More Constraints Than Houdini
|
|
|
- Calvin White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11/30/2005-8:00 am - 9:30 am Room:Swan 1 (Swan) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida More Constraints Than Houdini Thomas Short, P.E. - Munro & Associates, Inc. and Anthony Dudek MA31-3 Knowledge of constraints in Inventor is the key to escaping the bonds of time-consuming part and assembly creation. Join these master AU instructors for a detailed expose of the secrets of the part, assembly, and motion constraints in Autodesk Inventor. Review their features and see neat applications with tips and tricks that Houdini himself would have been proud of. This session will benefit anyone who is confused by the use of constraint-based technology to capture design intent. Many users try to achieve the same functionality via dimensions, workarounds, etc. About the Speaker: Tom is a mechanical engineer registered as a professional in Michigan. He has taught and consulted on AutoCAD, Autodesk Inventor, and Autodesk Mechanical Desktop for many years in the U.S. and other countries. At Munro & Associates, Inc., Tom is a consultant on Lean Design, and has worked with a variety of companies helping them improve their designs for simplicity and ease of assembly. He is also an author with books on Inventor and Mechanical Desktop. Tom has presented at every Autodesk University since its inception 12 years ago. One of Tony's main ideas overarching his 20-year-long career in engineering is that designing in 3D is a smarter and faster way to work. His philosophy is "Whatever it takes, do it right the first time." Tools like Autodesk Inventor can help achieve that goal. He believes that the engineering landscape in America has changed from an internal, ownership environment to an overextended and outsourced managed environment. Within this context, we are challenged to continue to deliver more quality in less time. This is the challenge of our generation of technology workers. The future is very promising with new technologies and methods being implemented every day. This will be Tony's 11th year at Autodesk University. dudea1@bp.com
2
3 November 28 December 1, 2005 Orlando, Florida More Constraints than Houdini Thomas Short & Anthony Dudek MA31-3 Knowledge of constraints in Inventor is the key to escaping the bonds of time-consuming part and assembly creation. Join these master AU instructors for a detailed expose of the secrets of the part, assembly, and motion constraints in Autodesk Inventor. Review their features and see neat applications with tips and tricks that Houdini himself would have been proud of. This session will benefit anyone who is confused by the use of constraint-based technology to capture design intent. Many users try to achieve the same functionality via dimensions, workarounds, etc. About the Speakers: One of Tony's main ideas overarching his 20-year-long career in engineering is that designing in 3D is a smarter and faster way to work. His philosophy is "Whatever it takes, do it right the first time." Tools like Autodesk Inventor can help achieve that goal. He believes that the engineering landscape in America has changed from an internal, ownership environment to an overextended and outsourced managed environment. Within this context, we are challenged to continue to deliver more quality in less time. This is the challenge of our generation of technology workers. The future is very promising with new technologies and methods being implemented every day. This will be Tony's 11th year at Autodesk University. Tom is a mechanical engineer registered as a professional in Michigan. He has taught and consulted on AutoCAD, Autodesk Inventor, and Autodesk Mechanical Desktop for many years in the U.S. and other countries. At Munro & Associates, Inc., Tom is a consultant on Lean Design, and has worked with a variety of companies helping them improve their designs for simplicity and ease of assembly. He is also an author with books on Inventor and Mechanical Desktop. Tom has presented at every Autodesk University since its inception 12 years ago. Objectives To review the control and use of the eleven 2D geometric constraints and the seven (1/2) 3D constraints in: Inventor Release 10 We will demonstrate most of these and review some of the lesser known features and their applications. 2D Geometric Constraints These are used on Profiles to geometrically relate the objects; the lines, arcs, and circles. Some are applied as you create the sketch and some you add to buildin your own geometric relationships. Our eventual goal in most parts is to have fully constrained sketches and that results in more robust parts and assemblies. Applying constraints reduces the number of dimensions required to fully constrain the sketch. 1
4 2D Constraints The constraints on a sketch can be displayed by: 1. Selecting display constraints from the sketch panel and picking an object. 2. Or select Display All Constraints from the right mouse menu. 3. Constraints are displayed as symbols on the objects. The size of the symbol cannot be changed. The relationship between symbols can be displayed by hovering over the symbol Objects and features you can select for constraints: lines, part edges, and projected features including work objects and their end points and mid-points Arcs and arc features and their end points and center points Circles and circular features and their center points Examples: 1. The midpoint coincident trick. 2. Vertical & Horizontal vs. Construction Geometry 3. Using projected work planes. 4. Using the Symmetric constraint. Symbol & Name Works On No. of Picks Function 1st Choice, Object to Change 2nd Choice, Object to Reference Special Line & Splines 2 Makes Line perpendicular to 2nd choice object Line or spline LLAN, Line or Spline For splines, end points must be coincident Line 2 Makes Line parallel to 2nd choice object Line LLAN or Line Both objects can't Line, Arc, Circle, or end points of Splines 2 Forces 1st object to be Line, Arc, Circle, tangent to 2nd or Spline LLAN, Line, Arc, be Lines. For Circle, or Spline splines, end points must be coincident Any Point (mid, end, Makes two points For point to line, center, spline point) 2 coincident or a point Any Point Point or Line the point can still and Lines coincident with a line slide along line Arc or Circle (includes Ellipse) 2 Forces two objects to have the same center. Arc or Circle Arc or Circle Coincident for center pints has the same effect Line or Ellipse Axis 2 Makes Line lie along the 2nd line or object Line or Ellipse Axis LLAN or Line or Ellipse Axis Forces a line to be parallel to the X-Axis. Line or Ellipse Axis or 1 or 2 Forces two points to Two Points have the same Y- Coordinate Line or Ellipse Axis or Point Point (no 2nd choice required for Line) LLAN means "Looks Like A line," A part edge or projected feature 2
5 Coordinate Forces a line to be parallel to the Y-Axis. Line or Ellipse Axis or 1 or 2 Forces two points to Two Points have the same X- Coordinate Forces two lines to the same length and arcs Line, Arc, or Circle 2 and circles to the same radius Line or Ellipse Axis or Point Line or LLAN Arc or Circle Point (no 2nd choice required for Line) Line or LLAN 2nd choice must be same type as Arc or Circle first Point (center, end, or mid) 1 Fixes the point in the coordinate system Point (none) Circles & Arcs can still change radius and lines can change length Line, Arc, or Circle 2 Fixes the object in the coordinate system Line, Arc, or Circle (none) For circles, fixes both the center and the radius. End points and/or lengths of arcs and lines can still change Line, Arc, or Circle 3 Line, Arc or Circle Normal, Forces objects to be then construction, or mirror images about an Line, Arc, or Circle corresponding centerline for the axis Line, Arc or Circle 3rd pick LLAN means "Looks Like A line," A part edge or projected feature 3D Constraints There are: 4 Assembly constraints used to position parts in relation to each other. These are:, Angle, Tangent, & Insert 2 Motion constraints used to control rotation and/or translation of pairs of parts such as gears 1 Transitional constraint used to relate the motion of a follower and a cam Assembly Constraints DOF symbol One of the parts is the Grounded part with no degrees of freedom. All other parts are constrained to the ground or each other. If you move the grounded part all other will follow when you update. 3
6 Assembly Constraints Angle Tangent Insert These are numerous combinations of the four assembly constraints and their object choices. In addition, every constraint has an optional Offset or Angle that can be be positive or negative. The object choices are: Points: vertices, centers of circular features, work points. Lines: Linear part edges, cylindrical axis, work axis. Faces: Planar faces, work planes, cylindrical faces. Driving Assembly Constraints & The Contact Set Marked components are in the Contact Set Angle constraint between two faces to control and drive motion Translational Rotational Name 1st Choice, On Solid 1 2nd Choice, On Solid 2 Offset Remarks Vertex, Center of Vertex, Center of Arc or Circle, Arc or Circle, Work Point Work Point 3 0 Moves 2nd part from 1st part along World X- axis. Vertex, Center of Arc or Circle, Work Point Work Axis 2 0 Moves 2nd part from 1st part along an axis perpendicular to the edge Vertex, Center of Arc or Circle, Face, Work Plane 1 0 Work Point Positive moves point from face along direction of arrow. Work Axis Work Axis 2 2 Separates the lines along axis perpendiualr to first line Positive or negative offset both move the same way Work Axis Face, Work Plane 1 1 Positive moves point from face along direction of arrow. Moves centerlines cylindrical shape cylindrical shape 2 2 apart. Direction is determined on order of selection not sign of Positive or negative offset both move the same way offset. 4
7 Name 1st Choice, On Solid 1 2nd Choice, On Solid 2 Translational Rotational Offset Remarks cylindrical shape Vertex, Center of Arc or Circle, Work Point 2 0 Constrains centerline on radius (of offset) from point. cylindrical shape Work Axis 2 2 Constrains centerline on radius (of offset) from line cylindrical shape Face, Work Plane 1 1 Positive moves point from face along direction of arrow. Face, Work Plane Face, Work Plane 1 2 Positives separates faces, Negative interferes faces. Flush Face, Work Plane Face, Work Plane 1 2 Moves 1st part in direction of arrows. Negative moves in direction of arrows Angle Face, Work Plane, Edge, Work Axis Face, Work Plane, Edge, Work Axis 0 2 Included angle between Picking an edge displays the positive arrows an arrow (vector) (vectors) Name 1st Choice, On Solid 1 2nd Choice, On Solid 2 Translational Rotational Offset Remarks Tangent Cylindrical Face Cylindrical Face 2 2 Moves perpendicual to the cylicrical face 2nd solution changes side of face that is tangent Tangent Cylindrical Face Face or Work Plane 1 1 Positive move along direction of face arrow One choice must be a cylindrical face. Tangent Edge, Work Axis, Center line 0 0 Cylindrical Face This constraint can be applied but has no effect whatever! Insert Cylindrical edge on part Cylindrical edge on part 3 2 Positive separates faces. Is a combination of mate two centerlines and mate two faces. You can pick the second solution and get a Flush. Motion Constraints Motion constraint controls rotation of pairs of parts such as gears. Pick faces of gears. Ratio is number of rotations for 2 nd pick relative to 1 st. For complex trains such as a planetary, Ratio must be a formula based on analysis. Second Type applies to a rack & pinion 5
8 Transitional Constraint The transitional constraint maintains contact between two surfaces one of which moves. There is no offset in this constraint Contact Solver If components are in a contact set and collision occurs when one component moves: 1. If the second component can move it will. 2. If the second component cannot move, motion of the first will cease 6
Autodesk Inventor 6 Essentials Instructor Guide Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the follow
 Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the following topics and provides exercises for students to practice their skills. Day Two Topic: How to create
Chapter Four: Creating Placed Features Chapter Outline This chapter provides instruction on the following topics and provides exercises for students to practice their skills. Day Two Topic: How to create
Working with Neutral Format Surface and Solid Models in Autodesk Inventor
 Working with Neutral Format Surface and Solid Models in Autodesk Inventor JD Mather Pennsylvania College of Technology Session ID ML205-1P In this class we will learn how to utilize neutral format data
Working with Neutral Format Surface and Solid Models in Autodesk Inventor JD Mather Pennsylvania College of Technology Session ID ML205-1P In this class we will learn how to utilize neutral format data
Introduction to Autodesk Revit Structure
 11/30/2005-5:00 pm - 6:30 pm Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon E2) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Nicolas Mangon - Autodesk SD35-1 This year, Autodesk is introducing the
11/30/2005-5:00 pm - 6:30 pm Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon E2) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Nicolas Mangon - Autodesk SD35-1 This year, Autodesk is introducing the
Tips & Techniques in Autodesk Inventor 2013/2014 PLTW - Wisconsin Dec. 10, 2013
 Tips & Techniques in Autodesk Inventor 2013/2014 PLTW - Wisconsin Dec. 10, 2013 Dan Banach Autodesk Inc. Dataset https://www.dropbox.com/sh/scpc4lkk94lmq8n/ydbxbxemet Instructors & students register for
Tips & Techniques in Autodesk Inventor 2013/2014 PLTW - Wisconsin Dec. 10, 2013 Dan Banach Autodesk Inc. Dataset https://www.dropbox.com/sh/scpc4lkk94lmq8n/ydbxbxemet Instructors & students register for
Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1
 Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1 Launch Inventor Professional 2015 1. Start a New part. Depending on how Inventor was installed, using this icon may get you an Inch or Metric file. To be
Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1 Launch Inventor Professional 2015 1. Start a New part. Depending on how Inventor was installed, using this icon may get you an Inch or Metric file. To be
An Introduction to Autodesk Revit Massing, Surface Divisions, and Adaptive Components
 An Introduction to Autodesk Revit Massing, Surface Divisions, and Adaptive Components Chad Smith KarelCAD, Australia AB2463-L As the Revit massing tools become more polished and robust, users are becoming
An Introduction to Autodesk Revit Massing, Surface Divisions, and Adaptive Components Chad Smith KarelCAD, Australia AB2463-L As the Revit massing tools become more polished and robust, users are becoming
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks
 Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Constraint Based Modeling Geometric and Dimensional. ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 03
 Constraint Based Modeling Geometric and Dimensional ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 03 Today s Objectives Using two different type of constraints in SolidWorks: Geometric Dimensional SW03 In-Class Activity List Geometric
Constraint Based Modeling Geometric and Dimensional ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 03 Today s Objectives Using two different type of constraints in SolidWorks: Geometric Dimensional SW03 In-Class Activity List Geometric
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
SOLIDWORKS 2018 Reference Guide
 SOLIDWORKS 2018 Reference Guide A comprehensive reference guide with over 250 standalone tutorials David C. Planchard, CSWP, SOLIDWORKS Accredited Educator SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
SOLIDWORKS 2018 Reference Guide A comprehensive reference guide with over 250 standalone tutorials David C. Planchard, CSWP, SOLIDWORKS Accredited Educator SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Skateboard. Hanger. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1. Fig. 2
 Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch1 Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1.
Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch1 Lines. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the Context toolbar, Fig. 1.
CO 2 Shell Car. Body. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch from the context toolbar, Fig. 1. on the Standard Views toolbar.
 CO 2 Shell Car Chapter 2 Body A. Save as "BODY". Step 1. If necessary, open your BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in BODY for the filename and press ENTER. B. FRONT Wheel Shell.
CO 2 Shell Car Chapter 2 Body A. Save as "BODY". Step 1. If necessary, open your BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in BODY for the filename and press ENTER. B. FRONT Wheel Shell.
MAE 455 COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN AND DRAFTING MIDTERM EXAM PRACTICE QUESTIONS. Name: You are allowed one sheet of notes.
 47 MAE 455 COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN AND DRAFTING MIDTERM EXAM PRACTICE QUESTIONS Name: You are allowed one sheet of notes. 1. What constraints could be added to fully constrain the wireframe shown? Include
47 MAE 455 COMPUTER-AIDED DESIGN AND DRAFTING MIDTERM EXAM PRACTICE QUESTIONS Name: You are allowed one sheet of notes. 1. What constraints could be added to fully constrain the wireframe shown? Include
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling
 Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling (Tutorial 2-Mouse) Surface-modeling Solid-modeling A- 1 Assembly Design Design with a Master Model Surface-modeling Tutorial 2A Import 2D outline drawing into Solidworks2006
Solidworks 2006 Surface-modeling (Tutorial 2-Mouse) Surface-modeling Solid-modeling A- 1 Assembly Design Design with a Master Model Surface-modeling Tutorial 2A Import 2D outline drawing into Solidworks2006
Doctor Walt s Solid Edge Version 19 Workbook 137
 Still using the SMART DIMENSION Tool, click on the left vertical edge of the sketch. Move the cursor to the left and click to set the text position. Type 1.5 for the value and hit the ENTER Key. Next,
Still using the SMART DIMENSION Tool, click on the left vertical edge of the sketch. Move the cursor to the left and click to set the text position. Type 1.5 for the value and hit the ENTER Key. Next,
GENIO CAD/CAM software powered by Autodesk technology for parametric programming of boring, routing and edge-banding work centers Genio SPAI SOFTWARE
 GENIO CAD/CAM software powered by Autodesk technology for parametric programming of boring, routing and edge-banding work centers Overview is a powerful CAD/CAM system powered by Autodesk 3D environment
GENIO CAD/CAM software powered by Autodesk technology for parametric programming of boring, routing and edge-banding work centers Overview is a powerful CAD/CAM system powered by Autodesk 3D environment
SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users
 SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com Table of Contents Dedication... 3 Preface... 15 Part 1. Introducing
SOLIDWORKS 2016: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com Table of Contents Dedication... 3 Preface... 15 Part 1. Introducing
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling
 CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
Lesson 3: Surface Creation
 Lesson 3: Surface Creation In this lesson, you will learn how to create surfaces from wireframes. Lesson Contents: Case Study: Surface Creation Design Intent Stages in the Process Choice of Surface Sweeping
Lesson 3: Surface Creation In this lesson, you will learn how to create surfaces from wireframes. Lesson Contents: Case Study: Surface Creation Design Intent Stages in the Process Choice of Surface Sweeping
Learning. Modeling, Assembly and Analysis SOLIDWORKS Randy H. Shih SDC. Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
 Learning SOLIDWORKS 2016 Modeling, Assembly and Analysis Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Learning SOLIDWORKS 2016 Modeling, Assembly and Analysis Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Assembly Modeling Constraints. ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05
 Assembly Modeling Constraints ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Creating assemblies by constraining 3D parts together Movement and Location dictated by Constraints SW05 Activity SW05 Application
Assembly Modeling Constraints ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Creating assemblies by constraining 3D parts together Movement and Location dictated by Constraints SW05 Activity SW05 Application
Technical Education Services
 Autodesk Fusion 360: Introduction to Parametric Modeling Course Length: 3 days Official Training Guide The Autodesk Fusion 360 Introduction to Parametric Modeling training course provides you with an understanding
Autodesk Fusion 360: Introduction to Parametric Modeling Course Length: 3 days Official Training Guide The Autodesk Fusion 360 Introduction to Parametric Modeling training course provides you with an understanding
SpaceClaim Professional The Natural 3D Design System. Advanced Technology
 SpaceClaim Professional The Natural 3D Design System SpaceClaim Professional is the 3D productivity tool for engineers who contribute to the design and manufacture of mechanical products across a broad
SpaceClaim Professional The Natural 3D Design System SpaceClaim Professional is the 3D productivity tool for engineers who contribute to the design and manufacture of mechanical products across a broad
SOLIDWORKS - SYLLABUS
 SOLIDWORKS - SYLLABUS SolidWorks Syllabus 1 Introduction to CAD, CAE, PDM Features of SolidWorks, Total Duration : 90 Hour Various products available in SolidWorks for Product Design, Simulation, Communication
SOLIDWORKS - SYLLABUS SolidWorks Syllabus 1 Introduction to CAD, CAE, PDM Features of SolidWorks, Total Duration : 90 Hour Various products available in SolidWorks for Product Design, Simulation, Communication
Autodesk Inventor 2018
 Parametric Modeling with Autodesk Inventor 2018 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Parametric Modeling with Autodesk Inventor 2018 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Autodesk Inventor Tips & Tricks Placing Features On
 1 Autodesk Inventor Tips & Tricks Placing Features On Cylindrical Shapes The adoption of parametric, feature based solid modeling will present many challenges to the new user as they are confronted for
1 Autodesk Inventor Tips & Tricks Placing Features On Cylindrical Shapes The adoption of parametric, feature based solid modeling will present many challenges to the new user as they are confronted for
Getting Along: Coordinating Architectural and Structural Design with Autodesk Revit Structure
 11/30/2005-8:00 am - 9:30 am Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon A2) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Getting Along: Coordinating Architectural and Structural Design with Autodesk
11/30/2005-8:00 am - 9:30 am Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon A2) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Getting Along: Coordinating Architectural and Structural Design with Autodesk
Lesson 14 Blends. For Resources go to > click on the Creo Parametric 2.0 Book cover
 Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Hole Pattern REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Hole Pattern REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Skateboard. Hanger. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch. (S) on the Sketch. Line
 Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch 1. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch Step
Chapter 3 Skateboard Hanger A. Sketch 1. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part Metric and OK. Step 2. Click Right Plane from the Content toolbar, Fig. 1. in the Feature Manager and click Sketch Step
Parametric Modeling. With. Autodesk Inventor. Randy H. Shih. Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS
 Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Instructor: Dr.Ashok Kaushal
 Continuing Education Department AutoCAD Instructor: Dr.Ashok Kaushal E-mail: ashok_kaushal@hotmail.com Topics Intro to CAD, Geometric commands, Absolute & Relative values, Line, Circle, Arc Dr. Ashok Kaushal
Continuing Education Department AutoCAD Instructor: Dr.Ashok Kaushal E-mail: ashok_kaushal@hotmail.com Topics Intro to CAD, Geometric commands, Absolute & Relative values, Line, Circle, Arc Dr. Ashok Kaushal
Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling. ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05
 Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Feature-Based Modeling (comprised of 2 sections as shown below) 1. Breaking it down into features Creating
Feature-Based Modeling and Optional Advanced Modeling ENGR 1182 SolidWorks 05 Today s Objectives Feature-Based Modeling (comprised of 2 sections as shown below) 1. Breaking it down into features Creating
Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Workbench Release 12.1 Environment
 ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Workbench Release 12.1 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Structural & Thermal Analysis Using the ANSYS Workbench Release 12.1 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
Creating T-Spline Forms
 1 / 28 Goals 1. Create a T-Spline Primitive Form 2. Create a T-Spline Revolve Form 3. Create a T-Spline Sweep Form 4. Create a T-Spline Loft Form 2 / 28 Instructions Step 1: Go to the Sculpt workspace
1 / 28 Goals 1. Create a T-Spline Primitive Form 2. Create a T-Spline Revolve Form 3. Create a T-Spline Sweep Form 4. Create a T-Spline Loft Form 2 / 28 Instructions Step 1: Go to the Sculpt workspace
Chapter 20 Assembly Model with VEX Robot Kit - Autodesk Inventor
 Tools for Design Using AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor 20-1 Chapter 20 Assembly Model with VEX Robot Kit - Autodesk Inventor Creating an Assembly Using Parts from the VEX Robot Kit Understand and Perform
Tools for Design Using AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor 20-1 Chapter 20 Assembly Model with VEX Robot Kit - Autodesk Inventor Creating an Assembly Using Parts from the VEX Robot Kit Understand and Perform
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011
 A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
Module 2 Review. Assemblies and Rendering. Why Use Assemblies. Assemblies - Key Concepts. Sketch Planes Sketched Features.
 Module 2 Review Assemblies and Rendering EF 101 Modules 3.1, 3.2 Sketch Planes Sketched Features Extrude, Revolve Placed Features Hole, Fillet, Chamfer, Shell, Rect. Pattern Drawing Views Base, Ortho,
Module 2 Review Assemblies and Rendering EF 101 Modules 3.1, 3.2 Sketch Planes Sketched Features Extrude, Revolve Placed Features Hole, Fillet, Chamfer, Shell, Rect. Pattern Drawing Views Base, Ortho,
Additional Exercises. You will perform the following exercises to practice the concepts learnt in this course:
 Additional Exercises You will perform the following exercises to practice the concepts learnt in this course: Master Exercise : Mobile Phone Plastic Bottle Exercise 1 Master Exercise : Mobile Phone In
Additional Exercises You will perform the following exercises to practice the concepts learnt in this course: Master Exercise : Mobile Phone Plastic Bottle Exercise 1 Master Exercise : Mobile Phone In
Lesson 1: Creating T- Spline Forms. In Samples section of your Data Panel, browse to: Fusion 101 Training > 03 Sculpt > 03_Sculpting_Introduction.
 3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
H Stab and V Stab. Chapter 6. Glider. A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file.
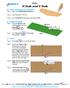 Chapter 6 Glider H Stab and V Stab A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in H STAB for the filename and press ENTER. B. Sketch
Chapter 6 Glider H Stab and V Stab A. Open and Save as "H STAB". Step 1. Open your STABILIZER BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in H STAB for the filename and press ENTER. B. Sketch
SIEMENS. Modeling assemblies. Self-Paced Training. spse01540
 SIEMENS Modeling assemblies Self-Paced Training spse01540 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
SIEMENS Modeling assemblies Self-Paced Training spse01540 Proprietary and restricted rights notice This software and related documentation are proprietary to Siemens Product Lifecycle Management Software
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 11.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Conics? Conics as Cross Sections Determine the conic section that results from the intersection of the double-napped cone shown and each plane described. 1.
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Conics? Conics as Cross Sections Determine the conic section that results from the intersection of the double-napped cone shown and each plane described. 1.
Minimal AutoCAD 2011
 PDHonline Course G371 (2 PDH) Minimal AutoCAD 2011 Instructor: Thomas Mason, P.E. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org
PDHonline Course G371 (2 PDH) Minimal AutoCAD 2011 Instructor: Thomas Mason, P.E. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org
Pro/Assembly. Figure Placing the first part: a) Create a new assembly called Tutorial2a. Accept the default template.
 Pro/Assembly An assembly is a collection of parts oriented and positioned together. Creating an assembly involves telling Pro/E how the various components fit together. To do this, we specify assembly
Pro/Assembly An assembly is a collection of parts oriented and positioned together. Creating an assembly involves telling Pro/E how the various components fit together. To do this, we specify assembly
ME Week 11 Create Joints Project
 One of the most important elements of dynamic simulation is setting up and verifying that proper joints are created. Joints are links between two rigid components that applies force from the first component
One of the most important elements of dynamic simulation is setting up and verifying that proper joints are created. Joints are links between two rigid components that applies force from the first component
CATIA Electrical Space Reservation TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Manual Format...2 Electrical Reservations...3 Equipment Reservations...5 Pathway Reservations...31 Advanced Reservations...49 Reservation Analysis...67 Clash...69 Sectioning...73
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Manual Format...2 Electrical Reservations...3 Equipment Reservations...5 Pathway Reservations...31 Advanced Reservations...49 Reservation Analysis...67 Clash...69 Sectioning...73
PROPORTION PLANAR GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONES AND GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIP
 PROPORTION PLANAR GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONES AND GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIP The relationship regarding dimensions between two or more figures, or between two parts or a part and the whole is called PROPORTION.
PROPORTION PLANAR GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONES AND GEOMETRIC RELATIONSHIP The relationship regarding dimensions between two or more figures, or between two parts or a part and the whole is called PROPORTION.
SolidWorks. An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs
 An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
Lesson 14 Blends. For Resources go to > click on the Creo Parametric Book cover
 Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Swept Blend REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Lesson 14 Blends Figure 14.1 Cap OBJECTIVES Create a Parallel Blend feature Use the Shell Tool Create a Swept Blend REFERENCES AND RESOURCES For Resources go to www.cad-resources.com > click on the Creo
Exploring Translations
 Exploring Translations 1. New Sketch: To open a new sketch go to FILE and click on New Sketch 2. Create a triangle. a. Using the SEGMENT tool, construct a triangle. b. Drag the cursor and release for each
Exploring Translations 1. New Sketch: To open a new sketch go to FILE and click on New Sketch 2. Create a triangle. a. Using the SEGMENT tool, construct a triangle. b. Drag the cursor and release for each
Lesson 12 Bottom-Up Assembly Modeling
 Lesson 12 Bottom-Up Assembly Modeling Upon successful completion of this lesson, you will be able to: Create a new assembly. Insert components into an assembly using all available techniques. Add mating
Lesson 12 Bottom-Up Assembly Modeling Upon successful completion of this lesson, you will be able to: Create a new assembly. Insert components into an assembly using all available techniques. Add mating
Introducing SolidWorks Assemblies
 Introducing SolidWorks Assemblies SAAST Robotics 2008 Assemblies Collection of related parts saved in one SW document file - *.sldasm Contains anywhere from 2 to over 1000 components or sub-assemblies
Introducing SolidWorks Assemblies SAAST Robotics 2008 Assemblies Collection of related parts saved in one SW document file - *.sldasm Contains anywhere from 2 to over 1000 components or sub-assemblies
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
 Assembly Modeling Model Files Initial and Final Solutions! with SolidWorks 2012 For the SolidWorks user who needs to understand Assembly modeling By Planchard & Planchard CSWP SDC SSoolliiddW Woorrkkss
Assembly Modeling Model Files Initial and Final Solutions! with SolidWorks 2012 For the SolidWorks user who needs to understand Assembly modeling By Planchard & Planchard CSWP SDC SSoolliiddW Woorrkkss
Complex Shapes Creation with Hybrid Modelling
 Complex Shapes Creation with Hybrid Modelling Peter De Strijker Technical Sales Executive MFG - Benelux Our Customer s Industries Discrete product manufacture Agenda Quality Analyses of sketches and surfaces
Complex Shapes Creation with Hybrid Modelling Peter De Strijker Technical Sales Executive MFG - Benelux Our Customer s Industries Discrete product manufacture Agenda Quality Analyses of sketches and surfaces
Intersection Design with Autodesk Civil 3D
 12/1/2005-8:00 am - 11:30 am Room:Osprey 1 [Lab] (Swan) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Intersection Design with Autodesk Civil 3D Daniel Philbrick - Autodesk and James Wedding
12/1/2005-8:00 am - 11:30 am Room:Osprey 1 [Lab] (Swan) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Intersection Design with Autodesk Civil 3D Daniel Philbrick - Autodesk and James Wedding
Propeller. Chapter 13. Airplane. A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK.
 Chapter 13 Airplane Propeller A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. Step 2. Click Top Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch toolbar, Fig. 1. from the Content Step
Chapter 13 Airplane Propeller A. Base for Blade. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. Step 2. Click Top Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch toolbar, Fig. 1. from the Content Step
Assembly Modeling & Assembling Parts
 This week you will learn assembly modeling & assembling parts. The steps to follow are: Assembly modeling Assembly hierarchy Assembly constraints Configurations Assembly strategy 1 Creating Assembly Components
This week you will learn assembly modeling & assembling parts. The steps to follow are: Assembly modeling Assembly hierarchy Assembly constraints Configurations Assembly strategy 1 Creating Assembly Components
MAE 323: Lab 7. Instructions. Pressure Vessel Alex Grishin MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1
 Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Instructions MAE 323 Lab Instructions 1 Problem Definition Determine how different element types perform for modeling a cylindrical pressure vessel over a wide range of r/t ratios, and how the hoop stress
Additional Surface Tools
 Additional Surface Tools Several additional surface tools, techniques, and related functions are available. This supplement provides a brief introduction to those functions. Panel Part Features Replace
Additional Surface Tools Several additional surface tools, techniques, and related functions are available. This supplement provides a brief introduction to those functions. Panel Part Features Replace
ROBOTWORKS CASE HISTORY COMPLEX POLISHING PATH DEVELOPMENT
 ROBOTWORKS CASE HISTORY COMPLEX POLISHING PATH DEVELOPMENT ABSTRACT This Case History describes how RobotWorks was used to develop a series of complex robotic polishing paths. Path shape specifications
ROBOTWORKS CASE HISTORY COMPLEX POLISHING PATH DEVELOPMENT ABSTRACT This Case History describes how RobotWorks was used to develop a series of complex robotic polishing paths. Path shape specifications
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual. Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC
 StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
StickFont Editor v1.01 User Manual Copyright 2012 NCPlot Software LLC StickFont Editor Manual Table of Contents Welcome... 1 Registering StickFont Editor... 3 Getting Started... 5 Getting Started...
2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions. ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations REFLECT
 2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions Essential question: How do you identify transformations that are rigid motions? ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations A transformation is a function that changes
2-1 Transformations and Rigid Motions Essential question: How do you identify transformations that are rigid motions? ENGAGE 1 ~ Introducing Transformations A transformation is a function that changes
Spline Options. Student Web Site. Using Bowties
 Spline Options Splines are complex curves that can be adjusted and calculated using a variety of methods. After creating a spline, right-click on the spline to access options for refining the spline shape.
Spline Options Splines are complex curves that can be adjusted and calculated using a variety of methods. After creating a spline, right-click on the spline to access options for refining the spline shape.
CATIA Surface Design
 CATIA V5 Training Exercises CATIA Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GS1_FX_V5R19 Table of Contents (1/2) Creating Wireframe Geometry: Recap Exercises 4 Creating Wireframe Geometry:
CATIA V5 Training Exercises CATIA Surface Design Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GS1_FX_V5R19 Table of Contents (1/2) Creating Wireframe Geometry: Recap Exercises 4 Creating Wireframe Geometry:
Structural & Thermal Analysis using the ANSYS Workbench Release 11.0 Environment. Kent L. Lawrence
 ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Structural & Thermal Analysis using the ANSYS Workbench Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
ANSYS Workbench Tutorial Structural & Thermal Analysis using the ANSYS Workbench Release 11.0 Environment Kent L. Lawrence Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Texas at Arlington SDC PUBLICATIONS
Glider. Wing. Top face click Sketch. on the Standard Views. (S) on the Sketch toolbar.
 Chapter 5 Glider Wing 4 Panel Tip A. Open and Save As "WING 4 PANEL". Step 1. Open your WING BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in WING 4 PANEL for the filename and press ENTER.
Chapter 5 Glider Wing 4 Panel Tip A. Open and Save As "WING 4 PANEL". Step 1. Open your WING BLANK file. Step 2. Click File Menu > Save As. Step 3. Key-in WING 4 PANEL for the filename and press ENTER.
Chapter 19 Assembly Modeling with the TETRIX by Pitsco Building System Autodesk Inventor
 Tools for Design Using AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor 19-1 Chapter 19 Assembly Modeling with the TETRIX by Pitsco Building System Autodesk Inventor Create and Use Subassemblies in Assemblies Creating an
Tools for Design Using AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor 19-1 Chapter 19 Assembly Modeling with the TETRIX by Pitsco Building System Autodesk Inventor Create and Use Subassemblies in Assemblies Creating an
Version 2011 R1 - Router
 GENERAL NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Convert Raster to Vector
GENERAL NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Convert Raster to Vector
Input CAD Solid Model Assemblies - Split into separate Part Files. DXF, IGES WMF, EMF STL, VDA, Rhino Parasolid, ACIS
 General NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Report Creator and Designer
General NC File Output List NC Code Post Processor Selection Printer/Plotter Output Insert Existing Drawing File Input NC Code as Geometry or Tool Paths Input Raster Image Files Report Creator and Designer
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors. UCF Engineering
 SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors UCF Engineering Solidworks Review Last lesson we discussed several more features that can be added to models in order to increase their complexity. We are now
SOLIDWORKS: Lesson III Patterns & Mirrors UCF Engineering Solidworks Review Last lesson we discussed several more features that can be added to models in order to increase their complexity. We are now
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Learning Task: Exploring Reflections and Rotations
 Learning Task: Exploring Reflections and Rotations Name Date Mathematical Goals Develop and demonstrate an understanding of reflections and rotations of figures in general and on a coordinate plane. Essential
Learning Task: Exploring Reflections and Rotations Name Date Mathematical Goals Develop and demonstrate an understanding of reflections and rotations of figures in general and on a coordinate plane. Essential
SolidWorks Assembly Files. Assemblies Mobility. The Mating Game Mating features. Mechanical Mates Relative rotation about axes
 Assemblies Mobility SolidWorks Assembly Files An assembly file is a collection of parts The first part brought into an assembly file is fixed Other parts are constrained relative to that part (or other
Assemblies Mobility SolidWorks Assembly Files An assembly file is a collection of parts The first part brought into an assembly file is fixed Other parts are constrained relative to that part (or other
Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas
 Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas 1 y axis origin x axis 2 Plot the points: ( 3, 5), (0,7), ( 6,0), (6,4) 3 Distance Formula y x 4 Finding the Distance Between Two Points Find the distance
Section 1.1 The Distance and Midpoint Formulas 1 y axis origin x axis 2 Plot the points: ( 3, 5), (0,7), ( 6,0), (6,4) 3 Distance Formula y x 4 Finding the Distance Between Two Points Find the distance
Autodesk Inventor : From Concept to Digital Prototype
 Autodesk Inventor : From Concept to Digital Prototype Bryan Fields Advanced Solutions, Inc. MA305-5 Using the tools available in Autodesk Inventor, this session will look at the progression from concept
Autodesk Inventor : From Concept to Digital Prototype Bryan Fields Advanced Solutions, Inc. MA305-5 Using the tools available in Autodesk Inventor, this session will look at the progression from concept
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017
 Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2017 NEW Contains a new chapter on 3D printing Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2010 and AutoCAD Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS. Schroff Development Corporation
 An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2010 and AutoCAD 2010 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2010 and AutoCAD 2010 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded
Autodesk Inventor 11 Certified User and Expert Exam Preparation Class [Part 2]
![Autodesk Inventor 11 Certified User and Expert Exam Preparation Class [Part 2] Autodesk Inventor 11 Certified User and Expert Exam Preparation Class [Part 2]](/thumbs/73/68780725.jpg) 11/29/2006-5:00 pm - 6:30 pm Room:Marcello - 4404 (MSD Campus) Autodesk Inventor 11 Certified User and Expert Exam Preparation Class [Part 2] Daniel Banach - MasterGraphics MA25-3 See MA24-2: Autodesk
11/29/2006-5:00 pm - 6:30 pm Room:Marcello - 4404 (MSD Campus) Autodesk Inventor 11 Certified User and Expert Exam Preparation Class [Part 2] Daniel Banach - MasterGraphics MA25-3 See MA24-2: Autodesk
Solid Modeling: Part 1
 Solid Modeling: Part 1 Basics of Revolving, Extruding, and Boolean Operations Revolving Exercise: Stepped Shaft Start AutoCAD and use the solid.dwt template file to create a new drawing. Create the top
Solid Modeling: Part 1 Basics of Revolving, Extruding, and Boolean Operations Revolving Exercise: Stepped Shaft Start AutoCAD and use the solid.dwt template file to create a new drawing. Create the top
3D ModelingChapter1: Chapter. Objectives
 Chapter 1 3D ModelingChapter1: The lessons covered in this chapter familiarize you with 3D modeling and how you view your designs as you create them. You also learn the coordinate system and how you can
Chapter 1 3D ModelingChapter1: The lessons covered in this chapter familiarize you with 3D modeling and how you view your designs as you create them. You also learn the coordinate system and how you can
xx SolidWorks for Designers
 Introduction SolidWorks 2004 Welcome to the entire new world of Computer Aided Designing (CAD) with SolidWorks. If you are a new user of this software package, you are going to join hands with thousands
Introduction SolidWorks 2004 Welcome to the entire new world of Computer Aided Designing (CAD) with SolidWorks. If you are a new user of this software package, you are going to join hands with thousands
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
Module 5: Creating Sheet Metal Transition Piece Between a Square Tube and a Rectangular Tube with Triangulation
 1 Module 5: Creating Sheet Metal Transition Piece Between a Square Tube and a Rectangular Tube with Triangulation In Module 5, we will learn how to create a 3D folded model of a sheet metal transition
1 Module 5: Creating Sheet Metal Transition Piece Between a Square Tube and a Rectangular Tube with Triangulation In Module 5, we will learn how to create a 3D folded model of a sheet metal transition
Autodesk Inventor 2016 Learn by doing. Tutorial Books
 Autodesk Inventor 2016 Learn by doing Tutorial Books Copyright 2015 Kishore This book may not be duplicated in any way without the express written consent of the publisher, except in the form of brief
Autodesk Inventor 2016 Learn by doing Tutorial Books Copyright 2015 Kishore This book may not be duplicated in any way without the express written consent of the publisher, except in the form of brief
A Quick Spin on Autodesk Architectural Studio
 December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas A Quick Spin on Autodesk Architectural Studio Mario Guttman, AIA Kevin Durham Christie Landry (Instructor) (Assistant) (Assistant) BD13-5L Autodesk Architectural
December 2-5, 2003 MGM Grand Hotel Las Vegas A Quick Spin on Autodesk Architectural Studio Mario Guttman, AIA Kevin Durham Christie Landry (Instructor) (Assistant) (Assistant) BD13-5L Autodesk Architectural
Speedway. Body. (S) on the Sketch toolbar. Fig. 1
 Chapter 1 A. New Part. Step 1. Click File Menu > New. Speedway Body Step 2. Click Part from the list and click OK, Fig. 1. B. Sketch Construction Rectangle. Step 1. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager
Chapter 1 A. New Part. Step 1. Click File Menu > New. Speedway Body Step 2. Click Part from the list and click OK, Fig. 1. B. Sketch Construction Rectangle. Step 1. Click Right Plane in the Feature Manager
Autodesk Inventor 2018
 Learning Autodesk Inventor 2018 Modeling, Assembly and Analysis Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Learning Autodesk Inventor 2018 Modeling, Assembly and Analysis Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2012 and AutoCAD Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS. Schroff Development Corporation
 An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2012 and AutoCAD 2012 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2012 and AutoCAD 2012 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
AutoCAD 2009 Configuration for MUS
 AutoCAD 2009 Configuration for MUS NOTE: The following steps do not apply to AutoCAD 2006 or earlier versions. These steps must be done before attempting to use MicroScribe Utility Software (MUS) with
AutoCAD 2009 Configuration for MUS NOTE: The following steps do not apply to AutoCAD 2006 or earlier versions. These steps must be done before attempting to use MicroScribe Utility Software (MUS) with
Nose Cone. Chapter 4. Rocket 3D Print. A. Revolve. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. SOLIDWORKS 16 Nose Cone ROCKET 3D PRINT Page 4-1
 Chapter 4 Rocket 3D Print Nose Cone A. Revolve. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the content toolbar, Fig. 1. Step
Chapter 4 Rocket 3D Print Nose Cone A. Revolve. Step 1. Click File Menu > New, click Part and OK. Step 2. Click Front Plane in the Feature Manager and click Sketch on the content toolbar, Fig. 1. Step
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS
 CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
CHAPTER 8 QUADRATIC RELATIONS AND CONIC SECTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Writing equations of conic sections ) Graphing equations of conic sections 3) Solving quadratic systems Section: Essential Question 8-1 Apply
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2013 and AutoCAD
 An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2013 and AutoCAD 2013 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2013 and AutoCAD 2013 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics
 SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
SOLIDWORKS 2016 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
SOLIDWORKS 2015: A Power Guide for Beginner and Intermediate Users
 SOLIDWORKS 2015: A Power Guide for Beginner and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com SOLIDWORKS 2015: A Power Guide for Beginner and Intermediate
SOLIDWORKS 2015: A Power Guide for Beginner and Intermediate Users The premium provider of learning products and solutions www.cadartifex.com SOLIDWORKS 2015: A Power Guide for Beginner and Intermediate
MEM30004A. AutoCAD Inventor Advanced Use CAD to create and display 3D models. MEM30004A Autodesk Inventor (Advanced)
 MEM30004A AutoCAD Inventor Advanced Use CAD to create and display 3D models. BlackLine Design Page 1 of 26 Table of Contents Conditions of Use:... 2 Unit Resource Manual... 2 Manufacturing Skills Australia
MEM30004A AutoCAD Inventor Advanced Use CAD to create and display 3D models. BlackLine Design Page 1 of 26 Table of Contents Conditions of Use:... 2 Unit Resource Manual... 2 Manufacturing Skills Australia
SOLIDWORKS Parametric Modeling with SDC. Covers material found on the CSWA exam. Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling
 Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2015 Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF
Parametric Modeling with SOLIDWORKS 2015 Covers material found on the CSWA exam Randy H. Shih Paul J. Schilling SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF
M Autodesk. Press. Thomson Learning
 .( '; f : 'L DANIEL T. BANACH-^ zzmechanical Desktop 4 Applying Designer and "Ässembly Modules M Autodesk Press Thomson Learning Africa Australia Canada Denmark Japan Mexico New Zealand Philippines Puerto
.( '; f : 'L DANIEL T. BANACH-^ zzmechanical Desktop 4 Applying Designer and "Ässembly Modules M Autodesk Press Thomson Learning Africa Australia Canada Denmark Japan Mexico New Zealand Philippines Puerto
Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical
 Lecture 6 Modeling Connections 15.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2012 ANSYS, Inc. February 12, 2014 Chapter Overview In this chapter, we will extend the discussion of contact control begun
Lecture 6 Modeling Connections 15.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2012 ANSYS, Inc. February 12, 2014 Chapter Overview In this chapter, we will extend the discussion of contact control begun
