements Quiz on Tuesday Project 3 code due Monday, April 17, by 11:59pm artifact due Wednesday, April 19, by 11:59pm Can we determine shape
CS4670: Computer Vision
 CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 30: Light, color, and reflectance Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Properties of light
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 30: Light, color, and reflectance Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Light by Ted Adelson Readings Szeliski, 2.2, 2.3.2 Properties of light
Coding and Modulation in Cameras
 Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Raskar 2007 Coding and Modulation in Cameras Ramesh Raskar with Ashok Veeraraghavan, Amit Agrawal, Jack Tumblin, Ankit Mohan Mitsubishi Electric Research Labs
Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories Raskar 2007 Coding and Modulation in Cameras Ramesh Raskar with Ashok Veeraraghavan, Amit Agrawal, Jack Tumblin, Ankit Mohan Mitsubishi Electric Research Labs
Image-based modeling (IBM) and image-based rendering (IBR)
 Image-based modeling (IBM) and image-based rendering (IBR) CS 248 - Introduction to Computer Graphics Autumn quarter, 2005 Slides for December 8 lecture The graphics pipeline modeling animation rendering
Image-based modeling (IBM) and image-based rendering (IBR) CS 248 - Introduction to Computer Graphics Autumn quarter, 2005 Slides for December 8 lecture The graphics pipeline modeling animation rendering
Introduction to Computer Vision. Introduction CMPSCI 591A/691A CMPSCI 570/670. Image Formation
 Introduction CMPSCI 591A/691A CMPSCI 570/670 Image Formation Lecture Outline Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic
Introduction CMPSCI 591A/691A CMPSCI 570/670 Image Formation Lecture Outline Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic
VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN
 VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD? Light field seems to have turned into a catch-all term for many advanced camera/display technologies. WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD?
VIDEO FOR VIRTUAL REALITY LIGHT FIELD BASICS JAMES TOMPKIN WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD? Light field seems to have turned into a catch-all term for many advanced camera/display technologies. WHAT IS A LIGHT FIELD?
Shading. Reading. Pinhole camera. Basic 3D graphics. Brian Curless CSE 557 Fall Required: Shirley, Chapter 10
 Reading Required: Shirley, Chapter 10 Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Fall 2014 1 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in their local coordinate systems into
Reading Required: Shirley, Chapter 10 Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Fall 2014 1 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in their local coordinate systems into
Radiometry Measuring Light
 1 Radiometry Measuring Light CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 How do we see? [Plato] from our eyes flows a light similar to the light of the sun [Chalcidius, middle ages] Therefore,
1 Radiometry Measuring Light CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University 2 How do we see? [Plato] from our eyes flows a light similar to the light of the sun [Chalcidius, middle ages] Therefore,
rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1 physically-based rendering synthesis algorithms that compute images by simulation the physical behavior of light computer
rendering equation computer graphics rendering equation 2009 fabio pellacini 1 physically-based rendering synthesis algorithms that compute images by simulation the physical behavior of light computer
Image-based Lighting
 Image-based Lighting 10/17/15 T2 Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois Many slides from Debevec, some from Efros Next week Derek away for ICCV (Venice) Zhizhong and Aditya will
Image-based Lighting 10/17/15 T2 Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois Many slides from Debevec, some from Efros Next week Derek away for ICCV (Venice) Zhizhong and Aditya will
Real Time Rendering. CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics. Songxiang Gu Jan, 31, 2005
 Real Time Rendering CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Songxiang Gu Jan, 31, 2005 Introduction Polygon based rendering Phong modeling Texture mapping Opengl, Directx Point based rendering VTK
Real Time Rendering CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Songxiang Gu Jan, 31, 2005 Introduction Polygon based rendering Phong modeling Texture mapping Opengl, Directx Point based rendering VTK
More and More on Light Fields. Last Lecture
 More and More on Light Fields Topics in Image-Based Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 4 Last Lecture Re-review with emphasis on radiometry Mosaics & Quicktime VR The Plenoptic function The main
More and More on Light Fields Topics in Image-Based Modeling and Rendering CSE291 J00 Lecture 4 Last Lecture Re-review with emphasis on radiometry Mosaics & Quicktime VR The Plenoptic function The main
Consider a partially transparent object that is illuminated with two lights, one visible from each side of the object. Start with a ray from the eye
 Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Ray Tracing What was the rendering equation? Motivate & list the terms. Relate the rendering equation to forward ray tracing. Why is forward ray tracing not good for image formation? What is the difference
Lighting affects appearance
 Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Computational Photography: Real Time Plenoptic Rendering
 Computational Photography: Real Time Plenoptic Rendering Andrew Lumsdaine, Georgi Chunev Indiana University Todor Georgiev Adobe Systems Who was at the Keynote Yesterday? 2 Overview Plenoptic cameras Rendering
Computational Photography: Real Time Plenoptic Rendering Andrew Lumsdaine, Georgi Chunev Indiana University Todor Georgiev Adobe Systems Who was at the Keynote Yesterday? 2 Overview Plenoptic cameras Rendering
Computer Vision Course Lecture 02. Image Formation Light and Color. Ceyhun Burak Akgül, PhD cba-research.com. Spring 2015 Last updated 04/03/2015
 Computer Vision Course Lecture 02 Image Formation Light and Color Ceyhun Burak Akgül, PhD cba-research.com Spring 2015 Last updated 04/03/2015 Photo credit: Olivier Teboul vision.mas.ecp.fr/personnel/teboul
Computer Vision Course Lecture 02 Image Formation Light and Color Ceyhun Burak Akgül, PhD cba-research.com Spring 2015 Last updated 04/03/2015 Photo credit: Olivier Teboul vision.mas.ecp.fr/personnel/teboul
Computational Cameras: Exploiting Spatial- Angular Temporal Tradeoffs in Photography
 Mitsubishi Electric Research Labs (MERL) Computational Cameras Computational Cameras: Exploiting Spatial- Angular Temporal Tradeoffs in Photography Amit Agrawal Mitsubishi Electric Research Labs (MERL)
Mitsubishi Electric Research Labs (MERL) Computational Cameras Computational Cameras: Exploiting Spatial- Angular Temporal Tradeoffs in Photography Amit Agrawal Mitsubishi Electric Research Labs (MERL)
Lenses: Focus and Defocus
 Lenses: Focus and Defocus circle of confusion A lens focuses light onto the film There is a specific distance at which objects are in focus other points project to a circle of confusion in the image Changing
Lenses: Focus and Defocus circle of confusion A lens focuses light onto the film There is a specific distance at which objects are in focus other points project to a circle of confusion in the image Changing
CS635 Spring Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Light Transport CS635 Spring 2010 Daniel G Aliaga Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Topics Local and GlobalIllumination Models Helmholtz Reciprocity Dual Photography/Light
Light Transport CS635 Spring 2010 Daniel G Aliaga Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Topics Local and GlobalIllumination Models Helmholtz Reciprocity Dual Photography/Light
Computational Photography
 End of Semester is the last lecture of new material Quiz on Friday 4/30 Sample problems are posted on website Computational Photography Final Project Presentations Wednesday May 12 1-5pm, CII 4040 Attendance
End of Semester is the last lecture of new material Quiz on Friday 4/30 Sample problems are posted on website Computational Photography Final Project Presentations Wednesday May 12 1-5pm, CII 4040 Attendance
Capturing light. Source: A. Efros
 Capturing light Source: A. Efros Review Pinhole projection models What are vanishing points and vanishing lines? What is orthographic projection? How can we approximate orthographic projection? Lenses
Capturing light Source: A. Efros Review Pinhole projection models What are vanishing points and vanishing lines? What is orthographic projection? How can we approximate orthographic projection? Lenses
Final project bits and pieces
 Final project bits and pieces The project is expected to take four weeks of time for up to four people. At 12 hours per week per person that comes out to: ~192 hours of work for a four person team. Capstone:
Final project bits and pieces The project is expected to take four weeks of time for up to four people. At 12 hours per week per person that comes out to: ~192 hours of work for a four person team. Capstone:
The Rendering Equation. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662
 The Rendering Equation Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662 Review: What is radiance? Radiance at point p in direction N is radiant energy ( #hits ) per unit time, per solid angle, per unit area perpendicular
The Rendering Equation Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662 Review: What is radiance? Radiance at point p in direction N is radiant energy ( #hits ) per unit time, per solid angle, per unit area perpendicular
AN O(N 2 LOG(N)) PER PLANE FAST DISCRETE FOCAL STACK TRANSFORM
 AN O(N 2 LOG(N)) PER PLANE FAST DISCRETE FOCAL STACK TRANSFORM Fernando Pérez Nava +, Jonás Philipp Lüke + Departamento de Estadística, Investigación Operativa y Computación Departamento de Física Fundamental
AN O(N 2 LOG(N)) PER PLANE FAST DISCRETE FOCAL STACK TRANSFORM Fernando Pérez Nava +, Jonás Philipp Lüke + Departamento de Estadística, Investigación Operativa y Computación Departamento de Física Fundamental
Local Illumination. CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Local Illumination CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Graphics Pipeline Hardware Modelling Transform Visibility Illumination + Shading Perception, Interaction Color Texture/ Realism
Multiple View Geometry
 Multiple View Geometry Martin Quinn with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Jianbo Shi 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 Our Goal The Plenoptic Function P(θ,φ,λ,t,V
Multiple View Geometry Martin Quinn with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Jianbo Shi 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2007 Our Goal The Plenoptic Function P(θ,φ,λ,t,V
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 21: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Announcements Final projects Midterm reports due November 24 (next Tuesday) by 11:59pm (upload to CMS) State the
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 21: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Announcements Final projects Midterm reports due November 24 (next Tuesday) by 11:59pm (upload to CMS) State the
Linearizing the Plenoptic Space
 Linearizing the Plenoptic Space Grégoire Nieto1, Frédéric Devernay1, James Crowley2 LJK, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 2 LIG, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 1 1 Goal: synthesize a new view Capture/sample
Linearizing the Plenoptic Space Grégoire Nieto1, Frédéric Devernay1, James Crowley2 LJK, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 2 LIG, Université Grenoble Alpes, France 1 1 Goal: synthesize a new view Capture/sample
CMSC427 Shading Intro. Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
Light Transport CS434. Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Light Transport CS434 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Topics Local and Global Illumination Models Helmholtz Reciprocity Dual Photography/Light Transport (in Real-World)
Light Transport CS434 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Topics Local and Global Illumination Models Helmholtz Reciprocity Dual Photography/Light Transport (in Real-World)
Next Generation CAT System
 Next Generation CAT System Jaewon Kim MIT Media Lab Advisor: Ramesh Raskar Associate Professor of Media Arts & Sciences MIT Media Lab Reader: V. Michael Bove Principal Research Scientist of Media Arts
Next Generation CAT System Jaewon Kim MIT Media Lab Advisor: Ramesh Raskar Associate Professor of Media Arts & Sciences MIT Media Lab Reader: V. Michael Bove Principal Research Scientist of Media Arts
Light Fields. Johns Hopkins Department of Computer Science Course : Rendering Techniques, Professor: Jonathan Cohen
 Light Fields Light Fields By Levoy and Hanrahan, SIGGRAPH 96 Representation for sampled plenoptic function stores data about visible light at various positions and directions Created from set of images
Light Fields Light Fields By Levoy and Hanrahan, SIGGRAPH 96 Representation for sampled plenoptic function stores data about visible light at various positions and directions Created from set of images
Radiance Photography. Todor Georgiev Adobe Systems. Andrew Lumsdaine Indiana University
 Radiance Photography Todor Georgiev Adobe Systems Andrew Lumsdaine Indiana University Course Goals Overview of radiance (aka lightfield) photography Mathematical treatment of theory and computation Hands
Radiance Photography Todor Georgiev Adobe Systems Andrew Lumsdaine Indiana University Course Goals Overview of radiance (aka lightfield) photography Mathematical treatment of theory and computation Hands
Introduction. Lighting model Light reflection model Local illumination model Reflectance model BRDF
 Shading Introduction Affine transformations help us to place objects into a scene. Before creating images of these objects, we ll look at models for how light interacts with their surfaces. Such a model
Shading Introduction Affine transformations help us to place objects into a scene. Before creating images of these objects, we ll look at models for how light interacts with their surfaces. Such a model
The Focused Plenoptic Camera. Lightfield photographers, focus your cameras! Karl Marx
 The Focused Plenoptic Camera Lightfield photographers, focus your cameras! Karl Marx Plenoptic Camera, Adelson 1992 Main lens focused on microlenses Plenoptic Camera, Adelson 1992 Microlenses focused on
The Focused Plenoptic Camera Lightfield photographers, focus your cameras! Karl Marx Plenoptic Camera, Adelson 1992 Main lens focused on microlenses Plenoptic Camera, Adelson 1992 Microlenses focused on
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 15 RAY TRACING 1 Announcements Programming Assignment 3 out today - overview @ end of the class Ray Tracing 2 Lecture Overview Review of last class Ray Tracing 3 Local
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS SESSION 15 RAY TRACING 1 Announcements Programming Assignment 3 out today - overview @ end of the class Ray Tracing 2 Lecture Overview Review of last class Ray Tracing 3 Local
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Lighting affects appearance
 Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
Lighting affects appearance 1 Source emits photons Light And then some reach the eye/camera. Photons travel in a straight line When they hit an object they: bounce off in a new direction or are absorbed
CS201 Computer Vision Lect 4 - Image Formation
 CS201 Computer Vision Lect 4 - Image Formation John Magee 9 September, 2014 Slides courtesy of Diane H. Theriault Question of the Day: Why is Computer Vision hard? Something to think about from our view
CS201 Computer Vision Lect 4 - Image Formation John Magee 9 September, 2014 Slides courtesy of Diane H. Theriault Question of the Day: Why is Computer Vision hard? Something to think about from our view
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Computational Imaging for Self-Driving Vehicles
 CVPR 2018 Computational Imaging for Self-Driving Vehicles Jan Kautz--------Ramesh Raskar--------Achuta Kadambi--------Guy Satat Computational Imaging for Self-Driving Vehicles Jan Kautz--------Ramesh Raskar--------Achuta
CVPR 2018 Computational Imaging for Self-Driving Vehicles Jan Kautz--------Ramesh Raskar--------Achuta Kadambi--------Guy Satat Computational Imaging for Self-Driving Vehicles Jan Kautz--------Ramesh Raskar--------Achuta
Rendering: Reality. Eye acts as pinhole camera. Photons from light hit objects
 Basic Ray Tracing Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as
Basic Ray Tracing Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as
Global Illumination CS334. Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Global Illumination CS334 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Recall: Lighting and Shading Light sources Point light Models an omnidirectional light source (e.g., a bulb)
Global Illumination CS334 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Recall: Lighting and Shading Light sources Point light Models an omnidirectional light source (e.g., a bulb)
A Review of Image- based Rendering Techniques Nisha 1, Vijaya Goel 2 1 Department of computer science, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
 A Review of Image- based Rendering Techniques Nisha 1, Vijaya Goel 2 1 Department of computer science, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Keshav Mahavidyalaya, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Abstract
A Review of Image- based Rendering Techniques Nisha 1, Vijaya Goel 2 1 Department of computer science, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Keshav Mahavidyalaya, University of Delhi, Delhi, India Abstract
Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]
![Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ] Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]](/thumbs/78/78594982.jpg) CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
And if that 120MP Camera was cool
 Reflectance, Lights and on to photometric stereo CSE 252A Lecture 7 And if that 120MP Camera was cool Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 3.2Gigapixel camera 189 CCD s, each with 16 megapixels Pixels are 10µm
Reflectance, Lights and on to photometric stereo CSE 252A Lecture 7 And if that 120MP Camera was cool Large Synoptic Survey Telescope 3.2Gigapixel camera 189 CCD s, each with 16 megapixels Pixels are 10µm
Global Illumination. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18. BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] 1 Global Illumination
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] 1 Global Illumination
Understanding Variability
 Understanding Variability Why so different? Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic aberration, radial distortion
Understanding Variability Why so different? Light and Optics Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Thin lens model Fundamental equation Distortion: spherical & chromatic aberration, radial distortion
Global Illumination. Global Illumination. Direct Illumination vs. Global Illumination. Indirect Illumination. Soft Shadows.
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] March 28, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Ch. 13.4-13.5] March 28, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
The 7d plenoptic function, indexing all light.
 Previous Lecture The 7d plenoptic function, indexing all light. Lightfields: a 4d (not 5d!) data structure which captures all outgoing light from a region and permits reconstruction of arbitrary synthetic
Previous Lecture The 7d plenoptic function, indexing all light. Lightfields: a 4d (not 5d!) data structure which captures all outgoing light from a region and permits reconstruction of arbitrary synthetic
CSc Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography
 CSc 83010 Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography Tuesdays 11:45-1:45 1:45 Room 3305 Ioannis Stamos istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Office: 1090F, Hunter North (Entrance at 69 th bw/ / Park and Lexington Avenues)
CSc 83010 Topics in Computer Graphics 3D Photography Tuesdays 11:45-1:45 1:45 Room 3305 Ioannis Stamos istamos@hunter.cuny.edu Office: 1090F, Hunter North (Entrance at 69 th bw/ / Park and Lexington Avenues)
(0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 1) (0, 1, 0) What is light? What is color? Terminology
 lecture 23 (0, 1, 1) (0, 0, 0) (0, 0, 1) (0, 1, 1) (1, 1, 1) (1, 1, 0) (0, 1, 0) hue - which ''? saturation - how pure? luminance (value) - intensity What is light? What is? Light consists of electromagnetic
lecture 23 (0, 1, 1) (0, 0, 0) (0, 0, 1) (0, 1, 1) (1, 1, 1) (1, 1, 0) (0, 1, 0) hue - which ''? saturation - how pure? luminance (value) - intensity What is light? What is? Light consists of electromagnetic
Global Illumination. Global Illumination. Direct Illumination vs. Global Illumination. Indirect Illumination. Soft Shadows.
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Angel Ch. 11] 1 Global Illumination
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 18 Global Illumination Jernej Barbic University of Southern California BRDFs Raytracing and Radiosity Subsurface Scattering Photon Mapping [Angel Ch. 11] 1 Global Illumination
Light. Computer Vision. James Hays
 Light Computer Vision James Hays Projection: world coordinatesimage coordinates Camera Center (,, ) z y x X... f z y ' ' v u x. v u z f x u * ' z f y v * ' 5 2 ' 2* u 5 2 ' 3* v If X = 2, Y = 3, Z = 5,
Light Computer Vision James Hays Projection: world coordinatesimage coordinates Camera Center (,, ) z y x X... f z y ' ' v u x. v u z f x u * ' z f y v * ' 5 2 ' 2* u 5 2 ' 3* v If X = 2, Y = 3, Z = 5,
Hybrid Rendering for Collaborative, Immersive Virtual Environments
 Hybrid Rendering for Collaborative, Immersive Virtual Environments Stephan Würmlin wuermlin@inf.ethz.ch Outline! Rendering techniques GBR, IBR and HR! From images to models! Novel view generation! Putting
Hybrid Rendering for Collaborative, Immersive Virtual Environments Stephan Würmlin wuermlin@inf.ethz.ch Outline! Rendering techniques GBR, IBR and HR! From images to models! Novel view generation! Putting
Computer Vision. The image formation process
 Computer Vision The image formation process Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2016/2017 The image
Computer Vision The image formation process Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2016/2017 The image
Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Views
 Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Views Chuck Dyer University of Wisconsin dyer@cs cs.wisc.edu www.cs cs.wisc.edu/~dyer Image-Based Scene Reconstruction Goal Automatic construction of photo-realistic
Volumetric Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Views Chuck Dyer University of Wisconsin dyer@cs cs.wisc.edu www.cs cs.wisc.edu/~dyer Image-Based Scene Reconstruction Goal Automatic construction of photo-realistic
A Brief Overview of. Global Illumination. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri Mälardalen University
 A Brief Overview of Global Illumination Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri Mälardalen University 1 What is Global illumination? Global illumination is a general name for realistic rendering algorithms Global
A Brief Overview of Global Illumination Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri Mälardalen University 1 What is Global illumination? Global illumination is a general name for realistic rendering algorithms Global
CS4670/5760: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Scott Wehrwein. Lecture 23: Photometric Stereo
 CS4670/5760: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Scott Wehrwein Lecture 23: Photometric Stereo Announcements PA3 Artifact due tonight PA3 Demos Thursday Signups close at 4:30 today No lecture on Friday Last Time:
CS4670/5760: Computer Vision Kavita Bala Scott Wehrwein Lecture 23: Photometric Stereo Announcements PA3 Artifact due tonight PA3 Demos Thursday Signups close at 4:30 today No lecture on Friday Last Time:
w Foley, Section16.1 Reading
 Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Re-live the Movie Matrix : From Harry Nyquist to Image-Based Rendering. Tsuhan Chen Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, USA
 Re-live the Movie Matrix : From Harry Nyquist to Image-Based Rendering Tsuhan Chen tsuhan@cmu.edu Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, USA Some History IEEE Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP) Technical
Re-live the Movie Matrix : From Harry Nyquist to Image-Based Rendering Tsuhan Chen tsuhan@cmu.edu Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, USA Some History IEEE Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP) Technical
Real-time Generation and Presentation of View-dependent Binocular Stereo Images Using a Sequence of Omnidirectional Images
 Real-time Generation and Presentation of View-dependent Binocular Stereo Images Using a Sequence of Omnidirectional Images Abstract This paper presents a new method to generate and present arbitrarily
Real-time Generation and Presentation of View-dependent Binocular Stereo Images Using a Sequence of Omnidirectional Images Abstract This paper presents a new method to generate and present arbitrarily
Reading. Shading. An abundance of photons. Introduction. Required: Angel , 6.5, Optional: Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5.
 Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction An abundance of photons So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. Properly
Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction An abundance of photons So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. Properly
The Rendering Equation. Computer Graphics CMU /15-662, Fall 2016
 The Rendering Equation Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Review: What is radiance? Radiance at point p in direction N is radiant energy ( #hits ) per unit time, per solid angle, per unit area
The Rendering Equation Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2016 Review: What is radiance? Radiance at point p in direction N is radiant energy ( #hits ) per unit time, per solid angle, per unit area
Other Rendering Techniques CSE 872 Fall Intro You have seen Scanline converter (+z-buffer) Painter s algorithm Radiosity CSE 872 Fall
 Other Rendering Techniques 1 Intro You have seen Scanline converter (+z-buffer) Painter s algorithm Radiosity 2 Intro Some more Raytracing Light maps Photon-map Reyes Shadow maps Sahdow volumes PRT BSSRF
Other Rendering Techniques 1 Intro You have seen Scanline converter (+z-buffer) Painter s algorithm Radiosity 2 Intro Some more Raytracing Light maps Photon-map Reyes Shadow maps Sahdow volumes PRT BSSRF
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Lecture 11. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134. Review for Exam. Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 11 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Review for Exam Lecture 11 PHY 112 Lecture 1 From Last Time Lenses Ray tracing a Convex Lens Announcements The midterm is Thursday
Rendering Light Reflection Models
 Rendering Light Reflection Models Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Donald P. Greenberg October 3, 2017 Lecture #13 Program of Computer Graphics, Cornell University General Electric - 167 Cornell in
Rendering Light Reflection Models Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Donald P. Greenberg October 3, 2017 Lecture #13 Program of Computer Graphics, Cornell University General Electric - 167 Cornell in
Bioluminescence Chris Fontas & Forrest Browning
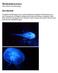 Bioluminescence Chris Fontas & Forrest Browning Introduction Our goal for the final project was to render a bioluminescent organism. Bioluminescence is a type of luminescence (cold light) resulting from
Bioluminescence Chris Fontas & Forrest Browning Introduction Our goal for the final project was to render a bioluminescent organism. Bioluminescence is a type of luminescence (cold light) resulting from
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Computational Photography
 Computational Photography Photography and Imaging Michael S. Brown Brown - 1 Part 1 Overview Photography Preliminaries Traditional Film Imaging (Camera) Part 2 General Imaging 5D Plenoptic Function (McMillan)
Computational Photography Photography and Imaging Michael S. Brown Brown - 1 Part 1 Overview Photography Preliminaries Traditional Film Imaging (Camera) Part 2 General Imaging 5D Plenoptic Function (McMillan)
Traditional Image Generation. Reflectance Fields. The Light Field. The Light Field. The Light Field. The Light Field
 Traditional Image Generation Course 10 Realistic Materials in Computer Graphics Surfaces + BRDFs Reflectance Fields USC Institute for Creative Technologies Volumetric scattering, density fields, phase
Traditional Image Generation Course 10 Realistic Materials in Computer Graphics Surfaces + BRDFs Reflectance Fields USC Institute for Creative Technologies Volumetric scattering, density fields, phase
INFOGR Computer Graphics. J. Bikker - April-July Lecture 10: Shading Models. Welcome!
 INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2016 - Lecture 10: Shading Models Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Light Transport Materials Sensors Shading INFOGR Lecture 10 Shading Models 3 Introduction
INFOGR Computer Graphics J. Bikker - April-July 2016 - Lecture 10: Shading Models Welcome! Today s Agenda: Introduction Light Transport Materials Sensors Shading INFOGR Lecture 10 Shading Models 3 Introduction
CS 684 Fall 2005 Image-based Modeling and Rendering. Ruigang Yang
 CS 684 Fall 2005 Image-based Modeling and Rendering Ruigang Yang Administrivia Classes: Monday and Wednesday, 4:00-5:15 PM Instructor: Ruigang Yang ryang@cs.uky.edu Office Hour: Robotics 514D, MW 1500-1600
CS 684 Fall 2005 Image-based Modeling and Rendering Ruigang Yang Administrivia Classes: Monday and Wednesday, 4:00-5:15 PM Instructor: Ruigang Yang ryang@cs.uky.edu Office Hour: Robotics 514D, MW 1500-1600
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Radiometry and reflectance
 Radiometry and reflectance http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 16 Course announcements Homework 4 is still ongoing - Any questions?
Radiometry and reflectance http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 16 Course announcements Homework 4 is still ongoing - Any questions?
Stereo and structured light
 Stereo and structured light http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 20 Course announcements Homework 5 is still ongoing. - Make sure
Stereo and structured light http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 20 Course announcements Homework 5 is still ongoing. - Make sure
Image Based Rendering. D.A. Forsyth, with slides from John Hart
 Image Based Rendering D.A. Forsyth, with slides from John Hart Topics Mosaics translating cameras reveal extra information, break occlusion Optical flow for very small movements of the camera Explicit
Image Based Rendering D.A. Forsyth, with slides from John Hart Topics Mosaics translating cameras reveal extra information, break occlusion Optical flow for very small movements of the camera Explicit
